A Deep Forest Algorithm Based on TropOMI Satellite Data to Estimate Near-Ground Ozone Concentration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Research Area
2.3. Modeling Method Based on Deep Forest Algorithm
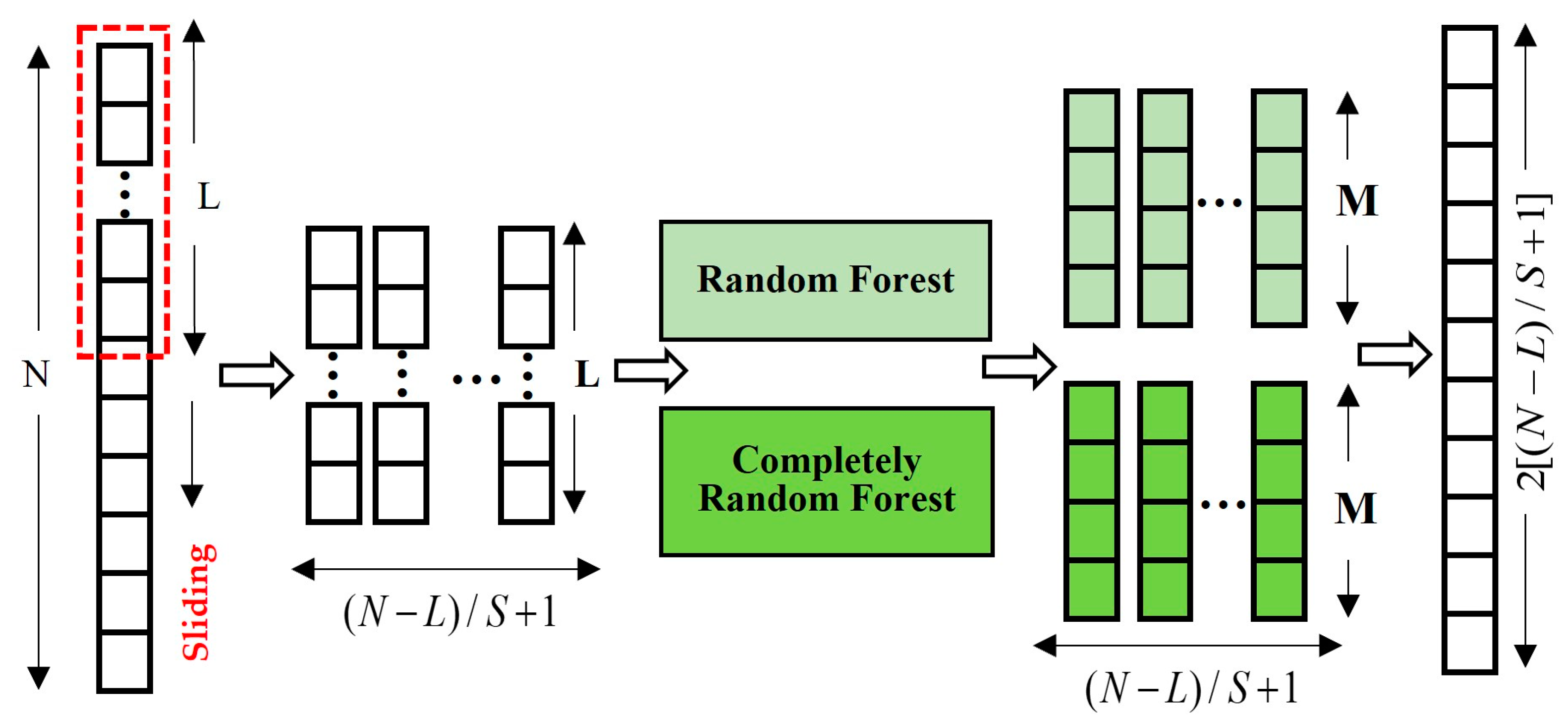
2.3.1. Multi-Granularity Scanning
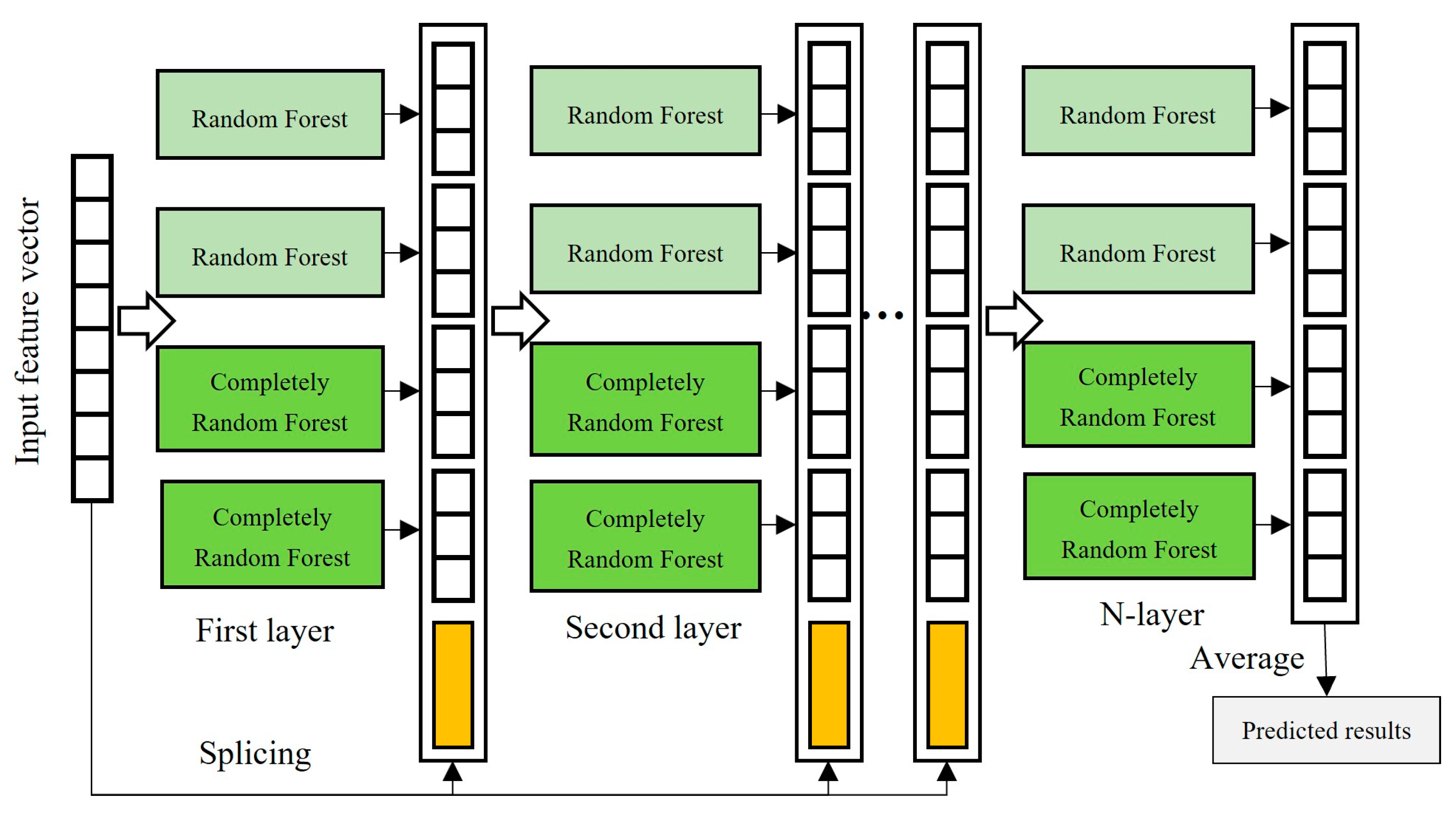
2.3.2. Cascade Forest
2.4. Data Collection
2.4.1. Near-Ground O3 Monitoring Data
2.4.2. Satellite Data
2.4.3. Meteorological and Elevation Data
2.5. Experimental Environment
2.6. Evaluation Indexes
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of the Coordinated Changes in O3, PM2.5, and NO2
3.2. Estimation and Comparative Analysis of Near-Ground Ozone Concentration
3.3. Spatiotemporal Distribution of Near-Ground-Level Ozone Concentrations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, Y.; Li, K.W.; Zhao, B.; Shen, J.D.; Bloss, W.J.; Azzi, M.; Zhang, Y.P. Evaluating the real changes of air quality due to clean air actions using a machine learning technique: Results from 12 Chinese megacities during 2013–2020. Chemosphere 2022, 300, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visser, C.; Gonzalez, C. Transportation Air Pollution in China: The Ongoing Challenge to Achieve a ‘Blue Sky’. In Transportation Air Pollutants; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 27–41. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, J.; Li, Z.Q.; Li, K.; Dickerson, R.R.; Pinker, R.T.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Sun, L.; Xue, W.H.; Cribb, M. Full-coverage mapping and spatiotemporal variations of ground-level ozone (O3) pollution from 2013 to 2020 across China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 270, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavinezhad, S.; Choi, Y.; Pouyaei, A.; Ghahremanloo, M.; Nelson, D.L. A comprehensive investigation of surface ozone pollution in China, 2015–2019: Separating the contributions from meteorology and precursor emissions. Atmos. Res. 2021, 257, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.B.; Zhu, J.; Liao, H.; Li, J.D.; Liang, M.X.; Yang, Y.; Yue, X. Co-occurrence of ozone and PM2.5 pollution in the Yangtze River Delta over 2013–2019: Spatiotemporal distribution and meteorological conditions. Atmos. Res. 2021, 249, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.L.; Liu, J.F.; Tao, W.; Yi, K.; Xu, J.Y.; Hu, X.R.; Liu, H.Z.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Yang, H.Z.; et al. Control of both PM2.5 and O3 in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei and the surrounding areas. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 224, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Chen, K.Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.X.; Shao, T.; Zhang, H.L. Coordinated control of PM2.5 and O3 is urgently needed in China after implementation of the “Air pollution prevention and control action plan”. Chemosphere 2021, 270, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.H.; Gao, W.K.; Wang, S.; Song, T.; Gong, Z.Y.; Ji, D.S.; Wang, L.L.; Liu, Z.R.; Tang, G.Q.; Huo, Y.F.; et al. Contrasting trends of PM2.5 and surface-ozone concentrations in China from 2013 to 2017. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2020, 7, 1331–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Cui, L.L.; Fu, H.B.; Li, J.L.; Zhao, Y.L.; Chen, J.M. Satellite-based estimation of full-coverage ozone (O3) concentration and health effect assessment across Hainan Island. J. Clean Prod. 2020, 244, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.R.; Wang, X.M.; Ling, Z.H.; Zhao, J.; Guo, H.; Shao, M.; Wang, Z. Contributions of different anthropogenic volatile organic compound sources to ozone formation at a receptor site in the Pearl River Delta region and its policy implications. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 8801–8816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.D.; Rohrer, F.; Holland, F.; Fuchs, H.; Bohn, B.; Brauers, T.; Chang, C.C.; Häseler, R.; Hu, M.; Kita, K.; et al. Observation and modelling of OH and HO2 concentrations in the Pearl River Delta 2006: A missing OH source in a VOC rich atmosphere. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 1541–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.W.; Wang, T.J.; Yuan, C.; Wu, H.; Gao, L.B.; Huang, C.W.; Li, Y.S.; Li, M.M.; Xie, M. The underlying mechanisms of PM2.5 and O3 synergistic pollution in East China: Photochemical and heterogeneous interactions. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 873, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, Y.Y.; Yao, J.; Qiao, D.W.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Zhong, C.Y.; Tang, L.J. Three-hourly PM2.5 and O3 concentrations prediction based on time series decomposition and LSTM model with attention mechanism. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2023, 14, 101879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; He, Y.; Fan, G.; Li, Z.; Liang, Z.; Fang, H.; Zeng, Z.C. Ozone Pollution and Its Response to Nitrogen Dioxide Change from a Dense Ground-Based Network in the Yangtze River Delta: Implications for Ozone Abatement in Urban Agglomeration. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Guo, F.; Xie, S. Diagnosing ozone–NOx–VOC sensitivity and revealing causes of ozone increases in China based on 2013–2021 satellite retrievals. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 15035–15047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Cheng, X.; Yan, H.Z.; Sun, Y.M.; Zhang, G.Q. Ground-Level Ozone Production over an Industrial Cluster of China: A Box Model Analysis of a Severe Photochemical Pollution Episode. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2022, 31, 1885–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.L.; Song, R.F.; Zhu, X.H.; Peng, Z.R.; Fu, Q.Y.; Pan, J. A hybrid deep learning model for regional O3 and NO2 concentrations prediction based on spatiotemporal dependencies in air quality monitoring network. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 320, 121075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, S.D.; Lai, V.; Hahzaman, F.H.; Ahmed, A.N.; Huang, Y.F.; Birima, A.H.; Shafie, A.E. Ozone concentration forecasting utilizing leveraging of regression machine learnings: A case study at Klang Valley, Malaysia. Results Eng. 2024, 21, 101872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Sun, J.; Liu, B.; Li, M.; Deng, Y.; Jing, W.; Yang, J. Factors Influencing O3 Concentration in Traffic and Urban Environments: A Case Study of Guangzhou City. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Shi, G.; Chen, Z. Spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of ground-level nitrogen dioxide and ozone across China during 2015–2020. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 124031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Jacob, D.J.; Liao, H.; Qiu, Y.L.; Shen, L.; Zhai, S.X.; Bates, K.H.; Sulprizio, M.P.; Song, S.J.; Lu, X.; et al. Ozone pollution in the North China Plain spreading into the late-winter haze season. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Gao, J.H.; Zhu, B.; Kumar, R.; Lu, X.; Song, S.J.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Jia, B.X.; Wang, P.; Beig, G.R.; et al. Ozone pollution over China and India: Seasonality and sources. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 4399–4414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biancofiore, F.; Verdecchia, M.; Di Carlo, P.; Tomassetti, B.; Aruffo, E.; Busilacchio, M.; Bianco, S.; Di Tommaso, S.; Colangeli, C. Analysis of surface ozone using a recurrent neural network. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 514, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, A.S.; Paredes, M.L.L.; de Oliveira, G.C.G.; Corrêa, S.M. Prediction of ozone concentration in tropospheric levels using artificial neural networks and support vector machine at Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 98, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Wang, X.; Ye, H.; Shi, H.; Pan, Y.; Wang, G. CO2 retrieval method based on GaoFen-5 satellite data. In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Spatial Atmospheric Marine Environmental Optics (SAME 2023), Qingdao, China, 23–26 October 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Mak, H.W.L.; Laughner, J.L.; Fung, J.C.H.; Zhu, Q.D.; Cohen, R.C. Improved Satellite Retrieval of Tropospheric NO2 Column Density via Updating of Air Mass Factor (AMF): Case Study of Southern China. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Z.Z.; Liu, Y.B.; Zhao, T.L.; Xia, J.R.; Wang, C.G.; Cao, L.; Wang, H.L.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, Y.; Shen, L.J.; et al. Elevated 3D structures of PM2.5 and impact of complex terrain-forcing circulations on heavy haze pollution over Sichuan Basin, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 9253–9268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.W.; Cheng, X. Estimating daily full-coverage surface ozone concentration using satellite observations and a spatiotemporally embedded deep learning approach. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 101, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.H.; Feng, J. Deep Forest: Towards an Alternative to Deep Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 26th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI), Melbourne, Australia, 19–25 August 2017; pp. 3553–3559. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.P.; Chen, J.Y.; Yu, Z.J.; Li, J.; Huang, G.S.; Haghighat, F.; Zhang, G.Q. A novel model based on multi-grained cascade forests with wavelet denoising for indoor occupancy estimation. Build. Environ. 