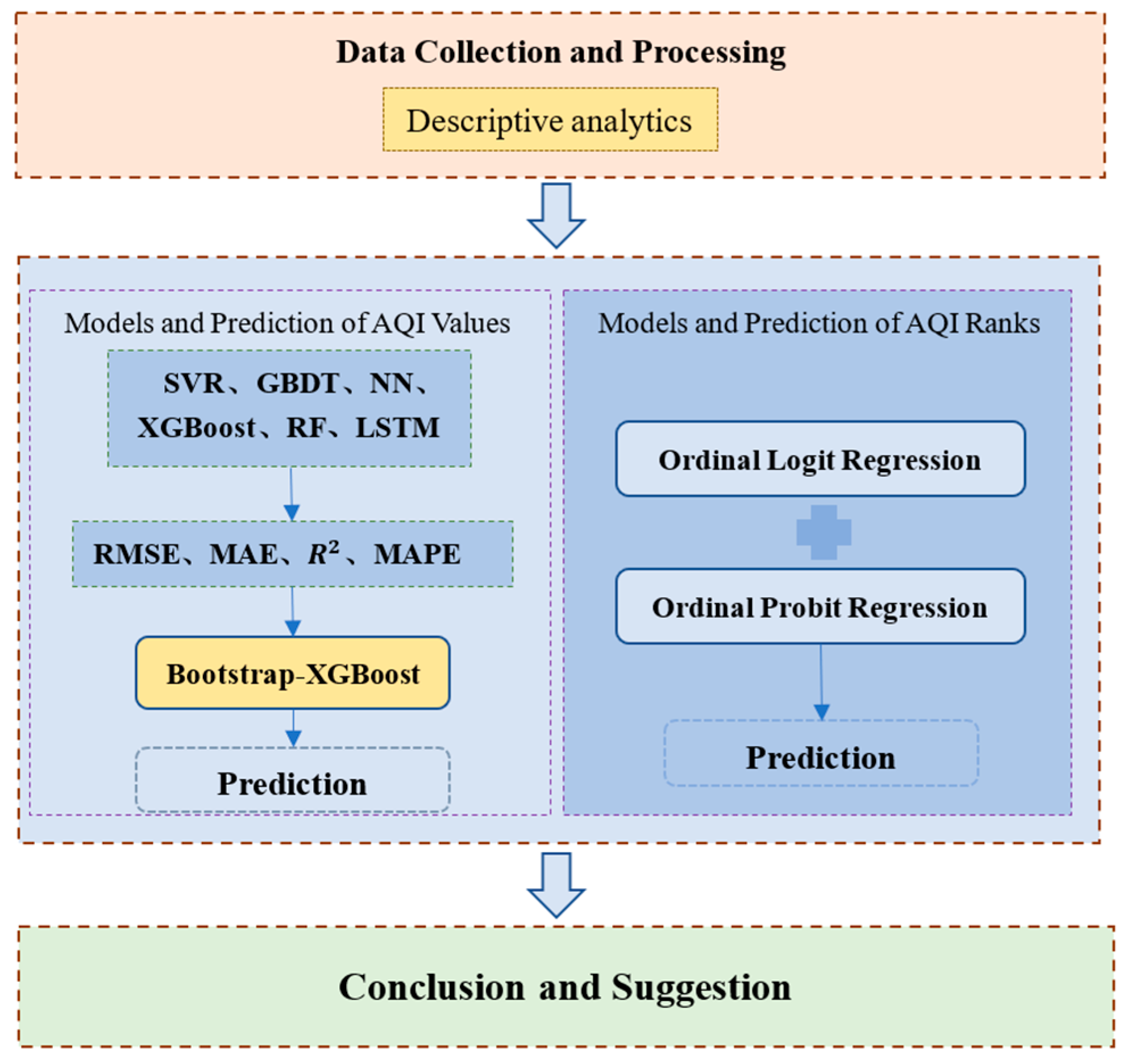
Air Quality Prediction and Ranking Assessment Based on Bootstrap-XGBoost Algorithm and Ordinal Classification Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data Sources and Preprocessing
2.1. Data Sources
