Assessment of Radon Concentration and Health Hazards in Natural Spring Water of a Sub-Himalayan District
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Water Sampling
2.3. Radon Monitoring Method
2.4. RAD-7 Detector
2.5. Annual Effective Dose
2.6. Cancer Risk
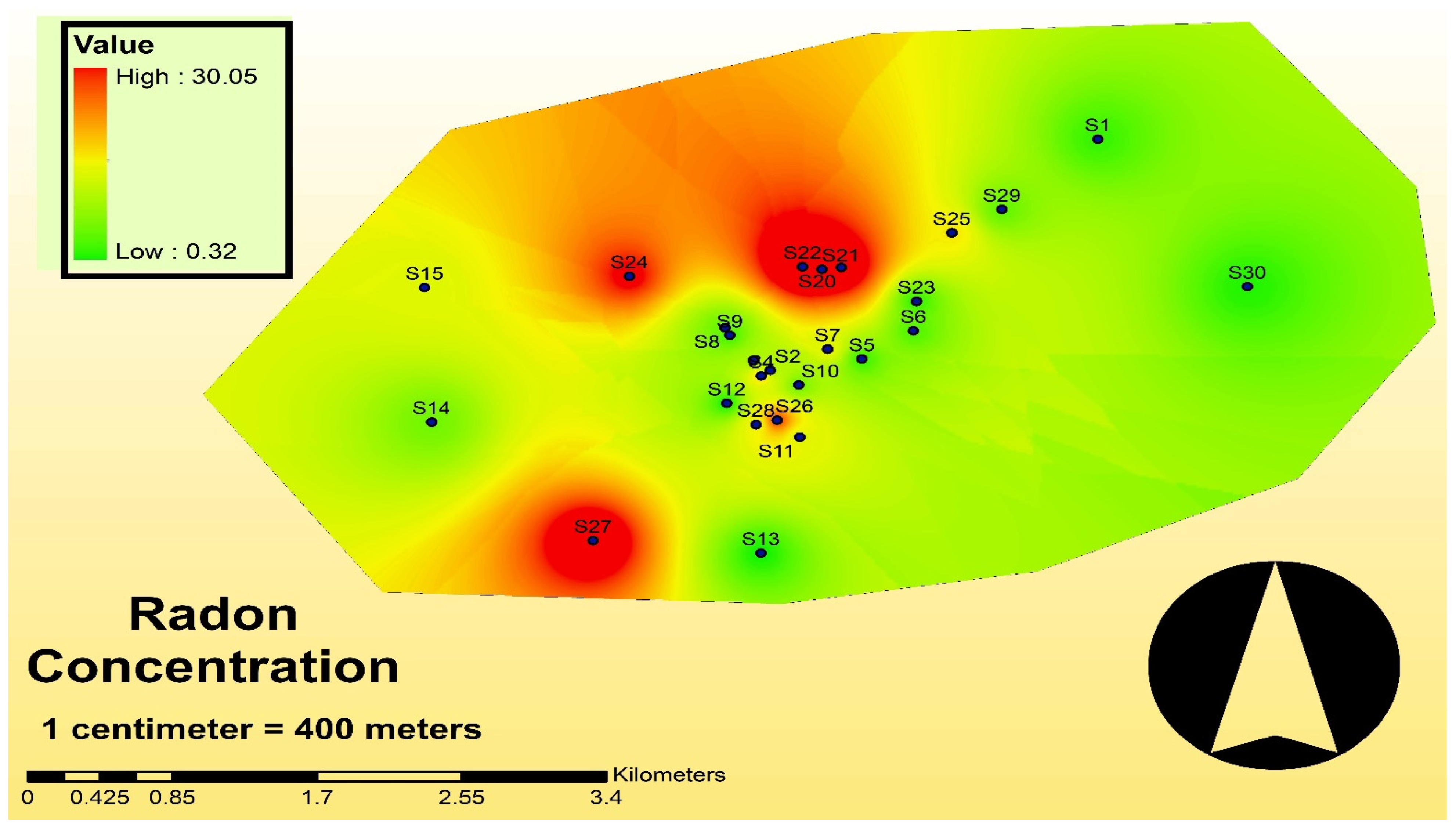
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Health Hazards
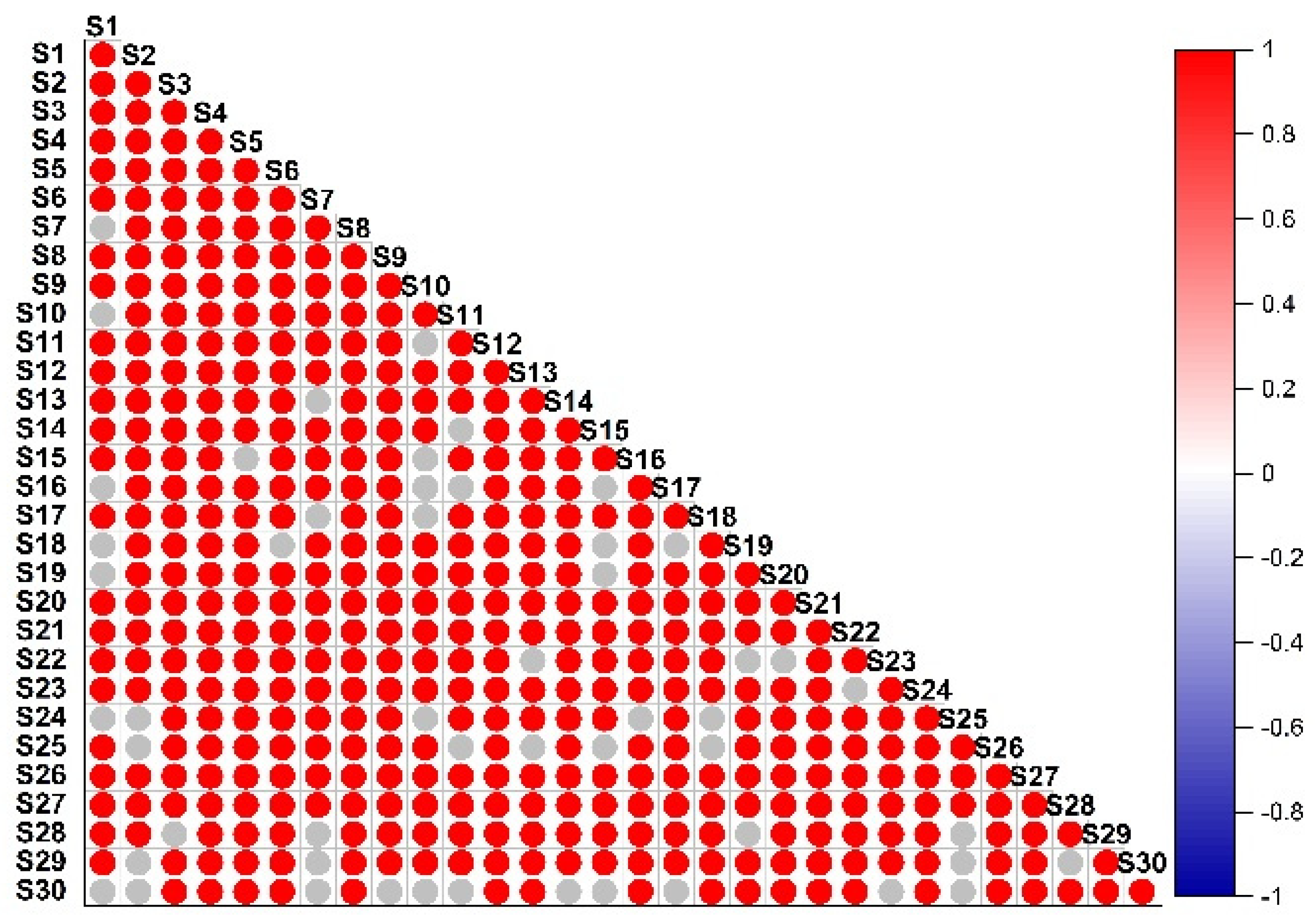
3.2. Correlation
3.3. Comparison of Spring and Bottled Water
3.4. Comparison with Other Studies
3.5. Strengths and Limitations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shah, S.S.A.; Asif, A.R.; Ilahi, M.; Haroon, H.; Islam, I.; Qadir, A.; Nisar, I.; Sani, M.M.U.; Iqbal, R.; ur Rahman, M.H.; et al. Geographical distribution of radon and associated health risks in drinking water samples collected from the Mulazai area of Peshawar, Pakistan. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 6042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjum, M.; Siddique, N.; Younis, H.; Faiz, Y.; Shafique, M.A.; Mahnoor, A.; Sajid, A.; Altaf, M. Heavy Metals and Radionuclides in Islamabad’s Industrial Area: A Comprehensive Analysis of Soil and Water Pollution, Source Apportionment and Health Effects Using Statistical and Geospatial Tools. J. Trace Elem. Miner. 2024, 8, 100127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzenbach, R.P.; Egli, T.; Hofstetter, T.B.; Von Gunten, U.; Wehrli, B. Global Water Pollution and Human Health. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2010, 35, 109–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, W.; Alharthy, R.D.; Zubair, M.; Ahmed, M.; Hameed, A.; Rafique, S. Toxic and heavy metals contamination assessment in soil and water to evaluate human health risk. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Mageed, A.I.; El-Kamel, A.E.-H.; Abbady, A.E.-B.; Harb, S.; Saleh, I.I. Natural radioactivity of ground and hot spring water in some areas in Yemen. Desalination 2013, 321, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pervin, S.; Yeasmin, S.; Khandaker, M.U.; Begum, A. Determination of radon concentration in bottled drinking water of Dhaka City. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2024, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrego-Alonso, D.; Quintana-Arnés, B.; Lozano, J.C. Natural radionuclides behaviour in drinking groundwaters from Castilla y León (Spain); radiological implications. Water Res. 2023, 245, 120616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangaswamy, D.R.; Srinivasa, E.; Srilatha, M.C.; Sannappa, J. Measurement of radon concentration in drinking water of Shimoga district, Karnataka, India. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2016, 307, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopke, P.K.; Borak, T.B.; Doull, J.; Cleaver, J.E.; Eckerman, K.F.; Gundersen, L.C.S.; Harley, N.H.; Hess, C.T.; Kinner, N.E.; Kopecky, K.J.; et al. Health Risks Due to Radon in Drinking Water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 921–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taalab, S.A.; Mohamed, W.H.; Abdel-Rahman, A.M.; Alqahtani, M.S.; La Verde, G.; Pugliese, M.; Hanfi, M.Y.; Ambrosino, F. Distribution maps and hazard of radioelements from granitic rocks in an Egypt region. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2023, 138, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, S.Q.; Khan, J.; Riaz, M.T.; Rafique, M.; Zaman, A.; Khan, S. Radon concentration in spring water as an indicator of seismic activity: A case study of the Muzaffarabad Fault in Pakistan. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 196, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara, E.; Rocha, Z.; Palmieri, H.E.L.; Santos, T.O.; Rios, F.J.; Oliveira, A.H. Radon concentration in soil gas and its correlations with pedologies, permeabilities and 226Ra content in the soil of the Metropolitan Region of Belo Horizonte—RMBH, Brazil. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2015, 116, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeem, U.; Younis, H.; Mehboob, K.; Ajaz, M.; Ali, M.; Hidayat, A.; Muhammad, W. Radionuclide concentrations in agricultural soil and lifetime cancer risk due to gamma radioactivity in district Swabi, KPK, Pakistan. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2023, 56, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjum, M.; Siddique, N.; Younis, H.; Faiz, Y.; Shafique, M.A.; Mahnoor; Feroze, R.; Abbasi, N.U.H. Evaluating heavy metal contamination and radiological effects in soil samples from Murree, Pakistan. Environ. Earth Sci. 2024, 83, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dettmering, T.; Zahnreich, S.; Colindres-Rojas, M.; Durante, M.; Taucher-Scholz, G.; Fournier, C. Increased effectiveness of carbon ions in the production of reactive oxygen species in normal human fibroblasts. J. Radiat. Res. 2015, 56, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darby, S.; Hill, D.; Auvinen, A.; Barros-Dios, J.M.; Baysson, H.; Bochicchio, F.; Deo, H.; Falk, R.; Forastiere, F.; Hakama, M.; et al. Radon in homes and risk of lung cancer: Collaborative analysis of individual data from 13 European case-control studies. BMJ 2005, 330, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheib, C.; Appleton, J.D.; Miles, J.C.H.; Hodgkinson, E. Geological controls on radon potential in England. Proc. Geol. Assoc. 