The Construction and Application of a Model for Evaluating Tourism Climate Suitability in Terraced Agricultural Cultural Heritage Sites: A Case Study of Longji Terraced Fields in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
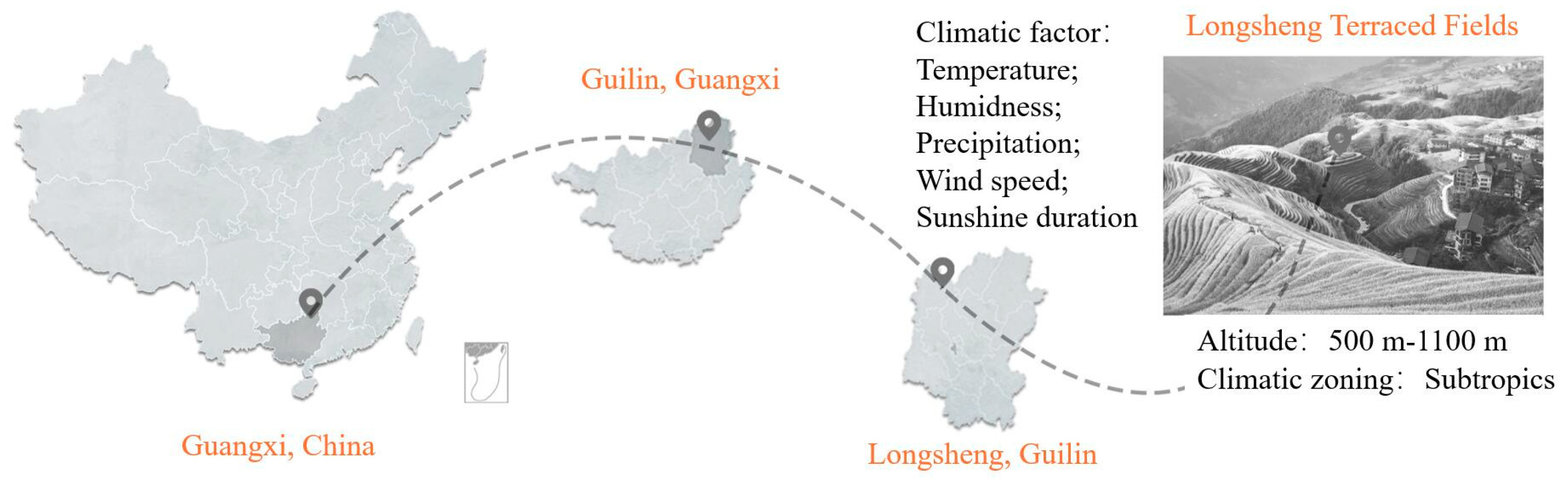
2.1. Study Location
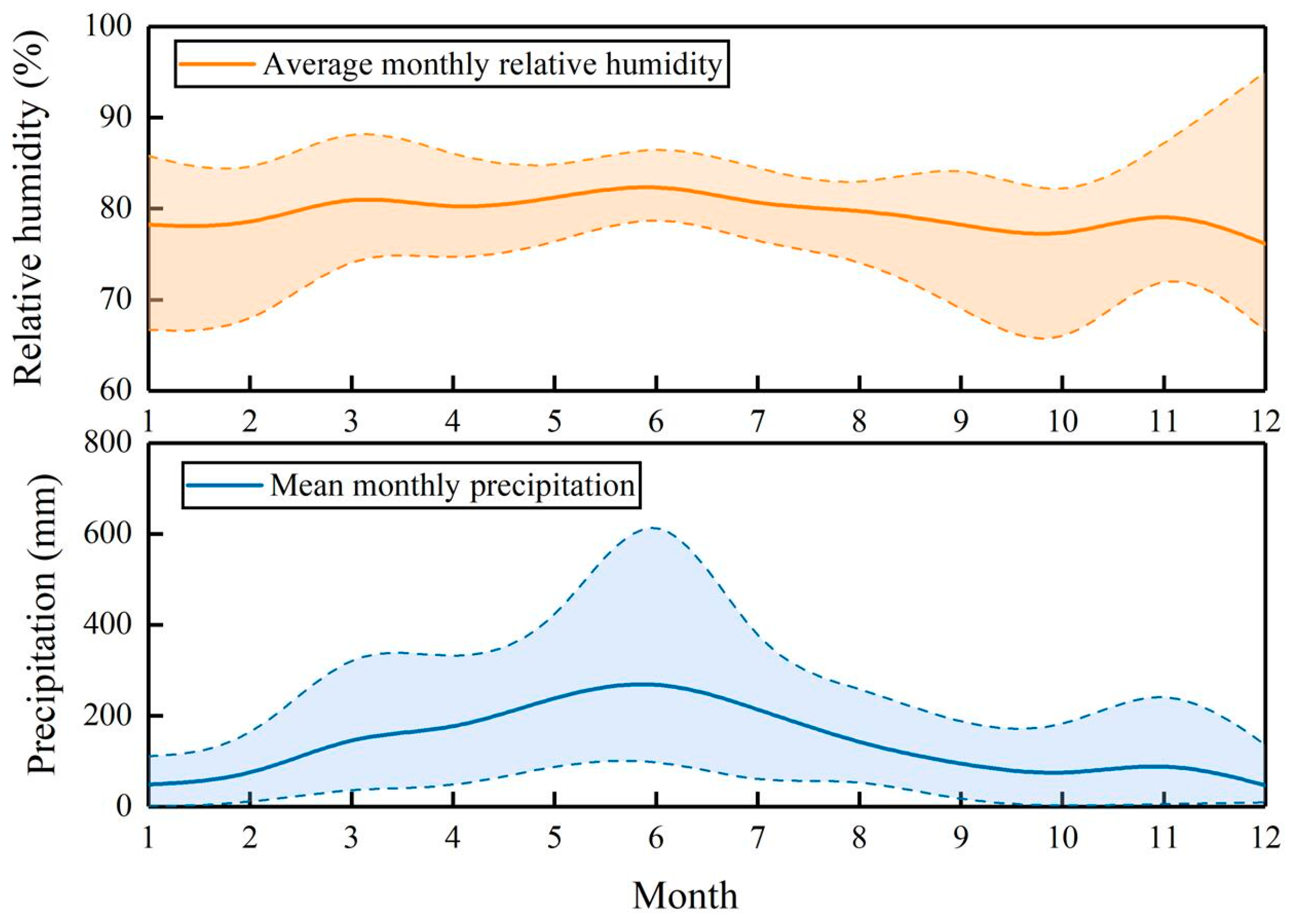
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Tourism Climate Suitability Models and Optimization
