Spatial and Temporal Variation of Aerosol Optical Depth in Huaihai Economic Zone from 1982 to 2021
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
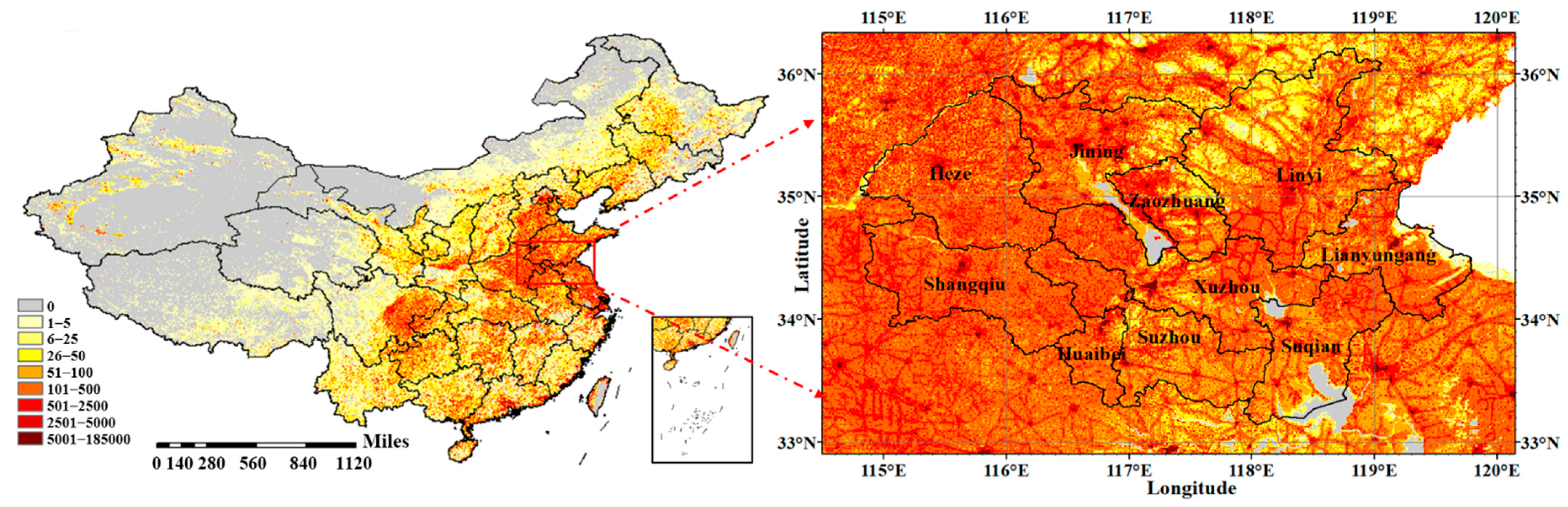
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Source and Description
2.2.1. Satellite AOD Data
2.2.2. Ground-Based Monitoring Data
2.3. Methods and Data Processing
3. Results and Discussion
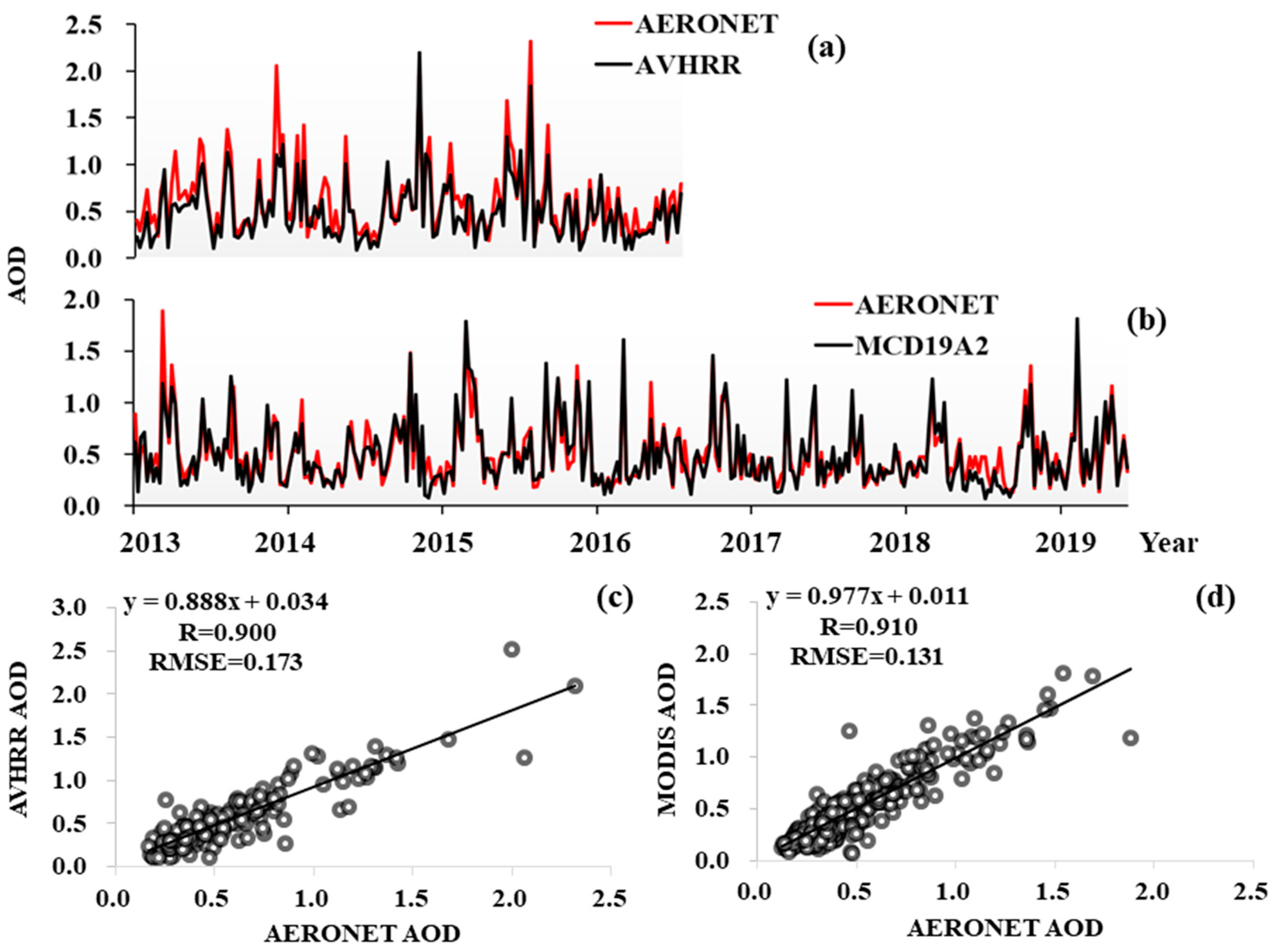
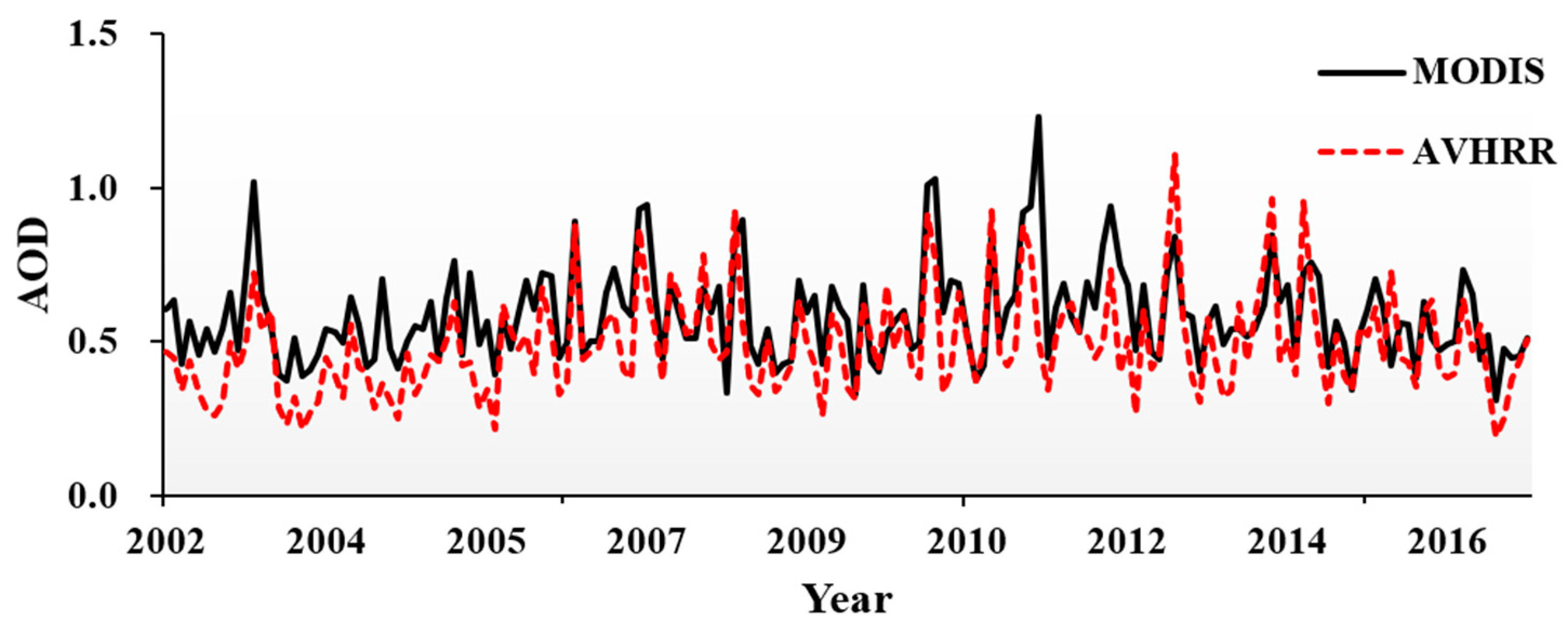
3.1. Evaluations of AVHRR AOD and MODIS AOD
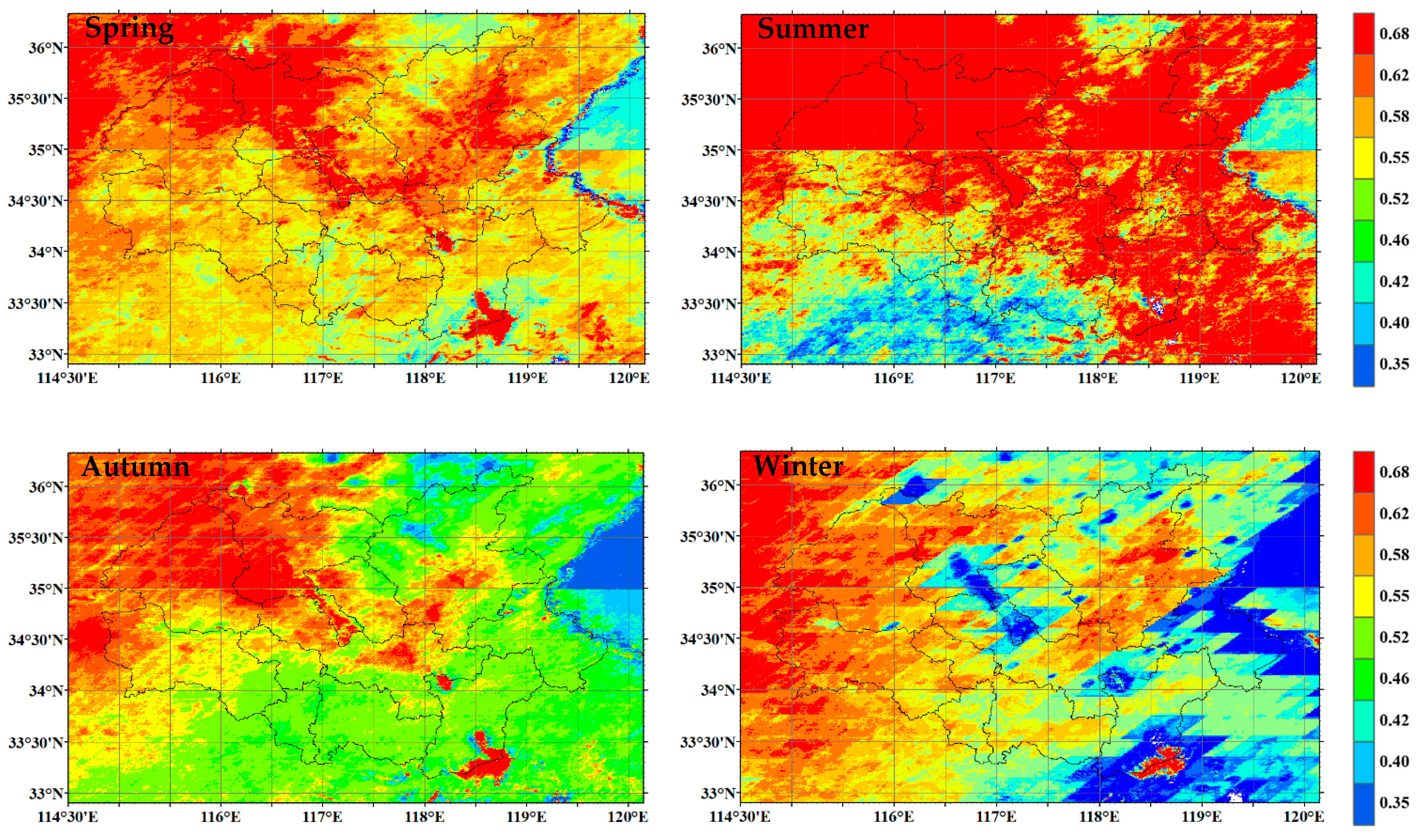
3.2. Spatial Patterns of AOD
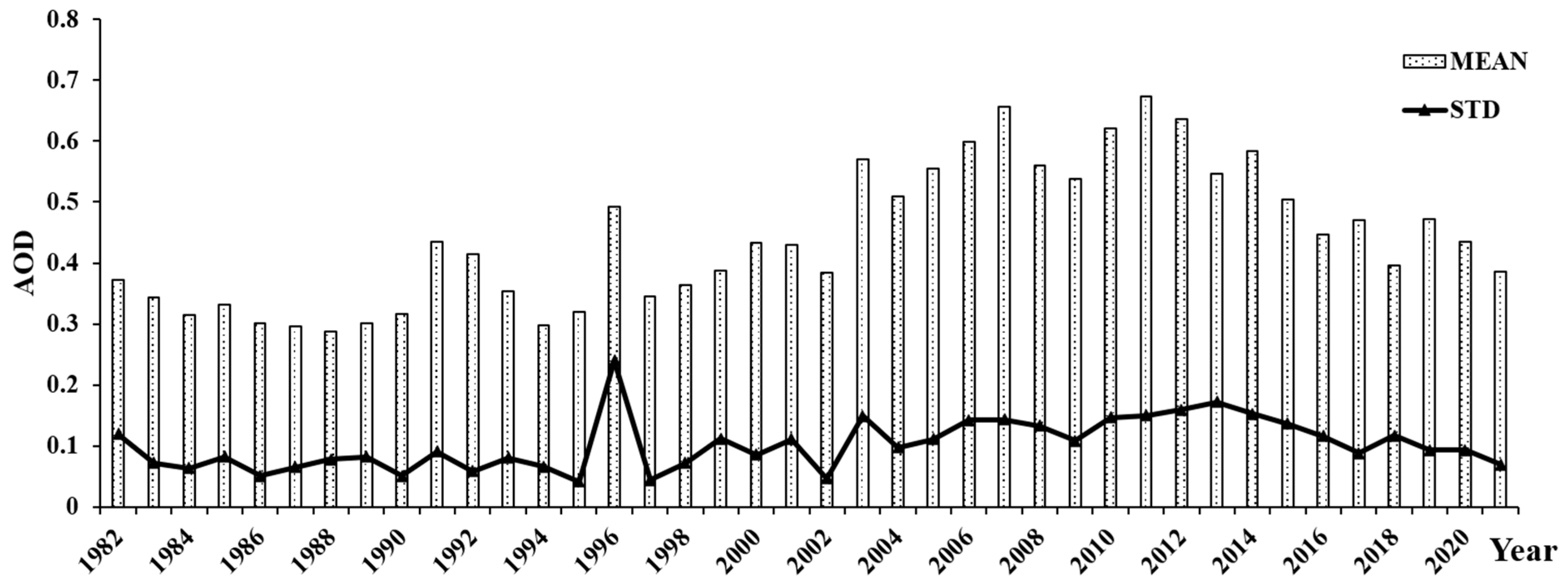
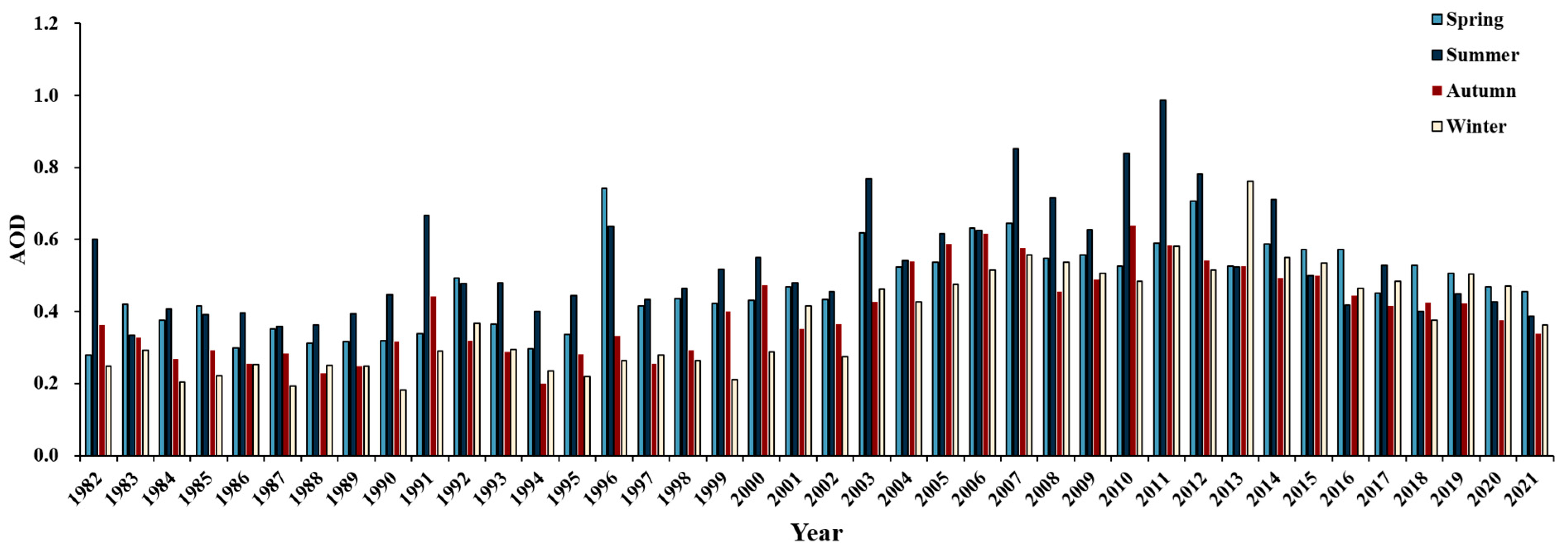
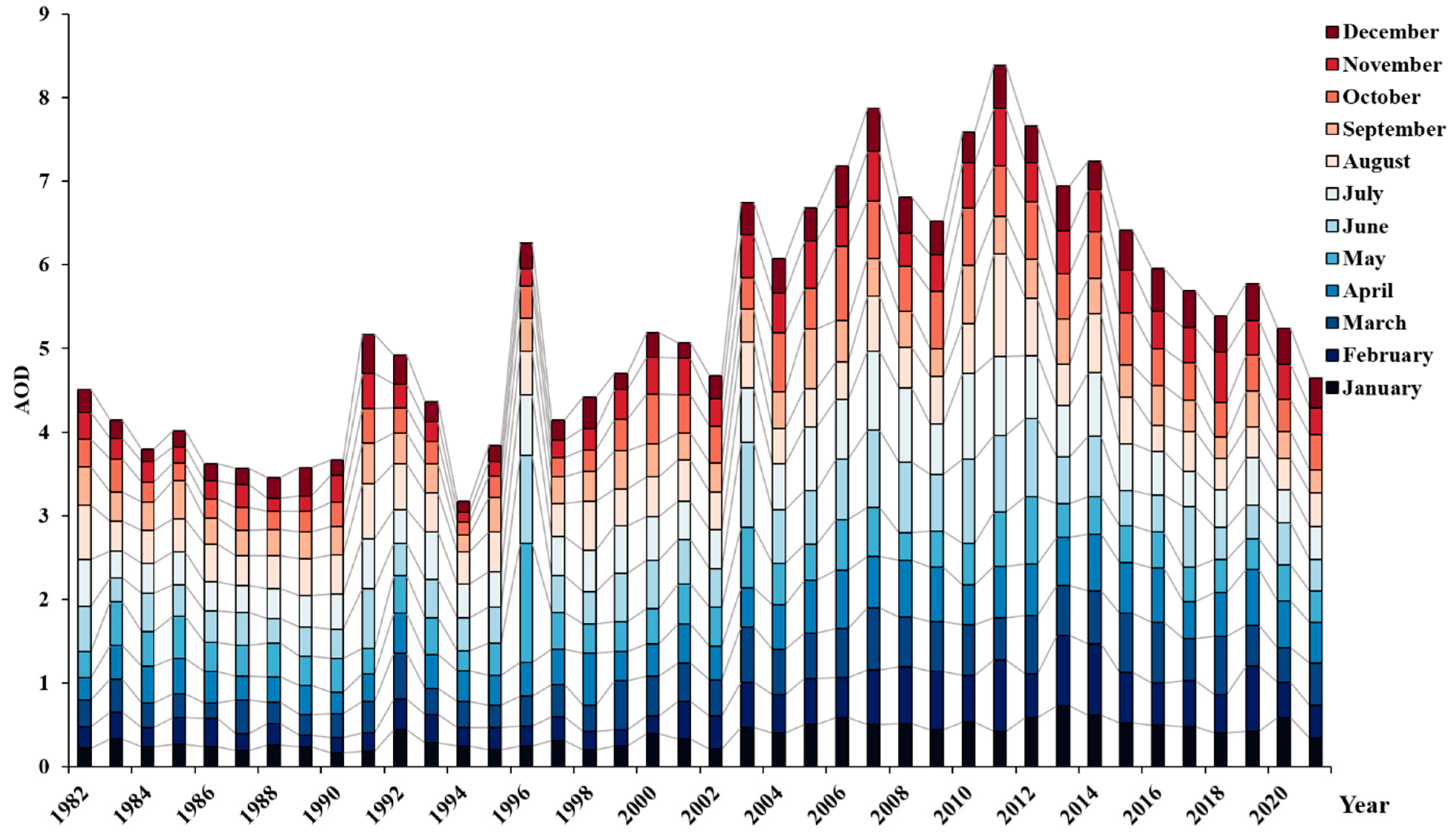
3.3. Temporal Variability of AOD
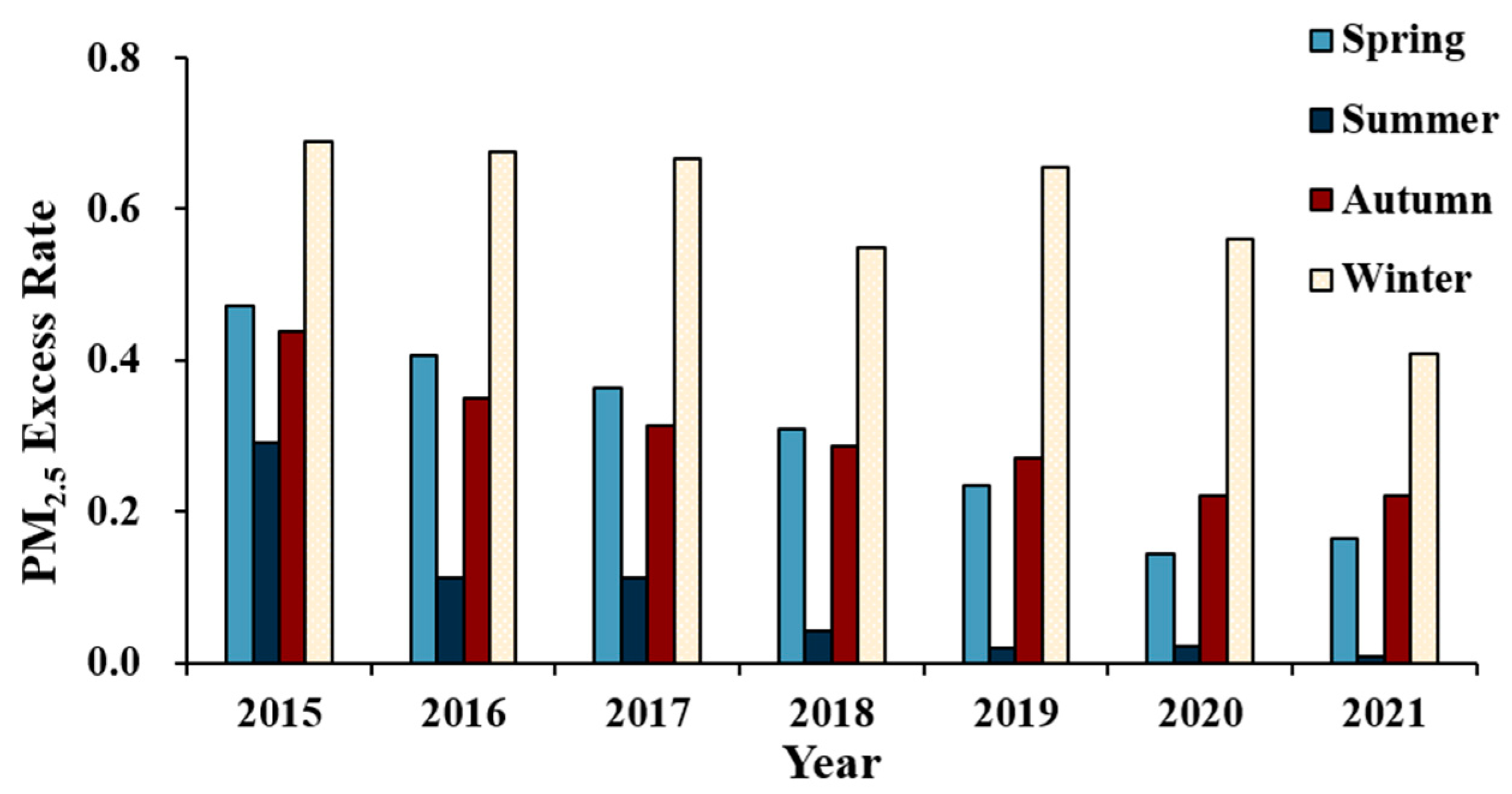
3.4. Relationship between AOD and PM2.5/AQI
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Tanré, D.; Boucher, O. A Satellite View of Aerosols in the Climate System. Nature 2002, 419, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenfeld, D.; Lohmann, U.; Raga, G.B.; O’Dowd, C.D.; Kulmala, M.; Fuzzi, S.; Reissell, A.; Andreae, M.O. Flood or Drought: How Do Aerosols Affect Precipitation? Science 2008, 321, 1309–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Turner, A.G.; Highwood, E.J. Local and Remote Impacts of Aerosol Species on Indian