The Generation of Seismogenic Anomalous Electric Fields in the Lower Atmosphere, and Its Application to Very-High-Frequency and Very-Low-Frequency/Low-Frequency Emissions: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Seismogenic Phenomena on the Earth’s Surface and in the Lowest Atmosphere
3. Growth of Seismogenic Electric Fields during the EQ Preparation Phase: Breakdown Electric Fields in the Lower Atmosphere
3.1. Experimental Observation of Atmospheric Electric Fields
- The enhancement in seismic activity produces clear DC electric field disturbances in the lower ionosphere.
- These disturbances occupy the region with a horizontal spatial scale from hundreds to thousands of kilometers over the seismic region.
- Meanwhile, DC electric field disturbances in the lower atmosphere as inferred from indirect VHF radio observations, etc., can reach the breakdown value “from hours to 10 days” in the atmosphere at altitudes of 1 to 10 km over the EQ zone a few days before an EQ.
- The quasi-stationary electric field on the Earth’s surface does not exceed its background value simultaneously in the seismic area during several days.
3.2. Theoretical Inference
4. Application to Seismogenic VHF Emissions
4.1. Application to VHF Radiation
4.2. Seismogenic VHF Emissions in Greece
4.3. Seismogenic VHF Emissions as Observed in Japan
5. Application to Seismogenic VLF/LF Lightning Discharges
5.1. Application to VLF/LF Lightning Discharges
5.2. Seismogenic VLF/LF Lightning Discharges
