Abstract
Industrialization, explosive population growth, anthropogenic activities, and vehicular exhaust deteriorate ambient air quality across the world. The current study aims at assessing the impacts on ambient air quality patterns and their co-relations in one of the world’s most polluted cities, i.e., Lahore, Pakistan, during a strict, moderate, and post-COVID-19 period of 28 months (March 2020–June 2022). The purpose of this study is to monitor and analyze the relationship between criteria air pollutants (SO2, particulate matter (PM 10 and 2.5), CO, O3, and NO2) through a Haz-Scanner 6000 and mobile van (ambient air quality monitoring station) over nine towns in Lahore. The results showed significantly lower concentrations of pollutants during strict lockdown which increased during the moderate and post-COVID-19 lockdown periods. The post-COVID-19 period illustrates a significant increase in the concentrations of SO2, PM10, PM2.5, CO, O3, and NO2, in a range of 100%, 270%, 500%, 300%, 70%, and 115%, respectively. Major peaks (pollution concentration) for PM10, PM2.5, NO2, and SO2 were found during the winter season. Multi-linear regression models show a significant correlation between PM with NO2 and SO2. The ratio of increase in the PM concentration with the increasing NO2 concentration is nearly 2.5 times higher than SO2. A significant positive correlation between a mobile van and Haz-Scanner was observed for CO and NO2 data as well as ground-based observation and satellite data of SO2, NO2, and CO. During the strict COVID-19 lockdowns, the reduction in the vehicular and industrial exhaust significantly improved the air quality of nine towns in Lahore. This research sets the ground for further research on the quantification of total emissions and the impacts of vehicular/industrial emissions on human health.
1. Introduction
Globally, the poor atmospheric quality due to increased air pollution critically impacts human health and leads to many challenges to biodiversity, human health, ecosystems, and regional climate [1,2,3]. The World Health Organization (WHO, Geneva, Switzerland) has reported that metro-political areas are at higher risk of air pollution; hence, respiratory ailments account for 80% of all chronic diseases [4,5,6]. Developing nations are at higher risk due to their fast industrial and urban growth, lack of health knowledge, rapid industrialization, vehicular exhaust, insufficient air quality standards, and obsolete technology as well as high-density population areas [7,8].
The Pakistan Air Quality Index (AQI) in different cities including Lahore, Peshawar, Karachi, and Islamabad does not meet WHO air quality guidelines, especially during winter and autumn seasons [9]. The Air Quality Index of Lahore was 484 on 30 October 2019, which is categorized as above the threshold limit of “Hazardous level” [10]. During the winter season of 2019–2020, intense smog was observed in various cities of Punjab including Lahore. Anthropogenic aerosols account for 65% of smog formation with a major contribution of NOx. The primary sources of NOx identified include transportation (58%) followed by power plants (34%) [11].
The increase in air pollution is linked with many diseases including respiratory ailments such as cardiovascular diseases including decreased lung function, premature mortality, cancer, diabetes, and obesity [1,10,12]. Many studies have highlighted the modification of body mechanisms due to air pollution such as inflammation, anxiety and other psychological changes, hormonal disruption, and oxidative stress [13,14,15]. Moreover, some studies also provide evidence of air pollutants being correlated with behavioral changes in children such as changes in physical activities or increases in caloric intake and eating habits [16,17,18,19]. Many studies have found a positive association between aerosol density and air pollutants including particulate matter of diameter ≤10 μm (PM10), carbon monoxide (CO), nitrogen oxides (NOx), sulfur dioxide (SO2), Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs), and PM2.5 [20,21,22,23,24,25]. Air pollution in densely populated areas is associated with asthma mainly due to the presence of PM2.5, PM10, NO2, SO2, and O3 [26,27]. Children are identified to be at higher risk of morphological and functional effects during fetal development. Moreover, in children, the higher risk is also due to the faster breathing rate and more intake of air as compared to adults [28].
The monitoring of air quality in Pakistan is challenging due to limited air quality monitoring stations. Remote sensing techniques are mainly used for air quality monitoring along with satellite observations. Miller and Marty [29] investigated the contribution of crop residue burning and urban–industrial emissions in Lahore using ground-based and satellite-based aerosol optical properties through Aerosol Optical Depth (AOD) in 2013. The Dark Target (DT) and DEEP Blue (DB) algorithm study using Aqua-MODIS (MYD04) level 2 aerosol products during 2007–2013 in Karachi and Lahore was carried out by Bilal et al. [28]. Many studies have been conducted to correlate the atmospheric trace gases, i.e., ground-level ozone, nitrogen dioxide (NO2), sulfur dioxide (SO2), and carbon dioxide (CO2) using remote sensing techniques [29,30,31,32,33,34]. However, the latest studies relating to the ground-based and satellite data air quality parameters and their effects on human health are still missing in Lahore.
The COVID-19 pandemic had globally adverse impacts on communities in terms of social, economic, and health perspectives. However, these pandemic episodes are also related to improved air quality in many regions of the world due to a decrease in anthropogenic activities such as a reduction in vehicular use, shutdown of industries, and remote working of offices. Studies have also highlighted the improvement of ambient air quality during strict lockdowns and post-COVID-19 lockdowns in many regions of the world such as Wuhan City [35], Central China [36], the northern cities of China [37,38], Spain [39], India [40,41,42], and Iran [43].
Lahore has been ranked among the most polluted cities in the world in the last decade. Unfortunately, this part of the world is the least studied and lacks an appropriate air quality monitoring network. It is imperative to investigate the deteriorated ambient air quality regularly and to check the efficacy of mitigation measures. This study primarily focuses on reporting the current state of criteria air pollutants SO2, CO, NO2, O3, and PM (PM2.5 and PM10). This study provides the deep spatial and temporal ambient air quality trends for the period of March 2020 to June 2022. Further emphasis is on the behavior of ambient air quality during two time periods of the COVID-19 lockdown period and post-COVID-19 period. In Pakistan, a strict lockdown during March 2020 and November 2020 shows an incredible reduction of all criteria air pollutants. This study provides a comparison of ground-based data with satellite monitoring during the study period. Based on these previous studies and analyzing the gaps, the following study is designed with major objectives including: (i) monitoring of ambient air quality parameters in a mega-city for 28 Months (March 2020–June 2022), (ii) discovering the coherence and relationship between particulate matter with active gaseous pollutions (CO, NO2, SO2, and O3) and (iii) assess the correlation between ground-based monitoring data and satellite data and meteorological conditions.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
Lahore is the 2nd largest city in Pakistan in terms of population and lies between 31.5204° N and 74.3587° E. The total area of Lahore is 1772 km2, with a population of 15,126,000 individuals [44]. The road density of Lahore is 0.47 per km2, which is higher than Punjab’s average road density (0.37 km2). Lahore is classified into nine major administrative divisions known as “towns” which are (i) Data Ganjh Bakhsh Town, (ii) Samanabad Town, (iii) Ravi Town, (iv) Aziz Bhatti Town, (v) Wahga Border, (vi) Gulberg Town, (vii) Iqbal Town, (viii) Shalimar Town, and (ix) Nishtar Town (Figure 1). The ambient air monitoring was conducted through the Haz-Scanner and mobile van in all of these towns.