Summer Monsoon Rainfall in a GCM. J. Clim. 2016, 29, 6937–6955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloog, I.; Koutrakis, P.; Coull, B.A.; Lee, H.J.; Schwartz, J. Assessing Temporally and Spatially Resolved PM2.5 Exposures for Epidemiological Studies Using Satellite Aerosol Optical Depth Measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 6267–6275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.; van Donkelaar, A.; Martin, R.V.; Burnett, R.; Rainham, D.G.; Birkett, N.J.; Krewski, D. Estimates of Global Mortality Attributable to Particulate Air Pollution Using Satellite Imagery. Environ. Res. 2013, 120, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Singh, R.S.; Banerjee, T. Associating Airborne Particulates and Human Health: Exploring Possibilities. Environ. Int. 2015, 84, 201–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, J.H.; Su, H. Atmospheric Responses to the Redistribution of Anthropogenic Aerosols. J. Geophys. Res. 2015, 120, 9625–9641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, T.; Kumar, M.; Mall, R.K.; Singh, R.S. Airing “clean Air” in Clean India Mission. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 6399–6413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-P.; Lu, C.-H.; Davies, J.E.; Ou-Yang, C.-F.; Lin, N.-H.; Huff, A.K.; Pierce, B.R.; Kondragunta, S.; Wang, J.