A Cluster Analysis Approach for Nocturnal Atmospheric Boundary Layer Height Estimation from Multi-Wavelength Lidar
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
2.1. Lidar Data
2.2. RS Data
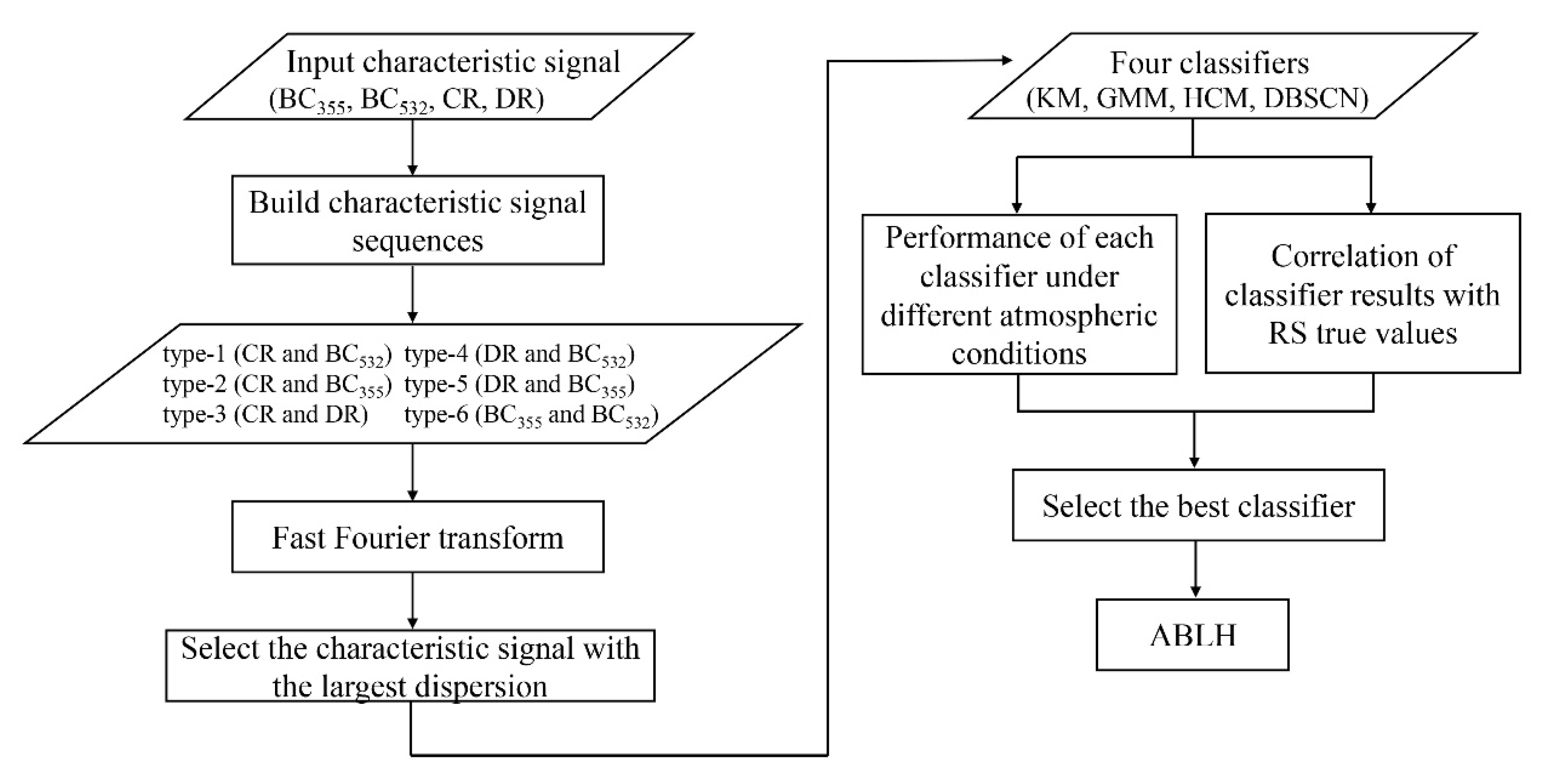
3. Methodology
4. Results
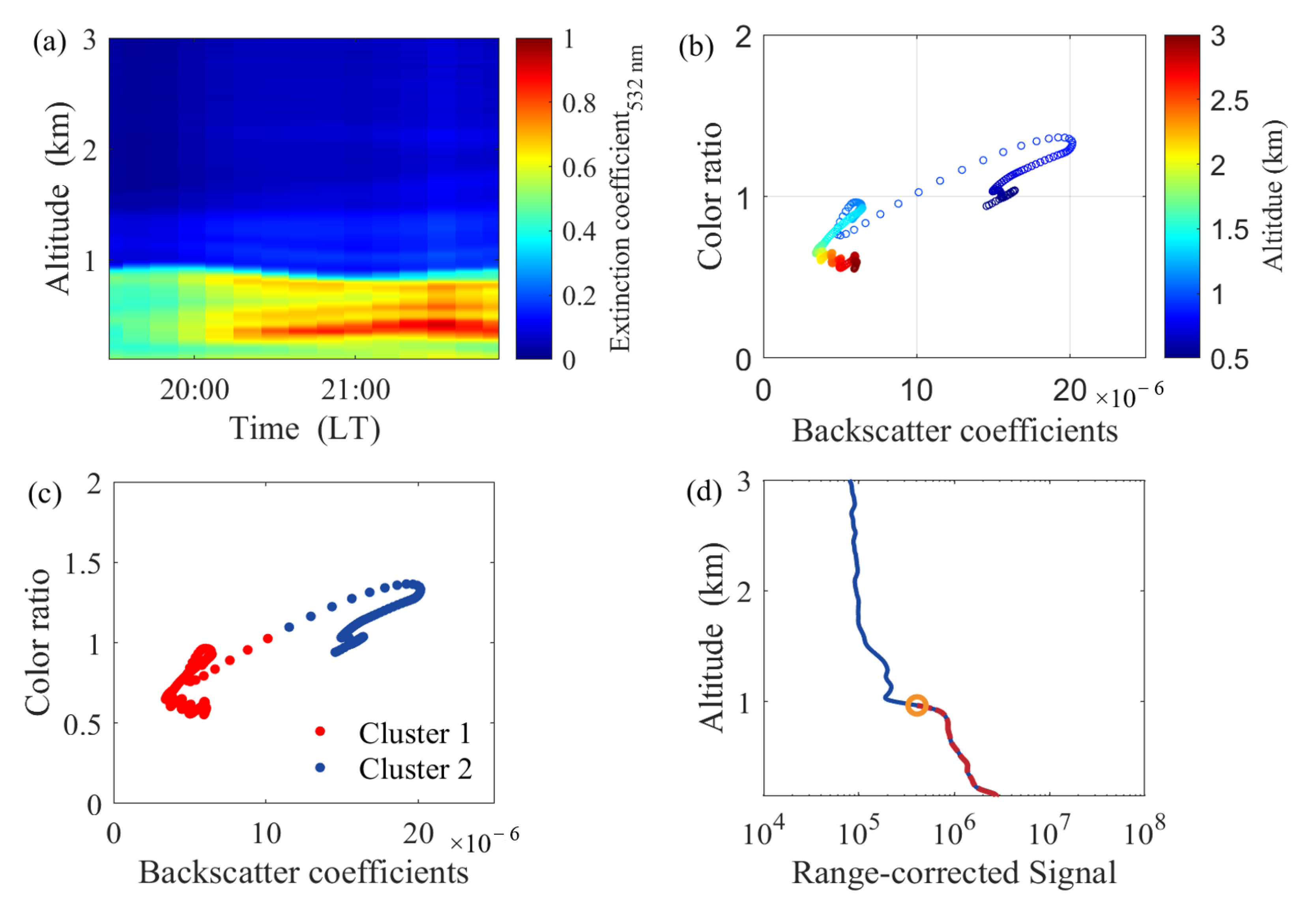
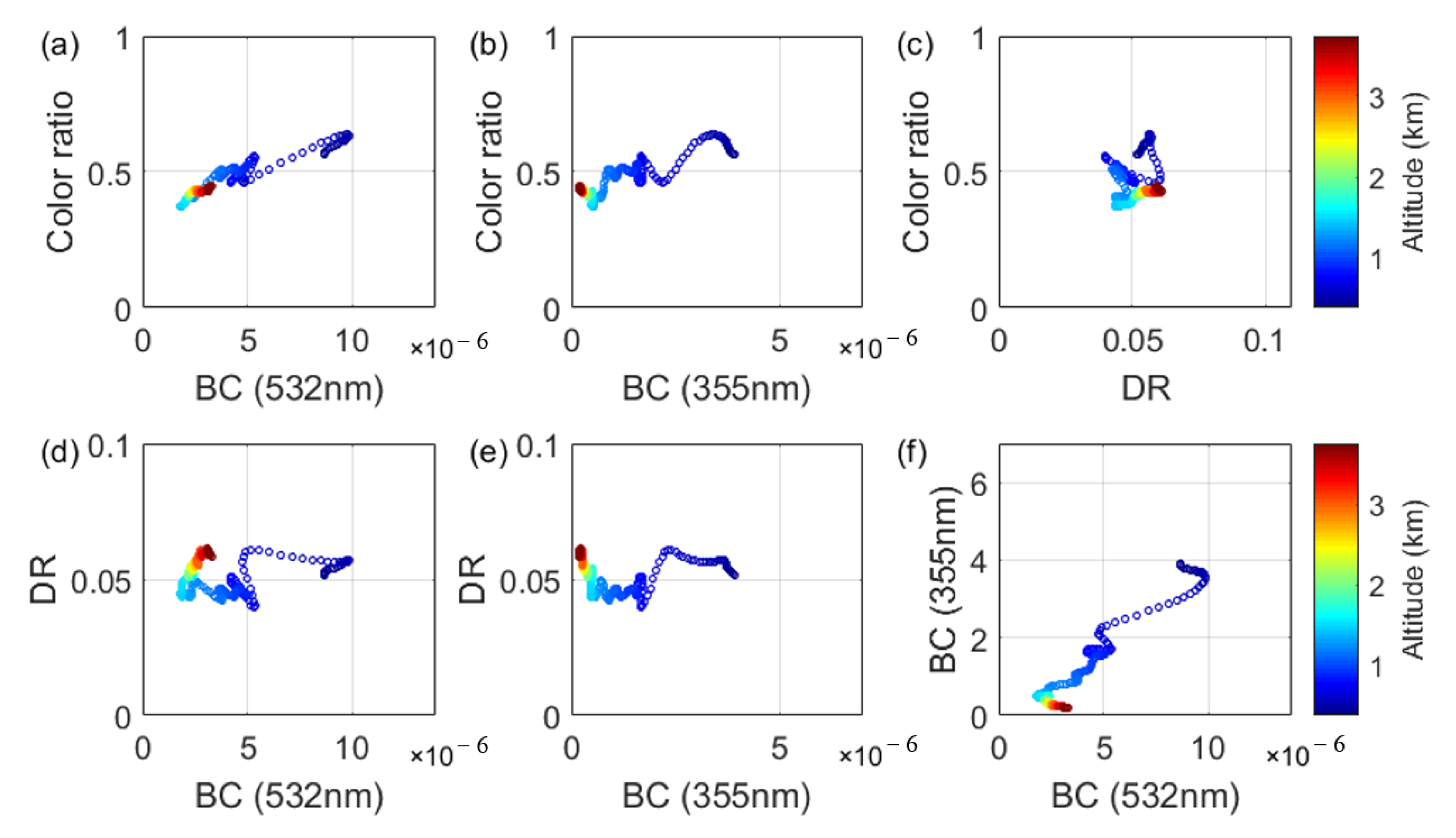
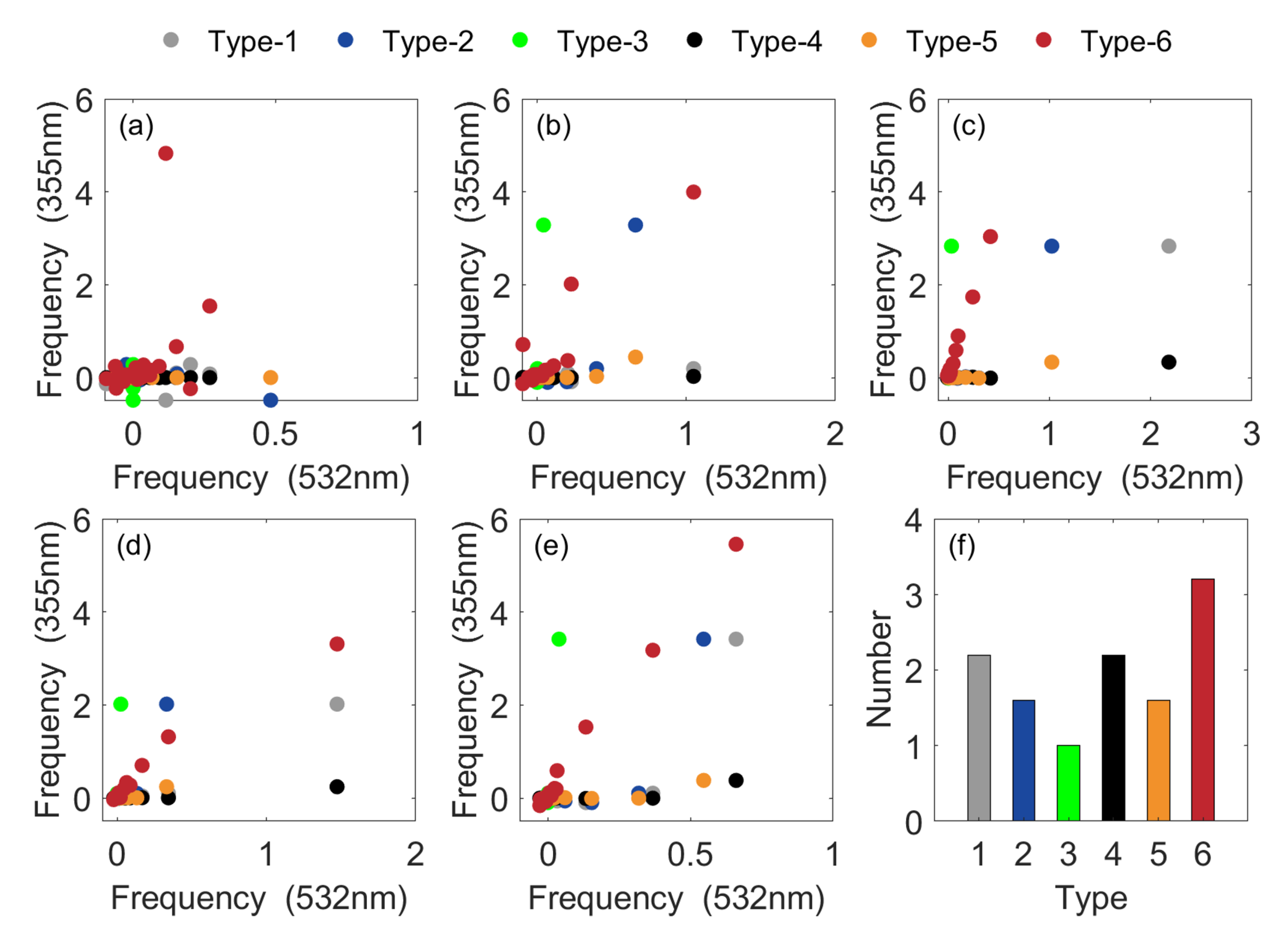
4.1. Determining the Characteristic Signal
4.2. Case Study
4.3. Classifier Performance Evaluation
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stull, R.B. An Introduction to Boundary Layer Meteorology; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Seibert, P.; Beyrich, F.; Gryning, S.E.; Joffre, S.; Rasmussen, A.; Tercier, P. Review and intercomparison of operational methods for the determination of the mixing height. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 1001–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Gbaguidi, A.; Sugimoto, N.; Wang, X.; Matsui, I.; Sun, Y. Technical note: Boundary layer height determination from lidar for improving air pollution episode modeling: Development of new algorithm and evaluation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 6125–6225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Liu, C.; Xie, Z.; Hu, Q.; Dong, Y.; Fan, G.; Zhang, T.; Xing, C.; Wang, Z.; Javed, Z.; et al. Comparison of mixing layer height inversion algorithms using lidar and a pollution case study in Baoding, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 79, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Huang, J.; Chen, B.; Zhou, T.; Yan, H.; Jin, H.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, B. Comparisons of PBL heights derived from CALIPSO and ECMWF reanalysis data over China. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2015, 153, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Ma, Y.; Gong, W.; Zhang, M.; Yang, J. Improved Two-wavelength Lidar algorithm for Retrieving Atmospheric Boundary Layer Height. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2019, 224, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yang, Y.; Hu, X.; Huang, Z.; Wang, G.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, T. Evaluation of retrieval methods of daytime convective boundary layer height based on lidar data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 4578–4593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, K.J.; Gamage, N.; Hagelberg, C.R.; Kiemle, C.; Lenschow, D.H.; Sullivan, P.P. An objective method for deriving atmospheric structure from airborne lidar observations. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2000, 17, 1455–1468. [Google Scholar]
- Hägeli, P.; Steyn, D.G.; Strawbridge, K.B. Strawbridge. Spatial and temporal variability of mixed layer depth and entrainment zone thickness. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2000, 97, 47–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, L.; Wilczak, J.M. Convective Boundary Layer Depth: Improved Measurement by Doppler Radar Wind Profiler Using Fuzzy Logic Methods. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2002, 19, 1745–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.R.; Hlavka, D.L.; Welton, E.J.; Flynn, C.J.; Turner, D.D.; Spinhirne, J.D. Full-time, eye-safe cloud and aerosol lidar observation at atmospheric radiation measurement program sites: Instruments and data processing. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2002, 19, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emeis, S.; Schafer, K.; Munkel, C. Surface-based remote sensing of the mixing layer height a review. Meteorol. Z. 2008, 17, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.; Li, J.; Li, C.; Xiang, P.; Lau AK, H.; Guo, J.; Yang, Y.; Miao, Y. An intercomparison of long-term planetary boundary layer heights retrieved from CALIPSO, ground-based lidar and radiosonde measurements over Hong Kong. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 3929–3943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregori, D.A.M.; Luis, G.R.J.; Ntonio, J.B.A.A.; Antonio, J.B.O.; Pablo, O.A.; Roberto, R.; Esteban AB, V.; Landulfo, E.; Lucas, A.A. Study of the planetary boundary layer by microwave radiometer, elastic lidar and Doppler lidar estimations in Southern Iberian Peninsula. Atmos. Res. 2018, 213, 185–195. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Liang, X. Observed diurnal cycle climatology of planetary boundary layer height, J. Clim. 2010, 23, 5790–5809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, D.J.; Ao, C.O.; Li, K. Estimating climatological planetary boundary layer heights from radiosonde observations: Comparison of methods and uncertainty analysis. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, D16113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Miao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, W.; He, J.; Luo, M.; Yan, Y.; Bian, L.; et al. The climatology of planetary boundary layer height in China derived from radiosonde and reanalysis data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 13309–13319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Huang, J.; Bi, J.; Wang, G.; Wang, W.; Fu, Q.; Li, Z.; Tsay, S.; Shi, J. Dust aerosol vertical structure measurements using three mpl lidars during 2008 China-U.S. joint dust field experiment. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, 1307–1314. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; He, W.; Liu, H.; Chen, H. Retrieval of Atmospheric Boundary Layer Height from Ground-based Microwave Radiometer Measurements. J. Appl. Meteorol. Sci. 2015, 26, 626–635. [Google Scholar]