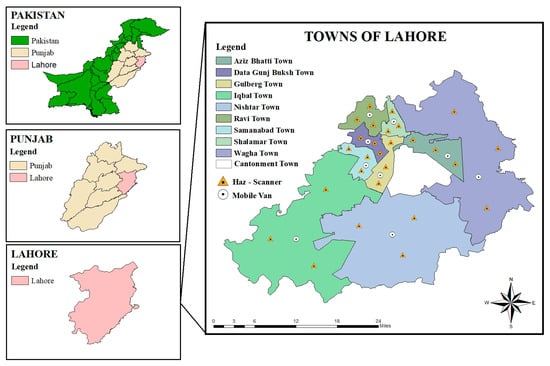
Figure 1.
Location Map of Ambient Air Quality Monitoring Sites of Lahore, Pakistan.
2.2. Research Design and Sampling Protocol
This research is designed for the assessment and characterization of ambient air quality in Lahore, Pakistan, for the period of 28 months, i.e., March 2020–June 2022. Two sampling locations from each town were selected. Daily monitoring was carried out in nine towns in Lahore with a mobile van (air quality station) and Haz-Scanner 6000 (Environmental Devices Corporation, USA, Power: 10 h on 12 V AGM Battery, Continuous on AC, Recording Time: 1 s to 44 weeks, Sampling Rate: 1 s, 1 min, 10 min, 1 h, adjustable, Sampling Pump: 2.0 lpm Adjustable, Digital Output: RS-232 (PC), RS-423 (MAC), Dimensions: 14″ × 6″ × 10″ weather proof case, Weight: 12 lbs, Operating Temperature: −20 °C to 60 °C). Parameters monitored include SO2, CO2, NO2, CO, PM2.5, and PM10. For further assessment, we compared our results for the duration, i.e., 2020, 2021, and 2022, to better estimate the changes in air patterns during COVID-19 and its post-effects. The satellite data were collected through a Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectro-radiometer (MODIS) over Lahore for a study period of 28 months (March 2020–June 2022). The satellite data provide near-surface (ground-level) concentrations through column integration and through physio-chemical and meteorological processes [45].
2.3. Study Duration
The present study was conducted for an extensive period of twenty-eight months. This duration is classified into three phases based on the COVID-19 lockdown as implemented by the government. The details of this duration are as follows:
- Strict lockdown (1st strict lockdown 1 April 2020–15 April 2020 and 20 November–15 December 2020)
- Moderate lockdown (six months of 22 April 2020–October 2020)
- Post-COVID-19 Lockdown (January 2021–June 2022).
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Firstly, a data quality control check was completed; the hourly data matrix of the entire 28 month data set was imported to a Sigma plot for the preparation of graphs. A total number of data sets (628) of each parameter was monitored along Lahore city. Pearson correlation coefficients were obtained. Multiple linear regressions were executed with the function “regress” at the 0.05 significance level. Normality analysis of the raw data was conducted before the statistical analysis. The mean average value of ambient air pollutants was obtained and graphically presented by using a sigma plot furthermore the significant correlation of particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10) with another gaseous pollutant (SO2, CO2, NO2, NO, being CO) being calculated by using multiple regression. The validity of ambient air quality results is then correlated with satellite MODIS data and represented as a coefficient of determination (R2). All the data were analyzed and illustrated in graphs using SigmaPlot 14.0. The mapping of nine towns of Lahore city was done with qGIS.
The regression model was designed as follows:
PM2.5 = 28.625 + (0.855 × NOx) + (0.599 × SOx) + (1.742 × CO) − (0.770 × O3)
The obtained regression of the p-value and other regression statistical parameters show that PM2.5 is more sensitive to other pollutants.
R = 0.978, Rsqr = 0.957, Adj Rsqr = 0.950 and Standard Error of Estimate = 8.431
Similarly, we conducted multiple linear regression analyses of daily values for the complete 28 months between PM10 and gaseous pollutants based on their linear correlations to evaluate the sensitivity of PM10 to these pollutants. The regression model was designed as follows:
PM10 = −9.831 + (3.468 × NOx) + (0.963 × SOx) + (7.648 × CO) − (3.586 × O3)
N = 688 R = 0.953 Rsqr = 0.908 Adj Rsqr = 0.892
For a better understanding of other relations between PM10, PM2.5, and other gaseous pollution, we tried to compare results for each year in Sigmaplot. The regression coefficient for PM2.5 and PM10 with other gaseous pollution are as follows:
PM2.5/10 = α × NO2 + β × SO2 + γ × CO + δ × O3
2.5. Meteorological Parameters
The weather station of Lahore is located at latitude 31.544° N and longitude 74.32° E. The meteorological data of maximum and minimum temperature, humidity, precipitation, and solar radiation were obtained for the study period from the Punjab Meteorological Department for the monitoring period (28 months). These data sets are then co-related with each parameter to identify their interrelation.
3. Results
Air pollution concentrations changed significantly in Pakistan in the last decade. The COVID-19 outbreak was declared the sixth public health emergency for international concern by World Health Organization (WHO) on 11 March 2020 [46]. This epidemic caused a lot of crises due to mortality and economic and social lockdowns in Pakistan, but on the positive side, it improved a vital need (ambient air quality) for human beings, as evident by the blue sky in one of the most polluted mega-cities (Lahore) in the world. The post-COVID-19 period illustrates a significant increase in the concentrations of SO2, PM10, PM2.5, CO, O3, and NO2 in the range of 100%, 270%, 500%, 300%, 70%, and 115%, respectively. This study was carried out to find the relationship between PM and active gaseous pollution impacts of the COVID-19 lockdowns and the overall effects of PM10, PM2.5, and criteria pollutants (SO2, CO, O3, and NO2).
Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6 and Figure 7 represent the overall trend of PM10, PM2.5, SO2, O3, NO2, and CO, respectively. The period is illustrated vertically (y-axis) while the concentration of atmospheric pollutants is represented horizontally (x-axis) in different towns of Lahore. The green dashes in the figures represent the strict lockdown (time duration as mentioned in Section 3 while blue dashes represent the moderate lockdown.
3.1. The trend of Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM10)
Overall trends of PM2.5 and PM10 showed lower peaks during strict lockdowns due to less vehicular pollution and fewer industrial activities. The results are within PEQS limits during March 2020 and November 2020 with a slight increase in concentration during moderate lockdown (April–October 2020) (Figure 2 and Figure 3). While the trend in the post-COVID-19 period revealed that the concentration of PM10 in ambient air is at its maximum in the winter due to temperature inversion, i.e., October–January, during the summer, i.e., May–June, the trend also showed a decline in the concentration of PM10. A sharp dip in concentration of PM10 was observed during monsoon months, i.e., July–August. The trend of PM10 concentrations of nine towns in Lahore is Shalimar Town > Nishtar Town > Iqbal Town > Gulberg Town > Wagha Town > Data Ganj Bakhash Town > Ravi Town > Aziz Bhatti Town > Samanabad. The trend of Haz-Scanner and mobile van monitoring showed a similar trend with slight variation in results. The overall trend of the Haz-Scanner results, during the COVID-19 lockdown, indicates that the lowest concentrations of PM10 were observed in Aziz Bhatti Town (72 µg/m3) which is within the PEQ limits while the highest concentration was found in Gulberg town (201 µg/m3) and while the post-COVID-19 period indicates that the lowest concentration was in Iqbal Town (172 µg/m3) and the highest concentration was in Gulberg Town (445 µg/m3). Similarly, the trend measured from the mobile van during the COVID-19 lockdown showed the lowest concentration in Nistar town (85.67 µg/m3) and the highest concentration in Gulberg Town (205.62 µg/m3), while the post-COVID-19 period showed the lowest concentration in Iqbal Town (175 µg/m3) and the highest concentration in Gulberg Town (447 µg/m3).