2013, 124, 910–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarahmadi, M.; Shahsavani, A.; Mahmoudian, M.H.; Shamsedini, N.; Rastkari, N.; Kermani, M. Estimation of the residential radon levels and the annual effective dose in dwellings of Shiraz, Iran, in 2015. Electron. Physician 2016, 8, 2497–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Khattak, N.U.; Hanif, M.; Al-Ansari, N.; Khan, M.B.; Ehsan, M.; Elbeltagi, A. Health risks associated with radon concentrations in carbonate and evaporite sequences of the uranium-rich district Karak, Pakistan. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1020028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edition, F. Guidelines for drinking-water quality. WHO Chron. 2011, 38, 104–108. [Google Scholar]
- EPA. Radon in drinking water health risk reduction and cost analysis. Fed. Reg. 1999, 64, 9560–9599. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA. National Primary Drinking Water Regulations; Radionuclides; Proposed Rule. Fed. Regist. 1991, 56, 33050–33127. [Google Scholar]
- Binesh, A.; Mowlavi, A.A.; Mohammadi, S. Estimation of the Effective Dose from Radon Ingestion and Inhalation in Drinking Water Sources of Mashhad, Iran. Iran. J. Radiat. Res. 2012, 10, 37–41. [Google Scholar]
- Salih, N.F. Determine the Contaminations of Radon in the Drinking Water Using NTDs (CR-39) and RAD7 Detectors. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2021, 46, 6061–6074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad Kashmir. Wikipedia. 2024. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Azad_Kashmir&oldid=1220222895 (accessed on 27 April 2024).
- Jobbágy, V.; Stroh, H.; Marissens, G.; Hult, M. Comprehensive study on the technical aspects of sampling, transporting and measuring radon-in-water. J. Environ. Radioact. 2019, 197, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diab, H.M. Accuracy and precision of RAD7 and RAD H2O accessories radon detector in water measurement based on counting statistics for sniff and normal modes. Rom. J. Biophys. 2019, 29, 1–11. Available online: https://www.rjb.ro/wp-content/uploads/Diab_7_F_ACC.pdf (accessed on 16 July 2024).
