The Influence of PE Initial Field Construction Method on Radio Wave Propagation Loss and Tropospheric Duct Inversion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. PE Model Theory of Radio Wave Propagation
2.1. Wide Angle PE Wave Propagation Model
2.2. Gaussian Beam Pattern
2.3. Half-Wave Dipole Pattern
3. Difference Analysis of Two Models
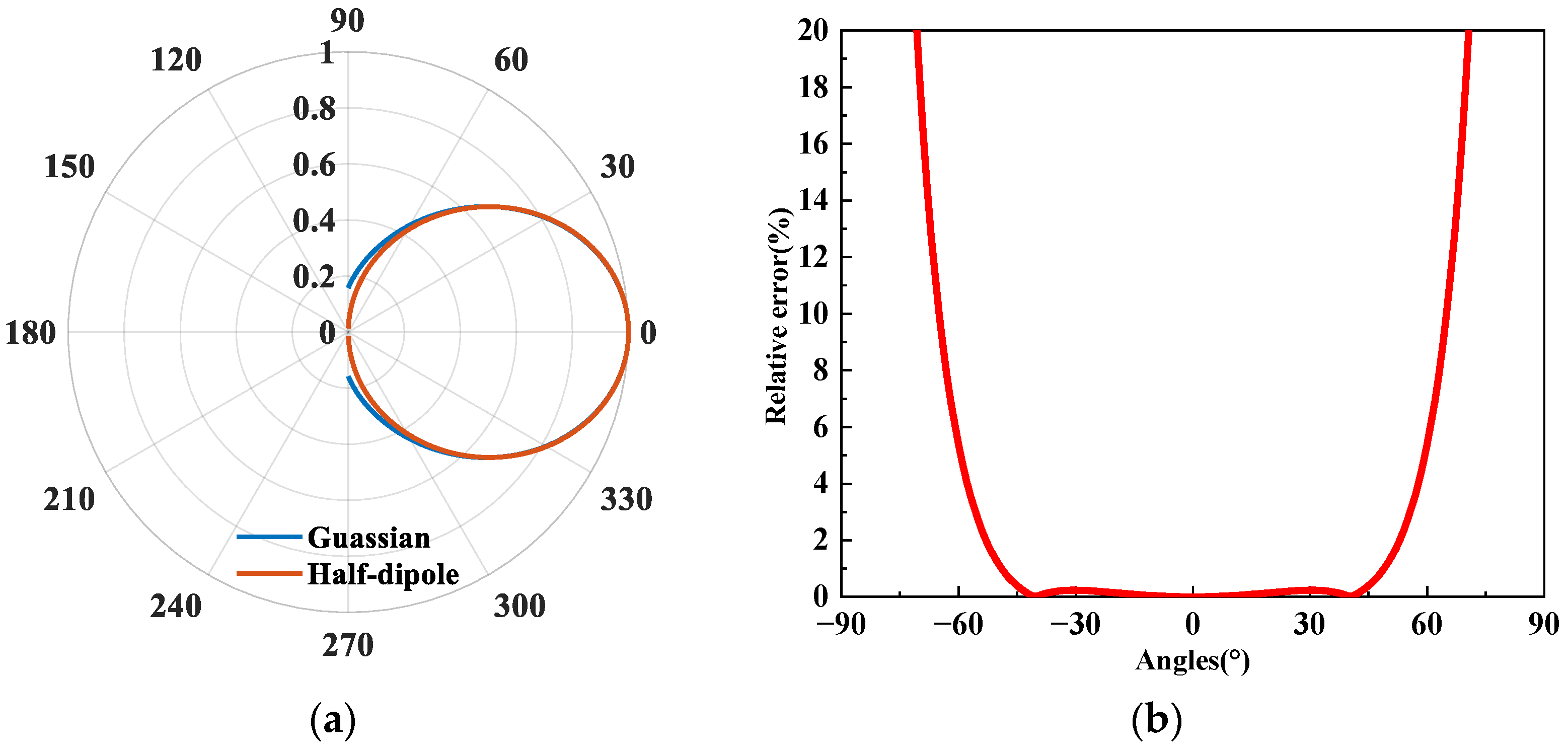
3.1. Antenna Pattern
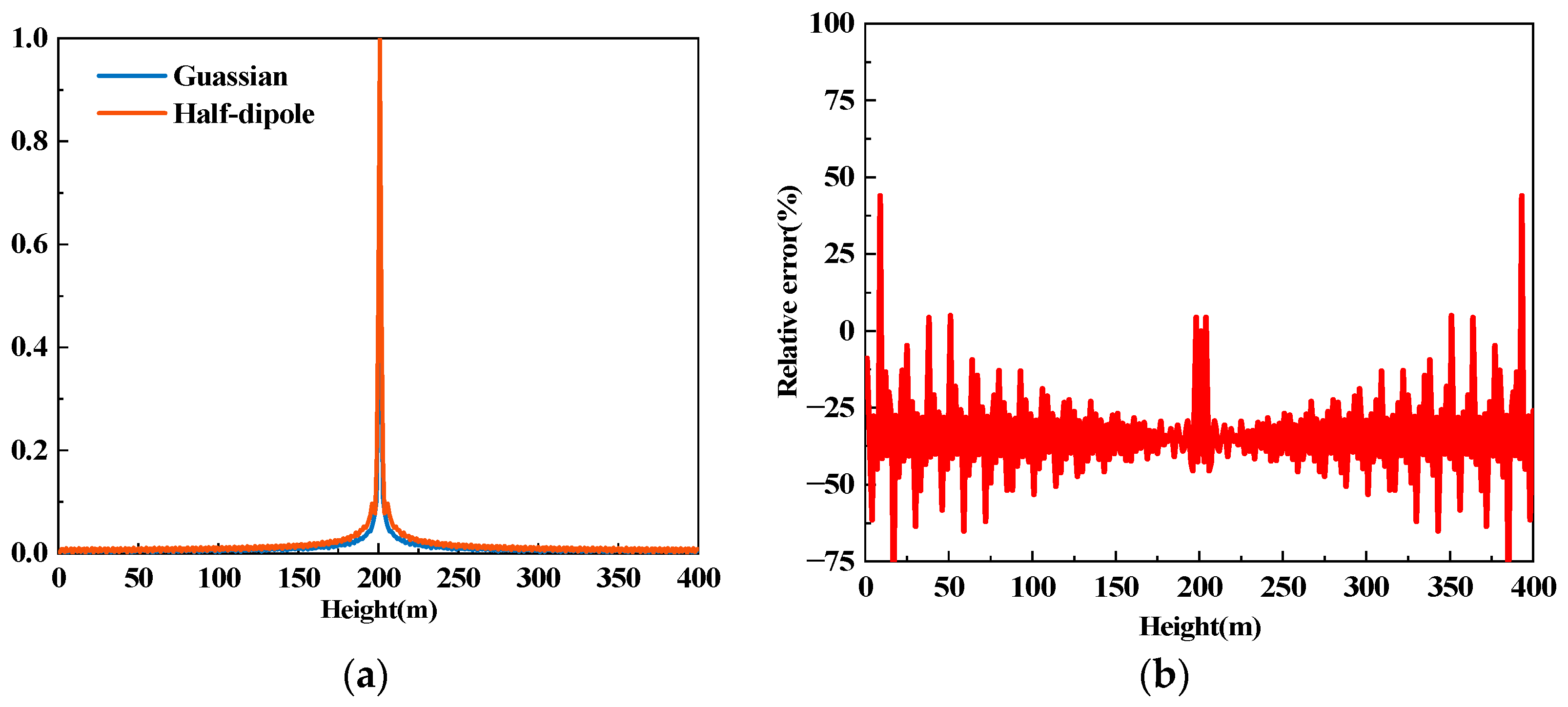
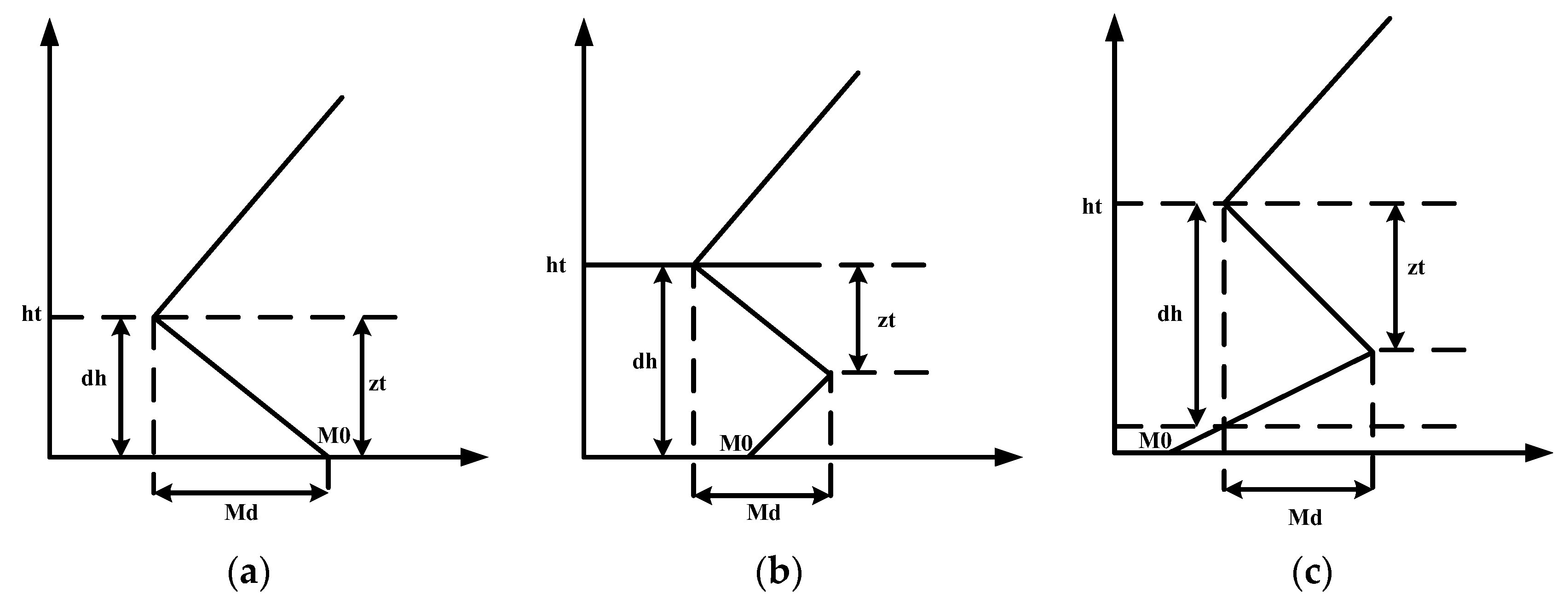
3.2. The Initial Field
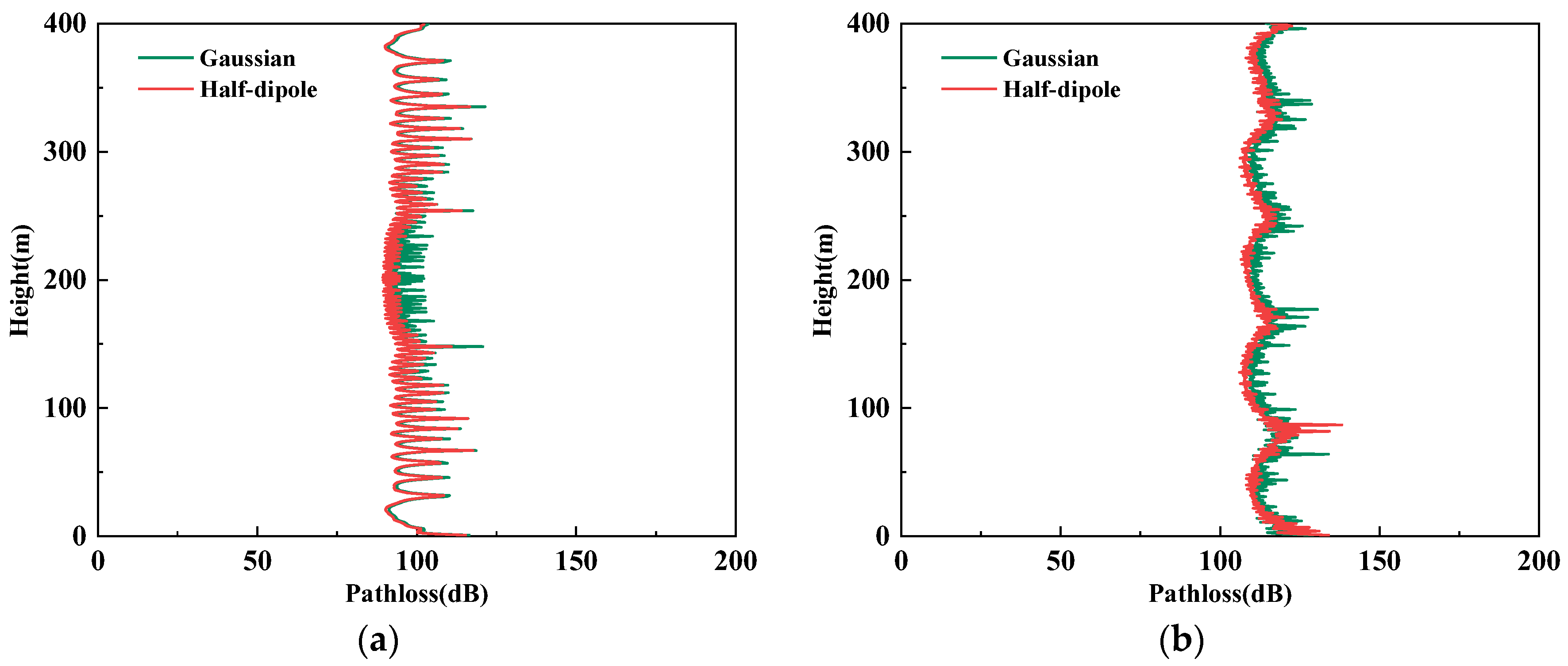
3.3. Propagation Loss Simulated with Wide-Angle PE Method
4. Evaluation Based on Experimental Data
4.1. Radio Wave Propagation Simulation
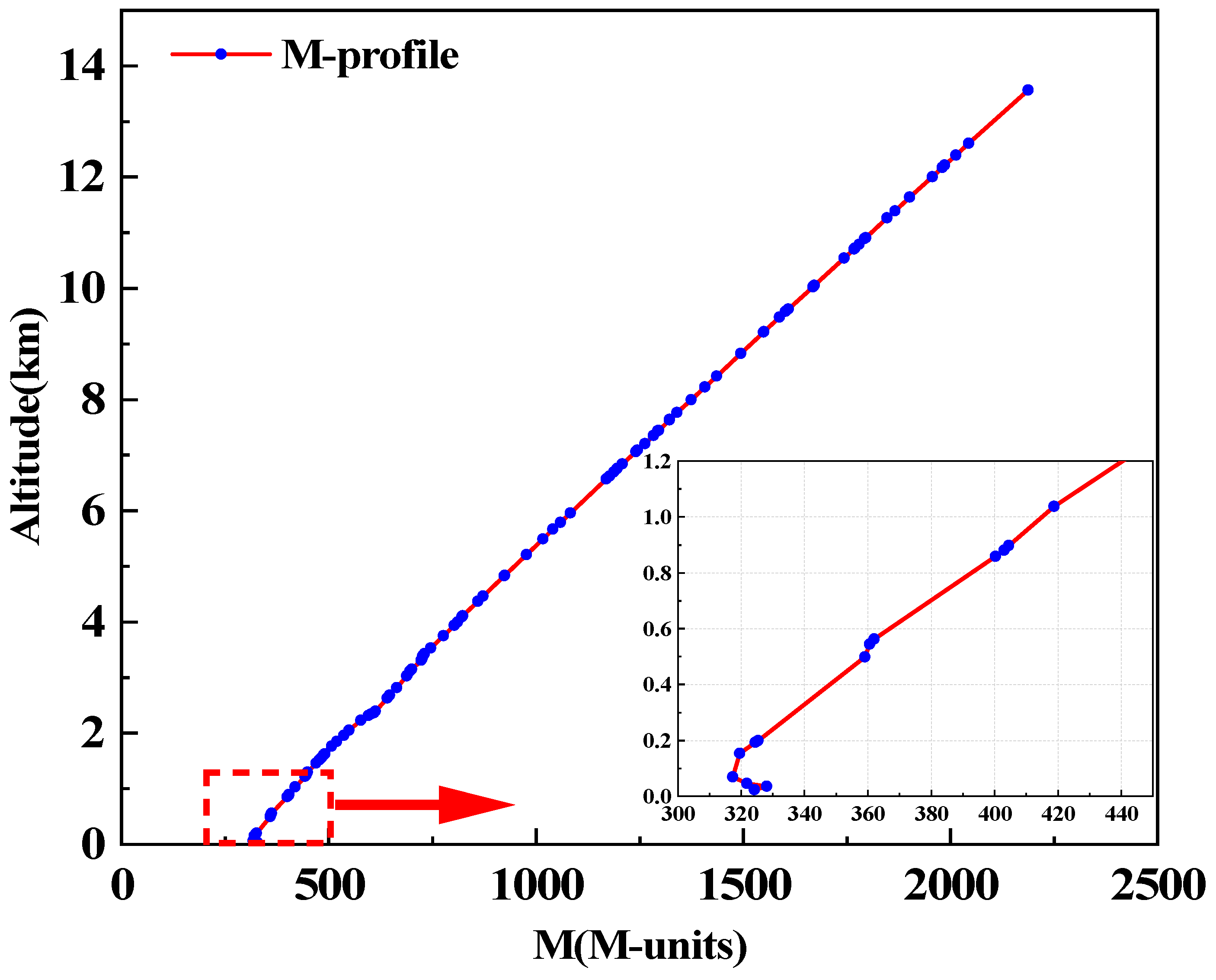
4.1.1. Atmospheric Structure
4.1.2. Underlying Surface Topographic Profile
4.1.3. Propagation Loss Calculation Results
4.2. Experimental Test Results of Radio Wave Propagation Loss
4.3. Differential Analysis
5. Inversion of Atmospheric Refractive Index Profile
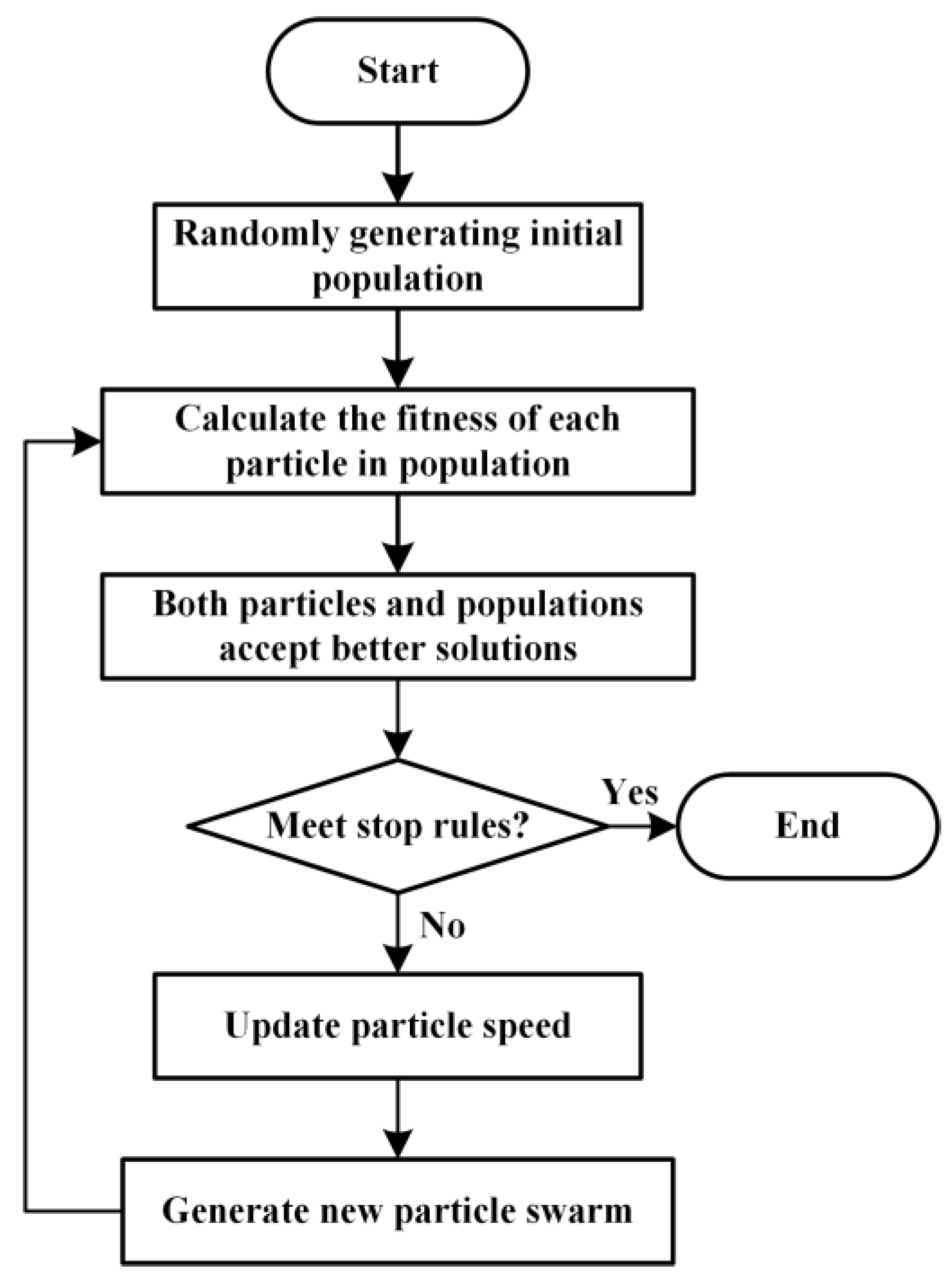
5.1. Inversion Algorithm