While the trend in the post-COVID-19 lockdown period showed that the concentration of PM2.5 in ambient air is higher in winter months, i.e., October–January, a sharp dip in concentration of PM2.5 was observed during the monsoon season, i.e., July–September Overall, it is also observed that during the strict lockdown, the concentration of PM2.5 was within the PEQS limits, i.e., 35 µg/m3. The trend of PM2.5 concentrations of nine towns in Lahore is Shalimar Town > Wagha Town > Aziz Bhatti Town > Gulberg Town > Ravi Town > Data Ganj Bakhash Town > Nishtar Town > Iqbal Town > Samanabad Town. The trend measured from the Haz-Scanner and mobile van monitoring showed a similar trend with slight variation in results. The overall trend of The Haz-Scanner results during the COVID-19 lockdown indicates that the lowest concentrations of PM2.5 were observed in Data Ganj Bakhash Town (32 µg/m3) which is within the PEQ limits, and the highest concentration was found in Gulberg town (201 µg/m3), while in the post-COVID-19 period, the highest concentration was measured in Nishtar Town (300 µg/m3). Similarly, the trends measured from the mobile van during the COVID-19 lockdown showed the lowest concentration in Wagha Town (30 µg/m3) and the highest concentration in Gulberg Town (274 µg/m3), while during the post-COVID-19 period, the lowest concentration was found in Nistar Town (135 µg/m3) and the highest concentration was found in Ravi Town (278 µg/m3).
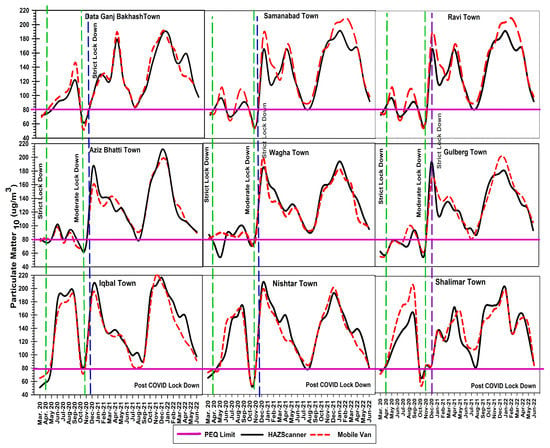
Figure 2.
Trend of ground-monitoring data of particulate matter 10 µg/m3 in nine towns in Lahore.
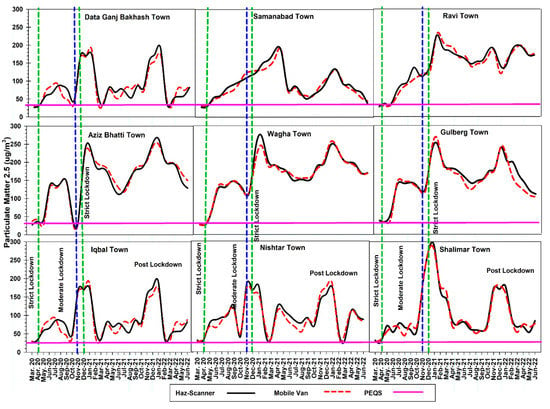
Figure 3.
Trend of ground-monitoring data of particulate matter 2.5 in nine towns in Lahore.
3.2. Active Pollutants
The monitoring of the active criteria air pollutants in Lahore indicated that some of the values were within the Punjab Environmental Quality Standards (PEQs) during the COVID-19 lockdown periods while a much higher concentration was found compared to PEQs during the post-COVID-19 period for all nine towns. Less variation the in Haz-Scanner and mobile monitoring laboratory was observed in the monitoring data.
3.2.1. Monitoring of Sulfur Dioxide in Ambient Air
Monitoring of sulfur dioxide in ambient air quality was carried out by the mobile van. The overall trends of SO2 showed lower peaks during strict lockdowns, i.e., (March 2020 and November 2020) with a slight increase in concentration during moderate lockdown (April–October 2020) (Figure 4). While the trend during the post-COVID-19 time showed that the concentration of SO2 in ambient air increased by 100% and is greatly higher in winter months, i.e., November–January, during the monsoon season, i.e., July–September, the trend also showed a decline in the concentration of SO2. A sharp dip in concentration of SO2 was observed during the summer months, i.e., May–June. Overall, it was also observed that during the strict lockdown, the concentration of SO2 was within the PEQ limits, i.e., 120 µg/m3, and a sudden upsurge was observed after the lockdown period. The trend of SO2 concentrations of nine towns in Lahore is Nishtar Town > Data Ganj Bakhash Town > Iqbal Town > Gulberg Town > Samanabad Town > Shalimar Town > Aziz Bhatti Town > Ravi Town and Wagha Town. The trend measured from the mobile van during the COVID-19 lockdown showed that the lowest concentration was in Wagha Town (90 µg/m3) and the highest concentration was in DGBT (145 µg/m3), while the post-COVID-19 period indicates that the lowest concentration was in Nistar Town (135 µg/m3) and the highest concentration was in Ravi Town (278 µg/m3).
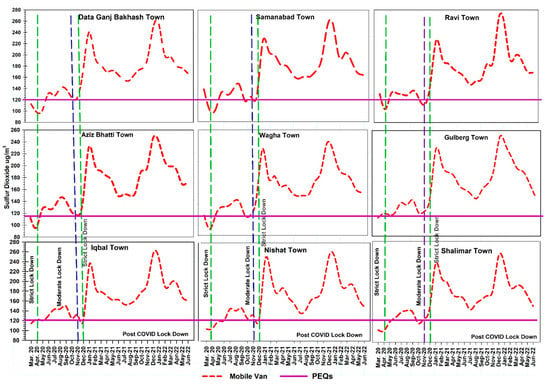
Figure 4.
Trend of ground-monitoring data of sulfur dioxide in nine towns in Lahore.
3.2.2. The Trend of Ozone in Ambient Air
The trends of ozone (O3) displayed in Figure 5 show lower peaks during strict lockdowns, i.e., (March 2020 and November 2020) with a slight increase in concentration during moderate lockdown (April–October 2020). While the trend in the post-COVID-19 period indicates that the concentration of ozone in ambient air is higher in the spring season, i.e., March–April, a significant reduction was found during winters because O3 is formed by the photochemical reactions amid its precursors as a secondary air pollutant. A sharp dip in the concentration of O3 was observed during winter months, i.e., November–January, because the increase in particulate matter reduces solar radiation which in turn reduces O3. Overall, it was also observed that during the strict lockdown, the concentration of O3 was within the PEQ limits, i.e., 60 µg/m3. The highest trend of O3 concentrations of nine towns in Lahore according to the Haz-Scanner was Iqbal Town (115.67 ± 12.32 µg/m3) > Ravi Town (111.8 ± 5.23 µg/m3) > Samanabad Town (108.67 ± 11.21 µg/m3) > Aziz Bhatti Town (103.87 ± 21.22 µg/m3) > Shalimar Town (101.56 ± 11.65 µg/m3) > Wagha Town (101.21 ± 10 µg/m3) > Gulberg Town (98.32 µg/m3) > Data Ganj Bakhash Town (98.67 µg/m3) and Nishtar Town (95.43 ± 15.65 µg/m3).