6. VHF and VLF/LF Emissions: Lithospheric or Atmospheric Effects?
7. Conclusions and Outlook
- The fundamental idea of this review is to accept the theoretical inference on the generation of anomalous DC electric fields in the lower atmosphere due to the emanation of radon and charged aerosols during the EQ preparation phase. That is, we expect the generation of a peculiar seismogenic thundercloud at the altitudes of a few to 6 km or so, in which the DC electric field exceeds the breakdown value. This layer has a height width of a few kilometers, with positive charges on the top and negative charges in the bottom of the layer.
- Seismogenic VHF electromagnetic emissions can be explained in terms of chaotic random discharges in such a highly charged layer, just like intra-cloud (IC) discharges in conventional lightning.
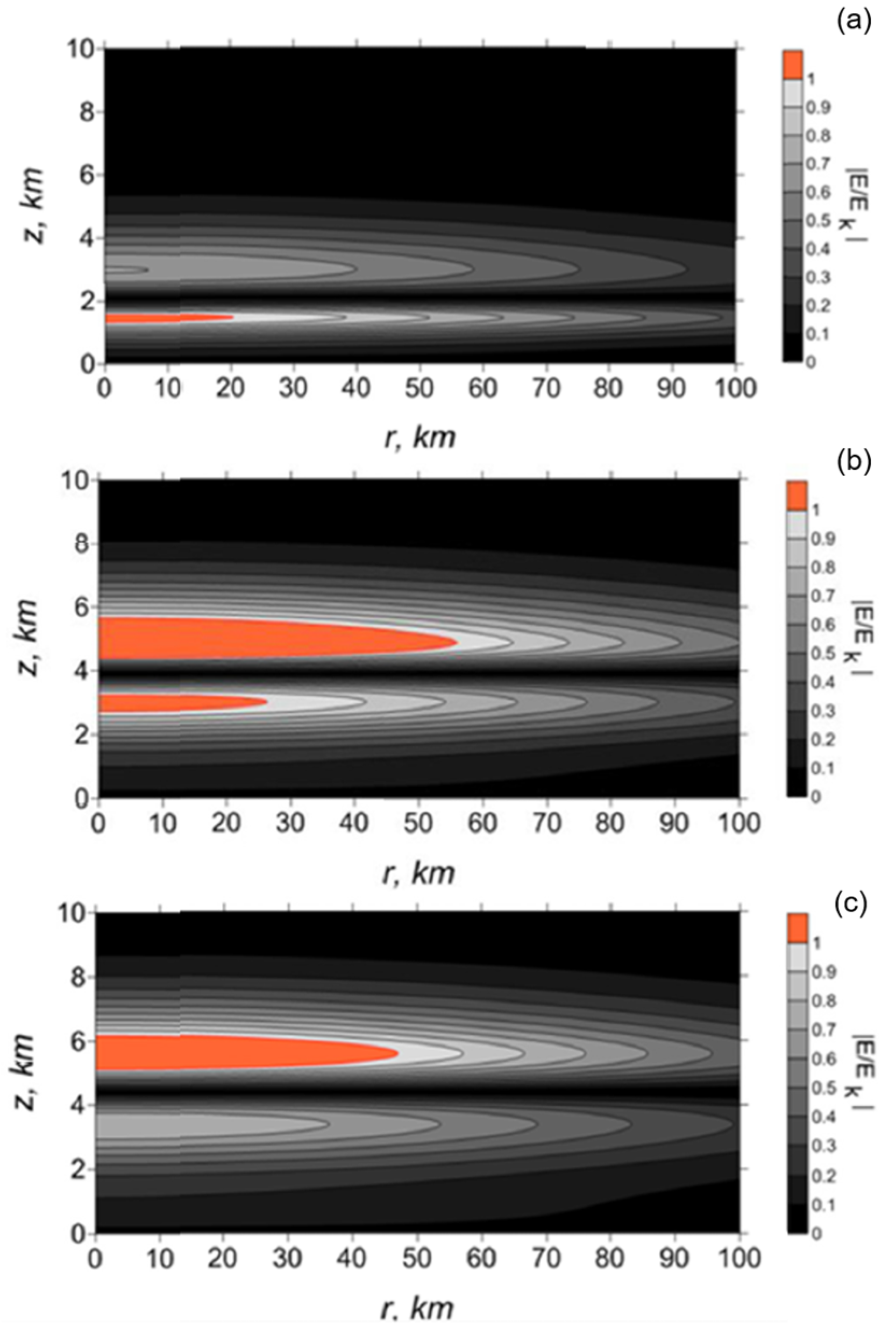
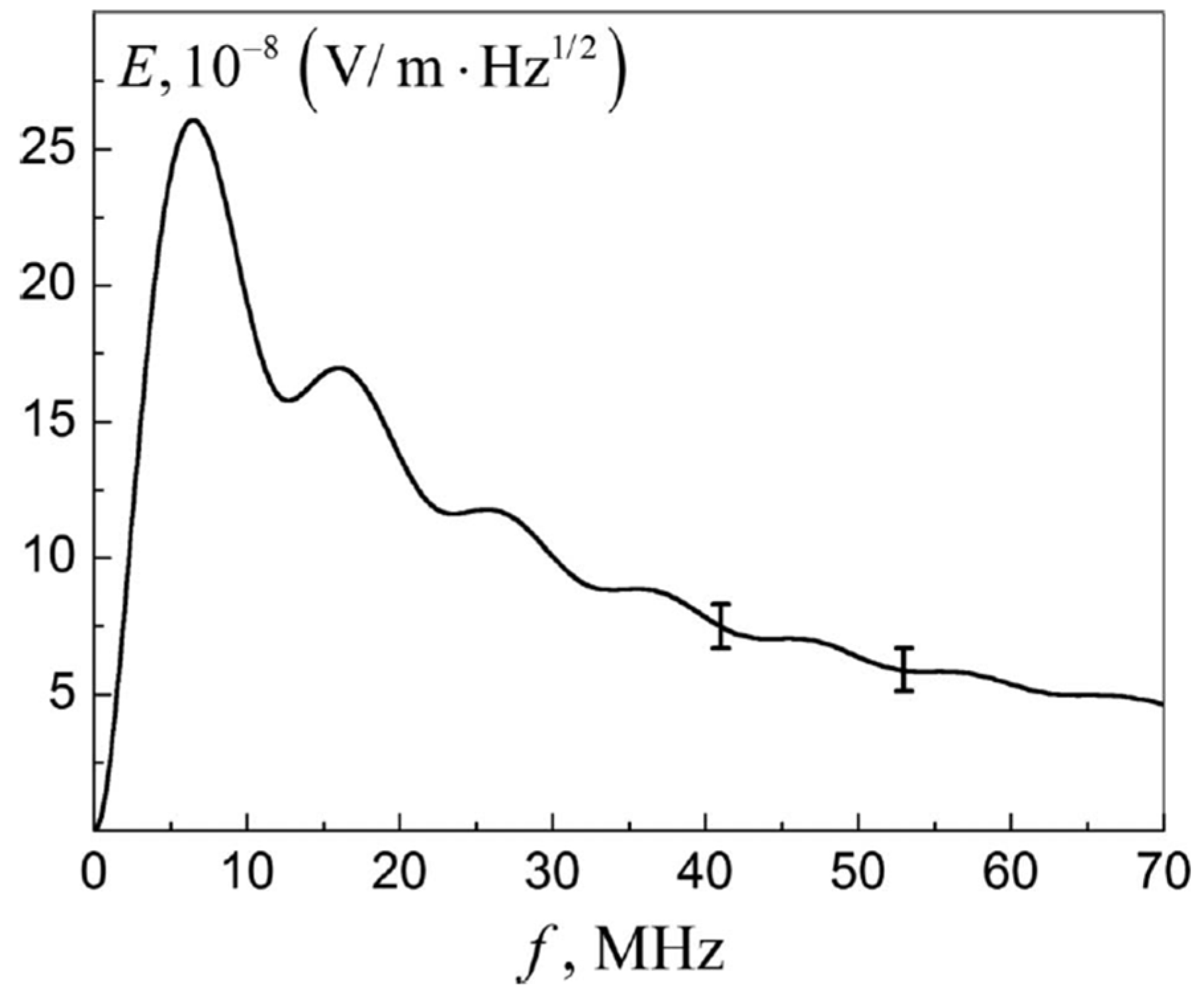
- The theoretical estimation of incoherent VHF radiation was performed on the frequency spectrum and intensity, which is found to be in good agreement with the experimental observations in Greece and in Japan.
- The same concept should be applied, for the first time, to the seismogenic VLF/LF lightning strokes, which are the discharges between the cloud charge source and the ground (CG discharges).
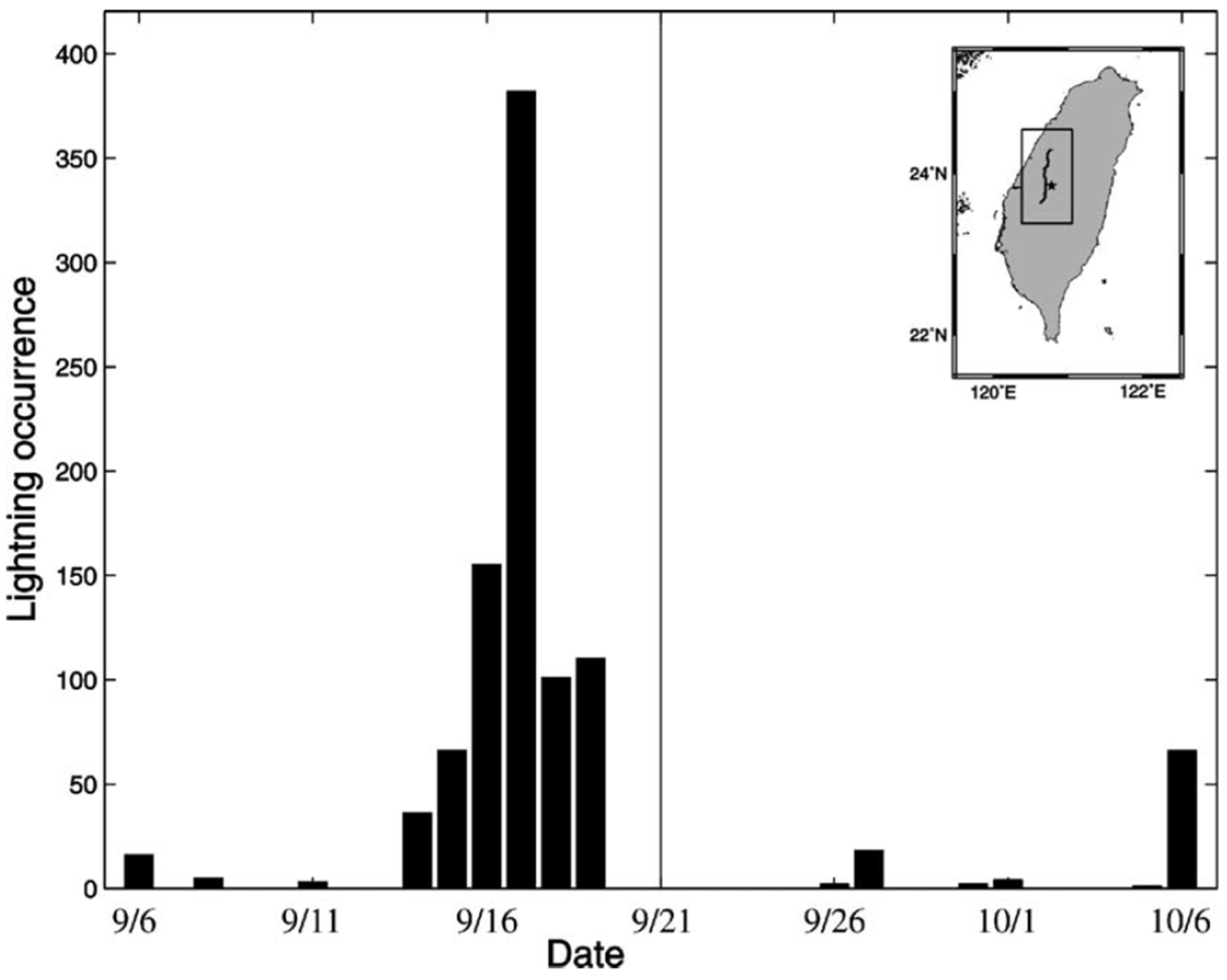
- This inference is supported by a good agreement with the observational results for Taiwan EQs; e.g., the VLF/LF radiation from lightning increased a few days prior to the 1999 Chi-chi EQ.
