Consideration of Altered Anthropogenic Behavior during the First Lockdown and Its Effects on Air Pollutants and Land Surface Temperature in European Cities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
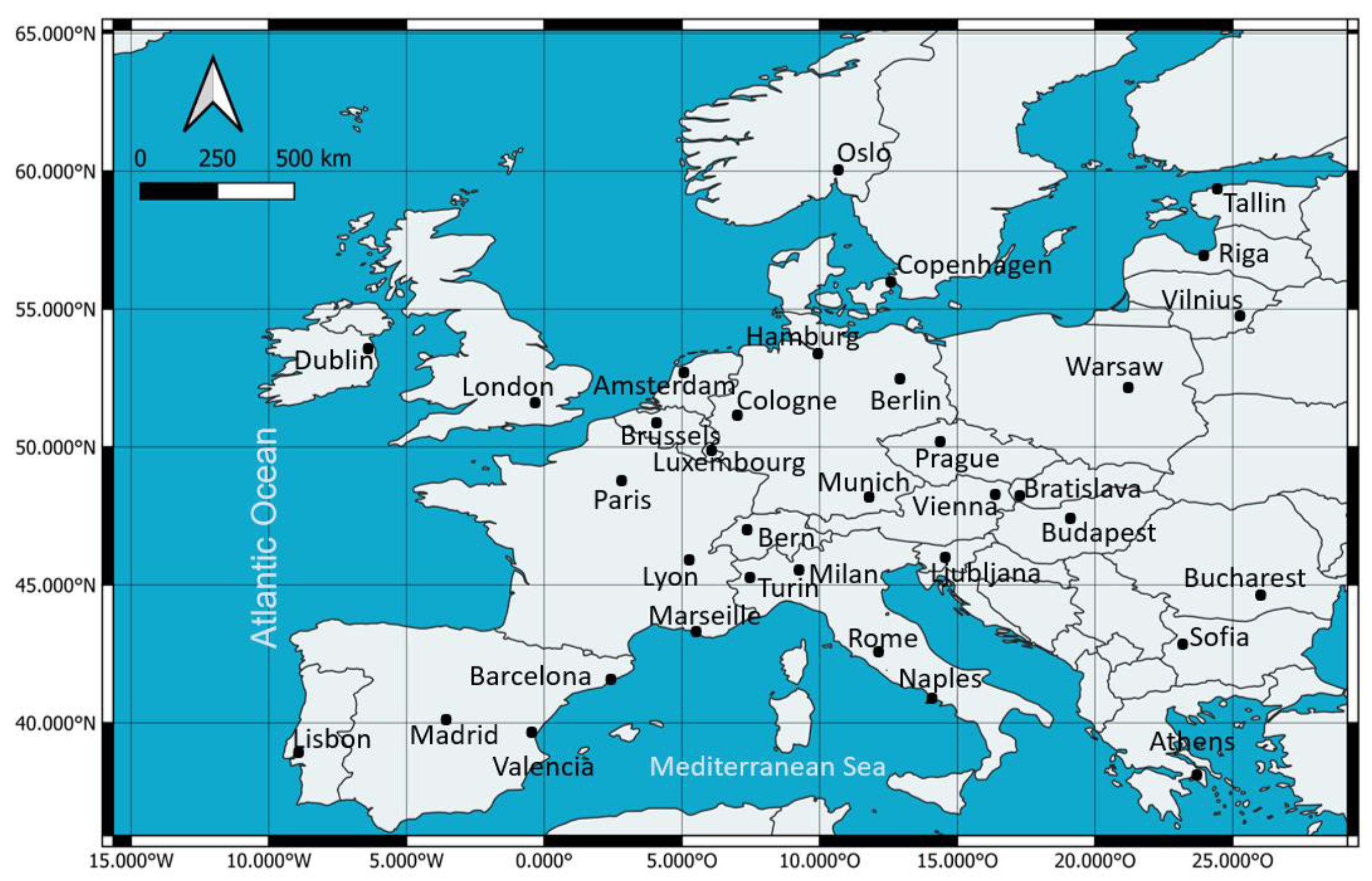
2.1. Investigation Period and Study Area
2.2. Air Pollutants under Study
2.3. Data
2.4. Statistical Analysis
- H0: the two distributions are identical, F(x) ≥ G(x) for all x, where F(x) is the lockdown and G(x) is the reference period.
- HA: they do not have the same distribution; the lockdown distributions are shifted toward lower values: F(x) < G(x) for at least one x.
- H0, ozone: the two distributions are identical, F(x) ≤ G(x) for all x, where F(x) is the lockdown and G(x) is the reference period.
- HA, ozone: they do not have the same distribution; the lockdown distributions are shifted toward higher values: F(x) > G(x) for at least one x.