- Charles, M. Effects of Ionizing Radiation: United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation: UNSCEAR 2006 Report, Volume 1—Report to the General Assembly, with Scientific Annexes A and B 2010; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2010; Available online: https://academic.oup.com/rpd/article-abstract/138/2/187/1647001 (accessed on 22 June 2024).
- Pourshabanian, M.; Nasseri, S.; Nodehi, R.N.; Hosseini, S.S.; Mahvi, A.H. Radon measurement and age-independent effective dose attributed to ingestion of bottled water in Iran: Sensitivity analysis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 12717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajibola, T.B.; Orosun, M.M.; Lawal, W.A.; Akinyose, F.C.; Salawu, N.B. Assessment of Annual Effective Dose Associated with Radon in Drinking Water from Gold and Bismuth Mining area of Edu, Kwara, North-central Nigeria. Pollution 2021, 7, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cousins, C.; Miller, D.L.; Bernardi, G.; Rehani, M.M.; Schofield, P.; Vañó, E.; Einstein, A.J.; Geiger, B.; Heintz, P.; Padovani, R. International commission on radiological protection. ICRP Publ. 2011, 120, 1–125. [Google Scholar]
- Eckerman, K.; Harrison, J.; Menzel, H.G.; Clement, C.H. ICRP publication 119: Compendium of dose coefficients based on ICRP publication 60. Ann. ICRP 2012, 41, 1–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, S. Landslide hazard mapping of Bagh district in Azad Kashmir. Int. J. Econ. Environ. Geol. 2019, 8, 47–50. [Google Scholar]
- Nunes, L.J.R.; Curado, A.; Lopes, S.I. The Relationship between Radon and Geology: Sources, Transport and Indoor Accumulation. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 7460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattak, N.; Khan, M.; Shah, M.; Javed, M. Radon concentration in drinking water sources of the Main Campus of the University of Peshawar and surrounding areas, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2011, 290, 493–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nita, D.C.; Moldovan, M.; Sferle, T.; Ona, V.D.; Burghele, B.D. Radon concentrations in water and indoor air in north-west regions of Romania. Cancer 2013, 2, 196–201. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Burghele-Bety-Denissa/publication/264047155_Radon_concentrations_in_water_and_indoor_air_in_North_-_West_regions_of_Romania/links/5583e68d08ae4738295bb281/Radon-concentrations-in-water-and-indoor-air-in-North-West-regions-of-Romania.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2024).