Moreover, the highest trend of O3 concentrations of nine towns in Lahore according to the mobile lab was Nishtar Town (192.32 ± 2.13 µg/m3) > Iqbal Town (124.3 ± 9.76 µg/m3) > Samanabad Town (120.17 ± 4.21 µg/m3) > Wagha Town (119.7 ± 11.22 µg/m3) > Gulberg Town (116.56 ± 11.65 µg/m3) > Shalimar Town (114.21 ± 17.21 µg/m3) > Ravi Town (113.34 ± 8.76 µg/m3) > Aziz Bhatti Town (110.87 µg/m3) and Data Ganh Bakhash Town (107.63 ± 15.65 µg/m3).
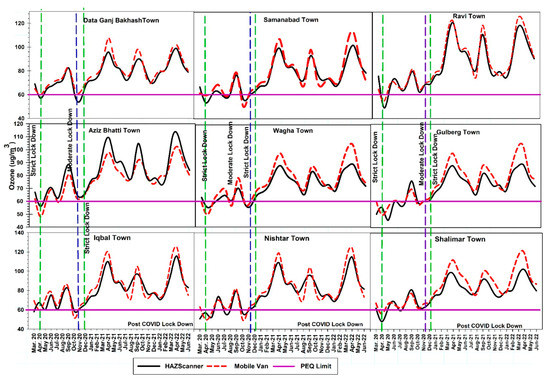
Figure 5.
Trend of ozone (µg/m3) in nine towns in Lahore.
3.2.3. The Trend of Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2) in Ambient Air
Overall, the trends of NO2 presented in Figure 6 demonstrate lower peaks during strict lockdowns, i.e., (March 2020 and November 2020) with a slight increase in concentration during moderate lockdown (April–October 2020). While the trend in the post-COVID-19 lockdown period showed that the concentration of NO2 increased by 115%, a higher concentration was found during the summer months and spring season. A sharp dip in the concentration of NO2 was observed during the winter months, i.e., November–January. Overall, through the Haz-Scanner and mobile van, it was also observed that during the strict lockdown, the concentration of NO2 was within the PEQ limits, i.e., 42 ppb. The post-COVID-19 trend of NO2 concentrations monitored through the Haz-Scanner of nine towns in Lahore is Iqbal Town (126.75 ± 51.05 ppb) > Ravi Town (121.21 ± 39.90 ppb) > Nishtar (119.21 ± 27.98 ppb) > Gulberg Town (109.76 ± 41.18 ppb) > Wagha Town (107.55 ± 36.21 ppb) > Shalimar Town (101 ± 48.29 ppb) > Aziz Bhatti Town (97.65 ± 30.96 ppb) > Samanabad Town (92.09 ± 29.80 ppb) and Data Ganjh Bakhash Town (89.44 ± 48.28 ppb).
The post-COVID-19 NO2 concentrations monitored through mobile vans of nine towns in Lahore is Iqbal Town (119.24 ± 49.47 ppb) > Nishtar Town (119.21 ± 30.54 ppb) > Aziz Bhatti Town (117.21 ± 42 ppb) > Gulberg Town (115.65 ± 32.80 ppb) > Ravi Town (114.32 ± 28.32 ppb) > Wagha Town (112.75 ± 77.68 ppb) > Samanabad Town (110.22 ± 35.89 ppb) > Shalimar Town (93 ± 35.89 ppb) and Data Ganjh Bakhash Town (90 ± 34.89 ppb).
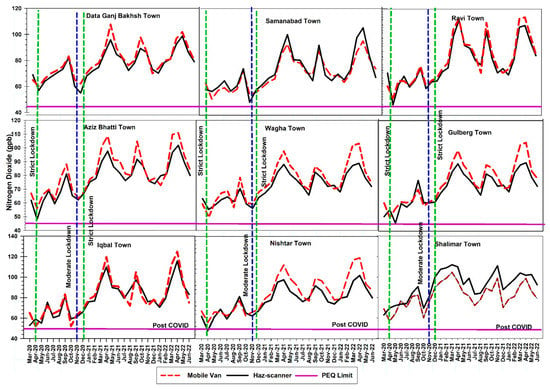
Figure 6.
Trend of nitrogen dioxide concentration of nine towns in Lahore.
3.2.4. Monitoring of Carbon Monoxide in Ambient Air
Figure 7 illustrates the overall trends of CO which showed lower peaks during strict lockdowns, i.e., (March 2020 and November 2020) with a slight increase in concentration during moderate lockdown (April–September 2020). While the trend during the post-COVID-19 lockdown period showed that the concentration of CO in ambient air is higher in spring and winter months, a dip in concentration of CO was observed during the summer months, i.e., May–June. Overall, it was also observed that during the strict lockdown, the concentration of CO was within the PEQ limits, i.e., 5 mg/m3.
The overall pattern of CO concentrations in nine towns in Lahore is Ravi Town > Gulberg Town > Shalimar Town > Nishtar Town > Samanabad Town > Iqbal Town > Data Ganj Bakhash Town > Wagha Town > Aziz Bhatti Town. The trends measured from the Haz-Scanner and mobile van monitoring showed a similar trend with slight variation in results. The overall trend of the Haz-Scanner results from during the COVID-19 lockdown indicates that the lowest concentrations of CO were observed in Wagha Town (2.7 mg/m3) which is within the PEQ limits while the highest concentration was found in Shalimar Town (9.5 mg/m3) and while the post-COVID-19 period indicates that the lowest concentration was in Aziz Bhatti Town (6.7 mg/m3) and the highest concentration was in Shalimar Town (32 mg/m3). Similarly, the trend measured from the mobile van during the COVID-19 lockdown showed the lowest concentration in Aziz Bhatti Town (3.2 mg/m3) and the highest concentration in Shalimar Town (12.4 mg/m3), while the post-COVID-19 period shows the lowest concentration in DGBT (5 mg/m3) and the highest concentration in Ravi Town (34 mg/m3).
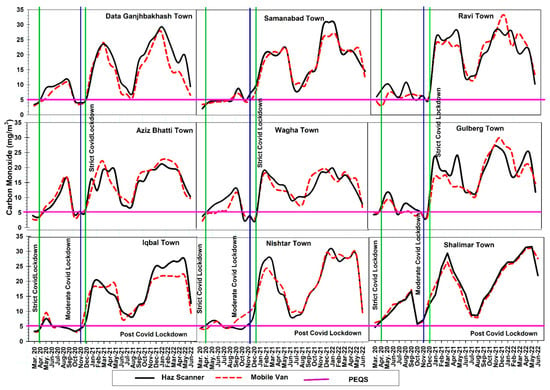
Figure 7.
Trend of carbon monoxide concentration of nine towns in Lahore.
3.3. Multiple Linear Regression Analysis of Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM10) and Gaseous Pollutants
We conducted multiple linear regression analyses of daily values for a complete 28 months between PM2.5 and gaseous pollutants based on their linear correlations to evaluate the sensitivity of PM2.5 to these pollutants as represented in Table 1 and Table 2 respectively.

Table 1.
Regressions coefficients between PM2.5 and other gaseous Pollutants.

Table 2.
Regressions coefficients between PM10 and other gaseous Pollutants.
3.4. Comparison of Satellite and Ground-Based Data Sets
The linear correlation of MODIS and ground-monitoring data for 28 months, i.e., from the Haz-Scanner and mobile van, was calculated and represented as a coefficient of determination (R2) (Figure 8). The CO results over 28 months indicated a significant correlation of MODIS with the Haz-Scanner, i.e., r2 = 0.43, and with the mobile lab, as R2 = 0.40. The SO2 correlation between MODIS and the mobile lab was also highly significant, i.e., r2 = 0.59. A similar trend of a significant correlation for NO2 was observed among MODIS and the Haz-Scanner, i.e., r2 = 0.44, and the mobile lab, as R2 = 0.40.15.
