Airglow Imaging Observations of Plasma Blobs: Merging and Bifurcation during Solar Minimum over Tropical Region
Abstract
1. Introduction
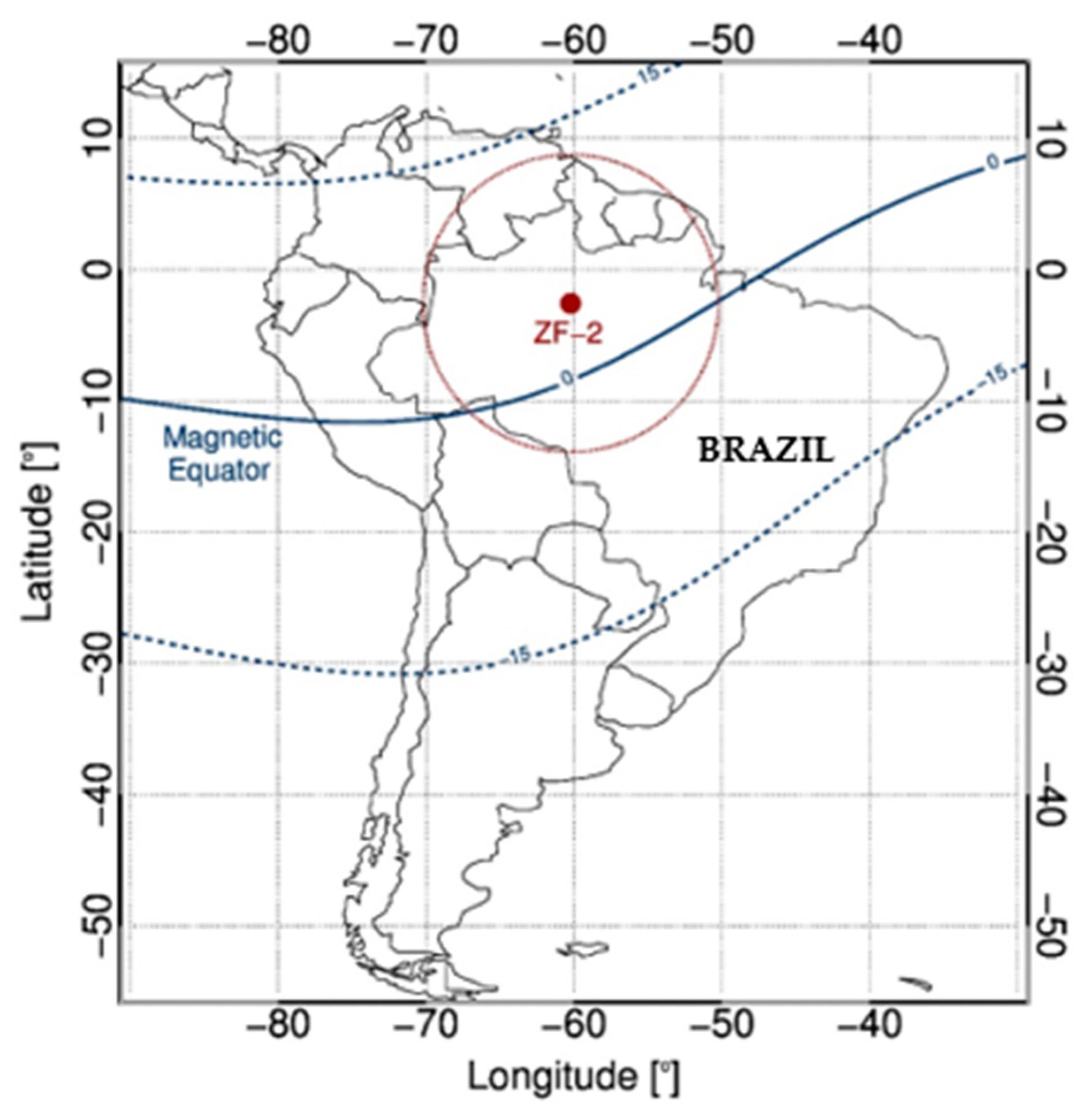
2. Instruments
3. Observations and Methodology
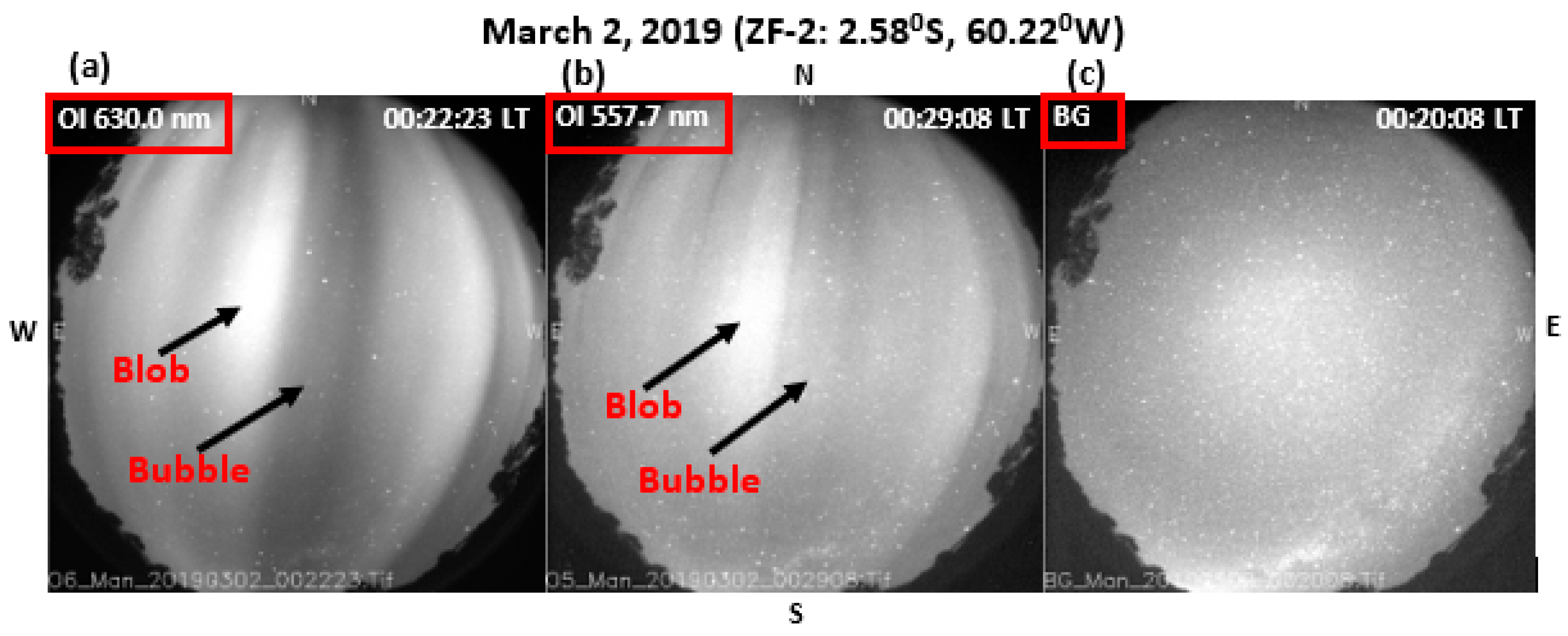