- Bonotto, D.M. 222Rn, 220Rn and other dissolved gases in mineral waters of southeast Brazil. J. Environ. Radioact. 2014, 132, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamun, A.; Alazmi, A.S. Investigation of Radon in Groundwater and the Corresponding Human-Health Risk Assessment in Northeastern Saudi Arabia. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.P.; Chandra, S.; Prasad, M.; Joshi, A.; Prasad, G.; Ramola, R.C. Estimation of radiation dose due to ingestion of radon in water samples of Garhwal Himalaya, India. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2023, 333, 2867–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, G.M.; Azeez, H.H.; Mustafa, H.T.; Ismaeel, A.O. A study of radon concentration and physicochemical parameters in spring water of Erbil city, Iraqi Kurdistan Region. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2023, 332, 775–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poje Sovilj, M.; Miklavčić, I.; Šmit, G.; Stanić, D.; Radolić, V. Estimation of the annual effective dose from exposure to radon in drinking water in Croatia. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2023, 200, 110950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virk, J.; Virk, H.S. Radon estimation in water of surrey region of British Columbia, Canada using LR-115 type II nuclear track detector. Earth 2021, 12, 50. [Google Scholar]
- Farai, I.P.; Muritala, A.A.; Oni, O.M.; Samuel, T.D.; Abraham, A. Radiological indices estimation from radon concentration in selected groundwater supplies in Abeokuta, south western Nigeria. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2023, 191, 110534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, F.; Muhammad, S.; Ali, W. Radon concentration and potential risks assessment through hot springs water consumption in the Gilgit and Chitral, Northern Pakistan. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