- The observation of seismogenic VHF radiation and VLF/LF discharges can be considered as indirect evidence of such anomalous enhancement in electric fields in the lowest atmosphere driven by the emanation of radon and charged aerosols during the EQ preparation phase.
- It seems that no consensus is reached on the generation mechanism of those VHF and VLF/LF noise bursts. The final issue is whether the observed VHF and VLF/LF noise bursts were of atmospheric origin as proposed in this review or if they were of the lithospheric origin hypothesized for a long time. The extensive review of earlier works has indicated that VLF/LF noises can be split into two types: (1) the impulsive noise, just like VLF/LF lightning discharges explainable by our hypothesis, and (2) the noise burst caused by an increase in continuous background noise, which is highly likely to be of lithospheric origin.
- Unfortunately, there have been no reports published so far of seismogenic electromagnetic radiation (either in VHF or in VLF/LF) that is simultaneous with observations of radon and charged aerosols, so we cannot prove the validity of our hypothesis proposed in this review. This will be part of a future work.
- Future areas of studies are suggested to clarify the generation mechanism of seismogenic natural electromagnetic radio emission: (i) studies of noise characteristics (coherent or incoherent?), (ii) frequency spectra, (iii) an application of a critical analysis to the noise data.
- When we prove that a considerable number of seismogenic natural emissions (either in VHF or in VLF/LF) are of atmospheric origin as proposed in this paper, they will be effectively integrated as a useful indicator of atmospheric perturbations in future LAIC studies.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hayakawa, M.; Molchanov, O.A. (Eds.) Seismo-Electromagnetics: Lithosphere-Atmosphere-Ionosphere Coupling; TERRAPUB: Tokyo, Japan, 2002; 477p. [Google Scholar]
- Pulinets, S.; Boyarchuk, K. Ionospheric Precursors of Earthquakes; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; 315p. [Google Scholar]
- Molchanov, O.A.; Hayakawa, M. Seismo Electromagnetics and Related Phenomena: History and Latest Results; Terrapub: Tokyo, Japan, 2008; 189p. [Google Scholar]
- Hayakawa, M. Earthquake Prediction with Radio Techniques; Wiley and Sons: Singapore, 2015; 294p. [Google Scholar]
- Sorokin, V.; Chmyrev, V.; Hayakawa, M. Electrodynamic Coupling of Lithosphere-Atmosphere-Ionosphere of the Earth; NOVA Science Pub. Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2015; 355p. [Google Scholar]
- Gokhberg, M.B.; Morgunov, V.A.; Yoshino, T.; Tomizawa, I. Experimental measurement of electromagnetic emissions possibly related to earthquakes in Japan. J. Geophys. Res. 1982, 87, 7824–7828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varotsos, P.; Alexopoulos, K. Physical properties of the variations of the electric field of the earth preceding earthquakes. Tectonophysics 1984, 110, 73–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser-Smith, A.C.; Bernardi, A.; McGill, P.R.; Ladd, M.E.; Helliwell, R.A.; Villard, O.G., Jr. Low-frequency magnetic field measurements near the epicenter of the Ms = 7.1 Loma Prieta earthquake. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1990, 17, 1465–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molchanov, O.A.; Kopytenko, Y.A.; Voronov, P.M.; Kopytenko, E.A.; Matiashvili, T.G.; Fraser-Smith, A.C.; Bernardy, A. Results of ULF magnetic field measurements near the epicenters of the Spitak (Ms = 6.9) and Loma Prieta (Ms = 7.1) earthquakes: Comparative analysis. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1992, 19, 1495–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopytenko, Y.A.; Matiashvili, T.G.; Voronov, P.M.; Kopytenko, E.A.; Molchanov, O.A. Detection of ultra-low-frequency emissions connected with the Spitak earthquake and its aftershock activity, based on geomagnetic pulsations data at Dusheti and Vardzia observatories. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 1993, 77, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, M.; Kawate, R.; Molchanov, O.A.; Yumoto, K. Result of ultra-low-frequency magnetic field measurements during the Guam earthquake of 8 August 1993. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1996, 23, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbatikov, A.V.; Molchanov, O.A.; Hayakawa, M.; Uyeda, S.; Hattori, K.; Nagao, T.; Tanaka, H.; Nikolaev, A.V.; Maltsev, P. Acoustic emission possibly related to earthquakes, observed at Matsushiro, Japan and its implications. In Seismo Electromagnetics: Lithosphere-Atmosphere-Ionosphere Coupling; Hayakawa, M., Molchanov, O.A., Eds.; TERRAPUB: Tokyo, Japan, 2002; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Hayakawa, M.; Molchanov, O.A.; Ondoh, T.; Kawai, E. The precursory signature effect of the Kobe earthquake on VLF subionospheric signals. J. Comm. Res. Lab. 1996, 43, 169–180. [Google Scholar]
- Molchanov, O.A.; Hayakawa, M. Subionospheric VLF signal perturbations possibly related to earthquakes. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 103, 17489–17504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozhnoi, A.; Solovieva, M.; Molchanov, O.A.; Hayakawa, M. Middle latitude LF (40 kHz) phase variations associated with earthquakes for quiet and disturbed geomagnetic conditions. Phys. Chem. Earth 2004, 29, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozhnoi, A.A.; Solovieva, M.S.; Molchanov, O.A.; Hayakawa, M.; Maekawa, S.; Biagi, P.F. Anomalies of LF signal during seismic activity in November–December 2004. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2005, 5, 657–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, M.; Kasahara, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Muto, F.; Horie, T.; Maekawa, S.; Hobara, Y.; Rozhnoi, A.; Solovieva, M.; Molchanov, O.A. A statistical study on the correlation between lower ionospheric perturbations as seen by subionospheric VLF/LF propagation and earthquakes. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, A09305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Y. Earthquake precursors observed in the ionospheric F-region. In Electromagnetic Phenomena Associated with Earthquakes; Hayakawa, M., Ed.; Transworld Research Network: Trivandrum, India, 2009; pp. 187–204. [Google Scholar]
