A Numerical Modeling Study on the Earth’s Surface Brightening Effect of Cirrus Thinning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiments and Methods
2.1. Two Kinds of Models Used in This Study
2.2. A Physically Feasible Method Used for Cirrus Thinning
2.3. Climate Simulation Setup
3. Results
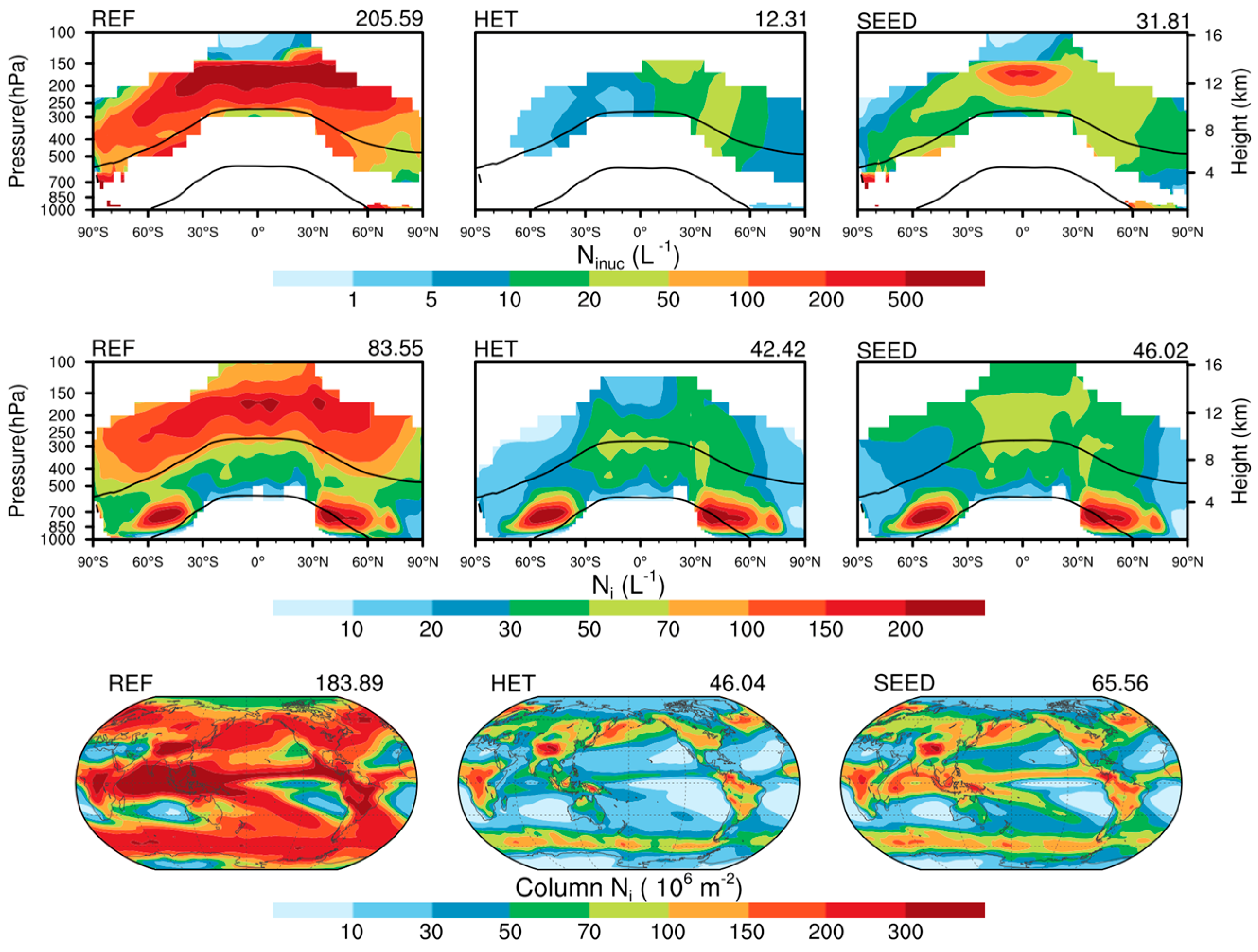
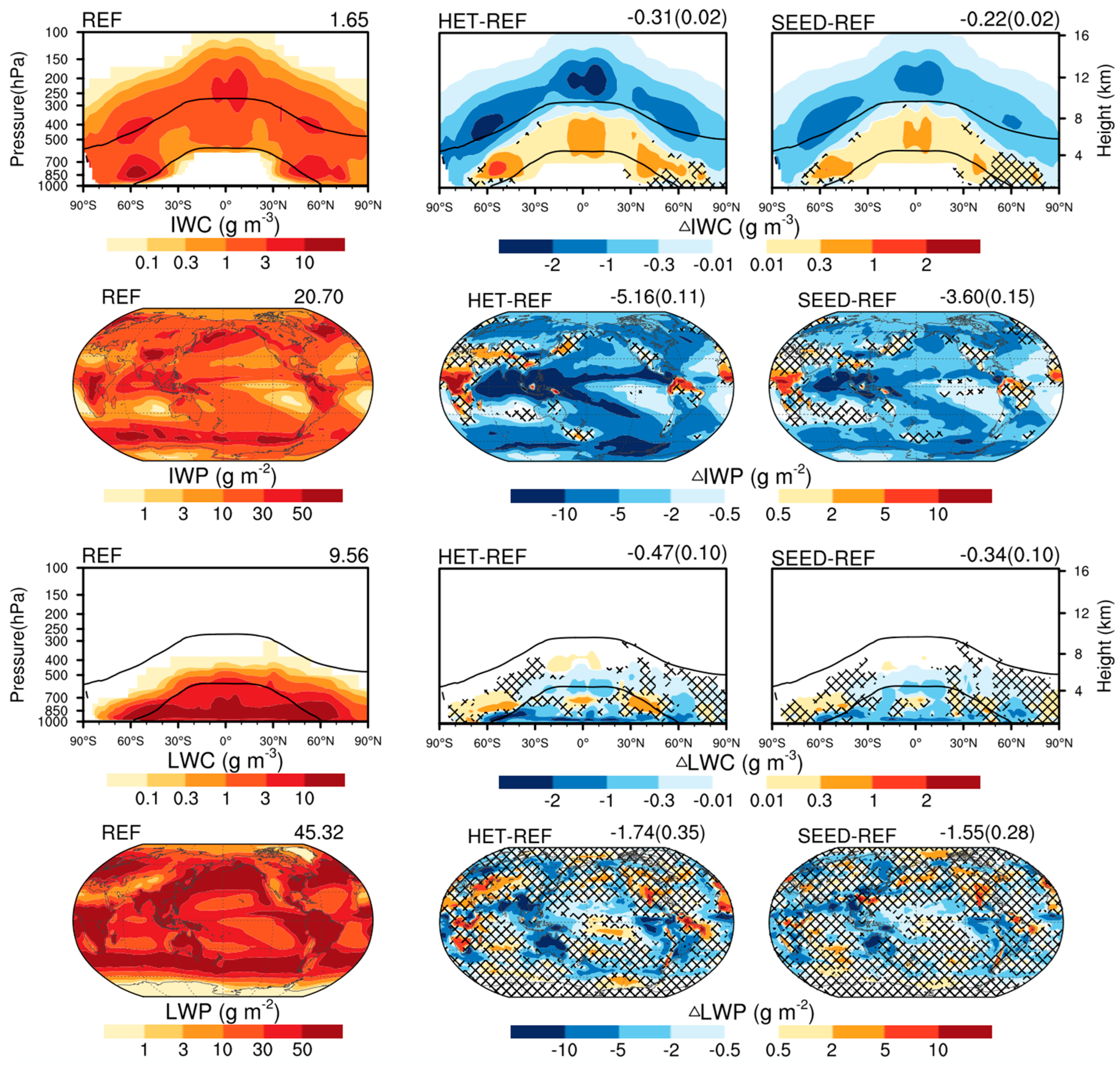
3.1. Impacts on Cloud Properties
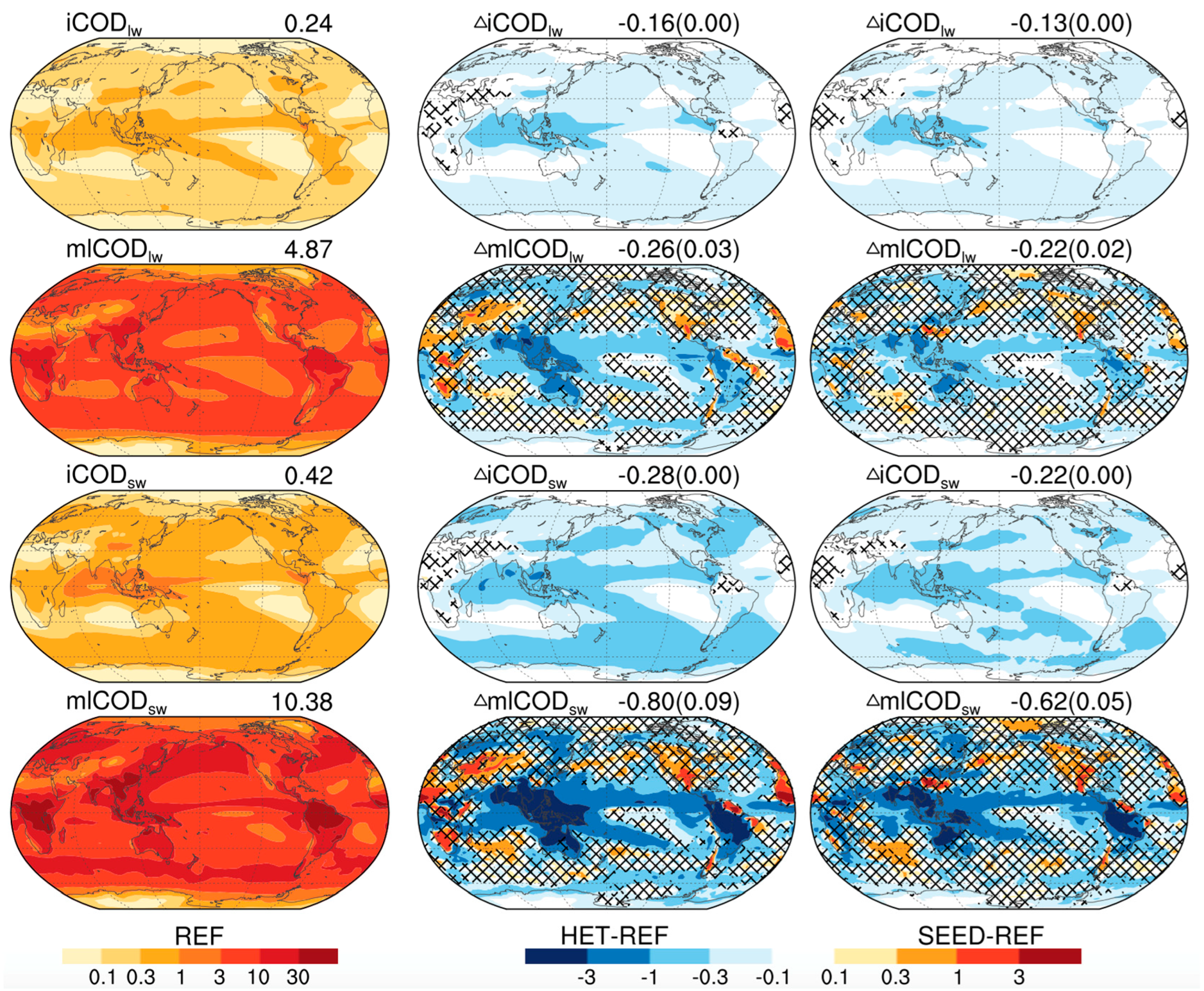
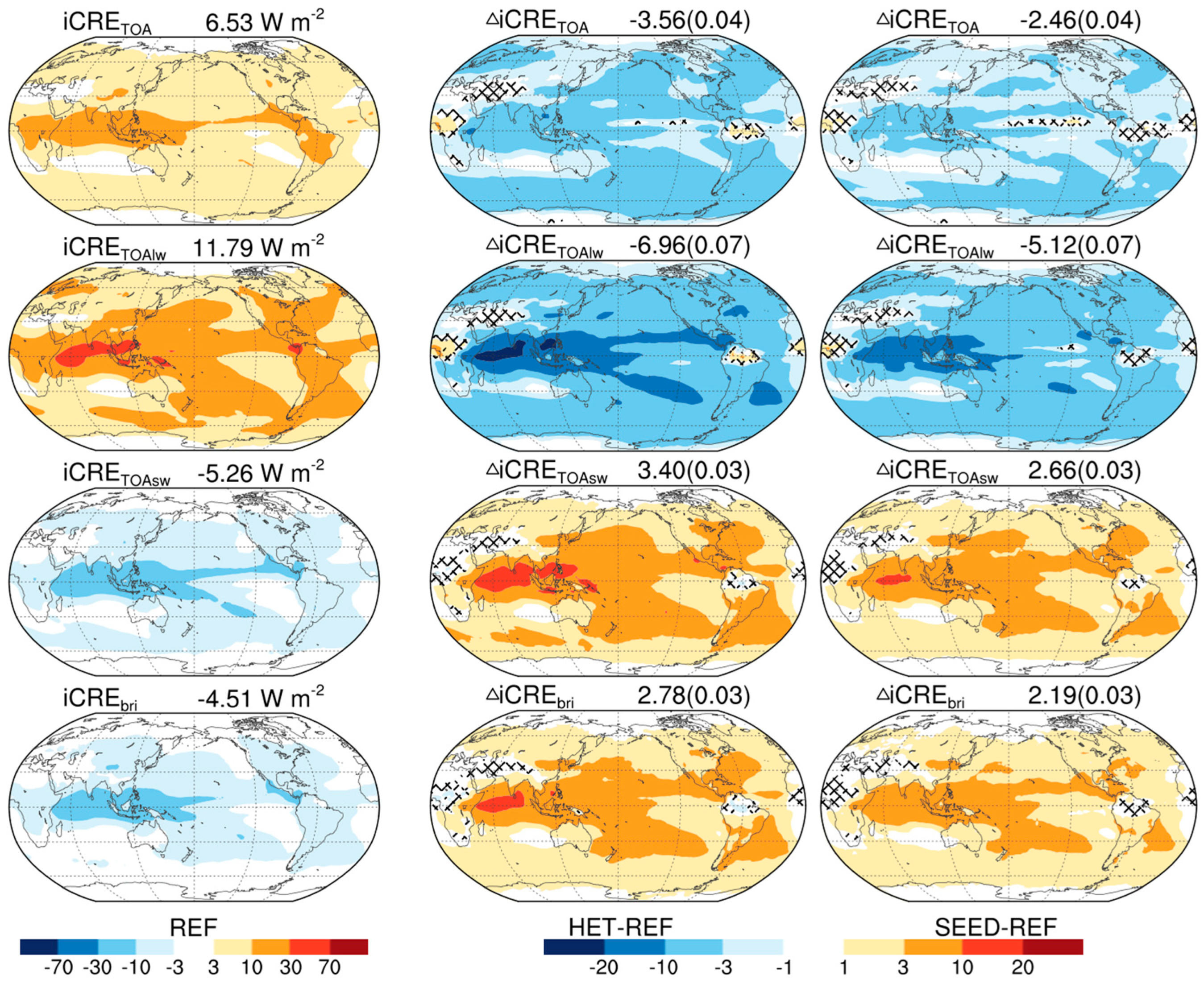
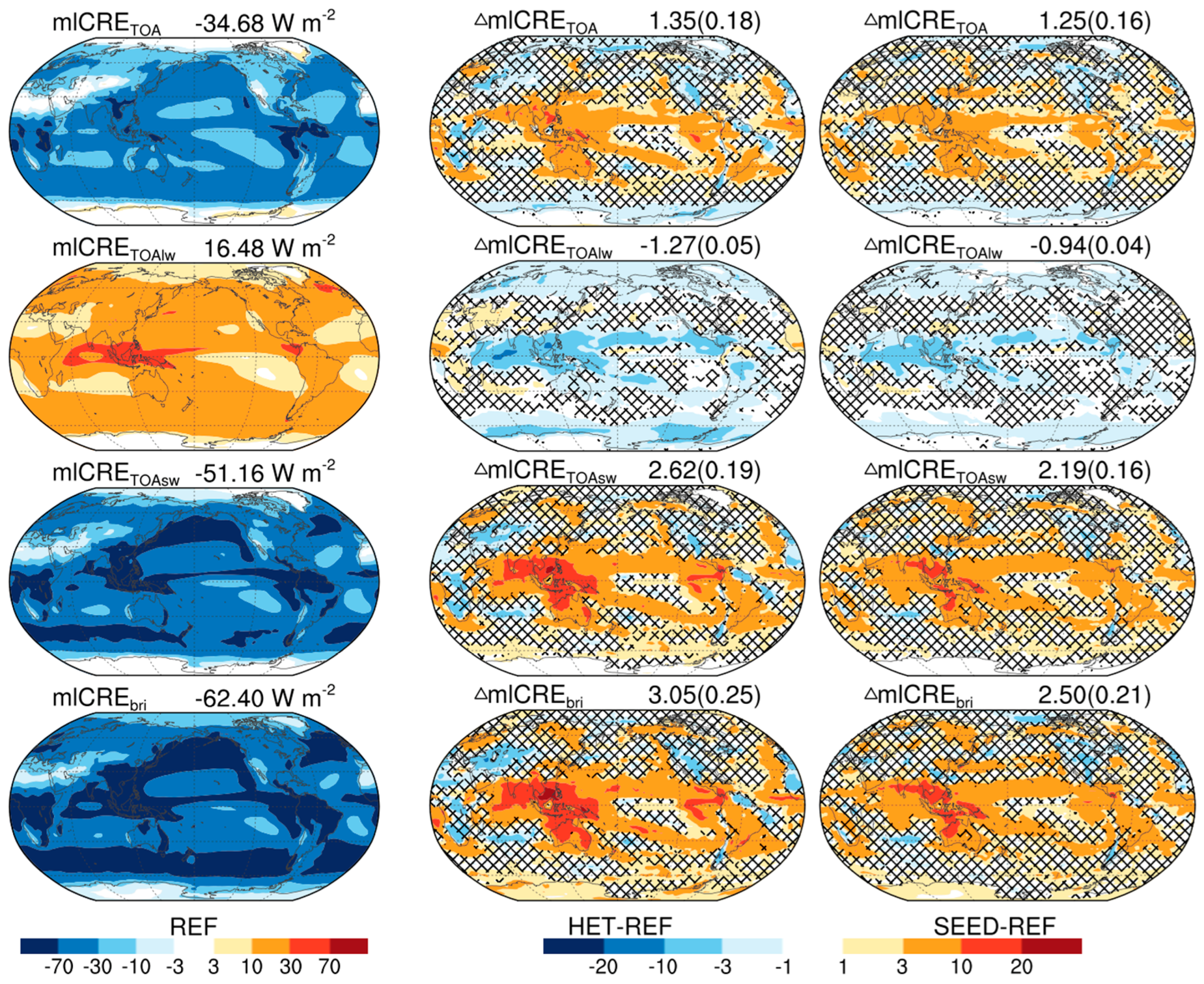
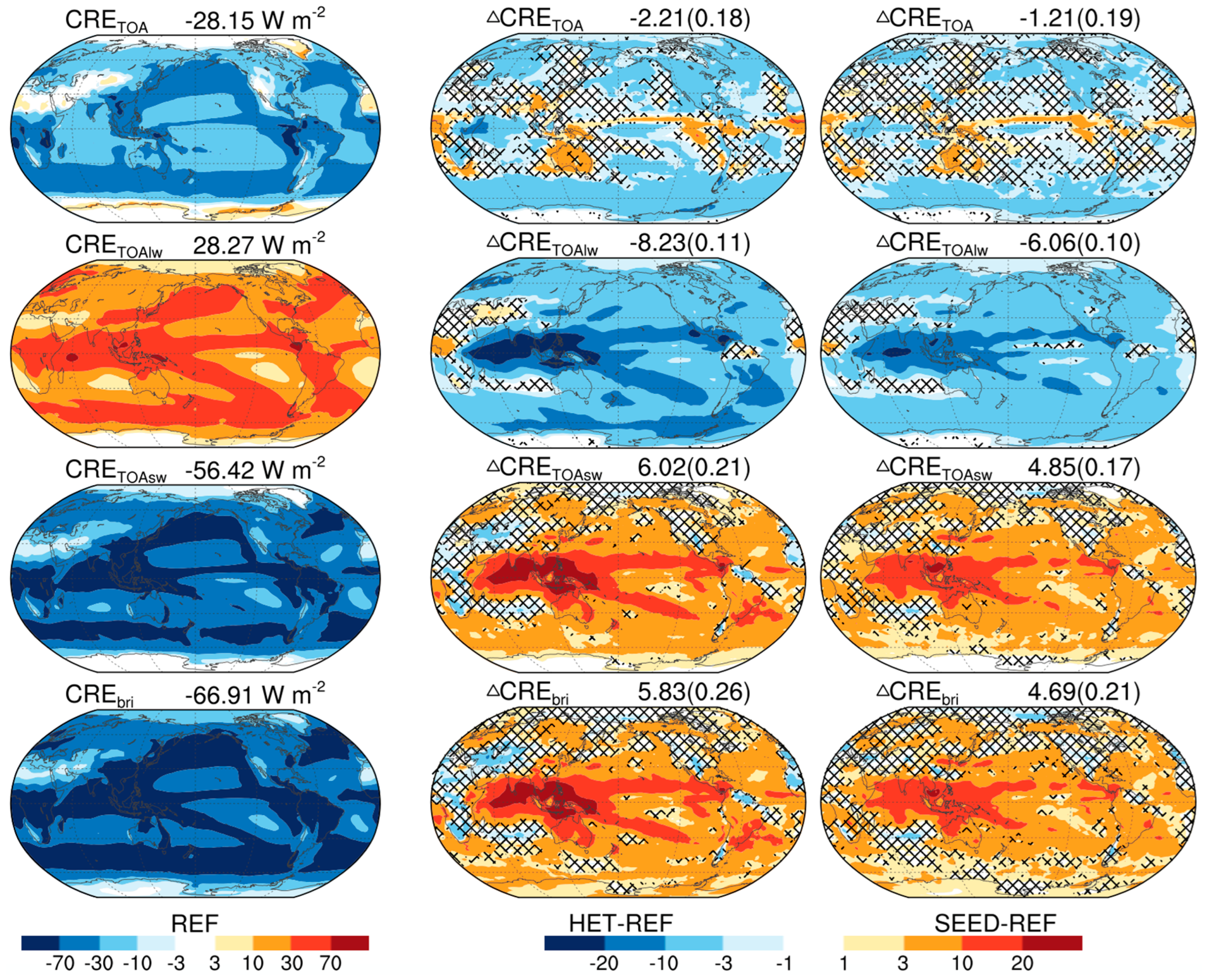
3.2. Brightening Effect and Cooling Effect
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, J.C.; Zhang, K.; Liu, J.F.; Ban-Weiss, G. Revisiting the climate impacts of cool roofs around the globe using an Earth system model. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 084014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Global Warming of 1.5 °C. An IPCC Special Report on the Impacts of Global Warming of 1.5 °C above Pre-Industrial Levels and Related Global Greenhouse Gas Emission Pathways, in the Context of Strengthening the Global Response to the Threat of Climate Change, Sustainable Development, and Efforts to Eradicate Poverty; Masson-Delmotte, V., Zhai, P., Pörtner, H.-O., Roberts, D., Skea, J., Shukla, P.R., Pirani, A., Moufouma-Okia, W., Péan, C., Pidcock, R., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, N.E.; Gough, C.; Mander, S.; Littleton, E.W.; Welfle, A.; Gernaat, D.E.H.J.; van Vuure, D.P. Evaluating the use of biomass energy with carbon capture and storage in low emission scenarios. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 044014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, S.; Blahak, U.; Haenel, F.; Kottmeier, C.; Leisner, T.; Muskatel, H.; Storelvmo, T.; Vogel, B. A process study on thinning of Arctic winter cirrus clouds with high-resolution ICON-ART simulations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 5860–5888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravitz, B.; MacMartin, D.G.; Visioni, D.; Boucher, O.; Cole, J.N.S.; Haywood, J.; Jones, A.; Lurton, T.; Nabat, P.; Niemeier, U.; et al. Comparing different generations of idealized solar geoengineering simulations in the Geoengineering Model Intercomparison Project (GeoMIP). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 4231–4247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, M.S.; Gettelman, A.; Lebsock, M.D.; McComiskey, A.; Russell, L.M.; Wood, R.; Feingold, G. To assess marine cloud brightening’s technical feasibility, we need to know what to study—And when to stop. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2118379119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacMartin, D.G.; Visioni, D.; Kravitz, B.; Richter, J.H.; Felgenhauer, T.; Lee, W.R.; Morrow, D.R.; Parson, E.A.; Sugiyama, M. Scenarios for modeling solar radiation modification. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2202230119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baur, S.; Nauels, A.; Nicholls, Z.; Sanderson, B.M.; Schleussner, C.-F. The deployment length of solar radiation modification: An interplay of mitigation, net-negative emissions and climate uncertainty. Earth Syst. Dynam. 2023, 14, 367–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldeira, K.; Bala, G.; Cao, L. The Science of Geoengineering. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2013, 41, 231–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, O.; Randall, D.; Artaxo, P.; Bretherton, C.; Feingold, G.; Forster, P.; Kerminen, V.M.; Kondo, Y.; Liao, H.; Lohmann, U.; et al. Clouds and Aerosols. In Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth As-sessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Stocker, T.F., Qin, D., Plattner, G.K., Tignor, M., Allen, S.K., Boschung, J., Nauels, A., Xia, Y., Bex, V., Midgley, P.M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 571–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2014: Mitigation of Climate Change. Contribution of Working Group III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Edenhofer, O., Pichs-Madruga, R., Sokona, Y., Farahani, E., Kadner, S., Seyboth, K., Adler, A., Baum, I., Brunner, S., Eickemeier, P., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irvine, P.J.; Kravitz, B.; Lawrence, M.G.; Muri, H. An overview of the Earth system science of solar geoengineering. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Clim. Change 2016, 7, 815–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L. Short commentary on CMIP6 Geoengineering Model Intercomparison Project (GeoMIP). Clim. Change Res. 2019, 15, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Masson-Delmotte, V., Zhai, P., Pirani, A., Connors, S.L., Péan, C., Berger, S., Caud, N., Chen, Y., Goldfarb, L., Gomis, M.I., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, D.P.; Lenton, A.; Scott, V.; Vaughan, N.E.; Bauer, N.; Ji, D.; Jones, C.D.; Kravitz, B.; Muri, H.; Zickfeld, K. The Carbon Dioxide Removal Model Intercomparison Project (CDRMIP): Rationale and experimental protocol for CMIP6. Geosci. Model Dev. 2018, 11, 1133–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minx, J.C.; Lamb, W.F.; Callaghan, M.W.; Fuss, S.; Hilaire, J.; Creutzig, F.; Amann, T.; Beringer, T.; de Oliveira Garcia, W.; Hartmann, J.; et al. Negative emissions—Part 1: Research landscape and synthesis. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 063001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickels, W.; Reith, F.; Keller, D.; Oschlies, A.; Quaas, M.F. Integrated Assessment of Carbon Dioxide Removal. Earth’s Future 2018, 6, 565–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L. Climate system response to carbon dioxide removal. Clim. Change Res. 2021, 17, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alterskjær, K.; Kristjánsson, J.E.; Seland, Ø. Sensitivity to deliberate sea salt seeding of marine clouds—Observations and model simulations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 2795–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, D.W.; MacMartin, D.G. A temporary, moderate and responsive scenario for solar geoengineering. Nat. Clim. Change 2015, 5, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.C.; Hawcroft, M.K.; Haywood, J.M.; Jones, A.; Guo, X.; Moore, J.C. Regional Climate Impacts of Stabilizing Global Warming at 1.5 K Using Solar Geoengineering. Earth’s Future 2018, 6, 230–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravitz, B.; Rasch, P.J.; Wang, H.; Robock, A.; Gabriel, C.; Boucher, O.; Cole, J.N.S.; Haywood, J.; Ji, D.; Jones, A.; et al. The climate effects of increasing ocean albedo: An idealized representation of solar geoengineering. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 13097–13113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparini, B.; McGraw, Z.; Storelvmo, T.; Lohmann, U. To what extent can cirrus cloud seeding counteract global warming? Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 054002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L. Climate system response to solar radiation modification. Clim. Change Res. 2021, 17, 671–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, N.E.; Lenton, T.M. A review of climate geoengineering proposals. Clim. Change 2011, 109, 745–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravitz, B.; Robock, A.; Tilmes, S.; Boucher, O.; English, J.M.; Irvine, P.J.; Jones, A.; Lawrence, M.G.; MacCracken, M.; Muri, H.; et al. The Geoengineering Model Intercomparison Project Phase 6 (GeoMIP6): Simulation design and preliminary results. Geosci. Model. Dev. 2015, 8, 3379–3392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y. A Brief Review and Outlook of Geoengineering. Adv. Meteor. Sci. Technol. 2016, 60, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Cao, L.; Bala, G.; Caldeira, K. Comparison of the fast and slow climate response to three radiation management geoengineering schemes. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 11980–12001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, M.G.; Schäfer, S.; Muri, H.; Scott, V.; Oschlies, A.; Vaughan, N.E.; Boucher, O.; Schmidt, H.; Haywood, J.; Scheffran, J. Evaluating climate geoengineering proposals in the context of the Paris Agreement temperature goals. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shepherd, J.; Caldeira, K.; Cox, P.; Haigh, J.; Keith, D.; Launder, B.; Mace, G.; MacKerron, G.; Pyle, J.; Raynor, S.; et al. Geoengineering the Climate: Science, Governance and Uncertainty; The Royal Society Publishing: London, UK, 2009; ISBN 978-0-85403-773-5. [Google Scholar]
- Fairbrother, M. Geoengineering, moral hazard, and trust in climate science: Evidence from a survey experiment in Britain. Clim. Change 2016, 139, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohmann, U.; Gasparini, B. A cirrus cloud climate dial? Science 2017, 357, 248–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heutel, G.; Moreno-Cruz, J.; Shayegh, S. Solar geoengineering, uncertainty, and the price of carbon. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2018, 87, 24–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzoli, P.; Emmerling, J.; Tavoni, M. SRM on the table: The role of geoengineering for the stability and effectiveness of climate coalitions. Clim. Change 2023, 176, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, V.; Wuebbles, D.; DeLucia, E.; Foley, J.A. Influence of Geoengineered Climate on the Terrestrial Biosphere. Environ. Manag. 2003, 32, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robock, A.; Marquardt, A.; Kravitz, B.; Stenchikov, G. Benefits, risks, and costs of stratospheric geoengineering. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L19703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitari, G.; Aquila, V.; Kravitz, B.; Robock, A.; Watanabe, S.; Cionni, I.; Luca, N.D.; Genova, G.D.; Mancini, E.; Tilmes, S. Stratospheric ozone response to sulfate geoengineering: Results from the Geoengineering Model Intercomparison Project (GeoMIP). J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 2629–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleidon, A.; Kravitz, B.; Renner, M. The hydrological sensitivity to global warming and solar geoengineering derived from thermodynamic constraints. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarnetske, P.L.; Gurevitch, J.; Franklin, J.; Groffman, P.M.; Harrison, C.S.; Hellmann, J.J.; Hoffman, F.M.; Kothari, S.; Robock, A.; Tilmes, S.; et al. Potential ecological impacts of climate intervention by reflecting sunlight to cool Earth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e1921854118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tye, M.R.; Dagon, K.; Molina, M.J.; Richter, J.H.; Visioni, D.; Kravitz, B.; Tilmes, S. Indices of extremes: Geographic patterns of change in extremes and associated vegetation impacts under climate intervention. Earth Syst. Dyn. 2022, 13, 1233–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.C.; Haywood, J.M.; Dunstone, N.; Emanuel, K.; Hawcroft, M.K.; Hodges, K.I.; Jones, A. Impacts of hemispheric solar geoengineering on tropical cyclone frequency. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristjánsson, J.E.; Muri, H.; Schmidt, H. The hydrological cycle response to cirrus cloud thinning. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 10807–10815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shi, X. Estimating the potential cooling effect of cirrus thinning achieved via the seeding approach. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 10609–10624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pongratz, J.; Lobell, D.B.; Cao, L.; Caldeira, K. Crop yields in a geoengineered climate. Nat. Clim. Change 2012, 2, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Robock, A.; Cole, J.; Curry, C.L.; Ji, D.; Jones, A.; Kravitz, B.; Moore, J.C.; Muri, H.; Niemeier, U.; et al. Solar radiation management impacts on agriculture in China: A case study in the Geoengineering Model Intercomparison Project (GeoMIP). J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 8695–8711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkes, B.; Challinor, A.; Nicklin, K. Crop failure rates in a geoengineered climate: Impact of climate change and marine cloud brightening. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 084003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, P.; Zhu, W.Q.; Zhang, T.Y.; Cui, X.F.; Li, N. Impacts of sulfate geoengineering on rice yield in China: Results from a multimodel ensemble. Earth’s Future 2019, 7, 395–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Tjiputra, J.F.; Muri, H.; Lombardozzi, D.L.; Park, C.; Wu, S.; Keith, D. Solar geoengineering can alleviate climate change pressures on crop yields. Nat. Food 2021, 2, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravitz, B. Effects of climate engineering on agriculture. Nat. Food 2021, 2, 320–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proctor, J. Atmospheric opacity has a nonlinear effect on global crop yields. Nat. Food 2021, 2, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanser, K.; Doherty, S.J.; Hurrell, J.W.; Wong, A. Near-term climate risks and solar radiation modification: A roadmap approach for physical sciences research. Clim. Change 2022, 174, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassidy, M.; Sandberg, A.; Mani, L. The ethics of volcano geoengineering. Earth’s Future 2023, 11, e2023EF003714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kortetmäki, T.; Oksanen, M. Right to Food and Geoengineering. J. Agric. Environ. Ethics 2023, 36, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, M. Geoengineering, climate change and ecological security. Environ. Polit. 