2020, 167, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Yu, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, L. A Long Short-Term Memory Neural Network for Daily NO2 Concentration Forecasting. Int. J. Inf. Technol. Web Eng. 2021, 16, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, H.W.; Lam, Y.F. Comparative assessments and insights of data openness of 50 smart cities in air quality aspects. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 69, 102868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvall, R.M.; Long, R.W.; Beaver, M.R.; Kronmiller, K.G.; Wheeler, M.L.; Szykman, J.J. Performance Evaluation and Community Application of Low-Cost Sensors for Ozone and Nitrogen Dioxide. Sensors 2016, 16, 1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.X.; Zang, L.; Wan, Y.C.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y. Ground-level PM2.5 estimation over urban agglomerations in China with high spatiotemporal resolution based on Himawari-8. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 676, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, X.; Xie, Z.L.; Liu, J.; Wei, L.Y.; Wang, X.Q.; Chen, M.W.; Ren, H. Global PM2.5-attributable health burden from 1990 to 2017: Estimates from the Global Burden of disease study 2017. Environ. Res. 2021, 197, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.Y.; Zhang, R.H.; Yu, W. The Effects of PM2.5 Concentrations and Relative Humidity on Atmospheric Visibility in Beijing. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 2235–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Wang, G.; Li, G.H.; Lang, J.L.; Zhang, H.Y. Air pollution episodes during the COVID-19 outbreak in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region of China: An insight into the transport pathways and source distribution. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Baosheng, L.; Xianglin, S. Calculation of Gini Efficient and Gini Efficient of Distribution. J. Ocean Univ. Qingdao 2002, 32, 663–666. [Google Scholar]
- Tamiminia, H.; Salehi, B.; Mahdianpari, M.; Quackenbush, L.; Adeli, S.; Brisco, B. Google Earth Engine for geo-big data applications: A meta-analysis and systematic review. ISPRS-J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 164, 152–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veefkind, J.P.; Aben, I.; McMullan, K.; Förster, H.; de Vries, J.; Otter, G.; Claas, J.; Eskes, H.J.; de Haan, J.F.; Kleipool, Q.; et al. TROPOMI on the ESA Sentinel-5 Precursor: A GMES mission for global observations of the atmospheric composition for climate, air quality and ozone layer applications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingmann, P.; Veihelmann, B.; Langen, J.; Lamarre, D.; Stark, H.; Courrèges-Lacoste, G.B. Requirements for the GMES Atmosphere Service and ESA’s implementation concept: Sentinels-4/-5 and-5p. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spurr, R.; Loyola, D.; Roozendael, M.V.; Lerot, C. S5P/TROPOMI Total Ozone ATBD. Dtsch. Zent. Für Luft Und Raumfahrt 2021, 67, 535. [Google Scholar]
