Abstract
CO2 emissions prediction plays a key role in atmospheric environment management and regional sustainable development. Taking the Four Provinces of Mountains and Rivers (Henan, Hebei, Shandong, and Shanxi) in China as an example, the Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average Model (ARIMA) and random forest importance analysis were used to calculate the future trend of the CO2 emission–influencing factors and obtain the main influencing factors. Based on the above, BP neural network (BPNN), support vector machine (SVR), and random forest (RF) models were used to predict the future apparent CO2 emissions of the four provinces. The results show that, in general, population, coal consumption, and per capita GDP are the main factors influencing CO2 emissions. The RF model has the best prediction performance; for instance, RMSE (81.86), R2 (0.905), and MAE (64.69). The prediction results show that the total apparent CO2 emissions of the Four Provinces of Mountains and Rivers will peak in 2028 (with a peak of about 4500 Mt). The apparent CO2 emissions of Henan, Hebei, and Shandong Province peaked in 2011 (with a peak of about 654 Mt), 2013 (with a peak of about 657 Mt), and 2020 (with a peak of about 1273 Mt), respectively. Shanxi is forecast to reach its peak (with a peak of about 2486 Mt) in 2029. The apparent CO2 emissions of all provinces showed an obvious downward trend after reaching their peak. Henan, Hebei Shandong, and Shanxi showed a significant downward trend in 2018, 2023, and 2032, respectively.
1. Introduction
Emissions of carbon-containing greenhouse gases will cause significant changes in climate and pose a serious threat to human living environment and health [1,2]. China’s anthropogenic CO2 emissions account for about 30% of global emissions, so its emissions reduction plays a crucial role in the global mitigation of climate change. The Chinese government has pledged to peak CO2 emissions per unit of gross domestic product (GDP) by 2030, reducing them by 60–65% from 2005 levels. Therefore, the analysis of the impact of economic policies and other factors on CO2 emissions and the forecast CO2 emissions to formulate CO2 emission plans and standards have become important ways to achieve the short-term carbon peak goal.
At present, the calculation of CO2 emissions is dominated by two approaches: “top-down” and “bottom-up” [3,4,5]. However, it is difficult for these two methods to evaluate the current amount of CO2 emissions, and there is a lag in the analysis of emission trends in the future period. The IPCC provides methods for calculating CO2 emissions for specific sectors (e.g., the construction sector and the electricity sector) and specific factors (e.g., cement production, steel production, and fossil energy consumption) [6]. However, its data quality requirements and operating costs are high. With the application of machine learning technology in the field of carbon emissions, the dependence on hypotheses in the study of the relationship between CO2 emissions and economic growth was removed, and the forecast of CO2 emissions based on indicators that influence CO2 emissions was realized [7,8].
At present, the research on CO2 emission forecasts using machine learning is mostly in the model verification stage, and no consensus can be reached on the selection of CO2 emission forecast models in different scenarios. The algorithms used in CO2 emission forecasting based on machine learning technology mainly include Manta ray foraging optimization—extreme learning machine [9], the BP neural network [10,11], regression integral moving average [12], support vector machine [13], random forest, and cubic exponential smoothing (Holt-Wints) [14]. Many scholars have verified that the BP neural network algorithm, support vector machine, and random forest can achieve relatively good forecasts in the field of CO2 emission forecasting.
The use of more comprehensive CO2 emission–influencing indicators as the input variable is the key to ensuring the reliability of CO2 emission forecast results. Zhao et al. (2018) used gross domestic product (GDP), population, energy consumption, economic structure, energy structure, urbanization rate, and energy intensity to establish China’s CO2 emission forecast model [15]. Xu et al. (2023) and Ambade et al. (2021) found that the urbanization rate, per capita GDP, and per capita consumption expenditure of urban and rural residents were positive driving factors for CO2 emissions, while the primary industry had a reverse driving effect on CO2 emissions [16,17]. In the research on global CO2 emission forecasting, Zeng et al. (2022) found that urban population, GDP, gas consumption, electricity consumption, and industrial structure are important factors affecting regional CO2 emissions from energy sources [18]. In addition, the CO2 emission forecast in the future period is based on the future value of the CO2 emission–influencing indicators. The quantitative calculation of the future trend of CO2 emission–influencing indicators is particularly important for the accuracy of CO2 emission forecast results. Wen et al. (2022) realized the forecast of CO2 emissions by using the autoregressive composite moving average (ARIMA) model and the seasonal autoregressive composite moving average (ARIMA) model [19]. Lian et al. (2024) used scenario analysis to show the future development of carbon emissions in Fujian Province under different scenarios [20].
In general, researchers have conducted a lot of research in the field of CO2 emissions prediction. However, this study makes an innovative attempt to realize the prediction of CO2 emissions with machine learning algorithms based on the future values of the CO2 emission–influencing indicators predicted using the ARIMA model. Therefore, this paper takes the Four Provinces of Mountains and Rivers in China (Henan, Hebei, Shandong, and Shanxi) as an example to predict the CO2 emissions and then determines the CO2 peak time and maximum emissions, thus verifying the feasibility of this method. A specific objective of our paper is to compare the performance of the BP neural network (BPNN), support vector machine (SVR), and random forest (RF) models to select the best one.
2. Methods
2.1. Method Flow
The future values of the indicators influencing CO2 emissions were forecast using time-series analysis combined with machine learning algorithms to forecast the CO2 emissions of the Four Provinces of Mountains and Rivers. The specific forecasting process is illustrated in Figure 1.