3.1. Model Selection Criteria
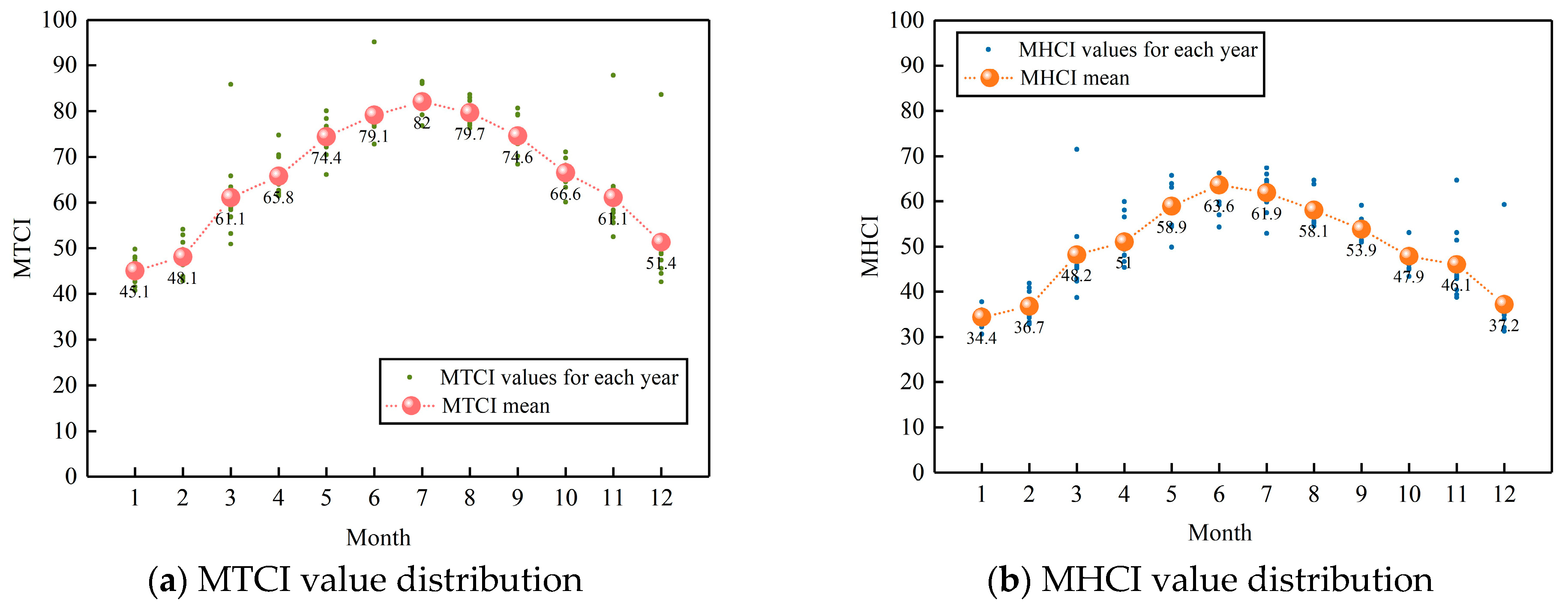
3.2. Construction and Analysis of MTCI and MHCI Models
3.2.1. Establishment of Mathematical Models
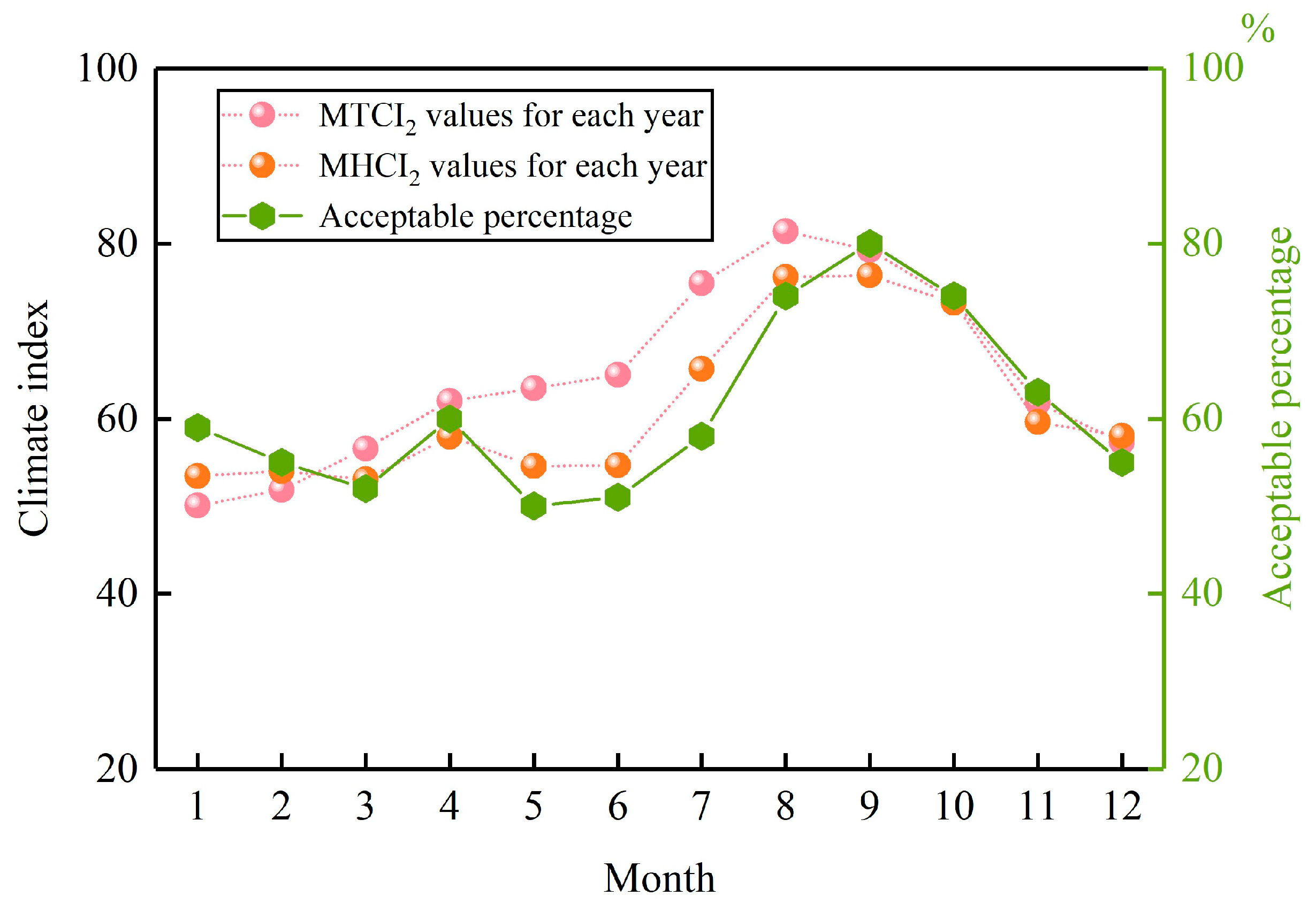