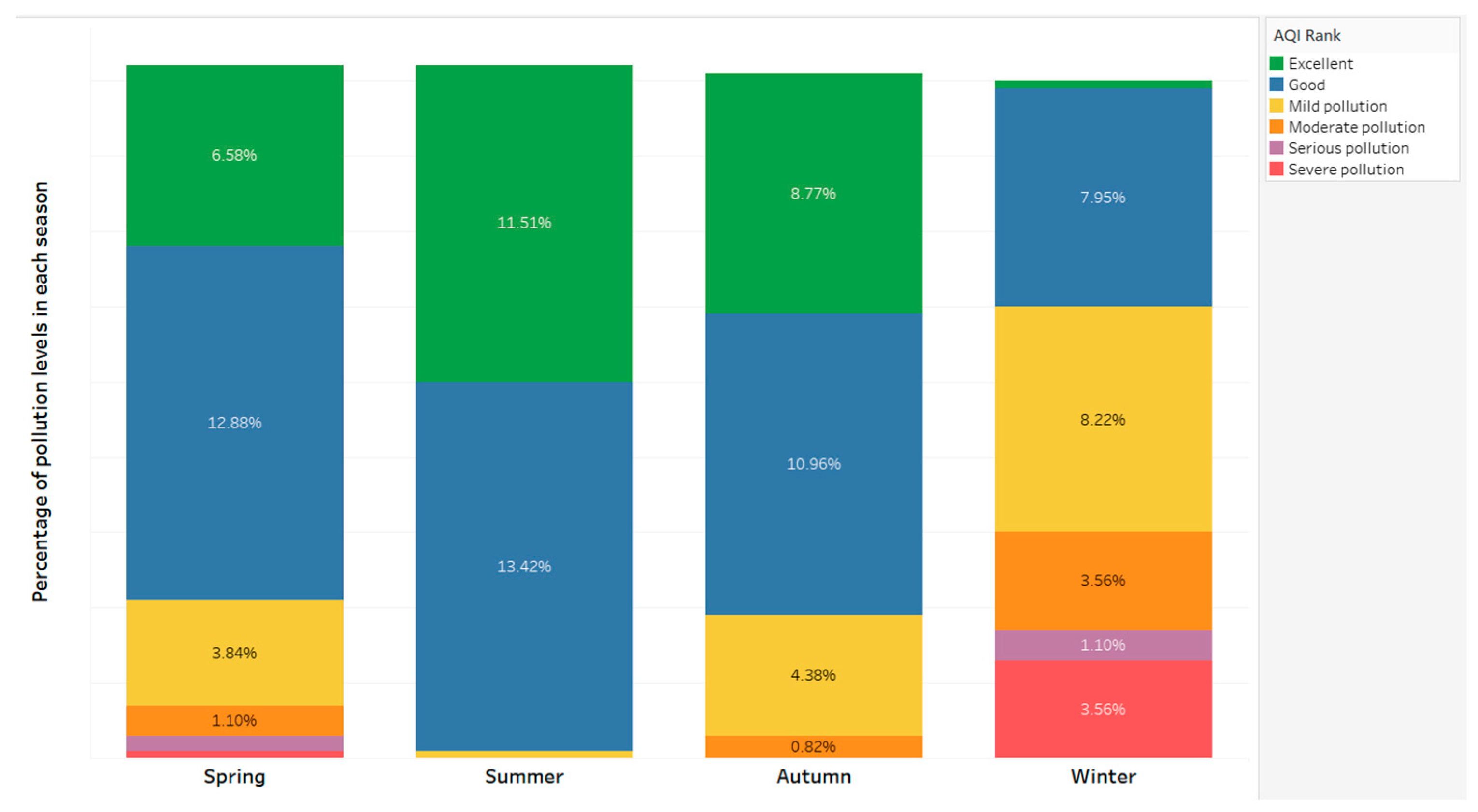
2.2. Data Preprocessing and Seasonal Air Pollution Percentage Analysis
3. Empirical Analysis of AQI Prediction
3.1. Analysis Based on SVR Model
3.2. Analysis Based on GBDT Model
- Initialise the learner:
- 2.
