On Applying Large-Scale Correction to Limited-Area Numerical Weather Prediction Models
Abstract
:1. Introduction
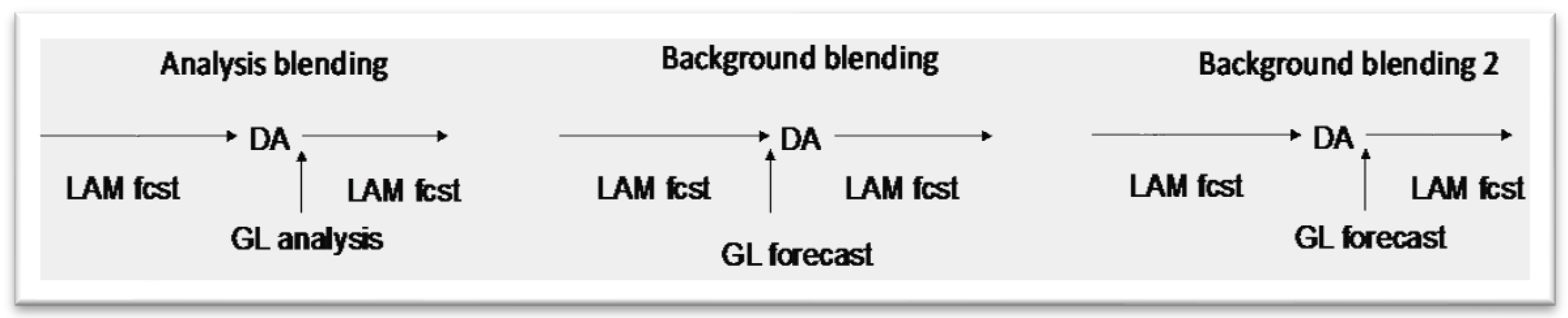
2. Blending Approaches
2.1. Analysis Blending
2.2. Background Blending
2.3. Forecast Blending