- Gladyshev, V.; Fishkova, L.M. Optical research of seismoactivity. In Electromagnetic Phenomena Related to Earthquake Prediction; Hayakawa, M., Fujinawa, Y., Eds.; TERRAPUB: Tokyo, Japan, 1994; pp. 35–42. [Google Scholar]
- Parrot, M. Anomalous seismic phenomena: View from space. In Electromagnetic Phenoemena Associated with Earthquakes; Hayakawa, M., Ed.; Transworld Research Network: Trivandrum, India, 2009; pp. 205–233. [Google Scholar]
- Liperovski, V.A.; Meister, C.V.; Schlegel, K.; Haldoupis, C. Currents and turbulence in and near mid-latitude sporadic E-layers caused by strong acoustic impulses. Ann. Geophys. 1997, 15, 767–773. [Google Scholar]
- Kilimenko, M.V.; Kilimenko, V.V.; Karpov, I.V.; Zakharenkova, I.E. Simulation of seismo-ionospheric effects initiated by internal gravity wave. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. 2001, B5, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokhberg, M.B.; Nekrasov, A.K.; Shalimov, S.L. On influence of greenhouse gases instable injection to the ionosphere in seismic active regions. Trans. USSR Acad. Sci. Phys. Earth 1996, 8, 52–59. [Google Scholar]
- Hayakawa, M.; Kasahara, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Hobara, Y.; Rozhnoi, A.; Solovieva, M.; Molchanov, O.; Korepanov, V. Atmospheric gravity waves as a possible candidate for seismo-ionospheric perturbations. J. Atmos. Electr. 2011, 31, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molchanov, O.A.; Hayakawa, M. Generation of ULF electromagnetic emissions by microfracturing. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1995, 22, 3091–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molchanov, O. Fracturing as an underlying mechanism of seismo-electric signals. In Atmospheric and Ionospheric Electromagnetic Phenomena Associated with Earthquakes; Hayakawa, M., Fujinawa, Y., Eds.; TERRAPUB: Tokyo, Japan, 1999; pp. 349–356. [Google Scholar]
- Surkov, V.; Pilipenko, V. The physics of pre-seismic electromagnetic ULF signals. In Atmospheric and Ionospheric Electromagnetic Phenomena Associated with Earthquakes; Hayakawa, M., Ed.; TERRAPUB: Tokyo, Japan, 1999; pp. 357–370. [Google Scholar]
- Molchanov, O.A.; Hayakawa, M.; Rafalsky, V.A. Penetration characteristics of electromagnetic emissions from an underground seismic source into the atmosphere, ionosphere, and magnetosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 1995, 100, 1691–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitterman, D.V. Theory of electrokinetic-magnetic anomalies in a faulted half–space. J. Geophys. Res. 1979, 84, 6031–6040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilipenko, V.A.; Fedorov, E.N.; Yagova, N.V.; Yumoto, K. Attempt to detect ULF electromagnetic activity preceding earthquake. In Atmospheric and Ionospheric Electromagnetic Phenomena Associated with Earthquakes; Hayakawa, M., Ed.; TERRAPUB: Tokyo, Japan, 1999; pp. 203–214. [Google Scholar]
- Molchanov, O.A.; Fedorov, E.; Schekotov, A.; Gordeev, E.; Chebrov, V.; Surkov, V.; Rozhnoi, A.; Andreevsky, S.; Iudin, D.; Yunga, S.; et al. Lithosphere-atmosphere-ionosphere coupling as governing mechanism for preseismic short-term events in atmosphere and ionosphere. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2004, 4, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulinets, S.A.; Ouzounov, D. Lithosphere-Atmosphere-Ionosphere Coupling (LAIC) model-A unified concept for earthquake precursors validation. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2011, 41, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouzounov, D.; Pulinets, S.; Hattori, K.; Taylor, P. (Eds.) Pre-Earthquake Processes: A Multidisciplinary Approach to Earthquake Prediction Studies; AGU Geophysical Monograph 234; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2018; 365p. [Google Scholar]
- De Santis, A.; Balasis, G.; Pavón-Carrasco, F.J.; Cianchini, G.; Mandea, M. Potential earthquake precursory pattern from space: The 2015 Nepal event as seen by magnetic Swarm satellites. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2017, 461, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Santis, A.; Cianchini, G.; Marchetti, D.; Piscini, A.; Sabbagh, D.; Perrone, L.; Campuzano, S.A.; Inan, S. A multiparametric approach to study the preparation phase of the 2019 M7.1 Ridgecrest (California, USA) earthquake. Front. Earth Sci. 2020, 8, 540398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhoondzadeh, M.; De Santis, A.; Marchetti, D.; Piscini, A.; Jin, S. Anomalous seismo-LAI variations potentially associated with the 2017 Mw = 7.3 Sarpole Zahab (Iran) earthquake from Swarm satellites, GPS-TEC and climatological data. Adv. Space Res. 2019, 64, 143–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouzounov, D.; Pulinets, S.; Davidenko, D.; Rozhnoi, A.; Solovieva, M.; Fedun, V.; Dwivedi, B.N.; Rybin, A.; Kafatos, M.; Taylor, P. Transient effects in atmosphere and ionosphere preceding the 2015 M7.8 and M7.3 Gorkha–Nepal earthquakes. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 757358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrot, M.; Tramutoli, V.; Liu, J.Y.; Pulinets, S.; Ouzounov, D.; Genzaro, N.; Lisi, M.; Hattori, K.; Namgaladze, A. Atmospheric and ionospheric coupling phenomena associated with large earthquakes. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2021, 230, 197–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasmal, S.; Chowdhury, S.; Kundu, S.; Politis, D.Z.; Potirakis, S.M.; Balasis, G.; Hayakawa, M.; Chakrabarti, S.K. Pre-seismic irregularities during the 2020 Samos (Greece) earthquake (M = 6.9) as investigated from multi-parameter approach by ground and space-based techniques. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, M.; Izutsu, J.; Schekotov, A.; Yang, S.S.; Solovieva, M.; Budilova, E. Lithosphere-atmosphere-ionosphere coupling effects based on multiparameter precursor observations for February-March 2021 earthquakes (M~7) in the offshore of Tohoku area of Japan. Geosciences 2021, 11, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, M.; Schekotov, A.; Izutsu, J.; Yang, S.S.; Solovieva, M.; Hobara, Y. Multi-Parameter Observations of Seismogenic Phenomena Related to the Tokyo Earthquake (M = 5.9) on 7 October 2021. Geosciences 2022, 12, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Arcangelo, S.; Regi, M.; De Santis, A.; Perrone, L.; Cianchini, G.; Soldani, M.; Piscini, A.; Fidani, C.; Sabbagh, D.; Lepidi, S.; et al. A multiparametric-multilayer comparison of two geophysical events in the Tonga-Kermadec subduction zone: The 2019 M7.2 earthquake and 2022 Hunga Ha’apai eruption. Front. Earth Sci. 2023, 11, 12677411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, D.; Zhu, Z.; Picsini, A.; Ghamry, E.; Shen, X.; Yan, R.; He, X.; Wang, T.; Chen, W.; Wen, J.; et al. Changes in the lithosphere, atmosphere and ionosphere before and after the Mw = 7.7 Jamaica 2020 earthquake. Remote Sens. Environ. 2024, 307, 114146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, M.; Hobara, Y. Integrated analysis of multi-parameter precursors to the Fukushima offshore earthquake (Mj = 7.3) on 13 February 2021 and lithosphere-atmosphere-ionosphere coupling channels. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voinov, V.V.; Gufeld, I.L.; Kruglikov, V.V. Effects in the ionosphere and atmosphere before the Spitack earthquake. Fiz. Zemli 1992, 3, 96–101. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Oike, K.; Yamada, T. Relationship between shallow earthquakes and electromagnetic noises in the LF and VLF ranges. In Electromagnetic Phenomena Related to Earthquake Prediction; Hayakawa, M., Fujinawa, Y., Eds.; Terra Scientific Publishing Company: Tokyo, Japan, 1994; pp. 115–130. [Google Scholar]
- Fujinawa, Y.; Takahashi, K. Anomalous VLF subsurface electric field changes preceding earthquakes. In Electromagnetic Phenomena Related to Earthquake Prediction; Hayakawa, M., Fujinawa, Y., Eds.; Terra Scientific Publishing Company: Tokyo, Japan, 1994; pp. 131–148. [Google Scholar]
- Varotsos, P.A. The Physics of Seismic Electric Signals; TERRAPUB: Tokyo, Japan, 2015; 388p. [Google Scholar]
- Hayakawa, M.; Schekotov, A.; Izutsu, J.; Hobara, Y. Seismogenic ULF/ELF wave phenomena: Recent advances and future perspectives. Open J. Earthq. Res. 2023, 12, 45–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, Z.J.; Dian, C.G.; Li, L.Z. Satellite thermal infrared precursors of two moderate—Strong earthquakes in Japan impending earthquake prediction. In Atmospheric and Ionospheric Electromagnetic Phenomena Associated with Earthquakes; Hayakawa, M., Ed.; TERRAPUB: Tokyo, Japan, 1999; pp. 745–747. [Google Scholar]
- Tronin, A.A. Satellite thermal survey application for earthquake prediction. In Atmospheric and Ionospheric Electromagnetic Phenomena Associated with Earthquakes; Hayakawa, M., Ed.; TERRAPUB: Tokyo, Japan, 1999; pp. 717–746. [Google Scholar]
- Tronin, A.A.; Hayakawa, M.; Molchanov, O.A. Thermal IR satellite data application for earthquake research in Japan and China. J. Geodyn. 2002, 33, 519–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tramutoli, V.; Cuomo, V.; Filizzola, C.; Pergola, N.; Pietrapertosa, C. Assessing the potential of thermal infrared satellite surveys for monitoring seismically active areas: The case of Kocaeli (Izmit) earthquake, August 17, 1999. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 96, 409–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouzounov, D.; Pulinets, S.; Hattori, K.; Kafatos, M.; Taylor, P. Atmospheric signals associated with major earthquakes: A multi-sensor approach. In The Frontier of Earthquake Prediction Studies; Hayakawa, M., Ed.; Nihon-senmontosho-Shuppan: Tokyo, Japan, 2012; pp. 510–531. [Google Scholar]
- Alekseev, V.A.; Alekseeva, N.G. Investigation of metal transfer in the biosphere during gaseous emission in zones of tectonic activity using methods of nuclear physics. Nucl. Geophys. 1992, 6, 99–105. [Google Scholar]
- Virk, H.S.; Singh, B. Radon recording of Uttarkashi earthquake. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1994, 21, 737–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heincke, J.; Koch, U.; Martinelli, G. CO2 and radon measurements in the Vogtland area (Germany)—A contribution to earthquake prediction research. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1995, 22, 774–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igarashi, G.; Saeki, T.; Takahata, N.; Sano, Y.; Sumikawa, K.; Tasaka, S.; Sasaki, Y.; Takahashi, M. Groundwater radon anomaly before the Kobe earthquake. Science 1995, 269, 60–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuoka, Y.; Igarashi, G.; Ishikawa, T.; Tokonami, S.; Shinogi, M. Evidence of precursor phenomena in the Kobe earthquake obtained from atmospheric radon concentration. Appl. Geochem. 2006, 21, 1064–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuoka, Y.; Ishikawa, T.; Nagahama, H.; Kawada, Y.; Omori, Y.; Tokonami, S.; Shinogi, M. Radon anomalies prior to earthquakes. In The Frontier of Earthquake Prediction Studies; Hayakawa, M., Ed.; Nihon-Senmontosho-Shuppan: Tokyo, Japan, 2012; pp. 410–427. [Google Scholar]
- Biagi, P.F. Pre and post seismic disturbances revealed on the geochemical data collected at Kamchatka (Russia) during the last 30 years. In Electromagnetic Phenomena Associated with Earthquakes; Hayakawa, M., Ed.; Transworld Research Network: Trivandrum, India, 2009; pp. 97–117. [Google Scholar]