5.2. Inversion Results Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Levy, M.F. Diffraction Studies in Urban Environment with Wide-Angle Parabolic Equation Method. Electron. Lett. 1992, 28, 1491–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.G.; Zhou, H.K.; Hu, W.T.; Duan, K.; Cheng, R.; Huang, L.; Guo, X.; Wang, H.; Cai, H. An inversion method of anomalous atmospheric refractive environment. Chin. J. Radio Sci. 2022, 37, 222–228. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hardin, R.H.; Tappert, F.D. Applications of the Split-Step Fourier Method to the Numerical Solution of Nonlinear and Variable Coefficient Wave Equations. SIAM Rev. Chron. 1973, 15, 423. [Google Scholar]
- Claerbout, J.F. Fundamentals of Geophysical Data Processing with Application to Petroleum Prospect; McGraw-Hill Press: New York, NY, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Feit, M.D.; Fleck, J.A. Light Propagation in Graded-Index Optical Fibers. Appl. Opt. 1978, 17, 3990–3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomson, D.J.; Chapman, N.R. A Wide-Angle Split-Step Algorithm for the Parabolic Equation. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1983, 74, 1848–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, R.R. The rational approximation to the acoustic wave equation with bottom interaction. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1984, 76, 1764–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, M.F. Parabolic Equation Methods for Electromagnetic Wave Propagation; Institution of Electrical Engineers: London, UK, 2000; pp. 40–41. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, B.; Carin, L. A Hybrid (Parabolic Equation)-(Gaussian Beam) Algorithm for Wave Propagation through Large Inhomogeneous regions. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1998, 46, 700–709. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Sarris, C.D. A Gaussian Beam Approximation Approach for Embedding Antennas into Vector Parabolic Equation-Based Wireless Channel Propagation Models. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2017, 65, 1301–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L’Hour, C.A.; Fabbro, V.; Chabory, A.; Sokoloff, J. 2-D Propagation Modeling in Inhomogeneous Refractive Atmosphere Based on Gaussian Beams Part II: Application to Radio Occultation. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2019, 67, 5487–5496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldsmith, P.F. Quasioptical Systems: Gaussian Beam Quasioptical Propagation and Applications; IEEE Press: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Trappe, N.; Murphy, J.A.; Withington, S. The Gaussian Beam Mode Analysis of Classical Phase Aberrations in Diffraction-Limited Optical Systems. Eur. J. Phys. 2003, 24, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Hu, J.; Zhong, K.; Sun, Y.; Xiao, X.; Zhu, G. MIMO Radar Transmit Waveform Design for Beampattern Matching via Complex Circle Optimization. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apaydin, G.; Sevgi, L. Groundwave Propagation at Short Ranges and Accurate Source Modeling. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 2013, 55, 244–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, C.G.; Zhong, M.; Wang, Y.; Yang, M. Radio Wave Propagation Path Loss in the Irregular Terrain environments. In Proceedings of the 2009 3rd IEEE International Symposium on Microwave, Antenna, Propagation and EMC Technologies for Wireless Communications, Beijing, China, 27–29 October 2009; pp. 627–630. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, F.J. On the Use of Windows for Harmonic Analysis with the Discrete Fourier Transform. Proc. IEEE 1978, 66, 51–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuttler, J.R.; Huffaker, J.D. Solving the Parabolic Wave Equation with a Rough Surface Boundary Condition. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1993, 94, 2451–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.B.; Mao, J.J.; Cai, S.L. Green’s Function of Wide-angle Parabolic Equation and Its Applications. J. Electron. 2006, 34, 517–521. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.Z. Mobile Communication Radio Wave Propagation; People’s Posts and Telecommunications Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2002. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Barrios, A.E. A terrain parabolic equation model for propagation in the troposphere. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1994, 42, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.T.; Liu, C.G.; Lin, F.J.; Zhang, Y.S.; Guo, X.M. Characteristics of atmospheric ducts and its impact on FM broadcasting. J. Radio Sci. 2020, 35, 856–867. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dupleich, D.; Müller, R.; Landmann, M.; Shinwasusin, E.A.; Saito, K.; Takada, J.I.; Luo, J.; Thomä, R.; Del Galdo, G. Multi-Band Propagation and Radio Channel Characterization in Street Canyon Scenarios for 5G and Beyond. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 160385–160396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


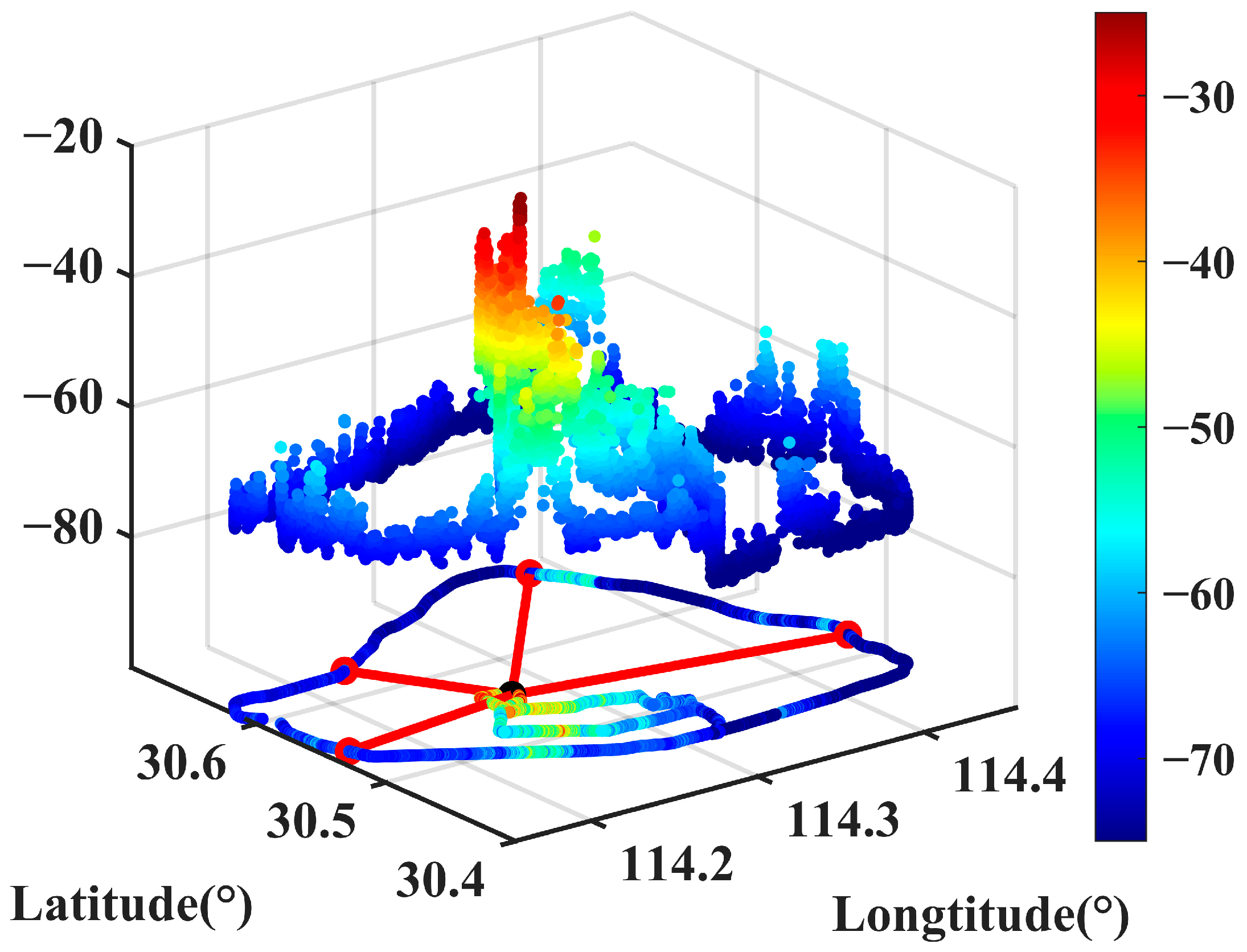
| Longitude (°) | Latitude (°) | Distance (km) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| transmitter | 114.2751 | 30.5580 | 0 |
| point 1 | 114.2320 | 30.6318 | 9.19 |
| point 2 | 114.3835 | 30.6835 | 17.39 |
| point 3 | 114.1663 | 30.5440 | 10.54 |
| point 4 | 114.4527 | 30.5267 | 17.36 |
| Height (m) | Point 1 (dB) | Point 2 (dB) | Point 3 (dB) | Point 4 (dB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 129.0 | 136.7 | 134.2 | 149.9 |
| 2 | 132.1 | 132.5 | 134.8 | 147.0 |
| 3 | 125.6 | 128.2 | 125.3 | 147.7 |
| 4 | 120.0 | 130.6 | 119.2 | 145.5 |
