Characters of Particulate Matter and Their Relationship with Meteorological Factors during Winter Nanyang 2021–2022
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
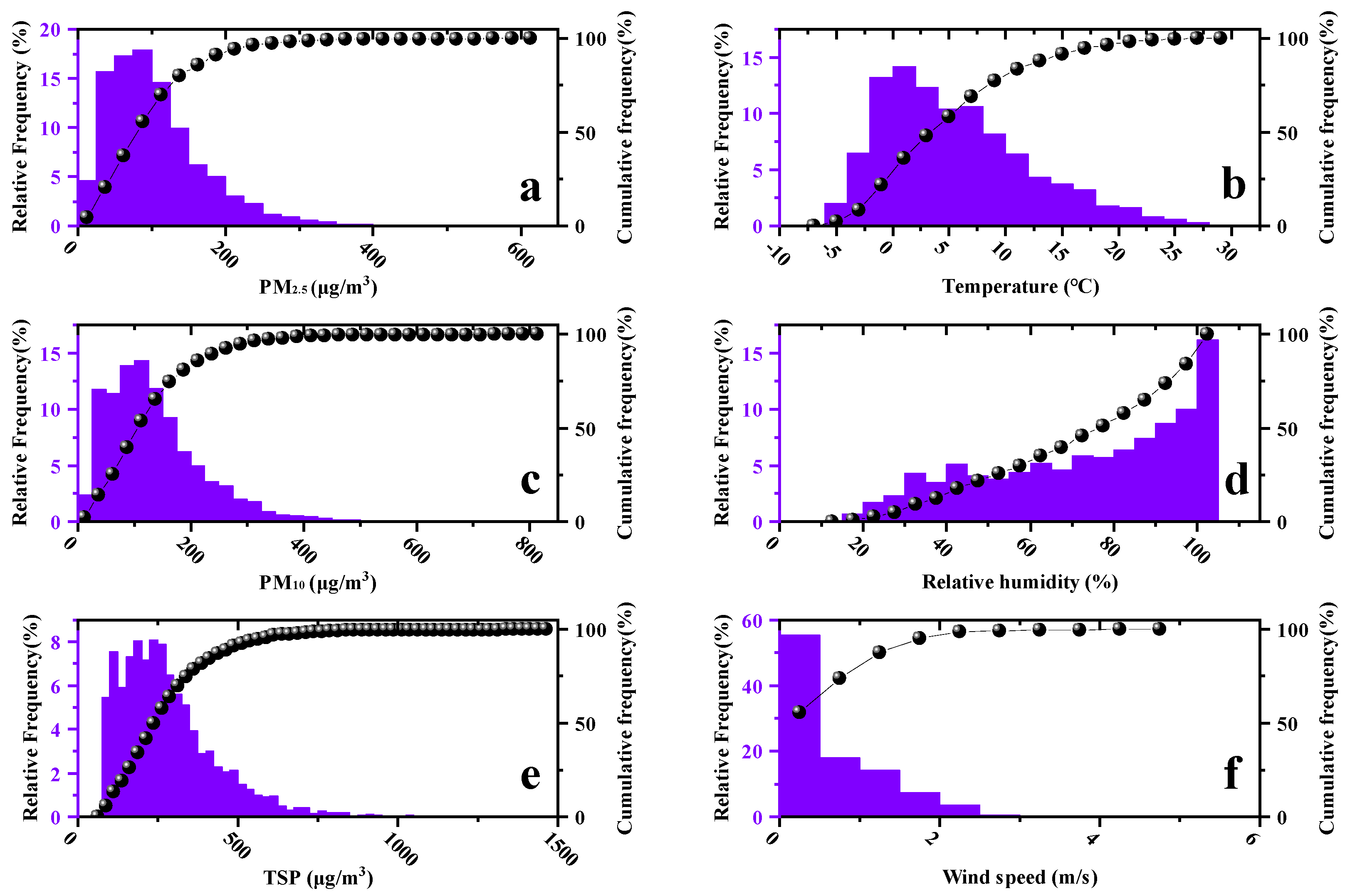
3.1. Temporal Behavior of Particulate Matters and Meteorological Factors
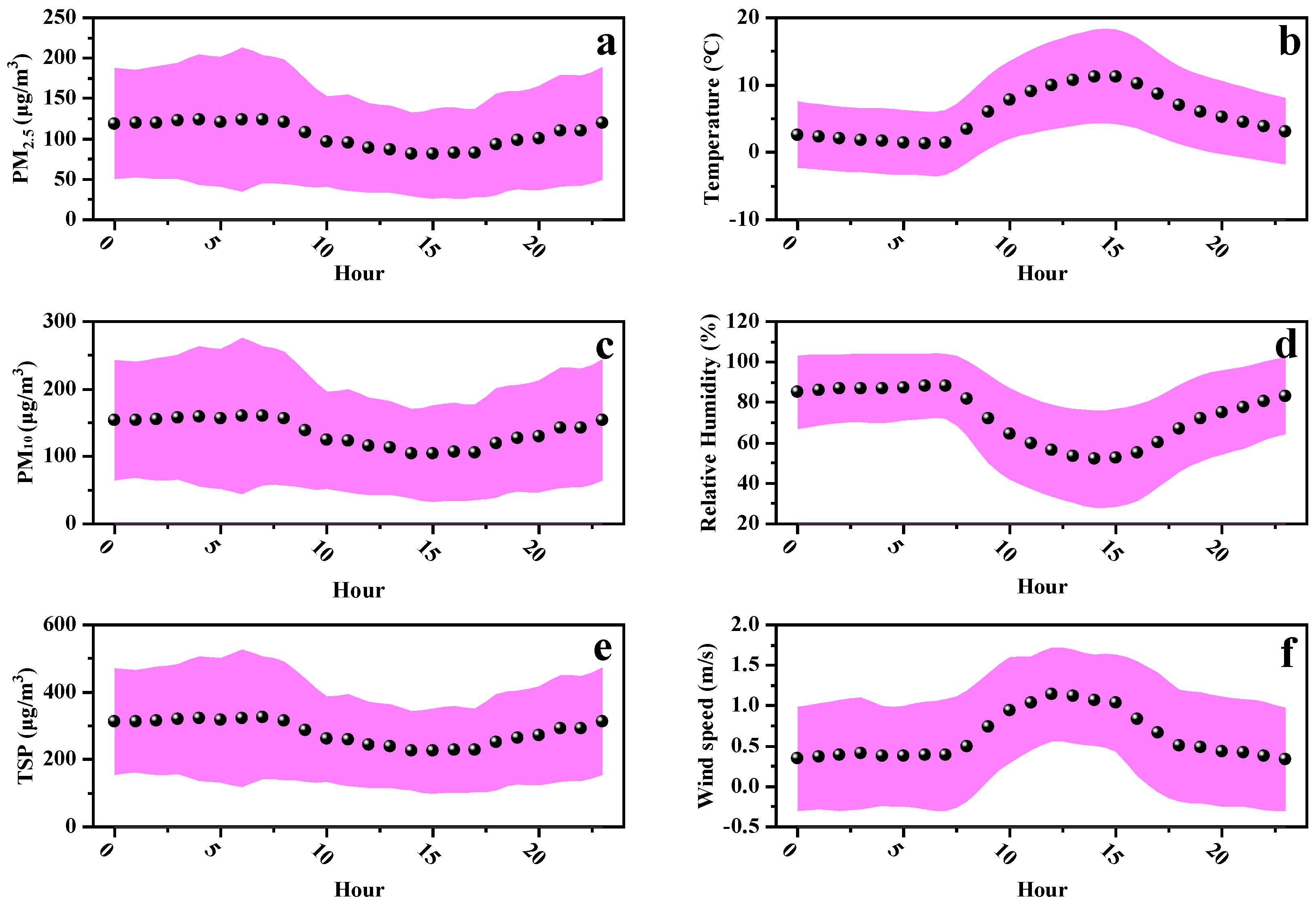
3.2. Diurnal Variation of Particle Concentrations and Meteorological Factors
3.3. Relationship between Particulate Matter Concentrations and Meteorological Parameters
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Tanré, D.; Boucher, O. A satellite view of aerosols in the climate system. Nature 2002, 419, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, V.; Crutzen, P.J.; Kiehl, J.T.; Rosenfeld, D. Aerosols, Climate, and the Hydrological Cycle. Science 2001, 294, 2119–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jocelyn, K.; Granmar, M. Mounting Evidence Indicts Fine-Particle Pollution. Science 2005, 307, 1858–1861. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson, M.Z. Strong radiative heating due to the mixing state of black carbon in atmospheric aerosols. Nature 2001, 409, 695–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edenhofer, O. Climate Change 2014: Mitigation of Climate Change: Working Group Iii Contribution to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Cappa, C.D.; Onasch, T.B.; Massoli, P.; Worsnop, D.R.; Bates, T.S.; Cross, E.S.; Davidovits, P.; Hakala, J.; Hayden, K.L.; Jobson, B.T.; et al. Radiative Absorption Enhancements Due to the Mixing State of Atmospheric Black Carbon. Science 2012, 337, 1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulmala, M.; Kontkanen, J.; Junninen, H.; Lehtipalo, K.; Manninen, H.E.; Nieminen, T.; Petäjä, T.; Sipilä, M.; Schobesberger, S.; Rantala, P.; et al. Direct Observations of Atmospheric Aerosol Nucleation. Science 2013, 339, 943–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackerman, A.S.; Kirkpatrick, M.P.; Stevens, D.E.; Toon, O.B. The impact of humidity above stratiform clouds on indirect aerosol climate forcing. Nature 2004, 432, 1014–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albrecht, B.A. Aerosols, Cloud Microphysics, and Fractional Cloudiness. Science 1989, 245, 1227–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crutzen, P.J.; Andreae, M.O. Biomass Burning in the Tropics: Impact on Atmospheric Chemistry and Biogeochemical Cycles. Science 1990, 250, 1669–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Z.; Dabdub, D.; Seinfeld, J.H. Chemical Coupling Between Atmospheric Ozone and Particulate Matter. Science 1997, 277, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Han, G.; Ma, X.; Gong, W.; Chen, W.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Pei, Z.; Gou, H.; Bu, L. Quantifying CO2 Uptakes Over Oceans Using LIDAR: A Tentative Experiment in Bohai Bay. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2020GL091160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Han, G.; Ma, X.; Zhang, M.; Pei, Z.; Xu, H.; Qiu, R.; Zhang, H.; Gong, W. An inversion method for estimating strong point carbon dioxide emissions using a differential absorption Lidar. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 271, 122434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Z.; Han, G.; Ma, X.; Shi, T.; Gong, W. A Method for Estimating the Background Column Concentration of CO2 Using the Lagrangian Approach. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, R.; Li, X.; Han, G.; Xiao, J.; Ma, X.; Gong, W. Monitoring drought impacts on crop productivity of the U.S. Midwest with solar-induced fluorescence: GOSIF outperforms GOME-2 SIF and MODIS NDVI, EVI, and NIRv. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2022, 323, 109038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, J. How Dirty Air Hurts the Heart. Science 2005, 307, 1858–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.J.; Zhang, Y.; Bozzetti, C.; Ho, K.F.; Cao, J.J.; Han, Y.; Daellenbach, K.R.; Slowik, J.G.; Platt, S.M.; Canonaco, F.; et al. High secondary aerosol contribution to particulate pollution during haze events in China. Nature 2014, 514, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Jiang, X.; Tong, D.; Davis, S.J.; Zhao, H.; Geng, G.; Feng, T.; Zheng, B.; Lu, Z.; Streets, D.G.; et al. Transboundary health impacts of transported global air pollution and international trade. Nature 2017, 543, 705–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambade, B. Characterization of PM10 over Urban and Rural Sites of Rajnandgaon, Central India. Nat. Hazards 2016, 80, 589–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, A.; Huang, X.; Nie, W.; Chi, X.; Xu, Z.; Zheng, L.; Xu, Z.; Xie, Y.; Qi, X.; Shen, Y.; et al. Significant Reduction of PM2.5 in Eastern China Due to Regional-Scale Emission Control: Evidences from the Sorpes Station, 2011–2018. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 11791–11801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Xu, H.; Xu, Q.; Chen, B.; Kan, H. Fine Particulate Matter Constituents and Cardiopulmonary Mortality in a Heavily Polluted Chinese City. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, A.; Nie, W.; Huang, X.; Chi, X.; Sun, J.; Kerminen, V.-M.; Xu, Z.; Guo, W.; Petäjä, T.; Yang, X.; et al. Long-term observation of air pollution-weather/climate interactions at the SORPES station: A review and outlook. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2016, 10, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.K.; Pathak, W.S.; Wu, T. Summertime PM2.5 Ionic Species in Four Major Cities of China: Nitrate Formation in an Ammonia-Deficient Atmosphere. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 1711–1722. [Google Scholar]