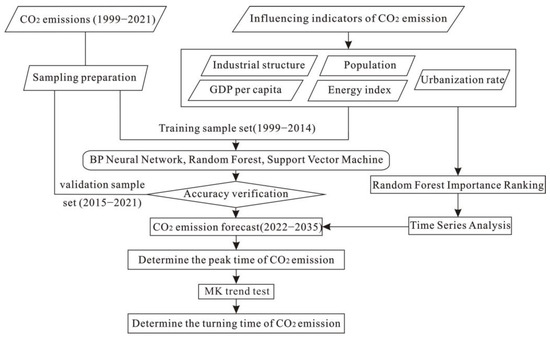
Figure 1.
Flow chart of CO2 emission forecasting.
2.2. Time-Series Forecasting
Time-series forecasting is a method that utilizes past time-series data to forecast future data. The basic principle involves capturing the characteristics of time-series data such as trends, seasonality, and periodicity, constructing a mathematical model, and then employing this model to forecast future data. In this paper, the time-series forecasting model utilized is the Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA) model. The equation is given as Equation (1).
where Yt is the time-series value at time t, α is the constant term, Φi is the autoregressive coefficient, yt-i is the value at time t-i, q is the number of moving average terms, θj is the moving average coefficient, εt is the error term, p is the autoregressive term, and d is the difference order.
2.3. Machine Learning
2.3.1. BP Neural Network (BPNN)
The concept of neural networks was first introduced by scientists led by Rumelhart and McClelland in 1986 [21]. Among these, the BP neural network (BPNN) model is a type of multilayer feedforward neural network trained using the error backpropagation algorithm, which stands as one of the most widely utilized neural network models. The learning rule of the BP neural network involves continuously adjusting the weights and thresholds of the network through backpropagation, employing the steepest descent method to minimize the sum of squared errors. The architecture of a BP neural network comprises an input layer, one or more hidden layers, and an output layer.
2.3.2. Support Vector Machine Regression (SVM)
The fundamental concept of the support vector machine Regression (SVM) algorithm is to identify an optimal hyperplane to fit the data [22]. SVM employs kernel tricks to handle nonlinear relationships and map data into higher-dimensional space, thereby enhancing its ability to adapt to various data distributions. Specifically, SVM addresses the following optimization problem:
Here, W and b are the model parameters to be solved, C is a penalty parameter used to control the complexity of the model, too large value of C can easily lead to overfitting, too small will lead to underfitting, and ξi is the introduced slack variable.
2.3.3. Random Forests (RF)
- (1)
- Principle of random forest algorithm
The random forest algorithm was proposed by Breiman in 2001 as an ensemble learning algorithm based on decision trees [23]. The details of the algorithm are as follows: (1) Select n samples from the sample set as a training set using the method of sampling with replacement (bootstrap). (2) Generate a decision tree from the sample set. At each node, d features are randomly selected without replacement, and the Gini coefficient is used to find the best partition feature to divide the sample set. (3) Repeat steps 1 and 2 k times, where k is the number of decision trees in the random forest. (4) Use the trained decision trees to forecast the samples and employ the weighted average method to determine the final forecasting result.
- (2)
- Importance Analysis of Random Forests
For each decision tree of the random forest, the degree of contribution of each feature to the Gini impurity of the node split is calculated. The equation is given as Equation (6).
where Tm represents node m, and pm,0 to pm,n represent the proportion of samples of each category in node m.
For each feature, the contribution of that feature to the average reduced impurity of node splitting across all decision trees is calculated. The equation is given as Equation (7).
where T denotes the number of decision trees, t denotes the t-th decision tree, and IG(tf) denotes the Gini impurity of decision tree t after splitting on feature f.
The importance values of all features are normalized so that their sum equals 1 using the following equation:
where Wf is the importance value of the feature f, VI(f) is the average reduced impurity of the feature f, and n is the number of features.
2.3.4. Accuracy Verification
The root mean square error (RMSE), the coefficient of determination (R2), and mean absolute error (MAE) were chosen as the accuracy verification parameters to evaluate the performance of each machine learning algorithm. RMSE measures the average size of the forecasting error of the model, with a smaller RMSE indicating a smaller difference between the forecast and true values (Equation (9)). R2 represents the proportion of variability in the dependent variable that the model explains, with a high R2 value indicating a good fit of the model to the data (Equation (10)). MAE is the average of the absolute error between the forecast and actual values (Equation (11)), measuring the magnitude of the average forecasting error of the model. A smaller MAE value suggests a better fit of the model to the data.
where yi represents the forecast value, represents the actual value, represents the actual mean, and n is the number of samples.
The three regression forecasting models mentioned above each have their own advantages and disadvantages in practical applications. The BP neural network exhibits adaptability to complex nonlinear relationships and possesses strong fitting capabilities. However, it is prone to overfitting when confronted with multicollinearity issues. The support vector machine performs well with high-dimensional and small-sample data, effectively handling nonlinear relationships. Nonetheless, selecting the appropriate kernel function and regularization parameter can be complex, requiring meticulous parameter tuning. On the other hand, random forest demonstrates competence in handling high-dimensional and large-scale datasets. It can yield satisfactory results even when dealing with correlated or collinear features and exhibits robustness against outliers and missing values. However, it is susceptible to overfitting in regression problems with substantial noise. This paper aims to assess the application effectiveness of these three methods in the field by comparing their accuracy in forecasting total CO2 emissions across the Four Provinces of Mountains and Rivers.