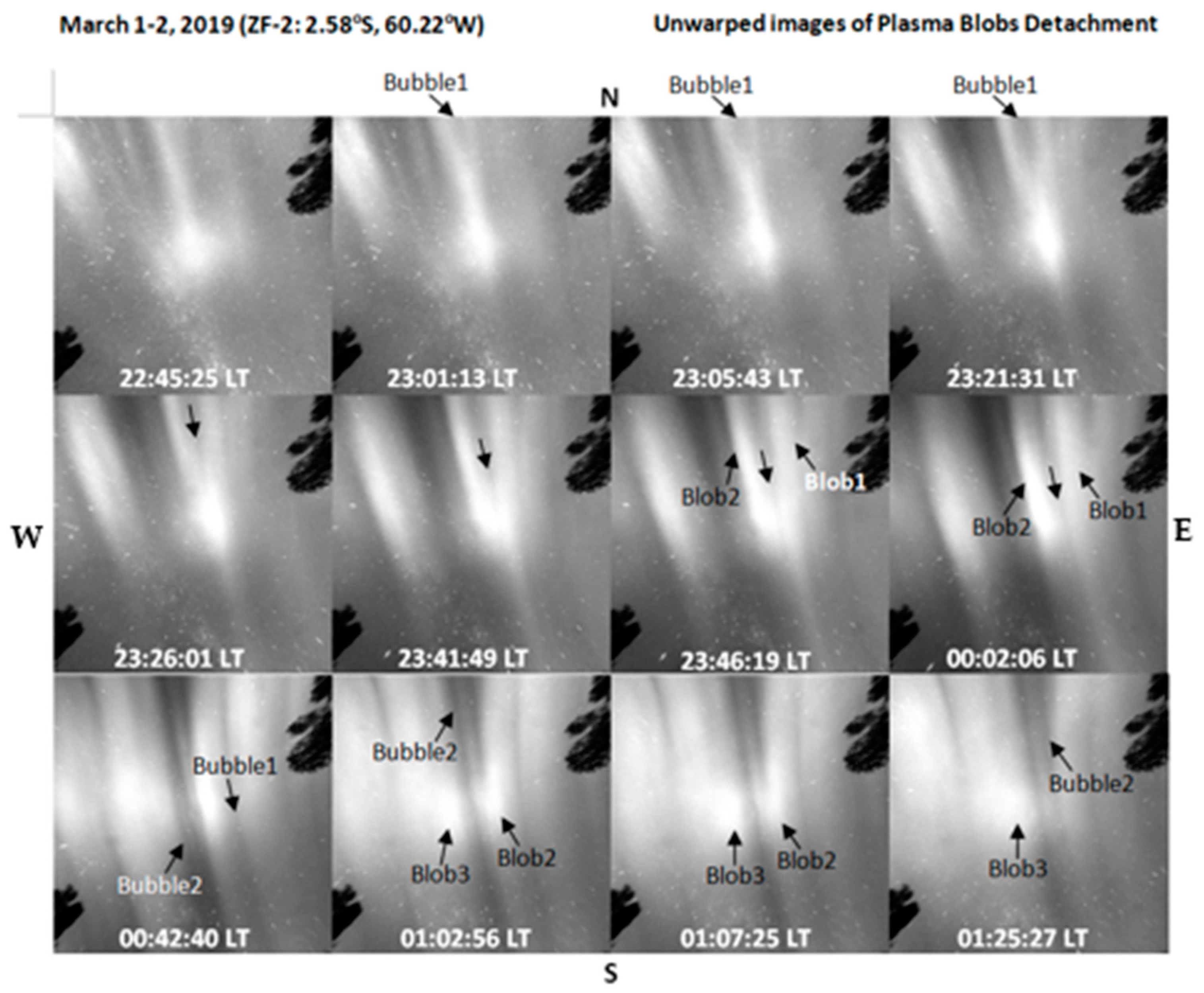
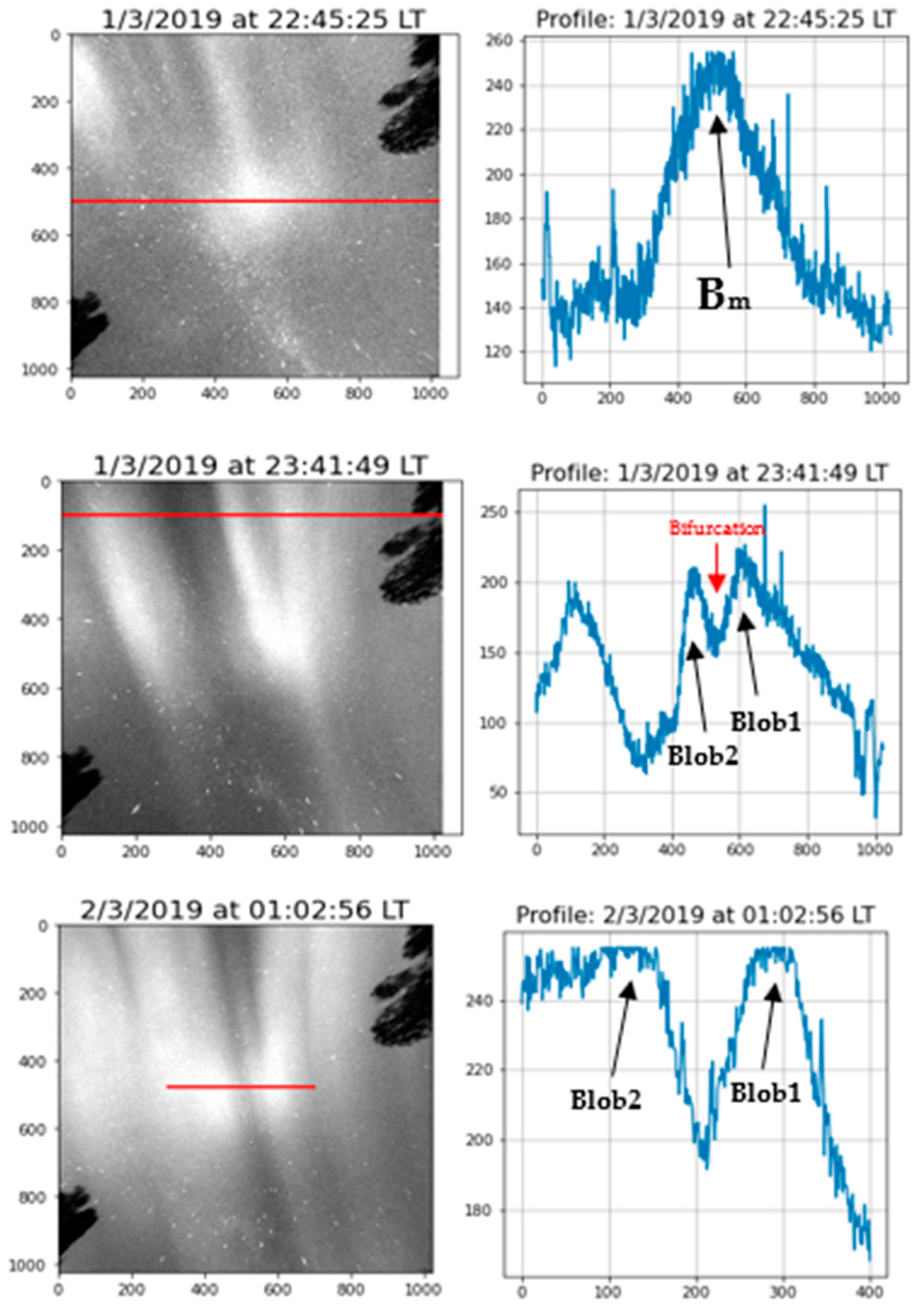
4. Results and Discussion
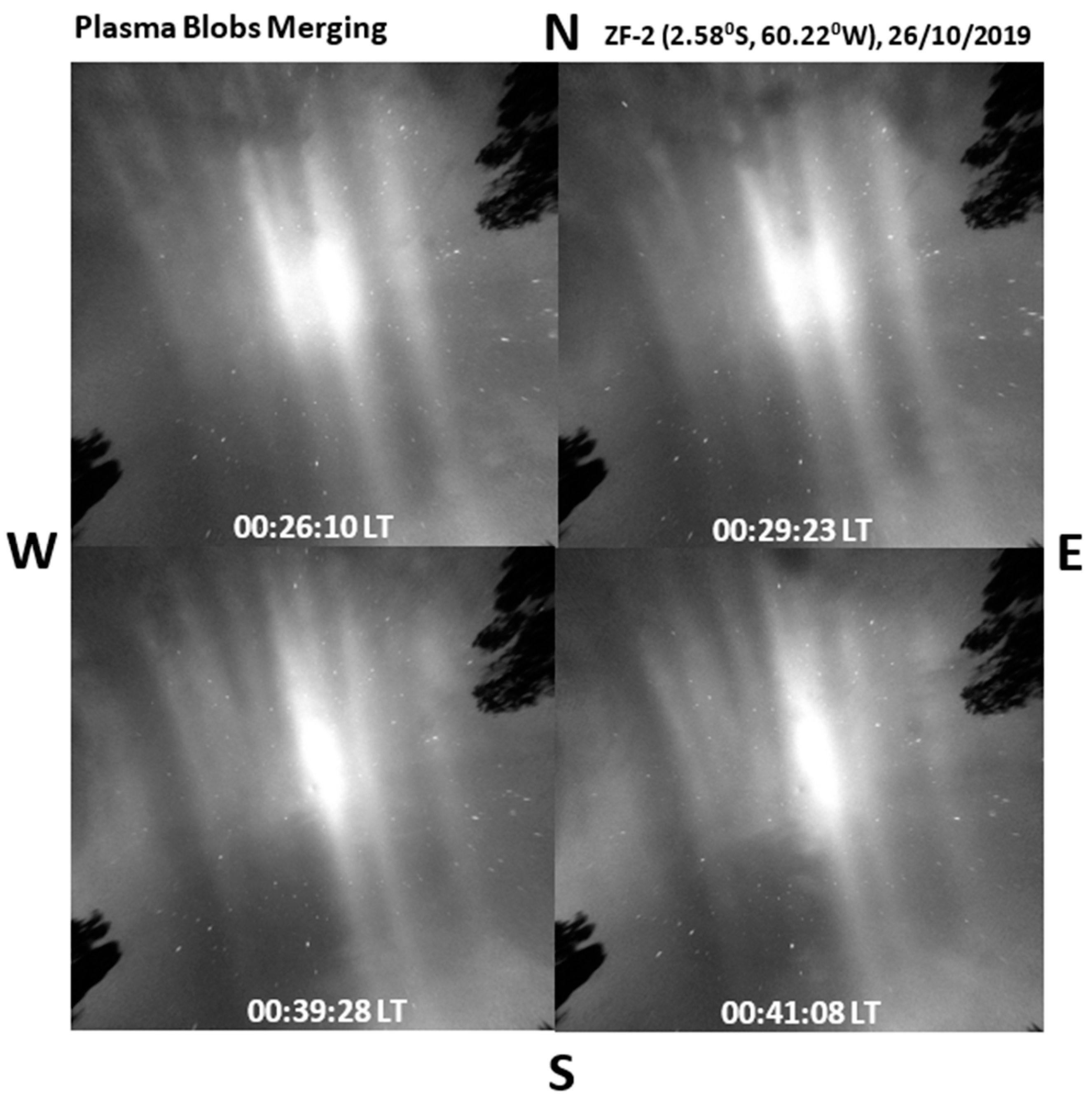
