Anthropogenic Impacts in the Lower Stratosphere: Scale Invariant Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Observed State via In Situ Methods
3. The Period of 1971–1984
XO + O → X + O2
nett: O + O3 → O2 + O2
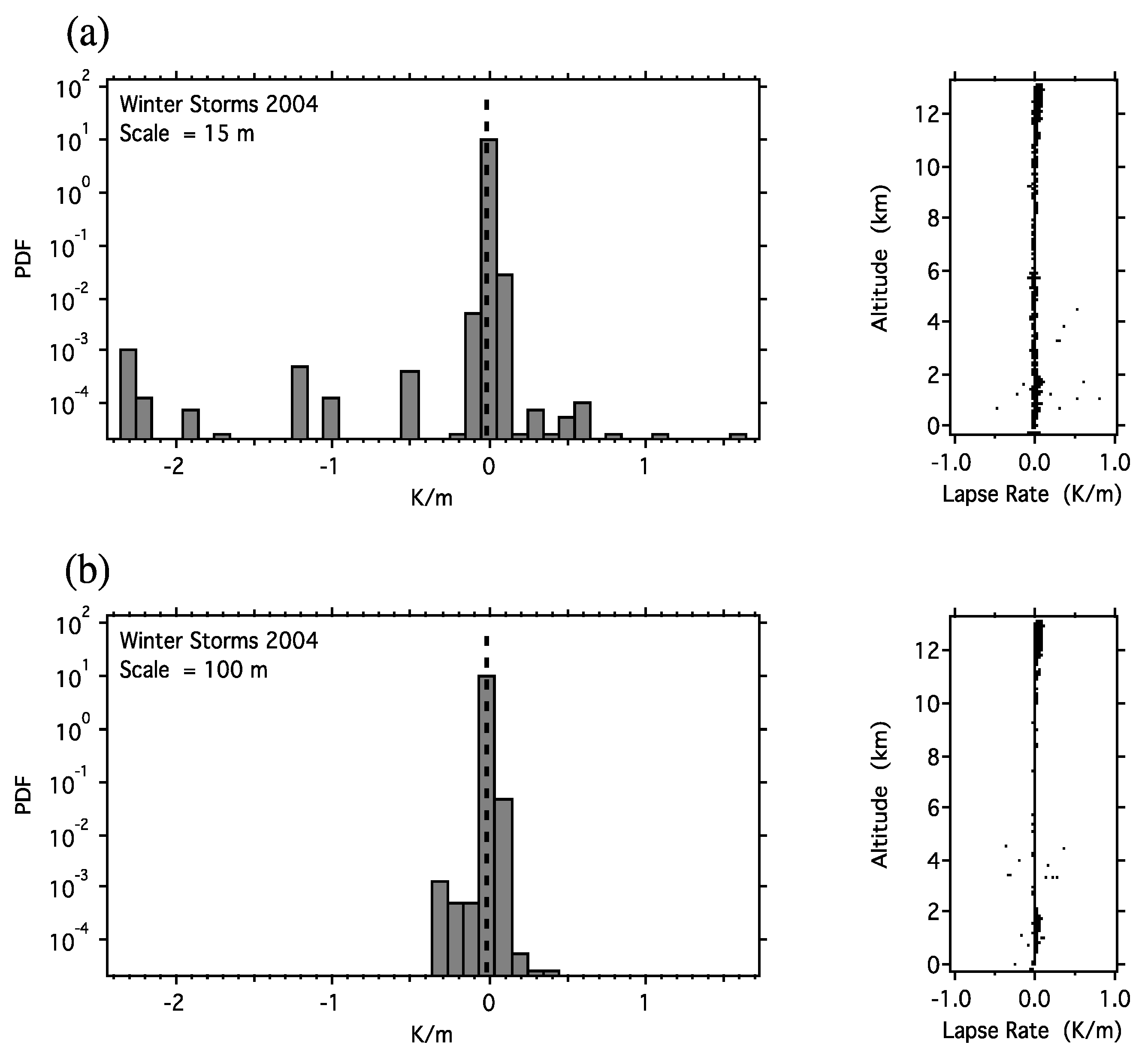
4. The Period of 1985–2006
5. WMO Reports and Assessments of Stratospheric Ozone
6. Forecasts: Macroweather and Climate
7. Discussion and Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dobson, G.M.B.; Brewer, A.W.; Cwilong, B.M. Meteorology of the lower stratosphere. Proc. R. Soc. A 1945, 185, 144–175. [Google Scholar]
- Brewer, A.W.; Cwilong, B.M.; Dobson, G.M.B. Measurement of absolute humidity in very dry air. Proc. Phys. Soc. 1948, 60, 52–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, A.W. Evidence for a world circulation provided by measurements of the helium and water vapour distributions in the stratosphere. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1949, 75, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foot, J.S. Aircraft measurements of the humidity in the lower stratosphere from 1977 to 1980 between 45° N and 65° N. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1984, 110, 303–319. [Google Scholar]
- Tuck, A.F.; Browell, E.V.; Danielsen, E.F.; Holton, J.R.; Hoskins, B.J.; Johnson, D.R.; Kley, D.; Krueger, A.J.; Mégie, G.; Newell, R.E.; et al. Stratosphere-Troposphere Exchange. In Atmospheric Ozone 1985; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1986; Chapter 5. [Google Scholar]
- Mattingly, S.R. The contribution of extratropical severe storms to the stratospheric water vapour budget. Meteorol. Mag. 1977, 106, 256–262. [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer, J.S. The dynamical systems of the lower stratosphere. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1951, 77, 480–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, R.J.; Danielsen, E.F. Fronts in the vicinity of the tropopause. Arch. Meteorol. Geophys. Bioklim. 1959, 11, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs, J.; Roach, W.T. Aircraft observations near jet streams. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1963, 89, 225–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuck, A.F.; Baumgardner, D.; Chan, K.R.; Dye, J.E.; Elkins, J.W.; Hovde, S.J.; Kelly, K.K.; Loewenstein, M.; Margitan, J.J.; May, R.D.; et al. The Brewer-Dobson circulation in the light of high altitude in situ aircraft observations. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1997, 123, 1–69. [Google Scholar]
- Tuck, A.F.; Hovde, S.J.; Kelly, K.K.; Mahoney, M.J.; Proffitt, M.H.; Richard, E.C.; Thompson, T.L. Exchange between the upper tropical troposphere and the lower stratosphere studied with aircraft observations. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 4734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murgatroyd, R.J.; Clews, C.J.B. Wind at 100,000 ft. over South-East England. In Meteorological Office Geophysical Memoirs; HMSO: London, UK, 1949; p. 83. [Google Scholar]
- Murgatroyd, R.J. Winds and temperatures between 20 km and 100 km—A review. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1957, 83, 417–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittock, A.B. A thin stable layer of anomalous ozone and dust content. J. Atmos. Sci. 1966, 23, 538–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dyer, A.J.; Hicks, B.B. Global spread of volcanic dust from the Bali eruption of 1963. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1968, 94, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newell, R.E. Stratospheric temperature change from the Mt. Agung volcanic eruption of 1963. J. Atmos. Sci. 1970, 27, 977–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junge, C.E. Air Chemistry and Radioactivity; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Brode, H.L. Review of nuclear weapon effects. Ann. Rev. Nucl. Sci. 1960, 18, 153–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, S.J.; Tuck, A.F.; Kiladis, G. On the changing abundance of ozone minima at northern midlatitudes. J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 12169–12180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, R. A brief history of stratospheric ozone research. Meteorol. Zeitschift 2009, 1, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, S. A theory of upper atmospheric ozone. Mem. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1930, 3, 103–109. [Google Scholar]
- Brewer, A.W.; Wilson, A.W. The regions of formation of atmospheric ozone. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1968, 94, 249–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, D.R.; Nicolet, M. The photochemistry of atmospheric water vapour. J. Geophys Res. 1950, 55, 301–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, B.G. Photochemistry of ozone in a moist atmosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 1966, 71, 1385–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampson, J. Photochemical Behaviour of the Ozone Layer; Technical Note 1627; Canadian Armament and Research Establishment: Valcartier, QC, Canada, 1964; pp. 1–280. [Google Scholar]