3. Results
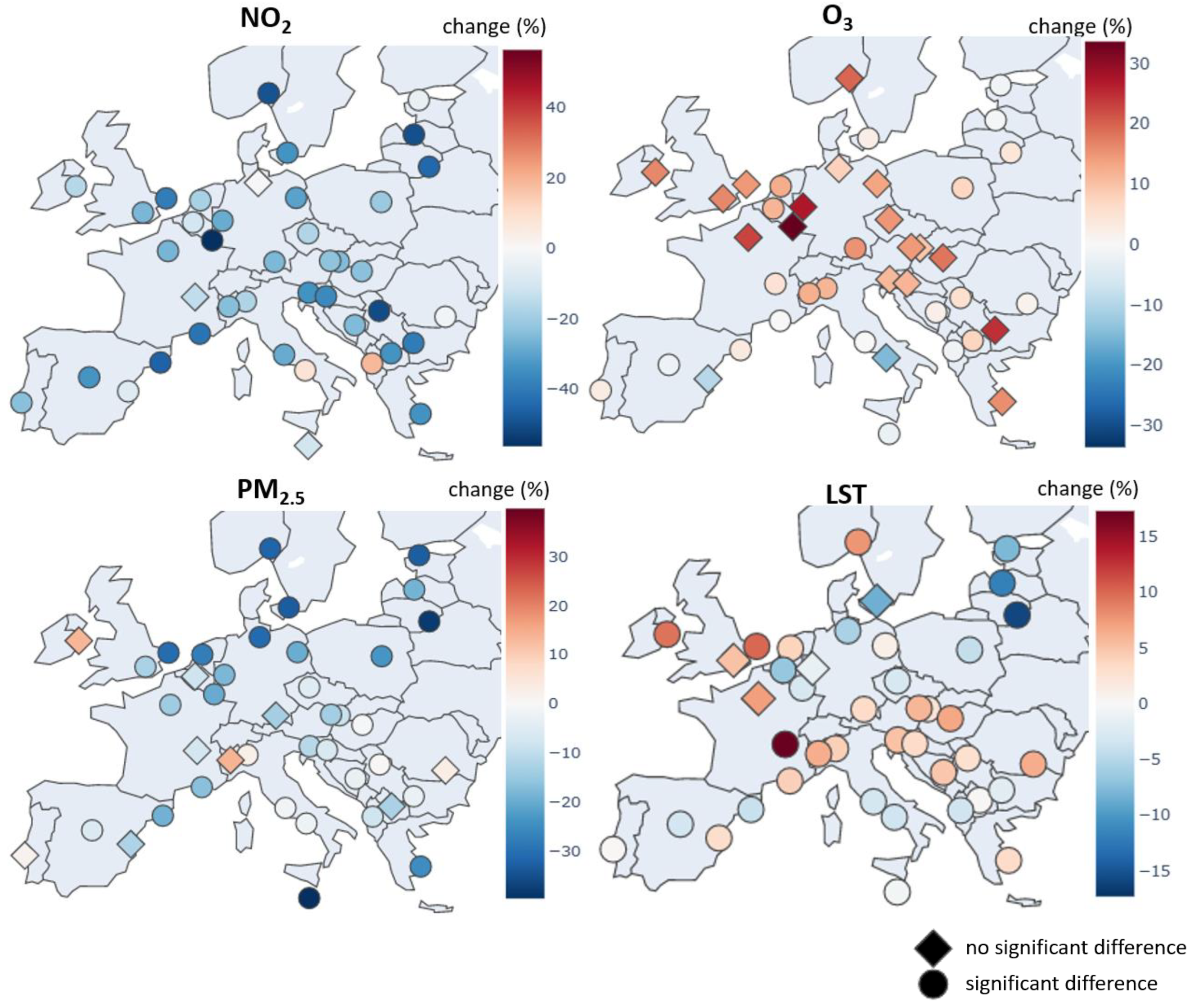
3.1. Multiparameter Overview
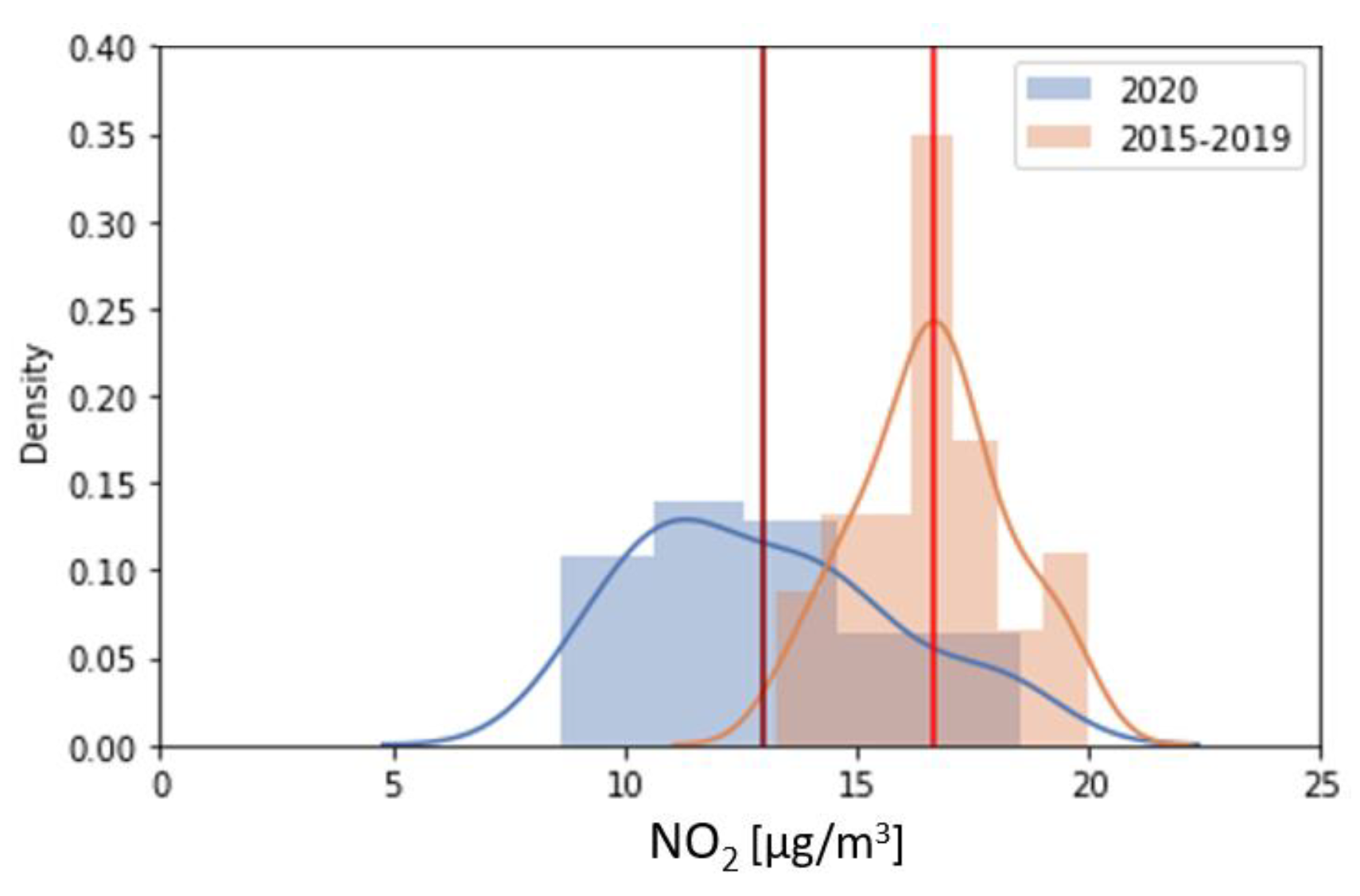
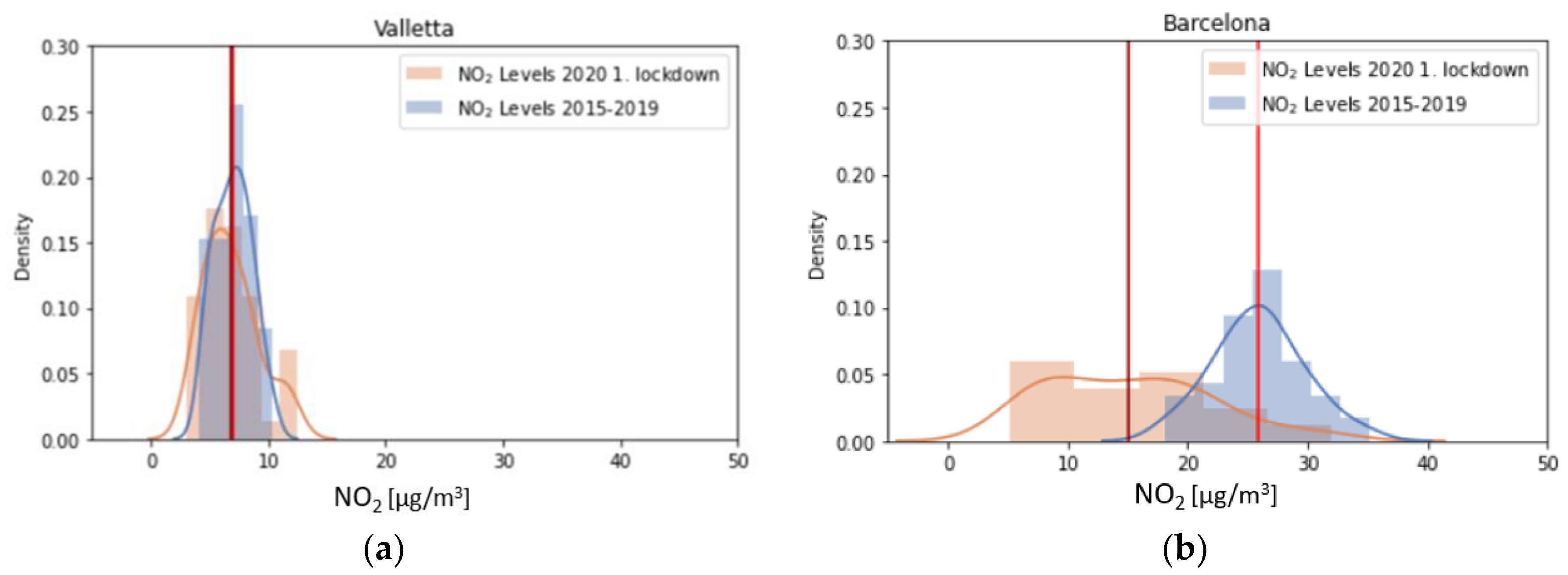
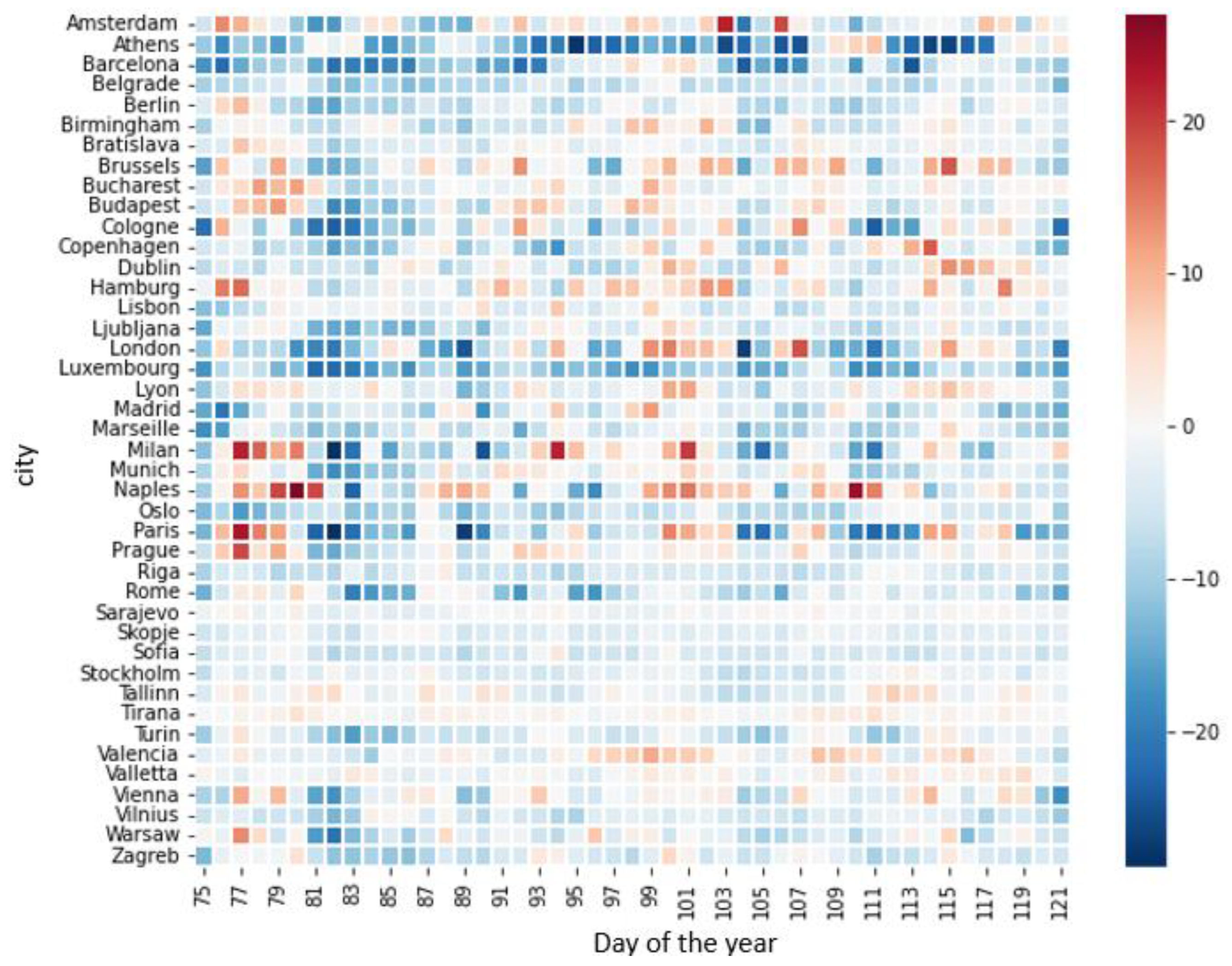
3.2. Nitrogen Dioxide
3.3. Ozone
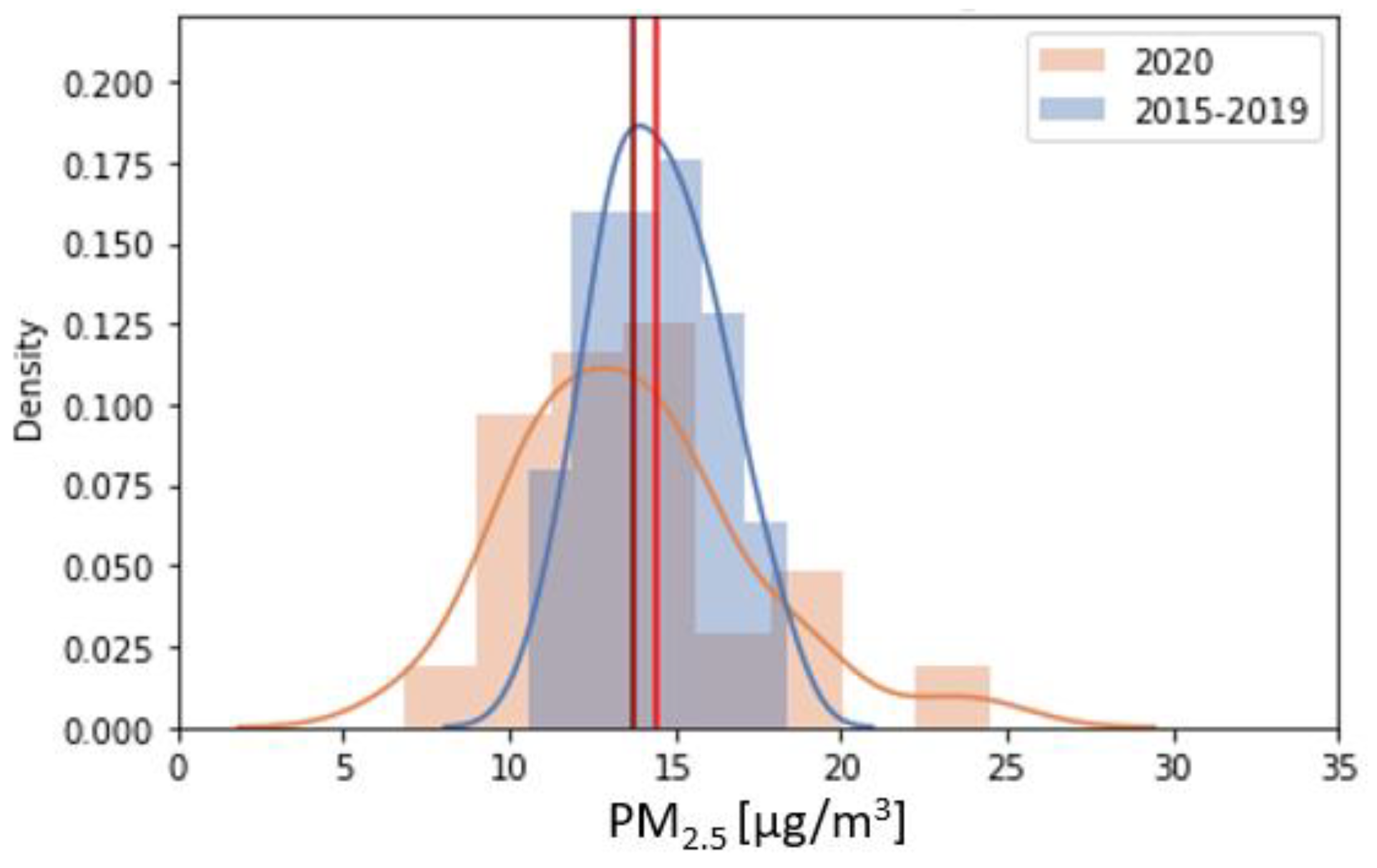
3.4. Particulate Matter
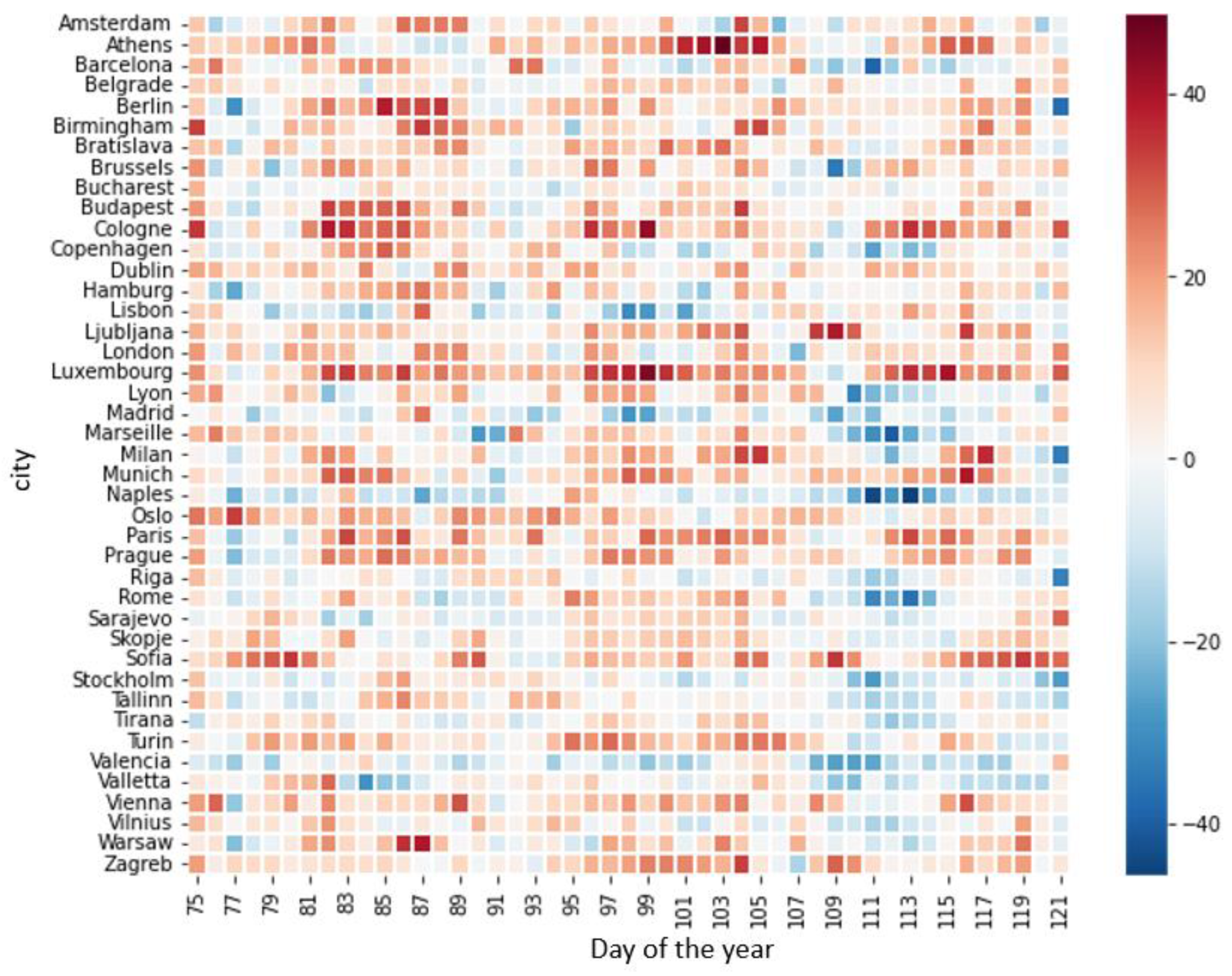
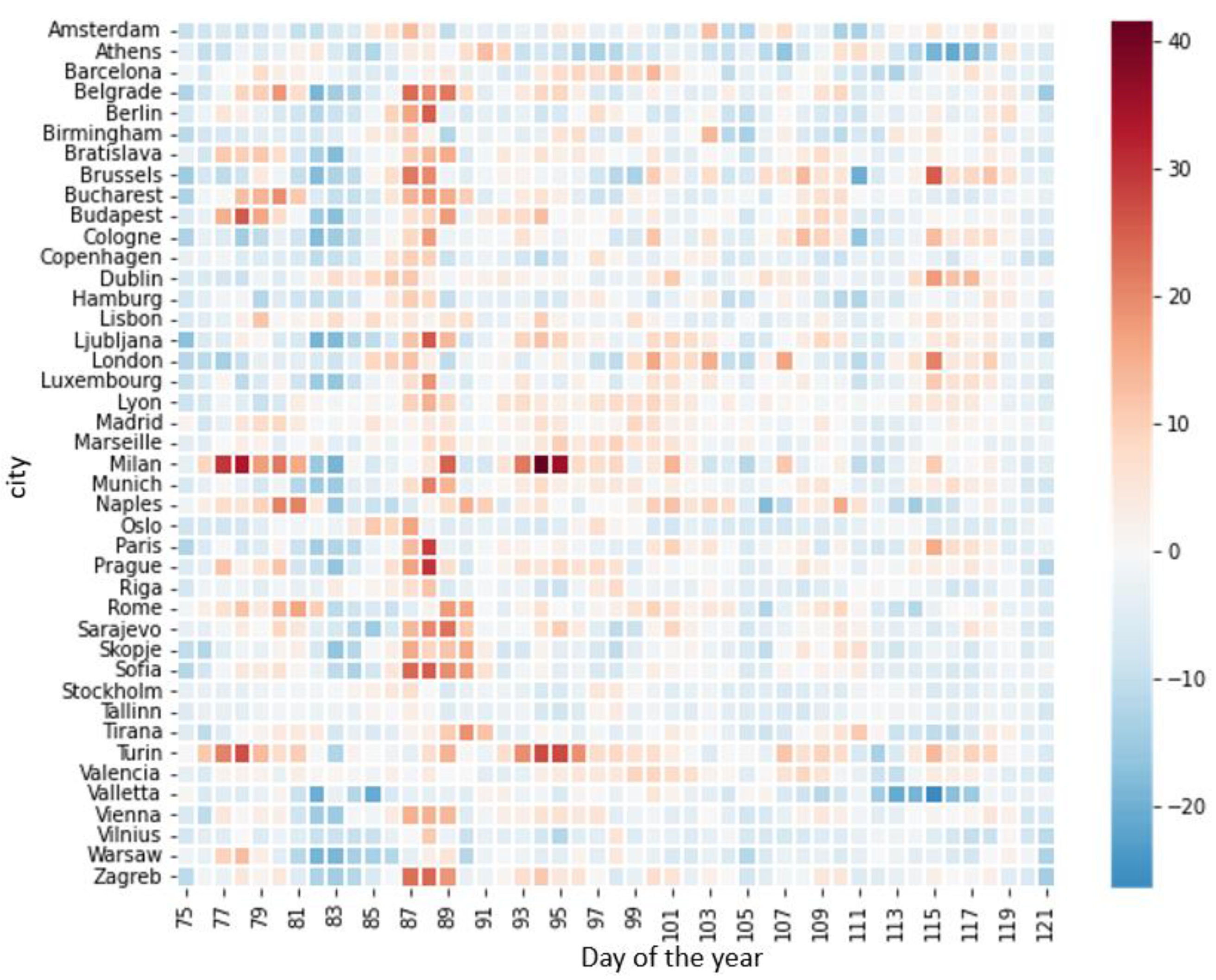
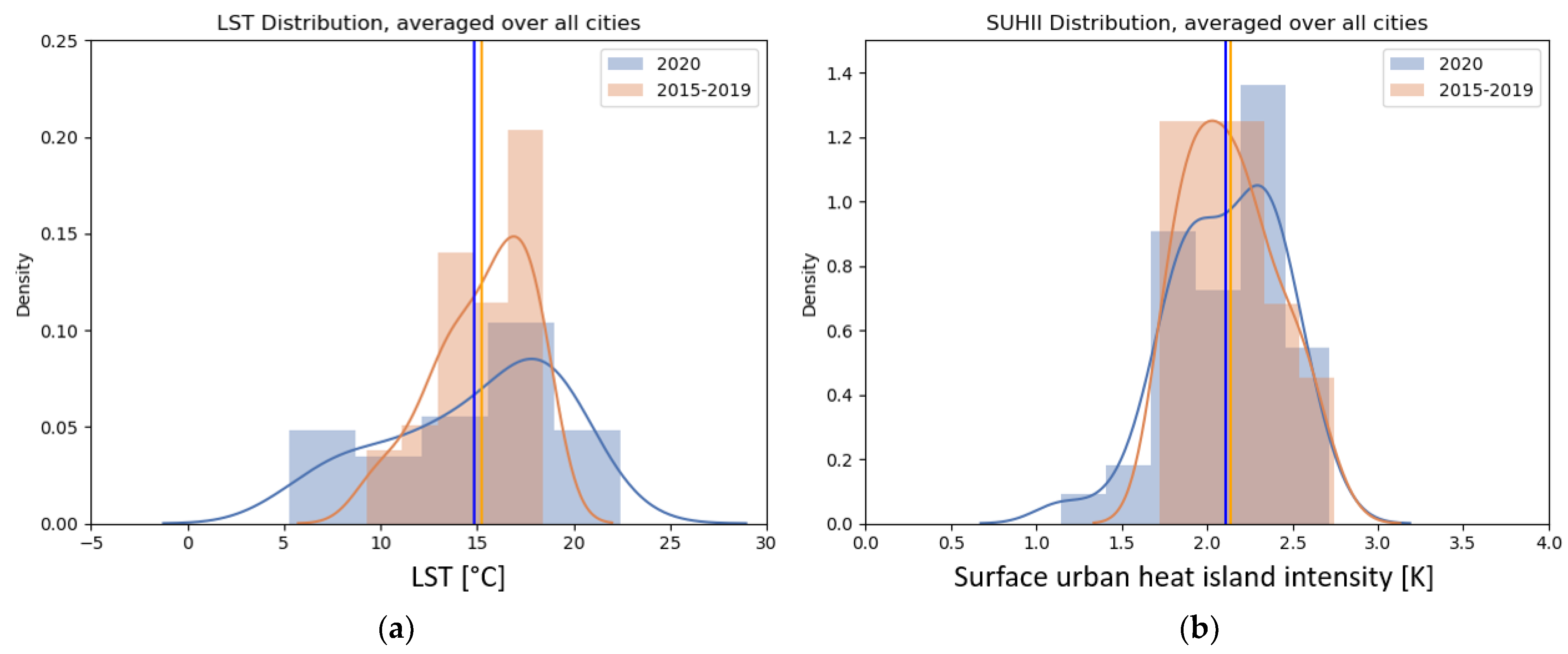
3.5. Land Surface Temperature
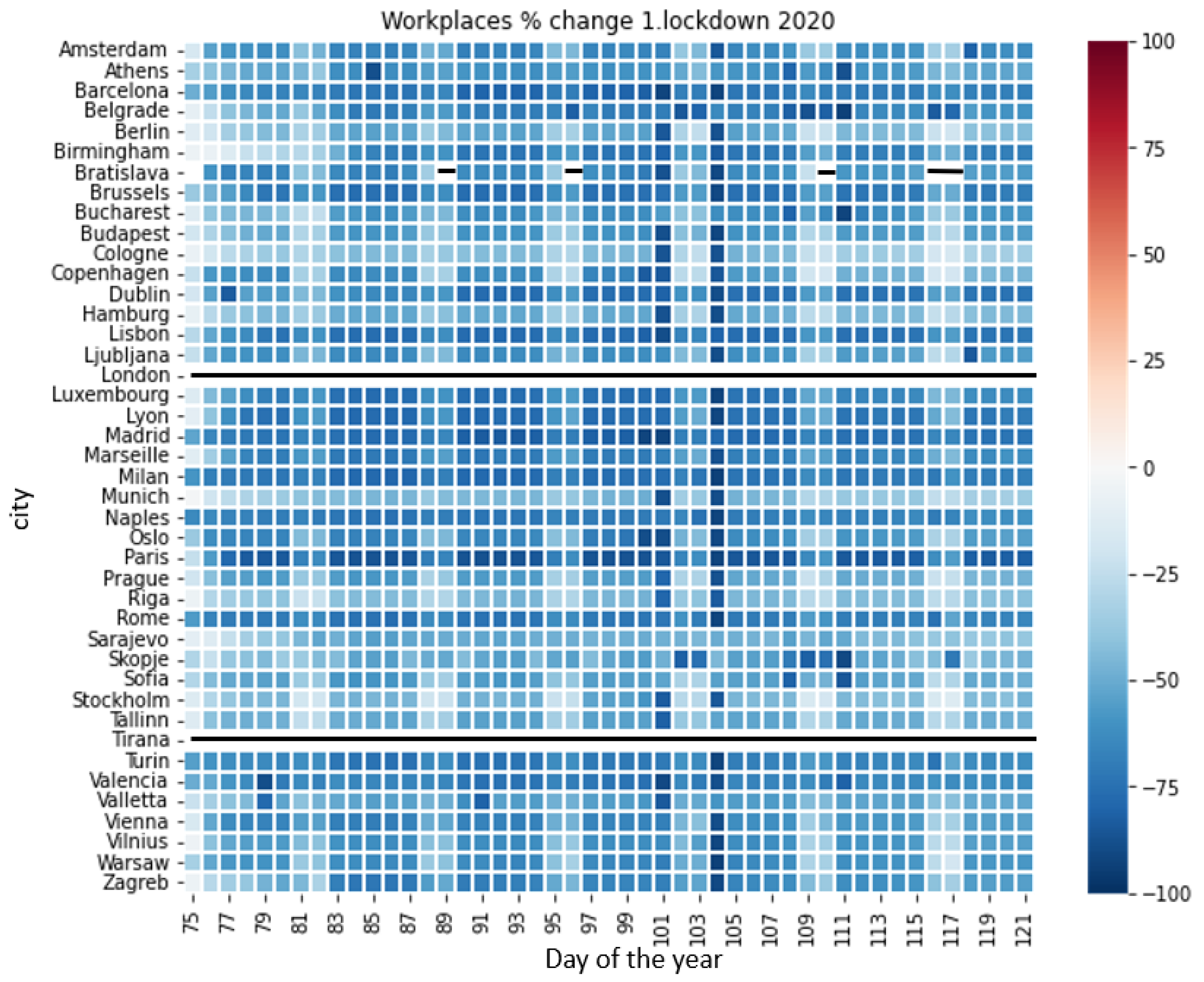
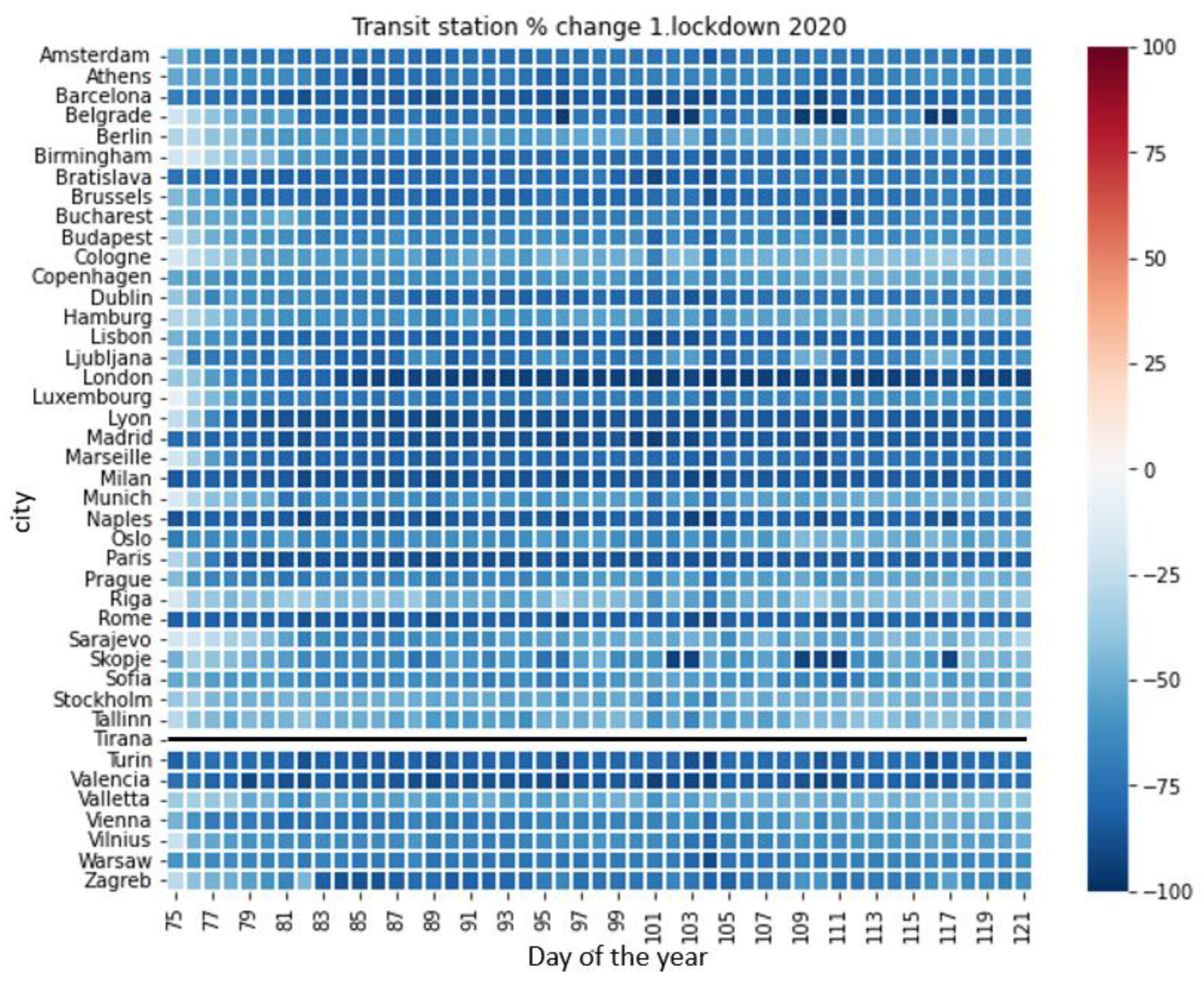
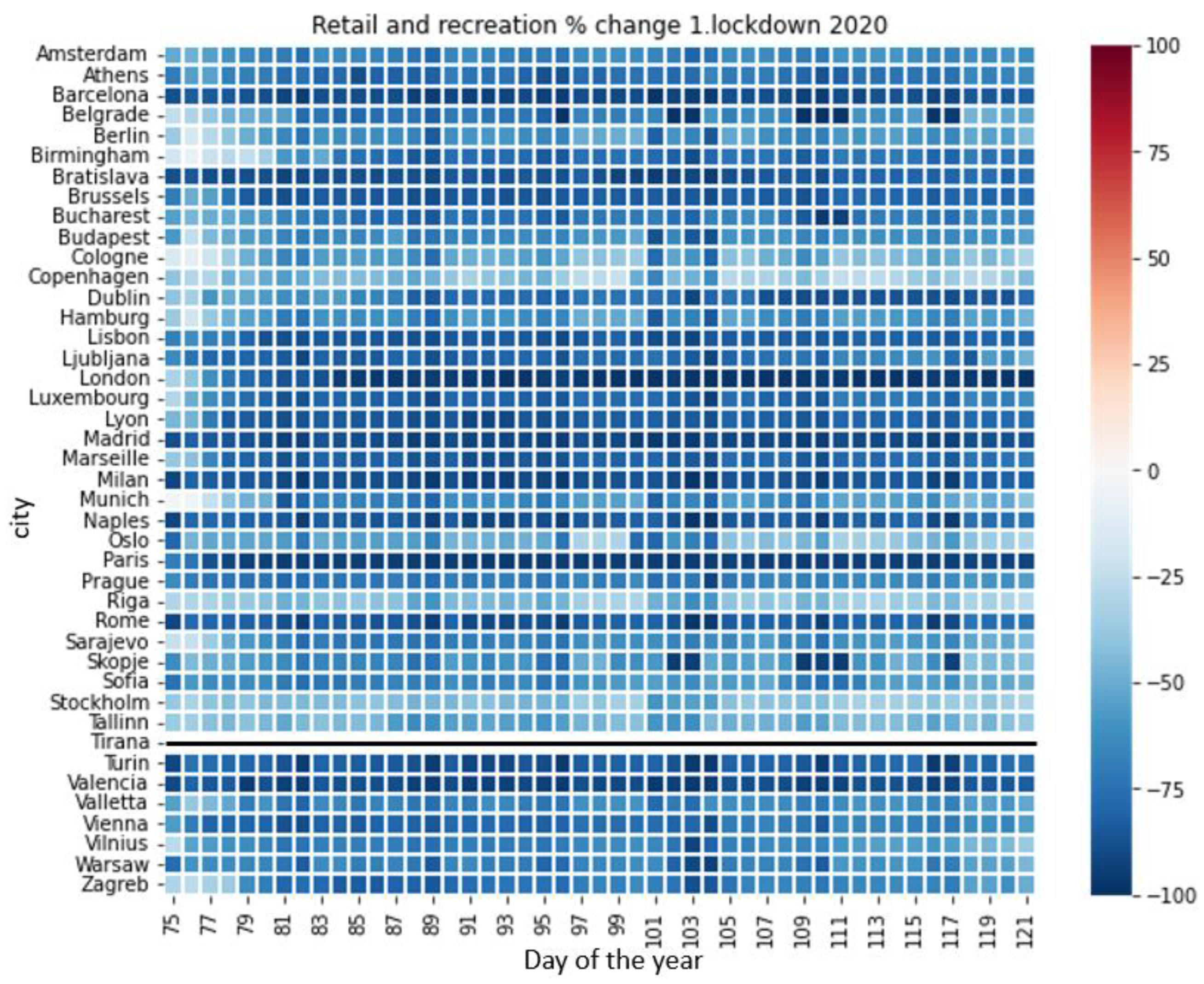
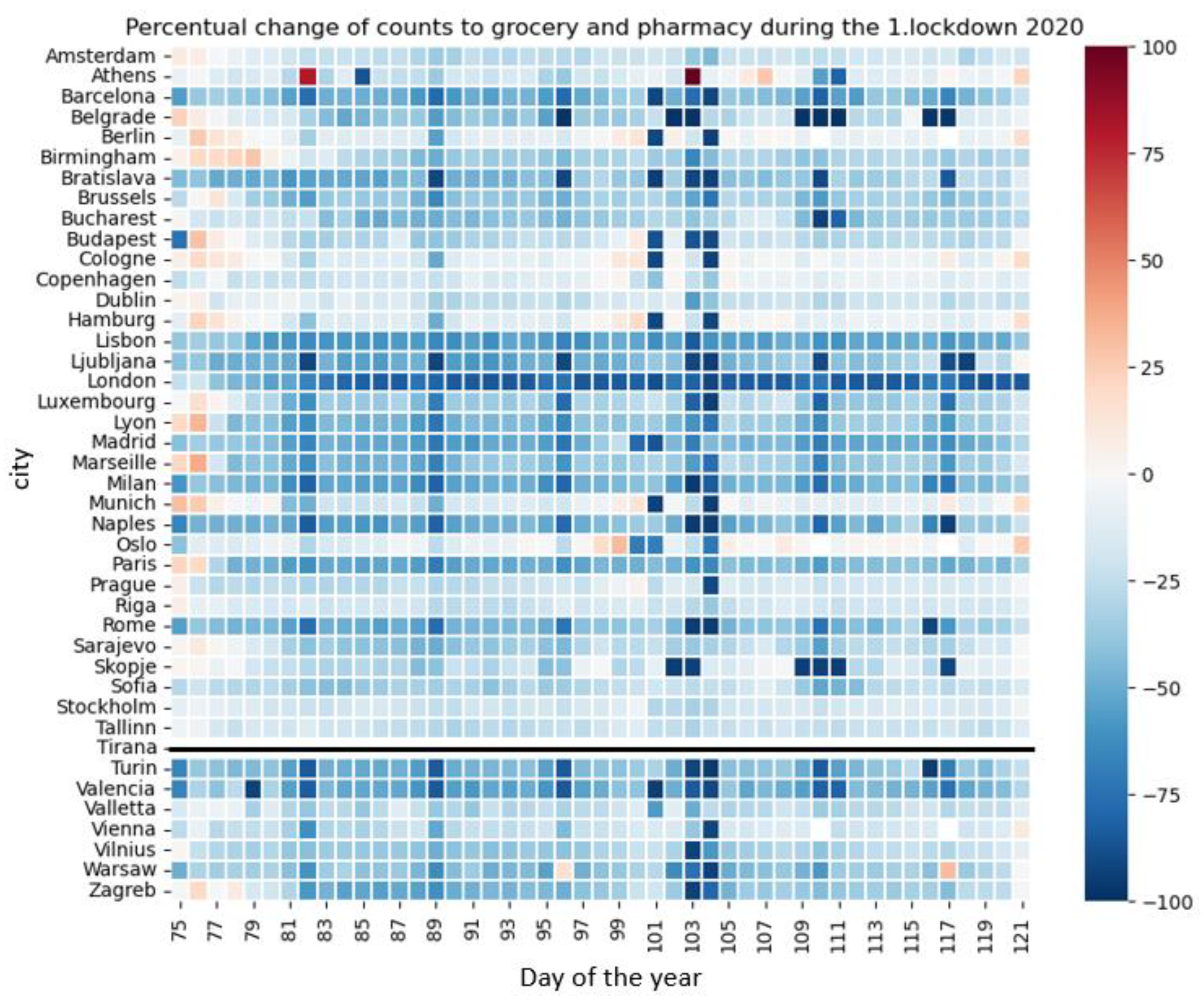
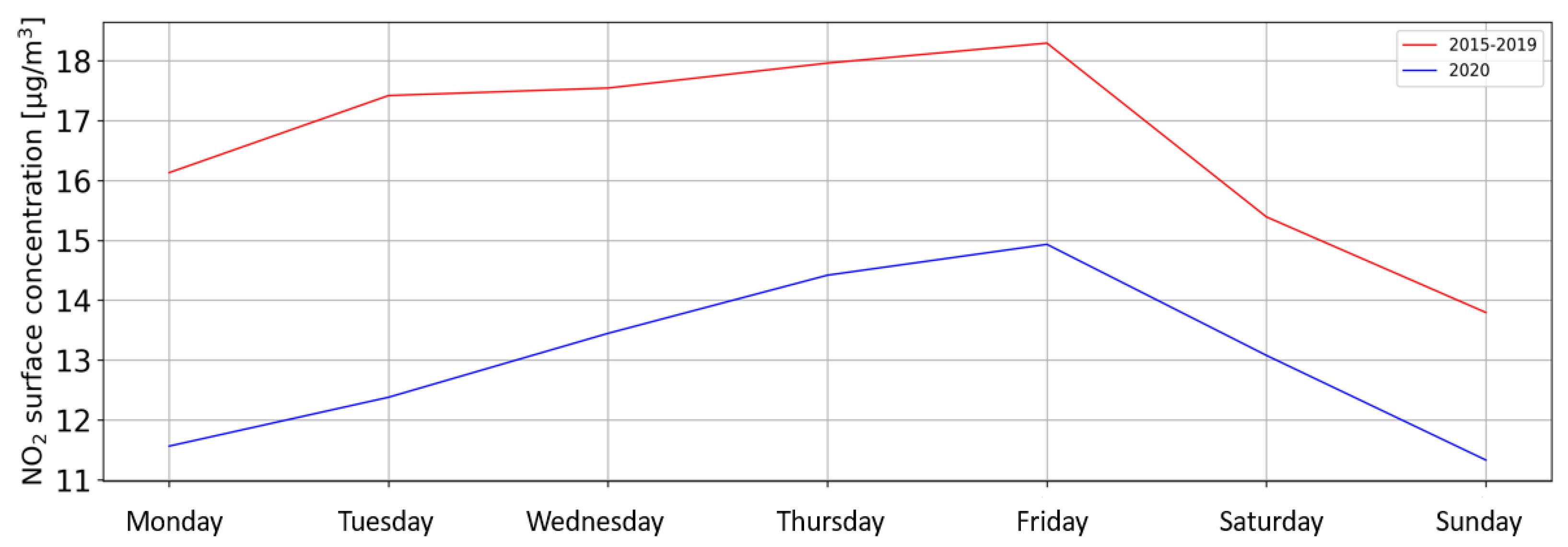
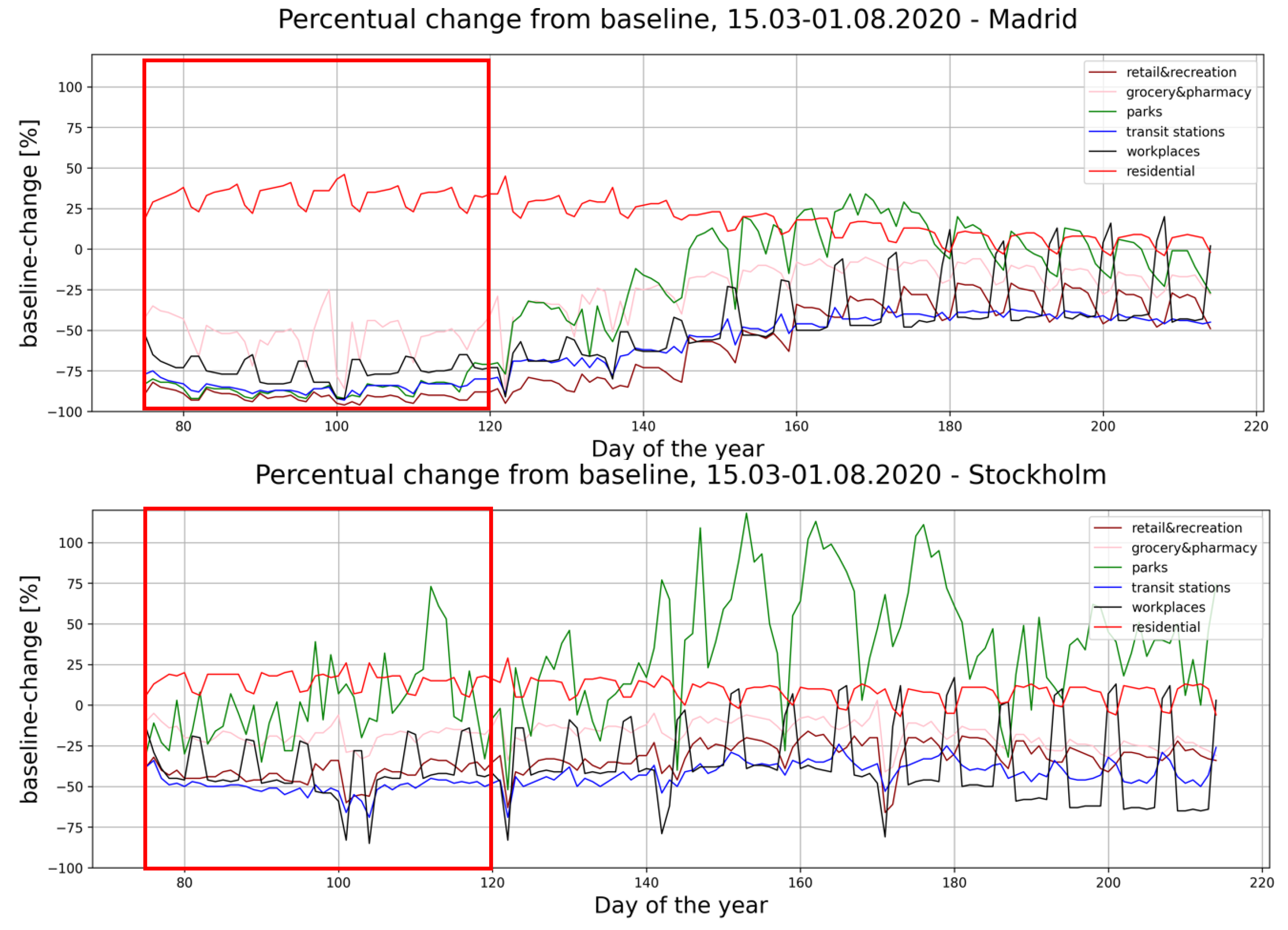
3.6. Mobility Data
4. Discussion
4.1. Nitrogen Dioxide
4.2. Ozone
4.3. Particulate Matter
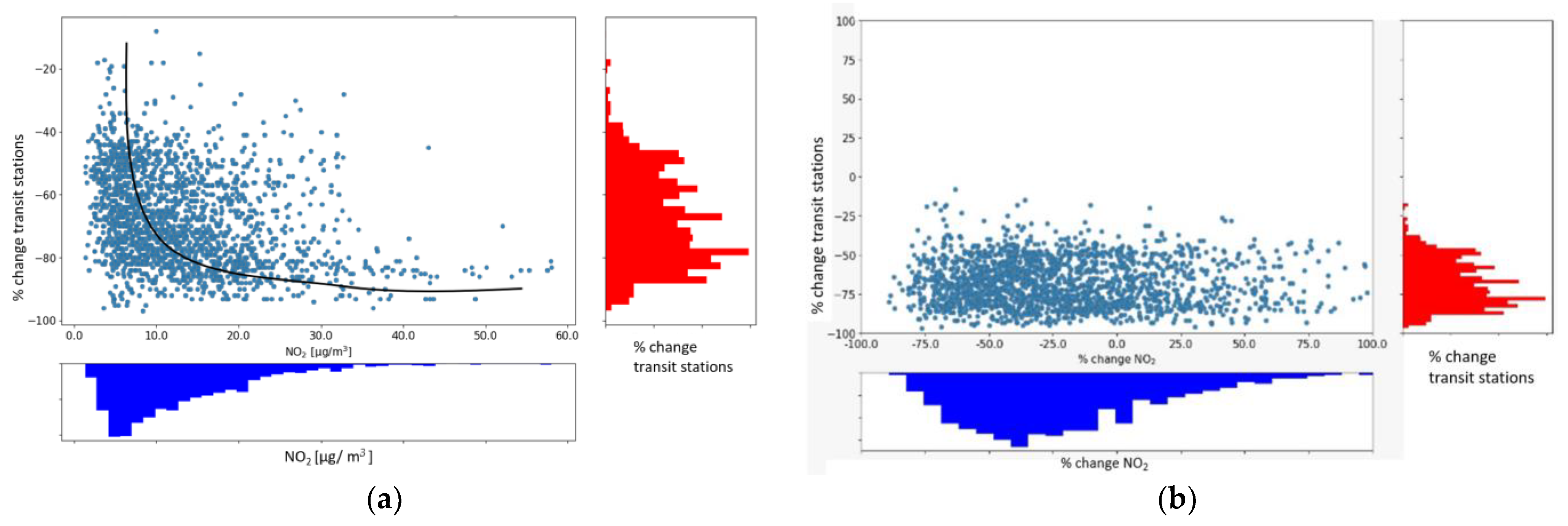
4.4. Relationship of the Air Quality Variables and LST with Mobility Data