-L. Infusing Satellite Data into Aerosol Forecast for near Real-Time Episode Detection and Diagnosis in East Asia. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 856, 158797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogacheva, L.; Rodriguez, E.; Kolmonen, P.; Virtanen, T.H.; Saponaro, G.; Leeuw, D.; Georgoulias, A.K. Spatial and Seasonal Variations of Aerosols over China from Two Decades of Multi-Satellite Observations. Part II: AOD Time Series for 1995–2017 Combined from ATSR ADV and MODIS C6.1 for AOD Tendencies Estimation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2018, 18, 16631–16652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Peng, Y.; Mahmood, R.; Sun, L.; Guo, J. Intercomparison in Spatial Distributions and Temporal Trends Derived from Multi-Source Satellite Aerosol Products. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 7183–7207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X. Variability of Aerosol Optical Depth and Angstrom Wavelength Exponent Derived from AERONET Observations in Recent Decades. Environ. Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 044011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, N.; Tolpekin, V.A.; Stein, A.; Reusen, I. Estimation of AOD under Uncertainty: An Approach for Hyperspectral Airborne Data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filonchyk, M.; Yan, H.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, S.; Li, W.; Li, Y. Combined Use of Satellite and Surface Observations to Study Aerosol Optical Depth in Different Regions of China. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Xue, Y.; Guang, J.; de Leeuw, G.; Self, R.; She, L.; Fan, C.; Xie, Y.; Chen, G. Spatial and Temporal Distribution Characteristics of Haze Days and Associated Factors in China from 1973 to 2017. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 214, 116862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I.; Tanré, D.; Buis, J.P.; Setzer, A.; Vermote, E.; Reagan, J.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Nakajima, T.; et al. AERONET-A Federated Instrument Network and Data Archive for Aerosol Characterization. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 66, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, J.F.; Dibb, J.E.; Campbell, J.W.; Moore, T.S. Physical and Chemical Properties of Surface and Column Aerosols at a Rural New England Site during MODIS Overpass. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 92, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, P.; Hao, W.M.; Nordgren, B.L.; Wang, S.; Liu, G.; Wang, L.; Wen, T.; et al. Aerosol Optical Depth (AOD) and Angstrom Exponent of Aerosols Observed by the Chinese Sun Hazemeter Network from August 2004 to September 2005. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2007, 112, D05203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.; Zhang, X.; Chen, H.; Damiri, B.; Goloub, P.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wei, Y.; Zhou, H.; Dong, F.; et al. Instrument Calibration and Aerosol Optical Depth Validation of the China Aerosol Remote Sensing Network. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114, D03206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Solano, J.; Redondas, A.; Carlund, T.; Rodriguez-Franco, J.J.; Diemoz, H.; Leon-Luis, S.F.; Hernandez-Cruz, B.; Guirado-Fuentes, C.; Kouremeti, N.; Grobner, J.; et al. Aerosol Optical Depth in the European Brewer Network. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 3885–3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimmer, J.S.; Redondas, A.; Karppinen, T. EuBrewNet-A European Brewer Network (COST Action ES1207), an Overview. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 10347–10353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Xie, Y.; Fu, Q.; Li, D.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.; Li, K. Validation of MODIS Aerosol Optical Depth Retrieval over Mountains in Central China Based on a Sun-Sky Radiometer Site of SONET. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilahome, O.; Ninssawan, W.; Jankondee, Y.; Janjai, S.; Kumharn, W. Long-Term Variations and Comparison of Aerosol Optical Properties Based on MODIS and Ground-Based Data in Thailand. Atmos. Environ. 2022, 286, 119218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Chang, N.-B.; Bai, K.; Gao, W. Satellite Remote Sensing of Aerosol Optical Depth: Advances, Challenges, and Perspectives. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 50, 1640–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Wang, L.; Lin, A.; Zhang, M.; Bilal, M.; Wei, J. Performance of the NPP-VIIRS and Aqua-MODIS Aerosol Optical Depth Products over the Yangtze River Basin. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; He, X.; de Leeuw, G.; Mei, L.; Che, Y.; Rippin, W.; Guang, J.; Hu, Y. Long-Time Series Aerosol Optical Depth Retrieval from AVHRR Data over Land in North China and Central Europe. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 198, 471–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stammes, P. OMI Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document Volume III Clouds, Aerosols, and Surface UV Irradiance, 2nd ed.; Stammes, P., Ed.; NASA Goddard Space Flight Center: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2002; Volume 3, pp. 1–114.