- For each tree and each sample , calculate the corresponding negative gradient, i.e., residuals
3.3. Analysis Based on XGBoost Model
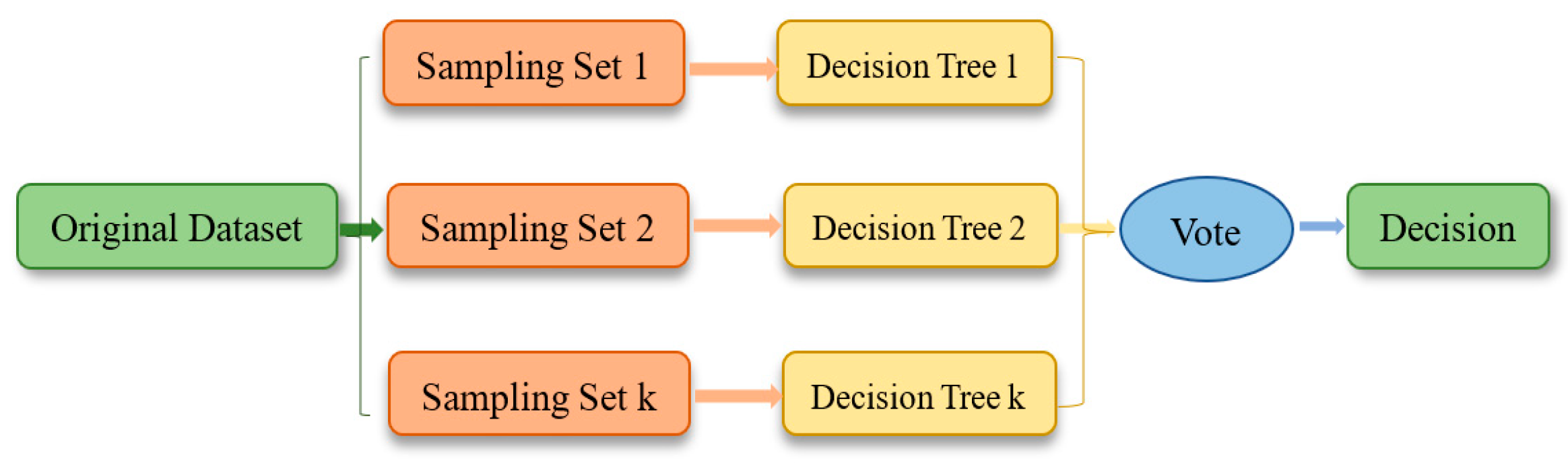
3.4. Analysis Based on RF Model
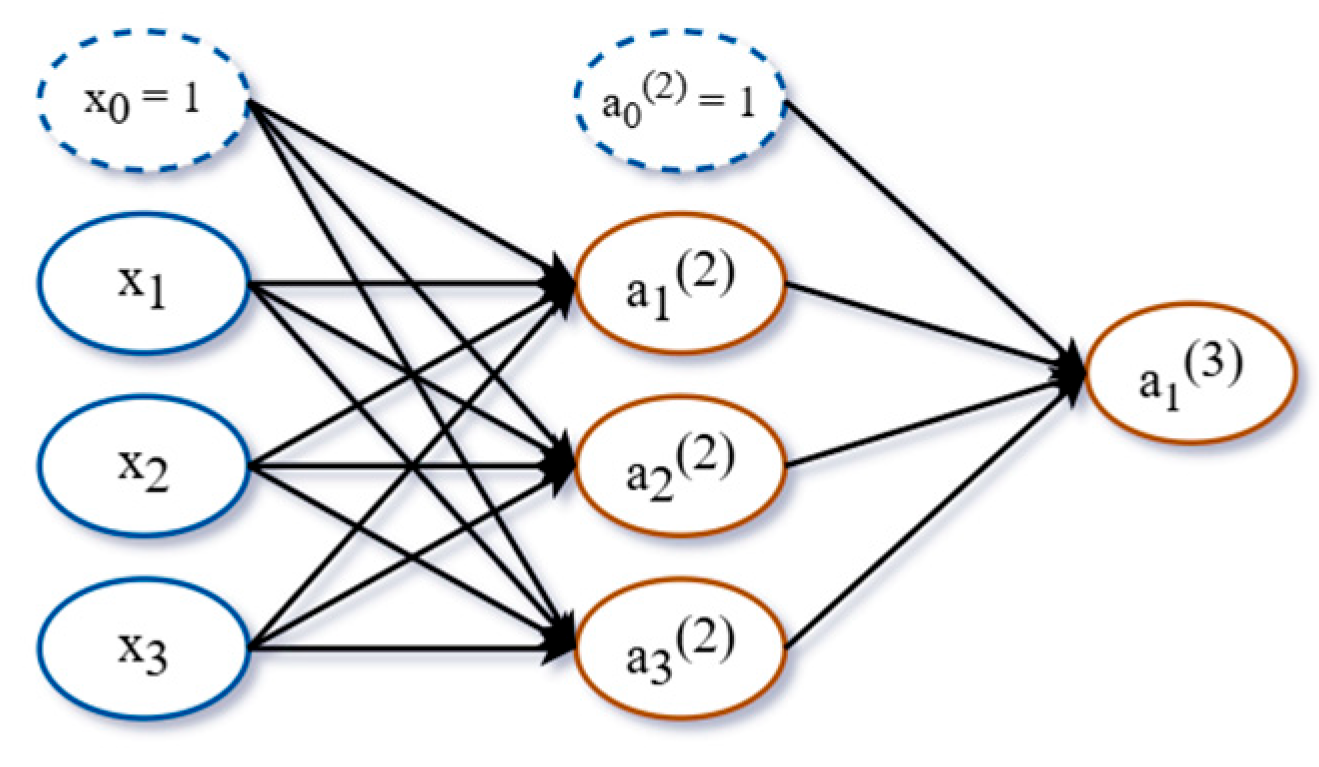
3.5. Analysis Based on NN Model
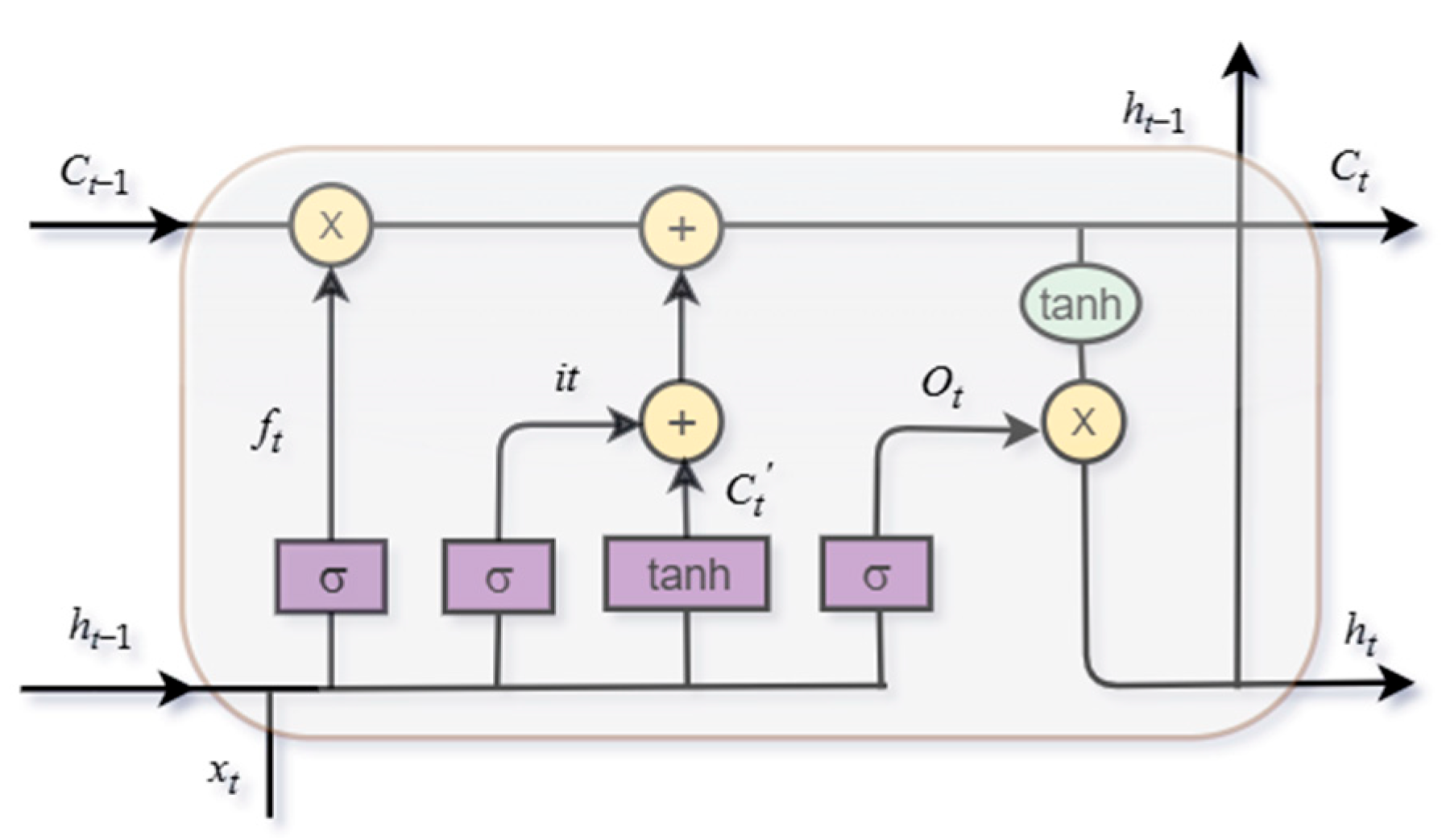
3.6. Analysis Based on LSTM Model
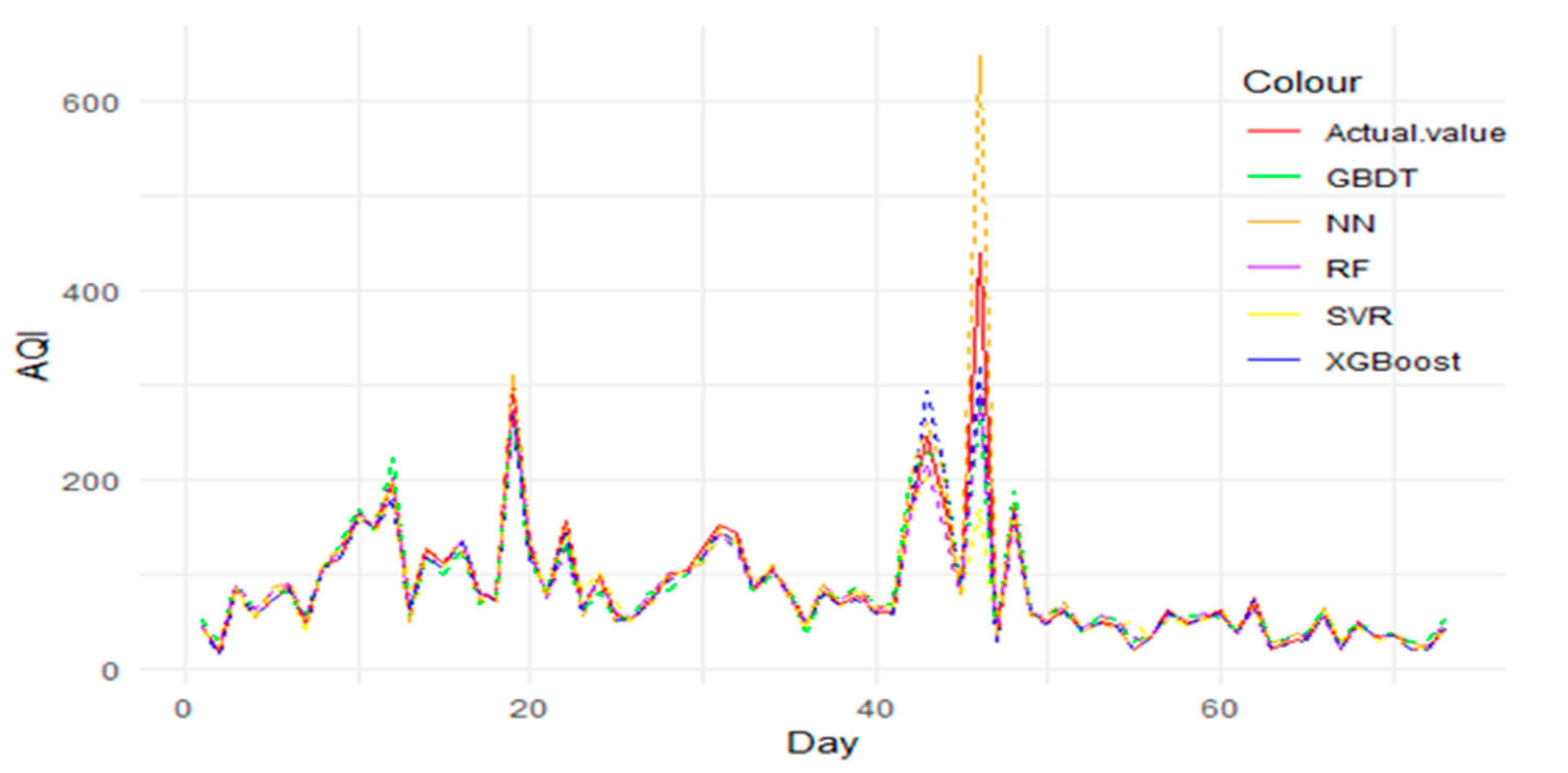
3.7. Forecast Results and Comparative Analysis
3.8. Model Evaluation
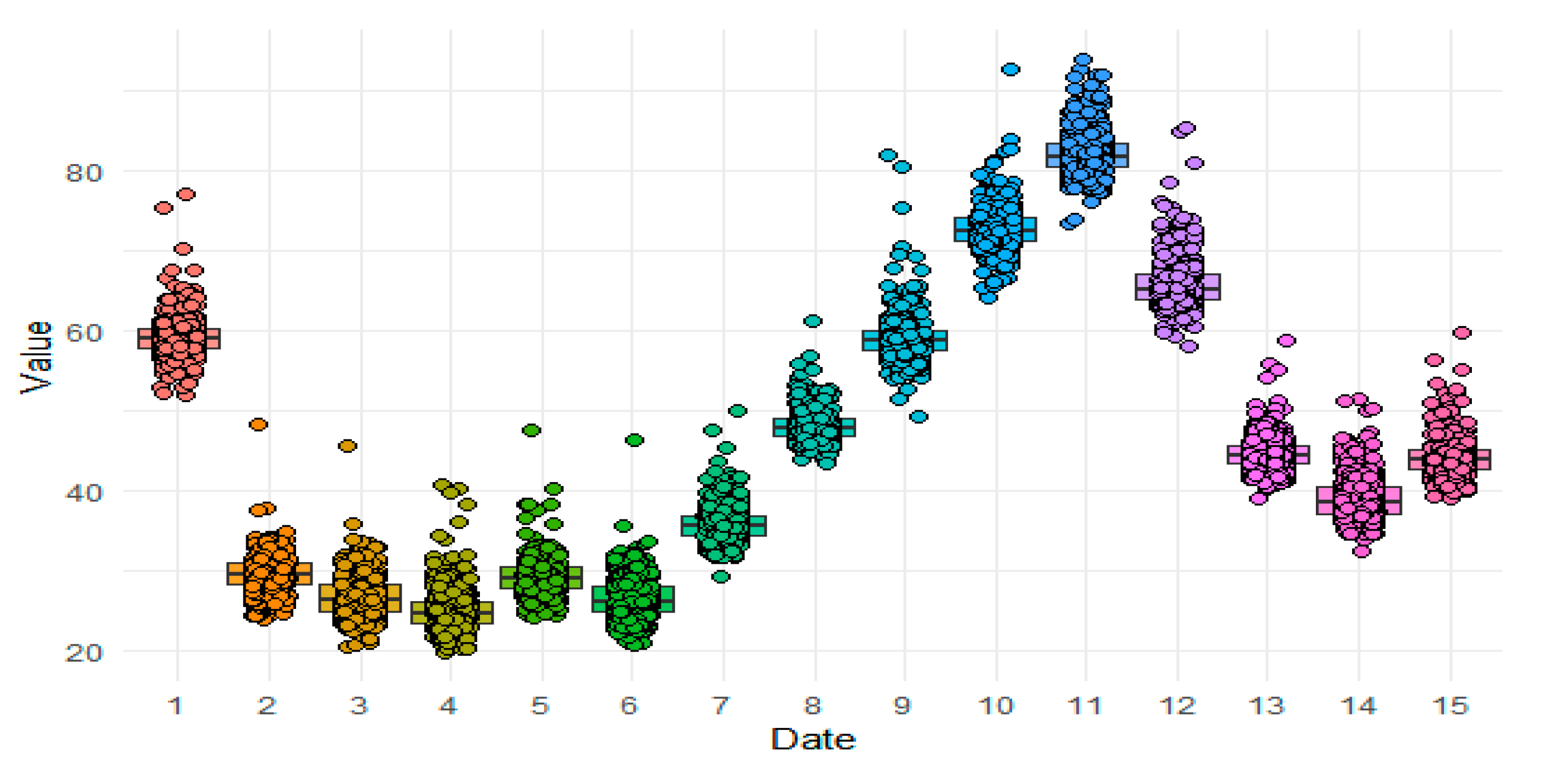
4. AQI Prediction Based on Bootstrap-XGBoost
| Algorithm 1: The Bootstrap-XGBoost algorithm |
| Bootstrap sample size times Boostrap prediction results 6: Residual Bootstrap step: } , the prediction standard deviation and 95% prediction interval are calculated |
5. AQI Rank Assessment
5.1. Ordinal Logit Model and Ordinal Probit Model
5.2. Model Estimation Results
5.3. AQI Ranking Forecast
6. Conclusions and Suggestions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Y. Ambient air pollution and daily hospital admissions for respiratory system–related diseases in a heavy polluted city in Northeast China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 10055–10064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, J. Particulate air pollution and chronic respiratory disease. Environ. Res. 1993, 62, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, G.; He, H.; Sha, Y.; Zhai, G.; Zong, S. Effect of PM2. 5 on daily outpatient visits for respiratory diseases in Lanzhou, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 1563–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Woodward, A.; Vardoulakis, S.; Kovats, S.; Wilkinson, P.; Li, L.; Xu, L.; Li, J.; Yang, J.; Cao, L.; et al. Haze, public health and mitigation measures in China: A review of the current evidence for further policy response. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 578, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graupe, D.; Krause, D.; Moore, J. Identification of autoregressive moving-average parameters of time series. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control. 1975, 20, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, B.; Yin, Y. The prediction and research of air quality in Chengdu based on ARMA model. Stat. Appl. 2016, 5, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, Y.P.; Zhang, M.B.; Bertolatti, D. An application of ARIMA model to predict submicron particle concentrations from meteorological factors at a busy roadside in Hangzhou, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 426, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedi, A.; Baygi, M.M.; Poursafa, P.; Mehrara, M.; Amin, M.M.; Hemami, F.; Zarean, M. Air pollution and hospitalisation: An autoregressive distributed lag (ARDL) approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 30673–30680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woldu, G. Impact of urbanisation and globalisation on environmental quality in Mozambique: An ARDL bound testing approach. Int. J. Clim. Chang. Impacts Responses 2021, 13, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.H.; Ng, S.C.H.; Kwok, K.C.M.; Yung, K.L. Applying Industrial Internet of Things Analytics to Manufacturing. Machines 2023, 11, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Cao, J.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, L. A Novel Flexible Geographically Weighted Neural Network for High-Precision PM2.5 Mapping across the Contiguous United States. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2024, 13, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.H.; Wong, Y.S.; Ip, W.H.; Lau, H.C.W.; Lee, C.K.M.; Ho, G.T.S. Modeling the cleanliness level of an ultrasonic cleaning system by using design of experiments and artificial neural networks. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2009, 41, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.M.; Lin, Y.S. TPTM-HANN-GA: A Novel Hyperparameter Optimization Framework Integrating the Taguchi Method, an Artificial Neural Network, and a Genetic Algorithm for the Precise Prediction of Cardiovascular Disease Risk. Mathematics 2024, 12, 1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biancofiore, F.; Busilacchio, M.; Verdecchia, M. Recursive neural network model for analysis and forecast of PM10 and PM2.5. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2017, 8, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Deng, M.; Xu, F.; Wang, H. Prediction of hourly PM2.5 using a space-time support vector regression model. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 181, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawul, M. Application of neural networks to the prediction of gas pollution of air. New Trends Prod. Eng. 2019, 2, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Ding, Y.; Cheng, J.C.P.; Jiang, F.; Tan, Y.; Gan, V.J.; Wan, Z. Identification of high impact factors of air quality on a national scale using big data and machine learning techniques. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 244, 118955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Qin, J.; He, Z.; Li, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, R. Combining forward with recurrent neural networks for hourly air quality prediction in Northwest of China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 28931–28948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekkar, A.; Hssina, B.; Douzi, S. Air-pollution prediction in smart city, deep learning approach. J. Big Data 2021, 8, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Ge, C.; Xiong, T.; Song, S.; Yang, L.; Liu, B.; Yin, W.; Wu, C. Large scale air pollution prediction with deep convolutional networks. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2021, 64, 192107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samad, A.; Garuda, S.; Vogt, U.; Yang, B. Air pollution prediction using machine learning techniques—An approach to replace existing monitoring stations with virtual monitoring stations. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 310, 119987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, S. Modeling air quality PM2. 5 forecasting using deep sparse attention-based transformer networks. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 20, 13535–13550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Hu, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J. Construction of air quality level prediction model based on STEPDISC-PCA-BP. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 8506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratković, K.; Kovač, N.; Simeunović, M. Hybrid LSTM Model to Predict the Level of Air Pollution in Montenegro. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 10152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, N.; Huang, X.; Yang, L.; Yang, W. Co-Training Semi-Supervised Learning for Fine-Grained Air Quality Analysis. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.H.; Jeon, H.W.; Sung, U.J.; Sohn, J.R. Impact of the COVID-19 outbreak on air quality in Korea. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-vector networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.H. Greedy function approximation: A gradient boosting machine. Ann. Stat. 2001, 29, 1189–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. Xgboost: A scalable tree boosting system. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/13853244_Long_Short-term_Memory (accessed on 29 November 2023). [CrossRef]
| Minimum | Maximum | Mean | Median | Mode | Skewness | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AQI | 13 | 439 | 86.1206 | 67 | 53 | 2.2285 |
| SO2 | 4 | 26 | 7.7342 | 7 | 6 | 2.1754 |
| NO2 | 8 | 90 | 36.3123 | 32 | 20 | 0.8220 |
| PM2.5 | 6 | 283 | 52.2740 | 33 | 17 | 2.1467 |
| CO | 0.3 | 2 | 0.7047 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 1.5547 |
| PM10 | 10 | 1072 | 98.6603 | 76 | 46 and 52 | 4.6481 |
| O3 | 5 | 147 | 56.3726 | 52 | 20 | 0.5450 |
| Model | MAE | RMSE | MAPE(%) | R-Squared |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVR | 9.6472 | 33.0640 | 10.68 | 0.7611 |
| XGBoost | 5.5969 | 16.1382 | 3.90 | 0.9431 |
| GBDT | 9.8143 | 21.3959 | 11.4 | 0.9000 |