2.4. Correlation Analysis and Trend Test
- (1)
- Pearson correlation analysis
Pearson correlation analysis was used to evaluate the correlation between the influencing indicators and CO2 emissions in the Four Provinces of Mountains and Rivers. Pearson’s correlation coefficient can evaluate the linear relationship between two continuous variables and is calculated as in Equation (12).
where , is the mean value of indicators variables and the value of indicator variables in each year, and , is the mean value of CO2 emissions in the Four Provinces of Mountains and Rivers and the CO2 emissions in each year, respectively. The correlation degree between each indicator and CO2 emissions is calculated. A value close to 0 represents no correlation, and a value close to 1 or −1 represents a strong correlation.
- (2)
- Mann–Kenddall (MK) test
The Mann–Kenddall (MK) test method is used to detect the variation trend of sequences [24]. The principle is to construct a sequential column Sk for a time series X with n sample sizes.
The order column Sk is the accumulation of the number of values when the number at the i-th time is greater than the number at the j-time. Under the assumption that the time series is random, the statistics are defined. The equation is given as Equation (14).
where UF1 = 0, E(Sk) and Var(Sk) are the mean and variance of Sk, respectively. When xn is independent of each other, they have the same continuous distribution, which can be deduced from Equation (15).
UFk is the standard normal distribution, which is the order of the time series X (x1, x2, …, xn). Given a significance level α, if UFi > Uα, there is an obvious trend change in the series.
Then, in the reverse order of time series X (xn, xn−1, …, x1), the above process is repeated, and (k = n, n−1, …, 1), UB1 = 0, and UBk = −UFk are set. Generally, the significance level α = 0.05, then the critical value U0.05 = ±1.96. The two statistic series curves of UFk and UBk and ±Uα are then plotted on a single graph. A value of UFk and UBk greater than 0 indicates an upward trend in the series, while a value less than 0 indicates a downward trend. When they exceed the critical line, it indicates a significant upward or downward trend, and the range beyond the critical line is determined as the time region where abrupt changes occur. If two curves UFk and UBk intersect, and the intersection point is between the critical line, then the moment corresponding to the intersection point is the time when the mutation starts.
3. The CO2 Emission–Influencing Indicators System Was Established
3.1. Acquisition of CO2 Emission–Influencing Indicators
A total of 24 effective papers on CO2 emission forecasting from 2011 to 2023 have been collected, among which the use of CO2 emission–influencing indicators is shown in Table 1. The second column is the number of articles with corresponding indicators, and the third column is the frequency of articles with corresponding indicators (the number of articles with corresponding indicators/the total number of articles).

Table 1.
The usage of CO2 emission–influencing indicators.
The literature review on CO2 emission forecast shows that population, GDP, industrial structure, and energy consumption are key factors influencing CO2 emissions [25,26]. This paper directly obtains the data on population, GDP, crude oil, crude oil, raw coal, natural gas, electricity, and other primary energy consumption in 2021 and the proportion of tertiary industry structure (calculated according to the contribution rate of each industry to domestic GDP) of China’s Sanjiang and four provinces through the provincial statistical yearbook website [27,28,29,30]. Data on apparent carbon dioxide emissions in four provinces from 1999 to 2021 were collected through the China Carbon Accounting Database Website (CEADs) [31,32,33,34,35]. Data sources, units, and related symbols are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Data sources and symbol setting of CO2 influencing indicators.
3.2. Analysis of Time-Series Characteristics of CO2 Emission–Influencing Indicators
Figure 2 shows that the change trends of total population, urbanization rate, crude oil consumption, per capita GDP, and apparent CO2 emissions in the four provinces had different growth trends during 1999–2021. The trend of CO2 emissions is very similar to that of coal and oil consumption. Coal consumption in the Four Provinces of Mountains and Rivers reached its peak in 2015 (Figure 2a). After 2015, the proportion of tertiary industry in the four provinces was higher than that of secondary industry (Figure 2d).
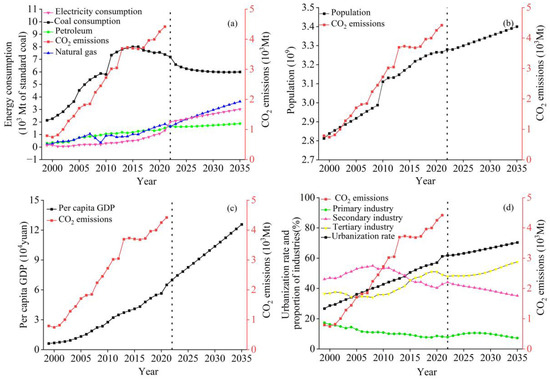
Figure 2.
Trend chart of the total carbon dioxide emissions influencing indicator in four provinces over time. (a) Energy consumption and CO2 emissions. (b) Population and CO2 emissions. (c) Per capita GDP and CO2 emissions. (d) Proportion of industry and CO2 emissions.
The future trend of the CO2 emission–influencing indicators is closely related to the past changing situation, as forecasted by the principle of ARIMA. The indicators of urbanization rate and GDP per capita have increased linearly in the past, and ARIMA predicts that they will increase linearly in the future. The coal consumption and the proportion of the secondary industry showed nonlinear changes in the past, and they are predicted to change non-linearly. The calculation results show that raw coal consumption began to decline after 2015. There will be dramatic changes in 2023. Due to policy adjustments, China’s energy structure is shifting from coal to diversification, and the rapid growth of renewable energy sources will make coal consumption undergo dramatic changes in 2023. Crude oil and natural gas consumption remained basically stable and showed an upward trend after 2015. Electricity consumption and natural gas consumption increased slowly (Figure 2a). The population of the Four Provinces of Mountains and Rivers will continue to grow at a low rate in the coming period of time (Figure 2b). The urbanization rate and per capita GDP will continue to grow (Figure 2c,d). The proportion of secondary industry continued to decline, the proportion of tertiary industry steadily increased, and the proportion of primary industry remained at a low level (Figure 2d).
