Experimental Investigation on the Reaction Characteristics between Ozone and Vehicle Cabin/Furniture Materials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiments and Methods
2.1. Tested Materials
2.2. Experimental System
2.3. Procedures of Experiments and VOC Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
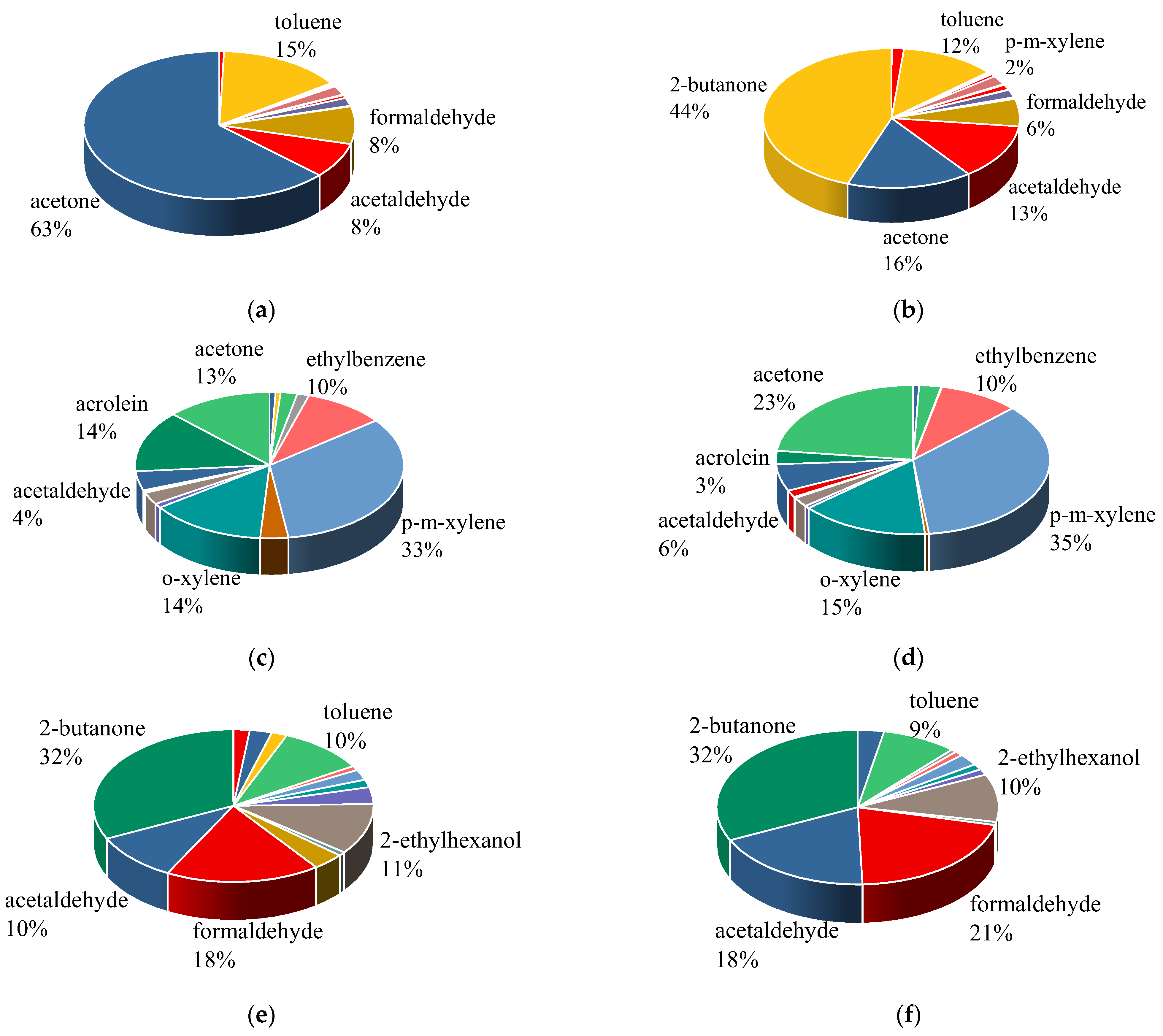
3.1. VOC Compositions of Different Materials
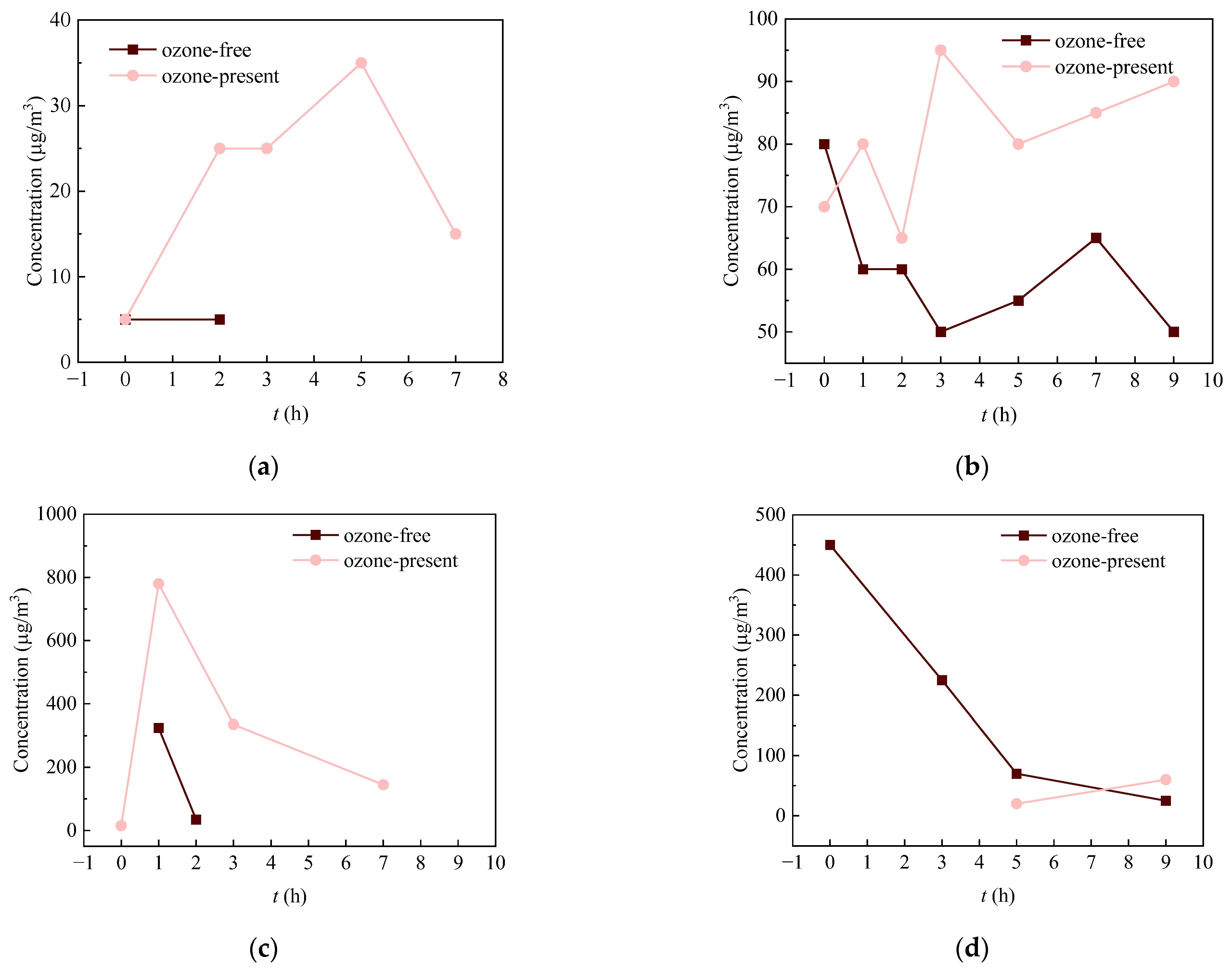
3.2. Comparative Analysis of Concentration Changes for Some Typical Aldehydes and Ketones in Different Tested Materials