| Height (m) | Point 1 (dB) | Point 2 (dB) | Point 3 (dB) | Point 4 (dB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 126.3 | 131.3 | 130.1 | 148.6 |
| 2 | 133.8 | 128.0 | 126.6 | 147.5 |
| 3 | 124.5 | 125.5 | 122.7 | 151.8 |
| 4 | 119.1 | 124.6 | 116.7 | 147.5 |
| Point | Gaussian (dB) | Half-Wave (dB) | Measured Value (dB) | Terrain Mean Height (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 126.3 | 129.0 | 134.0 | 16.14 |
| 2 | 131.3 | 136.7 | 141.2 | 5.13 |
| 3 | 130.1 | 134.2 | 135.5 | 19.61 |
| 4 | 148.6 | 149.9 | 142.9 | 22.94 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Maximum number of iterations | 50 |
| Number of particles | 100 |
| Individual learning factor | 1 |
| Social learning factor | 1 |
| Maximum inertia factor | 0.9 |
| Minimum inertia factor | 0.4 |
| Parameter | Gaussian | Half-Wave | Actual Atmospheric Parameter |
|---|---|---|---|
| (M-units) | 320.4 | 323.3 | 324 |
| (M-units) | 10 | 12 | 14 |
| (m) | 85.1 | 84.8 | 82 |
| (m) | 52.4 | 49.5 | 47 |
| (m) | 85.1 | 84.8 | 82 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, R.-S.; Liu, C.-G.; Cao, L.-F.; Xiao, T.; Tang, G.-P.; Huang, L.-F.; Wang, H.-G. The Influence of PE Initial Field Construction Method on Radio Wave Propagation Loss and Tropospheric Duct Inversion. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15010046
Cheng R-S, Liu C-G, Cao L-F, Xiao T, Tang G-P, Huang L-F, Wang H-G. The Influence of PE Initial Field Construction Method on Radio Wave Propagation Loss and Tropospheric Duct Inversion. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(1):46. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15010046
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Run-Sheng, Cheng-Guo Liu, Li-Feng Cao, Tong Xiao, Guang-Pu Tang, Li-Feng Huang, and Hong-Guang Wang. 2024. "The Influence of PE Initial Field Construction Method on Radio Wave Propagation Loss and Tropospheric Duct Inversion" Atmosphere 15, no. 1: 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15010046
APA StyleCheng, R.-S., Liu, C.-G., Cao, L.-F., Xiao, T., Tang, G.-P., Huang, L.-F., & Wang, H.-G. (2024). The Influence of PE Initial Field Construction Method on Radio Wave Propagation Loss and Tropospheric Duct Inversion. Atmosphere, 15(1), 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15010046