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- World Health Organization. Report of the WHO—China Joint Mission on Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Available online: https://www.who.int/publications-detail-redirect/report-of-the-who-china-joint-mission-on-coronavirus-disease-2019-(covid-19) (accessed on 18 August 2022).
- World Health Organization. Coronavirus. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/coronavirus (accessed on 10 November 2022).
- World Health Organization. WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int (accessed on 18 August 2022).
- Le Quéré, C.; Jackson, R.B.; Jones, M.W.; Smith, A.J.P.; Abernethy, S.; Andrew, R.M.; De-Gol, A.J.; Willis, D.R.; Shan, Y.; Canadell, J.G.; et al. Temporary Reduction in Daily Global CO2 Emissions during the COVID-19 Forced Confinement. Nat. Clim. Change 2020, 10, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anania, J.; Mello, B.A.; de Angrist, N.; Barnes, R.; Boby, T.; Cavalieri, A.; Edwards, B.; Webster, S.; Ellen, L.; Furst, R.; et al. Variation in Government Responses to COVID-19; Blavatnik School Government Work Paper; University of Oxford: Oxford, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Metya, A.; Dagupta, P.; Halder, S.; Chakraborty, S.; Tiwari, Y.K. COVID-19 Lockdowns Improve Air Quality in the South-East Asian Regions, as Seen by the Remote Sensing Satellites. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2020, 20, 1772–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Dickinson, R.E. Land Surface Skin Temperature Climatology: Benefitting from the Strengths of Satellite Observations. Environ. Res. Lett. 2010, 5, 044004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oke, T.R.; Mills, G.; Christen, A.; Voogt, J.A. Urban