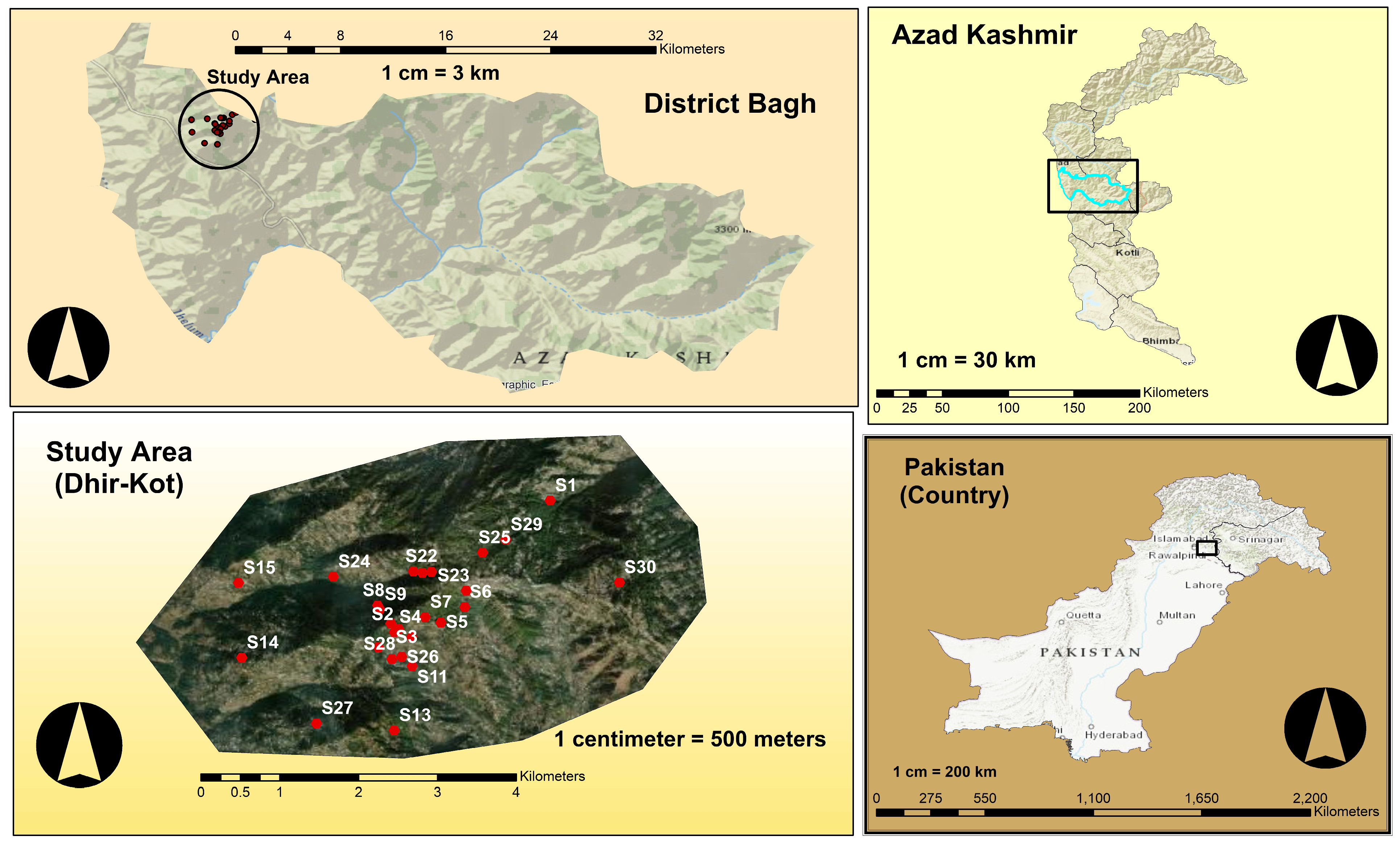




| Sample Number | Sample Cite | Coordinates | Altitude (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | Jandali | 34°04′25.3″ N 73°36′33.9″ E | 1751 |
| S2 | Narean | 34°03′32.0″ N 73°35′31.6″ E | 1947 |
| S3 | Bagla-1 | 34°03′34.3″ N 73°35′28.4″ E | 2001 |
| S4 | Zukh | 34°03′30.7″ N 73°35′29.9″ E | 1949 |
| S5 | Passi | 34°03′34.6″ N 73°35′49.0″ E | 1920 |
| S6 | Reanlii | 34°03′41.1″ N 73°35′58.8″ E | 1914 |
| S7 | Dahaka | 34°03′36.9″ N 73°35′42.5″ E | 1963 |
| S8 | Langer-1 | 34°03′41.8″ N 73°35′23.0″ E | 1909 |
| S9 | Langer-2 | 34°03′40.1″ N 73°35′23.8″ E | 1937 |
| S10 | Batala | 34°03′28.6″ N 73°35′37.0″ E | 1860 |
| S11 | Madrasa | 34°03′16.6″ N 73°35′37.0″ E | 1768 |
| S12 | Ahs | 34°03′24.4″ N 73°35′23.3″ E | 1959 |
| S13 | Koral Bagla | 34°02′49.9″ N 73°35′29.8″ E | 1807 |
| S14 | Kahana Murie | 34°03′20.0″ N 73°34′27.2″ E | 1690 |
| S15 | By Pass-1 | 34°03′51.1″ N 73°34′25.8″ E | 1630 |
| S16 | Nestle pure life | BW | - |
| S17 | Pirrifine | BW | - |
| S18 | Islamabad | BW | - |
| S19 | Prime drinking water | BW | - |
| S20 | Narota-1 | 34°03′55.7″ N 73°35′45.1″ E | 2134 |
| S21 | Narota-2 | 34°03′55.4″ N 73°35′41.4″ E | 2077 |
| S22 | Narota-3 | 34°03′55.8″ N 73°35′37.7″ E | 2019 |
| S23 | Darvaya (Berali) | 34°03′47.9″ N 73°35′59.4″ E | 2050 |
| S24 | Bagla | 34°03′53.7″ N 73°36′04.8″ E | 2125 |
| S25 | Ghoera | 34°04′03.7″ N 73°36′06.1″ E | 2041 |
| S26 | Bisan | 34°03′20.5″ N 73°35′32.9″ E | 1821 |