Pearson correlation analysis showed that the correlation between the population indicator and the apparent CO2 emissions in the Four Provinces of Mountains and Rivers was 0.99, the correlation between the urbanization rate indicator and the apparent CO2 emissions in the Four Provinces of Mountains and Rivers was 0.98, and the correlation between the crude oil consumption indicator and the apparent CO2 emissions in the Four Provinces of Mountains and Rivers was 0.98. The correlation between the per capita GDP indicator and apparent CO2 emissions in the Four Provinces of Mountains and Rivers is 0.97 (Figure 3). Correlation analysis showed that the population indicator, urbanization rate indicator, crude oil consumption indicator, and per capita GDP indicator were the most important factors affecting the apparent CO2 emissions of the Four Provinces of Mountains and Rivers from 1999 to 2021. When examining the relationship between CO2 emissions and influencing factors in Hebei Province, Sun et al., 2016 found that the correlation coefficient between coal consumption and CO2 emissions was greater than 0.8, and GDP, total population, and urbanization level were also significantly correlated with CO2 emissions [36].
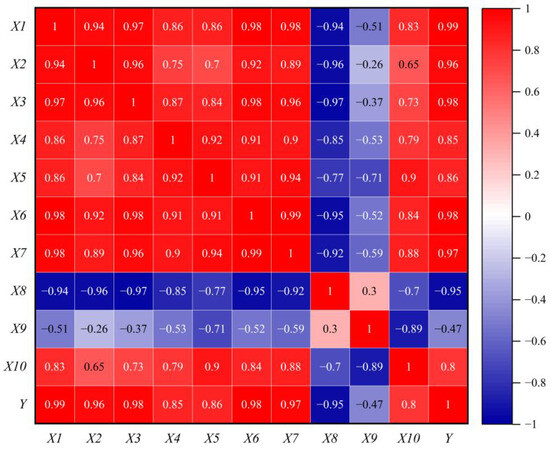
Figure 3.
Heat map of the correlation of each indicator.
3.3. Importance Analysis of CO2 Emission–Influencing Indicators in each Province
Under the background of current technological progress, industrial transformation and upgrading, and energy structure change, there are large differences in carbon intensity (CO2 emissions per unit output) between different industries. At the same time, there are complex supply chains and industrial associations between industries, and the internal influence mechanism of CO2 emissions is difficult to determine. Using the industrial GDP proportion indicator to evaluate the influence on CO2 emissions cannot accurately capture the complex relationship [37]. Therefore, this paper uses the random forest importance analysis method to select influencing indicators except for the proportion of industries to analyze the importance of apparent CO2 emission–influencing indicators in each province.
The importance analysis of random forest indicators shown in Figure 4 shows that the influence of each indicator on the apparent CO2 emissions in Henan, Hebei, and Shandong provinces is relatively balanced, and the difference is small. In contrast, there are large differences in the degree of influence of each indicator in Shanxi Province. The degree of influence of each indicator on the apparent CO2 emissions of each province is quite different. Population, electricity consumption, and per capita GDP are the main indicators affecting apparent CO2 emissions in Henan Province; coal consumption, population, and per capita GDP are the main indicators affecting apparent CO2 emissions in Hebei Province; population, crude oil consumption, and electricity consumption are the main indicators affecting apparent CO2 emissions in Shandong Province. Per capita GDP, urbanization rate, and electricity consumption are the main indicators affecting the apparent CO2 emissions in Shanxi Province.
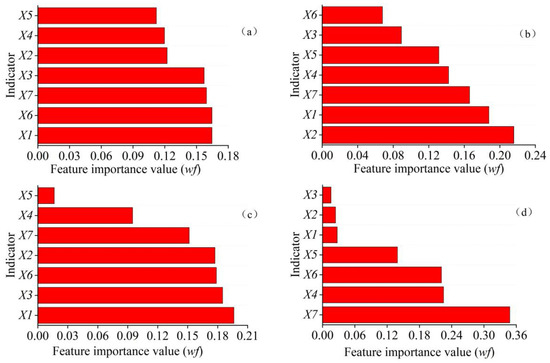
Figure 4.
Random forest importance analysis of carbon dioxide emission–influencing indicator in each province: (a) Henan Province; (b) Hebei Province; (c) Shandong Province; and (d) Shanxi Province.
4. Modeling of CO2 Emission Forecasting
4.1. Parameter Optimization and Model Optimization of Forecasting Model
A total of 23 groups (1999–2021) of population, GDP, crude oil, raw coal, natural gas, electricity, primary and other energy consumption, gross production ratio of primary, secondary, and tertiary industries, and the apparent CO2 emissions data of each province were collected, and the first 16 groups of data were selected as training sets. The remaining seven groups were used as the validation set (VS) to verify the accuracy of the forecasting results.
Considering the forecast accuracy, overfitting, and model complexity of each model under different parameters, parameters were divided into different ranges in the Python environment and manually tuned to determine the parameter settings under optimal model performance. The forecasting accuracy of the BPNN model is relatively optimal when using two hidden layers, and the number of iterations is set to 214, 59 and 1500 iterations (Figure 5a). The random forest shows higher forecasting accuracy when using 350 decision trees and 42 random seed numbers (Figure 5b). As shown in Figure 5c, as the penalty parameter increases, the SVM performs better in RMSE, R2, and MAE accuracy indicators, but a larger penalty parameter will support the generalization ability and practical application effect of the SVM. The optimal parameter settings are determined based on the experimental results to ensure that each forecasting model demonstrates improved generalization ability and practical application effectiveness. The detailed parameter settings are presented in Table 3.