- McGorman, D.R.; Rust, W.D. The Electrical Nature of Storms; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Rakov, V.A.; Uman, M.A. Lightning: Physics and Effects; Cambrdige University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Kondo, G. The variation of the atmospheric electric field at the time of earthquake. Mem. Kakioka Magn. Obs. 1968, 13, 11–23. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, J.G. Near earth surface anomalies of the atmospheric electric field and earthquakes. Acta Seismol. Sin. 1989, 2, 289–298. [Google Scholar]
- Nikiforova, N.N.; Michnowski, S. Atmospheric electric field anomalies analysis during great Carpatian Earthquake at Polish Observatory Swider. In IUGG XXI General Assembly Abstract; VA11D-16: Boulder, CO, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Vershinin, E.F.; Buzevich, A.V.; Yumoto, K.; Saita, K.; Tanaka, Y. Correlations of seismic activity with electromagnetic emissions and variations in Kamchatka region. In Atmospheric and Ionospheric Electromagnetic Phenomena Associated with Earthquakes; Hayakawa, M., Ed.; TERRAPUB: Tokyo, Japan, 1999; pp. 513–517. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, J.; Tang, T.; Li, D. Progress in the research of atmospheric electric field anomaly as an index for short-impending prediction of earthquakes. J. Earthq. Pred. Res. 2000, 8, 241–255. [Google Scholar]
- Rulenko, O.P. Operative precursors of earthquakes in the near-ground atmosphere electricity. Volcanol. Seismol. 2000, 4, 57–68. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, L.; Zhang, X. Identification and analysis of multi-station atmospheric electric field anomalies before the Yangbi Ms6.4 earthquake on 21 May 2021. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorokin, V.M.; Yaschenko, A.K.; Chmyrev, V.M.; Hayakawa, M. DC electric field amplification in the mid-latitude ionosphere over seismically active faults. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2005, 5, 661–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorokin, V.M.; Yaschenko, A.K.; Hayakawa, M. A perturbation of DC electric field caused by light ion adhesion to aerosols during the growth in seismic-related atmospheric radioactivity. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2007, 7, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorokin, V.M.; Ruzhin, Y.Y.; Kuznetsov, V.D.; Yaschenko, A.K. Model of electric discharges formation in the lower atmosphere over a seismic region. Geomatics. Nat. Hazards Risk 2012, 3, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorokin, V.; Hayakawa, M. Generation of seismic-related DC electric fields and lithosphere-atmosphere-ionosphere coupling. Mod. Appl. Sci. 2013, 7, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorokin, V.; Hayakawa, M. Plasma and electromagnetic effects caused by the seismic-related disturbances of electric current in the global circuit. Mod. Appl. Sci. 2014, 8, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorokin, V.M.; Ruzhin, Y.Y.; Yaschenko, A.K.; Hayakawa, M. Generation of VHF radio emissions by electric discharges in the lower atmosphere over a seismic region. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 2011, 73, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmyrev, V.; Isaev, N.V.; Bilichenko, S.V.; Stanev, G.A. Observation by space-borne detectors of electric fields and hydromagnetic waves in the ionosphere over an earthquake center. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 1989, 57, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gousheva, M.; Danov, D.; Hristov, P.; Matova, M. Quasi-static electric fields phenomena in the ionosphere associated with pre- and post earthquake effects. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2008, 8, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruzhin, Y.; Nomicos, C. Radio VHF precursors of earthquakes. Nat. Hazards 2007, 40, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Qian, F. Earthquake Lights: A Very Convincing Evidence of Energy Transfer from Earth to Air; IWSE (International Workshop of Seismo Electromagnetics), Abstracts; NASDA: Tokyo, Japan, 1997; p. 242. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, E.R. The electrification of thunder storms. J. Geophys. Res. 1989, 93, 992–993. [Google Scholar]
- Nomicos, K.; Vallianatos, F.; Kalliakatos, J.; Siders, F.; Bakatsakis, M. Latest aspects of telluric and electromagnetic variations associated with shallow and intermediate earthquakes in Soyh Agegean. Ann. Geophys. 1995, X1/2, 361–375. [Google Scholar]
- Vallianatos, F.; Nomicos, K. Seismogenic radioemissions as earthquake precursors in Greece. Phys. Chem. Earth 1988, 23, 953–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, A.; Sakai, K.; Yaji, Y.; Takano, T.; Shimakura, S. Observation of natural noise in VHF band which relates to earthquakes. In Seismo Electromagnatics: Lithosphere–Atmosphere–Ionosphere Coupling; Hayakawa, M., Molchanov, O.A., Eds.; Terrapub: Tokyo, Japan, 2002; pp. 255–257. [Google Scholar]
- Yonaiguchi, N.; Ida, Y.; Hayakawa, M.; Masuda, S. A comparison of different fractal analyses for VHF electromagnetic emissions and their self-organization for the off-sea Miyagi-prefecture earthquake. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2007, 7, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yonaiguchi, N.; Ida, Y.; Hayakawa, M.; Masuda, S. Fractal analysis for VHF electromagnetic noises and the identification of preseismic signature of an earthquake. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 2007, 69, 1825–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, M.; Ohta, K.; Maekawa, S.; Yamauchi, T.; Ida, Y.; Gotoh, T.; Yonaiguchi, N.; Sasaki, H.; Nakamura, T. Electromagnetic precursors to the 2004 Mid Niigata Prefecture earthquake. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2006, 31, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, Y.; Ida, Y.; Goto, T.; Hayakawa, M. Interferometric direction finding of over-horizon VHF transmitter signals and natural VHF radio emissions possibly associated with earthquakes. Radio Sci. 2009, 44, RS2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michimoto, K. A study of radar echoes and their relation to lightning discharge of thunderclouds in the Hokuriku district. Part II: Observation and analysis of «Single Flash» thunderclouds in midwinter. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 1993, 71, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, M.; Nakamura, T.; Hobara, Y.; Williams, E. Observation of sprites over the Sea of Japan and conditions for lightning-induced sprites in winter. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109, A01312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schekotov, A.; Molchanov, O.A.; Hayakawa, M.; Fedorov, E.N.; Chebrov, V.N.; Sinitsin, V.I.; Gordeev, E.E.; Belayev, G.G.; Yagova, N.V. ULF/ELF magnetic field variations from atmosphere induced by seismicity. Radio Sci. 2007, 42, RS6S90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schekotov, A.; Fedorov, E.; Molchanov, O.A.; Hayakawa, M. Low frequency electromagnetic precursors as a prospect for earthquake prediction. In Earthquake Prediction Studies: Seismo Electromagnetics; Hayakawa, M., Ed.; TERRAPUB: Tokyo, Japan, 2013; pp. 81–99. [Google Scholar]
- Hayakawa, M.; Nickolaenko, A.P. Variations of atmospheric ELF/VLF radio noises due to seismogenic modifications in tropospheric conductivity. Open J. Earth. Res. 2024, 13, 113–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasko, V.P. Theoretical Modeling of Sprites and Jets. In Sprites, Elves and Intense Lightning Discharges; Füllekrug, M., Mareev, E.A., Rycroft, M.J., Eds.; NATO Science Series II: Mathematics, Physics and Chemistry; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 252–311. [Google Scholar]
- Surkov, V.V.; Hayakawa, M. Lightning effects in the mesosphere. In Lightning Electromagnetics, Vol. 2: Electrical Processes and Effects; Cooray, V., Farhad, R., Marcos, R., Eds.; IET (The Institute of Enignineering and Technology): Stevenage, UK, 2022; Chapter 11; pp. 444–473. [Google Scholar]
- Nickolaenko, A.P.; Hayakawa, M.; Hobara, Y. Q-bursts: Natural ELF radio transients. Surv. Geophys. 2010, 31, 409–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Y.; Chen, Y.I.; Huang, C.H.; Ho, Y.Y.; Chen, C.H. A statistical study of lightning activities and M 5.0 earthquakes in Taiwan during 1993–2004. Surv. Geophys. 2015, 36, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.B.; Liu, J.Y.; Ma, K.F.; Yen, H.Y.; Chen, K.S.; Chen, Y.I.; Chen, C.P. Precursory phenomena associated with the 1999 Chi-chi earthquake in Taiwan as identified under the i-STEP program. Phy. Chem. Earth 2006, 31, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asada, T.; Baba, H.; Kawazoe, M.; Suguira, M. An attempt to delineate very low frequency electromagnetic signals associated with earthquakes. Earth Planets Space 2001, 53, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enomoto, Y.; Shimamoto, T.; Tsutsumi, A.; Hashimoto, H. Transient electric signals prior to rock fracturing: Potential use as an immediate earthquake precursor. In Electromagnetic Phenomena Related to Earthquake Prediction; Hayakawa, M., Fujinawa, Y., Eds.; TERRAPUB: Tokyo, Japan, 1994; pp. 253–259. [Google Scholar]
- Eftaxias, K.; Kapiris, P.; Dologlue, E.; Kopanas, J.; Bogris, N.; Antonopoulos, G.; Peratzakis, A.; Hajicontis, V. EM anomalies before the Kozani earthquake: A study of their behaviour through laboratory experiments. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 69/1–69/4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujinawa, Y.; Takahashi, K.; Matsumoto, T.; Kawakami, N. Experiments to locate sources of earthquake-related VLF electromagnetic signals. Proc. Japan Acad. 1997, 73, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gershenzon, N.; Bambakidis, G. Modeling of seismo-electromagnetic phenomena. Russ. J. Earth Sci. 2001, 3, 247–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warwick, J.; Stoker, C.; Meyer, T. Radio emissions associated with rock fracture: Possible application to the great Chilean earthquake of May 22, 1960. J. Geophys. Res. 1982, 87, 2851–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Liu, B.; Wang, Y. Mechanism of electromagnetic emissions associated with microscopic and macroscopic cracking in rocks. In Electromagnetic Phenomena Related to Earthquake Prediction; Hayakawa, M., Fujinawa, Y., Eds.; Terrapub: Tokyo, Japan, 1994; pp. 523–529. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshino, T.; Sato, H. The study of exciting process of seismogenic emissions at epicentre by magnetic flux based on the statistical analysis. In Electromagnetic Phenomena Related to Earthquake Prediction; Hayakawa, M., Fujinawa, Y., Eds.; Terrapub: Tokyo, Japan, 1994; pp. 631–640. [Google Scholar]
- Enomoto, Y.; Hashimoto, H. Emission of charged particles from indentation fracture of rocks. Nature 1990, 346, 641–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eftaxias, K.; Potirakis, S.M.; Contoyiannis, Y. Four-stage model of earthquake generation in terms of fracture-induced electromagnetic emissions. In Complexity of Seismic Time Series: Measurement and Application; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2018; pp. 437–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsarev, V.A.; Sasaki, H. Low frequency seismogenic electromagnetic radiation: How does it propagate in earth’s crust and where it can be detected? In Atmospheric and Ionospheric Phenomenon Associated with Earthquakes; Hayakawa, M., Ed.; TERRAPUB: Tokyo, Japan, 1999; pp. 383–393. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.P.; Singh, B.; Bansal, V.; Hayakawa, M. VLF electromagnetic noise bursts related to major seismic activities observed at Agra. J. Atmos. Electr. 2000, 20, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.P.; Singh, B.; Mishra, P.K.; Hayakawa, M. On the lithosphere-atmosphere coupling of seism-electromagnetic signals. Radio Sci. 2003, 38, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickolaenko, A.P.; Hayakawa, M. Resonances in the Earth-Ionosphere Cavity; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002; 380p. [Google Scholar]