| S27 | Thanda Nara | 34°02′52.8″ N 73°34′57.9″ E | 1800 |
| S28 | Gandan | 34°03′19.5″ N 73°35′28.9″ E | 1861 |
| S29 | Panyali | 34°04′09.1″ N 73°36′15.6″ E | 1956 |
| S30 | Kahna | 34°03′51.3″ N 73°37′02.3″ E | 1973 |
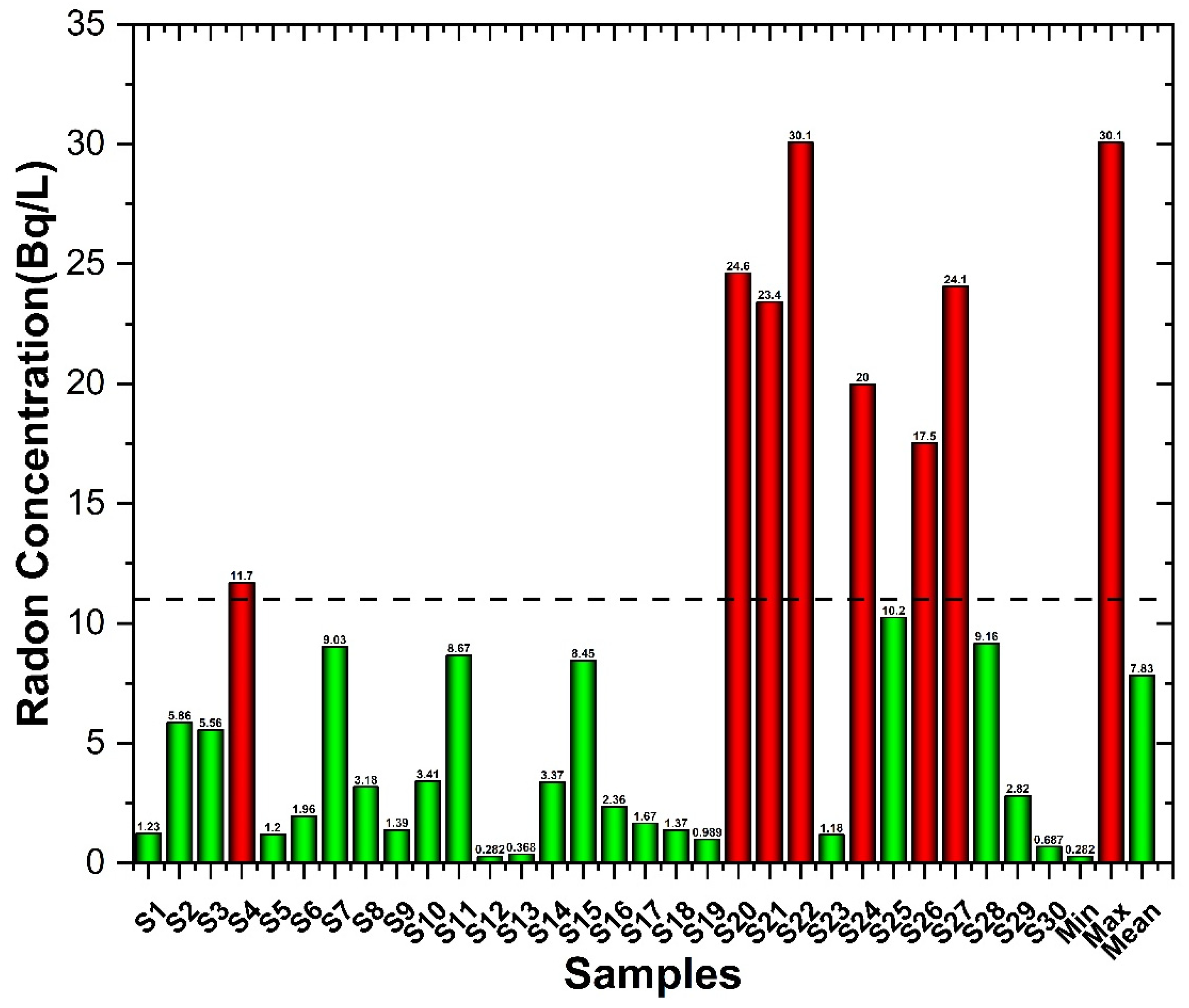
| Sample (ID) | Radon Activity (Bq/L) | E(inh) mSv/y × 10−3 | E(ing) Infants mSv/y × 10−3 | E(ing) Children mSv/y × 10−3 | E(ing) Adult mSv/y × 10−3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 1.23 ± 0.6 | 3.10 | 16.99 | 5.81 | 5.60 |
| S2 | 5.86 ± 2.1 | 14.76 | 80.85 | 27.65 | 26.66 |
| S3 | 5.56 ± 3.4 | 14.02 | 76.76 | 26.25 | 25.31 |
| S4 | 11.70 ± 5.5 | 29.49 | 161.52 | 55.24 | 53.25 |
| S5 | 1.20 ± 0.2 | 3.01 | 16.51 | 5.65 | 5.44 |
| S6 | 1.96 ± 0.3 | 4.93 | 27.00 | 9.23 | 8.90 |
| S7 | 9.03 ± 3.3 | 22.75 | 124.59 | 42.61 | 41.08 |
| S8 | 3.18 ± 0.6 | 8.02 | 43.91 | 15.02 | 14.48 |
| S9 | 1.39 ± 0.3 | 3.50 | 19.15 | 6.55 | 6.31 |
| S10 | 3.41 ± 0.6 | 8.60 | 47.11 | 16.11 | 15.53 |
| S11 | 8.67 ± 4.4 | 21.85 | 119.65 | 40.92 | 39.45 |
| S12 | 0.28 ± 0.1 | 0.71 | 3.89 | 1.33 | 1.28 |
| S13 | 0.37 ± 0.09 | 0.93 | 5.08 | 1.74 | 1.68 |
| S14 | 3.37 ± 2.2 | 8.50 | 46.55 | 15.92 | 15.35 |
| S15 | 8.45 ± 2.4 | 21.29 | 116.59 | 39.88 | 38.44 |
| S16 | 2.36 ± 1.1 | 5.95 | 32.56 | 11.14 | 10.74 |
| S17 | 1.67 ± 0.3 | 4.20 | 23.01 | 7.87 | 7.59 |
| S18 | 1.37 ± 0.4 | 3.46 | 18.96 | 6.48 | 6.25 |
| S19 | 0.99 ± 0.1 | 2.49 | 13.65 | 4.67 | 4.50 |
| S20 | 24.63 ± 3.7 | 62.07 | 339.89 | 116.25 | 112.06 |
| S21 | 23.42 ± 7.4 | 59.02 | 323.21 | 110.55 | 106.57 |
| S22 | 30.07 ± 3.7 | 75.77 | 414.95 | 141.92 | 136.81 |
| S23 | 1.18 ± 0.8 | 2.98 | 16.31 | 5.58 | 5.38 |
| S24 | 19.98 ± 4.5 | 50.35 | 275.72 | 94.31 | 90.91 |