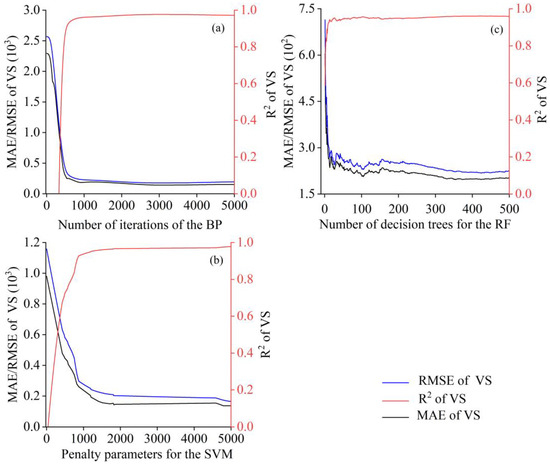
Figure 5.
Trend diagram of the forecasting effect of each model with the change of key parameters. (a) Variation of BP neural network prediction effect with iteration; (b) Variation of Random Forest Prediction effect with Number of Decision Trees; (c) Support Vector Machine Prediction effect with Penalty Parameters.

Table 3.
Parameter Settings of each model.
As depicted in Table 4, the RMSE, R2, and MAE accuracy indices of the validation set (VS) for each model were compared and analyzed. Specifically, the RMSE and MAE values for the random forest model are 81.86 and 64.69, respectively, which are smaller than the RMSE and MAE values of the BP neural network and support vector machine models, and the errors of the CO2 emission forecast results are relatively small. The determination coefficient R2 of the random forest model is 0.905, which is larger than that of the BP neural network and support vector machine model, and the model has a high degree of fitting. There exists a certain correlation among the apparent CO2 emissions indicators, and the issue of collinearity between these indicators contributes to the low accuracy of the BP neural network and support vector machine in regression forecasting. The random forest model demonstrates favorable results in addressing such challenges, with overall performance surpassing that of the BP neural network and support vector machine models. Specifically, the support vector machine exhibits proficiency in handling high-dimensional and small-sample data, along with nonlinear relationships, and it is less sensitive to collinearity problems. Consequently, the support vector machine outperforms the BP neural network in the CO2 emission forecast, as illustrated in Table 4.

Table 4.
Validation set (VS) accuracy of different models.
In summary, the random forest model exhibits higher forecasting accuracy in estimating the apparent CO2 emissions of the Four Provinces of Mountains and Rivers. Additionally, the random forest regression forecasting model developed in this study outperforms the CO2 emission forecast models proposed by Li et al., 2023 [38], which utilized extreme gradient boosting, support vector machine, and artificial neural network algorithms in terms of forecasting accuracy.
4.2. CO2 Emission Forecast of the Four Provinces of Mountains and Rivers
As shown in Figure 6, the future trend of apparent CO2 emissions in each province is predicted by combining the random forest algorithm with the future values of each influence factor predicted by ARIMA. By integrating historical data on apparent CO2 emissions from each province within the Four Provinces of Mountains and Rivers, it is projected that the total apparent CO2 emissions of the region will peak in 2028. Using 2011 as a watershed, apparent CO2 emissions across all provinces within the region exhibited a rapid growth trend from 2001 to 2011. Subsequently, from 2011 to 2021, both Henan and Hebei provinces experienced a stable decline in apparent CO2 emissions, with Henan reaching its peak in 2011 and Hebei in 2013. However, Shandong and Shanxi provinces continued to show an increasing trend in apparent CO2 emissions post-2013, albeit at a slower rate. The forecast results derived from the random forest model indicate that apparent CO2 emissions in Shandong Province will peak in 2020, while those in Shanxi Province are projected to peak in 2029.
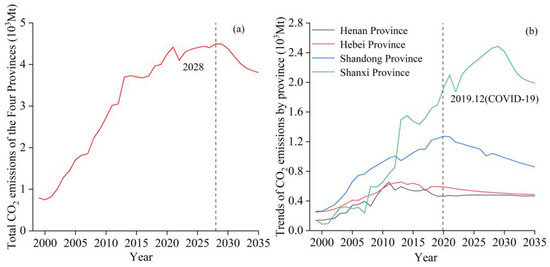
Figure 6.
Total CO2 emissions in the Four Provinces of Mountains and Rivers (a) and the changing trend of CO2 emissions in each province (b).
China’s accession to the WTO in 2001 ushered in a period of rapid development across all provinces and industries [39]. From 2001 to 2011, China’s per capita GDP grew at an average annual rate of 14.88%, significantly surpassing the average level of developing countries during the same period. Between 1990 and 2000, the average annual growth rates of crude oil and natural gas consumption were approximately 3% and 4.7%, respectively. However, from 2001 to 2011, these rates increased to about 6.67% and 16.92%, respectively. Consequently, due to the rapid economic development and the concurrent rise in energy consumption, the apparent CO2 emissions of the Four Provinces of Mountains and Rivers exhibited an upward trend from 2001 to 2011.
Subsequently, following the implementation of various plans and policies, such as the Action Plan for Air Pollution Prevention and Control and the Strategic Action Plan for Energy Development, China’s energy structure underwent transformation and upgrading. This led to a gradual slowdown in the apparent CO2 emissions of Chinese provinces [40]. For instance, the annual growth rate of apparent CO2 emissions in Shanxi Province decreased from 32.59% between 2001 and 2011 to 12.26% between 2011 and 2021.
