Is the Invasive Plant Amaranthus spinosus L. More Competitive than the Native Plant A. tricolor L. When Exposed to Acid Deposition with Different Sulfur–Nitrogen Ratios?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Determination of the Functional Indices, and Biochemical Constituents and Osmolytes Indices of the Two Amaranthus Species
2.3. Statistical Analysis
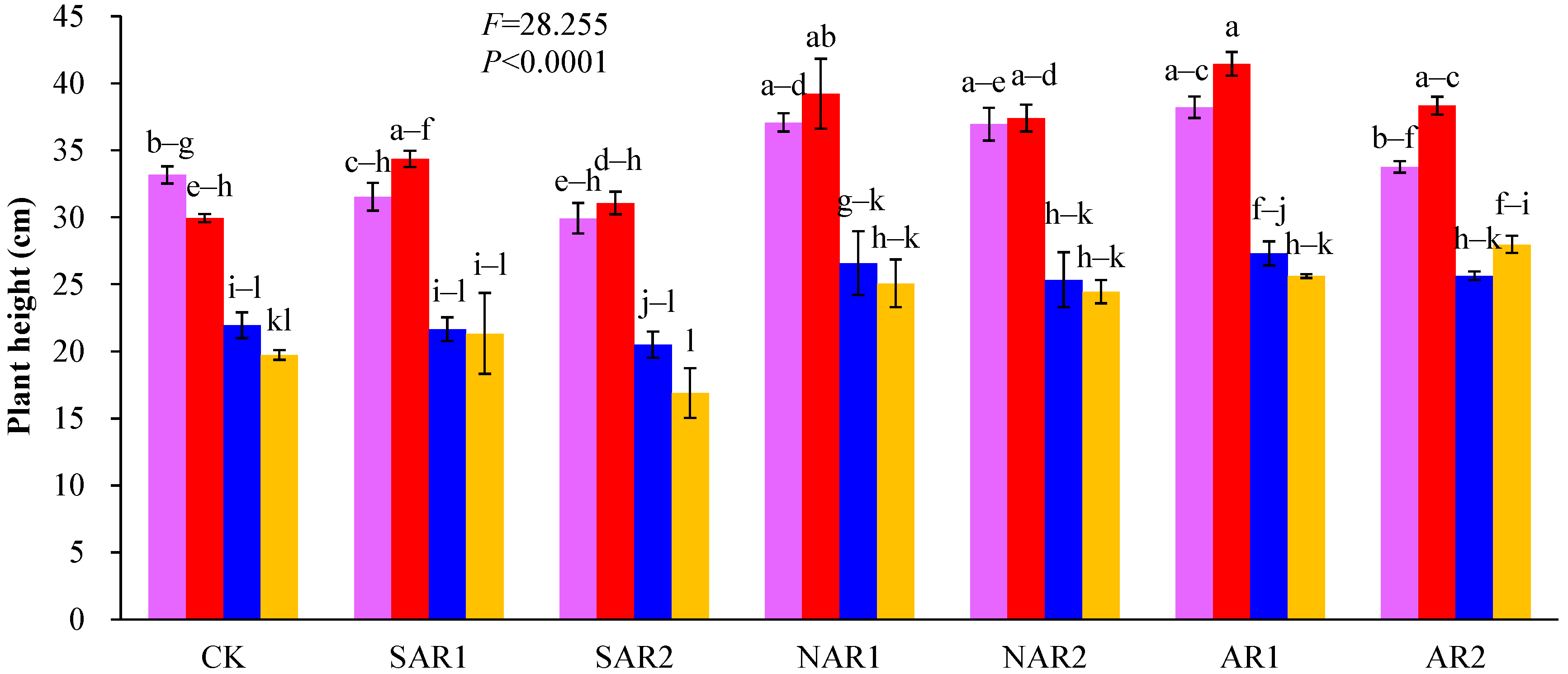
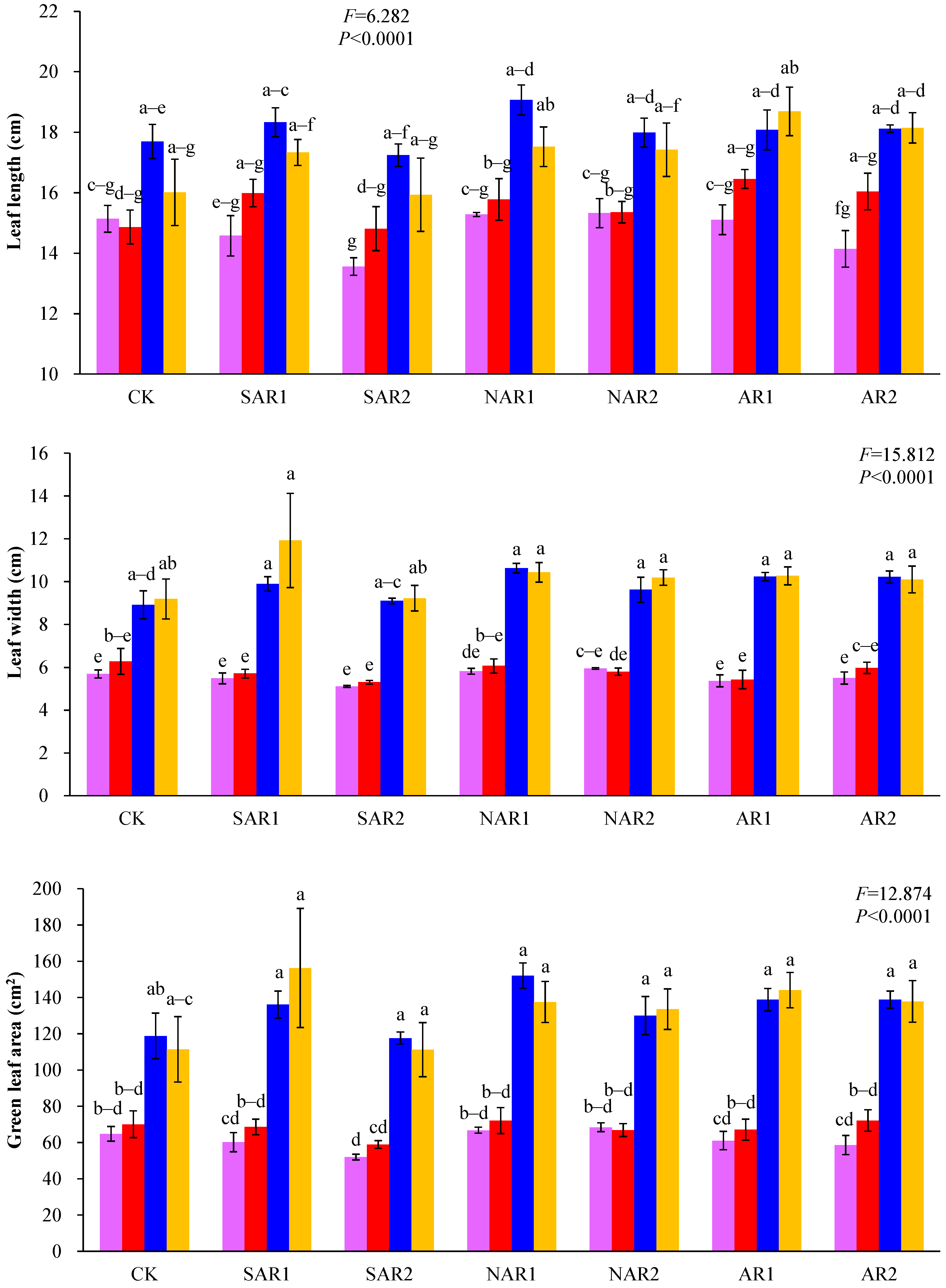
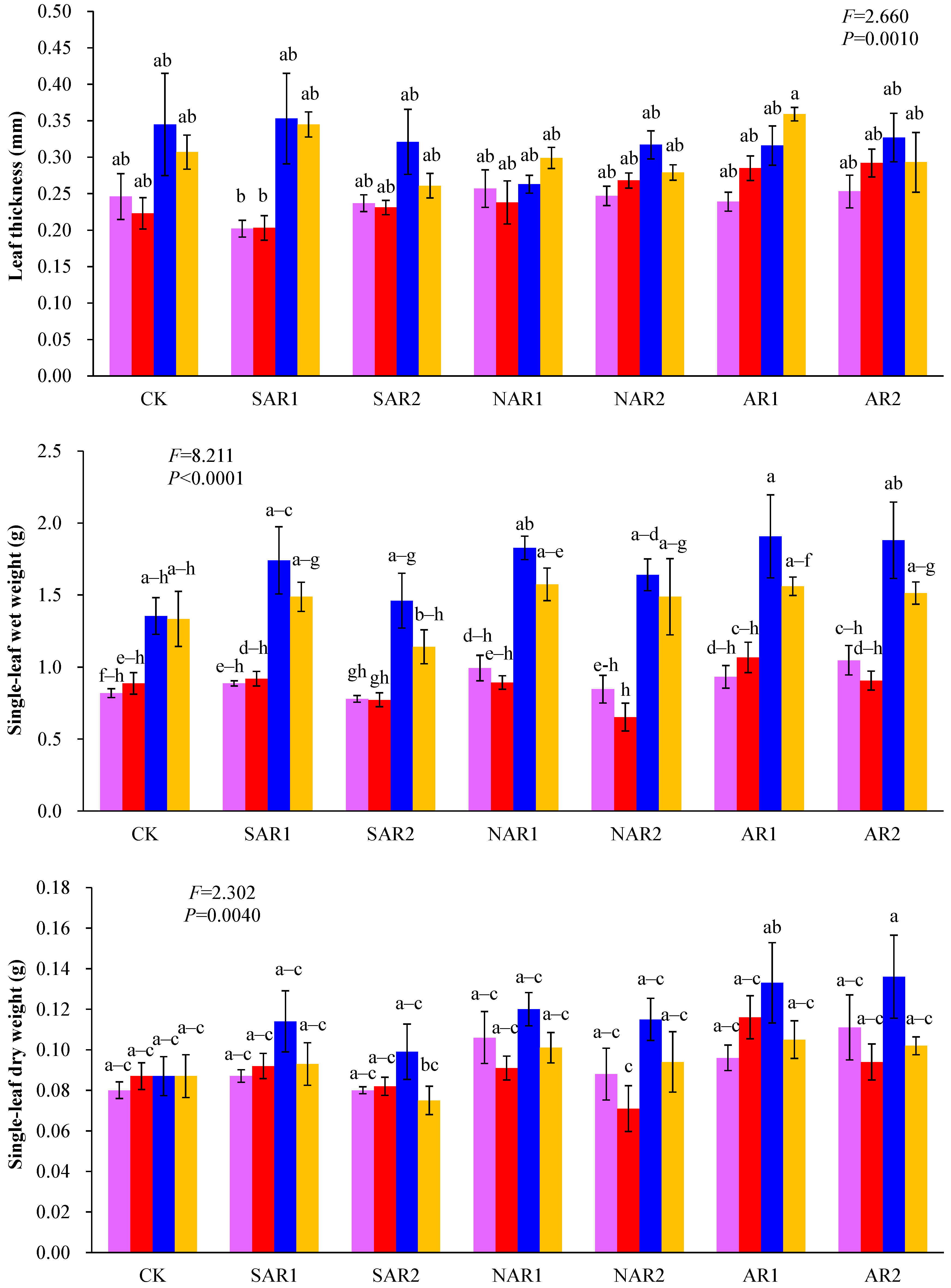
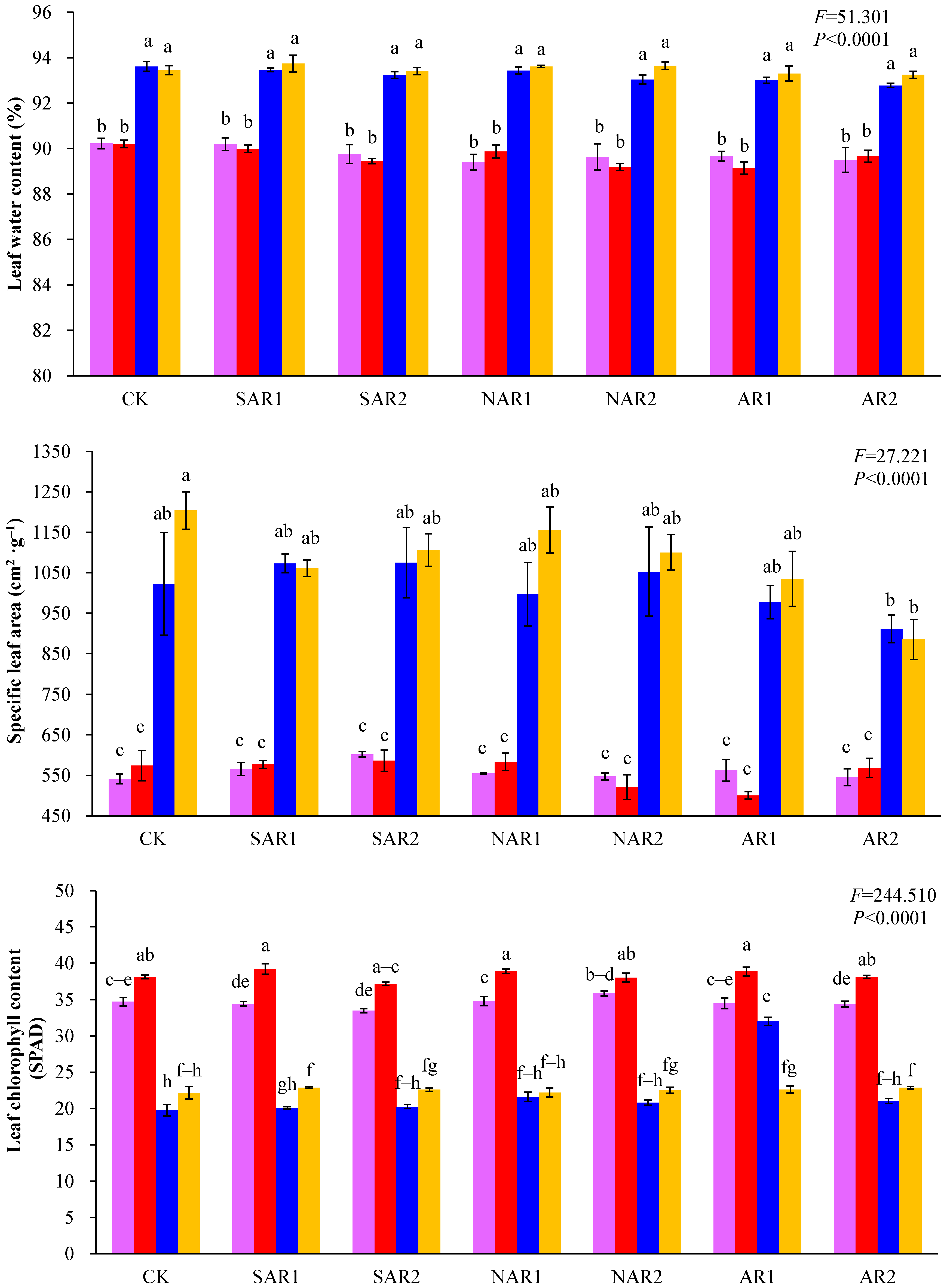
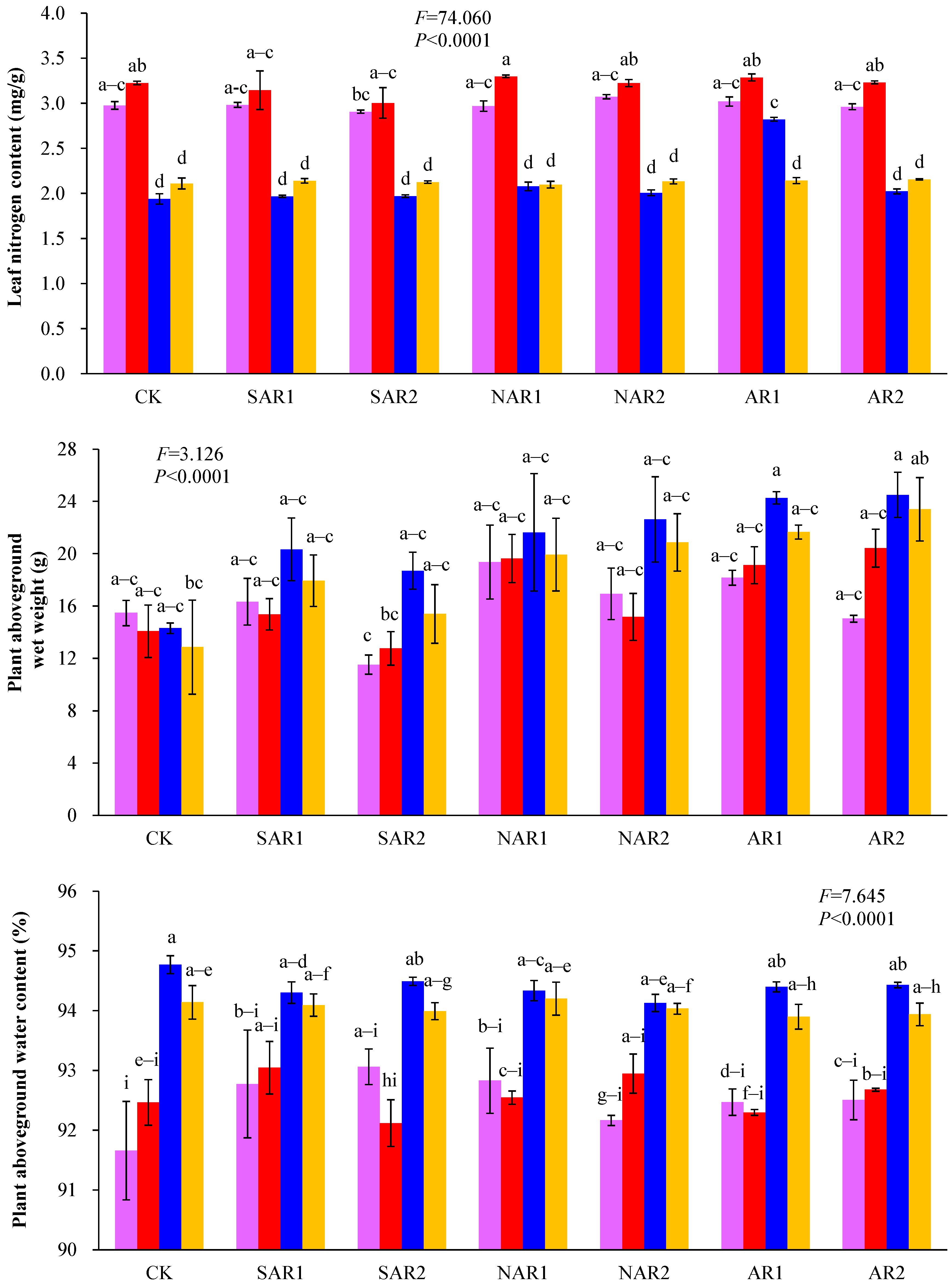
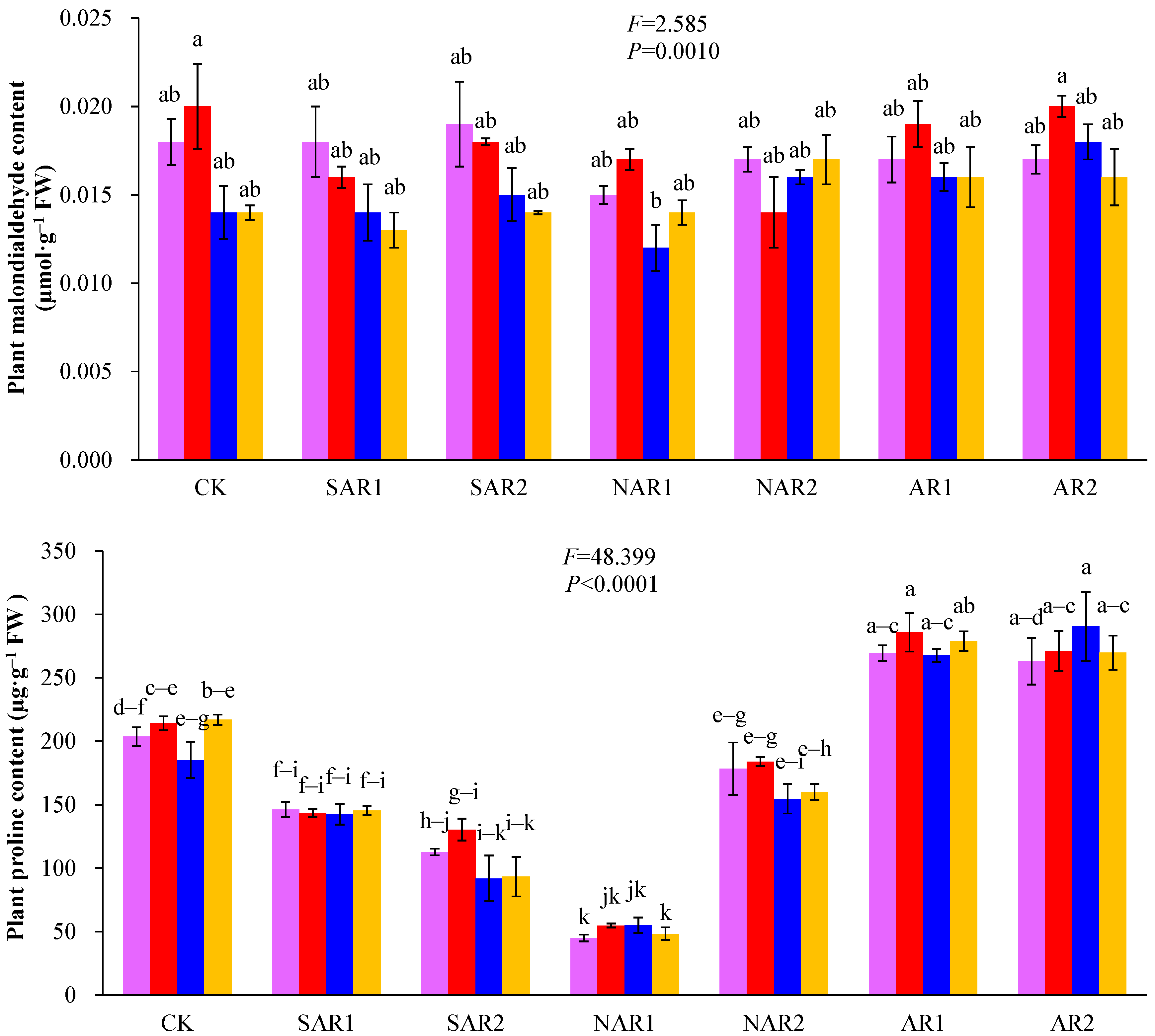
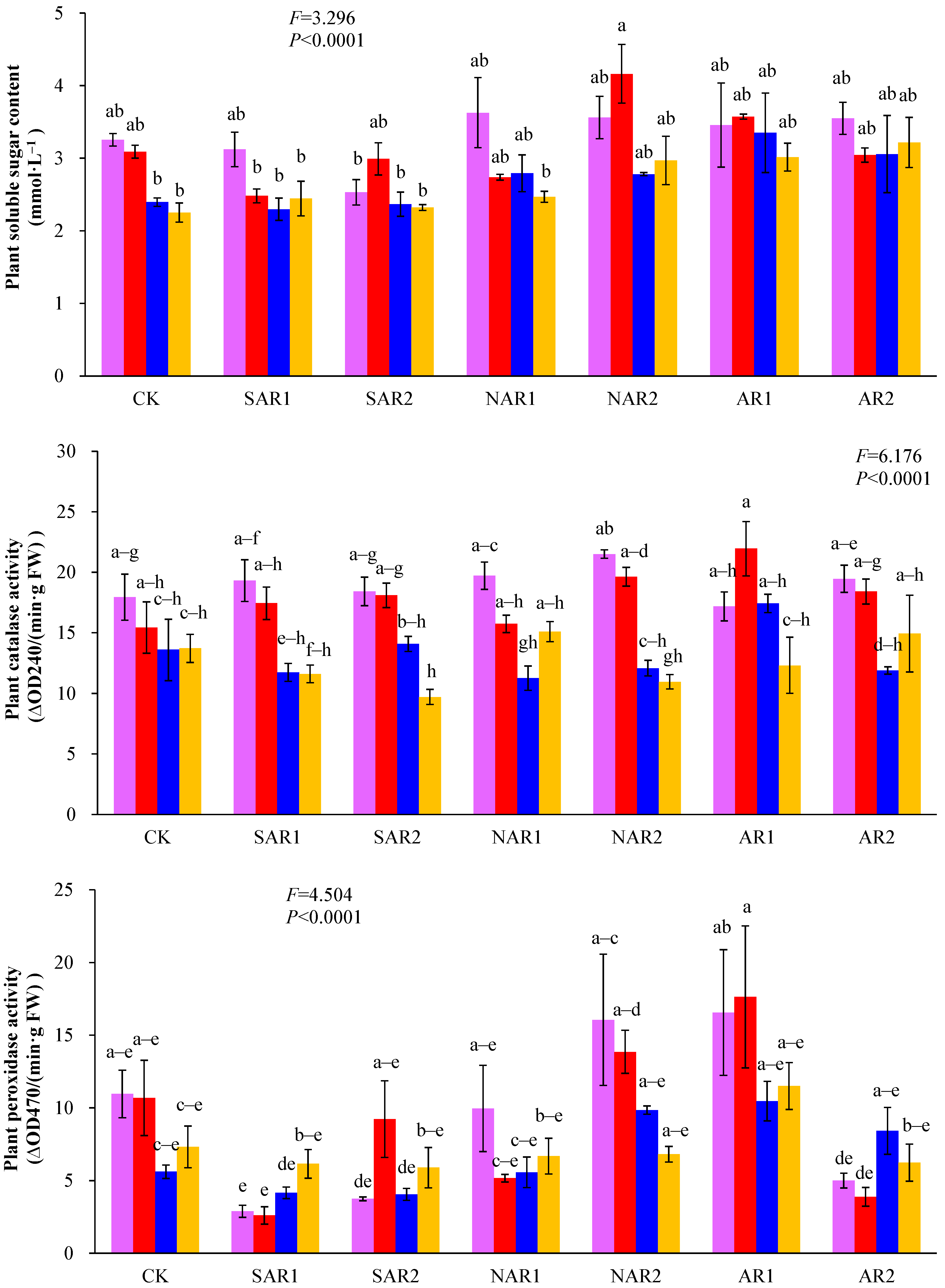
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Williams, R.J.; Dunn, A.M.; da Costa, L.M.; Hassall, C. Climate and habitat configuration limit range expansion and patterns of dispersal in a non-native lizard. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 3332–3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowie, B.W.; Byrne, M.J.; Witkowski, E.T.F. Small-scale insights into the above- and below-ground invasion dynamics of Parthenium hysterophorus in a South African savanna: The potential role of stocking rate. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2022, 144, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Cheng, H.Y.; Wang, S.; Wei, M.; Du, D.L. Plant community and the influence of plant taxonomic diversity on community stability and invasibility: A case study based on Solidago canadensis L. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 768, 144518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beshai, R.A.; Truong, D.A.; Henry, A.K.; Sorte, C.J.B. Biotic resistance or invasional meltdown? Diversity reduces invasibility but not exotic dominance in southern California epibenthic communities. Biol. Invasions 2023, 25, 533–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czortek, P.; Królak, E.; Borkowska, L.; Bielecka, A. Effects of surrounding landscape on the performance of Solidago canadensis L. and plant functional diversity on heavily invaded post-agricultural wastelands. Biol. Invasions 2023, 25, 2477–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.B.; Liu, W.X.; Wan, F.H.; Liu, B. An invasive aster (Ageratina adenophora) invades and dominates forest understories in China: Altered soil microbial communities facilitate the invader and inhibit natives. Plant Soil 2007, 294, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, J.G.; de la Riva, E.G.; Funk, J.L.; Vila, M. Functional segregation of resource-use strategies of native and invasive plants across Mediterranean biome communities. Biol. Invasions 2021, 23, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheppard, C.S. Relative performance of co-occurring alien plant invaders depends on traits related to competitive ability more than niche differences. Biol. Invasions 2019, 21, 1101–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helsen, K.; Matsushima, H.; Somers, B.; Honnay, O. A trait-based approach across the native and invaded range to understand plant invasiveness and community impact. Oikos 2021, 130, 1001–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.L.; Cheng, H.Y.; Wang, S.; Wei, M.; Wang, C.Y.; Du, D.L. Drought may be beneficial to the competitive advantage of Amaranthus spinosus. J. Plant Ecol. 2022, 15, 494–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Wu, B.D.; Jiang, K.; Zhou, J.W. Differences in functional traits between invasive and native Amaranthus species under simulated acid deposition with a gradient of pH levels. Acta Oecol. 