- Kumar, A.; Singh, N.; Anshumali; Solanki, R. Evaluation and Utilization of MODIS and CALIPSO Aerosol Retrievals over a Complex Terrain in Himalaya. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 206, 139–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formenti, P.; Mbemba Kabuiku, L.; Chiapello, I.; Ducos, F.; Dulac, F.; Tanré, D. Aerosol Optical Properties Derived from POLDER-3/PARASOL (2005-2013) over the Western Mediterranean Sea- Part 1: Quality Assessment with AERONET and in Situ Airborne Observations. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 6761–6784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chudnovsky, A.; Tang, C.; Lyapustin, A.; Wang, Y.; Schwartz, J.; Koutrakis, P. A Critical Assessment of High-Resolution Aerosol Optical Depth Retrievals for Fine Particulate Matter Predictions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 10907–10917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, J.; Gong, C.; Liu, Z.; Cong, Z.; Gao, W.; Song, T.; Pan, Y.; Sun, Y.; Ji, D.; Wang, L.; et al. The Observation-Based Relationships between PM2.5 and AOD over China. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2016, 121, 10701–10716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Chen, X.; Yang, S.; Tang, L.; Dong, J. Spatiotemporal Relationship between Himawari-8 Hourly Columnar Aerosol Optical Depth (AOD) and Ground-Level PM2.5 Mass Concentration in Mainland China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 765, 144241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Yuan, Q.; Yue, L.; Li, T.; Shen, H.; Zhang, L. The Relationships between PM2.5 and Aerosol Optical Depth (AOD) in Mainland China: About and behind the Spatio-Temporal Variations. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 248, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-M.; Koo, J.-H.; Lee, H.; Mok, J.; Choi, M.; Go, S.; Lee, S.; Cho, Y.; Hong, J.; Seo, S.; et al. Comparison of PM2.5 in Seoul, Korea Estimated from the Various Ground-Based and Satellite AOD. Appl. Sci.-Basel 2021, 11, 10755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Lee, J.; Im, J.; Song, C.-K.; Choi, M.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.; Park, R.; Kim, S.-M.; Yoon, J.; et al. Estimation of Spatially Continuous Daytime Particulate Matter Concentrations under All Sky Conditions through the Synergistic Use of Satellite-Based AOD and Numerical Models. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Huang, W.; Li, Z.; Xue, W.; Peng, Y.; Sun, L.; Cribb, M. Estimating 1-Km-Resolution PM2.5 Concentrations across China Using the Space-Time Random Forest Approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 231, 111221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Li, Z.; Lyapustin, A.; Sun, L.; Peng, Y.; Xue, W.; Su, T.; Cribb, M. Reconstructing 1-Km-Resolution High-Quality PM2.5 Data Records from 2000 to 2018 in China: Spatiotemporal Variations and Policy Implications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 252, 112136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Kondragunta, S. Daily and Hourly Surface PM2.5 Estimation from Satellite AOD. Earth Space Sci. 2021, 8, e2020EA001599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Li, R.-B.; Tian, X.-P.; Wei, J. Analysis of the Temporal and Spatial Variation of Aerosols in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region with a 1 Km AOD Product. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2017, 17, 923–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, Q.; Ban, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, R.; Li, S.; Li, T. Estimating the Daily PM2.5 Concentration in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region Using a Random Forest Model with a 0.01 Degrees x 0.01 Degrees Spatial Resolution. Environ. Int. 2020, 134, 105297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Qin, K.; Xu, J.; Yuan, L.; Li, D.; Jin, Z.; Zhang, K. Aerosol Vertical Distribution and Sources Estimation at a Site of the Yangtze River Delta Region of China. Atmos. Res. 2019, 217, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; de Leeuw, G.; Kerminen, V.-M.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, P.; Nie, W.; Qi, X.; Hong, J.; Wang, Y.; Ding, A.; et al. Analysis of Aerosol Effects on Warm Clouds over the Yangtze River Delta from Multi-Sensor Satellite Observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 5623–5641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, E.; Che, H.; Xu, X.; Wang, Z.; Lu, C.; Gui, K.; Zhao, H.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; et al. Variation in MERRA-2 Aerosol Optical Depth over the Yangtze River Delta from 1980 to 2016. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2019, 136, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Guo, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, X.; Xu, X. Monitoring Temporal-Spatial Variations of AOD over the Yangtze River Delta, China. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2018, 32, 2619–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chang, H.H.; Meng, X.; Geng, G.; Lyapustin, A.; Liu, Y. Full-Coverage High-Resolution Daily PM2.5 Estimation Using MAIAC AOD in the Yangtze River Delta of China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 199, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Jia, H.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Y. A Satellite-Based Geographically Weighted Regression Model for Regional PM2.5 Estimation over the Pearl River Delta Region in China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 154, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wang, L.; Gong, W.; Liu, B. Spatial Distribution and Temporal Variation of Aerosol Optical Depth and Radiative Effect in South China and Its Adjacent Area. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 188, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xie, P.; Li, A.; Xu, J.; Ren, H.; Ren, B.; Li, Y.; Li, J. Study of Aerosol Characteristics and Sources Using MAX-DOAS Measurement during Haze at an Urban Site in the Fenwei Plain. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 107, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- State Council of the People’s Republic of China. The Approval of the State Council on the Overall Urban Planning of Xuzhou. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2017-06/23/content_5204776.htm (accessed on 7 January 2023).
- National Development and Reform Commission. Notice of the National Development and Reform Commission concerning Printing and Distributing the Huaihe Ecological Ecomnmic Belt Development Plan. Available online: https://www.ndrc.gov.cn/xxgk/zcfb/ghwb/201811/t20181107_962252_ext.html (accessed on 7 January 2023).