Beginning in December 2019, the COVID-19 pandemic began to impact China’s economic development and human activities. Concurrently, the effects of China’s high-quality development strategy have gradually become apparent, further decelerating the growth rate of apparent CO2 emissions in provinces that have not yet peaked. For example, the average annual growth rate of CO2 emissions in Shanxi Province decreased from 12.26% during 2011–2021 to 2.31% during 2021–2029.
Figure 7 depicts the MK trend test results of apparent CO2 emissions after reaching the peak in each province of the Four Provinces of Mountains and Rivers. Where the UF value exceeds zero, apparent CO2 emissions exhibit an increasing trend, while a UF value less than zero indicates a decreasing trend. UF surpassing the critical line signifies a significant upward or downward trend. Notably, all Four Provinces of Mountains and Rivers exhibited a significant downward trend in apparent CO2 emissions after reaching their peak values. Henan Province and Hebei Province have demonstrated a significant downward trend since 2018, Shandong Province since 2023, and Shanxi Province is projected to exhibit a significant downward trend starting from 2032. The results of the peak year and trend analysis of apparent CO2 emissions in the Four Provinces of Mountains and Rivers are presented in Table 5.
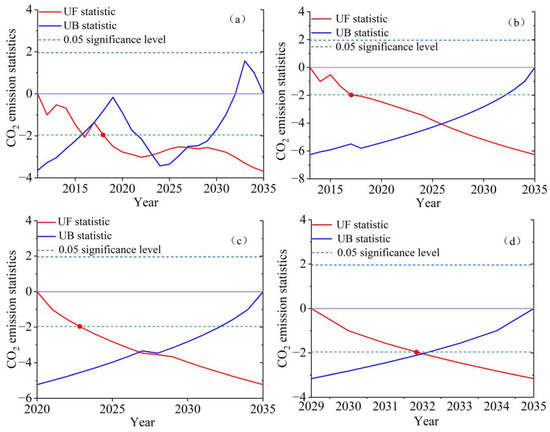
Figure 7.
Examination of MK trends in the provinces of the Four Provinces of Mountains and Rivers. (a) Henan Province; (b) Hebei Province; (c) Shandong Province; and (d) Shanxi Province.

Table 5.
Results of peak year and trend analysis of apparent CO2 emissions in the Four Provinces of Mountains and Rivers.
5. Discussion
5.1. Optimization of CO2 Emission Forecasting Model
In the training process, the random forest algorithm can detect interactions between indicators, is less influenced by individual indicators, and exhibits robust anti-overfitting capabilities [41,42,43,44,45]. Research on CO2 emission forecast in various scenarios has consistently shown that compared to linear, multiple linear, and support vector machine regression models, the random forest algorithm achieves higher determination coefficients and lower mean square errors, resulting in superior predictive performance. Our findings align with previous studies, indicating that even in the presence of multicollinearity in the data, the random forest algorithm maintains higher forecasting accuracy compared to support vector machine and BP neural network models. Therefore, we recommend employing the random forest model for the CO2 emission forecast.
5.2. Analysis of CO2 Emission–Influencing Indicators
The random forest importance analysis of the CO2 emission–influencing indicators of the Four Provinces of Mountains and Rivers on CO2 emissions revealed that population, urbanization rate, fossil energy consumption, and per capita GDP were the main factors in general. However, the importance degree of CO2 emission–influencing indicators has obvious differences in each province. Among them, the importance degree of the CO2 emission–influencing indicators varies the most in Shanxi Province, and the importance value of per capita GDP is 0.348, which is 0.123 and 0.127 higher than the second (urbanization rate) and the third (natural gas consumption) importance indicator, respectively. The development of the coal industry in Shanxi Province has increased the per capita GDP but also brought a lot of CO2 emissions. In Henan Province, the degree of importance of CO2 influencing emission indicators on CO2 emissions varies a little. The top three important indicators are population (0.165), urbanization rate (0.164), and per capita GDP (0.159). People’s production and living activities and urban development have the greatest impact on CO2 emissions in Henan Province.
5.3. Forecasting and Analysis of CO2 Emissions
The peak times of apparent CO2 emissions in the four provinces vary significantly. Henan Province and Hebei Province reached their peak apparent CO2 emissions in 2011 and 2013, respectively. However, the peak year for total CO2 emissions in the Four Provinces of Mountains and Rivers is forecast to be 2028. Our research results are the same as Wang et al. (2023), Cai et al. (2022), Zhu et al. (2016), and Wang et al. (2024) [46,47,48,49], aiming at the predicted trend of CO2 emissions in the four provinces. Over time, the proportion of apparent CO2 emissions from Shanxi Province within the total apparent CO2 emissions of the Four Provinces of Mountains and Rivers has increased from 17.9% in 1999 to 45.26% in 2021. Projections suggest that this proportion will continue to rise, eventually stabilizing at around 52% by 2035. Jiang et al.’s 2019 studies indicate that major energy-producing provinces play a significant role in determining China’s national CO2 emission trajectory [50]. Shanxi Province’s apparent CO2 emissions are expected to comprise 52% of the total apparent CO2 emissions of the Four Provinces of Mountains and Rivers. Therefore, reducing CO2 emissions from resource-based regions is critical to achieving regional and national carbon peaking and sustainable development [51].
5.4. Limitations and Potential Impact on Results
This study has the following limitations: (1) Due to the lack of timely updates of statistical yearbook data, we can only collect the latest indicator data until 2021. At the same time, data such as the number of car owners are difficult to obtain, resulting in the lack of comprehensive CO2 emission–influencing indicators. The above reasons may lead to inaccurate and late CO2 emissions predictions. (2) This paper does not consider the influence of policy background on carbon dioxide emissions. For example, China’s new energy policy and carbon trading policy will accelerate the energy transformation of enterprises in the future. These policies will lead to differences between the carbon dioxide emissions projected in this paper and the actual future values.