- Hampson, J. Chemiluminescent emissions observed in the stratosphere and mesosphere. In Les Problèmes Météorologiques de la Stratosphère et de la Mésosphère; Nicolet, M., Ed.; Centre National d’Études Spatiales: Paris, France, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Hampson, J. Atmospheric Energy Change by Pollution of the Upper Atmosphere; CARDE Technical Note 1738; Canadian Armament Research and Development Establishment: Valcartier, QC, Canada, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Crutzen, P.J. The influence of nitrogen oxides on the atmospheric ozone content. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1970, 96, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murcray, D.G.; Kyle, T.G.; Murcray, F.H.; Williams, W.J. Nitric acid and nitric oxide in the lower stratosphere. Nature 1968, 218, 78–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goody, R.M.; Walker, J.C.G. Atmospheres; Prentice Hall Inc.: Englewood Cliffs, NK, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Johnston, H. Reduction of stratospheric ozone by nitrogen oxide catalysts from supersonic transport exhaust. Science 1971, 173, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crutzen, P.J. Ozone production rates in an oxygen-hydrogen-nitrogen oxide atmosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 1971, 76, 7311–7333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zel’dovich, Y.B.; Raizer, Y.P. Physics of Shock Waves and High-Temperature Hydrodynamic Phenomena; Dover: Minola, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith, P.; Tuck, A.F.; Foot, J.S.; Simmons, E.L.; Newson, R.L. Nitrogen oxides, nuclear weapon testing, Concorde and stratospheric ozone. Nature 1973, 244, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuck, A.F. Production of nitrogen oxides by lightning discharges. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1976, 102, 749–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brune, W.H.; McFarland, P.J.; Bruning, E.; Waugh, S.; McGorman, D.; Miller, D.O.; Jenkins, M.J.; Ren, X.; Mao, J.; Peischl, J. Extreme oxidant amounts produced by lightning in storm clouds. Science 2021, 372, 711–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Pei, Y.; Yin, Y.; Shen, L.; Chen, K.; Shi, Z.; Chen, J. Observational evidence of lightning-generated ultrafine aerosols. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2021GL093771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahey, D.W.; Keim, E.R.; Boering, K.A.; Brock, C.A.; Wilson, J.C.; Jonsson, H.H.; Anthony, S.; Hanisco, T.F.; Wennberg, P.O.; Miake-Lye, R.C. Emission measurements of the Concorde supersonic aircraft in the lower stratosphere. Science 1995, 270, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, M.J.; Rowlad, F.S. Stratospheric sink for chlorofluoromethanes—Chlorine atom catalyzed destruction of ozone. Nature 1974, 249, 810–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovelock, J.E.; Maggs, R.J.; Wade, R.J. Halogenated hydrocarbons in and over the Atlantic. Nature 1973, 241, 194–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salawitch, R.J.; McBride, L.A.; Thompson, C.R.; Fleming, E.L.; McKenzie, R.L.; Rosenlof, K.H.; Doherty, S.J.; Fahey, D.W. Twenty Questions and Answers about the Ozone Layer: 2022 Update; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023; 75p. [Google Scholar]
- Groves, K.S.; Tuck, A.F. Stratospheric O3-CO2 coupling in a photochemical-radiative column model. II. With chlorine chemistry. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1980, 106, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.G.; Margitan, J.J.; Stedman, D.H. Atomic chlorine and the chlorine monoxide radical in the stratosphere: Three in situ observations. Science 1977, 198, 501–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmer, C.B.; Raper, O.F.; Norton, R.H. Spectroscopic detection and vertical distribution of HCl in the troposphere and stratosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1976, 3, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackerman, M.; Frimout, D.; Girard, A.; Gottignies, M.; Muller, C. Stratospheric HCl from infrared spectra. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1976, 3, 81–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, W.J.; Kosters, J.J.; Goldman, A.; Murcray, D.G. Measurement of the stratospheric mixing ratio of HCl using infrared absorption technique. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1976, 3, 383–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyre, J.R.; Roscoe, H.K. Radiometric measurement of stratospheric HCl. Nature 1977, 266, 243–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazrus, A.L.; Gandrud, B.W.; Woodward, E.N.; Sedlacek, W.A. Direct measurements of of stratospheric chlorine and bromine. J. Geophys. Res. 1976, 81, 1067–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clyne, M.A.A.; Watson, R.T. Kinetic studies for diatomic free radicals using mass spectrometry. Part 3.—Elementary reactions involving BrO X2Π radicals. J. Chem. Soc. Farad. Trans. 1 1975, 71, 336–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, J.H.; Sutherland, G.B.B.M.; Wormell, T.W. Nitrous oxide in the Earth’s atmosphere. Phys. Rev. 1948, 74, 978–979. [Google Scholar]
