Application of Functional Principal Component Analysis in the Spatiotemporal Land-Use Regression Modeling of PM2.5
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of the Study Area and Data
2.2. Ordinary LUR Model
2.3. Basis Expansion of Functional Data
2.4. Functional Principal Component Analysis
2.5. Functional Land-Use Regression Model
2.6. Validation Using an Alternative Model
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burnett, R.; Chen, H.; Szyszkowicz, M.; Fann, N.; Hubbell, B.; Pope, C.A.; Apte, J.S.; Brauer, M.; Cohen, A.; Weichenthal, S.; et al. Global estimates of mortality associated with long-term exposure to outdoor fine particulate matter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 9592–9597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- So, R.; Andersen, Z.J.; Chen, J.; Stafoggia, M.; de Hoogh, K.; Katsouyanni, K.; Vienneau, D.; Rodopoulou, S.; Samoli, E.; Lim, Y.-H.; et al. Long-term exposure to air pollution mortality in a Danish nationwide administrative cohort study: Beyond mortality from cardiopulmonary disease and lung cancer. Environ. Int. 2022, 164, 107241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khorrami, Z.; Pourkhosravani, M.; Rezapour, M.; Etemad, K.; Taghavi-Shahri, S.M.; Künzli, N.; Amini, H.; Khanjani, N. Multiple air pollutant exposure and lung cancer in Tehran, Iran. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khorrami, Z.; Pourkhosravani, M.; Eslahi, M.; Rezapour, M.; Akbari, M.E.; Amini, H.; Taghavi-Shahri, S.M.; Künzli, N.; Etemad, K.; Khanjani, N. Multiple air pollutants exposure and leukaemia incidence in Tehran, Iran from 2010 to 2016: A retrospective cohort study. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e060562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.-N.; Tao, F.; Ma, P.-L.; Wang, C.-Y.; Kong, W.; Chen, W.-K.; Zhou, T. A short-distance healthy route planning approach. J. Transp. Health 2022, 24, 101314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, H.; Lu, H. Application of a novel early warning system based on fuzzy time series in urban air quality forecasting in China. Appl. Soft Comput. 2018, 71, 783–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, H.; Taghavi-Shahri, S.-M.; Henderson, S.B.; Hosseini, V.; Hassankhany, H.; Naderi, M.; Ahadi, S.; Schindler, C.; Künzli, N.; Yunesian, M. Annual and seasonal spatial models for nitrogen oxides in Tehran, Iran. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, H.; Taghavi-Shahri, S.M.; Henderson, S.B.; Naddafi, K.; Nabizadeh, R.; Yunesian, M. Land use regression models to estimate the annual and seasonal spatial variability of sulfur dioxide and particulate matter in Tehran, Iran. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 488–489, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghavi-Shahri, S.M.; Fassò, A.; Mahaki, B.; Amini, H. Concurrent spatiotemporal daily land use regression modeling and missing data imputation of fine particulate matter using distributed space-time expectation maximization. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 224, 117202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi Basiri, E.; Taghavi-Shahri, S.M.; Mahaki, B.; Amini, H. Functional Kriging for Spatiotemporal Modeling of Nitrogen Dioxide in a Middle Eastern Megacity. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, P.H.; LeMasters, G.K. A Review of Land-use Regression Models for Characterizing Intraurban Air Pollution Exposure. Inhal. Toxicol. 2007, 19, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoek, G.; Beelen, R.; de Hoogh, K.; Vienneau, D.; Gulliver, J.; Fischer, P.; Briggs, D. A review of land-use regression models to assess spatial variation of outdoor air pollution. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 7561–7578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, H.; Yunesian, M.; Hosseini, V.; Schindler, C.; Henderson, S.B.; Künzli, N. A systematic review of land use regression models for volatile organic compounds. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 171, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Ban, J.; Wang, Q.; Li, T. Statistical spatial-temporal modeling of ambient ozone exposure for environmental epidemiology studies: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 701, 134463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Zhang, C.; Bi, J. Development of land use regression models for PM2.5, SO2, NO2 and O3 in Nanjing, China. Environ. Res. 2017, 158, 542–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashima, S.; Yorifuji, T.; Sawada, N.; Nakaya, T.; Eboshida, A. Comparison of land use regression models for NO2 based on routine and campaign monitoring data from an urban area of Japan. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631–632, 1029–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanpour Matikolaei, S.A.H.; Jamshidi, H.; Samimi, A. Characterizing the effect of traffic density on ambient CO, NO2, and PM2.5 in Tehran, Iran: An hourly land-use regression model. Transp. Lett. 2019, 11, 436–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsay, J.O.; Hooker, G.; Graves, S. Functional Data Analysis with R and MATLAB; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 1–207. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.-L.; Chiou, J.-M.; Müller, H.-G. Functional Data Analysis. Annu. Rev. Stat. Its Appl. 2016, 3, 257–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Finazzi, F.; Fassò, A. D-STEM v2: A Software for Modeling Functional Spatio-Temporal Data. J. Stat. Softw. 2021, 99, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassò, A.; Finazzi, F. Maximum likelihood estimation of the dynamic coregionalization model with heterotopic data. Environmetrics 2011, 22, 735–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehbi, H.-M.; Blangiardo, M.; Gulliver, J.; Fecht, D.; de Hoogh, K.; Al-Kanaani, Z.; Tillin, T.; Hardy, R.; Chaturvedi, N.; Hansell, A.L. Air pollution and cardiovascular mortality with over 25 years follow-up: A combined analysis of two British cohorts. Environ. Int. 2017, 99, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toro, R.; Downward, G.S.; van der Mark, M.; Brouwer, M.; Huss, A.; Peters, S.; Hoek, G.; Nijssen, P.; Mulleners, W.M.; Sas, A.; et al. Parkinson’s disease and long-term exposure to outdoor air pollution: A matched case-control study in the Netherlands. Environ. Int. 2019, 129, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Beelen, R.; Stafoggia, M.; Raaschou-Nielsen, O.; Andersen, Z.J.; Hoffmann, B.; Fischer, P.; Houthuijs, D.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.; Weinmayr, G.; et al. Long-term exposure to elemental constituents of particulate matter and cardiovascular mortality in 19 European cohorts: Results from the ESCAPE and TRANSPHORM projects. Environ. Int. 2014, 66, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Tang, R.; Qiu, H.; Lai, P.-C.; Wong, P.; Thach, T.-Q.; Allen, R.; Brauer, M.; Tian, L.; Barratt, B. Long term exposure to air pollution and mortality in an elderly cohort in Hong Kong. Environ. Int. 2018, 117, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yorifuji, T.; Kashima, S.; Tsuda, T.; Ishikawa-Takata, K.; Ohta, T.; Tsuruta, K.-i.; Doi, H. Long-term exposure to traffic-related air pollution and the risk of death from hemorrhagic stroke and lung cancer in Shizuoka, Japan. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 443, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefian, F.; Mahvi, A.H.; Yunesian, M.; Hassanvand, M.S.; Kashani, H.; Amini, H. Long-term exposure to ambient air pollution and autism spectrum disorder in children: A case-control study in Tehran, Iran. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 1216–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, K.; Li, S. The Functional Spatio-Temporal Statistical Model with Application to O3 Pollution in Beijing, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing, version 4.1.2. Windows; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Ramsay, J.; Graves, S.; Hooker, G. FDA: Functional Data Analysis, version 5.5.1; R Package: Vienna, Austria, 2021; Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=fda (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Hijmans, R.J. Raster: Geographic Data Analysis and Modeling, version 3.5-29; R Package: Vienna, Austria, 2021; Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=raster (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Finazzi, F.; Fassò, A. D-STEM: A Software for the Analysis and Mapping of Environmental Space-Time Variables. J. Stat. Softw. 2014, 62, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavousi, A.; Fallah, A.; Meshkani, M.R. Spatial Analysis of Air Pollution in Tehran City by a Bayesian Auto-Binomial Model. J. Basic. Appl. Sci. Res. 2013, 3, 961–968. [Google Scholar]
- Farzad, K.; Khorsandi, B.; Khorsandi, M.; Bouamra, O.; Maknoon, R. A study of cardiorespiratory related mortality as a result of exposure to black carbon. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 725, 138422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, A.; Aliasghari, P.; Hosseini, V. Black carbon and PM2.5 monitoring campaign on the roadside and residential urban background sites in the city of Tehran. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 218, 116928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbazi, H.; Reyhanian, M.; Hosseini, V.; Afshin, H. The Relative Contributions of Mobile Sources to Air Pollutant Emissions in Tehran, Iran: An Emission Inventory Approach. Emiss. Control Sci. Technol. 2016, 2, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dons, E.; Van Poppel, M.; Kochan, B.; Wets, G.; Int Panis, L. Modeling temporal and spatial variability of traffic-related air pollution: Hourly land use regression models for black carbon. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 74, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masiol, M.; Squizzato, S.; Chalupa, D.; Rich, D.Q.; Hopke, P.K. Spatial-temporal variations of summertime ozone concentrations across a metropolitan area using a network of low-cost monitors to develop 24 hourly land-use regression models. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 654, 1167–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masiol, M.; Zíková, N.; Chalupa, D.C.; Rich, D.Q.; Ferro, A.R.; Hopke, P.K. Hourly land-use regression models based on low-cost PM monitor data. Environ. Res. 2018, 167, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patton, A.P.; Collins, C.; Naumova, E.N.; Zamore, W.; Brugge, D.; Durant, J.L. An Hourly Regression Model for Ultrafine Particles in a Near-Highway Urban Area. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 3272–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


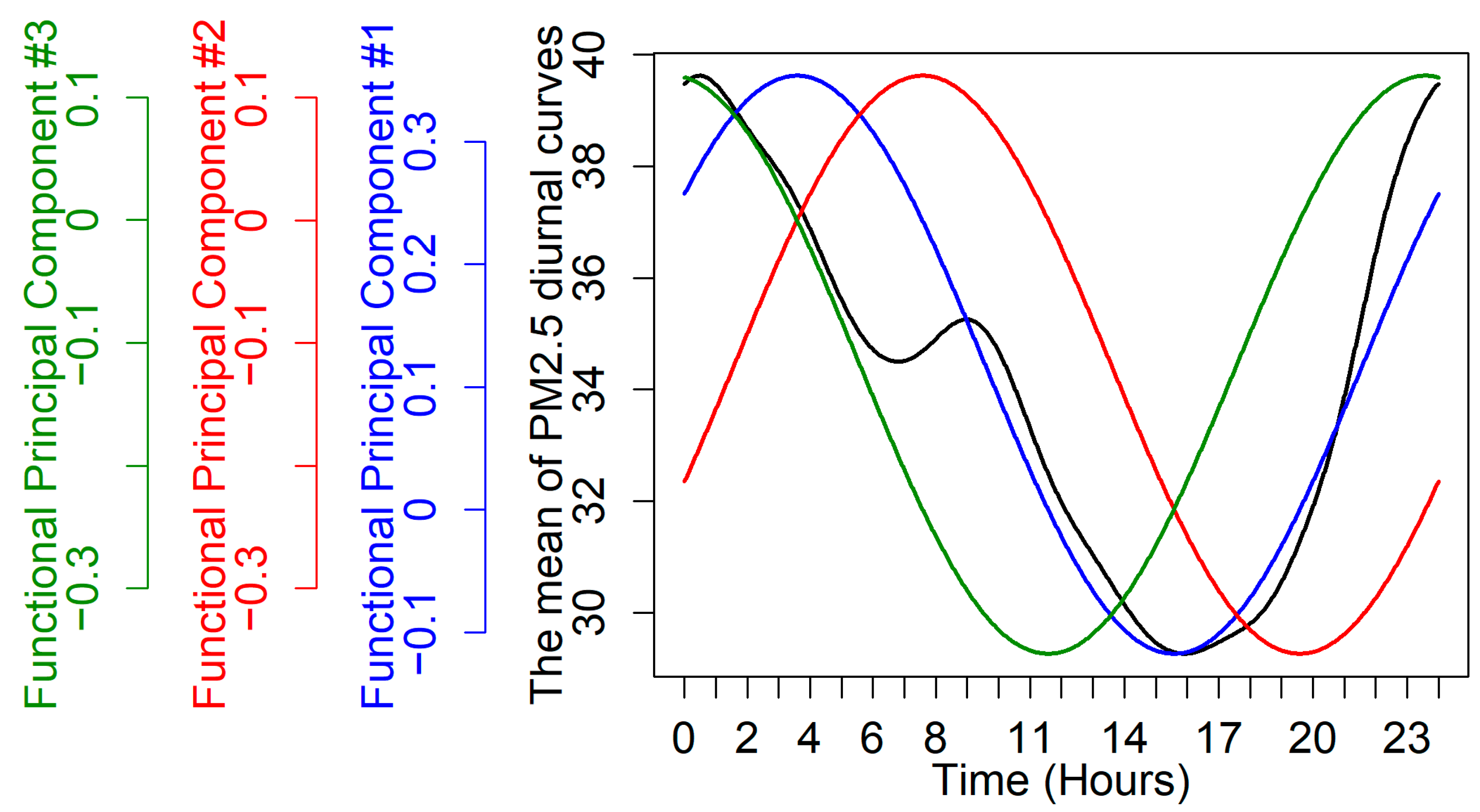

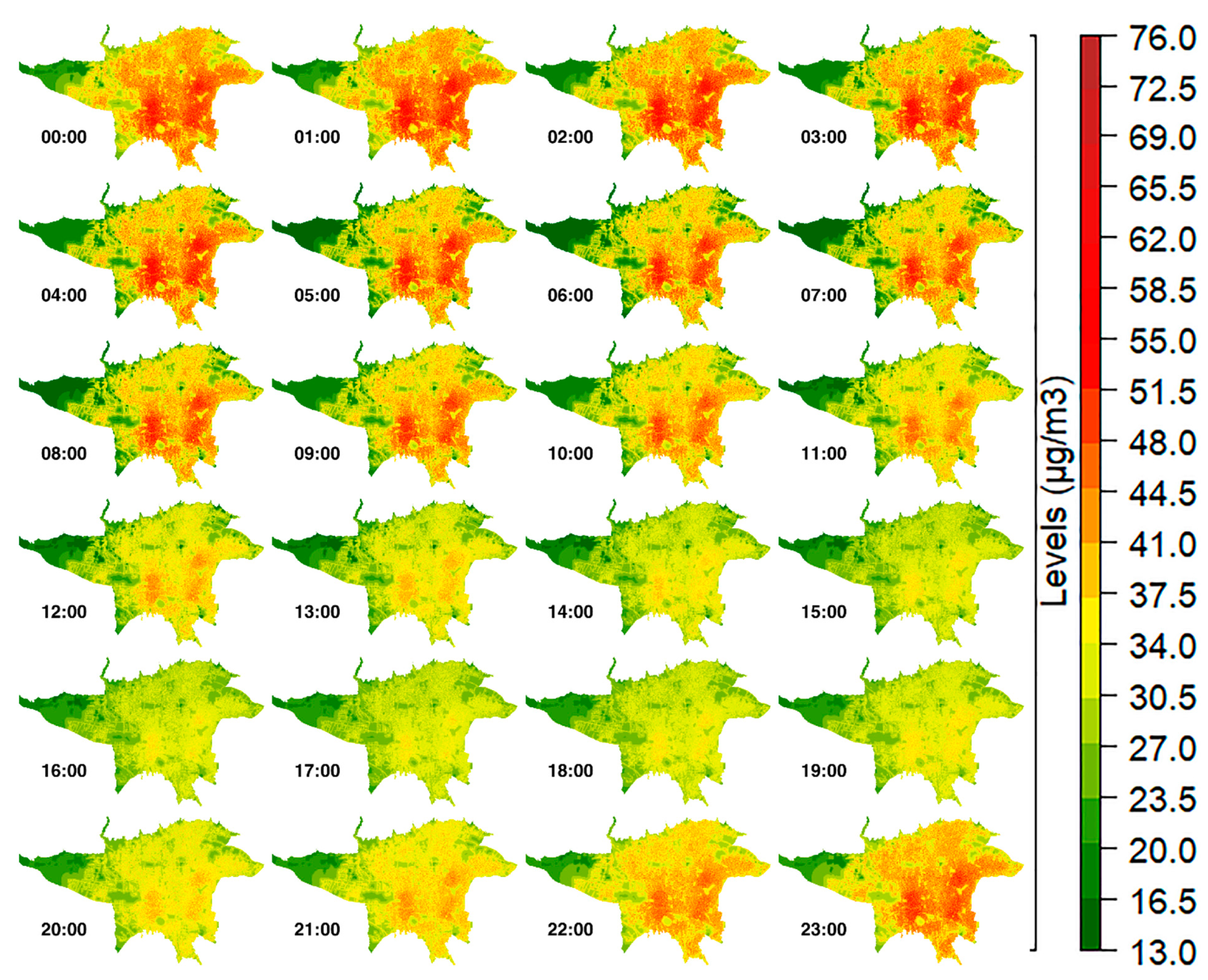
| Station ID | Station Name | Latitude (N) | Longitude (E) | FPCS #1 | FPCS #2 | FPCS #3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Region 11 | 35.672980 | 51.389730 | −5.83 | 1.57 | 7.25 |
| 2 | Golbarg | 35.731030 | 51.506130 | −34.19 | 2.18 | −0.06 |
| 3 | Elmo Sanat | 35.739811 | 51.511431 | 16.87 | −4.74 | −0.56 |
| 4 | Tehran university | 35.703356 | 51.397764 | 21.12 | 1.37 | −3.73 |
| 5 | Cheshme | 35.752714 | 51.262824 | −7.61 | −12.57 | 4.76 |
| 6 | Shokufe park | 35.685736 | 51.450761 | 17.16 | −3.61 | 6.50 |
| 7 | Region 15 | 35.641076 | 51.479964 | −12.29 | 13.55 | −7.97 |
| 8 | Setad | 35.727080 | 51.431200 | −0.01 | −3.98 | 2.67 |
| 9 | Atisaz | 35.797161 | 51.522739 | 7.31 | −22.75 | 3.48 |
| 10 | Aghdasyeh | 35.795870 | 51.484140 | −27.26 | −3.31 | 4.14 |
| 11 | Beheshti | 35.803375 | 51.395137 | −36.75 | −6.69 | −1.69 |
| 12 | Pasdaran | 35.789664 | 51.473361 | −40.13 | 17.48 | 2.53 |
| 13 | Farmandary Rey | 35.593005 | 51.427697 | 83.90 | 7.73 | −8.86 |
| 14 | Region 4 | 35.741820 | 51.506430 | −27.95 | −5.18 | −6.73 |
| 15 | Sharif University | 35.702270 | 51.350940 | 24.79 | −2.77 | −7.59 |
| 16 | Shad Abad | 35.670050 | 51.297350 | −15.74 | 3.15 | −1.54 |
| 17 | Poonak | 35.762300 | 51.331680 | −52.98 | 1.3 | −2.46 |
| 18 | Rose park | 35.739890 | 51.267891 | −17.40 | −10.39 | 2.01 |
| 19 | Salamat park | 35.648900 | 51.356078 | 34.71 | 5.11 | −5.78 |
| 20 | Shahre Rey | 35.603630 | 51.425710 | 7.14 | 6.94 | −4.53 |
| 21 | Ghaem park | 35.658217 | 51.328228 | 71.56 | 13.01 | 15.79 |
| 22 | Region 2 | 35.777089 | 51.368175 | −43.33 | −0.50 | −3.51 |
| 23 | Darous | 35.769994 | 51.454160 | 25.66 | −8.84 | −4.47 |
| 24 | Tarbiyat Modares university | 35.717510 | 51.381570 | −43.73 | 6.14 | −1.08 |
| 25 | Region 19 | 35.635210 | 51.362519 | 0.62 | 4.18 | 9.64 |
| 26 | Razi park | 35.670158 | 51.389386 | 79.87 | −7.21 | −2.85 |
| 27 | Region 10 | 35.697480 | 51.358031 | −7.97 | 4.92 | 2.82 |