6. Conclusions
This research illustrates that the total population, urbanization rate, crude oil consumption, per capita GDP, and apparent CO2 emissions in the Four Provinces of Mountains and Rivers had strong correlations. The relevant departments of each province could formulate corresponding emission reduction policies according to the degree of importance of CO2 emission–influencing indicators.
There were significant differences in the peak time of apparent CO2 emissions among the Four Provinces of Mountains and Rivers. The apparent CO2 emissions in Henan, Hebei, Shandong, and Shanxi provinces peaked in 2011, 2013, 2020, and 2029, respectively, and the peak of the apparent CO2 emissions in each province is about 654 Mt, 657 Mt, 1273 Mt, and 2486 Mt, respectively. It is estimated that 2028 will be the peak year of apparent CO2 emissions in the four provinces, and the peak apparent CO2 emissions will be about 4500 Mt.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.Z. and Z.L.; Data curation, X.Z., Z.L., L.W. and Y.W.; Formal analysis, Z.L.; Funding acquisition, X.Z.; Methodology, X.Z. and Z.L.; Project administration, X.Z. and L.W.; Resources, X.Z.; Software, Z.L.; Writing—original draft, X.Z. and Z.L.; Writing—review and editing, X.Z., Z.L., L.W. and Y.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research is funded by the Jiangxi Science and Technology Normal University doctoral research start-up fund (No. 2022BSQD06), the Jiangxi Province Earthquake Prevention and Disaster Reduction and Engineering Geological Disaster Detection Engineering Research Center open fund (No. SDGD202201), and the Science and technology research project of Jiangxi Provincial Department of Education (No. GJJ2201344).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
References
- Fang, H. Carbon peak and carbon neutrality: A strategic opportunity for China’s health system. Chin. Med. J. 2022, 102, 90–93. [Google Scholar]
- Ambade, B.; Sankar, T.K.; Panicker, A.; Gautam, A.S.; Gautam, S. Characterization, seasonal variation, source apportionment and health risk assessment of black carbon over an urban region of East India. Urban Clim. 2021, 38, 100896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Qin, S.; Chang, H.; Zhang, A. Disaggregation method of carbon emission: A case study in Wuhan, China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Niu, D.; Han, Y. Forecasting of energy-related CO2 emissions in China based on GM (1, 1) and least squares support vector machine optimized by modified shuffled frog lea** algorithm for sustainability. Sustainability 2018, 10, 958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, X.; Naminse, E.Y.; Du, J.; Zhuang, J. Nonrenewable energy, renewable energy, carbon dioxide emissions and economic growth in China from 1952 to 2012. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 52, 680–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.P.; Li, C. Development of Logistics Enterprises in Low-Carbon Era; Social Sciences Academic Press: Beijing, China, 2016; pp. 95–100. [Google Scholar]
- Ambade, B.; Kumar, A.; Latif, M. Emission sources, Characteristics and risk assessment of particulate bound Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) from traffic sites. Res. Sq. 2021, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar, T.K.; Ambade, B.; Mahato, D.K.; Kumar, A.; Jangde, R. Anthropogenic fine aerosol and black carbon distribution over urban environment. J. Umm Al-Qura Univ. Appl. Sci. 2023, 9, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, J. Determinants investigation and peak prediction of CO2 emissions in China’s transport sector utilizing bio-inspired extreme learning machine. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 55535–55553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ağbulut, U. Forecasting of transportation-related energy demand and CO2 emissions in Turkey with different machine learning algorithms. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2022, 1, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.Y.; Zhang, M.L. Forecasting and influencing factors of carbon dioxide emissions in Gansu province based on BP neural network. Environ. Eng. 2023, 41, 61–68+85. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, T.; AlArjani, A. A Comparative Study of CO2 Emission Forecasting in the Gulf Countries Using Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average, Artificial Neural Network, and Holt-Winters Exponential Smoothing Models. Adv. Meteorol. 2021, 2021, 8322590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Niu, W.; Yang, Y.; Hou, D.; Dong, B. Machine learning prediction models for compressive strength of calcined sludge-cement composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 346, 128442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Noman, H. Predicting CO2 Emission Footprint Using AI through Machine Learning. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Huang, G.; Yan, N. Forecasting energy-related CO2 emissions employing a novel SSA-LSSVM model: Considering structural factors in China. Energies 2018, 11, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, D.; Hao, P.; Wang, Z.; Hao, J. Analysis of the influence mechanism of CO2 emissions and verification of the environmental Kuznets curve in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.H.; Rogers, R.A.; Estrada, M.A.R. A Novel Prediction Model: ELM-ABC for Annual GDP in the Case of SCO Countries. Comput. Econ. 2023, 62, 1545–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Shao, B.; Bian, G.; Dai, H.; Zhou, F. Analysis of influencing factors and trend forecast of CO2 emission in Chengdu-Chongqing urban agglomeration. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.; Liu, Y.; Bai, Y.H.; Liu, H. Modeling and forecasting CO2 emissions in China and its regions using a novel ARIMA-LSTM model. Heliyon 2023, 9, e21241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Y.Q.; Su, D.H.; Shi, S.X. Prediction of carbon peak in Fujian Province based on STIRPAT and CNN-LSTM combination model. Environ. Sci. 2024, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumelhart, D.E.; Hinton, G.E.; Williams, R.J. Learning representations by back-propagating errors. Nature 1986, 323, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-vector networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantel, N.; Haenszel, W. Statistical aspects of the analysis of data from retrospective studies of disease. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1959, 22, 719–748. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q.; Li, J.; Li, C.Y. Analysis of Factors Estimation and Influence of Regional CO2 Emissions-A Case of Shandong Province Example. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Symposium on Energy Science and Chemical Engineering (Isesce 2015), Guangzhou, China, 12–13 December 2015; Volume 45, pp. 277–281. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.F.; Zhang, W.R.; Liu, J.P.; Yu, Y. Research on forecasting method of per capita carbon emission in urban demonstration area based on environmental Kuznets curve. Ecol. Econ. 2022, 38, 35–42+84. [Google Scholar]