Climates; Oke, T.R., Ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2017; ISBN 978-0-521-84950-0. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lai, J.; Zhan, W.; Bechtel, B.; Voogt, J.; Quan, J.; Hu, L.; Fu, P.; Huang, F.; Li, L.; et al. Urban Heat Islands Significantly Reduced by COVID-19 Lockdown. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2021GL096842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadibasyir, H.Z.; Rijal, S.S.; Sari, D.R. Comparison of Land Surface Temperature during and before the Emergence of COVID-19 Using Modis Imagery in Wuhan City, China. Forum Geogr. 2020, 34, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parida, B.R.; Bar, S.; Kaskaoutis, D.; Pandey, A.C.; Polade, S.D.; Goswami, S. Impact of COVID-19 Induced Lockdown on Land Surface Temperature, Aerosol, and Urban Heat in Europe and North America. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 75, 103336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taoufik, M.; Laghlimi, M.; Fekri, A. Comparison of Land Surface Temperature Before, During and After the COVID-19 Lockdown Using Landsat Imagery: A Case Study of Casablanca City, Morocco. Geomat. Environ. Eng. 2021, 15, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, D.H.; Díaz, J.A. Impacts of the COVID-19 Confinement on Air Quality, the Land Surface Temperature and the Urban Heat Island in Eight Cities of Andalusia (Spain). Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2022, 25, 100667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, M.G.; Tran, P.T.; Balasubramanian, R. Air Quality Changes in Cities during the COVID-19 Lockdown: A Critical Review. Atmos. Res. 2021, 264, 105823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barré, J.; Petetin, H.; Colette, A.; Guevara, M.; Peuch, V.-H.; Rouil, L.; Engelen, R.; Inness, A.; Flemming, J.; García-Pando, C.P.; et al. Estimating Lockdown-Induced European NO2 Changes Using Satellite and Surface Observations and Air Quality Models. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 7373–7394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicard, P.; De Marco, A.; Agathokleous, E.; Feng, Z.; Xu, X.; Paoletti, E.; Rodriguez, J.J.D.; Calatayud, V. Amplified Ozone Pollution in Cities during the COVID-19 Lockdown. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 735, 139542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NASA. Earth Science Data Systems Health and Air Quality Data Pathfinder. Available online: http://www.earthdata.nasa.gov/learn/pathfinders/health-and-air-quality-data-pathfinder (accessed on 18 August 2022).