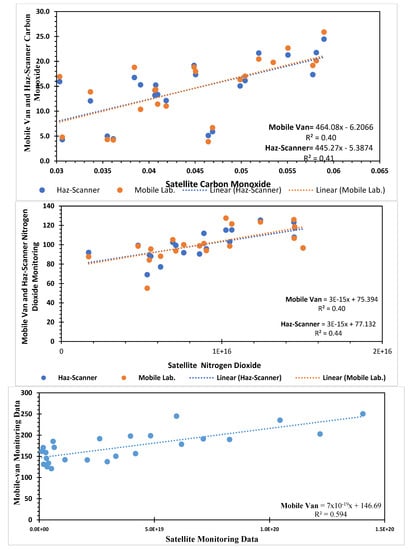
Figure 8.
Correlation of satellite data with monitoring data of Lahore CO, NO2, SO2.
3.5. Comparison of Satellite and Ground-Based Data
In principle, the satellite passes over the study area once a day, i.e., 12:00–2:00 p.m. Therefore, the comparison of ground-based monitoring data with satellite data during this time duration has been conducted. The comparison of satellite observations with a Haz-Scanner and the mobile van monitoring was conducted for NO2 and CO while for SO2 only the mobile van monitoring was compared (Figure 9). The results showed a significant positive correlation between ground-based and satellite data for NO2 i.e., the Haz-Scanner (r2 = 0.64) and mobile van (r2 = 0.64). Moreover, a substantial correlation was also observed for CO satellite-based data with the Haz-Scanner (r2 = 0.75) and mobile van (r2 = 0.77). Similarly, the satellite and mobile van data of SO2 were significantly raised (r2 = 0.67).
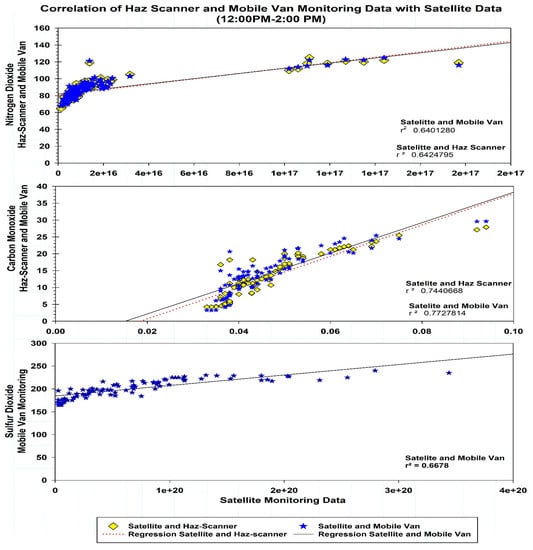
Figure 9.
Correlation of ambient air quality monitoring with satellite data.
3.6. The Trend of Meteorological Variation in Lahore
The trends of meteorological parameters during the study duration (March 2020–June 2022) are presented in Figure 10. The average monthly solar radiation varied from 14.19 to 28.93 Wm−2. The minimum average solar radiation was observed during December and January 2020 (17.4 ± 1.3 Wm−2 and 16.8 ± 4.4 Wm−2, respectively) and December and January 2021 (17.6 ± 1.5 and 14.2 ± 4.6 Wm−2, respectively), whereas the maximum average solar radiation was observed during May and June of each year. The maximum solar radiation was observed in May 2022 (28.9 ± 1.3 Wm−2) and May 2021 (28.1 ± 1.5 Wm−2). The average monthly dew point of Lahore varied from 8.57 ± 1.20 to 26.41 ± 2.45 °C. The minimum average dew point was observed during December 2020 and January 2021 (8.6 ± 3.20 °C and 8.69 ± 2.40 °C, respectively), whereas the maximum average dew point was observed during August 2020, i.e., 26.40 ± 0.8 °C.
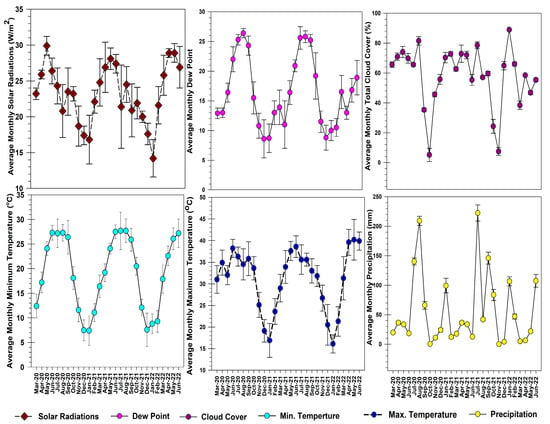
Figure 10.
Trend of Meteorological variation in Lahore.
The average monthly total cloud cover of Lahore varied from 5.2 ± 4.4% to 89.23 ± 0.6. The minimum average dew point was observed during October 2020 (5.2 ± 4.4%) and November 2021 (7.50 ± 2.6%), whereas the maximum average dew point was observed during January 2021, i.e., 89 ± 0.6%. The average monthly maximum temperature of Lahore varied from 16.07 ± 3.9 °C to 40.15 ± 4.45 °C. The minimum average minimum temperature was observed during January 2022 and 2021, i.e., 16.10 ± 2.10 and 16.91 ± 3.9 °C, respectively. The maximum average temperature was observed during April 2022 and June 22, i.e., 39.60 ± 3.00 °C and 40.20 ± 4.70 °C, respectively. Moreover, it was also observed that the trend has slightly increased from the previous year. The average monthly minimum temperature of Lahore varied from 7.4 ± 3.0 °C to 27.70 ± 3.80 °C. The least average minimum temperature was observed during December and January 2021, i.e., 7.5 ± 2.10 and 7.40 ± 3.0 °C respectively. Moreover, the highest average minimum temperature was observed during the months of June-August of each year i.e., June–August 2020 (27.30 ± 1.50 °C, 27.20 ± 2.90 °C, 27.30 ± 1.70 °C), June–August 2021 (27.50 ± 1.40 °C, 28.70 ± 3.80 °C, 27.70 ± 2.40 °C). Moreover, it was also observed that the trend has slightly increased from the previous year. The average monthly precipitation of Lahore varied from 0.5 ± 0.006 mm to 222.51 ± 13.8 mm. The least average precipitation was observed during November 2021 i.e., 0.1 ± 0.006 mm respectively. Moreover, the highest average precipitation was observed during the months of July 2021 i.e., 222.51 ± 13.80 mm. The ambient air pollutants trend varied the change in meteorological conditions. It can be observed that during the winter (November–January) the concentration of PM is much higher as compared to the summer (May–June). Moreover, during the strict lockdown, the concentration of PM2.5 and PM10 were lower which increased drastically in post COVID lockdown.
3.7. Correlation of Ground-Monitoring Data with Meteorological Parameters
Table 3 presents the correlation of ground–based monitoring data with meteorological parameters. A significant negative correlation between maximum temperature and solar radiation was observed with NO2, PM2.5, PM10, and SO2. PM2.5 and PM10 have a noticeable correlation with total cloud cover. Maximum cloud cover was observed during the winter, which as a result upsurged the concentrations of PM2.5 and PM10, while ozone and NO2 concentration can be seen to have a decreasing trend showing a negative correlation due to less solar radiation and low photochemical activities. The correlation of minimum temperature and the dew point was also highly significant for PM2.5 and PM10 and SO2, indicating lower temperatures and higher concentrations of these pollutants.