- Williamson, E.J.; Houghton, J.T. Radiometric measurements of emission from stratospheric water vapour. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1965, 91, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmeltekopf, A.L.; Goldan, P.D.; Henderson, W.R.; Harrop, W.J.; Thompson, T.L.; Fehsenfeld, F.C.; Schiff, H.I.; Crutzen, P.J.; Isaksen, I.S.A.; Ferguson, E.E. Measurements of stratospheric CFCl3, CF2Cl2 and N2O. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1975, 2, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldan, P.D.; Kuster, W.C.; Albritton, D.L.; Schmeltekopf, A.L. Stratospheric CFCl3, CF2Cl2, and N2O height profile measurements at several latitudes. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1979, 85, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delwiche, C.C. Biological production and utilization of N2O. Pure Appl. Geophys. 1978, 116, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland, F.S.; Spencer, J.E.; Molina, M.J. Stratospheric formation and photolysis of chlorine nitrate. J. Phys. Chem. 1976, 80, 2711–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, R.A.; Derwent, R.G.; Eggleton, A.E.J. Chlorine Nitrate—A Possible Stratospheric Sink for ClO Radicals and NOx with Significant Implications for Ozone Depletion; Atomic Energy Research Establishment Report 8383; AERE: Harwell, UK, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Brasseur, G.P.; Solomon, S. Aeronomy of the Middle Atmosphere, 3rd ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Harries, J.E. Measurements of some hydrogen-oxygen-nitrogen compounds in the stratosphere from Concorde 002. Nature 1973, 241, 515–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harries, J.E.; Moss, D.G.; Swann, N.R.W.; Neill, G.F.; Gildwarg, P. Simultaneous measurements of H2O, NO2 and HNO3 in the daytime stratosphere from 15 to 35 km. Nature 1976, 259, 300–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harries, J.E. Ratio of HNO3 to NO2 concentrations in daytime stratosphere. Nature 1978, 274, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.G. Odd chlorine processes. In Stratospheric Ozone and Man; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1982; Chapter 6. [Google Scholar]
- McCormick, M.P.; Hamill, P.; Pepin, T.J.; Chu, W.P.; Swissler, T.J.; McMaster, L.R. Satellite studies of the stratospheric aerosol. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1979, 60, 1038–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, M.P.; Steele, H.M.; Hamill, P.; Chu, W.P.; Swissler, T.J. Polar stratospheric cloud sightings by SAM II. J. Atmos. Sci. 1982, 40, 1387–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murgatroyd, R.J. Recent progress in studies of the stratosphere. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1982, 108, 271–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fels, S.B.; Mahlman, J.D.; Schwarzkopf, M.D.; Sinclair, R.W. Stratospheric sensitivity to perturbations in ozone and carbon dioxide: Radiative and dynamical response. J. Atmos. Sci. 1980, 38, 2265–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allam, R.J.; Tuck, A.F. Transport of water vapour in a stratosphere-troposphere general circulation model. I: Fluxes. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1984, 110, 321–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allam, R.J.; Tuck, A.F. Transport of water vapour in a stratosphere-troposphere general circulation model. II: Trajectories. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1984, 357–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, A. The dynamics of stratospheric warmings generated by a general circulation model of the troposphere and stratosphere. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1980, 106, 659–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, A.; Newson, R.L.; Murgatroyd, R.J. An analysis of the large-scale features of the upper troposphere and the stratosphere in a global, three-dimensional general circulation model. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1982, 108, 25–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newell, R.E.; Gould-Stewart, S. A stratospheric fountain? J. Atmos. Sci. 1981, 38, 2789–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, G.D. The transport of minor atmospheric constituents between troposphere and stratosphere. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1980, 106, 227–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamber, D.J.; Healey, P.G.W.; Jones, B.M.R.; Penkett, S.A.; Tuck, A.F.; Vaughan, G. Vertical profiles of tropospheric gases: Chemical consequences of stratospheric intrusions. Atmos. Environ. 1984, 18, 1759–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noxon, J.F. Stratospheric NO2 in the Antarctic winter. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1978, 5, 1021–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noxon, J.F. Stratospheric NO2, 2. Global behavior. J. Geophys. Res. 1984, 84, 5067–5076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farman, J.C.; Murgatroyd, R.J.; Silnickas, A.M.; Thrush, B.A. Ozone photochemistry in the Antarctic stratosphere in summer. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1985, 111, 1013–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farman, J.C.; Gardiner, B.G.; Shanklin, J.D. Large losses of total ozone in the Antarctica reveal seasonal ClOx/NOx interaction. Nature 1985, 315, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolarski, R.S.; Krueger, A.J.; Schoeberl, M.R.; McPeters, R.D.; Newman, P.A.; Alpert, J.C. Nimbus 7 satellite measurements of the springtime Antarctic ozone decrease. Nature 1986, 332, 808–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, S.; Garcia, R.R.; Rowland, F.S.; Wuebbles, D.J. On the depletion of Antarctic ozone. Nature 1986, 321, 755–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayman, G.D.; Davies, J.M.; Cox, R.A. Kinetics of the reaction ClO + ClO → products and its potential relevance to Antarctic ozone. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1986, 13, 1347–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, L.T.; Molina, M.J. Production of Cl2O2 from the self reaction of the ClO radical. J. Phys. Chem. 1987, 91, 433–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, J.; Garcia, R.R.; Russell, J.M., III; Solomon, S.; Tuck, A.F. On the atmospheric photochemistry of nitric acid. J. Geophys. Res. 1986, 91, 5477–5485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, J.; Remsberg, E.E.; Jones, R.L.; Tuck, A.F. Polar Stratospheric Clouds inferred for satellite data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1986, 13, 1256–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, D.; Mauersberger, K. Laboratory studies of the nitric acid hydrate: Implications for the south polar stratosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1988, 15, 855–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mount, G.H.; Sanders, R.W.; Schmeltekopf, A.L.; Solomon, S. Visible spectroscopy at McMurdo station, Antarctica, 1. Overview and daily variations of NO2 and O3 during austral spring, 1986. J. Geophys. Res. 1987, 92, 8320–8328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, S.; Mount, G.H.; Sanders, R.W.; Schmeltekopf, A.L. Visible spectroscopy at McMurdo station, Antarctica, 2. Observations of OClO. J. Geophys. Res. 1987, 92, 8329–8338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmer, C.B.; Toon, G.C.; Shaper, P.W.; Blavier, J.F.; Lowes, L.L. Ground-based measurements of the composition of the Antarctic atmosphere during the 1986 spring season, I, Stratospheric trace gases. Nature 1987, 329, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, D.J.; Harder, J.W.; Rolf, S.R.; Rosen, J.M. Balloon-borne observations of the temporal development and vertical structure of the Antarctic ozone hole in 1986. Nature 1987, 326, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komhyr, W.D.; Grass, R.D.; Reitelbach, P.J.; Kuester, S.E.; Franchois, P.R.; Fanning, M.L. Total ozone, ozone vertical distributions, and stratospheric temperatures at South Pole, Antarctica in 1986 and 1987. J. Geophys. Res. 1989, 94, 11429–11436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuck, A.F.; Watson, R.T.; Condon, E.P.; Margitan, J.J.; Toon, O.B. The planning and execution of ER-2 and DC-8 aircraft flights over Antarctica, August and September 1987. J. Geophys. Res. 1989, 94, 11181–11222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, K.K.; Tuck, A.F.; Murphy, D.M.; Proffitt, M.H.; Fahey, D.W.; Jones, R.L.; McKenna, D.S.; Loewenstein, M.; Podolske, J.R.; Strahan, S.E.; et al. Dehydration in the lower Antarctic stratosphere during late winter and early spring, 1987. J. Geophys. Res. 1989, 94, 11317–11358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahey, D.W.; Kelly, K.K.; Ferry, G.V.; Poole, L.R.; Wilson, J.C.; Murphy, D.M.; Loewenstein, M.; Chan, K.R. In situ measurements of total reactive nitrogen, total water, and aerosol in a polar stratospheric cloud in the Antarctic. J. Geophys. Res. 1989, 94, 11299–11316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahey, D.W.; Murphy, D.M.; Kelly, K.K.; Ko, M.K.W.; Proffitt, M.H.; Eubank, C.S.; Ferry, G.V.; Loewenstein, M.; Chan, K.R. Measurements of nitric oxide and total reactive nitrogen in the Antarctic stratosphere: Observations and chemical implications. J. Geophys. Res. 1989, 94, 16665–16682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.G.; Brune, W.H.; Proffitt, M.H. Ozone destruction by chlorine radicals within the Antarctic vortex: The spatial and temporal evolution of ClO-O3 anticorrelation based on in situ ER-2 data. J. Geophys. Res. 1989, 94, 11465–11480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brune, W.H.; Anderson, J.G.; Chan, K.R. In situ observations of BrO over Antarctica: ER-2 aircraft results from 54° S to 72° S latitude. J. Geophys. Res. 1989, 94, 16639–16648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brune, W.H.; Anderson, J.G.; Chan, K.R. In situ observations of ClO in the Antarctic: ER-2 aircraft results from 54° S to 72° S latitude. J. Geophys. Res. 1989, 94, 16649–16664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proffitt, M.H.; Powell, J.A.; Tuck, A.F.; Fahey, D.W.; Kelly, K.K.; Krueger, A.J.; Schoeberl, M.R.; Gary, B.L.; Margitan, J.J.; Chan, K.R.; et al. A chemical definition of the boundary of the Antarctic ozone hole. J. Geophys. Res. 1989, 94, 11437–11448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proffitt, M.H.; Steinkamp, M.J.; Powell, J.A.; McLaughlin, R.J.; Mills, O.A.; Schmeltekopf, A.L.; Thompson, T.L.; Tuck, A.F.; Tyler, T.; Winkler, R.H.; et al. In-situ measurements within the 1987 Antarctic ozone hole from a high-altitude ER-2 aircraft. J. Geophys. Res. 1989, 94, 16547–16556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loewenstein, M.; Podolske, J.R.; Chan, K.R.; Strahan, S.E. Nitrous oxide as a dynamical tracer in the 1987 Airborne Antarctic Ozone Experiment. J. Geophys. Res 1989, 94, 11589–11598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidt, L.E.; Vedder, J.F.; Pollock, W.H.; Lueb, R.A.; Henry, B.A. Trace gases in the Antarctic atmosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 1989, 94, 11599–11612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuck, A.F. Synoptic and chemical evolution in the Antarctic vortex in late winter and early spring, 1987. J. Geophys. Res. 1989, 94, 11687–11737, Erratum in J. Geophys. Res. 1989, 94, 16855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turco, R.P.; Plumb, R.A.; Condon, E. The Airborne Arctic Stratospheric Expedition: Prologue. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1990, 17, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brune, W.H.; Toohey, D.W.; Anderson, J.G.; Chan, K.R. In situ observations of ClO in the Arctic stratosphere: ER-2 aircraft results from 59° N to 80° N latitude. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1990, 17, 505–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hübler, G.; Fahey, D.W.; Kelly, K.K.; Montzka, D.D.; Carroll, M.A.; Tuck, A.F.; Heidt, L.E.; Pollock, W.H.; Gregory, G.L.; Vedder, J.F. Redistribution of reactive odd nitrogen in the lower Arctic stratosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett 1990, 17, 453–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dye, J.E.; Baumgardner, D.; Gandrud, B.W.; Kawa, S.R.; Kelly, K.K.; Loewenstein, M.; Ferry, G.V.; Chan, K.R.; Gary, B.L. Particle size distribution in Arctic polar stratospheric clouds, growth and freezing of sulfuric acid droplets, and implications for ice cloud formation. J. Geophys. Res. 1992, 97, 8015–8034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browell, E.V.; Butler, C.F.; Ismail, S.; Robinette, P.A.; Carter, A.F.; Higdon, N.S.; Toon, O.B.; Schoeberl, M.R.; Tuck, A.F. Airborne lidar observations in the wintertime Arctic stratosphere: Polar stratospheric clouds. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1990, 17, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.L.; McKenna, D.S.; Poole, L.R.; Solomon, S. On the influence of polar stratospheric cloud formation on chemical composition during the 1988/89 Arctic winter. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1990, 17, 545–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinne, S.; Toon, O.B. Radiative effects of polar stratospheric clouds. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1990, 17, 373–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, D.S.; Jones, R.L.; Poole, L.R.; Solomon, S.; Fahey, D.W.; Kelly, K.K.; Proffitt, M.H.; Brune, W.H.; Loewenstein, M.; Chan, K.R.; et al. Calculations of ozone destruction during the 1988/89 Arctic winter. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1990, 17, 553–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salawitch, R.J.; McElroy, M.B.; Yatteau, J.H.; Wofsy, S.C.; Schoeberl, M.R.; Lait, L.R.; Newman, P.A.; Chan, K.R.; Loewenstein, M.; Podolske, J.R.; et al. Loss of ozone in the Arctic vortex for the winter of 1989. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1990, 17, 561–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuck, A.F.; Davies, T.; Hovde, S.J.; Noguer-Alba, M.; Fahey, D.W.; Kawa, S.R.; Kelly, K.K.; Murphy, D.M.; Proffitt, M.H.; Margitan, J.J.; et al. Polar stratospheric cloud processed air and potential vorticity in the Northern Hemisphere lower stratosphere at mid-latitudes during winter. J. Geophys. Res. 1992, 97, 7883–7904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidt, L.E.; Hovde, S.J.; Tuck, A.F.; Vedder, J.F. Age of air within the polar vortex deduced from CO2 observations. EOS Trans. AGU 1989, 70, 1035. [Google Scholar]
- Solomon, S.; Mills, M.; Heidt, L.E.; Pollock, W.H.; Tuck, A.F. On the evaluation of ozone depletion potentials. J. Geophys. Res. 1992, 97, 825–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, J.M., III; Tuck, A.F.; Gordley, L.L.; Park, J.H.; Drayson, S.R.; Harries, J.E.; Cicerone, R.J.; Crutzen, P.J. HALOE Antarctic observations in the spring of 1991. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1993, 20, 719–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harries, J.E.; Russell, J.M., III; Park, J.; Tuck, A.F.; Drayson, S.R. Observation of absorbing layers in the Antarctic stratosphere in October 1991. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1995, 121, 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.G.; Toon, O.B. Airborne Arctic Ozone Expedition II: An overview. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1993, 20, 2499–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wofsy, S.C.; Cohen, R.C.; Schmeltekopf, A.L. Overview: The Stratospheric Photochemistry Aerosols and Dynamics Expedition (SPADE) and Airborne Arctic Stratospheric Expedition-II (AASE-II). Geophys. Res. Lett. 1994, 21, 2535–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wennberg, P.O.; Stimpfle, R.M.; Weinstock, E.M.; Dessler, A.E.; Lloyd, S.A.; Lapson, L.B.; Schwab, J.J.; Anderson, J.G. Simultaneous in situ measurements of OH, HO2, O3 and H2O: A test of modeled stratospheric HOx chemistry. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1990, 17, 1909–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wennberg, P.O.; Cohen, R.C.; Stimpfle, R.M.; Koplow, J.P.; Anderson, J.G.; Salawitch, R.J.; Fahey, D.W.; Woodbridge, E.R.; Keim, E.R.; Gao, R.-S.; et al. Removal of stratospheric O3 by radicals: In situ measurements of OH, HO2, NO, NO2, ClO and BrO. Science 1994, 266, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, J.C.; Jonsson, H.H.; Brock, C.A.; Toohey, D.W.; Avallome, L.M.; Baumgardner, D.; Dye, J.E.; Poole, L.R.; Woods, D.C.; DeCoursey, R.J.; et al. In situ observations of aerosol and chlorine monoxide after the 1991 eruption of Mount Pinatubo: Effect of reactions pn on sulfate aerosol. Science 1993, 261, 1140–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawa, S.R.; Fahey, D.W.; Wilson, J.C.; Schoeberl, M.R.; Douglass, A.R.; Stolarski, R.S.; Woodbridge, E.L.; Jonsson, H.; Lait, L.R.; Newman, P.A.; et al. Interpretation of NOx/NOy observations from AASE-II using a model of chemistry along trajectories. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1993, 20, 2507–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, J.; Pallister, R.C.; Pyle, J.A.; Tuck, A.F.; Zavody, A.M. Photochemical model comparisons with LIMS observations in a stratospheric trajectory coordinate system. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1987, 113, 361–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, J.W.; Froidevaux, L.; Manney, G.L.; Read, W.G.; Elson, L.S. MLS observations of lower stratospheric ClO and O3 in the 1992 southern winter. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1993, 20, 1219–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, J.W.; Manney, G.L.; Read, W.G.; Froidevaux, L.; Flower, D.A.; Jarnot, R.F. UARS MLS observations of lower stratospheric ClO in the 1992-93 and 1993-94 Arctic winter vortices. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1995, 22, 823–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuck, A.F. Summary of atmospheric chemistry observations from the Antarctic and Arctic aircraft campaigns. SPIE Remote Sens. Atmos. Chem. 1991, 1491, 252–272. [Google Scholar]