2018, 89, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljubojevic, M.; Tomic, M.; Simikic, M.; Savin, L.; Narandzic, T.; Pusic, M.; Grubac, M.; Vejnovic, S.; Marinkovic, M. Koelreuteria paniculata invasiveness, yielding capacity and harvest date influence on biodiesel feedstock properties. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 295, 113102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Fu, Z.H.; Zhang, B.; Zhai, L.; Meng, M.J.; Lin, J.; Zhuang, J.Y.; Wang, G.G.; Zhang, J.C. Effects of sulfuric, nitric, and mixed acid rain on Chinese fir sapling growth in Southern China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 160, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, S.S.; Xu, Z.L.; Li, Y.; Li, C.; Yu, Y.L.; Wang, C.Y.; Du, D.L. What modulates the impacts of acid rain on the allelopathy of the two Asteraceae invasives? Ecotoxicology 2023, 32, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.Y.; Wang, S.; Wei, M.; Yu, Y.L.; Wang, C.Y. Effect of leaf water extracts of four Asteraceae alien invasive plants on germination performance of Lactuca sativa L. under acid deposition. Plant Ecol. 2021, 222, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dentener, F.; Drevet, J.; Lamarque, J.F.; Bey, I.; Eickhout, B.; Fiore, A.M.; Hauglustaine, D.; Horowitz, L.W.; Krol, M.; Kulshrestha, U.C.; et al. Nitrogen and sulfur deposition on regional and global scales: A multimodel evaluation. GBioC 2006, 20, GB4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.L.; He, N.P.; Wang, Q.F.; Zhu, J.X.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y.H.; Jia, Y.L.; Yu, G.R. Development of atmospheric acid deposition in China from the 1990s to the 2010s. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Zhao, Y.H.; Liu, X.J.; Dore, A.J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, L.; Cheng, M.M. Atmospheric nitrogen deposition in the Yangtze River basin: Spatial pattern and source attribution. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 232, 546–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.J.; Qv, M.X.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Cui, M.H.; Zhang, H.Z. Simulated sulfuric and nitric acid rain inhibits leaf breakdown in streams: A microcosm study with artificial reconstituted fresh water. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 196, 110535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, W.R.; Wang, L.; Xie, D.J.; Huo, W.T.; Wu, Y.W.; Zhang, J.C. Comparative effects of sulfuric and nitric acid rain on litter decomposition and soil microbial community in subtropical plantation of Yangtze River Delta region. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601–602, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.Y.; Wang, S.; Wei, M.; Yu, Y.L.; Wang, C.Y. Alien invasive plant Amaranthus spinosus mainly altered the community structure instead of the α diversity of soil N-fixing bacteria under drought. Acta Oecol. 2021, 113, 103788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Yan, X.L.; Li, H.R.; Du, C.; Ma, J.S. Composition, time of introduction and spatial-temporal distribution of naturalized plants in East China. Biodivers. Sci. 2021, 29, 428–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, V. Evaluation of analgesic activity of Amaranthus spinosus Linn. leaves in mice. J. Pharm. Res. 2010, 3, 3088. [Google Scholar]