- (1)
- Sealing strip
- (2)
- Car carpet
- (3)
- MDF
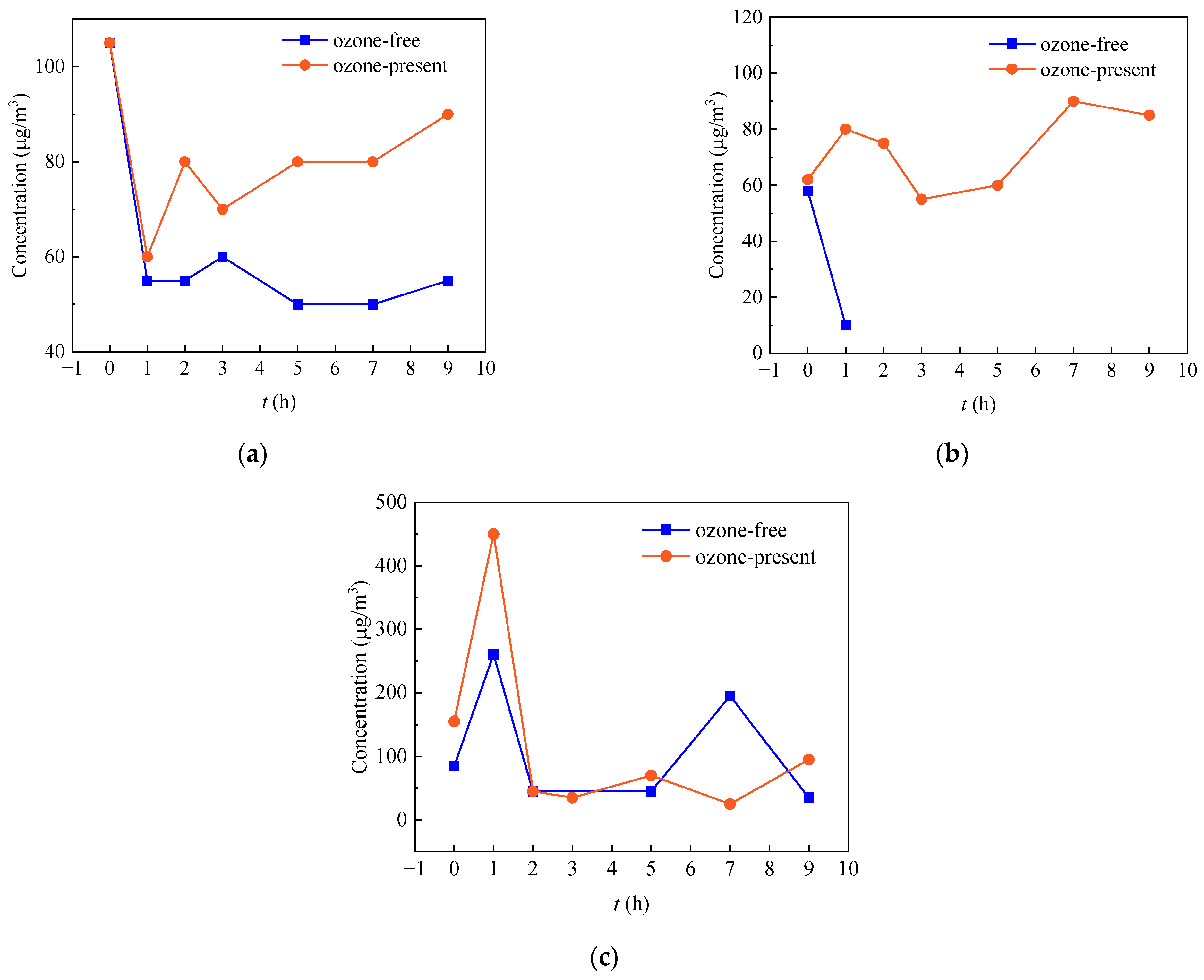
3.3. Comparative Analysis of Concentration Changes for Benzene Series in Different Tested Materials
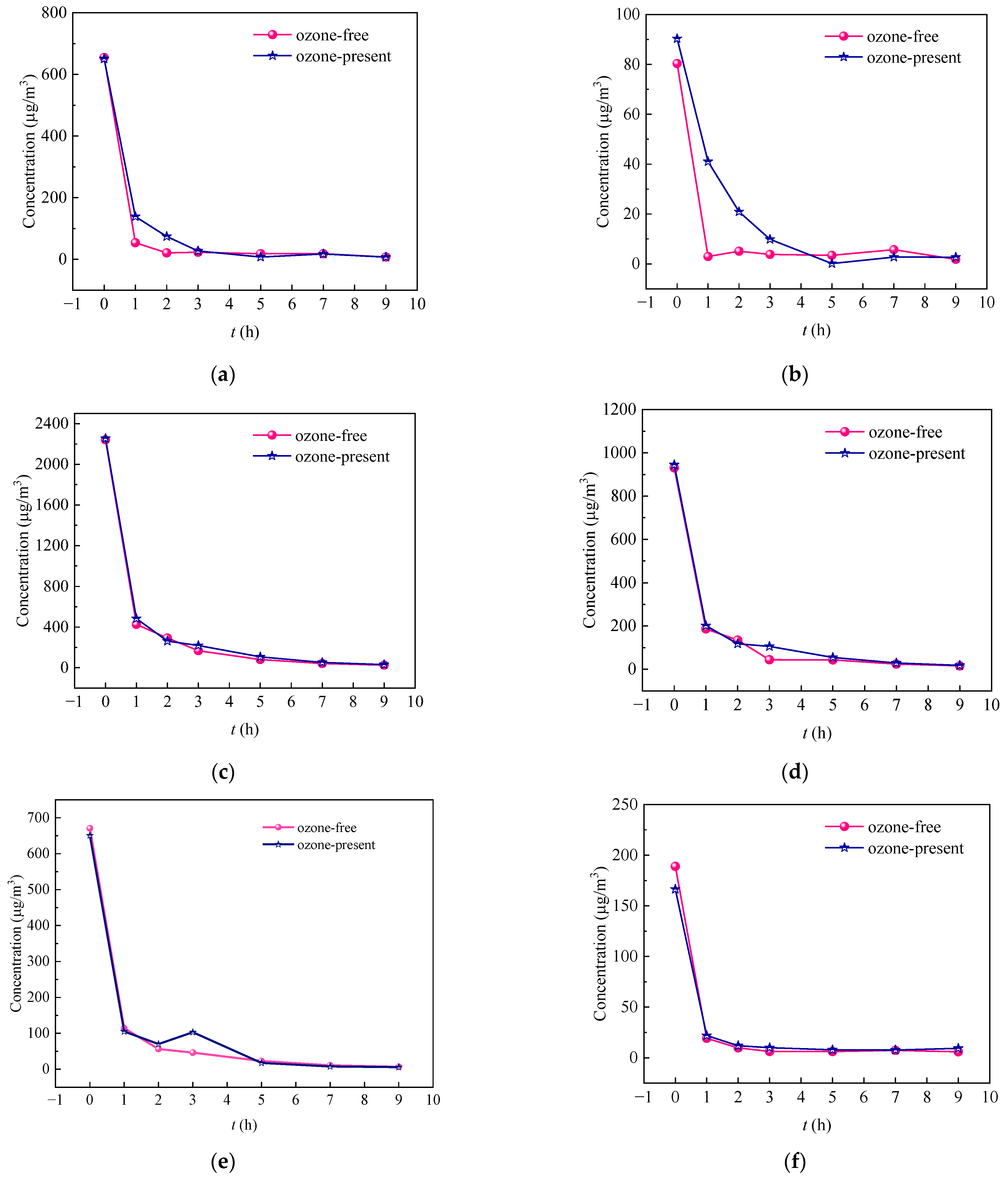
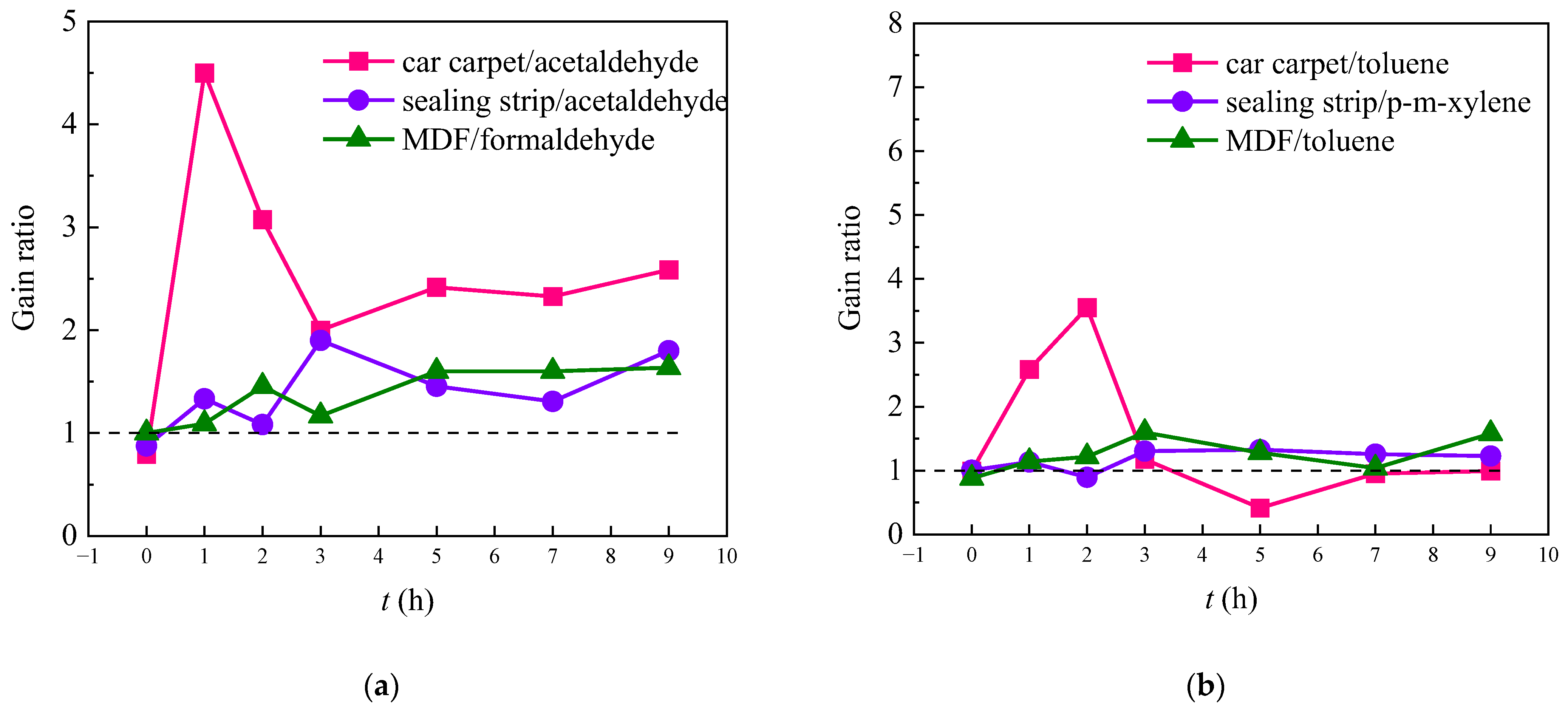
3.4. Calculation of Gain Ratio for the Oxidized Products
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Klepeis, N.E.; Nelson, W.C.; Ott, W.R.; Robinson, J.P.; Tsang, A.M.; Switzer, P.; Behar, J.V.; Hern, S.C.; Engelmann, W.H. The