- Jin, C.; Xue, Y.; Jiang, X.; Wu, S.; Sun, Y. Retrieval and Validation of Long-Term Aerosol Optical Depth from AVHRR Data over China. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2022, 15, 1817–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ångström, A. The Parameters of Atmospheric Turbidity. Tellus 1964, 16, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Zhang, M.; Huang, B. Spatio-Temporal Variation and Impact Factors Analysis of Satellite-Based Aerosol Optical Depth over China from 2002 to 2015. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 129, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Jiang, J.H.; Gu, Y.; Diner, D.; Worden, J.; Liou, K.-N.; Su, H.; Xing, J.; Garay, M.; Huang, L. Decadal-Scale Trends in Regional Aerosol Particle Properties and Their Linkage to Emission Changes. Environ. Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 054021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, M.; Singh, R.; Singh, A.; Singh, N.; Anshumali. Recent Global Aerosol Optical Depth Variations and Trends-A Comparative Study Using MODIS and MISR Level 3 Datasets. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 181, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Y.X.; Zhao, C.S.; Ma, N.; Chen, J.; Xu, W.Y. A Study of Aerosol Liquid Water Content Based on Hygroscopicity Measurements at High Relative Humidity in the North China Plain. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 6417–6426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Sun, J.Y.; Shen, X.J.; Zhang, Y.M.; Che, H.; Ma, Q.L.; Zhang, Y.W.; Zhang, X.Y.; Ogren, J.A. Observations of Relative Humidity Effects on Aerosol Light Scattering in the Yangtze River Delta of China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 8439–8454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.; Xu, C.; Duan, J.; Wang, Y.; Leng, C.; Tao, J.; Che, H.; He, Q.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, R.; et al. Seasonal Variation and Difference of Aerosol Optical Properties in Columnar and Surface Atmospheres over Shanghai. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 123, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, N.; Kumar, K.R.; Hu, K.; Yu, X.; Yin, Y. Long-Term (2002–2014) Evolution and Trend in Collection 5.1 Level-2 Aerosol Products Derived from the MODIS and MISR Sensors over the Chinese Yangtze River Delta. Atmos. Res. 2016, 181, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, M.; Kondragunta, S.; Ciren, P.; Xu, C. Comparison of GOES and MODIS Aerosol Optical Depth (AOD) to Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET) AOD and IMPROVE PM2.5 Mass at Bondville, Illinois. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2009, 59, 1082–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Liu, S.; Wang, L.; Wu, S.; Zhao, W. Fractional Vegetation Cover and Spatiotemporal Variations of PM2.5 Concentrations in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region of China. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Zheng, H.; Ding, D.; Ye, D.; Wang, S. Effects of Meteorology Changes on Inter-Annual Variations of Aerosol Optical Depth and Surface PM2.5 in China—Implications for PM2.5 Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




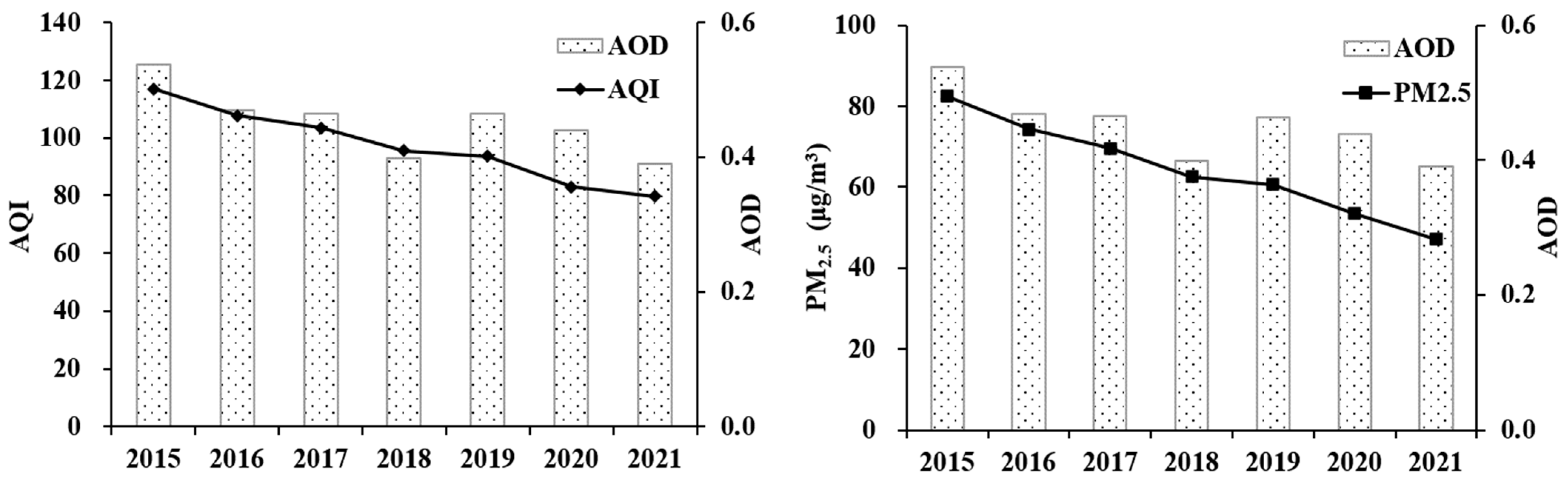
| Year | AQI | PM2.5 (μg/m3) | Days over the Limit (d) | Rate of PM2.5 Exceeds the Standard |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | 116.94 | 82.37 | 236 | 47.03% |
| 2016 | 107.67 | 74.21 | 173 | 38.49% |
| 2017 | 103.42 | 69.61 | 164 | 36.60% |
| 2018 | 95.51 | 62.48 | 133 | 29.68% |
| 2019 | 93.53 | 60.62 | 135 | 29.79% |
| 2020 | 82.99 | 53.36 | 109 | 23.71% |
| 2021 | 79.77 | 47.07 | 100 | 20.10% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, S.; Xue, Y.; Sun, Y.; Jin, C.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, X.; Lu, X. Spatial and Temporal Variation of Aerosol Optical Depth in Huaihai Economic Zone from 1982 to 2021. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 822. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14050822
Wu S, Xue Y, Sun Y, Jin C, Zhang M, Jiang X, Lu X. Spatial and Temporal Variation of Aerosol Optical Depth in Huaihai Economic Zone from 1982 to 2021. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(5):822. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14050822
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Shuhui, Yong Xue, Yuxin Sun, Chunlin Jin, Minghao Zhang, Xingxing Jiang, and Xi Lu. 2023. "Spatial and Temporal Variation of Aerosol Optical Depth in Huaihai Economic Zone from 1982 to 2021" Atmosphere 14, no. 5: 822. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14050822
APA StyleWu, S., Xue, Y., Sun, Y., Jin, C., Zhang, M., Jiang, X., & Lu, X. (2023). Spatial and Temporal Variation of Aerosol Optical Depth in Huaihai Economic Zone from 1982 to 2021. Atmosphere, 14(5), 822. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14050822