- Landgraf, J.; de Brugh, J.; Scheepmaker, R.; Borsdorff, T.; Houweling, S.; Hasekamp, O. Algorithm Theoretical Baseline Document for Sentinel-5 Precursor: Carbon Monoxide Total Column Retrieval; SRON-S5P-LEV2-RP-002; Netherlands Institute for Space Research: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Willmott, C.J. Some comments on the evaluation of model performance. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1982, 63, 1309–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Fan, S.R.; Xia, K.W.; Wang, L. Estimation of Regional Ground-Level PM2.5 Concentrations Directly from Satellite Top-of-Atmosphere Reflectance Using A Hybrid Learning Model. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Pang, X.B.; Li, J.J.; Xing, B.; An, T.C.; Yuan, K.B.; Dai, S.; Wu, Z.T.; Wang, S.Q.; Wang, Q.; et al. Vertical profiles of O3, NO2 and PM in a major fine chemical industry park in the Yangtze River Delta of China detected by a sensor package on an unmanned aerial vehicle. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 845, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Xue, L.K.; Brimblecombe, P.; Lam, Y.F.; Li, L.; Zhang, L. Ozone pollution in China: A review of concentrations, meteorological influences, chemical precursors, and effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 1582–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kornilova, A.; Saccon, M.; O’Brien, J.M.; Huang, L.; Rudolph, J. Stable Carbon Isotope Ratios and the Photochemical Age of Atmospheric Volatile Organic Compounds. Atmos. Ocean 2015, 53, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.Q.; Bian, H.; Feng, Y.C.; Liu, A.X.; Li, X.J.; Zeng, F.; Zhang, X.L. Analysis of the Relationship between O3, NO and NO2 in Tianjin, China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2011, 11, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, R.D.; Vázquez, M.A. Evaluation of Machine Learning Models for Ozone Concentration Forecasting in the Metropolitan Valley of Mexico. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, R.; Luo, Z.; Xue, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Z.-J. Prediction of Autumn Ozone Concentration in the Pearl River Delta Based on Machine Learning. Huan Jing Ke Xue = Huanjing Kexue 2024, 45, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Gong, X.; Liu, X.; Zhao, X.; Meng, H.; Dong, Q.; Liu, G.; Gao, H. Deep Sequence Learning for Prediction of Daily NO2 Concentration in Coastal Cities of Northern China. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Yang, Q.; Yuan, Q.; Zhu, L. Estimation of high spatial resolution ground-level ozone concentrations based on Landsat 8 TIR bands with deep forest model. Chemosphere 2022, 301, 134817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziwei, L.I.; Qingxun, M.A.; Jie, L. BP neural network for near-surface ozone estimation and spatial and temporal characteristics analysis. Bull. Surv. Mapp. 2021, 6, 28–36. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Yang, J.; Song, G.; Li, S. Method for Realizing Near-Ground Ozone Inversion Based on Near-Ground UV Radiation for Use in Ozone Research, Involves Training the Deep Learning Model Based on Satellite Observation, and Estimating near Ground Ozone Concentration in Satellite Observation Area by Deep Learning Model. US2023131036-A1 27 Apr 2023 G06N-003/04 202336 English. 2022. Available online: https://webofscience.clarivate.cn/wos/alldb/full-record/DIIDW:202228283Y (accessed on 17 August 2024).