- Wijnands, J.S.; Nice, K.A.; Seneviratne, S.; Thompson, J.; Stevenson, M. The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Air Pollution: A Global Assessment Using Machine Learning Techniques. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2022, 13, 101438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Arshad, A.; Zhang, C.; Hussain, S.; Li, W. Unprecedented Temporary Reduction in Global Air Pollution Associated with COVID-19 Forced Confinement: A Continental and City Scale Analysis. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Space Agency. Air Pollution Remains Low as Europeans Stay at Home. Available online: https://www.esa.int/Applications/Observing_the_Earth/Copernicus/Sentinel-5P/Air_pollution_remains_low_as_Europeans_stay_at_home (accessed on 18 August 2022).
- Tobías, A.; Carnerero, C.; Reche, C.; Massagué, J.; Via, M.; Minguillón, M.C.; Alastuey, A.; Querol, X. Changes in Air Quality during the Lockdown in Barcelona (Spain) One Month into the SARS-CoV-2 Epidemic. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 726, 138540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, G.; Pan, Y.; Tanaka, T. The Short-Term Impacts of COVID-19 Lockdown on Urban Air Pollution in China. Nat. Sustain. 2020, 3, 1005–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichol, J.E.; Bilal, M.; Ali, A.; Qiu, Z. Air Pollution Scenario over China during COVID-19. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqasemi, A.S.; Hereher, M.E.; Kaplan, G.; Al-Quraishi, A.M.F.; Saibi, H. Impact of COVID-19 Lockdown upon the Air Quality and Surface Urban Heat Island Intensity over the United Arab Emirates. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 767, 144330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venter, Z.S.; Aunan, K.; Chowdhury, S.; Lelieveld, J. COVID-19 Lockdowns Cause Global Air Pollution Declines. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 18984–18990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beirle, S.; Boersma, K.F.; Platt, U.; Lawrence, M.G.; Wagner, T. Megacity Emissions and Lifetimes of Nitrogen Oxides Probed from Space. Science 2011, 333, 1737–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshorbany, Y.F.; Kleffmann, J.; Kurtenbach, R.; Rubio, M.; Lissi, E.; Villena, G.; Gramsch, E.; Rickard, R.; Pilling, M.J.; Wiesen, P. Summertime Photochemical Ozone Formation in Santiago, Chile. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 6398–6407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Environment Agency. European Union Emission Inventory Report 1990–2018 under the UNECE Convention on Long-Range Transboundary Air Pollution (LRTAP); European Environment Agency Publications Office: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2020.
- Sismanidis, P.; Bechtel, B.; Perry, M.; Ghent, D. The Seasonality of Surface Urban Heat Islands across Climates. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, I.D.; Oke, T.R. Local Climate Zones for Urban Temperature Studies. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2012, 93, 1879–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CAMS. European Air Quality Information in Support of the COVID-19 Crisis|Copernicus. Available online: https://atmosphere.copernicus.eu/european-air-quality-information-support-covid-19-crisis (accessed on 18 August 2022).
- Google LLC. COVID-19 Community Mobility Report. Available online: https://www.google.com/covid19/mobility?hl=en-GB (accessed on 18 August 2022).
- Gao, X. Nonparametric Statistics. In Encyclopedia of Research Design; Salkind, N.J., Ed.; SAGE Publications Ltd.: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2010; pp. 915–920. [Google Scholar]
- Codagnone, C.; Bogliacino, F.; Gómez, C.; Folkvord, F.; Liva, G.; Charris, R.; Montealegre, F.; Villanueva, F.L.; Veltri, G.A. Restarting “Normal” Life after COVID-19 and the Lockdown: Evidence from Spain, the United Kingdom, and Italy. Soc. Indic. Res. 2021, 158, 241–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairless, T. How Germany Kept Its Factories Open during the Pandemic. The Wall Street Journal, 6 May 2020. Available online: https://br.advfn.com/noticias/DJN/2020/artigo/82392711 (accessed on 27 April 2023).
- Menut, L.; Bessagnet, B.; Siour, G.; Mailler, S.; Pennel, R.; Cholakian, A. Impact of Lockdown Measures to Combat COVID-19 on Air Quality over Western Europe. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 140426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, R.; Ceccato, R.; Gastaldi, M. Effect of Road Traffic on Air Pollution. Experimental Evidence from COVID-19 Lockdown. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masiol, M.; Squizzato, S.; Formenton, G.; Harrison, R.M.; Agostinelli, C. Air Quality Across a European Hotspot: Spatial Gradients, Seasonality, Diurnal Cycles and Trends in the Veneto Region, NE Italy. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 576, 210–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jesemann, A.-S.; Matthias, V.; Böhner, J.; Bechtel, B. Using Neural Network NO2-Predictions to Understand Air Quality Changes in Urban Areas—A Case Study in Hamburg. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Song, C.; Liu, B.; Lu, G.; Xu, J.; Van Vu, T.; Elliott, R.J.R.; Li, W.; Bloss, W.J.; Harrison, R.M. Abrupt But Smaller Than Expected Changes in Surface Air Quality Attributable to COVID-19 Lockdowns. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabd6696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Charlesworth, E.; Yin, C.; Yan, X.; Deng, X.; Li, F. The Weekday/Weekend Ozone Differences Induced by the Emissions Change during Summer and Autumn in Guangzhou, China. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 199, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adame, J.A.; Hernández-Ceballos, M.; Sorribas, M.; Lozano, A.; De la Morena, B.A. Weekend-Weekday Effect Assessment for O3, NOx, CO and PM10 in Andalusia, Spain (2003–2008). Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2014, 14, 1862–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hörmann, S.; Jammoul, F.; Kuenzer, T.; Stadlober, E. Separating the Impact of Gradual Lockdown Measures on Air Pollutants from Seasonal Variability. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2021, 12, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munir, S.; Coskuner, G.; Jassim, M.S.; Aina, Y.A.; Ali, A.; Mayfield, M. Changes in Air Quality Associated with Mobility Trends and Meteorological Conditions during COVID-19 Lockdown in Northern England, UK. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanableh, A.; Al-Ruzouq, R.; Khalil, M.A.; Gibril, M.B.A.; Hamad, K.; Alhosani, M.; Stietiya, M.H.; Bardan, M.; Mansoori, S.A.; Hammouri, N.A. COVID-19 Lockdown and the Impact on Mobility, Air Quality, and Utility Consumption: A Case Study from Sharjah, United Arab Emirates. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hale, T.; Angrist, N.; Goldszmidt, R.; Kira, B.; Petherick, A.; Phillips, T.; Webster, S.; Cameron-Blake, E.; Hallas, L.; Majumdar, S.; et al. A Global Panel Database of Pandemic Policies (Oxford COVID-19 Government Response Tracker). Nat. Hum. Behav. 2021, 5, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ropkins, K.; Tate, J.E. Early Observations on the Impact of the COVID-19 Lockdown on Air Quality Trends Across the UK. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 754, 142374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efe, B. Air quality Improvement and Its Relation to Mobility during COVID-19 Lockdown in Marmara Region, Turkey. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorrochategui, E.; Hernandez, I.; Pérez-Gabucio, E.; Lacorte, S.; Tauler, R. Temporal Air Quality (NO2, O3, and PM10) Changes in Urban and Rural Stations in Catalonia during COVID-19 Lockdown: An Association with Human Mobility and Satellite Data. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 18905–18922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, S.; Mayfield, M.; Coca, D.; Mihaylova, L.; Osammor, O. Analysis of Air Pollution in Urban Areas with Airviro Dispersion Model—A Case Study in the City of Sheffield, United Kingdom. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Glocke, P.; Bechtel, B.; Sismanidis, P. Consideration of Altered Anthropogenic Behavior during the First Lockdown and Its Effects on Air Pollutants and Land Surface Temperature in European Cities. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1025. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14061025
Glocke P, Bechtel B, Sismanidis P. Consideration of Altered Anthropogenic Behavior during the First Lockdown and Its Effects on Air Pollutants and Land Surface Temperature in European Cities. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(6):1025. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14061025
Chicago/Turabian StyleGlocke, Patricia, Benjamin Bechtel, and Panagiotis Sismanidis. 2023. "Consideration of Altered Anthropogenic Behavior during the First Lockdown and Its Effects on Air Pollutants and Land Surface Temperature in European Cities" Atmosphere 14, no. 6: 1025. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14061025
APA StyleGlocke, P., Bechtel, B., & Sismanidis, P. (2023). Consideration of Altered Anthropogenic Behavior during the First Lockdown and Its Effects on Air Pollutants and Land Surface Temperature in European Cities. Atmosphere, 14(6), 1025. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14061025







