A Comprehensive Review of Surface Ozone Variations in Several Indian Hotspots
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Photochemical Production of Surface O3
2.1. Role of CO and VOCs on Surface O3 Formation
2.2. Photochemical Destruction of Surface O3
3. Surface O3 Measurements in India
3.1. Concise Overview in the Indian Region
3.2. Comparison of O3 Variations at Different Sites in India
4. Surface O3Measurements in the Kerala Region
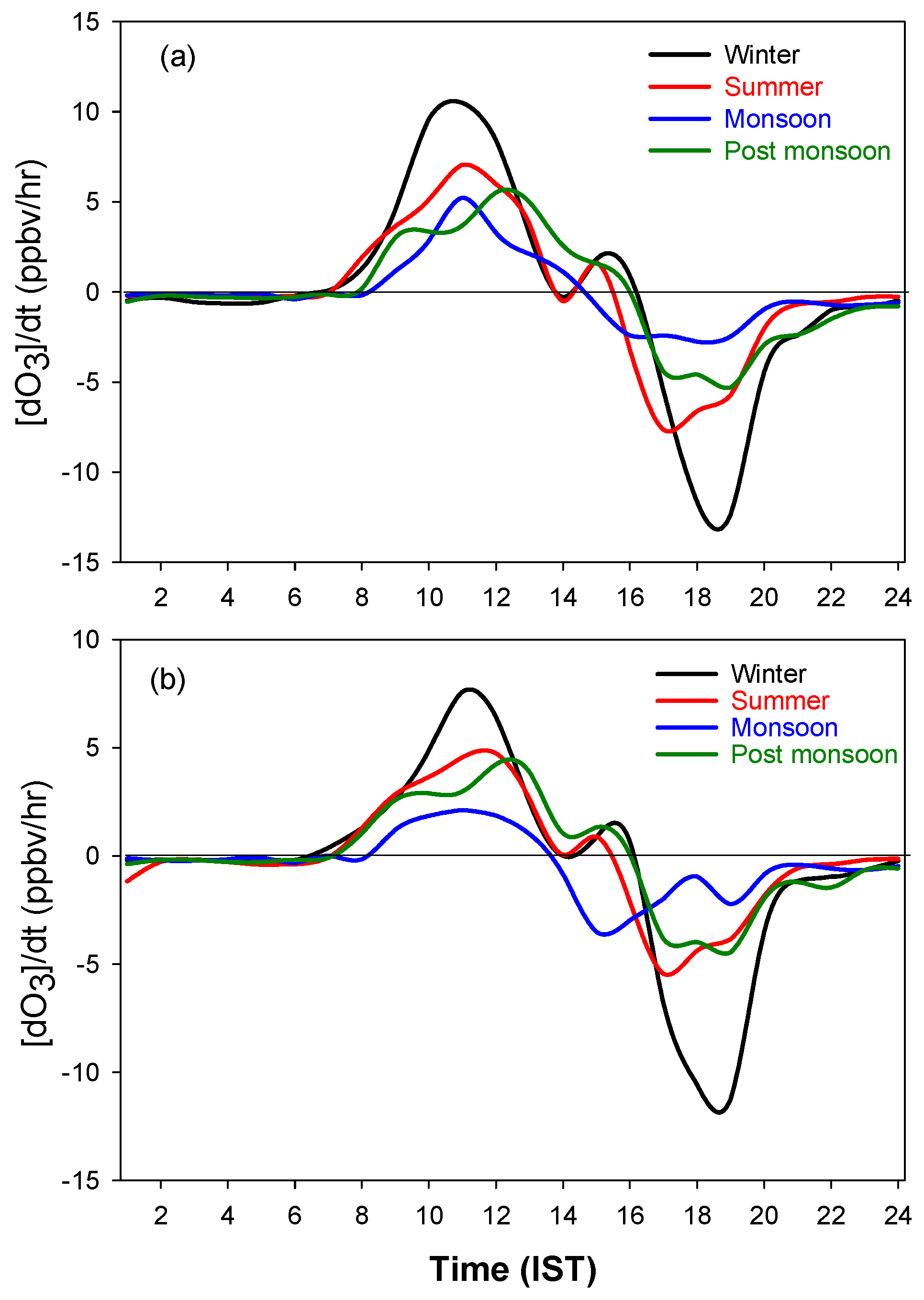
5. Long-Term Variation in Surface O3 over Two Locations in Kannur
6. Surface O3 Variations during Special Episodes in India
6.1. Surface O3 Variations during Fireworks
6.2. Surface O3 Variations during Different Solar Eclipse
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meo, S.A.; Salih, M.A.; Hussain, F.A.; Alkhalifah, J.M.; Meo, A.S.; Akram, A. Environmental pollutants PM2.5, PM10, carbon monoxide (CO), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), sulfur dioxide (SO2), and ozone (O3) impair human cognitive functions. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2024, 28, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masiol, M.; Hopke, P.K.; Felton, H.D.; Frank, B.P.; Rattigan, O.V.; Wurth, M.J.; LaDuke, G.H. Analysis of Major Air Pollutants and Submicron Particles in New York City and Long Island. J. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 48, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, H. Air pollution in cities. J. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 4029–4037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crutzen, P.J. The role of NO and NO2 in the chemistry of the troposphere and stratosphere. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 1979, 7, 443–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prather, M.J.; Zhu, X.; Tang, Q.; Hsu, J.; Neu, J.L. An atmospheric chemist in search of the tropopause. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, 2156–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myhre, G.; Shindell, D.; Breìon, F.-M.; Collins, W.; Fuglestvedt, J.; Huang, J.; Koch, D.; Lamarque, J.-F.; Lee, D.; Mendoza, B.; et al. Anthropogenic and natural radiative forcing, in: Climate Change: The physical science basis. In Contribution of Working Wroup I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 659–740. [Google Scholar]
- Staehelin, J.; Harris, N.R.P.; Appenzeller, C.; Eberhard, J. Ozone trends: A review. Rev. Geophys. 2001, 39, 231–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, V.; Dickinson, R.E.J. The role of stratospheric O3 in the zonal and seasonal radiative energy balance of the Earth-troposphere system. Atmos. Sci. 1979, 36, 1084–1104. [Google Scholar]
- Archibald, A.T.; Neu, J.L.; Elshorbany, Y.; Cooper, O.R.; Young, P.J.; Akiyoshi, H.; Cox, R.A.; Coyle, M.; Derwent, R.; Deushi, M.; et al. Tropospheric ozone assessment report: A critical review of changes in the tropospheric ozone burden and budget from 1850 to 2100. Elem. Sci. Anthr. 2020, 8, 034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasick, D.; Galbally, I.E.; Cooper, O.R.; Schultz, M.G.; Ancellet, G.; Leblanc, T.; Wallington, T.J.; Ziemke, J.; Liu, X.; Steinbacher, M.; et al. Tropospheric Ozone Assessment Report: Tropospheric ozone from 1877 to 2016, observed levels, trends and uncertainties. Elem. Sci. Anthr. 2019, 7, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, G.; Pleijel, H.; Malley, C.S.; Sinha, B.; Cooper, O.R.; Schultz, M.G.; Neufeld, H.S.; Simpson, D.; Sharps, K.; Feng, Z.; et al. Tropospheric Ozone Assessment Report: Present-day tropospheric ozone distribution and trends relevant to vegetation. Elem. Sci. Anthr. 2018, 6, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefohn, A.S.; Malley, C.S.; Smith, L.; Wells, B.; Simon, H.; Naik, V.; Mills, G.; Schultz, M.G.; De Marco, A.; Xu, X.; et al. Tropospheric ozone assessment report: Global ozone metrics for climate change, human health, and crop/ecosystem research. Elem. Sci. Anthr. 2018, 6, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, Z.; Doherty, R.M.; Schneidemesser, E.; Malley, C.S.; Cooper, O.R.; Pinto, J.P.; Colette, A.; Xu, X.; Simpson, D.; Schultz, M.G.; et al. Tropospheric Ozone Assessment Report: Present-day ozone distribution and trends relevant to human health. Elem. Sci. Anthr. 2018, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudel, A.; Cooper, O.R.; Ancellet, G.; Barret, B.; Boynard, A.; Burrows, J.P.; Clerbaux, C.; Cuesta, J.; Cuevas, E.; Doniki, S.; et al. Tropospheric Ozone Assessment Report: Present-day distribution and trends of tropospheric ozone relevant to climate and global atmospheric chemistry model evaluation. Elem. Sci. Anthr. 2018, 6, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudel, A.; Bourgeois, I.; Li, M.; Chang, K.-L.; Ziemke, J.; Sauvage, B.; Stauffer, R.M.; Thompson, A.M.; Kollonige, D.E.; Smith, N.; et al. Tropical tropospheric ozone distribution and trends from in situ and satellite data. EGUsphere 2024, 1–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chameides, W.; Walker, J.C.G. A photochemical theory of tropospheric ozone. J. Geophys. Res. 1973, 78, 8751–8760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camalier, L.; Cox, W.; Dolwick, P. The effects of meteorology on ozone in urban areas and their use in assessing O3 trends. J. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 41, 7127–7137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiore, A.M.; Jacob, D.J.; Logan, J.A.; Yin, J.H. Long-term trends in ground level ozone over the contiguous United States, 1980–1995. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1998, 103, 1471–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. EPA’s Report on the Environment 2008, EPA/600/R-07/045F; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2008; p. 20460. [Google Scholar]