- Wait, J.R. Electromagnetic Waves in Stratified Media; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshino, T.; Tomizawa, I. LF seismogenic emissions and its application on earthquake prediction. IEICE Tech. Comm. Electromagn. Compat. 1988, 88, 39–45. [Google Scholar]
- Kingsley, S.P. On the possibilities for detecting radio emissions from earthquakes. Nuova C. 1989, 12, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshino, T. Low-frequency seismogenic electromagnetic emissions as precursors to earthquakes and volcanic eruptions in Japan. J. Sci. Explor. 1991, 5, 121–144. [Google Scholar]
- Hayakawa, M.; Sazhin, S. Mid-latitude and plasmaspheric hiss: A review. Planet. Space Sci. 1992, 40, 1325–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshino, T.; Tomizawa, I.; Sugimoto, T. Result of statistical analysis of LF seismogenic emissions as precursors to the earthquake and volcanic eruptions. Res. Lett. Atmos. Electr. 1992, 12, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hata, M.; Takumi, I.; Yabashi, S. A model of earthquake seen by electromagnetic observation- gaseous emission from the Earth as main source of pre-seismic electromagnetic precursor and trigger of followed earthquake. Ann. Geophys. 1998, 16, C1188–C1197. [Google Scholar]
- Oike, K.; Ogawa, T. Electromagnetic radiation from shallow earthquakes observed in the LF range. J. Geomagn. Geoelectr. 1986, 38, 1031–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kapiris, P.; Polygiannakis, J.; Peratzakis, A.; Nomicos, K.; Eftaxias, K. VHF-electromagnetic evidence of the underlying pre-seismic critical stage. Earth Planets Space 2002, 54, 1237–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, M.; Ito, T.; Smirnova, N. Fractal analysis of ULF geomagnetic data associated with the Guam earthquake on August 8, 1993. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1999, 26, 2797–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, M.; Hattori, K.; Nickolaenko, A.P.; Rabinowicz, L.M. Relation between the enery of earthquake swarm and the Hurst exponent of random variations of the geomagnetic field. Phys. Chem. Earth 2004, 29, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potirakis, S.M.; Minadakis, G.; Eftaxias, K. Analysis of electromagnetic pre-seismic emissions using Fisher information and Tsallis entropy. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2012, 391, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petraki, E.; Nikolopoulos, D.; Nomicos, C.; Stonham, J.; Cantzos, D.; Yannakopoulos, P.; Kottou, S. Electromagnetic pre-earthquake precursors: Mechanisms, data and models- A review. Earth Sci. Clim. Chang. 2015, 6, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokhberg, M.B.; Pilipenko, V.A.; Pokhotelov, O.A. Satellite observation of the electromagnetic radiation above the epicentral region of an incipient earthquake. Dokl. Acad. Sci. USSR Earth Sci. Ser. 1983, 268, 5–7. [Google Scholar]
- Larkina, V.I.; Nalivayko, A.V.; Gershenzon, N.I.; Gokhberg, M.B.; Liperovskiy, V.A.; Shalimov, S.L. Observation of VLF emission related with seismic activity on the Intercosmos-19 satellite. Geomagn. Aeron. 1983, 23, 684–687. [Google Scholar]
- Larkina, V.I.; Migulin, V.V.; Molchanov, O.A.; Kharkov, I.P.; Inchin, A.S.; Schvetsova, V.B. Some statistical results on very low frequency radio wave emissions in the upper ionosphere over earthquake zones. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 1989, 57, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrot, M.; Lefeuvre, F. Correlation between GEOS VLF emissions and earthquakes. Ann. Geophys. 1985, 3, 737–748. [Google Scholar]
- Parrot, M.; Mogilevsky, M.M. VLF emissions associated with earthquakes and observed in the ionosphere and magnetosphere. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 1989, 57, 86–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molchanov, O.A.; Mazhaera, O.A.; Golyavin, A.N.; Hayakawa, M. Observation by the Intercosmos-24 satellite of ELF-VLF electromagnetic emissions associated with earthquakes. Ann. Geophys. 1993, 11, 431–440. [Google Scholar]
- Parrot, M. Statistical study of ELF/VLF emissions recorded by low-latitude satellite during seismic events. J. Geophys.Res. 1994, 99, 339–347. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, F.; Hu, Y.; Zhima, Z.; Sun, X.; Lu, C.; Yang, D. The upward propagating ionospheric hiss waves during the seismic time observed by the China seismo-electromagnetic satellite. Front. Astron. Space Sci. 2023, 10, 1127738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hayakawa, M.; Hobara, Y.; Michimoto, K.; Nickolaenko, A.P. The Generation of Seismogenic Anomalous Electric Fields in the Lower Atmosphere, and Its Application to Very-High-Frequency and Very-Low-Frequency/Low-Frequency Emissions: A Review. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 1173. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15101173
Hayakawa M, Hobara Y, Michimoto K, Nickolaenko AP. The Generation of Seismogenic Anomalous Electric Fields in the Lower Atmosphere, and Its Application to Very-High-Frequency and Very-Low-Frequency/Low-Frequency Emissions: A Review. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(10):1173. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15101173
Chicago/Turabian StyleHayakawa, Masashi, Yasuhide Hobara, Koichiro Michimoto, and Alexander P. Nickolaenko. 2024. "The Generation of Seismogenic Anomalous Electric Fields in the Lower Atmosphere, and Its Application to Very-High-Frequency and Very-Low-Frequency/Low-Frequency Emissions: A Review" Atmosphere 15, no. 10: 1173. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15101173
APA StyleHayakawa, M., Hobara, Y., Michimoto, K., & Nickolaenko, A. P. (2024). The Generation of Seismogenic Anomalous Electric Fields in the Lower Atmosphere, and Its Application to Very-High-Frequency and Very-Low-Frequency/Low-Frequency Emissions: A Review. Atmosphere, 15(10), 1173. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15101173