- Basant, S.; Balram, A. Review on Composition, Emission Sources of Rspm, Tspm, Heavy Metals and Ions with Effect on Environment and Health. Res. J. Chem. Environ. 2016, 20, 31–43. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Ma, Y.; Gong, W.; Zhu, Z. Aerosol Optical Properties of a Haze Episode in Wuhan Based on Ground-Based and Satellite Observations. Atmosphere 2014, 5, 699–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, N.; Hong, Y. Temporal and spatial analyses of particulate matter (PM10 and PM2.5) and its relationship with meteorological parameters over an urban city in northeast China. Atmos. Res. 2017, 198, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Gui, H.; Du, P.; Yu, T.; Wang, J.; Lu, Y.; Liu, W. Identification of Long-Range Transport Pathways and Potential Sources of PM2.5 and PM10 in Beijing from 2014 to 2015. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 56, 214–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, R.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Cao, J.; Zhang, Y. Control of PM2.5 in Guangzhou during the 16th Asian Games period: Implication for hazy weather prevention. Sci. Total. Environ. 2015, 508, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Yang, F.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yao, X.; Chan, C.K.; Cadle, S.; Chan, T.; Mulawa, P. The Characteristics of PM2.5 in Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 4959–4970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Cheng, S.; Chen, D.; Guo, X.; Chen, S.; Li, X.; Xing, X.; Wang, H. Trends of PM2.5 and Chemical Composition in Beijing, 2000–2015. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2017, 17, 412–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, A.J.; Fu, C.B.; Yang, X.Q.; Sun, J.N.; Zheng, L.F.; Xie, Y.N.; Herrmann, E.; Nie, W.; Petäjä, T.; Kerminen, V.-M.; et al. Ozone and fine particle in the western Yangtze River Delta: An overview of 1 yr data at the SORPES station. Atmospheric Meas. Tech. 2013, 13, 5813–5830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Hu, J.; Ying, Q.; Hu, X.-M. Relationships between meteorological parameters and criteria air pollutants in three megacities in China. Environ. Res. 2015, 140, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Wu, D.; Su, B.; Bilal, M.; Li, Y.; Li, B.L. Spatio-Temporal Characteristics of PM2.5, PM10, and Aod over Canal Head Taocha Station, Henan Province. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, D.; Wang, H.; Tan, Y.; Yin, Y.; Wu, Z.; Guo, S.; Shen, L.; Zhu, B.; Wang, J.; Kong, X. Optical Properties of Aerosols and Chemical Composition Apportionment under Different Pollution Levels in Wuhan during January 2018. Atmosphere 2019, 11, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Mhawish, A.; Nichol, J.E.; Qiu, Z.; Nazeer, M.; Ali, M.A.; de Leeuw, G.; Levy, R.C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; et al. Air Pollution Scenario over Pakistan: Characterization and Ranking of Extremely Polluted Cities Using Long-Term Concentrations of Aerosols and Trace Gases. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 264, 112617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Wang, H.; Yu, Y.; Gao, S.; Feng, J.; Gao, S.; Wang, L. Chemical Characterization of Water-Soluble Components of PM10 and PM2.5 Atmospheric Aerosols in Five Locations of Nanjing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 2893–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, Z.; Tan, Y.; Xu, S.; Kong, S.; Wu, G.; Wu, X.; Li, H. Comparison of Inorganic Chemical Compositions of Atmospheric Tsp, PM10 and PM2.5 in Northern and Southern Chinese Coastal Cities. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 55, 339–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Q.; Zhao, H.; Wang, L.; Tao, R. Variations in PM10, PM2.5 and PM1.0 in an Urban Area of the Sichuan Basin and Their Relation to Meteorological Factors. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 150–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, K.F.; Lee, S.C.; Chan, C.K.; Jimmy, C.Y.; Chow, J.C.; Yao, X.H. Characterization of Chemical Species in PM2.5 and PM10 Aerosols in Hong Kong. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Tan, M.; Li, Y.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Shan, Z.; Zhang, G.; Li, Y. Characteristics of Trace Elements and Lead Isotope Ratios in PM2.5 from Four Sites in Shanghai. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 156, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Zhang, M.; Han, G.; Ma, X.; Zhu, Z. An Investigation of Aerosol Scattering and Absorption Properties in Wuhan, Central China. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 503–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, M.; Wang, Y.; Tang, G.; Song, T.; Zhou, P.; Liu, Z.; Hu, B.; Ji, D.; Wang, L.; et al. Rapid formation of intense haze episodes via aerosol–boundary layer feedback in Beijing. Atmospheric Meas. Tech. 2020, 20, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Tao, J.; Zhang, R.; Cheng, T.; Leng, C.; Chen, J.; Huang, G.; Li, X.; Zhu, Z. Measurements of surface aerosol optical properties in winter of Shanghai. Atmospheric Res. 2012, 109–110, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreae, M.O.; Schmid, O.; Yang, H.; Chand, D.; Yu, J.Z.; Zeng, L.-M.; Zhang, Y.-H. Optical properties and chemical composition of the atmospheric aerosol in urban Guangzhou, China. Atmospheric Environ. 2008, 42, 6335–6350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameters | Unit | Accuracy | Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| PM2.5 | (μg/m³) | ≤1 | 0~1000 |
| PM10 | (μg/m³) | ≤1 | 0~1000 |
| TSP | (μg/m³) | ≤1 | 0~1000 |
| WS | (m·s−1) | ±0.3 | 0~30 |
| T | (°C) | ±0.3 | −30–70 |
| RH | (%) | ±5 | 0~100 |
| Parameters | Unit | Mean | SD | Number | Skewness | Percentiles | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10% | 25% | 50% | 75% | 90% | ||||||