2023, 32, 565–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, E.; Mace, G.G. Cloud properties and radiative effects of the Asian summer monsoon derived from A-Train data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 9492–9508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Liu, G.; Li, J.F. Assessing the Radiative Effects of Global Ice Clouds Based on CloudSat and CALIPSO Measurements. J. Clim. 2016, 29, 7651–7674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matus, A.V.; L’Ecuyer, T.S. The role of cloud phase in Earth’s radiation budget. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 2559–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storelvmo, T.; Herger, N. Cirrus cloud susceptibility to the injection of ice nuclei in the upper troposphere. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 2375–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparini, B.; Münch, S.; Poncet, L.; Feldmann, M.; Lohmann, U. Is increasing ice crystal sedimentation velocity in geoengineering simulations a good proxy for cirrus cloud seeding? Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 4871–4885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, D.; Fang, S.; Curry, C.L.; Kashimura, H.; Watanabe, S.; Cole, J.N.S.; Lenton, A.; Muri, H.; Kravitz, B.; Moore, J.C. Extreme temperature and precipitation response to solar dimming and stratospheric aerosol geoengineering. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 10133–10156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J. Cooling the earth and brightening the surface by cirrus thinning geoengineering. In Proceedings of the GeoMIP Meeting, Online, 29 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, L.; Cao, L.; Bala, G.; Caldeira, K. A model-based investigation of terrestrial plant carbon uptake response to four radiation modification approaches. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, e2019JD031883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercado, L.; Bellouin, N.; Sitch, S.; Boucher, O.; Huntingford, C.; Wild, M.; Cox, P.M. Impact of changes in diffuse radiation on the global land carbon sink. Nature 2009, 458, 1014–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, M.; Roesch, A.; Ammann, C. Global dimming and brightening—Evidence and agricultural implications. CABI Rev. 2012, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.Y.; Dobbie, S.; Ramirez-Villegas, J.; Feng, K.; Challinor, A.J.; Chen, B.; Gao, Y.; Lee, L.; Yin, Y.; Sun, L.X.; et al. Potential negative consequences of geoengineering on crop production: A study of Indian groundnut. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 11786–11795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proctor, J.; Hsiang, S.; Burney, J.; Burke, M.; Schlenker, W. Estimating global agricultural effects of geoengineering using volcanic eruptions. Nature 2018, 560, 480–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Liu, B.; Yang, H.; Chen, X. Solar dimming decreased maize yield potential on the North China Plain. Food Energy Secur. 2020, 9, e235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruppacher, H.; Klett, J. Microphysics of Clouds and Precipitation; Atmospheric and Oceanographic Sciences Library; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherland, 2010; Volume 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Liu, X. Effect of cloud-scale vertical velocity on the contribution of homogeneous nucleation to cirrus formation and radiative forcing. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 6588–6595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neale, R.B.; Gettelman, A.; Park, S.; Chen, C.-C.; Lauritzen, P.H.; Williamson, D.L.; Conley, A.J.; Kinnison, D.; Marsh, D.; Smith, A.K.; et al. Description of the NCAR Community Atmosphere Model (CAM 5.0); NCAR/TN-486+STR; National Center for Atmospheric Research: Boulder, CO, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, H.; Gettelman, A. A New Two-Moment Bulk Stratiform Cloud Microphysics Scheme in the Community Atmosphere Model, Version 3 (CAM3). Part I: Description and Numerical Tests. J. Clim. 2008, 21, 3642–3659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Penner, J.E. Ice nucleation parameterization for global models. Meteorol. Z. 2005, 14, 499–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barahona, D.; Nenes, A. Parameterizing the competition between homogeneous and heterogeneous freezing in ice cloud formation—Polydisperse ice nuclei. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 5933–5948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, K. Effects of pre-existing ice crystals on cirrus clouds and comparison between different ice nucleation parameterizations with the Community Atmosphere Model (CAM5). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 1503–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Liu, X. Sensitivity study of anthropogenic aerosol indirect forcing through cirrus clouds with CAM5 using three ice nucleation parameterizations. J. Meteorol. Res. 2018, 32, 693–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohmann, U.; Spichtinger, P.; Jess, S.; Peter, T.; Smit, H. Cirrus cloud formation and ice supersaturated regions in a global climate model. Environ. Res. Lett. 2008, 3, 045022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kärcher, B.; Lohmann, U. A parameterization of cirrus cloud formation: Homogenous freezing of supercooled aerosols. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107, 4010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storelvmo, T.; Kristjansson, J.E.; Muri, H.; Pfeffer, M.; Barahona, D.; Nenes, A. Cirrus cloud seeding has potential to cool climate. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoose, C.; Möhler, O. Heterogeneous ice nucleation on atmospheric aerosols: A review of results from laboratory experiments. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 9817–9854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparini, B.; Lohmann, U. Why cirrus cloud seeding cannot substantially cool the planet. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 4877–4893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, D.L.; Finnegan, W. Modification of cirrus clouds to reduce global warming. Environ. Res. Lett. 2009, 4, 045102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapp, A.D.; Kummerow, C.D.; Fowler, L. Interactions between warm rain clouds and atmospheric preconditioning for deep convection in the tropics. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, D23210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muench, S.; Lohmann, U. Developing a cloud scheme with prognostic cloud fraction and two moment microphysics for ECHAM-HAM. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2020, 12, e2019MS001824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Duan, L.; Bala, G.; Caldeira, K. Simultaneous stabilization of global temperature and precipitation through cocktail geoengineering. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 7429–7437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J. A Numerical Modeling Study on the Earth’s Surface Brightening Effect of Cirrus Thinning. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15020189
Shi X, Liu Y, Liu J. A Numerical Modeling Study on the Earth’s Surface Brightening Effect of Cirrus Thinning. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(2):189. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15020189
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Xiangjun, Yuxin Liu, and Jiaojiao Liu. 2024. "A Numerical Modeling Study on the Earth’s Surface Brightening Effect of Cirrus Thinning" Atmosphere 15, no. 2: 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15020189
APA StyleShi, X., Liu, Y., & Liu, J. (2024). A Numerical Modeling Study on the Earth’s Surface Brightening Effect of Cirrus Thinning. Atmosphere, 15(2), 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15020189