- Fahey, D.W.; Keim, E.R.; Woodbridge, E.L.; Gao, R.-S.; Boering, K.A.; Daube, B.C.; Wofsy, S.C.; Lohmann, R.P.; Hintsa, E.J.; Dessler, A.E.; et al. In situ observations in aircraft exhaust plumes in the lower stratosphere at midlatitudes. J. Geophys. Res. 1995, 100, 3065–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keim, E.R.; Fahey, D.W.; Del Negro, L.A.; Woodbridge, E.L.; Gao, R.S.; Wennberg, P.O.; Cohen, R.C.; Stimpfle, R.M.; Kelly, K.K.; Hintsa, E.J.; et al. Observations of large reductions in the NO/NOy ratio near the mid-latitude tropopause and the role of heterogeneous chemistry. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1996, 23, 3223–3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuck, A.F.; Brune, W.H.; Hipskind, R.S. Airborne Southern Hemisphere Ozone Experiment/Measurements for Assessing the Effects of Stratospheric Aircraft (ASHOE/MAESA): A road map. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 3901–3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicke, J.; Tuck, A.; Smith, W. A comparison of Antarctic stratospheric radiative heating rates calculated from high-resolution interferometer sounder and U.K. Meteorological Office data. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 103, 19691–19707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicke, J.; Tuck, A. Polar stratospheric cloud impacts on Antarctic heating rates. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2001, 127, 1645–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waugh, D.W.; Plumb, R.A.; Elkins, J.W.; Fahey, D.W.; Boering, K.A.; Dutton, G.S.; Volk, C.M.; Keim, E.; Gao, R.-S.; Daube, B.C.; et al. Mixing of polar vortex air into middle latitudes as revealed by tracer-tracer correlation plots. J. Geophys Res. 1997, 102, 13119–13134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenlof, K.H.; Tuck, A.F.; Kelly, K.K.; Russell, J.M., III; McCormick, M.P. Hemispheric asymmetries in water vapor and inferences about transport in the lower stratosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 13213–13234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folkins, I.; Chatfield, R.; Baumgardner, D.; Proffitt, M. Biomass burning and deep convection in southeastern Asia: Results from ASHOE/MAESA. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 13291–13299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahey, D.W.; Newman, P.A. Photochemistry of Ozone Loss in the Arctic Region in Summer, December 1997. Available online: https://espo.nasa.gov/polaris/content/POLARIS_End_of_Mission_Statement (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- Newman, P.A.; Fahey, D.W.; Brune, W.H.; Kurylo, M.J.; Kawa, S.R. Preface. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1999, 104, 26481–26495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McElroy, C.T. A spectroradiometer for the measurement of direct and scattered solar irradiance from on-board the NASA ER-2 high-altitude research aircraft. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1995, 22, 1361–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuck, A.F.; Hovde, S.J.; Richard, E.C.; Gao, R.-S.; Bui, T.P.; Swartz, W.H.; Lloyd, S.A. Molecular velocity distributions and generalized scale invariance in the turbulent atmosphere. Faraday Discuss. 2005, 130, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, P.A.; Harris, N.R.P.; Adriani, A.; Amanatidis, G.T.; Anderson, J.G.; Braathen, G.O.; Brune, W.H.; Carslaw, K.S.; Craig, M.S.; DeCola, P.L.; et al. An overview of the SOLVE/THESEO 2000 campaign. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107, 8259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, D.M.; Thomson, D.S.; Mahoney, M.J. In situ measurements of organics, meteoritic material, mercury and other elements in aerosols at 5 to 19 kilometers. Science 1998, 282, 1664–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellison, G.B.; Tuck, A.F.; Vaida, V. Processing of organic aerosols. J. Geophys. Res. D 1999, 104, 11633–11641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tervahattu, H.; Hartonen, K.; Kerminen, V.-M.; Kupiainen, K.; Aarnio, P.; Koskentalo, K.; Tuck, A.F.; Vaida, V. New evidence of an organic layer on marine aerosols. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2002, 107, AAC1–AAC8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tervahattu, H.; Juhanoja, J.; Vaida, V.; Tuck, A.F.; Niemi, J.V.; Kupiainen, K.; Kulmala, M.; Vehkamäki, H. Fatty acids on continental sulfate aerosol particles. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2005, 110, D06207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dye, J.E.; Ridley, B.A.; Skamarock, W.; Barth, M.; Venticinque, M.; Defer, E.; Blanchet, P.; Thery, C.; Laroche, P.; Baumann, K.; et al. An overview of the Stratospheric Tropospheric Experiment: Radiation, Aerosols and Ozone (STERAO)—Deep convection experiment with results for the July 10, 1996 storm. J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 10023–10045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuck, A.F.; Hovde, S.J.; Kelly, K.K.; Reid, S.J.; Richard, E.C.; Atlas, E.L.; Donnelly, S.G.; Stroud, V.R.; Cziczo, D.J.; Murphy, D.M.; et al. Horizontal variability 1–2 km below the tropical tropopause. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109, D05310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, E.C.; Kelly, K.K.; Winkler, R.H.; Wilson, R.; Thompson, T.L.; McLaughlin, R.J.; Schmeltekopf, A.L.; Tuck, A.F. A fast-response near-infrared tunable diode laser absorption spectrometer for in situ measurements of CH4 in the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere. Appl. Phys. Lett. B 2002, 75, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, M.N.; Toohey, D.W.; Rawlins, W.T.; Richard, E.C.; Kelly, K.K.; Tuck, A.F.; Proffitt, M.H.; Hagen, D.E.; Hopkins, A.R.; Whitefield, P.D.; et al. Observation of stratospheric ozone depletion associated with Delta II rocket emissions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2000, 27, 2209–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, R.G.; Marais, E.A.; Balhatchet, C.J.; Eastham, S.D. Impact of rocket launch and space débris air pollutant emissions on stratospheric ozone and global climate. Earth’s Future 2022, 10, e2021EF002612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goss, L.M.; Sharpe, S.W.; Blake, T.A.; Vaida, V.; Brault, J.W. Direct absorption spectroscopy of water clusters. J. Phys. Chem. A 1999, 103, 8620–8624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaida, V.; Daniel, J.S.; Kjaergaard, H.G.; Goss, L.M.; Tuck, A.F. Atmospheric absorption of near infrared and visible solar radiation by the hydrogen bonded water dimer. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2001, 127, 1627–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaldson, D.J.; Frost, G.J.; Rosenlof, K.H.; Tuck, A.A.; Vaida, V. Atmospheric radical production by excitation of vibrational overtones via absorption of visible light. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1997, 24, 2651–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wennberg, P.O.; Salawitch, R.J.; Donaldson, D.J.; Hanisco, T.F.; Lanzendorf, E.J.; Perkins, K.K.; Lloyd, S.A.; Vaida, V.; Gao, R.-S.; Hintsa, E.J.; et al. Twilight observations suggest unknown sources of HOx. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1999, 26, 1373–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaida, V.; Kjaergaard, H.G.; Hintze, P.E.; Donaldson, D.J. Photolysis of sulfuric acid vapor by visible solar radiation. Science 2003, 299, 1566–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahey, D.W.; Gao, R.-S.; Carslaw, K.S.; Kettleborough, J.; Popp, P.J.; Northway, M.J.; Holecek, J.C.; Ciciora, S.C.; McLaughlin, R.J.; Thompson, T.L.; et al. The detection of large HNO3-containing particles in the winter Arctic stratosphere. Science 2001, 291, 1026–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Richard, E.C.; Aikin, K.C.; Andrews, A.E.; Daube, B.C., Jr.; Gerbig, C.; Wofsy, S.C.; Romashkin, P.A.; Hurst, D.F.; Ray, E.A.; Moore, F.L.; et al. Severe chemical ozone loss inside the Arctic polar vortex during winter 1999–2000 inferred from in situ airborne measurements. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2001, 28, 2197–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuck, A.F.; Hovde, S.J.; Richard, E.C.; Fahey, D.W.; Gao, R.-S.; Bui, T.P. A scaling analysis of ER-2 data in the inner Arctic vortex during January-March 2000. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, SOL 49-1–SOL 49-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuck, A.F.; Hovde, S.J.; Gao, R.-S.; Richard, E.C. Law of mass action in the Arctic lower stratospheric polar vortex: ClO scaling and the calculation of ozone loss rates in a turbulent fractal medium. J. Geophys. Res. D 2003, 108, 4451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jost, H.-J.; Drdla, K.; Stohl, A.; Pfister, L.; Loewenstein, M.; Lopez, J.P.; Hudson, P.K.; Murphy, D.M.; Cziczo, D.J.; Fromm, M.; et al. In-situ observations of mid-latitude forest fire plumes deep in the stratosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L11101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, E.C.; Tuck, A.F.; Aikin, K.C.; Kelly, K.K.; Herman, R.L.; Troy, R.F.; Hovde, S.J.; Rosenlof, K.H.; Thompson, T.L.; Ray, E.A. High-resolution airborne profiles of CH4, O3 and water vapor near tropical Central America in late January to early February 2004. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, D13304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, D.; Froyd, K.; Schwarz, J.; Wilson, J. Observations of the chemical composition of stratospheric aerosol particles. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 140, 1269–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovde, S.J.; Tuck, A.F.; Lovejoy, S.; Schertzer, D. Vertical scaling of temperature, wind and humidity fluctuations: Dropsondes from 13 km to the surface of the Pacific Ocean. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 5891–5918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuck, A.F. Turbulence: Vertical shear of the horizontal wind, jet streams, symmetry breaking, scale invariance and Gibbs free energy. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, O.R.; Stohl, A.; Hübler, G.; Hsie, E.Y.; Parrish, D.D.; Tuck, A.F.; Kiladis, G.N.; Oltmans, S.J.; Johnson, B.J.; Shapiro, M.; et al. Direct transport of midlatitude stratospheric ozone into the lower troposphere and marine boundary layer of the tropical Pacific Ocean. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, D23310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, B.F.; Toohey, D.W.; Tuck, A.F.; Elkins, J.W.; Kelly, K.K.; Hovde, S.J.; Richard, E.C.; Rosenlof, K.H.; Thompson, T.L.; Mahoney, M.J.; et al. Chlorine activation near the midlatitude tropopause. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, D18306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaldson, D.J.; Vaida, V. The influence of organic films at the air-aqueous boundary on atmospheric processes. Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 1445–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaida, V. Perspective: Water cluster mediated atmospheric chemistry. J. Chem. Phys. 2011, 135, 3608919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuck, A.F. Air temperature intermittency and photofragment excitation. Meteorology 2023, 2, 445–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuck, A.F. Atmospheric Turbulence: A Molecular Dynamics Perspective; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- World Meteorological Organization (WMO). Scientific Assessment of Stratospheric of Ozone Depletion: 2022; GAW Report No. 278; WMO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022; 509p. [Google Scholar]
- Crutzen, P.J. Albedo enhancement by stratospheric sulfur injections: A contribution to resolving a policy dilemma? Clim. Chang. 2006, 77, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicerone, R.J. Geoengineering: Encouraging research and overseeing implementation. Clim. Chang. 2006, 77, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tuck, A.F.; Donaldson, D.J.; Hitchman, M.H.; Richard, E.C.; Tervahattu, H.; Vaida, V.; Wilson, J.C. On geoengineering with sulphate aerosols in the tropical upper troposphere and lower stratosphere. Clim. Chang. 2008, 90, 315–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, A.; Oatley, C.L.; Charlton-Perez, A.J.; Mitchell, D.M.; Jung, T. Vortex splitting on a planetary scale in the stratosphere by cyclogenesis on a subplanetary scale in the troposphere. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2017, 143, 691–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovejoy, S. The future of climate modelling: Weather details, macroweather stochastics—Or both? Meteorology 2022, 1, 414–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovejoy, S. A hybrid stochastic—GCM system for monthly, seasonal and interannual predictions. Meteorology 2023, 2, 509–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovejoy, S. Review article: Scaling dynamical regimes and stratification. How long does weather last? How big is a cloud? Nonlin. Process. Geophys. 2023, 30, 311–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuck, A.F. Scaling up: Molecular to meteorological via symmetry breaking and statistical multifractality. Meteorology 2022, 1, 4–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, I.R.; McKinnon, K.A.; Kennedy, D.; Lawrences, D.M.; Lehner, F.; Seager, R. Observed humidity trends in dry regions contradict climate models. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2302480120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boretti, A. Reassessing the cooling that followed the 1991 volcanic eruption of Mt. Pinatubo. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2024, 256, 106187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, D.M.; Abou-Ghanem, M.; Cziczo, D.J.; Froyd, K.D.; Jacquot, J.; Lawler, M.J.; Maloney, C.; Plane, J.M.C.; Ross, M.N.; Schill, G.P.; et al. Metals from spacecraft reentry in stratospheric aerosol particles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2313374120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asher, E.; Todt, M.; Rosenlof, K.; Thornberry, T.; Gao, R.; Taha, G.; Walter, P.; Alvarez, S.; Flynn, J.; Davis, S.; et al. Unexpected rapid aerosol formation in the Hunga Tonga plume. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2219547120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evan, S.; Brioude, J.; Rosenlof, K.H.; Gao, R.-S.; Portmann, R.W.; Zhu, Y.; Volkamer, R.; Lee, C.F.; Metzger, J.-M.; Lamy, K.; et al. Rapid ozone depletion after humidification of the stratosphere by the Hunga Tonga eruption. Science 2023, 382, eadg2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
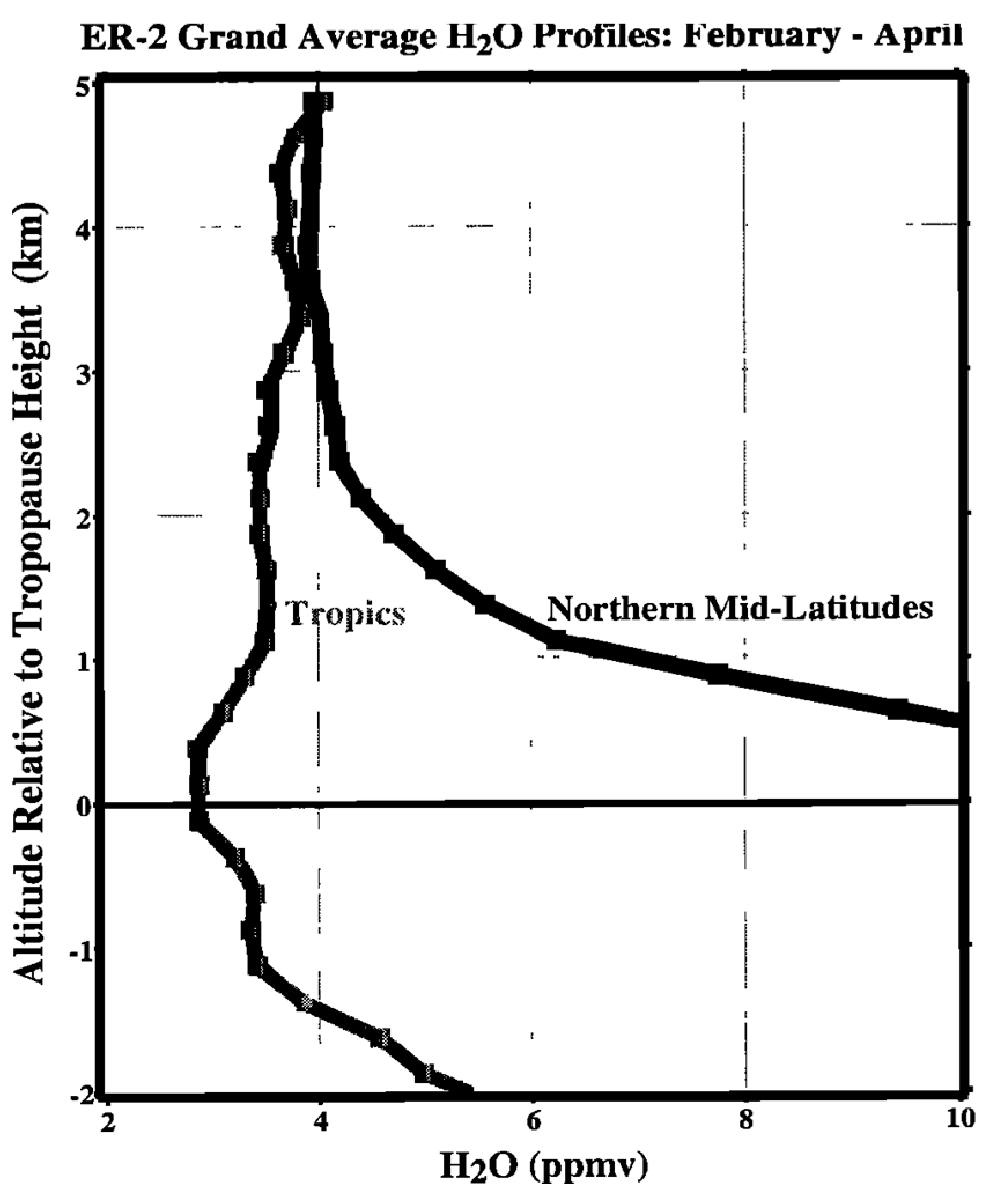
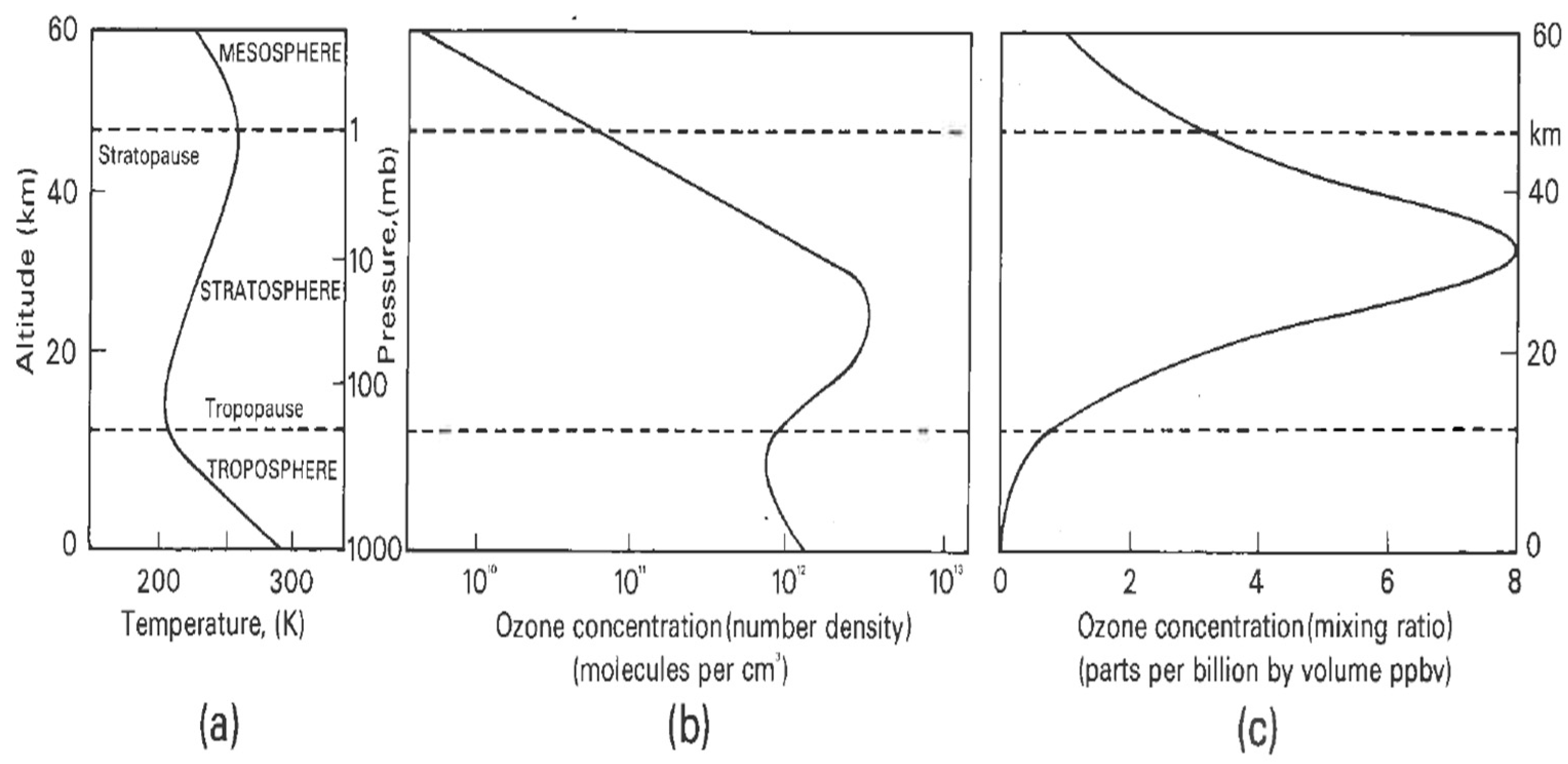
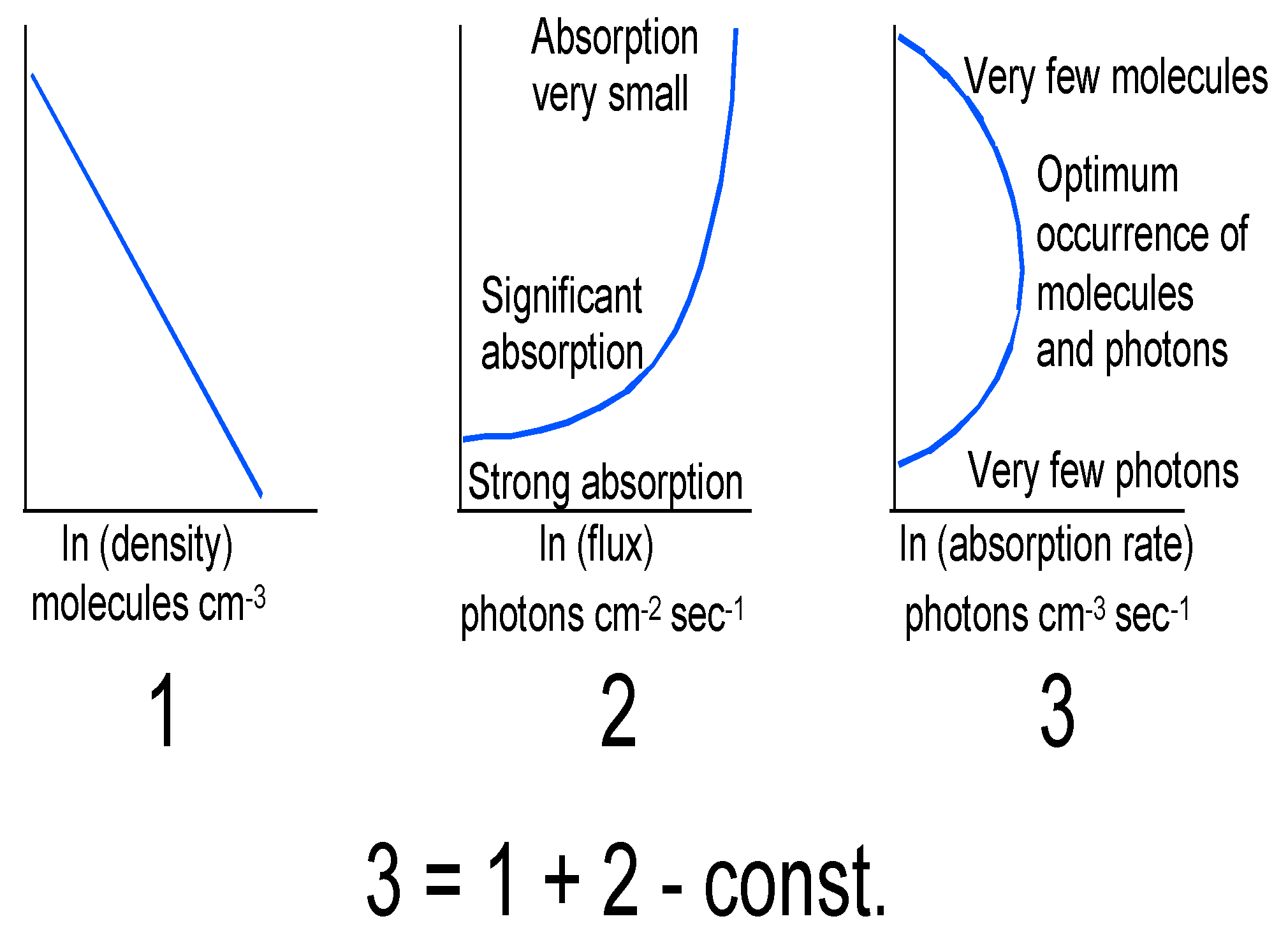
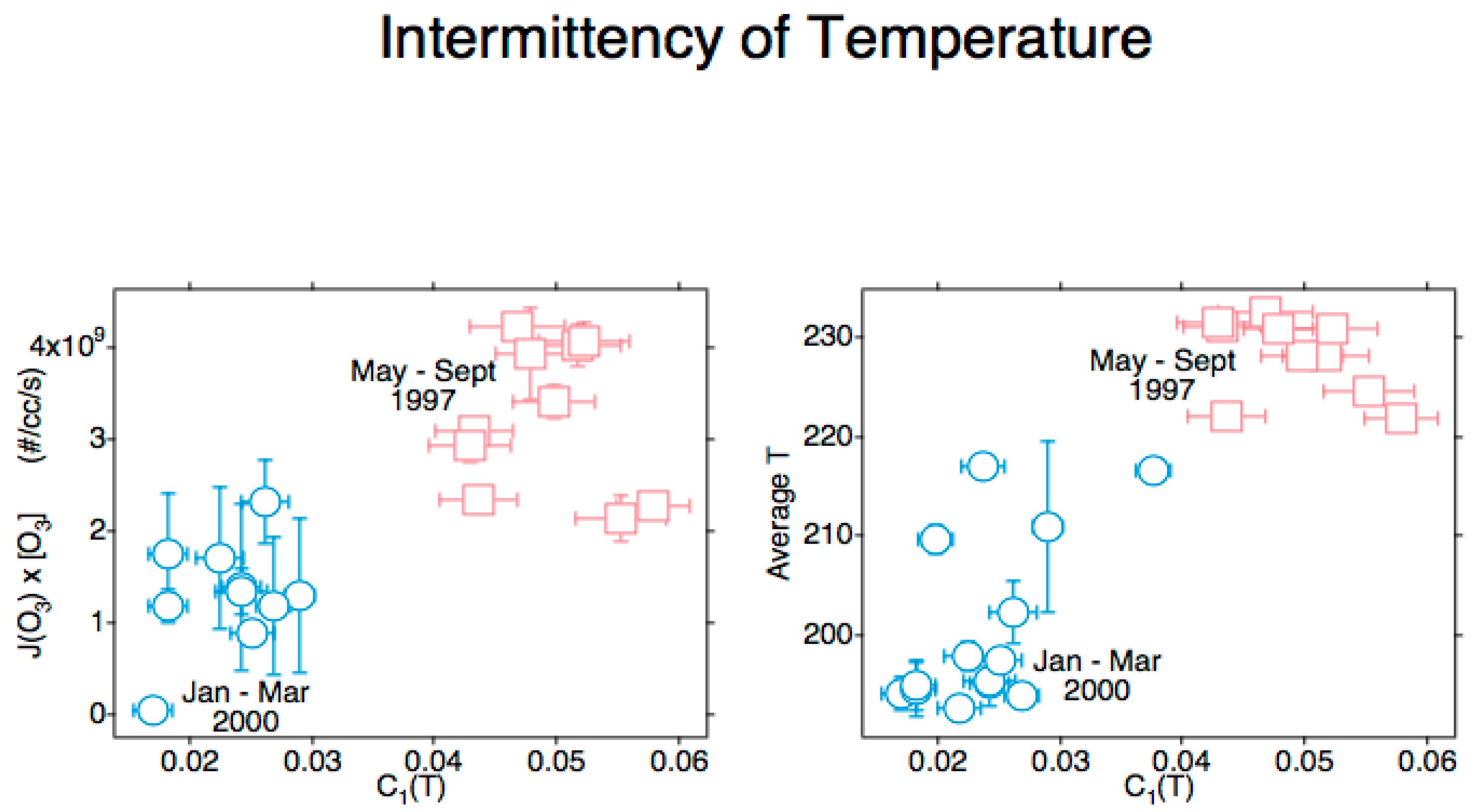
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tuck, A.F. Anthropogenic Impacts in the Lower Stratosphere: Scale Invariant Analysis. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 465. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15040465
Tuck AF. Anthropogenic Impacts in the Lower Stratosphere: Scale Invariant Analysis. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(4):465. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15040465
Chicago/Turabian StyleTuck, Adrian F. 2024. "Anthropogenic Impacts in the Lower Stratosphere: Scale Invariant Analysis" Atmosphere 15, no. 4: 465. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15040465
APA StyleTuck, A. F. (2024). Anthropogenic Impacts in the Lower Stratosphere: Scale Invariant Analysis. Atmosphere, 15(4), 465. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15040465