| RF | 7.6624 | 19.2412 | 8.05 | 0.9191 |
| CNN | 9.1216 | 25.8005 | 9.86 | 0.8546 |
| LSTM | 6.2284 | 7.6542 | 38.11 | 0.2235 |
| Forecast Date | Actual Value | Forecast Value | Standard Deviation | 95% Prediction Interval |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| October 1 | 56 | 56.8184 | 2.4194 | [55.0003, 64.3353] |
| October 2 | 26 | 28.5179 | 2.2609 | [25.3514, 33.7640] |
| October 3 | 25 | 23.0133 | 2.6373 | [22.8364, 32.3976] |
| October 4 | 22 | 22.6515 | 2.6171 | [21.0723, 30.7458] |
| October 5 | 26 | 28.0114 | 2.3195 | [25.0484, 33.1558] |
| October 6 | 24 | 23.0133 | 2.5359 | [22.7003, 31.5158] |
| October 7 | 36 | 33.5798 | 2.2505 | [32.3784, 41.1384] |
| October 8 | 44 | 45.4493 | 1.9171 | [44.9358, 52.4214] |
| October 9 | 56 | 56.8184 | 2.8158 | [54.9225, 64.9447] |
| October 10 | 70 | 69.2584 | 2.6190 | [68.1752, 78.4387] |
| October 11 | 77 | 77.8555 | 2.7382 | [77.8773, 88.8032] |
| October 12 | 66 | 63.8876 | 3.2501 | [61.4553, 73.4492] |
| October 13 | 41 | 41.7567 | 2.0295 | [41.7567, 48.7301] |
| October 14 | 39 | 36.6577 | 2.7054 | [34.8364, 45.4578] |
| October 15 | 40 | 41.7567 | 2.3040 | [40.5036, 49.5267] |
| Ordinal Logit Regression | Ordinal Probit Regression | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Estimate | S.E | p-Value | Estimate | S.E | p-Value |
| 9.5826 | 1.6391 | 0.0000 | 5.4850 | 0.9473 | 0.0000 | |
| 23.2516 | 3.0082 | 0.0000 | 14.0113 | 1.7184 | 0.0000 | |
| 34.9270 | 4.4030 | 0.0000 | 20.7566 | 2.4414 | 0.0000 | |
| 46.4949 | 5.8521 | 0.0000 | 28.0236 | 3.3141 | 0.0000 | |
| 67.1061 | 8.7257 | 0.0000 | 41.2004 | 4.8089 | 0.0000 | |
| PM2.5 | 0.1729 | 0.0260 | 0.0000 | 0.1109 | 0.0146 | 0.0000 |
| PM10 | 0.1033 | 0.0147 | 0.0000 | 0.0632 | 0.0086 | 0.0000 |
| SO2 | −0.3825 | 0.1456 | 0.0086 | −0.2405 | 0.0893 | 0.0071 |
| NO2 | 0.0415 | 0.0240 | 0.0834 | 0.0170 | 0.0136 | 0.2104 |
| O3 | 0.0379 | 0.0091 | 0.0000 | 0.0224 | 0.0053 | 0.0000 |
| CO | −1.2952 | 1.6675 | 0.4373 | −0.9499 | 0.9723 | 0.3286 |
| Model | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|
