Particulate and Gaseous Emissions from a Large Two-Stroke Slow-Speed Marine Engine Equipped with Open-Loop Scrubber under Real Sailing Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Measurement Campaign
2.2. Fuels
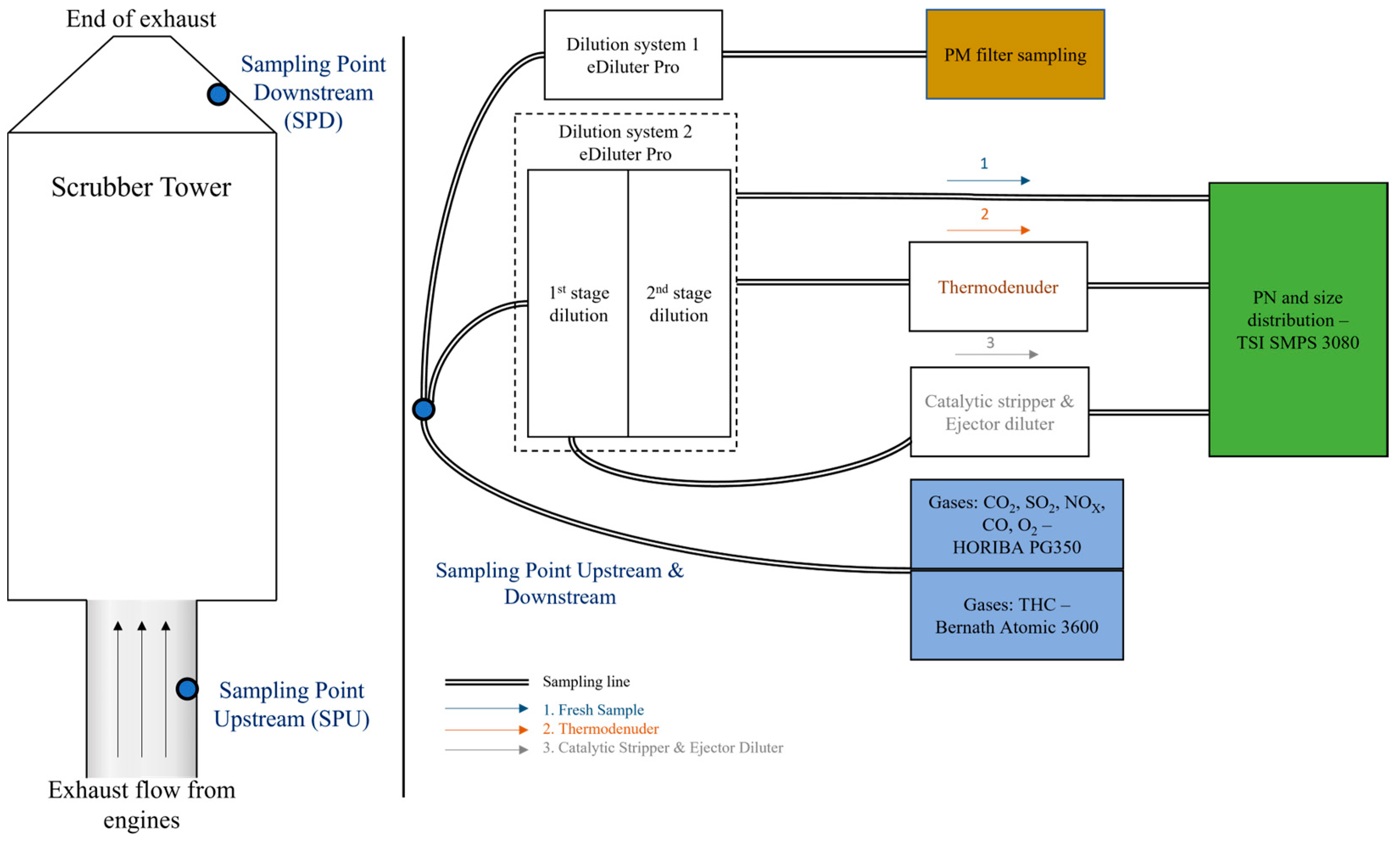
2.3. Testing and Sampling
3. Results and Discussion
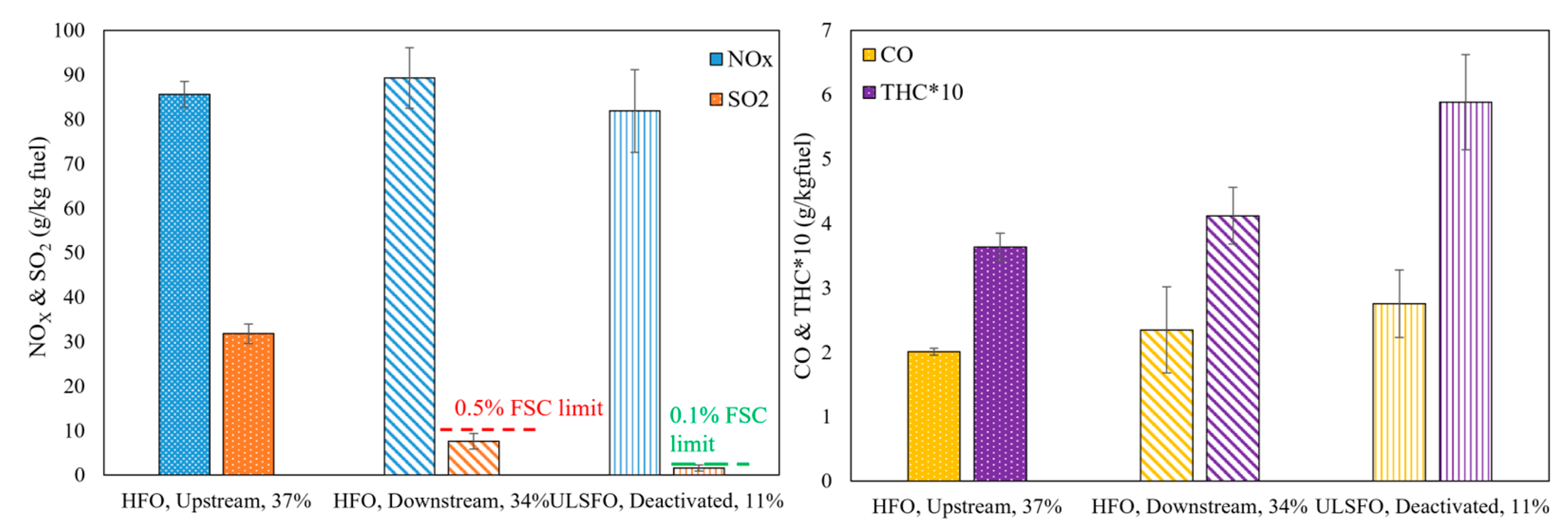
3.1. Overview of Gaseous Emissions
3.2. Particulate Matter
3.2.1. Scrubber Effect
3.2.2. Fuel Effect
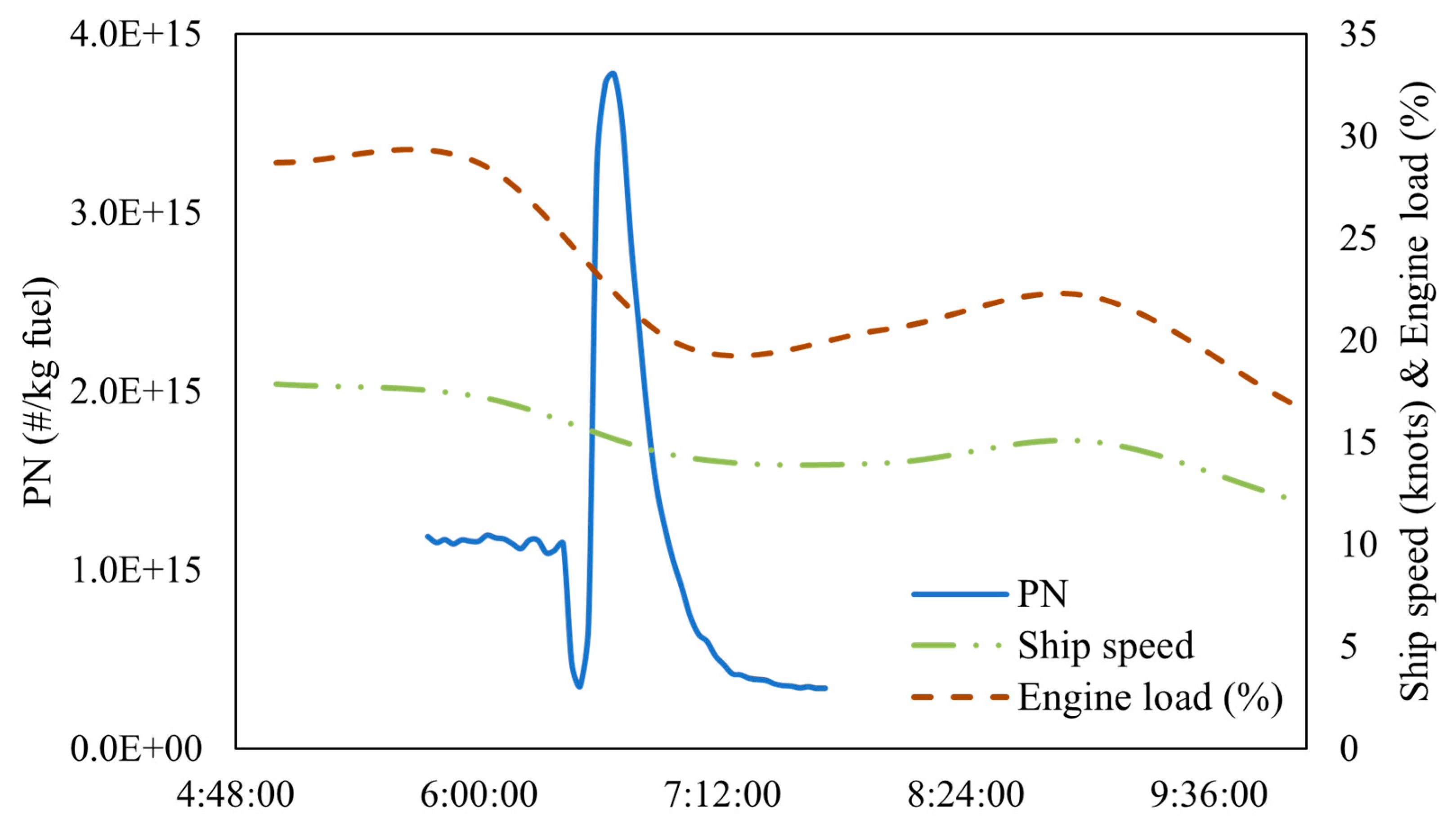
3.2.3. Fuel Transition
3.2.4. Effects of Sample Conditioning
4. Policy Implications
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AE | auxiliary engine |
| APC | AVL particle counter |
| CLA | chemiluminescence analyzer |
| CO | carbon monoxide |
| CS | catalytic stripper |
| DR | dilution ratio |
| ECA | emission control area |
| ED | ejector diluter |
| EF | emission factor |
| EU | European Union |
| FID | flame ionization detector |
| FSC | fuel sulfur content |
| GHG | greenhouse gas |
| HFO | heavy fuel oil |
| IMO | International Maritime Organization |
| ME | main engine |
| MSD | medium speed diesel |
| NDIR | non-dispersive infrared |
| NECA | nitrogen emission control area |
| NMVOC | non-methane volatile organic compounds |
| PAH | polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons |
| PM | particulate matter |
| PN | particulate number |
| PSD | particle size distribution |
| Rpm | revolutions per minute |
| SECA | sulfur emission control area |
| SFOC | specific fuel oil consumption |
| SMPS | scanning mobility particle sizer |
| SOG | speed over ground |
| SPD | sampling point downstream |
| TD | thermodenuder |
| TEU | twenty-foot-equivalent unit |
| THC | total hydrocarbon |
| ULSFO | ultra-low sulfur fuel oil |
References
- United Nations Conference on Trade and Development. Review of Maritime Transport 2022; United Nations Conference on Trade and Development: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023; ISBN 9789211130737. [Google Scholar]
- Matthias, V.; Bewersdorff, I.; Aulinger, A.; Quante, M. The Contribution of Ship Emissions to Air Pollution in the North Sea Regions. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 2241–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winebrake, J.J.; Corbett, J.J.; Green, E.H.; Lauer, A.; Eyring, V. Mitigating the Health Impacts of Pollution from Oceangoing Shipping: An Assessment of Low-Sulfur Fuel Mandates. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 4776–4782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Chen, Y.; Su, P.; Cui, M.; Han, Y.; Matthias, V.; Wang, G. Variations and Characteristics of Carbonaceous Substances Emitted from a Heavy Fuel Oil Ship Engine under Different Operating Loads. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 284, 117388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehtoranta, K.; Aakko-Saksa, P.; Murtonen, T.; Vesala, H.; Kuittinen, N.; Rönkkö, T.; Ntziachristos, L.; Karjalainen, P.; Timonen, H.; Teinilä, K. Particle and Gaseous Emissions from Marine Engines Utilizing Various Fuels and Aftertreatment Systems. In Proceedings of the 29th CIMAC World Congress on Combustion Engine, Vancouver, QC, Canada, 10–14 June 2019; p. 399. [Google Scholar]