- Zhu, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, S.; Li, W.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Method for Performing Near-Ground Ozone Concentration Inversion Based on Combination of Machine Learning and Deep Learning for Ground Observation and Atmospheric Simulation in Rural and Remote Areas Involves Inputting Satellite Remote Sensing Information of Monitoring Area into Inversion Model. CN113657023-A Chinese. 2022. Available online: https://webofscience.clarivate.cn/wos/alldb/full-record/DIIDW:2021D60319 (accessed on 17 August 2024).
- Zhao, L.; Liu, X.; Fan, L.; Liu, C.; Wang, S.; Ma, X. Pollution Characteristic and Source Apportionment of VOCs During Summer Typical Periods in Shijiazhuang. Environ. Monit. China 2019, 35, 78–84. [Google Scholar]









| Category | Variable | Spatial Resolution | Temporal Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ground data | O3 | ||
| PM2.5 | — | Daily | |
| NO2 | |||
| Remote sensing data | TropOMI O3 | 1 km | Daily |
| Meteorological element data | Boundary Layer Height, Surface Pressure, 2 m temperature, total-column water content, total-column ozone, 10 m u-component of wind, 10 m v-component of wind | 0.25° × 0.25° | Hourly |
| Auxiliary data | Digital Elevation Model | 1 km | Yearly |
| Model | (μg/m3) | (μg/m3) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (a) | Deep forest with NO2 and PM2.5 | 0.9560 | 13.2542 | 9.0250 |
| (b) | Deep forest with PM2.5 | 0.9499 | 14.1409 | 9.4926 |
| (c) | Deep forest with NO2 | 0.9487 | 14.3146 | 9.5011 |
| (d) | Deep forest without NO2 and PM2.5 | 0.9463 | 14.6358 | 9.5159 |
| (e) | LightGBM | 0.9066 | 19.0485 | 12.2511 |
| (f) | Random forest | 0.8956 | 20.1452 | 11.7856 |
| (g) | GBDT | 0.8877 | 20.8950 | 12.2659 |
| (h) | Catboost | 0.8869 | 20.9635 | 13.2224 |
| (i) | XGBoost | 0.8861 | 21.0428 | 13.1755 |
| (j) | Decision Tree | 0.8146 | 26.8411 | 16.5232 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zong, M.; Song, T.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Fan, S. A Deep Forest Algorithm Based on TropOMI Satellite Data to Estimate Near-Ground Ozone Concentration. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 1020. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15091020
Zong M, Song T, Zhang Y, Feng Y, Fan S. A Deep Forest Algorithm Based on TropOMI Satellite Data to Estimate Near-Ground Ozone Concentration. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(9):1020. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15091020
Chicago/Turabian StyleZong, Mao, Tianhong Song, Yan Zhang, Yu Feng, and Shurui Fan. 2024. "A Deep Forest Algorithm Based on TropOMI Satellite Data to Estimate Near-Ground Ozone Concentration" Atmosphere 15, no. 9: 1020. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15091020
APA StyleZong, M., Song, T., Zhang, Y., Feng, Y., & Fan, S. (2024). A Deep Forest Algorithm Based on TropOMI Satellite Data to Estimate Near-Ground Ozone Concentration. Atmosphere, 15(9), 1020. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15091020