3. Simulation Details
4. Results and Discussion
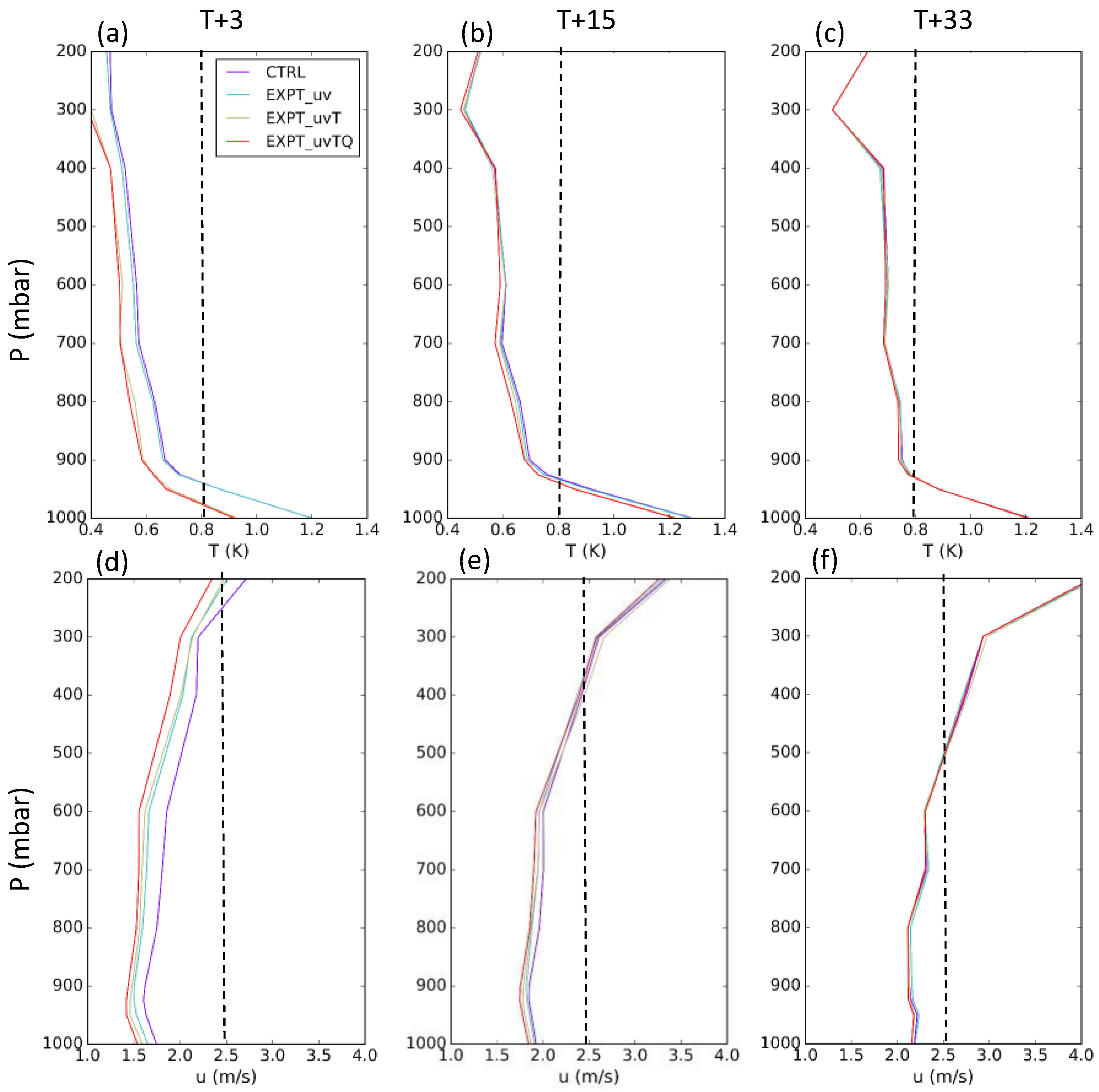
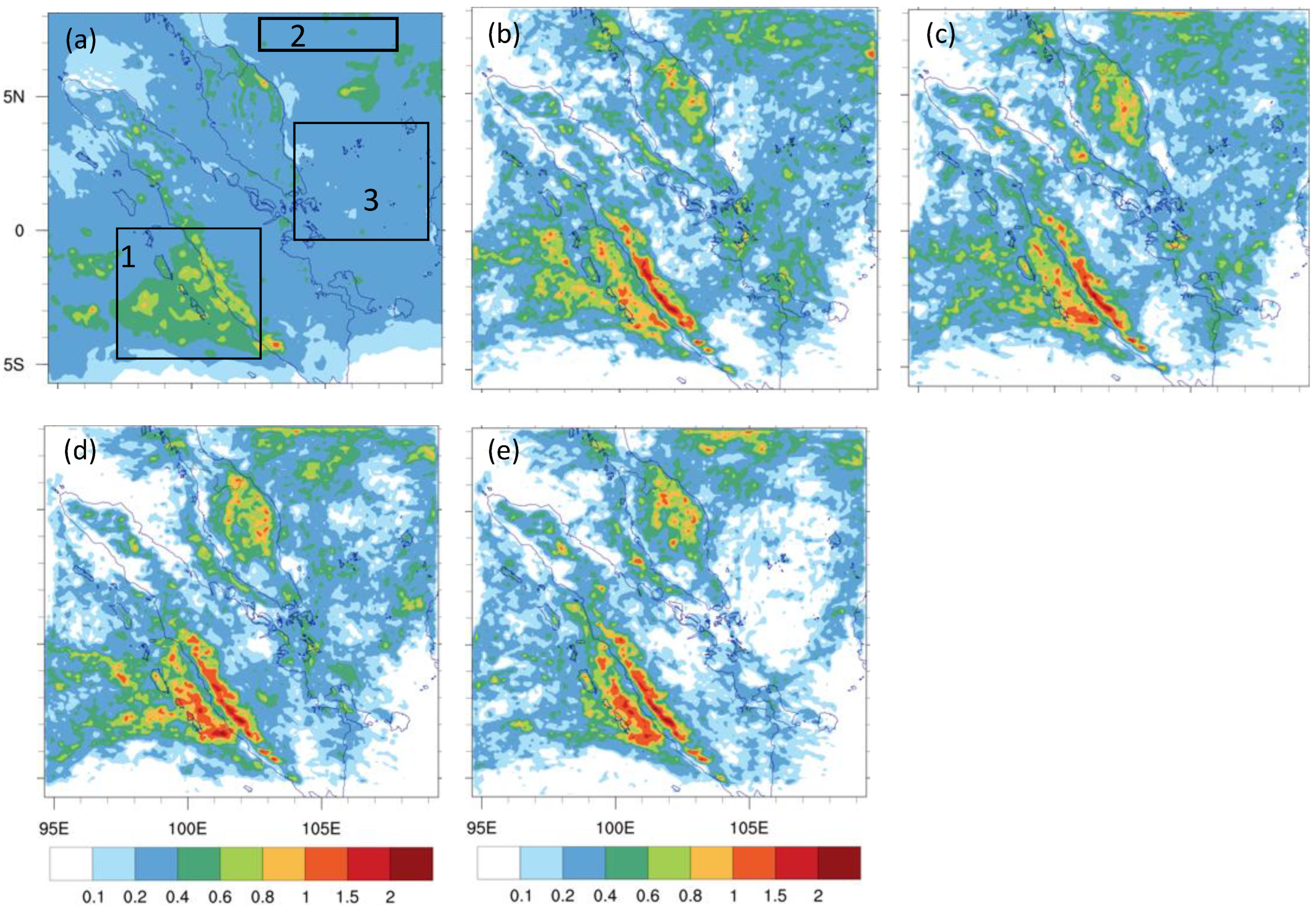