- Viana, M.; Hammingh, P.; Colette, A.; Querol, X.; Degraeuwe, B.; de Vlieger, I.; van Aardenne, J. Impact of Maritime Transport Emissions on Coastal Air Quality in Europe. Atmos Environ. 2014, 90, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Guo, J.; Hao, C.; Feng, Y. Particle Emissions from a Marine Diesel Engine Burning Two Kinds of Sulphur Diesel Oils with an EGR & Scrubber System: Size, Number & Mass. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 163, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IMO. Fourth IMO GHG Study 2020 Full Report; IMO: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Alanen, J.; Isotalo, M.; Kuittinen, N.; Simonen, P.; Martikainen, S.; Kuuluvainen, H.; Honkanen, M.; Lehtoranta, K.; Nyyssönen, S.; Vesala, H.; et al. Physical Characteristics of Particle Emissions from a Medium Speed Ship Engine Fueled with Natural Gas and Low-Sulfur Liquid Fuels. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 5376–5384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayaram, V.; Agrawal, H.; Welch, W.A.; Miller, J.W.; Cocker, D.R. Real-Time Gaseous, PM and Ultrafine Particle Emissions from a Modern Marine Engine Operating on Biodiesel. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 2286–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Milojević, S.; Glišović, J.; Savić, S.; Bošković, G.; Bukvić, M.; Stojanović, B. Particulate Matter Emission and Air Pollution Reduction by Applying Variable Systems in Tribologically Optimized Diesel Engines for Vehicles in Road Traffic. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Natale, F.; Carotenuto, C. Particulate Matter in Marine Diesel Engines Exhausts: Emissions and Control Strategies. Transp. Res. D Transp. Environ. 2015, 40, 166–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuittinen, N.; Jalkanen, J.P.; Alanen, J.; Ntziachristos, L.; Hannuniemi, H.; Johansson, L.; Karjalainen, P.; Saukko, E.; Isotalo, M.; Aakko-Saksa, P.; et al. Shipping Remains a Globally Significant Source of Anthropogenic PN Emissions Even after 2020 Sulfur Regulation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoriadis, A. Onboard Particulate and Gaseous Emission Measurements from Slow Speed Marine Engine Equipped with Open-Loop Scrubber under Real World Operation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Postgraduate Research in Maritime Technology, Online, 29 November 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Chu-Van, T.; Ristovski, Z.; Pourkhesalian, A.M.; Rainey, T.; Garaniya, V.; Abbassi, R.; Jahangiri, S.; Enshaei, H.; Kam, U.S.; Kimball, R.; et al. On-Board Measurements of Particle and Gaseous Emissions from a Large Cargo Vessel at Different Operating Conditions. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 237, 832–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grigoriadis, A.; Kousias, N.; Raptopoulos, A.; Mamarikas, S.; Kontses, A.; Toumasatos, Z.; Salberg, H.; Lunde-Hermansson, A.; Moldanová, J.; Ntziachristos, L.; et al. Particulate and Gaseous Emissions from a Large 2-Stroke Slow Speed Marine Engine Equipped with Open-Loop Scrubber under Real Sailing Conditions. In Proceedings of the Joint TAP and S&E Conference, Gothenburg, Sweden, 27 September 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Vallabani, N.V.S.; Gruzieva, O.; Elihn, K.; Juárez-Facio, A.T.; Steimer, S.S.; Kuhn, J.; Silvergren, S.; Portugal, J.; Piña, B.; Olofsson, U.; et al. Toxicity and Health Effects of Ultrafine Particles: Towards an Understanding of the Relative Impacts of Different Transport Modes. Environ. Res. 2023, 231, 116186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vouitsis, I.; Portugal, J.; Kontses, A.; Karlsson, H.L.; Faria, M.; Elihn, K.; Juárez-Facio, A.T.; Amato, F.; Piña, B.; Samaras, Z. Transport-Related Airborne Nanoparticles: Sources, Different Aerosol Modes, and Their Toxicity. Atmos Environ. 2023, 301, 119698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Tang, T.; Jiang, Y.; Karavalakis, G.; Durbin, T.D.; Wayne Miller, J.; Cocker, D.R.; Johnson, K.C. Controlling Emissions from an Ocean-Going Container Vessel with a Wet Scrubber System. Fuel 2021, 304, 121323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GloMEEP Project Coordination Unit. Ship Emissions Toolkit. Guide No.1: Rapid Assessment of Ship Emissions in the National Context; GloMEEP Project Coordination Unit: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- IMO. Initial IMO Strategy on Reduction of GHG Emissions from Ships; IMO: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Integrating Maritime Transport Emissions in the EU’s Greenhouse Gas Reduction Policies; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- IMO. Inclusion of Regulations on Energy Efficiency for Ships in MARPOL Annex VI; IMO: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bettles, J.; Perez, A.; Björk, S.; Barcarolo, D.; Hintze, M. Assessing Impacts of EU and US Policies on Accelerated Deployment of Alternative Maritime Fuels Transatlantic Testing Ground; Center for Zero Carbon Shipping: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Zhang, M.; Xiao, G. Opportunities and Challenges of EU ETS to the Global Marine Industry. Front Mar Sci 2024, 11, 1382498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IMO. List of Special Areas, Emission Control Areaw and Particularly Sensitive Sea Areas; IMO: London, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- IMO. Effective Date of Implementation of the Fuel Oil Standard in Regulatio 14.1.3 of MARPOL VI; IMO: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Weng, J.; Han, T.; Shi, K.; Li, G. Impact Analysis of ECA Policies on Ship Trajectories and Emissions. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 179, 113687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zannis, T.C.; Katsanis, J.S.; Christopoulos, G.P.; Yfantis, E.A.; Papagiannakis, R.G.; Pariotis, E.G.; Rakopoulos, D.C.; Rakopoulos, C.D.; Vallis, A.G. Marine Exhaust Gas Treatment Systems for Compliance with the IMO 2020 Global Sulfur Cap and Tier III NOx Limits: A Review. Energies 2022, 15, 3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lauretis, R.; Ntziachristos, L.; Trozzi, C.; Fontelle, J.-P.; Fridell, E.; Grigoriadis, A.; Hill, N.; Kilde, N.; Lavender, K.; Mamarikas, S.; et al. EMEP/EEA Air Pollutant Emission Inventory Guidebook 2019, Update 2021; EMEP/EEA: Brussels, Belgium, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Brynolf, S.; Magnusson, M.; Fridell, E.; Andersson, K. Compliance Possibilities for the Future ECA Regulations through the Use of Abatement Technologies or Change of Fuels. Transp. Res. D Transp. Environ. 2014, 28, 6–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.A. Research of the Scrubber Systems to Clean Marine Diesel Engine Exhaust Gases on Ships. J. Mar. Sci. Res. Dev. 2017, 7, 1000243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermansson, A.-L.; Hassellöv, I.M.; Grönholm, T.; Jalkanen, J.P.; Fridell, E.; Parsmo, R.; Hassellöv, J.; Ytreberg, E. Strong Economic Incentives of Ship Scrubbers Promoting Pollution. Nat. Sustain. 2024, 7, 812–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altarriba, E.; Rahiala, S.; Tanhuanpää, T. Open-Loop Scrubbers and Restricted Waterways: A Case Study Investigation of Travemünde Port and Increased Sulphur Emissions Immediately After the Scrubbers Are Turned Off. TransNav 2023, 17, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comer, B.; Georgeff, E.; Osipova, L. Air Emissions and Water Pollution Discharges from Ships with Scrubbers; International Council on Clean Transportation: Washington, DC, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Winnes, H.; Fridell, E.; Moldanová, J. Effects of Marine Exhaust Gas Scrubbers on Gas and Particle Emissions. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridell, E.; Salo, K. Measurements of Abatement of Particles and Exhaust Gases in a Marine Gas Scrubber. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part M J. Eng. Marit. Environ. 2016, 230, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushakov, S.; Stenersen, D.; Einang, P.M.; Ask, T.Ø. Meeting Future Emission Regulation at Sea by Combining Low-Pressure EGR and Seawater Scrubbing. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2020, 25, 482–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutherford, D.; Comer, B.; Johnson, K.; Miller, W.; Durbin, T.