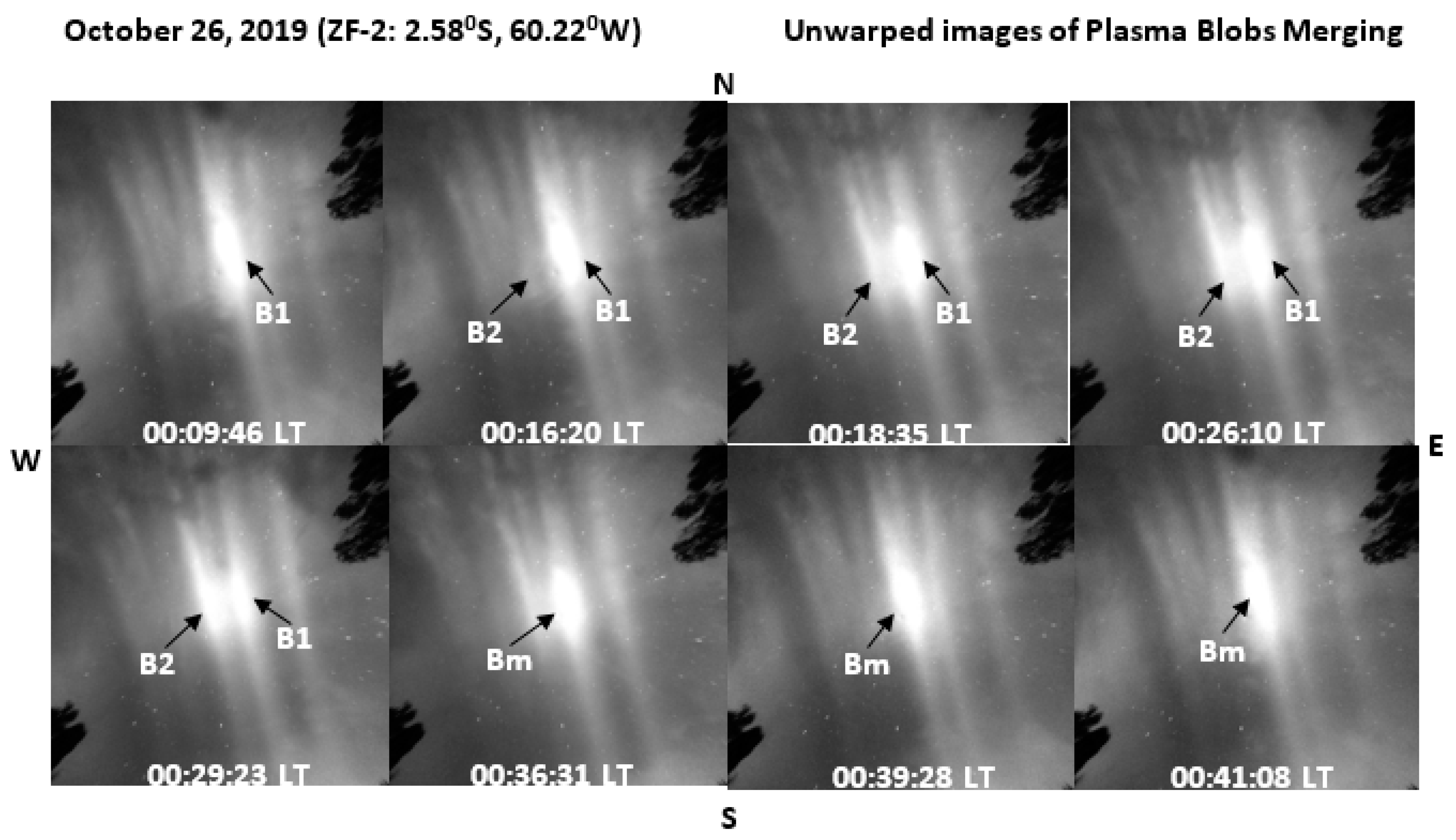
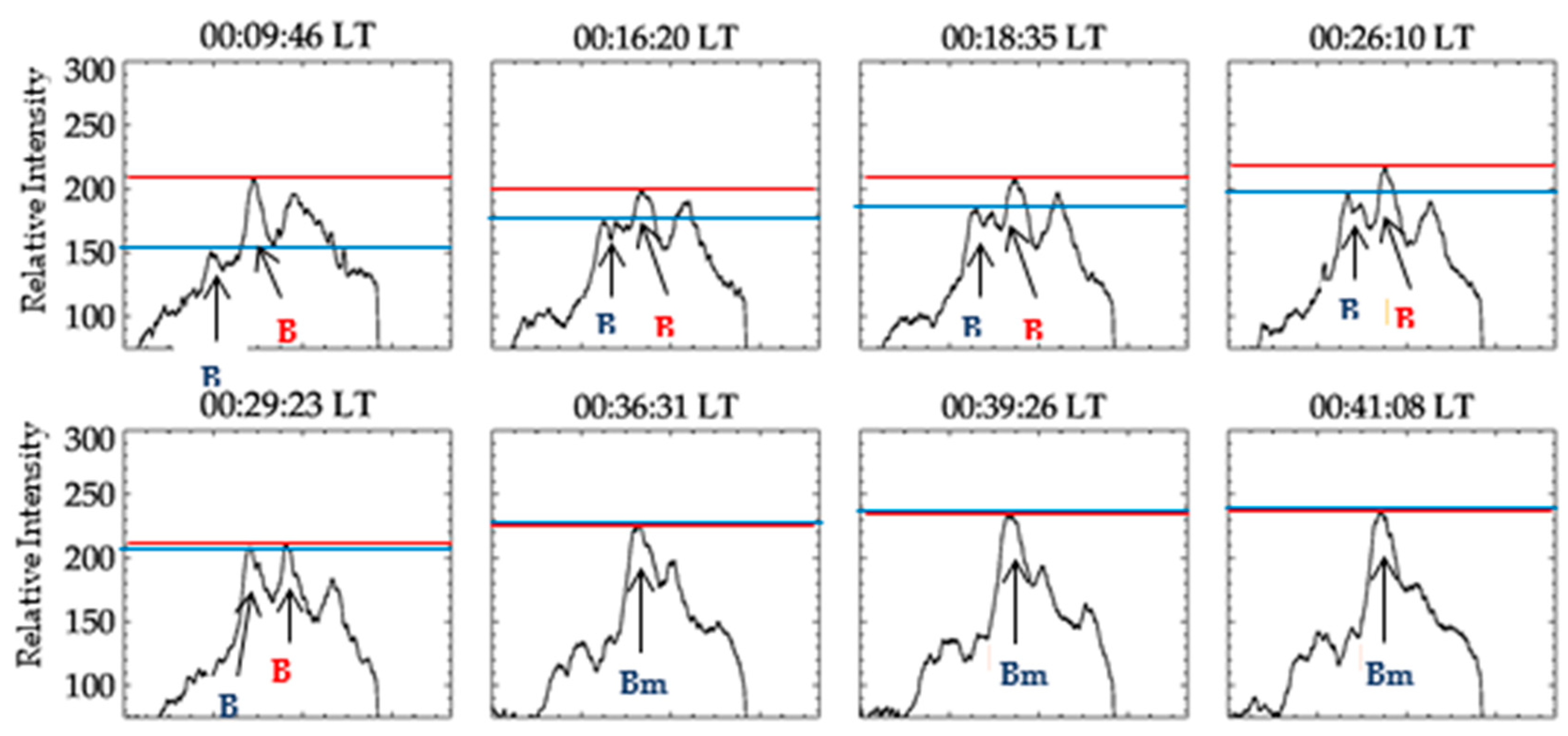
4.1. Plasma Blobs Merging
4.2. Plasma Blobs Bifurcation
5. Conclusions
- Wind Reversion Effect (WRE) mechanism: in this mechanism, the change in the direction of the zonal thermospheric wind from eastward to westward at the equatorial region may cause the steepening of plasma; in some cases, the slower drifting plasma blobs may merge with faster ones.