- Granados-Muñoz, M.J.; Navas-Guzmán, F.; Bravo-Aranda, J.A.; Guerrero-Rascado, J.L.; Lyamani, H.; Fernández-Gálvez, J.; Alados-Arboledas, L. Automatic determination of the planetary boundary layer height using lidar: One-year analysis over southeastern Spain. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, D18208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, T.; Yuan, R.; Wang, Z. Lidar-based remote sensing of atmospheric boundary layer height over land and ocean. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo, D.; Córdoba-Jabonero, C.; Adame, J.A.; Benito DL, M.; Gil-Ojeda, M. Estimation of the atmospheric boundary layer height during different atmospheric conditions: A comparison on reliability of several methods applied to lidar measurements. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 3203–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emeis, S.; Jahn, C.; Munkel, C.; Munsterer, C.; Schafer, K. Multiple atmospheric layering and mixing-layer height in the Inn valley observed by remote sensing. Meteorol. Z. 2007, 16, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steyn, D.G.; Baldi, M.; Hoff, R.M. The detection of mixed layer depth and entrainment zone thickness from lidar backscatter profiles. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1999, 16, 953–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, I.M. Finding boundary layer top: Application of a wavelet covariance transform to lidar backscatter profiles. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2003, 20, 1092–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, N.S.; Hoff, R.M.; Bacmeister, J.T. Validation of Goddard Earth Observing System-version 5 MERRA planetary boundary layer heights using CALIPSO. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, D24218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cao, X.; Zhang, L.; Notholt, J.; Zhou, B.; Liu, R. Lidar measurement of planetary boundary layer height and comparison with microwave profiling radiometer observation. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2012, 5, 1965–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Ma, Y.; Gong, W.; Yang, J.; Zhang, M. Two-wavelength Lidar inversion algorithm for determining planetary boundary layer height. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2018, 206, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, D.; Tiana-Alsina, J.; Saeed, U.; Tomás, S.; Rocadenbosch, F. Atmospheric Boundary Layer Height Monitoring Using a Kalman Filter and Backscatter Lidar Returns. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 52, 4717–4728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Haeffelin, M.; Batchvarova, E. Exploring a geophysical process-based attribution technique for the determination of the atmospheric boundary layer depth using aerosol lidar and near-surface meteorological measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 9277–9295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruine, M.D.; Apituley, A.; Donovan, D.; Baltink, H.K.; Haij, M.D. Pathfinder: Applying graph theory for consistent tracking of daytime mixed layer height with backscatter lidar. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 1893–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo, D.; Córdoba-Jabonero, C.; Gil-Ojeda, M. Cluster Analysis: A new approach applied to lidar measurements for Atmospheric Boundary Layer height estimation. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2014, 31, 422–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Yang, J.; Shi, S.; Song, S.; Luo, Y.; Du, L. The rising impact of urbanization-caused CO2 emissions on terrestrial vegetation, Ecological Indicators. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 148, 110079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Ma, Y.; Gong, W.; Zhang, M. Observations of aerosol color ratio and depolarization ratio over wuhan. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2017, 8, 1113–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Ma, Y.; Shi, Y.; Jin, S.; Jin, Y.; Gong, W. The characteristics and sources of the aerosols within the nocturnal residual layer over Wuhan, China. Atmos. Res 2020, 241, 104959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, B.; Ma, X.; Ma, Y.; Jin, S.; Fan, R.; Wang, W.; Fang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Gong, W. The Influence of Temperature Inversion on the Vertical Distribution of Aerosols. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.K. Data clustering: 50 years beyond K-means. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2010, 31, 651–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birant, D.; Kut, A. ST-DBSCAN: An algorithm for clustering spatial–temporal data. Data Knowl. Eng. 2007, 60, 208–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biernacki, C.; Celeux, G.; Govaert, G. Assessing a mixture model for clustering with the integrated completed likelihood. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2000, 22, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartigan, J.A.; Wong, M.A. Algorithm AS 136: A k-means clustering algorithm. J. R. Stat. Society. Ser. C Appl. Stat. 1979, 28, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langfelder, P.; Zhang, B.; Horvath, S. Defining clusters from a hierarchical cluster tree: The Dynamic Tree Cut package for R. Bioinformatics 2007, 24, 719–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Shi, R.; Jin, S.; Wang, W.; Fan, R.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhao, P.; Gong, W.; Zhao, Y. Study of Persistent Haze Pollution in Winter over Jinan (China) Based on Ground-Based and Satellite Observations. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, B.; Ma, X.; Jin, S.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Gong, W. Evaluation of retrieval methods for planetary boundary layer height based on radiosonde data. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2021, 14, 5977–5986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Ma, X.; Ma, Y.; Li, H.; Jin, S.; Fan, R.; Gong, W. The relationship between atmospheric boundary layer and temperature inversion layer and their aerosol capture capabilities. Atmos. Res. 2022, 271, 106121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Wang, W.; Wang, N.; Chen, B. New Algorithm for Himawari-8 Aerosol Optical Depth Retrieval by Integrating Regional PM2.5 Concentrations. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 3155503. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, T.; Han, G.; Ma, X.; Mao, H.; Chen, C.; Han, Z.; Gong, W. Quantifying factory-scale CO2/CH4 emission based on mobile measurements and EMISSION-PARTITION model: Cases in China. Environ. Res. Lett. 2023, 18, 034028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Ma, X.; Guo, J.; Li, H.; Jin, S.; Ma, Y.; Gong, W. Estimating hub-height wind speed based on a machine learning algorithm: Implications for wind energy assessment. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2023, 23, 3181–3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Tan, J.; Wang, W.; Dai, W.; Ao, M.; Chen, C. Tomographic Reconstruction of Water Vapor Density Fields from the Integration of GNSS Observations and Fengyun-4A Products. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 4100712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
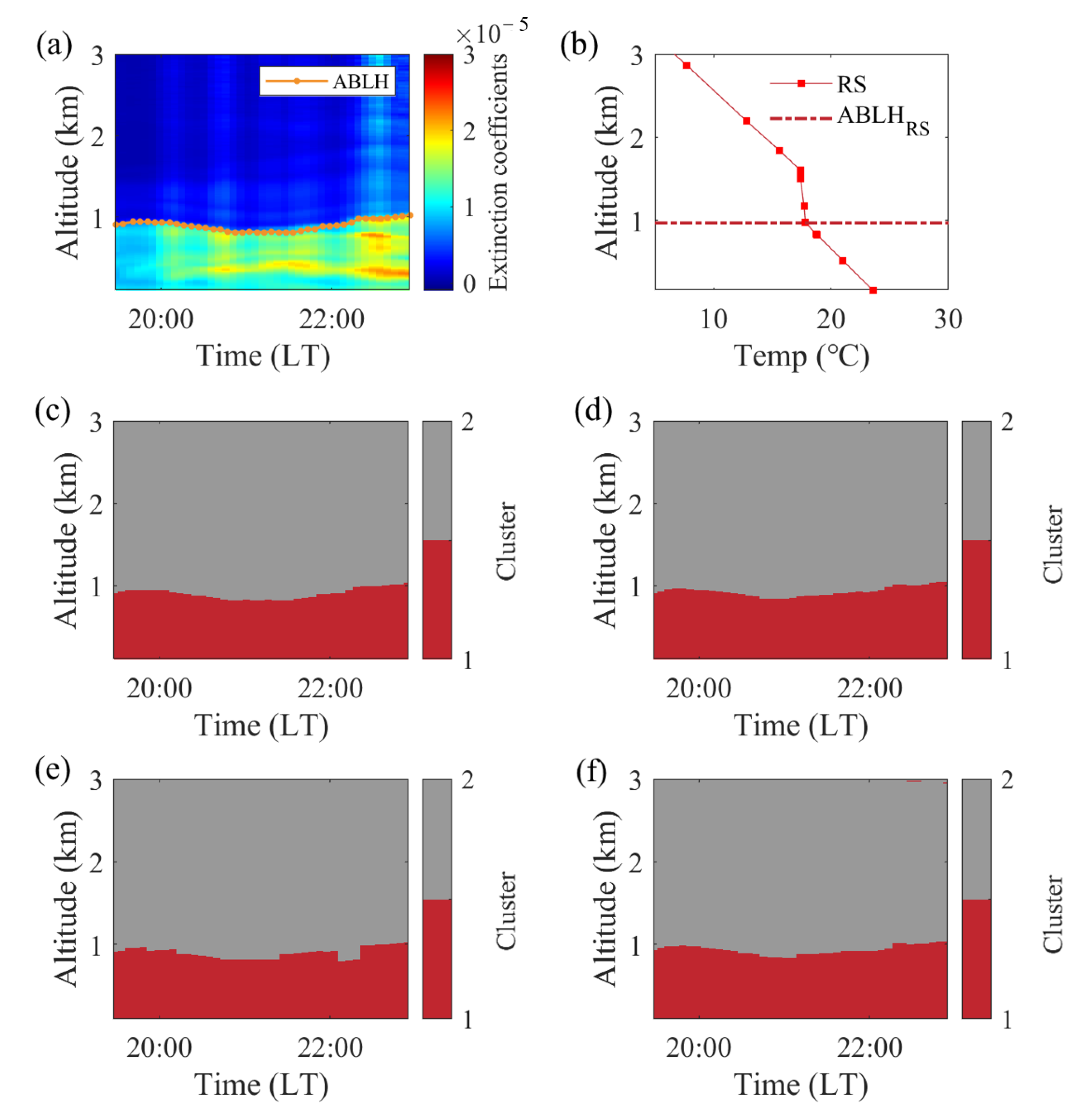

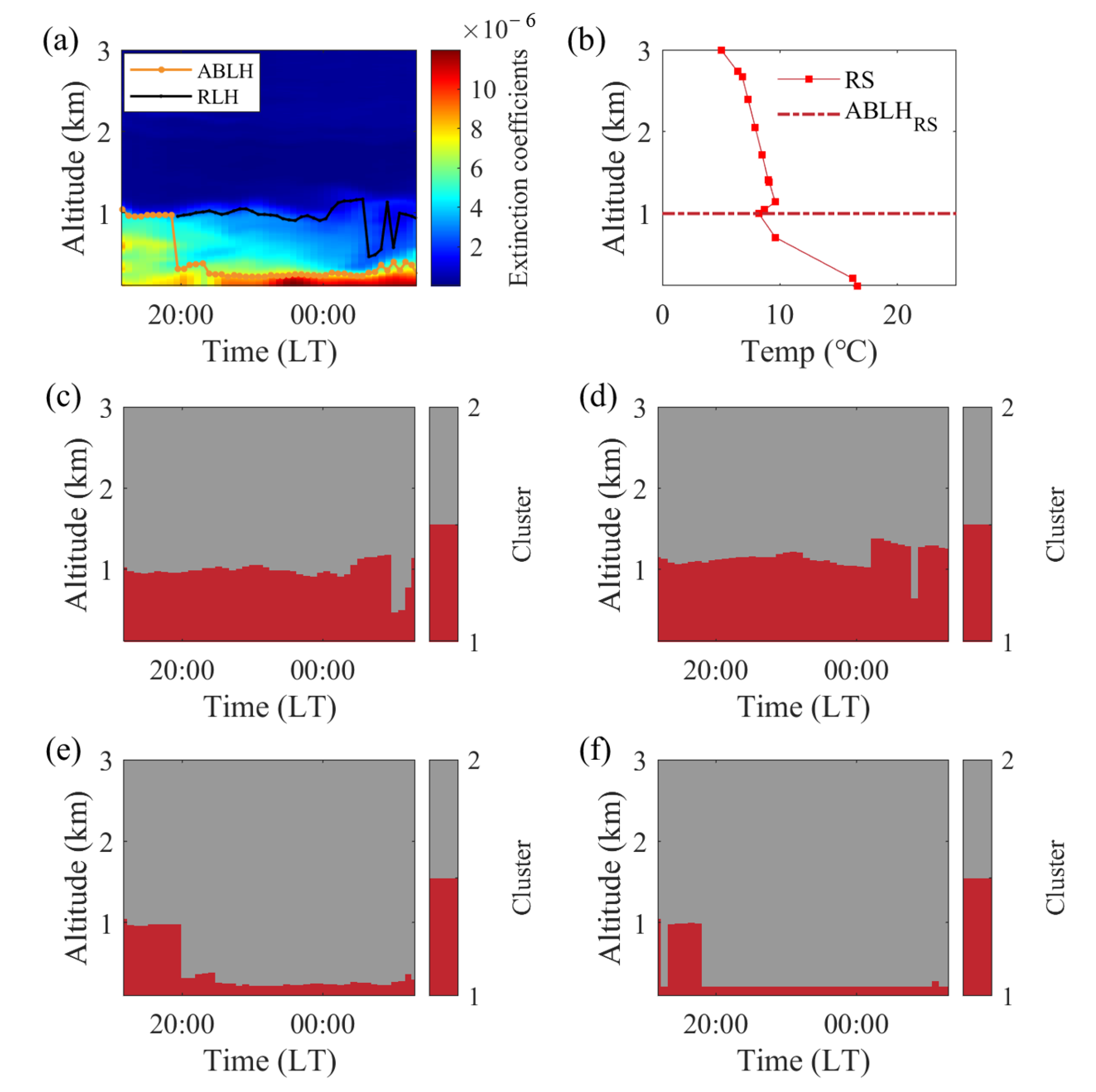
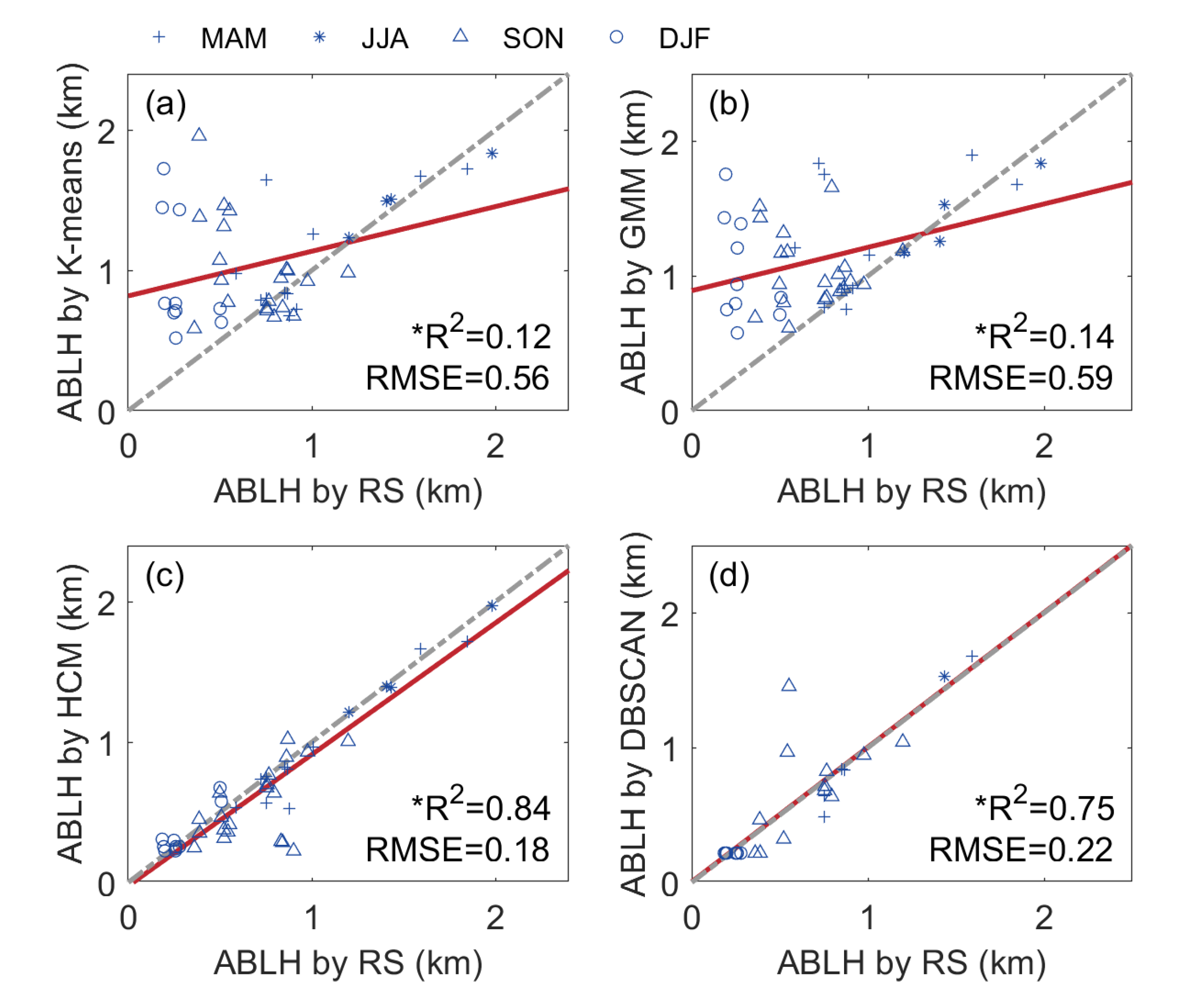
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Z.; Li, H.; Zhou, X.; Fan, S.; Xu, W.; Gong, W. A Cluster Analysis Approach for Nocturnal Atmospheric Boundary Layer Height Estimation from Multi-Wavelength Lidar. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 847. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14050847
Zhu Z, Li H, Zhou X, Fan S, Xu W, Gong W. A Cluster Analysis Approach for Nocturnal Atmospheric Boundary Layer Height Estimation from Multi-Wavelength Lidar. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(5):847. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14050847
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Zhongmin, Hui Li, Xiangyang Zhou, Shumin Fan, Wenfa Xu, and Wei Gong. 2023. "A Cluster Analysis Approach for Nocturnal Atmospheric Boundary Layer Height Estimation from Multi-Wavelength Lidar" Atmosphere 14, no. 5: 847. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14050847
APA StyleZhu, Z., Li, H., Zhou, X., Fan, S., Xu, W., & Gong, W. (2023). A Cluster Analysis Approach for Nocturnal Atmospheric Boundary Layer Height Estimation from Multi-Wavelength Lidar. Atmosphere, 14(5), 847. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14050847