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, J.; Karavalakis, G.; Cocker, D.; Fofi, E.; et al. Black Carbon Measurement Methods and Emission Factors from Ships; University of California: Riverside, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Zhou, S.; Zhu, Y. Characterization of Particle and Gaseous Emissions from Marine Diesel Engines with Different Fuels and Impact of After-Treatment Technology. Energies 2017, 10, 1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, L.F.E.; Salo, K.; Thomson, E.S. Quantification and Physical Analysis of Nanoparticle Emissions from a Marine Engine Using Different Fuels and a Laboratory Wet Scrubber. Environ. Sci. Process Impacts 2022, 24, 1769–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, S.; Bendl, J.; Saraji-Bozorgzad, M.; Käfer, U.; Etzien, U.; Schade, J.; Bauer, M.; Jakobi, G.; Orasche, J.; Fisch, K.; et al. Aerosol Emissions from a Marine Diesel Engine Running on Different Fuels and Effects of Exhaust Gas Cleaning Measures. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 316, 120526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karjalainen, P.; Teinilä, K.; Kuittinen, N.; Aakko-Saksa, P.; Bloss, M.; Vesala, H.; Pettinen, R.; Saarikoski, S.; Jalkanen, J.P.; Timonen, H. Real-World Particle Emissions and Secondary Aerosol Formation from a Diesel Oxidation Catalyst and Scrubber Equipped Ship Operating with Two Fuels in a SECA Area. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 292, 118278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehtoranta, K.; Aakko-Saksa, P.; Murtonen, T.; Vesala, H.; Ntziachristos, L.; Rönkkö, T.; Karjalainen, P.; Kuittinen, N.; Timonen, H. Particulate Mass and Nonvolatile Particle Number Emissions from Marine Engines Using Low-Sulfur Fuels, Natural Gas, or Scrubbers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 3315–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.; Miller, W.; Yang, J. Evaluation of a Modern Tier 2 Ocean-Going Vessel Equipped with a Scrubber; Final report prepared for CARB; University of California: Riverside, CA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 8178-1; Reciprocating Combustion Engines—Exhaust Emission Measurement—Part 1: Test-Bed Measurement of Gaseous Particulate Emissions. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020.
- Agrawal, H.; Malloy, Q.G.J.; Welch, W.A.; Wayne Miller, J.; Cocker, D.R. In-Use Gaseous and Particulate Matter Emissions from a Modern Ocean Going Container Vessel. Atmos Environ. 2008, 42, 5504–5510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winnes, H.; Fridell, E. Emissions of NOX and Particles from Manoeuvring Ships. Transp. Res. D Transp. Environ. 2010, 15, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntziachristos, L.; Saukko, E.; Lehtoranta, K.; Rönkkö, T.; Timonen, H.; Simonen, P.; Karjalainen, P.; Keskinen, J. Particle Emissions Characterization from a Medium-Speed Marine Diesel Engine with Two Fuels at Different Sampling Conditions. Fuel 2016, 186, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemelä, V.; Lamminen, E. Performance Evaluation of the Dekati® EDiluterTM Conditioning System. In Proceedings of the 29th CRC Real World Emissions Workshop, Long Beach, CA, USA, 10–13 March 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Amanatidis, S.; Ntziachristos, L.; Karjalainen, P.; Saukko, E.; Simonen, P.; Kuittinen, N.; Aakko-Saksa, P.; Timonen, H.; Rönkkö, T.; Keskinen, J. Comparative Performance of a Thermal Denuder and a Catalytic Stripper in Sampling Laboratory and Marine Exhaust Aerosols. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 420–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekati. Dekati EDiluter Pro Performance Evaluation; Dekati: Kangasala, Finland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Carriero, M.; Martini, G.; Krasenbrink, A.; Scheder, D. Calibration and Validation of Various Commercial Particle Number Measurement Systems. SAE Int. J. Fuels Lubr. 2009, 2, 512–530. [Google Scholar]
- Amanatidis, S.; Ntziachristos, L.; Giechaskiel, B.; Katsaounis, D.; Samaras, Z.; Bergmann, A. Evaluation of an Oxidation Catalyst (“catalytic Stripper”) in Eliminating Volatile Material from Combustion Aerosol. J. Aerosol. Sci. 2013, 57, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Commission Regulation (EU) 2017/1151; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations. Agreement Concerning the Adoption of Uniform Technical Prescriptions for Wheeled Vehicles, Equipment and Parts Which Can Be Fitted and/or Be Used on Wheeled Vehicles and the Conditions for Reciprocal Recognition of Approvals Granted on the Basis of These Prescriptions; Regulation No. 49; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations. Agreement Concerning the Adoption of Uniform Technical Prescriptions for Wheeled Vehicles, Equipment and Parts Which Can Be Fitted and/or Be Used on Wheeled Vehicles and the Conditions for Reciprocal Recognition of Approvals Granted on the Basis of These Prescriptions, Regulation No. 83; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Dekati. Dekati Thermodenuder, User Manual; Dekati: Kangasala, Finland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, D.; Seo, H.; Hong, K.J.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, Y.J.; Han, B.; Lee, G.Y.; Chun, S.N.; Hwang, J. Dilution Ratio and Particle Loss Performance of a Newly Developed Ejector Porous Tube Diluter Compared to a Commercial Diluter. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2020, 20, 2396–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melas, A.D.; Koidi, V.; Deloglou, D.; Daskalos, E.; Zarvalis, D.; Papaioannou, E.; Konstandopoulos, A.G. Development and Evaluation of a Catalytic Stripper for the Measurement of Solid Ultrafine Particle Emissions from Internal Combustion Engines. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 704–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milojević, S.; Savić, S.; Marić, D.; Stopka, O.; Krstić, B.; Stojanović, B. Correlation between Emission and Combustion Characteristics with the Compression Ratio and Fuel Injection Timing in Tribologically Optimized Diesel Engine. Tehnicki Vjesnik 2022, 29, 1210–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IMO. 2021 Guidelines for Exhaust Gas Cleaning Systems; IMO: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Grigoriadis, A.; Mamarikas, S.; Ioannidis, I.; Majamäki, E.; Jalkanen, J.P.; Ntziachristos, L. Development of Exhaust Emission Factors for Vessels: A Review and Meta-Analysis of Available Data. Atmos Environ. X 2021, 12, 100142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.K.; Raj Mohan, B.; Byeon, S.H.; Lim, K.S.; Hong, E.P. Evaluating the Performance of a Turbulent Wet Scrubber for Scrubbing Particulate Matter. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2013, 63, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasper, A.; Aufdenblatten, S.; Forss, A.; Mohr, M.; Burtscher, H. Particulate Emissions from a Low-Speed Marine Diesel Engine. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lack, D.A.; Corbett, J.J.; Onasch, T.; Lerner, B.; Massoli, P.; Quinn, P.K.; Bates, T.S.; Covert, D.S.; Coffman, D.; Sierau, B.; et al. Particulate Emissions from Commercial Shipping: Chemical, Physical, and Optical Properties. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114, 2008JD011300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Essen, H.; van Wijngaarden, L.; Schroten, A.; Sutter, D.; Bieler, C.; Maffii, S.; Brambilla, M.; Fiorello, D.; Fermi, F.; Parolin, R.; et al. Handbook on the External Costs of Transport. European Commnission: Brussels, Belgium, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Genitsaris, S.; Kourkoutmani, P.; Stefanidou, N.; Michaloudi, E.; Gros, M.; García-Gómez, E.; Petrović, M.; Ntziachristos, L.; Moustaka-Gouni, M. Effects from Maritime Scrubber Effluent on Phytoplankton and Bacterioplankton Communities of a Coastal Area, Eastern Mediterranean Sea. Ecol. Inform. 2023, 77, 102154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picone, M.; Russo, M.; Distefano, G.G.; Baccichet, M.; Marchetto, D.; Volpi Ghirardini, A.; Lunde Hermansson, A.; Petrovic, M.; Gros, M.; Garcia, E.; et al. Impacts of Exhaust Gas Cleaning Systems (EGCS) Discharge Waters on Planktonic Biological Indicators. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 190, 114846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genitsaris, S.; Stefanidou, N.; Hatzinikolaou, D.; Kourkoutmani, P.; Michaloudi, E.; Voutsa, D.; Gros, M.; García-Gómez, E.; Petrović, M.; Ntziachristos, L.; et al. Marine Microbiota Responses to Shipping Scrubber Effluent Assessed at Community Structure and Function Endpoints. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2024, 43, 1012–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Gross tonnage (tonnes) | 75,201 |
| Deadweight (tonnes) | 78,243 |
| Length (m) | 300 |
| Breadth (m) | 40.1 |
| Container capacity (20-foot equivalent units—TEUs) | 6160 |
| Year built | 2002 |
| Main engine | Wärtsilä-Sulzer 12RTA96C |
| Main engine power (kW)/nominal rpm | 62,587/98 |