- Secondly, based on the results revealed from the scale-size evolution of plasma blobs during merging, we proposed that the accumulated plasma blob along the magnetic field lines would merge with adjacent blob when its scale size (E-W extension) is substantially large, and the decrease in zonal thermospheric wind velocity and ion diffusion along field lines in the F- region could be responsible for this process. Nevertheless, the three merging cases observed in this study give an average zonal scale-size of 105 ± 7 km. As the cases are few statistically, we could not infer the scale-size of blobs liable for merging. Thus, further studies on larger sample size of the cases could reveal the scale-size of plasma blobs liable for merging.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kelley, M.C. The Earth’s Ionosphere: Plasma Physics and Electrodynamics; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ossakow, S.; Zalesak, S.; McDonald, B.; Chaturvedi, P. Nonlinear equatorial spread F: Dependence on altitude of the F peak and bottomside background electron density gradient scale length. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1979, 84, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendillo, M.; Baumgardner, J. Airglow characteristics of equatorial plasma depletions. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1982, 87, 7641–7652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, S.; Oya, H. Occurrence characteristics of low latitude ionosphere irregularities observed by impedance probe on board the Hinotori satellite. J. Geomagn. Geoelectr. 1986, 38, 125–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimenta, A.; Sahai, Y.; Bittencourt, J.; Abdu, M.; Takahashi, H.; Taylor, M.J. Plasma blobs observed by ground-based optical and radio techniques in the Brazilian tropical sector. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L12810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Lühr, H.; Stolle, C.; Rother, M.; Min, K.; Michaelis, I. Field-aligned current associated with low-latitude plasma blobs as observed by the CHAMP satellite. Ann. Geophys. 2010, 28, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-S.; Le, G.; de La Beaujardiere, O.; Roddy, P.A.; Hunton, D.E.; Pfaff, R.F.; Hairston, M.R. Relationship between plasma bubbles and density enhancements: Observations and interpretation. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2014, 119, 1325–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Xiong, C.; Zhu, Z.; Mei, X. Onset condition of plasma density enhancements: A case study for the effects of meridional wind during 17–18 August 2003. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2018, 123, 6714–6726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Min, K.W.; Eastes, R.W.; Chao, C.K.; Kim, H.-E.; Lee, J.; Sohn, J.; Ryu, K.; Seo, H.; Yoo, J.-H.; et al. Low-latitude plasma blobs above Africa: Exploiting GOLD and multi-satellite in situ measurements. Adv. Space Res. 2022; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kil, H.; Paxton, L.J.; Jee, G.; Nikoukar, R. Plasma blobs associated with medium-scale traveling ionospheric disturbances. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 3575–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, A.; Ganaie, B.A.; Ramkumar, T.K.; Malik, M.A. Bifurcation and merging of low mid-latitude plasma irregularities seeded by Medium Scale Traveling Ionospheric Disturbances over Srinagar, Jammu and Kashmir, India. AGU Fall Meet. Abstr. 2020, 2020, SA009-0004. [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco, A.; Batista, I.; Wrasse, C.; Takahashi, H.; Pimenta, A. Disconnection and reconnection in plasma bubbles observed by OI 630 nm airglow images from Cariri Observatory. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2022, 127, e2021JA030042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahai, Y.; Abalde, J.; Fagundes, P.; Pillat, V.; Bittencourt, J. First observations of detached equatorial ionospheric plasma depletions using OI 630.0 nm and OI 777.4 nm emissions nightglow imaging. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L11104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimenta, A.; Fagundes, P.; Bittencourt, J.; Sahai, Y. Relevant aspects of equatorial plasma bubbles under different solar activity conditions. Adv. Space Res. 2001, 27, 1213–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huba, J.; Wu, T.; Makela, J. Electrostatic reconnection in the ionosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 1626–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurav, O.; Narayanan, V.; Sharma, A.; Ghodpage, R.; Gaikwad, H.; Patil, P. Airglow imaging observations of some evolutionary aspects of equatorial plasma bubbles from Indian sector. Adv. Space Res. 2019, 64, 385–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chian, A.C.-L.; Abalde, J.R.; Miranda, R.A.; Borotto, F.A.; Hysell, D.L.; Rempel, E.L.; Ruffolo, D. Multi-spectral optical imaging of the spatiotemporal dynamics of ionospheric intermittent turbulence. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowley, G.; Ridley, A.J.; Deist, D.; Wing, S.; Knipp, D.J.; Emery, B.A.; Foster, J.; Heelis, R.; Hairston, M.; Reinisch, B.W. Transformation of high-latitude ionospheric F region patches into blobs during the March 21, 1990, storm. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2000, 105, 5215–5230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Manoharan, P. Eruption of a plasma blob, associated M-class flare, and large-scale extreme-ultraviolet wave observed by SDO. Astron. Astrophys. 2013, 553, A109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Keyser, J.; Darrouzet, R.; Roth, M.; Vaisberg, O.L.; Rybjeva, N.; Smirnov, V.; Avanov, L.; Němeček, Z.; Safrankova, J. Transients at the dusk side magnetospheric boundary: Surface waves or isolated plasma blobs? J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2001, 106, 25503–25516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manz, P.; Ribeiro, T.T.; Scott, B.D.; Birkenmeier, G.; Carralero, D.; Fuchert, G.; Müller, S.H.; Müller, H.W.; Stroth, U.; Wolfrum, E. Origin and turbulence spreading of plasma blobs. Phys. Plasmas 2015, 22, 022308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, T. Observations of quasi-periodic scintillations and their possible relation to the dynamics of E s plasma blobs. Radio Sci. 1991, 26, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, F.; Taylor, M.J.; Kelley, M. Two-dimensional spectral analysis of mesospheric airglow image data. Appl. Opt. 1997, 36, 7374–7385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalgarno, A.; Walker, J.C. The red line of atomic oxygen in the day airglow. J. Atmos. Sci. 1964, 21, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rishbeth, H.; Garriott, O.K. Introduction to Ionospheric Physics; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Abdu, M.A.; Bhattacharyya, A.; Pancheva, D. Aeronomy of the Earth’s Atmosphere and Ionosphere; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2011; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, M.J.; Eccles, J.; LaBelle, J.; Sobral, J. High resolution OI (630 nm) image measurements of F-region depletion drifts during the Guará Campaign. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1997, 24, 1699–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, W.D.; Joselyn, J.A.; Kamide, Y.; Kroehl, H.W.; Rostoker, G.; Tsurutani, B.T.; Vasyliunas, V.M. What is a geomagnetic storm? J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1994, 99, 5771–5792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimenta, A.; Sahai, Y.; Bittencourt, J.; Rich, F. Ionospheric plasma blobs observed by OI 630 nm all-sky imaging in the Brazilian tropical sector during the major geomagnetic storm of April 6–7, 2000. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L02820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, P.M.; Kockarts, G. Aeronomy; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Krall, J.; Huba, J.; Joyce, G.; Yokoyama, T. Density enhancements associated with equatorial spread F. Ann. Geophys. 2010, 28, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabusky, N.; Doles, J., III; Perkins, F. Deformation and striation of plasma clouds in the ionosphere: 2. Numerical simulation of a nonlinear two-dimensional model. J. Geophys. Res. 1973, 78, 711–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Paula, E.R.; de Oliveira, C.B.; Caton, R.G.; Negreti, P.M.; Batista, I.S.; Martinon, A.R.; Neto, A.C.; Abdu, M.A.; Monico, J.F.; Sousasantos, J.; et al. Ionospheric irregularity behavior during the September 6–10, 2017 magnetic storm over Brazilian equatorial–low latitudes. Earth Planets Space 2019, 71, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, T.; Su, S.; Fukao, S. Plasma blobs and irregularities concurrently observed by ROCSAT-1 and Equatorial Atmosphere Radar. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2007, 112, A05311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, H.; Shi, J.; Wang, G.; Wang, X. Plasma blobs concurrently observed with bubbles in the Asian-Oceanian sector during solar maximum. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2019, 124, 7062–7071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| S/N | Bifurcation Events | Dst (nT) | Merging Events | Dst (nT) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 March 2019 | >−29 | 8 March 2019 | >−16 |
| 2 | 9 October 2019 | >−9 | 13 March 2019 | >−16 |
| 3 | 19 October 2019 | >−4 | 25–26 March 2019 | >−34 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Adebayo, M.O.; Pimenta, A.A.; Savio, S.; Nyassor, P.K. Airglow Imaging Observations of Plasma Blobs: Merging and Bifurcation during Solar Minimum over Tropical Region. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 514. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14030514
Adebayo MO, Pimenta AA, Savio S, Nyassor PK. Airglow Imaging Observations of Plasma Blobs: Merging and Bifurcation during Solar Minimum over Tropical Region. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(3):514. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14030514
Chicago/Turabian StyleAdebayo, Micheal O., Alexandre A. Pimenta, Siomel Savio, and Prosper K. Nyassor. 2023. "Airglow Imaging Observations of Plasma Blobs: Merging and Bifurcation during Solar Minimum over Tropical Region" Atmosphere 14, no. 3: 514. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14030514
APA StyleAdebayo, M. O., Pimenta, A. A., Savio, S., & Nyassor, P. K. (2023). Airglow Imaging Observations of Plasma Blobs: Merging and Bifurcation during Solar Minimum over Tropical Region. Atmosphere, 14(3), 514. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14030514