National Human Activity Pattern Survey (NHAPS): A resource for assessing exposure to environmental pollutants. J. Expo. Anal. Environ. Epidemiol. 2001, 11, 231–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.P.; Liu, Y.K.; Dou, Y.Z.; Hao, L.; Wang, X.; Xiong, J.Y. Study on the effect of an intermittent ventilation strategy on controlling formaldehyde concentrations in office rooms. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Eiguren-Fernandez, A.; Hinds, W.C.; Miguel, A.H. In-cabin commuter exposure to ultrafine particles on Los Angeles freeways. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 2138–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knibbs, L.D.; Cole-Hunter, T.; Morawska, L. A review of commuter exposure to ultrafine particles and its health effects. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 2611–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudda, N.; Kostenidou, E.; Sioutas, C.; Delfino, R.J.; Fruin, S.A. Vehicle and driving characteristics that influence in-cabin particle number concentrations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 8691–8697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, T.; Matsunaga, I.; Tomioka, K.; Kumagai, S. Interior air pollution in automotive cabins by volatile organic compounds diffusing from interior materials: I. Survey of 101 types of Japanese domestically produced cars for private use. Indoor Built Environ. 2006, 15, 425–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 27630-2011; Guideline for Air Quality Assessment of Passenger Car. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2011.