| Ordinal logit regression model | 89.04 |
| Ordinal probit regression model | 86.30 |
| Forecast Date | True Rank | Prediction Rank (Predicted Probability) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ordinal Logit Regression | Ordinal Probit Regression | ||
| October 1 | II | II (0.6531) | II (0.6729) |
| October 2 | I | I (0.9870) | I (0.9935) |
| October 3 | I | I (0.9956) | I (0.9994) |
| October 4 | I | I (0.9961) | I (0.9996) |
| October 5 | I | I (0.9904) | I (0.9966) |
| October 6 | I | I (0.9914) | I (0.9971) |
| October 7 | I | I (0.9407) | I (0.9493) |
| October 8 | I | I (0.8979) | I (0.9049) |
| October 9 | II | II (0.5727) | II (0.5560) |
| October 10 | II | II (0.9978) | II (0.9999) |
| October 11 | II | II (0.9923) | II (0.9989) |
| October 12 | II | II (0.9974) | II (0.9999) |
| October 13 | I | I (0.9157) | I (0.9213) |
| October 14 | I | I (0.9159) | I (0.9258) |
| October 15 | I | I (0.9078) | I (0.9249) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, J.; Tian, Y.; Wu, C.H. Air Quality Prediction and Ranking Assessment Based on Bootstrap-XGBoost Algorithm and Ordinal Classification Models. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 925. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15080925
Yang J, Tian Y, Wu CH. Air Quality Prediction and Ranking Assessment Based on Bootstrap-XGBoost Algorithm and Ordinal Classification Models. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(8):925. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15080925
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Jingnan, Yuzhu Tian, and Chun Ho Wu. 2024. "Air Quality Prediction and Ranking Assessment Based on Bootstrap-XGBoost Algorithm and Ordinal Classification Models" Atmosphere 15, no. 8: 925. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15080925
APA StyleYang, J., Tian, Y., & Wu, C. H. (2024). Air Quality Prediction and Ranking Assessment Based on Bootstrap-XGBoost Algorithm and Ordinal Classification Models. Atmosphere, 15(8), 925. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15080925







