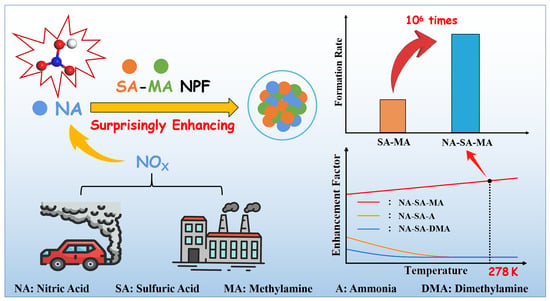
A Surprisingly High Enhancing Potential of Nitric Acid in Sulfuric Acid–Methylamine Nucleation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Configurational Sampling
2.2. Atmospheric Cluster Dynamics Code Simulations
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Cluster Structures
3.2. Evaporation Rates
3.3. Addition Free Energies of NA to the Clusters
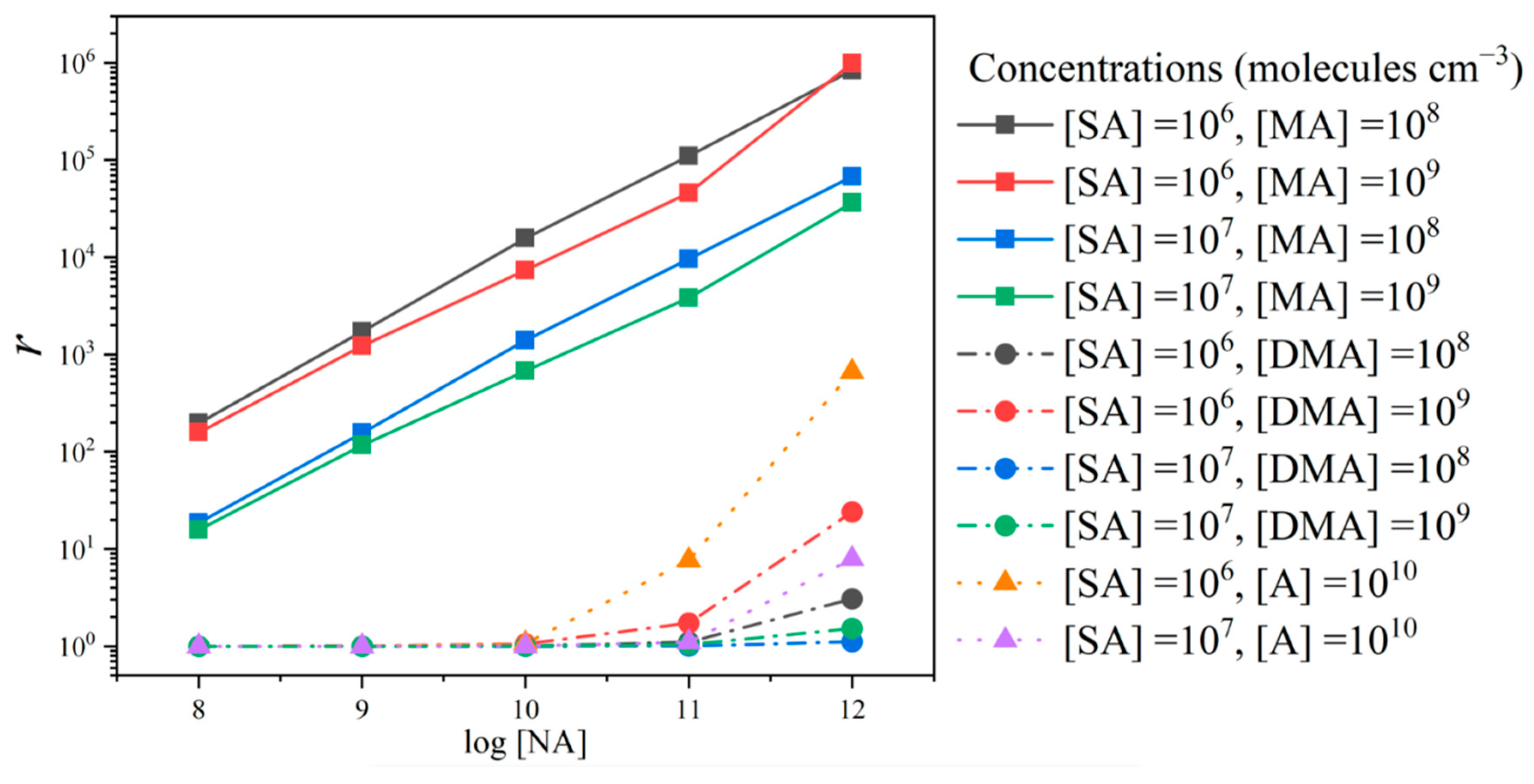
3.4. Enhancement Effect of NA on Cluster Formation Rates
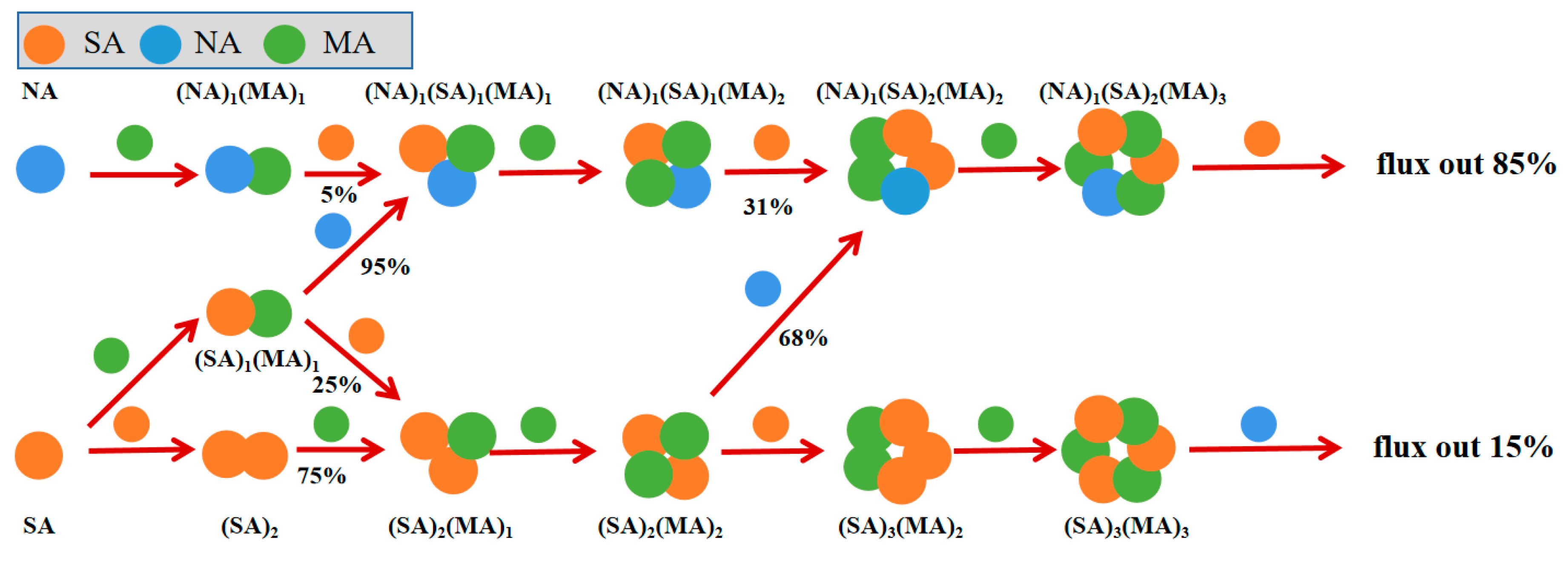
3.5. Mechanism of the NA-SA-MA Nucleation System
4. Implications and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Specific Details of Multi-Step Sampling Approach and Employed Calculation Methods
Appendix A.2. Physical Principles of ACDC
Appendix A.3. Selection of Boundary Clusters
References
- Wang, M.; Kong, W.; Marten, R.; He, X.-C.; Chen, D.; Pfeifer, J.; Heitto, A.; Kontkanen, J.; Dada, L.; Kürten, A.; et al. Rapid Growth of New Atmospheric Particles by Nitric Acid and Ammonia Condensation. Nature 2020, 581, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riccobono, F.; Schobesberger, S.; Scott, C.E.; Dommen, J.; Ortega, I.K.; Rondo, L.; Almeida, J.; Amorim, A.; Bianchi, F.; Breitenlechner, M.; et al. Oxidation Products of Biogenic Emissions Contribute to Nucleation of Atmospheric Particles. Science 2014, 344, 717–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, L.; Garmash, O.; Bianchi, F.; Zheng, J.; Yan, C.; Kontkanen, J.; Junninen, H.; Mazon, S.B.; Ehn, M.; Paasonen, P.; et al. Atmospheric New Particle Formation from Sulfuric Acid and Amines in A Chinese Megacity. Science 2018, 361, 278–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Khalizov, A.; Wang, L.; Hu, M.; Xu, W. Nucleation and Growth of Nanoparticles in the Atmosphere. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 1957–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zu, H.; Zhang, S.; Liu, L.; Zhang, X. The vital role of sulfuric acid in iodine oxoacids nucleation: Impacts of urban pollutants on marine atmosphere. Environ. Res. Lett. 2024, 19, 014076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkby, J.; Curtius, J.; Almeida, J.; Dunne, E.; Duplissy, J.; Ehrhart, S.; Franchin, A.; Gagné, S.; Ickes, L.; Kürten, A.; et al. Role of Sulphuric Acid, Ammonia and Galactic Cosmic Rays in Atmospheric Aerosol Nucleation. Nature 2011, 476, 429–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feketeová, L.; Bertier, P.; Salbaing, T.; Azuma, T.; Calvo, F.; Farizon, B.; Farizon, M.; Märk, T.D. Impact of A Hydrophobic Ion on the Early Stage of Atmospheric Aerosol Formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 22540–22544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Finlayson-Pitts, B.J. New Particle Formation from Methanesulfonic Acid and Amines/Ammonia as a Function of Temperature. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, C.; Zha, Q.; Dada, L.; Yan, C.; Lehtipalo, K.; Junninen, H.; Mazon, S.B.; Jokinen, T.; Sarnela, N.; Sipilä, M.; et al. Observations of Biogenic Ion-induced Cluster Formation in the Atmosphere. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaar5218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhong, J.; Vehkamäki, H.; Kurtén, T.; Du, L.; Zhang, X.; Francisco, J.S.; Zeng, X.C. Unexpected Quenching Effect on New Particle Formation from the Atmospheric Reaction of Methanol with SO3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 24966–24971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkby, J.; Duplissy, J.; Sengupta, K.; Frege, C.; Gordon, H.; Williamson, C.; Heinritzi, M.; Simon, M.; Yan, C.; Almeida, J.; et al. Ion-induced Nucleation of Pure Biogenic Particles. Nature 2016, 533, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schobesberger, S.; Junninen, H.; Bianchi, F.; Lonn, G.; Ehn, M.; Lehtipalo, K.; Dommen, J.; Ehrhart, S.; Ortega, I.K.; Franchin, A.; et al. Molecular Understanding of Atmospheric Particle Formation from Sulfuric Acid and Large Oxidized Organic Molecules. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 17223–17228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, J.; Schobesberger, S.; Kurtén, A.; Ortega, I.K.; Kupiainen-Maatta, O.; Praplan, A.P.; Adamov, A.; Amorim, A.; Bianchi, F.; Breitenlechner, M.; et al. Molecular Understanding of Sulphuric Acid-amine Particle Nucleation in the Atmosphere. Nature 2013, 502, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtén, T.; Loukonen, V.; Vehkamäki, H.; Kulmala, M. Amines Are Likely to Enhance Neutral and Ion-induced Sulfuric Acid-water Nucleation in the Atmosphere More Effectively than Ammonia. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 4095–4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, S.M.; Sorooshian, A.; Kroll, J.H.; Ng, N.L.; Chhabra, P.; Tong, C.; Surratt, J.D.; Knipping, E.; Flagan, R.C.; Seinfeld, J.H. Secondary Aerosol Formation from Atmospheric Reactions of Aliphatic Amines. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 2313–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.N.; Barsanti, K.C.; Friedli, H.R.; Ehn, M.; Kulmala, M.; Collins, D.R.; Scheckman, J.H.; Williams, B.J.; McMurry, P.H. Observations of Aminium Salts in Atmospheric Nanoparticles and Possible Climatic Implications. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 6634–6639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loukonen, V.; Kurtén, T.; Ortega, I.K.; Vehkamäki, H.; Pádua, A.A.H.; Sellegri, K.; Kulmala, M. Enhancing Effect of Dimethylamine in Sulfuric Acid Nucleation in the Presence of Water-A Computational Study. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 4961–4974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Smith, J.N.; Eisele, F.L.; Chen, M.; Kuang, C.; McMurry, P.H. Observation of Neutral Sulfuric Acid-amine Containing Clusters in Laboratory and Ambient Measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 10823–10836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtipalo, K.; Rondo, L.; Kontkanen, J.; Schobesberger, S.; Jokinen, T.; Sarnela, N.; Kuerten, A.; Ehrhart, S.; Franchin, A.; Nieminen, T.; et al. The Effect of Acid-base Clustering and Ions on the Growth of Atmospheric Nano-particles. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Titcombe, M.; Jiang, J.; Jen, C.; Kuang, C.; Fischer, M.L.; Eisele, F.L.; Siepmann, J.I.; Hanson, D.R.; Zhao, J.; et al. Acid-base Chemical Reaction Model for Nucleation Rates in the Polluted Atmospheric Boundary Layer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 18713–18718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erupe, M.E.; Viggiano, A.A.; Lee, S.H. The Effect of Trimethylamine on Atmospheric Nucleation Involving H2SO4. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 4767–4775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.-S.; Miao, S.-K.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, M.-M.; Wen, Y.; Wang, C.-Y.; Zhu, Y.-P.; Huang, W. Properties and Atmospheric Implication of Methylamine-Sulfuric Acid-Water Clusters. J. Phys. Chem. A 2015, 119, 8657–8666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sipila, M.; Berndt, T.; Petaja, T.; Brus, D.; Vanhanen, J.; Stratmann, F.; Patokoski, J.; Mauldin, R.L.; Hyvarinen, A.P.; Lihavainen, H.; et al. The Role of Sulfuric Acid in Atmospheric Nucleation. Science 2010, 327, 1243–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olenius, T.; Halonen, R.; Kurtén, T.; Henschel, H.; Kupiainen-Määttä, O.; Ortega, I.K.; Jen, C.N.; Vehkamäki, H.; Riipinen, I. New Particle Formation from Sulfuric Acid and Amines: Comparison of Monomethylamine, Dimethylamine, and Trimethylamine. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 7103–7118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadykto, A.B.; Yu, F.; Jakovleva, M.V.; Herb, J.; Xu, Y. Amines in the Earth’s Atmosphere: A Density Functional Theory Study of the Thermochemistry of Pre-Nucleation Clusters. Entropy 2011, 13, 554–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadykto, A.; Herb, J.; Yu, F.; Xu, Y.; Nazarenko, E. Estimating the Lower Limit of the Impact of Amines on Nucleation in the Earth’s Atmosphere. Entropy 2015, 17, 2764–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadykto, A.B.; Herb, J.; Yu, F.; Xu, Y. Enhancement in the Production of Nucleating Clusters due to Dimethylamine and Large Uncertainties in the Thermochemistry of Amine-enhanced Nucleation. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2014, 609, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jen, C.N.; McMurry, P.H.; Hanson, D.R. Stabilization of Sulfuric Acid Dimers by Ammonia, Methylamine, Dimethylamine, and Trimethylamine. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 7502–7514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.; Zhang, R.Y. Multiphase Chemistry of Atmospheric Amines. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 5738–5752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Wang, L.; Khalizov, A.F.; Zhao, J.; Zheng, J.; McGraw, R.L.; Molina, L.T. Formation of Nanoparticles of Blue Haze Enhanced by Anthropogenic Pollution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 17650–17654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zhang, R.Y. A Theoretical Study of Hydrated Molecular Clusters of Amines and Dicarboxylic Acids. J. Chem. Phys. 2013, 139, 064312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myllys, N.; Elm, J.; Halonen, R.; Kurtén, T.; Vehkamäki, H. Coupled Cluster Evaluation of the Stability of Atmospheric Acid-Base Clusters with up to 10 Molecules. J. Phys. Chem. A 2016, 120, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Ren, L.; Kanawade, V.P. New Particle Formation and Growth Mechanisms in Highly Polluted Environments. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2017, 3, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Gordon, H.; Yu, H.; Lehtipalo, K.; Haley, R.; Li, Y.; Zhang, R. New Particle Formation in the Atmosphere: From Molecular Clusters to Global Climate. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 7098–7146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, R.; Yan, C.; Yang, D.; Yin, R.; Lu, Y.; Deng, C.; Fu, Y.; Ruan, J.; Li, X.; Kontkanen, J.; et al. Sulfuric acid-Amine Nucleation in Urban Beijing. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 2457–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.S.; Ryerson, T.B.; Wollny, A.G.; Brock, C.A.; Peltier, R.; Sullivan, A.P.; Weber, R.J.; Dubé, W.P.; Trainer, M.; Meagher, J.F.; et al. Variability in Nocturnal Nitrogen Oxide Processing and Its Role in Regional Air Quality. Science 2006, 311, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vayenas, D.V.; Takahama, S.; Davidson, C.I.; Pandis, S.N. Simulation of the Thermodynamics and Removal Processes in the Sulfate-Ammonia-Nitric acid system during Winter: Implications for PM2.5 Control Strategies. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2005, 110, D07S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seinfeld, J.H.; Pandis, S.N. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics from Air Pollution to Climate Change, 3rd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, M.; Zhong, J.; Zeng, X.C.; Francisco, J.S. Reaction of Criegee Intermediate with Nitric Acid at the Air-Water Interface. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 4913–4921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acker, K.; Möller, D.; Auel, R.; Wieprecht, W.; Kalaß, D. Concentrations of Nitrous acid, Nitric acid, Nitrite and Nitrate in the Gas and Aerosol Phase at a Site in the Emission Zone During ESCOMPTE 2001 Experiment. Atmos. Res. 2005, 74, 507–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezuman, K.; Bauer, S.E.; Tsigaridis, K. Evaluating Secondary Inorganic Aerosols in Three Dimensions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 10651–10669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.H.; Carmichael, G.R. A Three-Dimensional Modeling Investigation of the Evolution Processes of Dust and Sea-Salt Particles in East Asia. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 18131–18154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Sun, X.; Shi, A.; Huang, Y.; Yan, J.; Nie, T.; Yan, X.; Li, X. Secondary Inorganic Aerosols Formation During Haze Episodes at an Urban Site in Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 177, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Zhao, P.; Su, J.; Dong, Q.; Du, X.; Zhang, Y. Aerosol pH and Its Driving Factors in Beijing. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 7939–7954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairlie, T.D.; Jacob, D.J.; Dibb, J.E.; Alexander, B.; Avery, M.A.; van Donkelaar, A.; Zhang, L. Impact of Mineral Dust on Nitrate, Sulfate, and Ozone in Transpacific Asian Pollution Plumes. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 3999–4012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Xiao, M.; Bertozzi, B.; Marie, G.; Rörup, B.; Schulze, B.; Bardakov, R.; He, X.-C.; Shen, J.; Scholz, W. Synergistic HNO3-H2SO4-NH3 Upper Tropospheric Particle Formation. Nature 2022, 605, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhong, J.; Bai, Y.; Ge, M.