- Solomon, P.; Cowling, E.; Hidy, G.; Furiness, C. Comparison of scientific findings from major ozone field studies in North America and Europe. Atmos Environ. 2000, 34, 1885–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloomfield, P.; Royle, J.A.; Steinberg, L.J.; Yang, Q. Accounting for meteorological effects in measuring urban ozone levels and trends. Atmos. Environ. 1996, 30, 3067–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, W.M.; Chu, S.H. Assessment of interannual ozone variation in urban areas from a climatological perspective. Atmos. Environ. 1996, 30, 2615–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mickley, L.J.; Murti, P.P.; Jacob, D.J.; Logan, J.A.; Koch, D.M.; Rind, D. Radiative Forcing from Tropospheric Ozone Calculated with a Unified Chemistry-Climate Model. J. Geophys. Res. 1999, 104, 30153–30172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.D.; Thompson, B.; Revadekar, J.V. On the variation of the tropospheric ozone over Indian region in relation to the meteorological parameters. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 2813–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerefos, C.; Kourtidis, K.A.; Melas, D.; Balis, D.; Zanis, P.; Katsaros, L.; Mantis, H.T.; Repapis, C.; Isaksen, I.; Sundet, J.; et al. Photochemical Activity and Solar Ultraviolet Radiation Modulation Factors (PAUR): An overview of the project. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107, D18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, R.; Weilenmann, M.; Favez, J.Y. Evidence of increased mass fraction of NO2 within real world NOx emissions of modern light vehicles derived from a reliable online measuring method. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 4699–4707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aneja, V.P.; Businger, S.; Li, Z.; Ciaiborn, C.S.; Murthy, A. Ozone climatology at high elevations in the southern Appalachians. J. Geophys. Res. 1991, 96, 1007–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonasoni, P.; Laj, P.; Angelini, F.; Arduini, J.; Bonafè, U.; Calzolari, F.; Cristofanelli, P.; Decesari, S. The ABC-Pyramid Atmospheric Research Observatory in Himalaya for aerosol, O3 and halocarbon measurements. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 391, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossioli, E.; Tombrou, M.; Dandou, A.; Soulakellis, N. Simulation of the effects of critical factors on ozone formation and accumulation in the greater Athens area. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, D02309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burley, J.D.; Bytnerowicz, A.; Ray, J.D.; Schilling, S.; Allen, E.B. Surface ozone in Joshua tree national park. J. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 87, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, N.; Venkataramani, S.; Lal, S.; Pozzer, A. Effects of convection and long-range transport on the distribution of carbon monoxide in the troposphere over India. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2016, 7, 775–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Q.; Liu, L.; Li, G.; Tie, X. Increasing wintertime ozone levels and secondary aerosol formation in the Guanzhong basin, central China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 745, 140961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finch, D.P.; Palmer, P.I. Increasing ambient surface ozone levels over the UK accompanied by fewer extreme events. J. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 237, 117627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, C.; Lu, X.; Ran, L.; Han, M.; Li, P.; Li, X. Differences in ozone photochemical characteristics between the megacity Tianjin and its rural surroundings. J. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 79, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.C.; Moon, B.K.; Wie, J. Seasonal changes in surface ozone over South Korea. Heliyon 2018, 4, e00515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kourtidis, K.; Zerefos, C.; Rapsomanikis, S.; Simeonov, V.; Balis, D.; Perros, P.E. Regional levels of O3 in the troposphere over eastern Mediterranean. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107, 8140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunchala, R.K.; Singh, B.B.; Karumuri, R.K.; Attada, R.; Seelanki, V.; Kumar, N.K. Understanding the spatiotemporal variability and trends of surface ozone over India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 6219–6236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzeo, A.N.; Venegas, E.L.; Choren, H. Analysis of NO, NO2, O3 and NOx concentrations measured at a green area of Buenos Aires City during wintertime. J. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 3055–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, G.W.K.; Semple, J.L. High concentration of surface O3 observed along the Khumbu Valley Nepal April 2007. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L14809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Tonnesen, G.S.; Wang, Z. One-hour and eight-hour average O3 in the California south coast air quality management district: Trends in peak values and sensitivity to precursors. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 2197–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, M.L.; García, M.A.; Pérez, I.A.; de Torre, B. Evaluation of surface ozone measurements during 2000–2005 at a rural area in the upper Spanish plateau. J. Atmos. Chem. 2018, 60, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, W.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ding, Y. Observational study of surface O3 at an urban site in East China. Atmos. Res. 2008, 89, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solberg, S.; Hov, Ø.; Søvde, A.; Isaksen, I.S.A.; Coddeville, P.; De Backer, H.; Forster, C.; Orsolini, Y.; Uhse, K. European surface O3 in the extreme summer 2003. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, D07307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Shin, J.Y.; Atresino, R.J.; Gao, Y. Relationships among the springtime ground-level NOx, O3 and NO3 in the vicinity of highways in the US East Coast. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2011, 2, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strode, S.A.; Ziemke, J.R.; Oman, L.D.; Lamsal, L.N.; Olsen, M.A.; Liu, J. Global changes in the diurnal cycle of surface ozone. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 199, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wai, K.; Yuan, Q.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, S.; Qi, Q.; Wang, W. Simultaneous measurement of particulate and gaseous pollutants in an urban city in North China Plain during the heating period: Implication of source contribution. Atmos. Res. 2013, 134, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, H.W.; Jobson, B.T.; Erickson, M.H.; McCoskey, J.K.; VanReken, T.M.; Lamb, B.K.; Vaughan, J.K.; Hardy, R.J.; Cole, J.L.; Strachan, S.M.; et al. Comparison of wintertime CO to NOx ratios to MOVES and MOBILE6.2 on-road emissions inventories. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 63, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarwood, N.G.; Grant, J.; Koo, B.; Dunker, A.M. Modeling weekday to weekend changes in emissions and O3 in the Los Angeles basin for 1997 and 2010. Atmos Environ. 2008, 42, 3765–3779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naja, M.; Lal, S. Changes in surface ozone amount and its diurnal and seasonal patterns, from 1954–1955 to 1991–1993, measured at Ahmedabad (23ºN). India. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1996, 23, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadnavis, S.; Anoop, S.M.; Choudhary, A.D.; Roy, C.; Singh, M.; Biswas, M.S.; Pandithurai, G.; Prabhakaran, T.; Lal, S.; Venkatraman, C.; et al. Atmospheric Aerosols and Trace Gases: Assessment of Climate Change over the Indian Region; Springer: Singapore, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henschel, S.; Querol, X.; Atkinson, R.; Pandolfi, M.; Zeka, A.; Tertre, A.; Analitis, A.; Katsouyanni, K.; Chanel, O.; Pascal, M.; et al. Ambient air SO2 patterns in 6 European cities. J. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 79, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wei, X.L.; Ding, A.J.; Poon, C.N.; Lam, K.S.; Li, Y.S.; Chan, L.Y.; Anson, M. Increasing surface ozone concentrations in the background atmosphere of Southern China, 1994–2007. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 6217–6227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutsumi, Y.; Zaizen, T.; Makino, Y. Tropospheric ozone measurement at the top of Mt. Fuji. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1994, 21, 1727–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oltmans, S.J. Long-term changes in tropospheric ozone. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 3156–3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Payra, S.; Bhatla, R.; Verm, S. WRF-Chem modeling study of heat wave driven ozone over southeast region, India. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 340, 122744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyrgu, A.; Hadjinicolaou, P.; Santamouris, M. Enhanced near-surface ozone under heatwave conditions in a Mediterranean island. Nat. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zittis, G.; Hadjinicolaou, P.; Fnais, M. Projected changes in heat wave characteristics in the eastern Mediterranean and the Middle East. Reg. Environ. Change 2016, 16, 1863–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Xu, H.; Qi, B.; Du, R.; Gui, K.; Wang, H.; Jiang, W.; Liang, L.; Xu, W. Characterization of atmospheric trace gases and particulate matter in Hangzhou, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 1705–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monks, P.S.; Archibald, A.T.; Colette, A.; Cooper, O.; Coyle, M.; Derwent, R.; Fowler, D.; Granier, C.; Law, K.S.; Mills, G.; et al. Tropospheric ozone and its precursors from the urban to the global scale from air quality to short-lived climate forcer. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 8889–8973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seinfeld, J.H.; Pandis, S.N. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics from Air Pollution to Climate Change; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Carbon Brief Clear on Climate. Carbon Brief Profile, India. 2019. Available online: https://www.carbonbrief.org/the-carbon-brief-profile-india (accessed on 14 March 2019).