Table 3.
Correlation of Ground Monitoring Data with Meteorological Parameters.
4. Discussion
To the best of our knowledge, the present study is the first in-depth study covering an extensive duration of twenty-eight months particularly about criteria air pollution in Lahore, which has been ranked among the most polluted cities in the world for last decade. This study presents monitoring and analyses of air quality patterns for 28 months during the active COVID-19 and post-COVID-19 periods. This study proposes that the government’s policies regarding the lockdowns during COVID-19 provided a positive effect on decreasing air pollution due to less anthropogenic activities, low vehicular exhaust, and the shutdown of industrial units.
In this study, we compared the ambient air quality patterns during a strict, moderate, and post-COVID-19 lockdown, with 28 months of monitoring for PM (2.5 and 10) and active air pollutants (SO2, CO, CO2, NOX, and O3) through ground-based monitoring data (i.e., a Haz-Scanner and mobile van) and satellite data.
The PM (2.5 and 10) was within the limits of PEQs during the strict lockdown and increased during the moderate lockdown. However, during the post-lockdown period, a significant increase was observed in nine towns in Lahore (Figure 2 and Figure 3). Many studies have related the complex phenomena of PM in ambient air during, before, and after COVID-19 lockdown periods [40,45,46,47,48]. The main reason identified behind this reduction in PM concentration being decreased is due to the reduction of anthropogenic activities up to 90%. Interestingly, in three towns in Lahore (Nishter Town, DGBT, and Iqbal Town), we found sharp dips representing very low PM concentration during February–March 2021, and an investigation showed that more COVID-19 cases were found in hotspot areas in these towns due to their large population. More and longer lockdowns were implemented by the government in these areas which caused a significant reduction in PM during February–March 2021. In many COVID-19-affected countries in strict lockdown, a reduction in NO2, SO2, and PM was observed [44,45,46]. Winter showed major peaks for PM concentration due to temperature inversion. Table 1 shows a significant correlation of PM with total cloud cover and dew point in Lahore, a representation of more primary and secondary aerosols in ambient air since a higher percentage of aerosols causes more PM concentration.
Multilinear regression for PM (2.5 and 10) with all other active pollutants (NO2, O3, SO2, and CO) shows a significant correlation between active pollutants and particulate matter. The regression model shows that significant correlation was found among particulate matter with NO2 and SO2. The ratio of the increase in particulate matter concentration with increasing NO2 concentration is nearly three times more than that for SO2. The chemistry behind this was twofold: (1) NOx can be converted into nitrate, and (2) NOx contributes to atmospheric oxidation capacity. Possible reasons for the high correlation between them are due to NOx playing its role in the formation of secondary PM2.5 by the formation of nitrate directly and enhancing aerosol-phase oxidation indirectly. Due to the multifaceted air pollution in Lahore, complex reactions related to NOx have become important due to excessive concentration of aerosol and NH3 that leads to secondary aerosol during the smog episodes in Lahore. Surprisingly, our results show that SO2 was negatively correlated during 2020 with particulate matter. The reason behind this can be demonstrated as that during the COVID-19 period, many industrial units around the city were shut down.
Pearson correlation value ≤ 0.05 shows a significantly positive correlation. Many of those industrial units mainly operate on fossil fuels such as coal. The decrease in PM concentration coincides with an increase in ozone concentration specifically in the summer due to more photochemical reactions. A negative to positive correlation was found between ozone and PM as air quality improved.
Our results showed that active air pollutants were much higher in in the post-COVID-19 period as compared to during strict and moderate lockdowns. The study of [33] analyzed an increase in SO2 concentration during 2004–2015 with an increasing trend of 4.4% per year. The study also found a relationship with the winter peak of SO2, i.e., during November. Contrary to these results, the peaks of SO2 in our results are observed in January. Similarly, the trend of the lowest concentration of atmospheric SO2 was observed during the monsoon (July–September) period, which is linked to higher concentrations of OH and H2O2 production that cause dilution and wet scavenging as reported in many other studies [16,30]. The decline in SO2 concentrations during monsoon season is also similar to other countries such as India, in which a 40-45% reduction has been reported through monsoon washout [36], and similar trends of higher SO2 during winter can be found in northern China.
Long-term exposure to ozone has chronic impacts on humans. Globally, it is estimated that approximately 8.8 million excess deaths annually are due to ozone [49,50]. In the troposphere, O3 is majorly composed of precursors such as CO, NOx, and VOCs. Methane is also one of the major precursors of O3. Tropospheric ozone is mainly produced due to photochemical reactions of CO, NOx, and VOCs in the presence of sunlight [51].
A similar study by Elansky et al. [52] conducted in Moscow to identify the weekly concentration of ambient air pollutants showed the highest concentrations on Friday and the minimum on Sunday. A major reason for this fluctuation in weekly concentration is due to an increase in anthropogenic activities such as vehicles and industries at the start of the week, decreasing to a minimum on weekends. Moreover, the trend of ambient air pollution (NO2, SO2, PM2.5, and PM10) showed a negative trend with rainfall which is supported by the similar trends observed by different studies [15,18,53,54]. The decrease in PM concentration results in less heterogeneous HO2 loss and more actinic flux that coincides with an increase in ozone concentration. PM and ozone also show a positive correlation due to some of the common precursors such as VOCs and NOx, specifically in the summer due to more photochemical reactions.
The linear correlation of satellite data with ground monitoring shows a significant increase in correlation during 12:00–2:00 p.m. because in principle the satellite passes over the study period just once a day. Comparing satellite data, one should be careful to note that while the satellite has only one observation a day, it has a longer spatial footprint, and it observes the average ground pixels’ size, while ground-based monitoring is point-based data. It is clear that the correlation can be improved by taking measurements as presented in Figure 8.
A significant negative correlation between maximum temperature and solar radiation was observed with NO2, PM2.5, PM10, and SO2. PM2.5 and PM10 have a noticeable correlation with total cloud cover. Maximum cloud cover was observed during the winter, which as a result upsurged the concentration of PM2.5 and PM10. While ozone and NO2 concentration can be seen to have a decreasing trend showing a negative correlation due to less solar radiation and low photochemical activities, the correlation of minimum temperature and dew point was also highly significant for PM2.5 and PM10 and SO2, indicating lower temperature and a higher concentration of these pollutants
5. Conclusions
The impression of lockdown on ambient air quality as a consequence of COVID-19 in Lahore was assessed by monitoring and comparing the concentrations of the six criteria air pollutants for 28 months. The lockdowns restricted mobility and anthropogenic activities which resulted in a decrease in atmospheric emissions. This reduction in emissions from shutdown during lockdowns has resulted in a decline in the levels of criteria air pollutants such as SO2, CO2, NO2, CO, PM2.5, and PM10 in the atmosphere. During the strict COVID-19 lockdowns, the ambient air pollutants were significantly reduced in nine towns in Lahore and were within the ambient air quality standards of the PEQs. The post-COVID-19 period presented a significant increase in the concentrations of SO2, PM10, PM2.5, CO, O3, and NO2, in ranges of 100%, 270%, 500%, 300%, 70%, and 115%, respectively. The variation in ground and satellite data showed less variation for daily- and hourly-based datasets. The concentration of ambient air pollutants was observed to be higher in winter, i.e., November–January, while in summer the concentrations were lower but still higher than the PEQs. The multilinear regression model for PM (2.5 and 10) with all other active pollutants (NO2, O3, SO2, and CO) shows a significant correlation between active pollutants and PM. The regression model showed a significant correlation between PM and NO2 and SO2. The ratio of increase in the PM concentration with increasing NO2 concentration is nearly three times higher than SO2. The highest correlation was found between PM2.5 and NO2 during smog accumulation periods demonstrating the presence of active NOx-related secondary aerosol processes during accumulation. A negative to positive correlation was found between O3 and PM as air quality improved. The research highlights the need for a stringent policy for ambient air quality monitoring and mitigation to achieve better ambient air quality in Lahore.