| Auxiliary engine | Daihatsu 8DK32 |
| Auxiliary engine power-mechanical (kW)/nominal rpm | 2942/720 |
| Design/service speed (knots) | 25/18 |
| Pollutant | Instrument | Operational Principle | Range | Uncertainty |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SO2 | Horiba PG 350E | Non-dispersive infrared (NDIR) | 0–500 ppm (vol) | ±5 ppm |
| NOX | Chemiluminescence analyzer (CLA) | 0–2500 ppm (vol) | ±12.5 ppm | |
| CO2 | Non-dispersive infrared (NDIR) | 0–30% vol | ±0.3% vol | |
| O2 | Para-magnetic | 0–25%vol | ±0.25% vol | |
| CO | Non-dispersive infrared (NDIR) | 0–1000 ppm (vol) | ±10 ppm | |
| THC | Bernath Atomic BA 3006 | Flame ionization detector (FID) | 0.05 ppm-10% (vol) | ±0.1% vol |
| PN concentration and size distribution | TSI SMPS 3080 and CPC 3776 | Particle size classification and particle counter | 5.9–225 nm | ±10% |
| Sampling Point | Gaseous Pollutants | THC | PN Concentration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Upstream scrubber | 4.60 | 6.33 | 12.0 |
| Downstream scrubber | 36.0 | 6.75 | 16.7 |
| ULSFO and deactivated scrubber | 7.27 | 0.733 | 7.23 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grigoriadis, A.; Kousias, N.; Raptopoulos-Chatzistefanou, A.; Salberg, H.; Moldanová, J.; Hermansson, A.-L.; Cha, Y.; Kontses, A.; Toumasatos, Z.; Mamarikas, S.; et al. Particulate and Gaseous Emissions from a Large Two-Stroke Slow-Speed Marine Engine Equipped with Open-Loop Scrubber under Real Sailing Conditions. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 845. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15070845
Grigoriadis A, Kousias N, Raptopoulos-Chatzistefanou A, Salberg H, Moldanová J, Hermansson A-L, Cha Y, Kontses A, Toumasatos Z, Mamarikas S, et al. Particulate and Gaseous Emissions from a Large Two-Stroke Slow-Speed Marine Engine Equipped with Open-Loop Scrubber under Real Sailing Conditions. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(7):845. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15070845
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrigoriadis, Achilleas, Nikolaos Kousias, Anastasios Raptopoulos-Chatzistefanou, Håkan Salberg, Jana Moldanová, Anna-Lunde Hermansson, Yingying Cha, Anastasios Kontses, Zisimos Toumasatos, Sokratis Mamarikas, and et al. 2024. "Particulate and Gaseous Emissions from a Large Two-Stroke Slow-Speed Marine Engine Equipped with Open-Loop Scrubber under Real Sailing Conditions" Atmosphere 15, no. 7: 845. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15070845
APA StyleGrigoriadis, A., Kousias, N., Raptopoulos-Chatzistefanou, A., Salberg, H., Moldanová, J., Hermansson, A.-L., Cha, Y., Kontses, A., Toumasatos, Z., Mamarikas, S., & Ntziachristos, L. (2024). Particulate and Gaseous Emissions from a Large Two-Stroke Slow-Speed Marine Engine Equipped with Open-Loop Scrubber under Real Sailing Conditions. Atmosphere, 15(7), 845. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15070845