| 28 | Region 16 | 35.644584 | 51.397657 | −9.95 | 5.75 | 2.96 |
| 29 | Masoudiyeh | 35.630030 | 51.499020 | 0.55 | −1.81 | −0.82 |
| 30 | Tehransar | 35.712960 | 51.214490 | −8.15 | −0.04 | −0.33 |
| Regression Intercept and Predictors | Estimated Coefficients for the Main FPCS | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| FPCS #1 | FPCS #2 | FPCS #3 | |
| 0. Intercept | 2.908 × 101 | −6.643 × 10−2 | 5.868 × 10−1 |
| 1. Residual of recognizable land-use areas in buffer radii of 400 m (m2) | −1.495 × 10−3 | 4.702 × 10−5 | −3.206 × 10−5 |
| 2. Natural logarithm of distance to the nearest road (m) | −1.313 × 101 | −1.202 × 100 | −3.579 × 10−1 |
| 3. Total population density in buffer radii of 2750 m (persons per km2) | 1.622 × 10−3 | 3.484 × 10−4 | 2.405 × 10−5 |
| 4. Arid or undeveloped land-use area in buffer radii of 200 m (m2) | −4.563 × 10−4 | −1.220 × 10−4 | 7.129 × 10−5 |
| Dimensions | FLUR Model Assessment | D-STEM Model Assessment | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R-Squared | RMSE | R-Squared | RMSE | |
| Spatial | 32.75% | 5.6580 | 33.62% | 5.6578 |
| Temporal | 99.99% | 0.0041 | 99.44% | 0.6727 |
| Spatiotemporal | 43.35% | 6.0820 | 42.20% | 6.1895 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Taghavi, M.; Ghanizadeh, G.; Ghasemi, M.; Fassò, A.; Hoek, G.; Hushmandi, K.; Raei, M. Application of Functional Principal Component Analysis in the Spatiotemporal Land-Use Regression Modeling of PM2.5. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 926. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14060926
Taghavi M, Ghanizadeh G, Ghasemi M, Fassò A, Hoek G, Hushmandi K, Raei M. Application of Functional Principal Component Analysis in the Spatiotemporal Land-Use Regression Modeling of PM2.5. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(6):926. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14060926
Chicago/Turabian StyleTaghavi, Mahmood, Ghader Ghanizadeh, Mohammad Ghasemi, Alessandro Fassò, Gerard Hoek, Kiavash Hushmandi, and Mehdi Raei. 2023. "Application of Functional Principal Component Analysis in the Spatiotemporal Land-Use Regression Modeling of PM2.5" Atmosphere 14, no. 6: 926. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14060926
APA StyleTaghavi, M., Ghanizadeh, G., Ghasemi, M., Fassò, A., Hoek, G., Hushmandi, K., & Raei, M. (2023). Application of Functional Principal Component Analysis in the Spatiotemporal Land-Use Regression Modeling of PM2.5. Atmosphere, 14(6), 926. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14060926