- WHO. Health and the Environment: Addressing the Health Impact of Air Pollution; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, A.C.; Jenkins, D.; Whitty, C.J.M. Indoor air pollution: Five ways to fight the hidden harms. Nature 2023, 614, 220–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. WHO Guidelines for Indoor Air Quality: Selected Pollutants; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.M.; Xiong, J.Y.; Wei, W.J. Measurement methods and impact factors for the key parameters of VOC/SVOC emissions from materials in indoor and vehicular environments: A review. Environ. Int. 2022, 168, 107451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Gao, K.; Yang, X.D. Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) formation due to interactions between ozone and skin-oiled clothing: Measurements by extraction analysis-reaction method. Build. Environ. 2016, 103, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weschler, C.J.; Carslaw, N. Indoor chemistry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 2419–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Xiong, J.; Liu, Y.; Misztal, P.K.; Goldstein, A.H. Physical-chemical coupling model for characterizing the reaction of ozone with squalene in realistic indoor environments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 1690–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wisthaler, A.; Weschler, C.J. Reactions of ozone with human skin lipids: Sources of carbonyls, dicarbonyls, and hydroxycarbonyls in indoor air. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 6568–6575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleman, B.K.; Destaillats, H.; Hodgson, A.T.; Nazaroff, W.W. Ozone consumption and volatile byproduct formation from surface reactions with aircraft cabin materials and clothing fabrics. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 642–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandrangi, L.S.; Morrison, G.C. Ozone interactions with human hair: Ozone uptake rates and product formation. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 5079–5089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, A.; Guo, B.; Lin, C.H.; Zhang, J.; Pei, J.; Chen, Q. Ozone reaction with clothing and its initiated VOC emissions in an environmental chamber. Indoor Air 2014, 24, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamas, G.; Weschler, C.J.; Bako-Biro, Z.; Wyon, D.P.; Strøm-Tejsen, P. Factors affecting ozone removal rates in a simulated aircraft cabin environment. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 6122–6133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weschler, C.J.; Wisthaler, A.; Cowlin, S.; Tamás, G.; Strøm-Tejsen, P.; Hodgson, A.T.; Destaillats, H.; Herrington, J.; Zhang, J.; Nazaroff, W.W. Ozone-initiated chemistry in an occupied simulated aircraft cabin. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 6177–6184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakey, P.S.; Wisthaler, A.; Berkemeier, T.; Mikoviny, T.; Pöschl, U.; Shiraiwa, M. Chemical kinetics of multiphase reactions between ozone and human skin lipids: Implications for indoor air quality and health effects. Indoor Air 2017, 27, 816–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.X.; Gao, Y.; Xiong, J.Y. Characterization of the off-body squalene ozonolysis on indoor surfaces. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 132772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffaro, B.; Weisel, C.B. Reactions and products of squalene and ozone: A review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 7396–7411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, R.; Carter, W.P.L. Kinetics and mechanisms of the gas-phase reactions of ozone with organic compounds under atmospheric conditions. Chem. Rev. 1984, 84, 437–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weschler, C.J.; Hodgson, A.T.; Wooley, J.D. Indoor chemistry-ozone, volatile organic-compounds, and carpets. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1992, 26, 2371–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Morrison, G.C. Ozone-surface reactions in five homes: Surface reaction probabilities, aldehyde yields, and trends. Indoor Air 2010, 20, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, G.C.; Nazaroff, W.W. The rate of ozone uptake on carpets: Experimental studies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 4963–4968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolas, M.; Ramalho, O.; Maupetit, F. Experimental study of reactions between ozone and building products. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference of Healthy Buildings, Singapore, 7–11 December 2003; pp. 343–348. [Google Scholar]