- Prajitha, V.; Thoppil, J. Genotoxic and antigenotoxic potential of the aqueous leaf extracts of Amaranthus spinosus Linn. using Allium cepa assay. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2016, 102, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odero, D.C.; Wright, A.L. Preemergence and postemergence spiny amaranth (Amaranthus spinosus) and common lambsquarters (Chenopodium album) control in lettuce on organic soils. Weed Technol. 2022, 36, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Wu, H.P. Zhenjiang Yearbook: Overview of Zhenjiang; Organized by Zhenjiang Municipal People’s Government & Written by Zhenjiang Local Records Office; Yu, W., Ye, Z.G., Sun, W.Y., Yang, Z.H., Zong, C.J., Qian, J.J., Pan, Y., Eds.; Publishing House of Local Records: Beijing, China, 2020; pp. 14–15. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, H.Y.; Wei, M.; Wang, S.; Wu, B.D.; Wang, C.Y. Atmospheric N deposition alleviates the unfavorable effects of drought on wheat growth. Braz. J. Bot. 2020, 43, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wei, M.; Cheng, H.Y.; Wu, B.D.; Du, D.L.; Wang, C.Y. Indigenous plant species and invasive alien species tend to diverge functionally under heavy metal pollution and drought stress. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 205, 111160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L. Experimental Guidance of Plant Physiology Module, 1st ed.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.E. Experimental Methods and Techniques Commonly Used in Ecology; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Hodges, D.M.; DeLong, J.M.; Forney, C.F.; Prange, R.K. Improving the thiobarbituric acid-reactive-substances assay for