3.2.2. Model Applicability Analysis
3.3. Optimization and Solution of MTCI and MHCI Models
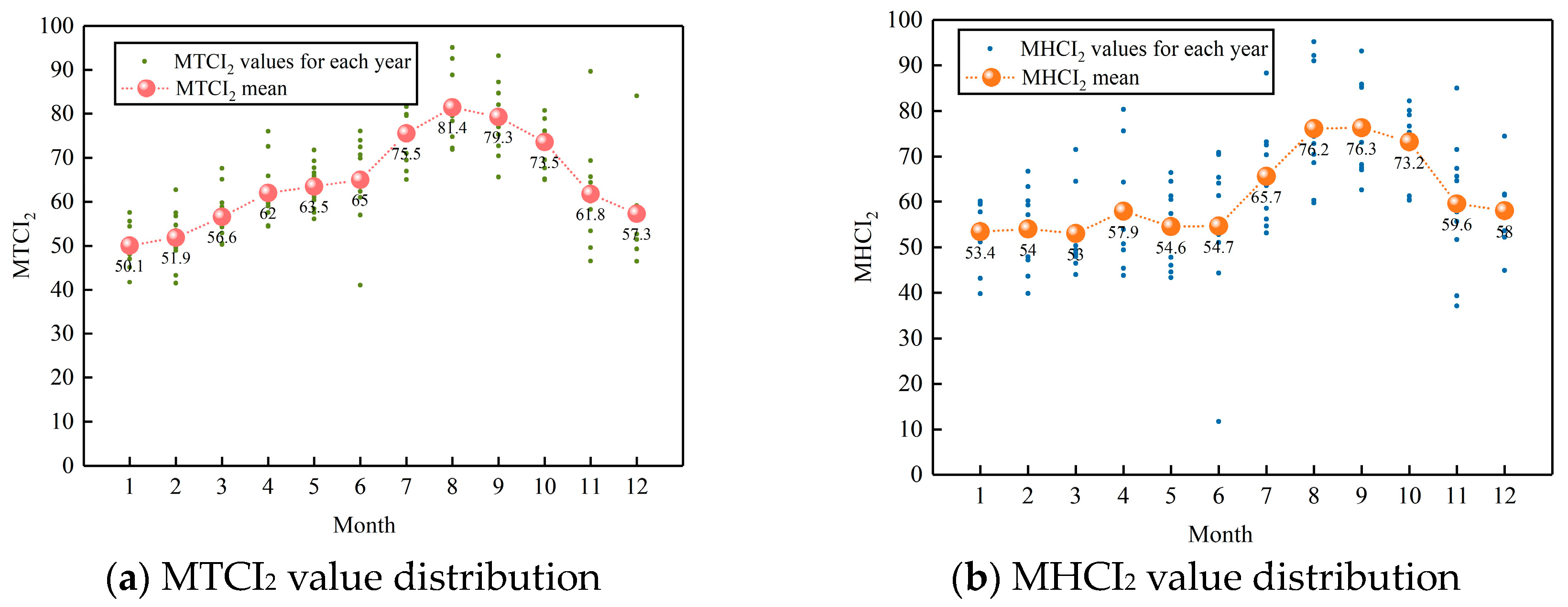
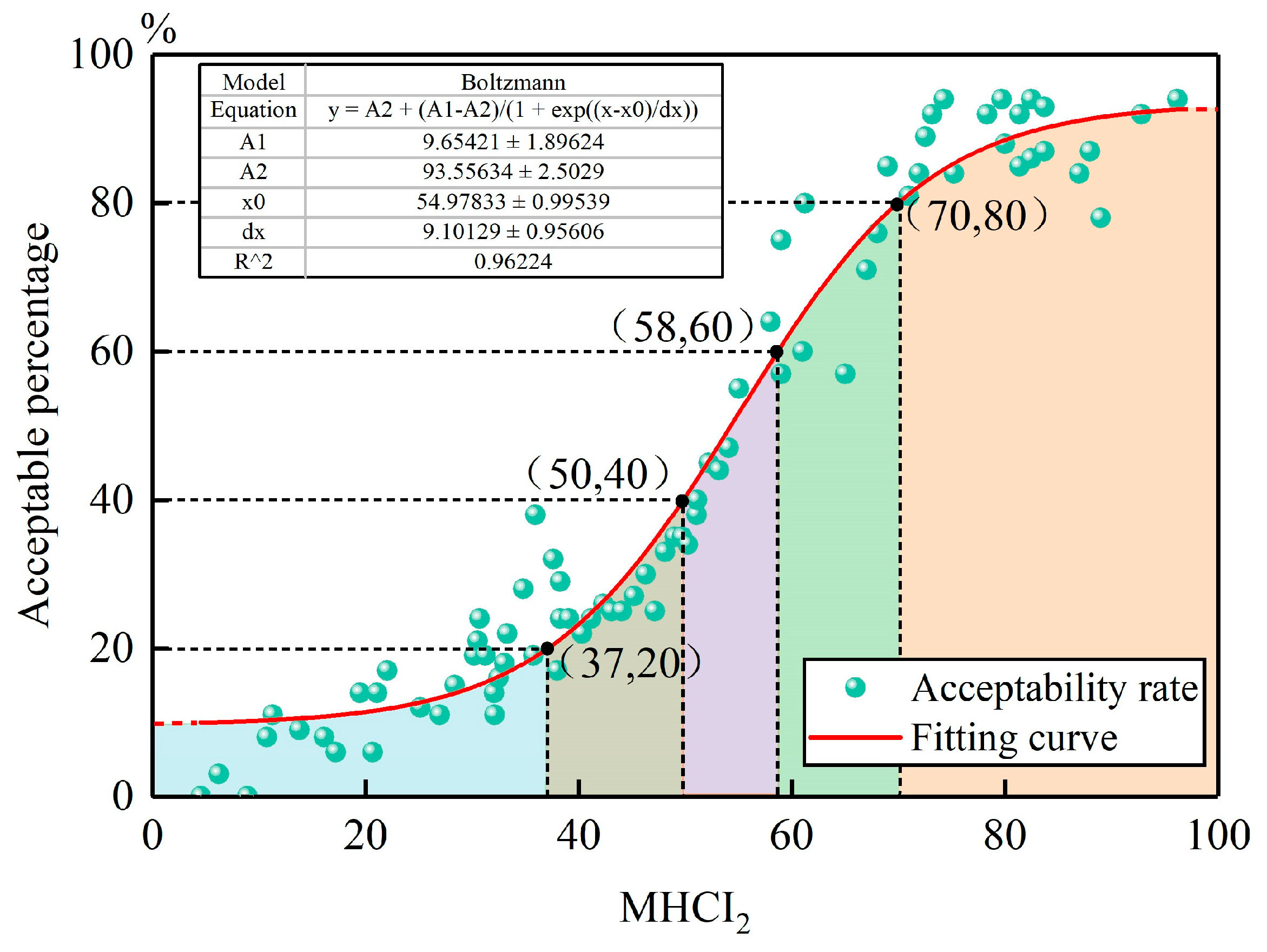