Author Contributions
W.A.K., Conceptualization and collecting primary data, investigation, analysis, and write-up; F.S., Review and editing; M.F.K., Data carnation, validation, and proofreading; L.S., Draft preparation and formal analysis; N.E., Visualization, data interpretation, and write-up, M.J., Visualization, review, and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The presented study was partially funded by the Office of Research and innovation center, Government College University Lahore.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Government College University, Lahore, and approved by the Advanced Studies and Research Board of Government College University Lahore Pakistan (51th meeting on 30–31 March 2022).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The metrological data used during this research were obtained from the Meteorology Punjab. The satellite data were obtained from the National University of Science and Technology (NUST), and all other data mentioned in this research are primary data obtained by the authors from ground-based monitoring.
Acknowledgments
All authors are highly appreciative of Punjab Meteorological Department for providing the weather data. This research was technically supported by the National University of Science and Technology (NUST) and EnterTech Labs. The authors are grateful to the anonymous reviewers for their time and insightful comments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kim, K.H.; Kabir, E.; Kabir, S. A Review on the Human Health Impact of Airborne Particulate Matter. Environ. Int. 2015, 74, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allabakash, S.; Lim, S.; Chong, K.-S.; Yamada, T.J. Particulate Matter Concentrations over South Korea: Impact of Meteorology and Other Pollutants. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monks, P.; Granier, C.; Fuzzi, S.; Stohl, A.; Williams, M.; Akimoto, H.; Amann, M.; Baklanov, A.; Baltensperger, U.; Bey, I.; et al. Atmospheric composition change–global and regional air quality. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 5268–5350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahanzaib, M.; Sharma, S.; Bakht, A.; Heo, J.; Park, D. Analyzing the Effectiveness of Air Curtain in Reducing Particulate Matter Generated by Human-Induced Slipstream. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 170, 834–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Bakht, A.; Jahanzaib, M.; Lee, H.; Park, D. Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Common Indoor Plants in Improving the Indoor Air Quality of Studio Apartments. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, A.; Zeeshan, M.; Jahanzaib, M. Indoor Temperature, Relative Humidity and CO2 Levels Assessment in Academic Buildings with Different Heating, Ventilation and Air-Conditioning Systems. Build. Environ. 2018, 133, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, M.U.; Waseef, R.F.; Ahmed, H. Perception about the Factors Associated with Smog among Medical Students. Biomedica 2018, 34, 264. [Google Scholar]
- Kermani, M.; Jonidi Jafari, A.; Gholami, M.; Taghizadeh, F.; Masroor, K.; Abdolahnejad, A.; Shahsavani, A.; Fanaei, F. Characterisation of PM2.5–Bound PAHs in Outdoor Air of Karaj Megacity: The Effect of Meteorological Factors. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2021, 103, 3290–3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrow, A.; Miller, K.A.; Myllyvirta, L. Toxic Air: The Price of Fossil Fuels. Greenpeace Southeast Asia. 2020, pp. 1–44. Available online: https://www.greenpeace.org/static/planet4-southeastasia-stateless/2020/02/21b480fa-toxic-air-report-110220.pdf (accessed on 17 January 2023).
- PAQI. Lahore Smog, Just How Bad Is It? Pakistan Air Quality Initiative. 2018. Available online: https://www.iqair.com/profile/pakistan-air-quality-initiative (accessed on 20 June 2020).
- Air Quality Index (AQI) of Lahore. 2022. Available online: https://epd.punjab.gov.pk/system/files?file=21.09.2022%20%281%29.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2022).
- Kampa, M.; Castanas, E. Human Health Effects of Air Pollution. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 151, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlong, M.A.; Klimentidis, Y.C. Associations of Air Pollution with Obesity and Body Fat Percentage, and Modification by Polygenic Risk Score for BMI in the UK Biobank. Environ. Res. 2020, 185, 109364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Yue, P.; Deiuliis, J.A.; Lumeng, C.N.; Kampfrath, T.; Mikolaj, M.B.; Cai, Y.; Ostrowski, M.C.; Lu, B.; Parthasarathy, S.; et al. Ambient Air Pollution Exaggerates Adipose Inflammation and Insulin Resistance in a Mouse Model of Diet-Induced Obesity. Circulation 2009, 119, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Yavar, Z.; Verdin, M.; Ying, Z.; Mihai, G.; Kampfrath, T.; Wang, A.; Zhong, M.; Lippmann, M.; Chen, L.C.; et al. Effect of Early Particulate Air Pollution Exposure on Obesity in Mice: Role of P47phox. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2010, 30, 2518–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Huang, Q.; Hong, A.; Yu, C.; Xiao, Q.; Zou, B.; Ji, S.; Zhang, L.; Zou, K.; et al. Traffic-Related Environmental Factors and Childhood Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Obes. Rev. 2021, 22, e12995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerrett, M.; McConnell, R.; Wolch, J.; Chang, R.; Lam, C.; Dunton, G.; Gilliland, F.; Lurmann, F.; Islam, T.; Berhane, K. Traffic-Related Air Pollution and Obesity Formation in Children: A Longitudinal, Multilevel Analysis. Environ. Health Glob. Access Sci. Source 2014, 13, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.H.; Wang, J.; Zeng, X.W.; Chen, L.; Qin, X.D.; Zhou, Y.; Li, M.; Yang, M.; Zhao, Y.; Ren, W.H.; et al. Interactions between Air Pollution and Obesity on Blood Pressure and Hypertension in Chinese Children. Epidemiology 2015, 26, 740–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloemsma, L.D.; Wijga, A.H.; Klompmaker, J.O.; Janssen, N.A.H.; Smit, H.A.; Koppelman, G.H.; Brunekreef, B.; Lebret, E.; Hoek, G.; Gehring, U. The Associations of Air Pollution, Traffic Noise and Green Space with Overweight throughout Childhood: The PIAMA Birth Cohort Study. Environ. Res. 2019, 169, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bont, J.; Casas, M.; Barrera-Gómez, J.; Cirach, M.; Rivas, I.; Valvi, D.; Álvarez, M.; Dadvand, P.; Sunyer, J.; Vrijheid, M. Ambient Air Pollution and Overweight and Obesity in School-Aged Children in Barcelona, Spain. Environ. Int. 2019, 125, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.L.; Su, H.J.; Sheu, H.M.; Yu, H.S.; Guo, Y.L. Traffic-Related Air Pollution, Climate, and Prevalence of Eczema in Taiwanese School Children. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2008, 128, 2412–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgenstern, V.; Zutavern, A.; Cyrys, J.; Brockow, I.; Koletzko, S.; Krämer, U.; Behrendt, H.; Herbarth, O.; Von Berg, A.; Bauer, C.P.; et al. Atopic Diseases, Allergic Sensitization, and Exposure to Traffic-Related Air Pollution in Children. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 177, 1331–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pénard-Morand, C.; Raherison, C.; Charpin, D.; Kopferschmitt, C.; Lavaud, F.; Caillaud, D.; Annesi-Maesano, I. Long-Term Exposure to Close-Proximity Air Pollution and Asthma and Allergies in Urban Children. Eur. Respir. J. 2010, 36, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Lee, K.; Lee, Y.M.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.I.; Yu, S.D.; Paek, D. Acute Health Effects of Urban Fine and Ultrafine Particles on Children with Atopic Dermatitis. Environ. Res. 2011, 111, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, E.H.; Oh, I.; Jung, K.; Han, Y.; Cheong, H.K.; Ahn, K. Symptoms of Atopic Dermatitis Are Influenced by Outdoor Air Pollution. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 132, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathuria, P.; Silverberg, J.I. Association of Pollution and Climate with Atopic Eczema in US Children. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2016, 27, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pant, P.; Lal, R.M.; Guttikunda, S.K.; Russell, A.G.; Nagpure, A.S.; Ramaswami, A.; Peltier, R.E. Monitoring Particulate Matter in India: Recent Trends and Future Outlook. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2019, 12, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbanian, A.; Jafari, A.J.; Shahsavani, A.; Abdolahnejad, A.; Kermani, M.; Fanaei, F. Quantification of Mortality and Morbidity in General Population of Heavily-Industrialized City of Abadan: Effect of Long-Term Exposure. J. Air Pollut. Health 2020, 5, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.D.; Marty, M.A. Impact of Environmental Chemicals on Lung Development. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 1155–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilal, M.; Mahwish, A.; Nichol, J.E.; Qiu, Z.; Nazeer, M.; Ali, M.A.; de Leeuw, G.; Levy, R.C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; et al. Air Pollution Scenario over Pakistan: Characterization and Ranking of Extremely Polluted Cities Using Long-Term Concentrations of Aerosols and Trace Gases. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 264, 112617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, S.; Ul-Haq, Z.; Ali, M. Analysis of Optical and Physical Properties of Aerosols during Crop Residue Burning Event of October 2010 over Lahore, Pakistan. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2015, 6, 969–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ul-Haq, Z.; Tariq, S.; Ali, M.; Mahmood, K.; Batool, S.A.; Rana, A.D. A Study of Tropospheric NO2 Variability over Pakistan Using OMI Data. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2014, 5, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khokhar, M.F.; Yasmin, N.; Fatima, N.; Beirle, S.; Wagner, T. Detection of Trends and Seasonal Variation in Tropospheric Nitrogen Dioxide over Pakistan. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2015, 15, 2508–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khokhar, M.F.; Mehdi, H.; Abbas, Z.; Javed, Z. Temporal Assessment of NO2 Pollution Levels in Urban Centers of Pakistan by Employing Ground-Based and Satellite Observations. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2016, 16, 1854–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ul-Haq, Z.; Tariq, S.; Ali, M. Spatiotemporal Assessment of CO2 Emissions and Its Satellite Remote Sensing over Pakistan and Neighboring Regions. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 2017, 152–153, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, S. COVID-19: Air Pollution Remains Low as People Stay at Home. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2020, 13, 853–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Cui, K.; Young, L.H.; Wang, Y.F.; Hsieh, Y.K.; Wan, S.; Zhang, J. Air Quality Index, Indicatory Air Pollutants and Impact of COVID-19 Event on the Air Quality near Central China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2020, 20, 1204–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, Q.; Huang, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, A.; Xu, J.; Liu, Z.; Li, H.; Shi, L.; Li, R.; et al. Air Quality Changes during the COVID-19 Lockdown over the Yangtze River Delta Region: An Insight into the Impact of Human Activity Pattern Changes on Air Pollution Variation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 732, 139282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.; Li, S.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, S.; Ding, D.; Dong, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Hao, J. Quantifying the Emission Changes and Associated Air Quality Impacts during the COVID-19 Pandemic on the North China Plain: A Response Modeling Study. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 14347–14359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldasano, J.M. COVID-19 Lockdown Effects on Air Quality by NO2 in the Cities of Barcelona and Madrid (Spain). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 140353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Zhang, M.; Anshika; Gao, J.; Zhang, H.; Kota, S.H. Effect of Restricted Emissions during COVID-19 on Air Quality in India. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahato, S.; Pal, S.; Ghosh, K.G. Effect of Lockdown amid COVID-19 Pandemic on Air Quality of the Megacity Delhi, India. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 730, 139086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mor, S.; Kumar, S.; Singh, T.; Dogra, S.; Pandey, V.; Ravindra, K. Impact of COVID-19 Lockdown on Air Quality in Chandigarh, India: Understanding the Emission Sources during Controlled Anthropogenic Activities. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 127978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistical Bureau of Punjab; Government of Punjab. 2021. Available online: https://bos.punjab.gov.pk/system/files/PIF-2022.pdf (accessed on 30 May 2022).
- Asna-ashary, M.; Farzanegan, M.R.; Feizi, M.; Sadati, S.M. COVID-19 Outbreak and Air Pollution in Iran: A Panel VAR Analysis. MAGKS Papers on Economics 202016, Philipps-Universität Marburg, Faculty of Business Administration and Economics, Department of Economics (Volkswirtschaftliche Abteilung). 2020. Available online: https://ideas.repec.org/p/mar/magkse/202016.html (accessed on 17 January 2023).
- United Nation News. WHO Chief Declares End to COVID-19 as a Global Health Emergency. 2020. Available online: https://news.un.org/en/story/2023/05/1136367 (accessed on 21 June 2022).
- Zambrano-Monserrate, M.A.; Ruano, M.A.; Sanchez-Alcalde, L. Indirect Effects of COVID-19 on the Environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhammad, S.; Long, X.; Salman, M. COVID-19 Pandemic and Environmental Pollution: A Blessing in Disguise? Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadat, S.; Rawtani, D.; Hussain, C.M. Environmental Perspective of COVID-19. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnett, R.; Chen, H.; Szyszkowicz, M.; Fann, N.; Hubbell, B.; Pope, C.A.; Apte, J.S.; Brauer, M.; Cohen, A.; Weichenthal, S.; et al. Global Estimates of Mortality Associated with Longterm Exposure to Outdoor Fine Particulate Matter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 9592–9597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lelieveld, J.; Pozzer, A.; Pöschl, U.; Fnais, M.; Haines, A.; Münzel, T. Loss of Life Expectancy from Air Pollution Compared to Other Risk Factors: A Worldwide Perspective. Cardiovasc. Res. 2020, 116, 1910–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elansky, N.F.; Kouznetsov, R.D.; Verevkin, Y.M.; Ponomarev, N.A.; Rakitin, V.S.; Shilkin, A.V.; Semutnikova, E.G.; Zakharova, P.V. Time variations in the concentration of pollutants in the atmosphere over Moscow and estimation of their emissions. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 231, 012014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szep, R.; Matyas, L.; Keresztes, R.; Ghimpusan, M. Tropospheric Ozone Concentrations—Seasonal and Daily Analysis and Its Association with NO and NO2 as a Function of NOx in Ciuc Depression—Romania. Rev. Chim. 2016, 67, 205–213. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Q.; Fan, S.; He, J.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zu, F. Particle Size Distribution and Characteristics of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons during a Heavy Haze Episode in Nanjing, China. Particuology 2015, 18, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).