- HNPBS. Statistical Yearbook of Henan Province. China Statistical Publishing House, Henan 1999–2021. 2023. Available online: https://tjj.henan.gov.cn/tjfw/tjcbw/tjnj/ (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- HBPBS. Statistical Yearbook of Hebei Province. China Statistical Publishing House, Hebei 1999–2021. 2023. Available online: http://tjj.hebei.gov.cn/ (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- SDPBS. Statistical Yearbook of Shandong Province. China Statistical Publishing House, Shandong 1999–2021. 2023. Available online: http://tjj.shandong.gov.cn/ (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- SXPBS. Statistical Yearbook of Shanxi Province. China Statistical Publishing House, Shanxi 1999–2021. 2023. Available online: http://tjj.shanxi.gov.cn/ (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- Xu, J.; Guan, Y.; Oldfield, J.; Guan, D.; Shan, Y. China carbon emission accounts 2020–2021. Appl. Energy 2024, 360, 122837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Shan, Y.; Huang, Q.; Chen, H.; Wang, D.; Hubacek, K. Assessment to China’s recent emission pattern shifts. Earth’s Future 2021, 9, e2021EF002241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Y.; Huang, Q.; Guan, D.; Hubacek, K. China CO2 emission accounts 2016–2017. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Y.; Guan, D.; Zheng, H.; Ou, J.; Li, Y.; Meng, J.; Mi, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Q. China CO2 emission accounts 1997–2015. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 170201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, Z.; Xu, X.; Shao, S.; Wang, P.; Guan, D. New provincial CO2 emission inventories in China based on apparent energy consumption data and updated emission factors. Appl. Energy 2016, 184, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Ye, M.Q.; Xu, Y.F. Study of carbon dioxide emissions forecasting in Hebei province, China using a BPNN based on GA. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2016, 8, 043101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Yuan, X. Forecasting CO2 emissions in Chinas commercial department, through BP neural network based on random forest and PSO. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 718, 137194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.X.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Yi, M.; Han, Y. Forecasting of carbon emission reduction status of online ride-hailing based on machine learning. Transp. Syst. Eng. Inf. 2023, 23, 254–264. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Ahmad, M.; Fareed, Z.; Hassan, T.; Kirikkaleli, D. Role of trade openness, export diversification, and renewable electricity output in realizing carbon neutrality dream of China. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 297, 113419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Pan, X.; Li, C.; Song, J.; Zhang, J. Effects of China’s environmental policy on carbon emission efficiency. Int. J. Clim. Change Strateg. Manag. 2019, 11, 326–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.T.; Hu, D.W. Construction and analysis of transportation carbon emission prediction model based on machine learning. Environ. Sci. 2024, 45, 3421–3432. [Google Scholar]
- Yahsi, M.; Canakoglu, E.; Agrali, S. Carbon price forecasting models based on big data analytics. Carbon Manag. 2019, 10, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, R.L.M.; Oliveira, S.R.M.; Barros, F.M.M.; Farhate, C.V.V.; de Souza, Z.M.; La Scala, N., Jr. Prediction of soil CO2 flux in sugarcane management systems using the Random Forest approach. Sci. Agric. 2018, 75, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Lu, X.; Li, H. A random forest-based model for the prediction of construction-stage carbon emissions at the early design stage. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 328, 129657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Peng, J.; Wang, R.; Zhang, M.; Gao, C.; Yu, Y. Use of random forest based on the effects of urban governance elements to forecast CO2 emissions in Chinese cities. Heliyon 2023, 9, e16693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.Q.; Lou, Y.Y.; Zhang, P.Y.; Wang, C.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Z. Calculation of carbon emission and prediction of carbon peak in Henan province under the background of energy consumption. J. Henan Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2023, 53, 47–59. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, K.; Wu, L. Using grey Gompertz model to explore the carbon emission and its peak in 16 provinces of China. Energy Build. 2022, 277, 112545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.E.; Li, L.F.; He, S.S.; Li, H.; Wang, Y. Annual prediction of carbon emission peak in Shanxi Province based on IPAT model and scenario analysis method. Resour. Sci. 2016, 38, 2316–2325. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.L.; Li, Y.W.; Wang, H.; Dong, P.; Teng, Y.; Lin, Y.; Liu, L. Prediction of carbon emission in Hebei province based on improved BP neural network. Ecol. Econ. 2024, 40, 30–37. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; Ye, B.; Liu, J. Peak of CO2 emissions in various sectors and provinces of China: Recent progress and avenues for further research. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 112, 813–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.J.; Li, J.Q. Spatio-temporal evolution and influencing factors of carbon emissions in coal resource-based areas: A case study of Shanxi Province. J. Xi’an Univ. Technol. 2024, 1–12. Available online: http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/61.1294.N.20231103.1001.004.html (accessed on 1 March 2024).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).