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X. The Role of Nitric Acid in Atmospheric New Particle Formation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 17406–17414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Yu, F.; Du, L.; Yang, Z.; Francisco, J.S.; Zhang, X. Rapid Sulfuric Acid-Dimethylamine Nucleation Enhanced by Nitric Acid in Polluted Regions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2108384118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knattrup, Y.; Elm, J. Clusteromics IV: The Role of Nitric Acid in Atmospheric Cluster Formation. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 31551–31560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knattrup, Y.; Kubečka, J.; Elm, J. Nitric Acid and Organic Acids Suppress the Role of Methanesulfonic Acid in Atmospheric New Particle Formation. J. Phys. Chem. A 2023, 127, 7568–7578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, W.; Wang, Q. Mechanistic Understanding of Rapid H2SO4-HNO3-NH3 Nucleation in the Upper Troposphere. Sci. Total. Environ. 2023, 883, 163477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schade, G.W.; Crutzen, P.J. Emission of Aliphatic Amines from Animal Husbandry and Their Reactions: Potential Source of N2O and HCN. J. Atmos. Chem. 1995, 22, 319–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.B.; Elm, J.; Halonen, R.; Myllys, N.; Kurten, T.; Kulmala, M.; Vehkamaki, H. Atmospheric Fate of Monoethanolamine: Enhancing New Particle Formation of Sulfuric Acid as an Important Removal Process. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 8422–8431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Varner, M.E.; Gerber, R.B.; Finlayson-Pitts, B.J. Reactions of Methanesulfonic Acid with Amines and Ammonia as a Source of New Particles in Air. J. Phys. Chem. B 2016, 120, 1526–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waller, S.E.; Yang, Y.; Castracane, E.; Racow, E.E.; Kreinbihl, J.J.; Nickson, K.A.; Johnson, C.J. The Interplay between Hydrogen Bonding and Coulombic Forces in Determining the Structure of Sulfuric Acid-Amine Clusters. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 1216–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Waller, S.E.; Kreinbihl, J.J.; Johnson, C.J. Direct Link between Structure and Hydration in Ammonium and Aminium Bisulfate Clusters Implicated in Atmospheric New Particle Formation. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 5647–5652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath, M.J.; Olenius, T.; Ortega, I.K.; Loukonen, V.; Paasonen, P.; Kurtén, T.; Kulmala, M.; Vehkamäki, H. Atmospheric Cluster Dynamics Code: A Flexible Method for Solution of the Birth-death Equations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 2345–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Xie, H.B.; Ma, F.; Chen, J.; Iyer, S.; Simon, M.; Heinritzi, M.; Shen, J.; Tham, Y.J.; Kurten, T.; et al. Critical Role of Iodous Acid in Neutral Iodine Oxoacid Nucleation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 14166–14177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, R.; Yin, R.; Li, X.; Xie, H.-B.; Yang, D.; Kerminen, V.-M.; Smith, J.N.; Ma, Y.; Hao, J.; Chen, J.; et al. Significant Contributions of Trimethylamine to Sulfuric Acid Nucleation in Polluted Environments. Npj Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2023, 6, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Xie, H.-B.; Zhang, R.; Su, L.; Jiang, Q.; Tang, W.; Chen, J.; Engsvang, M.; Elm, J.; He, X.-C. Enhancement of Atmospheric Nucleation Precursors on Iodic Acid-Induced Nucleation: Predictive Model and Mechanism. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 6944–6954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elm, J. Elucidating the Limiting Steps in Sulfuric Acid-Base New Particle Formation. J. Phys. Chem. A 2017, 121, 8288–8295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Dolg, M. ABCluster: The Artificial Bee Colony Algorithm for Cluster Global Optimization. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 24173–24181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Dolg, M. Global Optimization of Clusters of Rigid Molecules using the Artificial Bee Colony Algorithm. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 3003–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.A.; et al. Gaussian 09; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Neese, F. The ORCA program system. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Mol. Sci. 2012, 2, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olenius, T.; Kupiainen-Määttä, O.; Ortega, I.K.; Kurtén, T.; Vehkamäki, H. Free Energy Barrier in the Growth of Sulfuric Acid-Ammonia and Sulfuric Acid-Dimethylamine clusters. J. Chem. Phys. 2013, 139, 084312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kupiainen-Määttä, O.; Olenius, T.; Kurtén, T.; Vehkamäki, H. CIMS Sulfuric Acid Detection Efficiency Enhanced by Amines Due to Higher Dipole Moments: A Computational Study. J. Phys. Chem. A 2013, 117, 14109–14119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temelso, B.; Morrison, E.F.; Speer, D.L.; Cao, B.C.; Appiah-Padi, N.; Kim, G.; Shields, G.C. Effect of Mixing Ammonia and Alkylamines on Sulfate Aerosol Formation. J. Phys. Chem. A 2018, 122, 1612–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elm, J. Clusteromics I: Principles, Protocols, and Applications to Sulfuric Acid-Base Cluster Formation. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 7804–7814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubečka, J.; Neefjes, I.; Besel, V.; Qiao, F.; Xie, H.-B.; Elm, J. Atmospheric Sulfuric Acid-Multi-Base New Particle Formation Revealed through Quantum Chemistry Enhanced by Machine Learning. J. Phys. Chem. A 2023, 127, 2091–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
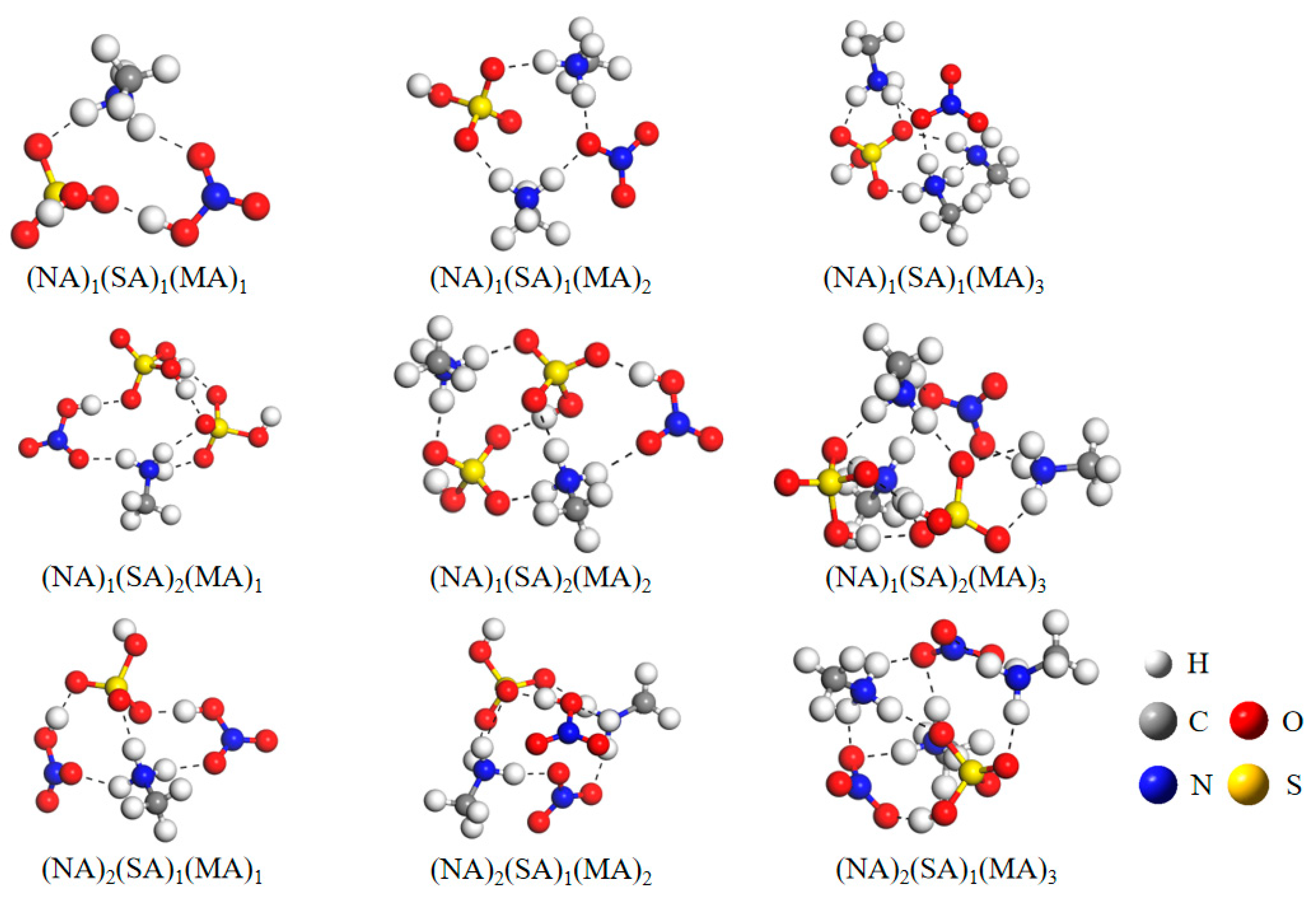

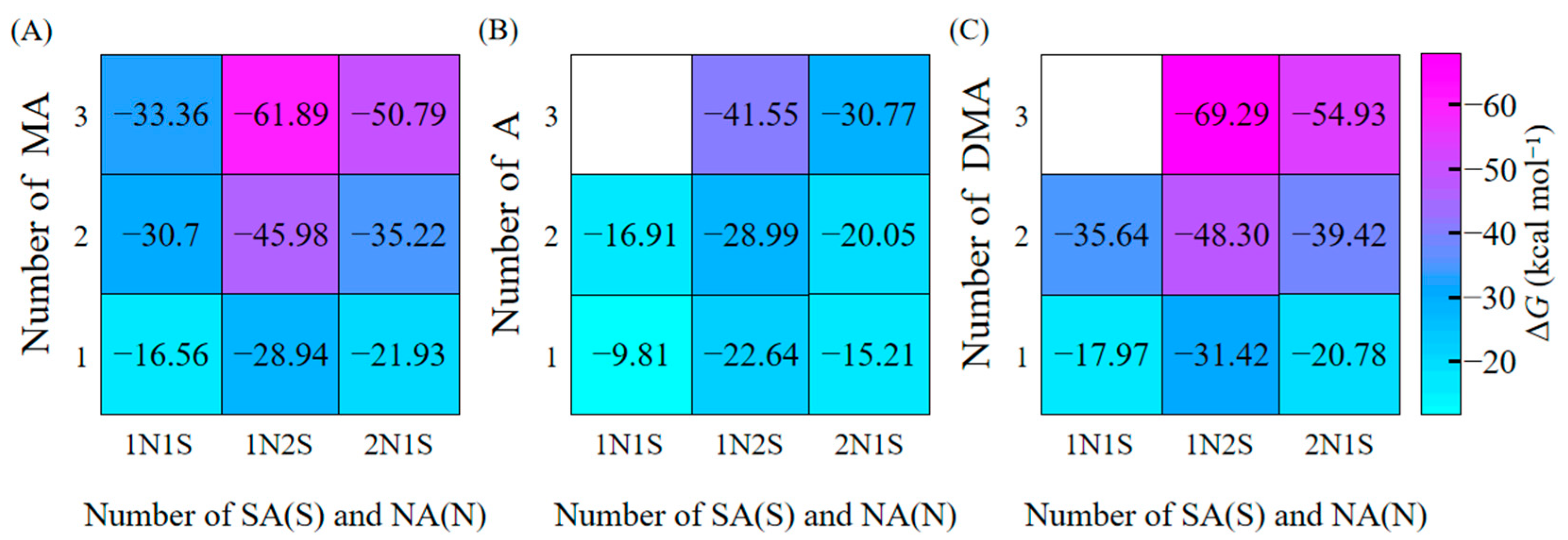
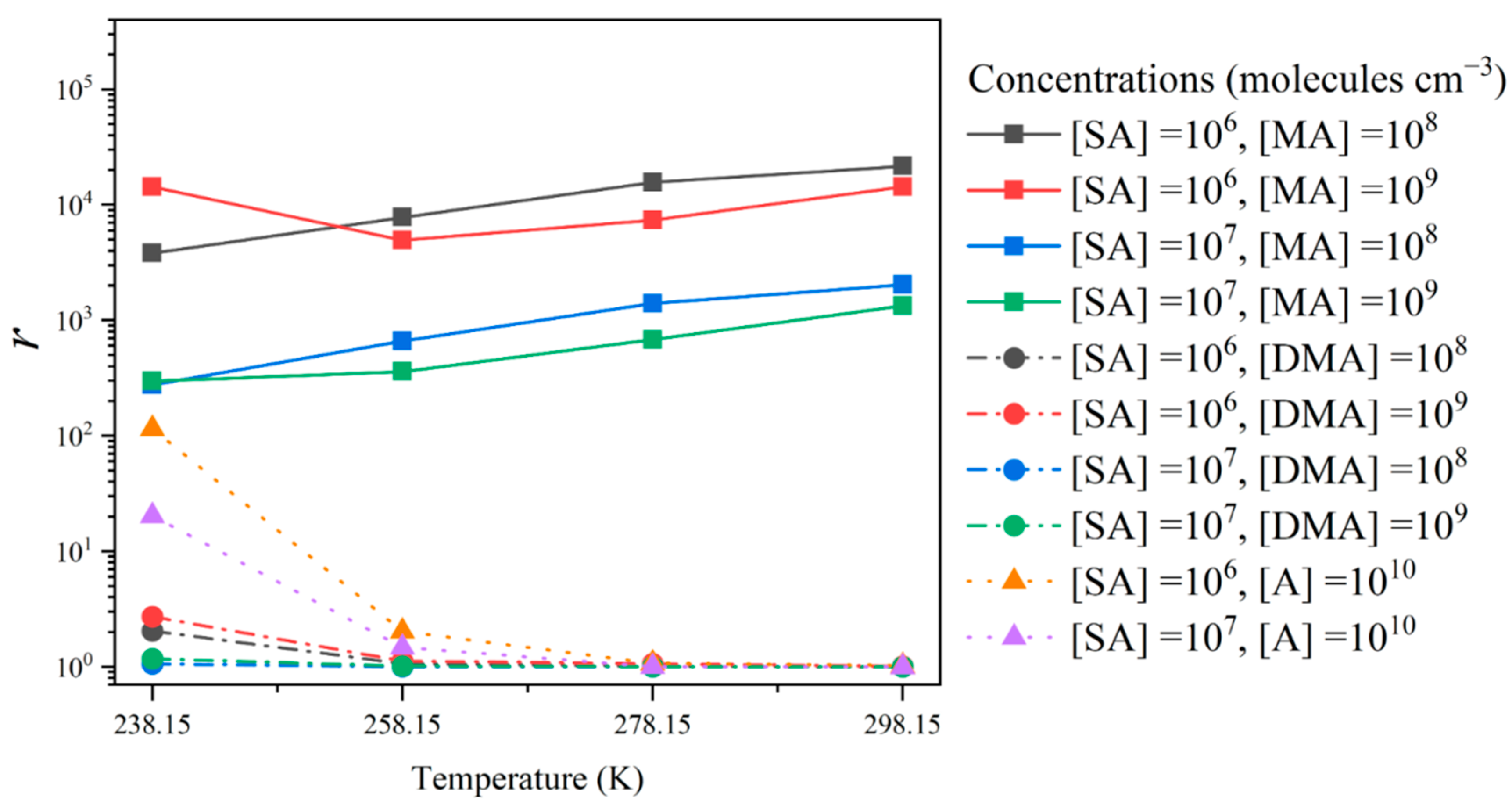
| Clusters | n | Clusters | n | Clusters | n |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (NA)1(SA)1(MA)1 | 3 | (NA)1(SA)1(DMA)1 | 4 | (NA)1(SA)1(A)1 | 3 |
| (NA)1(SA)1(MA)2 | 4 | (NA)1(SA)1(DMA)2 | 5 | (NA)1(SA)1(A)2 | 5 |
| (NA)2(SA)1(MA)1 | 5 | (NA)2(SA)1(DMA)1 | 5 | (NA)2(SA)1(A)1 | 5 |
| (NA)2(SA)1(MA)2 | 7 | (NA)2(SA)1(DMA)2 | 6 | (NA)2(SA)1(A)2 | 8 |
| (NA)2(SA)1(MA)3 | 10 | (NA)2(SA)1(DMA)3 | 7 | (NA)2(SA)1(A)3 | 9 |
| (NA)1(SA)2(MA)1 | 6 | (NA)1(SA)2(DMA)1 | 5 | (NA)1(SA)2(A)1 | 6 |
| (NA)1(SA)2(MA)2 | 7 | (NA)1(SA)2(DMA)2 | 7 | (NA)1(SA)2(A)2 | 8 |
| (NA)1(SA)2(MA)3 | 11 | (NA)1(SA)2(DMA)3 | 8 | (NA)1(SA)2(A)3 | 10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiao, F.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, Q.; Ma, F.; Chen, J.; Xie, H.-B. A Surprisingly High Enhancing Potential of Nitric Acid in Sulfuric Acid–Methylamine Nucleation. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 467. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15040467
Qiao F, Zhang R, Zhao Q, Ma F, Chen J, Xie H-B. A Surprisingly High Enhancing Potential of Nitric Acid in Sulfuric Acid–Methylamine Nucleation. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(4):467. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15040467
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiao, Fukang, Rongjie Zhang, Qiaojing Zhao, Fangfang Ma, Jingwen Chen, and Hong-Bin Xie. 2024. "A Surprisingly High Enhancing Potential of Nitric Acid in Sulfuric Acid–Methylamine Nucleation" Atmosphere 15, no. 4: 467. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15040467
APA StyleQiao, F., Zhang, R., Zhao, Q., Ma, F., Chen, J., & Xie, H.-B. (2024). A Surprisingly High Enhancing Potential of Nitric Acid in Sulfuric Acid–Methylamine Nucleation. Atmosphere, 15(4), 467. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15040467