- David, L.M.; Ravishankara, A.R. Boundary layer ozone across the Indian subcontinent: Who influences whom? J. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 10008–10014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jethva, H.; Satheesh, S.K.; Srinivasan, J. Seasonal variability of aerosols over the Indo-Gangetic basin. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojha, N.; Sharma, A.; Kumar, M.; Girach, I.; Ansari, T.U.; Sharma, S.K.; Singh, N.; Pozzer, A.; Gunthe, S.S. On the widespread enhancement in fine particulate matter across the Indo-Gangetic Plain towards winter. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, V.; Kumar, V.; Sarkar, C. Chemical composition of pre-monsoon air in the Indo-Gangetic Plain measured using a new air quality facility and PTR-MS: High surface ozone and strong influence of biomass burning. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 5921–5941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, N.; Sahu, L.K.; Wang, L.; Vats, P.; Soni, M.; Kumar, P.; Satish, R.V.; Bhattu, D.; Sahu, R.; Patel, K.; et al. Characteristics of VOC composition at urban and suburban sites of New Delhi, India in winter. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2022, 127, e2021JD035342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Naja, M.; Venkataramani, S.; Wild, O. Variations in surface ozone at Nainital: A high-altitude site in the central Himalayas. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarangi, T.; Naja, M.; Ojha, N.; Kumar, R.; Lal, S.; Venkataramani, S.; Kumar, A.; Sagar, R.; Chandola, H.C. First simultaneous measurements of ozone, CO, and NOy at a high-altitude regional representative site in the central Himalayas. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 1592–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harithasree, S.; Sharma, K.; Girach, I.A.; Sahu, L.K.; Nair, P.R.; Singh, N.; Flemming, J.; Babu, S.S.; Ojha, N. Surface ozone over Doon valley of the Indian Himalaya: Characteristics, impact assessment, and model results. J. Atmos. Environ. X 2024, 21, 100247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, M.; Ojha, N.; Imran, G. Impact of COVID-19 Lockdown on Surface Ozone Build-up at an Urban Site in Western India Based On Photochemical Box Modelling. Curr. Sci. 2021, 120, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Sinha, V. Season-wise analyses of VOCs, hydroxyl radicals and ozone formation chemistry over north-west India reveal isoprene and acetaldehyde as the most potent ozone precursors throughout the year. Chemosphere 2021, 283, 131184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, B.S.; Stewart, G.J.; Drysdale, W.S.; Newland, M.J.; Vaughan, A.R.; Dunmore, R.E.; Edwards, P.M.; Lewis, A.C.; Hamilton, J.F.; Acton, W.J.; et al. In situ ozone production is highly sensitive to volatile organic compounds in Delhi, India. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 13609–13630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, B.; Singh, J.; Beig, G. Seasonal progression of surface ozone and NOx concentrations over three tropical stations in North-East India. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 258, 113662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hama, S.M.L.; Kumar, P.; Harrison, R.M.; Bloss, W.J.; Khare, M.; Mishra, S.; Namdeo, A.; Sokhi, R.; Goodman, P.; Sharma, C. Four-year assessment of ambient particulate matter and trace gases in the Delhi-NCR region of India. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 54, 102003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumka, U.C.; Gautam, A.S.; Tiwari, S.; Mahar, D.S.; Attri, S.D.; Chakrabarty, R.K.; Permita, P.; Hopke, P.K. Evaluation of urban O3 in the Brahmaputra river valley. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 11, 610–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanchana, A.L.; Sagar, V.K.; Pathakoti, M.; Mahalakshmi, D.V.; Mallikarjun, K.; Gharai, B. Ozone variability: Influence by its precursors and meteorological parameters- an investigation. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 2020, 211, 105468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.; Sahu, L.K.; Beig, G.; Tripathi, N.; Maji, S.; Jaaffrey, S.N.A. The role of local meteorology on ambient particulate and gaseous species at an urban site of western India. Urban Clim. 2019, 28, 100449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, P.; Naja, M.; Rupakheti, M.; Lupascu, A.; Mues, A.; Panday, A.K.; Kumar, R.; Mahata, K.S.; Lal, S.; Lawrence, M.G. Variations in surface O3 and CO in the Kathmandu Valley and surrounding broader regions during SusKat-ABC field campaign: Role of local and regional sources. J. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 11949–11971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pancholi, P.; Kumar, A.; Bikundia, D.S.; Chourasiya, S. An observation of seasonal and diurnal behavior of O3-NOx relationships and local/regional oxidant (OX = O3 + NO2) levels at a semi-arid urban site of western India. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2018, 28, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahapatra, P.S.; Kumar, R.; Mallik, C.; Panda, S.; Sahu, S.C.; Das, T. Investigation of a regional ozonereduction event over eastern India by integrating in situ and satellite measurements with WRF-Chem simulations. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2018, 137, 399–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, R.; Taneja, A.; Singh, P. Surface ozone scenario and air quality in the north-central part of India. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 59, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.; Sahu, L.K.; Beig, G.; Jaaffrey, S.N.A. Role of long-range transport and local meteorology in seasonal variation of surface ozone and its precursors at an urban site of India. Atmos. Res. 2016, 176, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Sharma, S.K.; Rohtash; Mandal, T.K. Influence of ozone precursors and particulate matter on the variation of surface ozone at an urban site of Delhi, India. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2016, 26, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, S.; Tiwari, S.; Mishra, A.; Hopke, P.K.; Bisht, D.S. Spatial variability of concentrations of gaseous pollutants across the National Capital Region of Delhi, India. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2016, 7, 808–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallik, C.; Lal, S.; Venkataramani, S. Trace gases at a semi-arid urban site in western India: Variability and inter-correlations. J. Atmos. Chem. 2015, 72, 143–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, T.K.; Peshin, S.K.; Sharma, C.; Raj, R.; Sharma, S.K. Study of surface ozone at Port Blair, India, a remote marine station in the Bay of Bengal. J. Atmos. Solar Terr. Phys. 2015, 129, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, S.; Venkataramani, S.; Chandra, N.; Cooper, O.R.; Naja, M. Transport effects on the vertical distribution of tropospheric ozone over western India. J. Geophys. Res. 2014, 119, 10012–10026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojha, N.; Naja, M.; Sarangi, T.; Kumar, R.; Bhardwaj, P.; Lal, S.; Venkataramani, S.; Sagar, R.; Kumar, A.; Chandola, H.C. On the processes influencing the vertical distribution of ozone over the central Himalayas: Analysis of yearlong ozonesonde observations. J. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 88, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojha, N.; Naja, M.; Singh, K.P.; Sarangi, T.; Kumar, R.; Lal, S.; Lawrence, M.G.; Butler, T.M. Variabilities in O3 at a semi-urban site in the Indo-Gangetic Plain region: Association with the meteorology and regional processes. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, D20301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahapatra, P.S.; Panda, S.; Walvekar, P.P.; Kumar, R.; Das, T.; Gurjar, B.R. Seasonal trends meteorological impacts and associated health risks with atmospheric concentrations of gaseous pollutants at an Indian coastal city. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 11418–11432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhuyan, P.K.; Bharali, C.; Pathak, B.; Kalita, G. The role of precursor gases and meteorology on temporal evolution of O3 at a tropical location in northeast India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 6696–6713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaur, A.; Tripathi, S.N.; Kanawade, V.P.; Tare, V.; Shukla, S.P. Four-year measurements of trace gases (SO2, NOx, CO, and O3) at an urban location, Kanpur, in Northern India. J. Atmos. Chem. 2014, 71, 283–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swamy, Y.V.; Venkanna, R.; Nikhil1, G.N.; Chitanya, D.N.S.K.; Sinha, P.R.; Ramakrishna, M.; Rao, A.G. Impact of oxides of Nitrogen, VolatileOrganic Carbons and Black Carbon emissions on Ozone weekend/weekdayvariations at a semi arid urban site in Hyderabad. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2012, 12, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, B.S.K.; Kumar, R.K.; Balakrishnaiah, G.; Rama Gopal, K.; Reddy, R.R.; Ahammed, Y.N.; Narasimhulu, K.; Reddy, S.S.L.; Lal, S. Observationalstudies on the variations in surface O3 concentration at Anantapur in southern India. Atmos. Res. 2010, 98, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singla, V.; Satsangi, A.; Pachauri, T.; Lakhani, A.; Kumari, K.M. O3 formation and destruction at a sub-urban site in North Central region of India. Atmos. Res. 2011, 101, 373–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debaje, S.; Jeyakumar, S.J. High O3 at coastal sites in India. Int. J Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 993–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debaje, S.B.; Kakade, A.D. Surface O3 variability over western Maharashtra, India. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 161, 686–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghude, D.; Jain, S.L.; Arya, B.C.; Beig, G.; Ahammed, Y.N.; Kumar, A.; Tyagi, B. O3 in ambient air at a tropical megacity, Delhi: Characteristics, trends and cumulative O3 exposure indices. J. Atmos. Chem. 2008, 60, 237–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beig, G.; Gunthe, S.; Jadhav, D.B. Simultaneous measurements of ozone and its precursors on a diurnal scale at a semi urban site in India. J. Atmos. Chem. 2007, 57, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naja, M.; Lal, S.; Chand, D. Diurnal and seasonal variabilities in surface O3 at a high altitude site Mt Abu (24.60 N, 72.70 E, 1680 m asl) in India. J. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 4205–4215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naja, M.; Lal, S. Surface O3 and precursor gases at Gadanki (13.5° N, 79.2° E), a tropical rural site in India. J. Geophys Res. 2002, 107, ACH-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, S.; Naja, M.; Subbaraya, B.H. Seasonal variations in surface O3 and its precursors over an urban site in India. J. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 2713–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sai Krishnaveni, A.; Madhavan, B.L.; Jain, C.D.; Venkat Ratnam, M. Spatial, temporal features and influence of meteorology on PM2.5 and O3 association across urban and rural environments of India. Atmos. Environ. X 2024, 22, 100265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resmi, C.T.; Fei, Y.; Sarang, S.; Nishanth, T.; Satheesh Kumar, M.K.; Balachandramohan, M.; Manivannan, D.; Hu, J.; Valsaraj, K.T. Variation of trace gases in Kannur town, a coastal South Indian city. Environ. Chall. 2021, 5, 100336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resmi, C.T.; Nishanth, T.; Satheesh Kumar, M.K.; Balachandramohan, M.; Valsaraj, K.T. Long-term variations of air quality influenced by surface ozone in a coastal site in India: Association with synoptic meteorological conditions with model simulations. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, P.R.; Ajayakumar, R.S.; David, L.M.; Girach, I.A.; Kavitha, M. Decadal changes in surface ozone at the tropical station Thiruvananthapuram (8.542° N, 76.858° E), India: Effects of anthropogenic activities and meteorological variability. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 14827–14843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopal, R.K.; Lingaswamy, A.P.; Arafath, S.M.; Balakrishnaiah, G.; Kumari, P.S.; Devi, U.K.; Reddy, S.K.N.; Reddy, R.K.B.; Reddy, R.R.; Azeem, A.P.; et al. Seasonal heterogeneity in ozone and its precursors (NOx) by in-situ and model observations on semi-arid station in Anantapur (A.P.), South India. J. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 84, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udayasoorian, C.; Jayabalakrishnan, R.M.; Suguna, A.R.; Venkataramani, S.; Lal, S. Diurnal and seasonal characteristics of ozone and NOx over a high altitude Western Ghats location in Southern India. Adv. Appl. Sci. Res. 2013, 4, 309–320. [Google Scholar]
- Girach, I.A.; Ojha, N.; Babu, S.S. Ozone chemistry and dynamics at a tropical coastal site impacted by the COVID-19 lockdown. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 130, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, L.M.; Nair, P.R. Diurnal and seasonal variability of surface ozone and NOx at a tropical coastal site: Association with mesoscale and synoptic meteorological conditions. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, D10303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, P.R.; Chand, D.; Lal, S.; Modh, K.S.; Naja, M.; Parameswaran, K.; Ravindran, S.; Venkataramani, S. Temporal variations in surface O3 at Thumba (8.6° N, 77° E) —A tropical coastal site in India. J. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishanth, T.; Satheesh Kumar, M.K.; Valsaraj, K.T. Variations in surface ozone and NOx at Kannur: A tropical, coastal site in India. J. Atmos. Chem. 2012, 69, 101–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishanth, T.; Praseed, K.M.; Satheesh Kumar, M.K.; Valsaraj, K.T. Influence of ozone precursors and PM10 on the variation of surface O3 over Kannur, India. Atmos. Res. 2014, 138, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revathy, A.S.; Girach, I.A.; Soni, M.; Ojha, N.; Babu, S.S. Processes governing the surface ozone over a tropical hill station in the Western Ghats. Atmos. Environ. 2024, 319, 120286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, Y.; Dipesh, R.; Lin, H.; Nishanth, T.; Satheesh Kumar, M.K.; Lin, L.; Valsaraj, K.T.; Hu, J. Integrated process analysis retrieval of changes in ground-level ozone and fine particulate matter during the COVID-19 outbreak in the coastal city of Kannur, India. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 307, 119468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, D.; Ray, J. Increase in surface ozone at rural sites in the western US. J. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 5452–5463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilleri, R.; Vella, A.J. Effect of fireworks on ambient air quality in Malta. J. Atmos Environ. 2010, 44, 4521–4527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croteau, G.; Dills, R.; Beaudreau, M.; Davis, M. Emission factors and exposures from ground level pyrotechnics. J. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 3295–3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shon, Z.H.; Jeong, J.H.; Kim, Y.K. Characteristics of atmospheric metalliferous particles during large-scale fireworks in Korea. Adv. Meteorol. 2015, 2015, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehner, B.; Weidensohler, A.; Heintzenberg, J. Sub micrometer aerosol sized istributions and mass concentrations of the millennium fireworks 2000 in Leipzig, Germany. J. Aerosol. Sci. 2000, 31, 1489–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attri, A.K.; Kumar, U.; Jain, V.K. Formation of ozone by fireworks. Nature 2001, 411, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, N.D.; Tzanis, C.G.; Philippopoulos, K.; Deligiorgi, D.; Ganguly, N.D.; Tzanis, C.G.; Philippopoulos, K.; Deligiorgi, D. Analysis of a severe air pollution episode in India during Diwali festival—A nationwide approach. Atmósfera 2019, 32, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, J.; Chanda, A.; Samanta, S. Air pollution in three megacities of India during the Diwali festival amidst COVID-19 pandemic. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 76, 103504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, P.; Srivastava, A.; Verma, S.; Singh, L.; Sonwani, S. Analysis of Atmospheric Pollutants During Fireworks Festival ‘Diwali’ at a Residential Site Delhi in India. In Measurement, Analysis and Remediation of Environmental Pollutants. Energy, Environment, and Sustainability; Gupta, T., Singh, S., Rajput, P., Agarwal, A., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, A.; Sharma, P.; Beig, G.; Ghosh, C. Temporal Mount in Air Pollutants Allied with Religious Fiesta: Diwali, Festival of Lights. In Emerging Issues in Ecology and Environmental Science: Case Studies from India; SpringerBriefs in Environmental Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambade, B. The air pollution during Diwali festival by the burning of fireworks in Jamshedpur city, India. Urban Clim. 2018, 26, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peshin, S.K.; Sinha, P.; Bisht, A. Impact of Diwali firework emissions on air quality of New Delhi, India during 2013–2015. Mausam 2017, 68, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resmi, C.T.; Nishanth, T.; Satheesh Kumar, M.K.; Balachandramohan, M.; Valsaraj, K.T. Assessment of extreme fireworks episode in a coastal city of Southern India- Kannur as a Case Study. In Atmospheric Processes, Phenomena and Its Related Extremities; Springer Nature Publications: Singapore, 2022; ISBN 978-981-16-7727-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resmi, C.T.; Nishanth, T.; Satheesh Kumar, M.K.; Balachandramohan, M.; Valsaraj, K.T. Temporal changes in air quality during a festival season in Kannur, India. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishanth, T.; Praseed, K.M.; Rathnakaran, K.; Satheesh Kumar, M.K.; RaviKrishna, R.; Valsaraj, K.T. Atmospheric pollution in a semi-urban, coastal region in India following festival seasons. J. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 47, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, W.E.; Westenberg, A.A. Study of the reaction of hydroxyl radical with methane by quantitative ESR. Symp. (Int.) Combust. 1967, 11, 1143–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, D.; Kumar, V.P.; Ratnam, M.V.; Mohammad, S.; Kumar, M.C.A.; Rao, P.V.; Rahaman, K. Response of tropical lower atmosphere to annular solar eclipse of 15 January 2010. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2011, 73, 1907–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenan, R.; Dammalage, T.L.; Panda, S.K. Ionospheric total electron content response to September-2017 geomagnetic storm and December-2019 annular solar eclipse over Sri Lankan region. Acta Astronaut. 2021, 180, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurdyaeva, Y.; Borchevkina, O.; Karpov, I.; Kshevetskii, S. Thermospheric disturbances caused by the propagation of acoustic-gravity waves from the lower atmosphere during a solar eclipse. Advanc. Space Res. 2021, 68, 1390–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.S.; Chakraborty, M.; Singh, A.K. A study on TEC reduction during the tail phase of the 21st June 2020 annular solar eclipse. Adv. Space Res. 2021, 67, 1948–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senturk, E.; Adil, M.A.; Saqib, M. Ionospheric total electron content response to annular solar eclipse on June 21, 2020. Adv. Space Res. 2021, 67, 1937–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerasopoulos, E.; Zerefos, C.S.; Tsagouri, I.; Founda, D.; Amiridis, V.; Bais, A.F.; Belehaki, A.; Christou, N.; Economou, G.; Kanakidou, M.; et al. The total solar eclipse of March 2006: Overview. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 5205–5220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarty, D.K.; Shah, N.C.; Pandya, K.V. Fluctuation in ozone column over Ahmedabad during the solar eclipse of 24 October 1995. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1997, 24, 3001–3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, S.; Subbaraya, B.H. Solar eclipse induced variations in mesospheric ozone concentrations. Adv. Space Res. 1983, 2, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkat Ratnam, M.; Basha, G.; Roja Raman, M.; Kumar Mehta, S.; Murthy, K.; Jayaraman, A. Unusual enhancement in temperature and ozone vertical distribution in the lower stratosphere observed over Gadanki, India, following the 15 January 2010 annular eclipse. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanis, P.; Katragkou, E.; Kanakidou, M.; Psiloglou, B.E.; Karathanasis, S.; Vrekoussis, M.; Gerasopoulos, E.; Markakis, K.; Poupkou, A.; Amiridis, V.; et al. Effects on surface atmospheric photo-oxidants over Greece during the total solar eclipse event of 29 March 2006. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 6061–6073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manchanda, R.K.; Sinha, P.R.; Sreenivasan, S.; Trivedi, D.B.; Kapardhi, B.V.N.; Kumar, B.S.; Kumar, P.R.; Satyaprakash, U.; Rao, V.N. In-situ measurements of vertical structure of O3 during the solar eclipse of 15 January 2010. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2012, 84, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anoop, P.; Muhsin, M.; Shebin, J.; Aiswarya, S.; Arun, P.T.; Deepa, V.; Ravi, V. Trace pollutant fluctuations observed in Calicut city, India, during the annular solar eclipse on 26 December 2019. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 11, 2049–2055. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, C.D.; Ratnam, M.V.; Madhavan, B.L. Direct and indirect photochemical impacts on the trace gases observed during the solar eclipse over a tropical rural location. J. Atmos. Sol. -Terr. Phys. 2020, 211, 105451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resmi, C.T.; Nishanth, T.; Satheesh Kumar, M.K.; Balachandramohan, M.; Valsaraj, K.T. Annular solar eclipse on 26 December 2019 and its effect on trace pollutant concentrations and meteorological parameters in Kannur, India: A coastal city. Asian J. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 14, 290–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishanth, T.; Ojha, N.; Satheesh Kumar, M.K.; Naja, M. Influence of solar eclipse of 15 January 2010 on surface O3. J. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 1752–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.K.; Mandal, T.K.; Arya, B.C.; Saxena, M.; Shukla, D.K.; Mukherjee, A.; Bhatnagar, R.P.; Nath, S.; Yadav, S.; Gautam, R.; et al. Effects of solar eclipse on 15 January on the surface O3, NO, NO2, NH3, CO mixing ratio and the meteorological parameters at Thiruvananthapuram India. Ann. Geophys. 2010, 28, 1199–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhil Raj, S.T.; Ratnam, M.V. Ozone vertical distribution during the solar eclipse of 26 December 2019 over Gadanki: Role of background dynamics. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2021, 12, 101116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Locations | Category | Daytime Average/Maximum (ppbv) (Season) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Doon Valley | Himalaya region | 63.8 ± 15.3 (Pre monsoon) | [69] |
| Ahmedabad | Semi-arid urban | 40–60 (Summer) | [70] |
| Aizwal | Himalayan Valley | 27.1 (Pre-Monsoon) | [73] |
| Tezpur | Himalayan Valley | 31.0 (Pre-Monsoon) | [73] |
| Guwahati | River valley | 18.31 ± 5.8 Pre monsoon | [75] |
| Hyderabad | Sub-urban region | 35.54 ± 7.16 (Winter) | [76] |
| Jodhpur | Semi-arid, | 47 ± 11.5 (Pre monsoon) | [79] |
| Agra | Urban | 32.5 ± 19.3 (Summer) | [81] |
| Udaipur | Semi-arid | 46 ± 12.5 (Pre monsoon) | [82] |
| NCR Delhi | Urban | 45.3 ± 9.5 (Winter) | [84] |
| Port Blair | Marine site | 30 ± 5 (Winter) | [86] |
| Pantnagar | Semi-Urban | 48.7 ± 13.8 (Spring) | [89] |
| Bhubaneswar | Urban | 61.7 ± 12.7 (Winter) | [90] |
| Dibrugarh | Sub Himalayan | 42.9 ± 10.3 (Pre monsoon) | [91] |
| Kanpur | Urban | 27.9 ± 17.8 (Summer) | [92] |
| Dayalbag | Suburban | 56 ± 10.8 (Summer) | [95] |
| Kannur Town | Urban city | 48.25 ± 7.2 (Winter) | [104] |
| Kannur University | Rural | 35.47 ± 10.5 (Winter) | [105] |
| Trivandrum | Coastal | 40 ± 8.5 (Winter) | [106] |
| Anantapur | Semi-arid, Rural | 64.9 ± 5.3 (Summer) | [107] |
| Ootty | High altitude | 53.5 ± 8.2 (Winter) | [108] |
| Period of Observation at Rural Site | Statistics | O3 Concentration (ppbv) | Period of Observation at Urban Site | Statistics | O3 Concentration (ppbv) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 January 2016– 31 December 2016 | Average | 34.38 | 1 January 2019– 31 December 2019 | Average | 34.38 |
| Standard deviation | 11.1 | Standard deviation | 11.48 | ||
| Daytime maximum | 56.12 | Daytime maximum | 46.78 | ||
| Daytime minimum | 12.4 | Daytime minimum | 13.58 | ||
| Number of datapoints | 41,760 | Number of datapoints | 36,540 | ||
| 1 January 2017– 31 December 2017 | Average | 35.12 | 1 January 2020– 31 December 2020 | Average | 32.33 |
| Standard deviation | 12.2 | Standard deviation | 10.56 | ||
| Daytime maximum | 57.6 | Daytime maximum | 48.52 | ||
| Daytime minimum | 12.02 | Daytime minimum | 14.42 | ||
| Number of datapoints | 40,880 | Number of datapoints | 37,560 | ||
| 1 January 2018– 31 December 2018 | Average | 35.47 | 1 January 2021– 31 December 2021 | Average | 32.78 |
| Standard deviation | 10.5 | Standard deviation | 11.87 | ||
| Daytime maximum | 58.5 | Daytime maximum | 47.98 | ||
| Daytime minimum | 12.45 | Daytime minimum | 13.96 | ||
| Number of datapoints | 39,320 | Number of datapoints | 38,440 | ||
| 1 January 2019– 31 December 2019 | Average | 35.97 | 1 January 2022– 31 December 2022 | Average | 33.32 |
| Standard deviation | 8.52 | Standard deviation | 11.41 | ||
| Daytime maximum | 59.21 | Daytime maximum | 48.98 | ||
| Daytime minimum | 12.68 | Daytime minimum | 13.38 | ||
| Number of datapoints | 36,558 | Number of data points | 37,960 | ||
| 1 January 2020– 31 December 2020 | Average | 36.42 | 1 January 2023– 31 December 2023 | Average | 33.88 |
| Standard deviation | 9.6 | Standard deviation | 11.54 | ||
| Daytime maximum | 59.85 | Daytime maximum | 50.21 | ||
| Daytime minimum | 12.18 | Daytime minimum | 14.28 | ||
| Number of datapoints | 40,240 | Number of datapoints | 38,540 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Keerthi Lakshmi, K.A.; Nishanth, T.; Satheesh Kumar, M.K.; Valsaraj, K.T. A Comprehensive Review of Surface Ozone Variations in Several Indian Hotspots. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 852. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15070852
Keerthi Lakshmi KA, Nishanth T, Satheesh Kumar MK, Valsaraj KT. A Comprehensive Review of Surface Ozone Variations in Several Indian Hotspots. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(7):852. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15070852
Chicago/Turabian StyleKeerthi Lakshmi, K. A., T. Nishanth, M. K. Satheesh Kumar, and K. T. Valsaraj. 2024. "A Comprehensive Review of Surface Ozone Variations in Several Indian Hotspots" Atmosphere 15, no. 7: 852. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15070852
APA StyleKeerthi Lakshmi, K. A., Nishanth, T., Satheesh Kumar, M. K., & Valsaraj, K. T. (2024). A Comprehensive Review of Surface Ozone Variations in Several Indian Hotspots. Atmosphere, 15(7), 852. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15070852