- Schripp, T.; Langer, S.; Salthammer, T. Interaction of ozone with wooden building products, treated wood samples and exotic wood species. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 54, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, D.C.; Guo, B.; Zhou, J.; Cheng, H.M.; Chen, X.K. Indoor air formaldehyde (HCHO) pollution of urban coach cabins. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Chen, X.K.; Xiong, J.Y. Air quality inside motor vehicles’ cabins: A review. Indoor Built Environ. 2018, 27, 452–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Matsunaga, I. A case study on identification of airborne organic compounds and time courses of their concentrations in the cabin of a new car for private use. Environ. Int. 2006, 32, 58–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiss, O.; Tirendi, S.; Barrero-Moreno, J.; Kotzias, D. Investigation of volatile organic compounds and phthalates present in the cabin air of used private cars. Environ. Int. 2009, 35, 1188–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.M.; Zheng, J.H.; Yang, T.; He, Z.C.; Zhang, P.; Liu, Y.F.; Zhang, M.X.; Sun, L.H.; Yu, X.F.; Zhao, J.; et al. Predicting the emission characteristics of VOCs in a simulated vehicle cabin environment based on small-scale chamber tests: Parameter determination and validation. Environ. Int. 2020, 142, 105817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, S.K.; Elumalai, S.P. The Influence of School Bus Ventilation Scenarios over in-Cabin PM Number Concentration and Air Exchange Rates. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 11, 1396–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, W.; Klepeis, N.; Switzer, P. Air Change Rates of Motor Vehicles and in-Vehicle Pollutant Concentrations from Secondhand Smoke. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2007, 18, 312–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.M.; Guo, D.D.; Zhang, W.R.; Zhang, R.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, X.K.; Liu, W.; Wu, W.; Sun, L.H.; Yu, X.F.; et al. Observation, prediction, and risk assessment of volatile organic compounds in a vehicle cabin environment. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2023, 4, 101375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, P.S. Ozonation in Organic Chemistry Olefinic Compounds; Academic Press, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1978; Volume 1, pp. 285–298. [Google Scholar]
- Criegee, R. Mechanisms of ozonolysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1975, 14, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, R. Gas-Phase Tropospheric Chemistry of Organic Compounds: A Review. Atmos. Environ. 1990, 24, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, W.P.L. A Detailed Mechanism for the Gas-Phase Atmospheric Reactions of Organic Compounds. Atmos. Environ. 1990, 24, 481–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, R.; Aschmann, S.M. Hydroxyl Radical Production from the Gas-Phase Reactions of Ozone with a Series of Alkenes under Atmospheric Conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1993, 27, 1357–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosjean, E.; Williams, E.L.; Grosjean, D. Atmospheric Chemistry of Acrolein. Sci. Total Environ. 1994, 153, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Zhang, S.; Yue, J.; Zhang, S. Theoretical Study on the Reaction Mechanism and Kinetics of Criegee Intermediate CH2OO with Acrolein. J. Phys. Chem. A 2018, 122, 8729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Tan, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, K.; Ji, W.; Sun, L.; Yu, X.; Zhao, J.; Xu, B.; et al. Measurement of the Key Parameters of VOC Emissions from Wooden Furniture, and the Impact of Temperature. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 259, 118510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Yang, T.; Tan, J.; Li, L.; Ge, Y. Characterization of VOC Emission from Materials in Vehicular Environment at Varied Temperatures: Correlation Development and Validation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, N.L.; Guay, M.; Gauvin, D.; Dietz, R.N.; Chan, C.C.; Lévesque, B. Air Change Rate and Concentration of Formaldehyde in Residential Indoor Air. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 2424–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hult, E.L.; Willem, H.; Price, P.N.; Hotchi, T.; Russell, M.L.; Singer, B.C. Formaldehyde and Acetaldehyde Exposure Mitigation in US Residences: In-Home Measurements of Ventilation Control and Source Control. Indoor Air 2014, 25, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arata, C.; Heine, N.; Wang, N.; Misztal, P.K.; Wargocki, P.; Beko, G.; Williams, J.; Nazaroff, W.W.; Wilson, K.R.; Goldstein, A.H. Heterogeneous ozonolysis of squalene: Gas-phase products depend on water vapor concentration. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 14441–14448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Tested Materials | Temperature | Relative Humidity | Dimensions (cm × cm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Car carpet | 23.6 °C | 50% | 15 × 12 |
| Sealing strip | 25.0 °C | 50% | 12 × 8 |
| Medium-density fiberboard (MDF) | 25.0 °C | 50% | 10 × 10 (3 pieces) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, H.; Xiong, J. Experimental Investigation on the Reaction Characteristics between Ozone and Vehicle Cabin/Furniture Materials. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 769. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14050769
Gao Y, Zhang M, Wang H, Xiong J. Experimental Investigation on the Reaction Characteristics between Ozone and Vehicle Cabin/Furniture Materials. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(5):769. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14050769
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Ying, Meixia Zhang, Haimei Wang, and Jianyin Xiong. 2023. "Experimental Investigation on the Reaction Characteristics between Ozone and Vehicle Cabin/Furniture Materials" Atmosphere 14, no. 5: 769. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14050769
APA StyleGao, Y., Zhang, M., Wang, H., & Xiong, J. (2023). Experimental Investigation on the Reaction Characteristics between Ozone and Vehicle Cabin/Furniture Materials. Atmosphere, 14(5), 769. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14050769