| PM2.5 | (μg/m³) | 106.47 | 57.35 | 2888 | 1.10 | 39.60 | 69.14 | 96.85 | 101.90 | 131.77 |
| PM10 | (μg/m³) | 137.32 | 74.20 | 2888 | 1.09 | 50.76 | 89.06 | 125.27 | 170.23 | 236.35 |
| TSP | (μg/m³) | 283.40 | 131.28 | 2888 | 1.09 | 130.27 | 198.04 | 262.10 | 341.61 | 458.63 |
| WS | (m·s−1) | 0.61 | 0.53 | 2888 | 2.34 | 0.18 | 0.26 | 0.44 | 0.75 | 1.30 |
| T | (°C) | 5.59 | 5.04 | 2888 | 0.98 | 0.38 | 2.21 | 4.18 | 8.30 | 13.98 |
| RH | (%) | 73.31 | 16.54 | 2888 | −0.32 | 51.62 | 61.96 | 73.41 | 86.56 | 93.97 |
| SITE | TYPE | PERIOD | SEASON | PM2.5 (μg/m3) | PM10 (μg/m3) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NYNU (China) | urban | November 2021–March 2022 | Winter | 106 ± 57 | 137 ± 74 | This work |
| Taocha (China) | rural | October 2018–September 2019 | Annual | 51 ± 22 | 57 ± 25 | [33] |
| Wuhan (China) | urban | 18–21 January 2018 | Winter | 170 | —— | [34] |
| Shenyang (China) | urban | 2014–2015 | Annual | 72 | 118 | [26] |
| Nanjing (China) | urban | 2001 | Annual | 222 | 316 | [36] |
| Chengdu (China) | urban | 2009–2011 | Annual | 60 | 71 | [38] |
| Hongkong (China) | urban | January 2000–December 2001 | Winter | 50.2 | 78.9 | [39] |
| Shanghai (China) | urban | January 2004–December 2005 | Winter | 68 | 118 | [40] |
| Beijing (China) | urban | September 2017–August 2019 | Annual | 108 | 172 | [32] |
| Guangzhou (China) | urban | March 2013–February 2014 | Annual | 52 | 73 | [32] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, M.; Chen, S.; Zhang, X.; Guo, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, F.; Chen, J.; Qi, P.; Lu, F.; Chen, M.; et al. Characters of Particulate Matter and Their Relationship with Meteorological Factors during Winter Nanyang 2021–2022. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14010137
Zhang M, Chen S, Zhang X, Guo S, Wang Y, Zhao F, Chen J, Qi P, Lu F, Chen M, et al. Characters of Particulate Matter and Their Relationship with Meteorological Factors during Winter Nanyang 2021–2022. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(1):137. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14010137
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Miao, Shiyong Chen, Xingang Zhang, Si Guo, Yunuo Wang, Feifei Zhao, Jinhan Chen, Pengcheng Qi, Fengxian Lu, Mingchun Chen, and et al. 2023. "Characters of Particulate Matter and Their Relationship with Meteorological Factors during Winter Nanyang 2021–2022" Atmosphere 14, no. 1: 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14010137
APA StyleZhang, M., Chen, S., Zhang, X., Guo, S., Wang, Y., Zhao, F., Chen, J., Qi, P., Lu, F., Chen, M., & Bilal, M. (2023). Characters of Particulate Matter and Their Relationship with Meteorological Factors during Winter Nanyang 2021–2022. Atmosphere, 14(1), 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14010137