3.4. Model Optimization Evaluation and Determination
3.4.1. Climate Suitability Questionnaire Survey
3.4.2. Model Determination
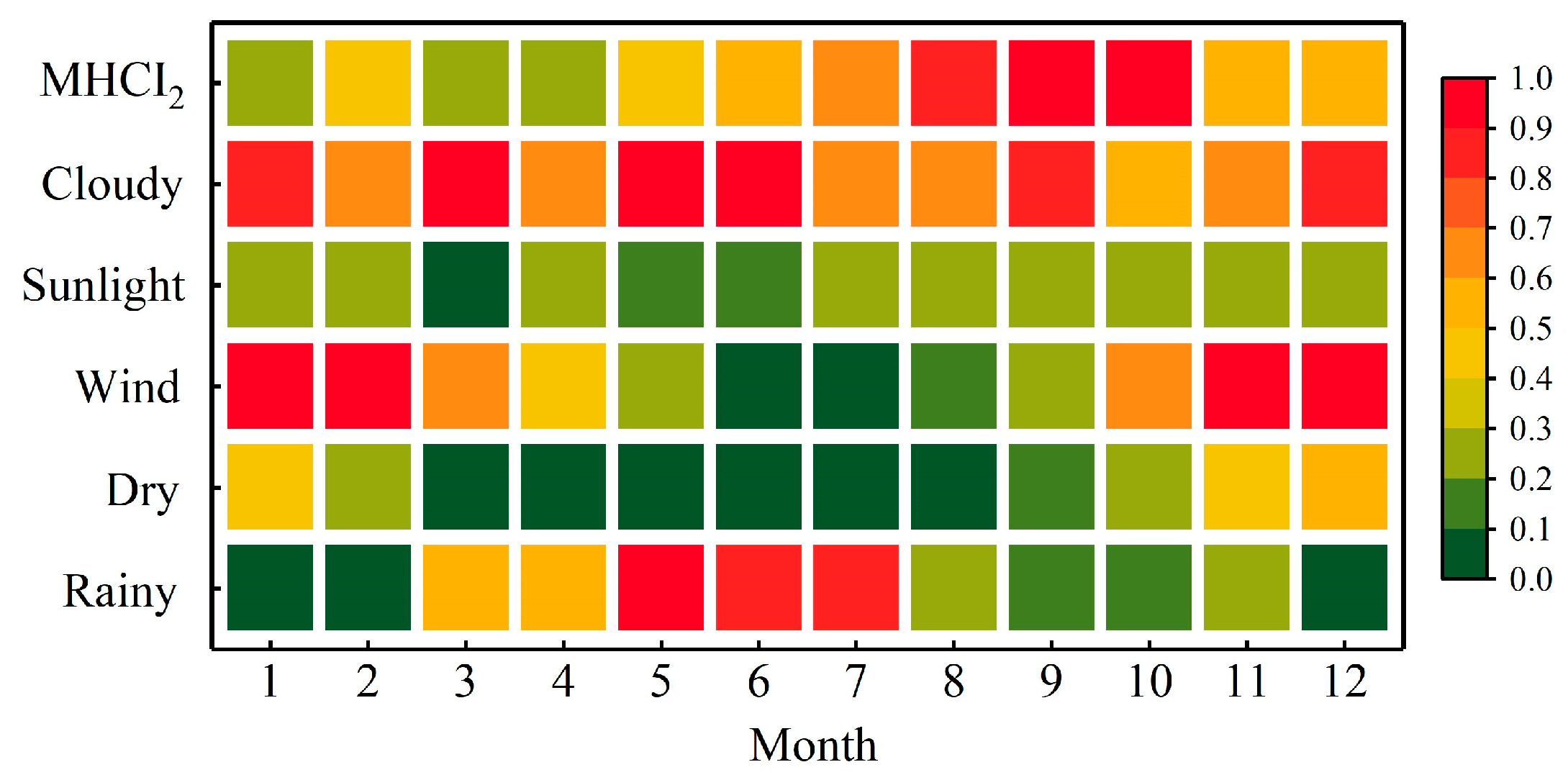
4. Analysis of Climate Suitability for Longsheng Tourism
- (1)
- Comfort (MHCI2 value > 60);
- (2)
- Cloudiness (Cloud cover > 0.6);
- (3)
- Sunshine (Cloud cover < 5/8);
- (4)
- Windy (Wind speed > 8 m/s);
- (5)
- Dry (Precipitation < 1 mm);
- (6)
- Rainy (Precipitation > 5 mm).
5. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, D.; Wei, W.; Chen, L.D. History and distribution of terraced landscapes and typical international cases analysis. J. Appl. Ecol. 2017, 28, 689–698. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.-G.; Li, Y.; Dai, S.-W.; Liu, Z.-J.; Wang, W.-F. Changes of China agricultural climate resources under the background of climate change: IX. Spatiotemporal change characteristics of China agricultural climate resources. J. Appl. Ecol. 2011, 22, 3177–3188. [Google Scholar]
- Su, M.M.; Dong, Y.; Wall, G.; Sun, Y. A value-based analysis of the tourism use of agricultural heritage systems: Duotian Agrosystem, Jiangsu Province, China. J. Sustain. Tour. 2020, 28, 2136–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.A. Evaluation of tourism climate comfort in order to attract more tourists–Case study: Sanandaj city in Iran. Life Sci. J. 2012, 9, 623–629. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.-Y.; Yu, H.-W.; Hsieh, C.-M. Evaluating forest visitors’ place attachment, recreational activities, and travel intentions under different climate scenarios. Forests 2021, 12, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Chen, D. Progress and prospects of tourism climate research in China. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.-P.; Zhong, F.-L. Evaluation of tourism climate comfort in the Grand Shangri-La region. J. Mt. Sci. 2019, 16, 1452–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Yang, X.; Shen, Z.; Yi, Z. Long-term trends and spatiotemporal variations of climate comfort in China during 1966–2016. Therm. Sci. 2020, 24, 2445–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Fan, J.; Yang, W. Flooding Risk Assessment and Analysis Based on GIS and the TFN-AHP Method: A Case Study of Chongqing, China. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junyuan, Z.; Shengjie, W. Spatio-temporal evolution and prediction of tourism comprehensive climate comfort in Henan province, China. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gungor, S.; Cetin, M.; Adiguzel, F. Calculation of comfortable thermal conditions for Mersin urban city planning in Turkey. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2021, 14, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mieczkowski, Z. The tourism climatic index: A method of evaluating world climates for tourism. Can. Geogr. 1985, 29, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Freitas, C.R.; Scott, D.; McBoyle, G. A second generation climate index for tourism (CIT): Specification and verification. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2008, 52, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, R.; Gatell, E.; Junyent, R.; Micallef, A.; Özhan, E.; Williams, A.T. An improved user-based beach climate index. J. Coast. Conserv. 2000, 6, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, D.; Rutty, M.; Amelung, B.; Tang, M. An inter-comparison of the holiday climate index (HCI) and the tourism climate index (TCI) in Europe. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Schwartz, Z.; Walsh, J.E. A weather-resolving index for assessing the impact of climate change on tourism related climate resources. Clim. Chang. 2009, 95, 551–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gössling, S.; Bredberg, M.; Randow, A.; Sandström, E.; Svensson, P. Tourist perceptions of climate change: A study of international tourists in Zanzibar. Curr. Issues Tour. 2006, 9, 419–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutty, M.; Scott, D. Comparison of climate preferences for domestic and international beach holidays: A case study of Canadian travelers. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Freitas, C.R. Recreation climate assessment. Int. J. Climatol. 1990, 10, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Freitas, C.R. Tourism climatology: Evaluating environmental information for decision making and business planning in the recreation and tourism sector. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2003, 48, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, D.; McBoyle, G.; Schwartzentruber, M. Climate change and the distribution of climatic resources for tourism in North America. Clim. Res. 2004, 27, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, D.R., IV; Debbage, K.G. Weather and tourism: Thermal comfort and zoological park visitor attendance. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteith, J.L. Light distribution and photosynthesis in field crops. Ann. Bot. 1965, 29, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thom, E.C. The discomfort index. Weatherwise 1959, 12, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Yu, H.; Zeng, Y. Impact of climate change on Tibet tourism based on tourism climate index. J. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 29, 2085–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.-D.; Li, S.; Guo, Z.-Y. Evaluating the tourist climate comfortable period of China in a changing climate. Adv. Meteorol. 2020, 2020, 8886316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; You, Q.; Liu, G.; Wu, F. Climatology and trend of tourism climate index over China during 1979–2020. Atmos. Res. 2022, 277, 106321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Han, J.; Zhao, Y.; Han, Q.; Wu, L.; Wang, X.; Qiu, Z.; Zou, T.; Fan, C. A study of the temporal and spatial variations in the suitability of the environment in Chinese cities for tourism and in strategies for optimizing the environment. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2022, 15, 527–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, Z. Analysis and Evaluation of Tourism Climate Resources in Turpan Region. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 869, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Chi, X. Thermal comfort and tourism climate changes in the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau in the last 50 years. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2014, 117, 613–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matzarakis, A.; Fröhlich, D.; Bermon, S.; Adami, P.E. Visualization of Climate Factors for Sports Events and Activities–The Tokyo 2020 Olympic Games. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.-P.; Matzarakis, A. Tourism climate information based on human thermal perception in Taiwan and Eastern China. Tour. Manag. 2011, 32, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahabi Abed, S.; Matzarakis, A. Quantification of the Tourism Climate of Algeria Based on the Climate-Tourism-Information-Scheme. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Tang, J.; Shi, L.; Zhao, T.; Chen, J. Emotional wellbeing in intercity travel: Factors affecting passengers’ long-distance travel moods. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 1046922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Dimension | TCI | BCI | CIT | MCIT | HCI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Formula | TCI = 4CID + CIA + 2P + 2S + W | BCT = 0.18Ts + 0.26W + 0.27S + 0.29P + 0.28Tw | CIT = f [(T,B) × P] | HCI = 4TC + 3P + 2A + W | |
| Number of Variables | 7 | 9 | 7 | 4 | 5 |
| Concrete indicators | precipitation factor (P), daylight factor son (S), wind speed factor (W) | Skin temperature (Ts), average wind speed, sunshine ratio, cumulative precipitation, bath water temperature () | Thermal comfort (T), beauty (A), precipitation factor | Perceived temperature (PT), wind speed, significant weather (SW), visibility (V) | Thermal comfort (TC), physical effects, beauty (A) |
| Data Granularity | Monthly | Monthly | Daily | Hourly | Daily |
| Model Form | Weighted sum | Weighted sum | Composite assignment | Multiplication | Weighted sum |
| Average Classification | 10 levels | 5 levels | 7 levels | 3 levels | 10 levels |
| Applicable Range | Local/regional | Local | Local | Local | Local/regional |
| Question | Are You Satisfied with Today’s Tourism Climate | |
|---|---|---|
| Total number of respondents | 3247 | |
| gender | Male | 51.3% |
| Female | 48.7% | |
| Age range of respondents | Children | 28.9% |
| Teenagers | 37.8% | |
| Middle-aged and elderly | 33.3% | |
| Identity of respondents | Local tourists | 48.3% |
| Out-of-town tourists | 51.7% | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, L.; Guo, X.; Yan, P.; Li, X. The Construction and Application of a Model for Evaluating Tourism Climate Suitability in Terraced Agricultural Cultural Heritage Sites: A Case Study of Longji Terraced Fields in China. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 756. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15070756
Hu L, Guo X, Yan P, Li X. The Construction and Application of a Model for Evaluating Tourism Climate Suitability in Terraced Agricultural Cultural Heritage Sites: A Case Study of Longji Terraced Fields in China. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(7):756. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15070756
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Luyao, Xiaoyu Guo, Pengbo Yan, and Xinkai Li. 2024. "The Construction and Application of a Model for Evaluating Tourism Climate Suitability in Terraced Agricultural Cultural Heritage Sites: A Case Study of Longji Terraced Fields in China" Atmosphere 15, no. 7: 756. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15070756
APA StyleHu, L., Guo, X., Yan, P., & Li, X. (2024). The Construction and Application of a Model for Evaluating Tourism Climate Suitability in Terraced Agricultural Cultural Heritage Sites: A Case Study of Longji Terraced Fields in China. Atmosphere, 15(7), 756. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15070756