| S25 | 10.25 ± 3.2 | 25.83 | 141.44 | 48.38 | 46.63 |
| S26 | 17.52 ± 6.7 | 44.15 | 241.75 | 82.69 | 79.71 |
| S27 | 24.06 ± 3.6 | 60.64 | 332.06 | 113.57 | 109.48 |
| S28 | 9.16 ± 5.5 | 23.09 | 126.46 | 43.25 | 41.69 |
| S29 | 2.82 ± 1.4 | 7.10 | 38.86 | 13.29 | 12.81 |
| S30 | 0.69 ± 0.4 | 1.73 | 9.48 | 3.24 | 3.13 |
| Min | 0.28 ± 0.1 | 0.71 | 3.89 | 1.33 | 1.28 |
| Max | 30.07 ± 3.7 | 75.77 | 414.95 | 141.92 | 136.81 |
| Mean | 7.86 ± 2.3 | 19.81 | 108.48 | 37.10 | 35.77 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sajid, A.; Anjum, M.; Younis, H.; Salouci, M.; Mehboob, K.; Haj Ismail, A. Assessment of Radon Concentration and Health Hazards in Natural Spring Water of a Sub-Himalayan District. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 940. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15080940
Sajid A, Anjum M, Younis H, Salouci M, Mehboob K, Haj Ismail A. Assessment of Radon Concentration and Health Hazards in Natural Spring Water of a Sub-Himalayan District. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(8):940. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15080940
Chicago/Turabian StyleSajid, Ayesha, Mavia Anjum, Hannan Younis, Moustafa Salouci, Khurram Mehboob, and Abd Haj Ismail. 2024. "Assessment of Radon Concentration and Health Hazards in Natural Spring Water of a Sub-Himalayan District" Atmosphere 15, no. 8: 940. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15080940
APA StyleSajid, A., Anjum, M., Younis, H., Salouci, M., Mehboob, K., & Haj Ismail, A. (2024). Assessment of Radon Concentration and Health Hazards in Natural Spring Water of a Sub-Himalayan District. Atmosphere, 15(8), 940. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15080940