estimating lipid peroxidation in plant tissues containing anthocyanin and other interfering compounds. Planta 1999, 207, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Luo, Q.X.; Tian, Y.; Meng, F.J. Physiological and proteomic analyses of the drought stress response in Amygdalus Mira (Koehne) Yü et Lu roots. BMC Plant Biol. 2017, 17, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.F.; Guo, W.H.; Ding, W.J.; Du, N.; Luo, Y.J.; Liu, J.; Xu, F.; Wang, R.Q. Competitive interaction between the exotic plant Rhus typhina L. and the native tree Quercus acutissima Carr. in Northern China under different soil N:P ratios. Plant Soil 2013, 372, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Wang, R.; Yuan, Y.; Liang, X.; Liu, J. Effects of nitrogen deposition on growth and relationship of Robinia pseudoacacia and Quercus acutissima seedlings. Dendrobiology 2012, 67, 3–13. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, B.D.; Zhang, H.S.; Jiang, K.; Zhou, J.W.; Wang, C.Y. Erigeron canadensis affects the taxonomic and functional diversity of plant communities in two climate zones in the North of China. Ecol. Res. 2019, 34, 535–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Cheng, H.Y.; Wu, B.D.; Jiang, K.; Wang, S.; Wei, M.; Du, D.L. The functional diversity of native ecosystems increases during the major invasion by the invasive alien species, Conyza canadensis. Ecol. Eng. 2021, 159, 106093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Li, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhong, S.; Xu, Z.; Yu, Y.; Du, D.; Wang, C. Photosynthetic capacity of Erigeron canadensis L. may be more critical to its growth performance than photosynthetic area. Biologia 2023, 78, 1315–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, H.Y.; Zhong, Y.D.; Huang, J.G.; Fu, X.F.; Wang, L.H.; Teng, W.C. Growth and physiological response of an endangered tree, Horsfieldia hainanensis merr., to simulated sulfuric and nitric acid rain in southern China. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 144, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, W.; Meng, M.; Fu, Z.; Xu, L.; Zha, Y.; Yue, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, J. Comparative effects of simulated acid rain of different ratios of SO42− to NO3− on fine root in subtropical plantation of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 618, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.Y.; Xiao, H.G.; Zhao, L.L.; Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, F.; Shi, Y.C.; Du, D.L. The allelopathic effects of invasive plant Solidago canadensis on seed germination and growth of Lactuca sativa enhanced by different types of acid deposition. Ecotoxicology 2016, 25, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, W.H.; Liu, T.W.; Wu, F.H.; Zheng, H.L. Photosynthetic and antioxidant responses of Liquidambar formosana and Schima superba seedlings to sulfuric-rich and nitric-rich simulated acid rain. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 64, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, C.L.; Bossdorf, O.; Muth, N.Z.; Gurevitch, J.; Pigliucci, M. Jack of all trades, master of some? On the role of phenotypic plasticity in plant invasions. Ecol. Lett. 2006, 9, 981–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, A.M.; Jennions, M.; Nicotra, A.B. Do invasive species show higher phenotypic plasticity than native species and, if so, is it adaptive? A meta-analysis. Ecol. Lett. 2011, 14, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matzek, V. Trait values, not trait plasticity, best explain invasive species’ performance in a changing environment. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
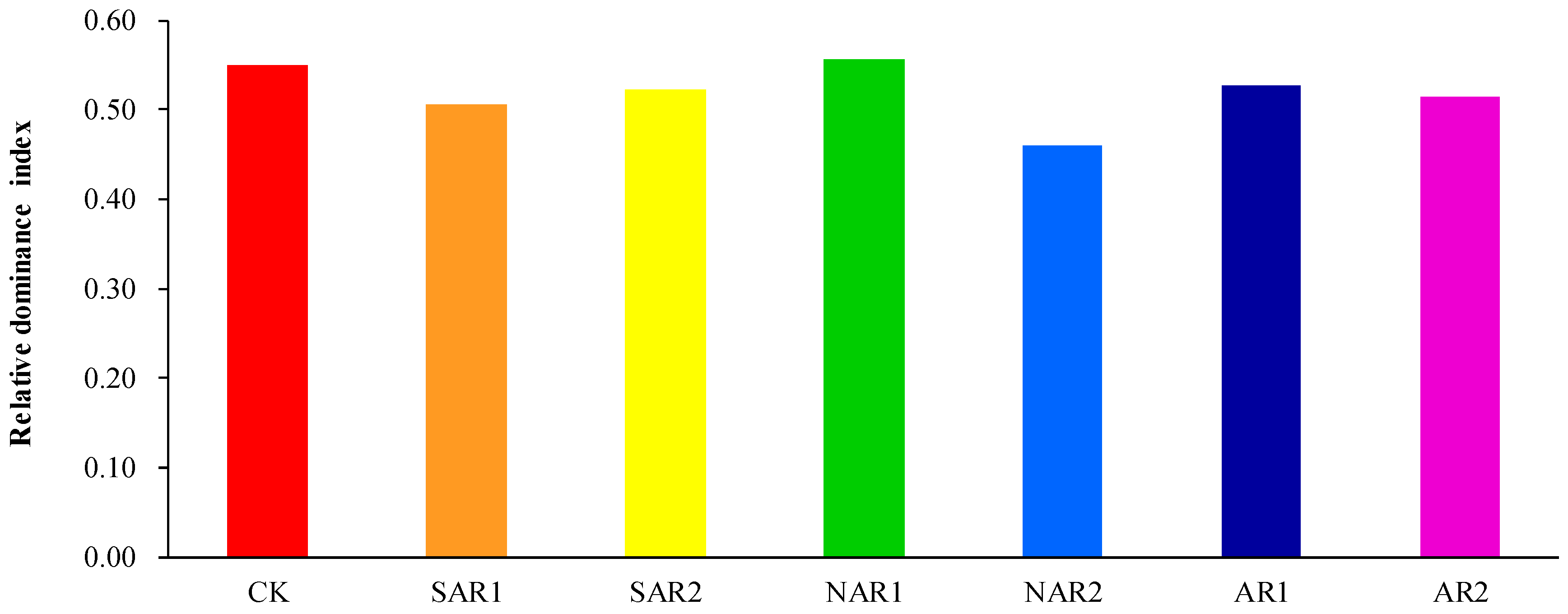
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Li, C.; Zhong, S.; Xu, Z.; Liu, J.; Xu, Z.; Zhu, M.; Wang, C.; Du, D. Is the Invasive Plant Amaranthus spinosus L. More Competitive than the Native Plant A. tricolor L. When Exposed to Acid Deposition with Different Sulfur–Nitrogen Ratios? Atmosphere 2024, 15, 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15010029
Li Y, Li C, Zhong S, Xu Z, Liu J, Xu Z, Zhu M, Wang C, Du D. Is the Invasive Plant Amaranthus spinosus L. More Competitive than the Native Plant A. tricolor L. When Exposed to Acid Deposition with Different Sulfur–Nitrogen Ratios? Atmosphere. 2024; 15(1):29. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15010029
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yue, Chuang Li, Shanshan Zhong, Zhelun Xu, Jun Liu, Zhongyi Xu, Mawei Zhu, Congyan Wang, and Daolin Du. 2024. "Is the Invasive Plant Amaranthus spinosus L. More Competitive than the Native Plant A. tricolor L. When Exposed to Acid Deposition with Different Sulfur–Nitrogen Ratios?" Atmosphere 15, no. 1: 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15010029
APA StyleLi, Y., Li, C., Zhong, S., Xu, Z., Liu, J., Xu, Z., Zhu, M., Wang, C., & Du, D. (2024). Is the Invasive Plant Amaranthus spinosus L. More Competitive than the Native Plant A. tricolor L. When Exposed to Acid Deposition with Different Sulfur–Nitrogen Ratios? Atmosphere, 15(1), 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15010029