4.1. Blending Effectiveness
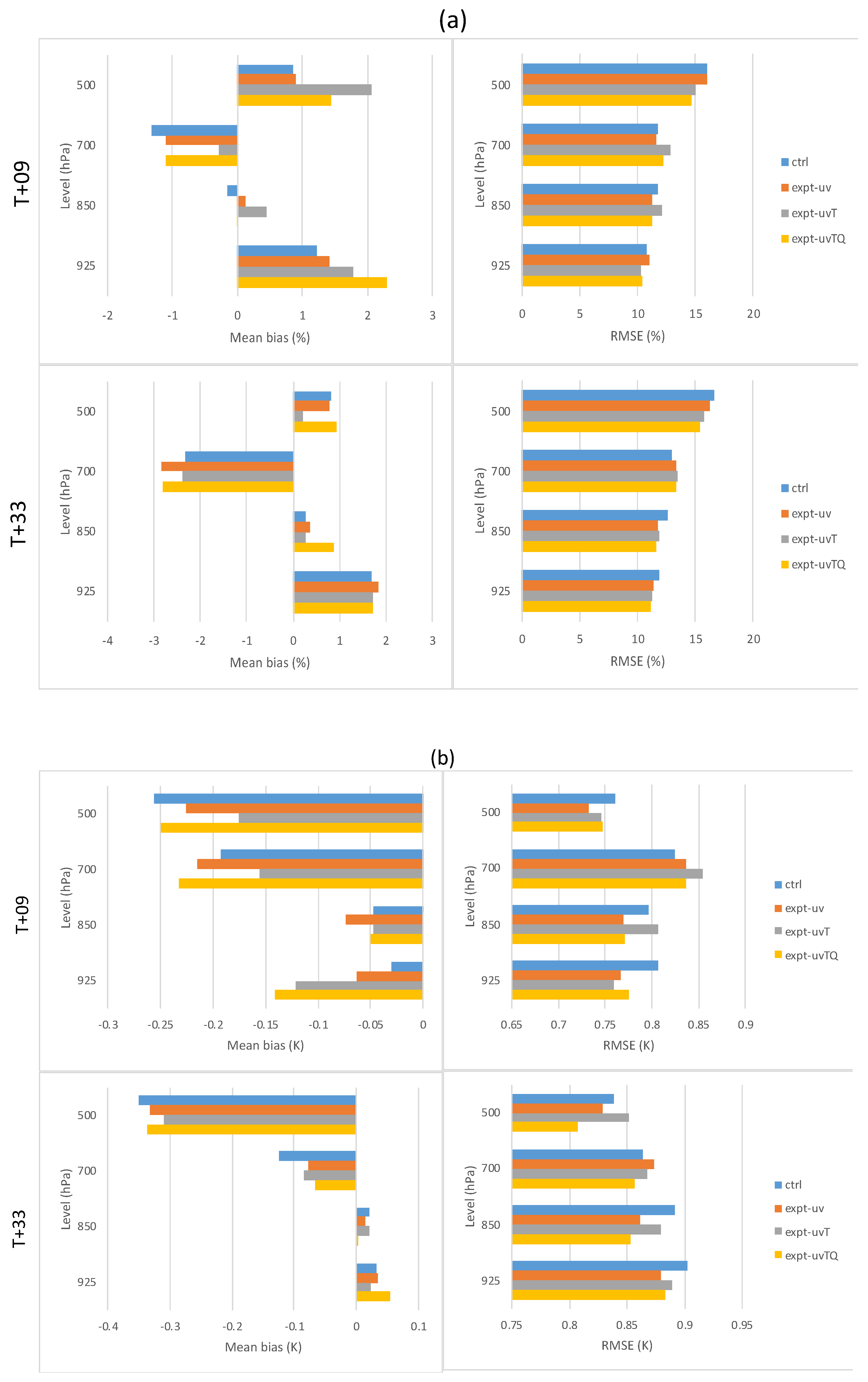
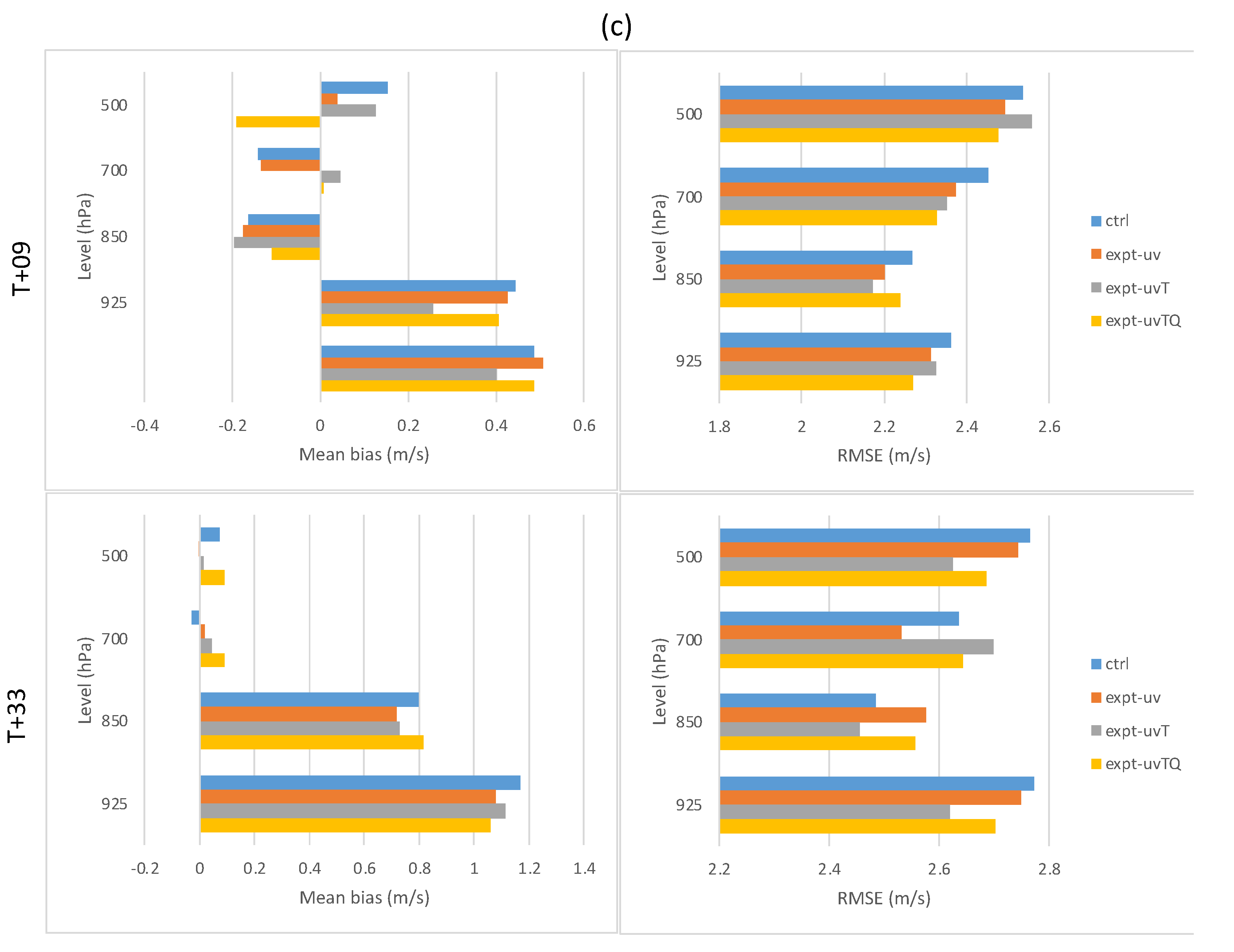
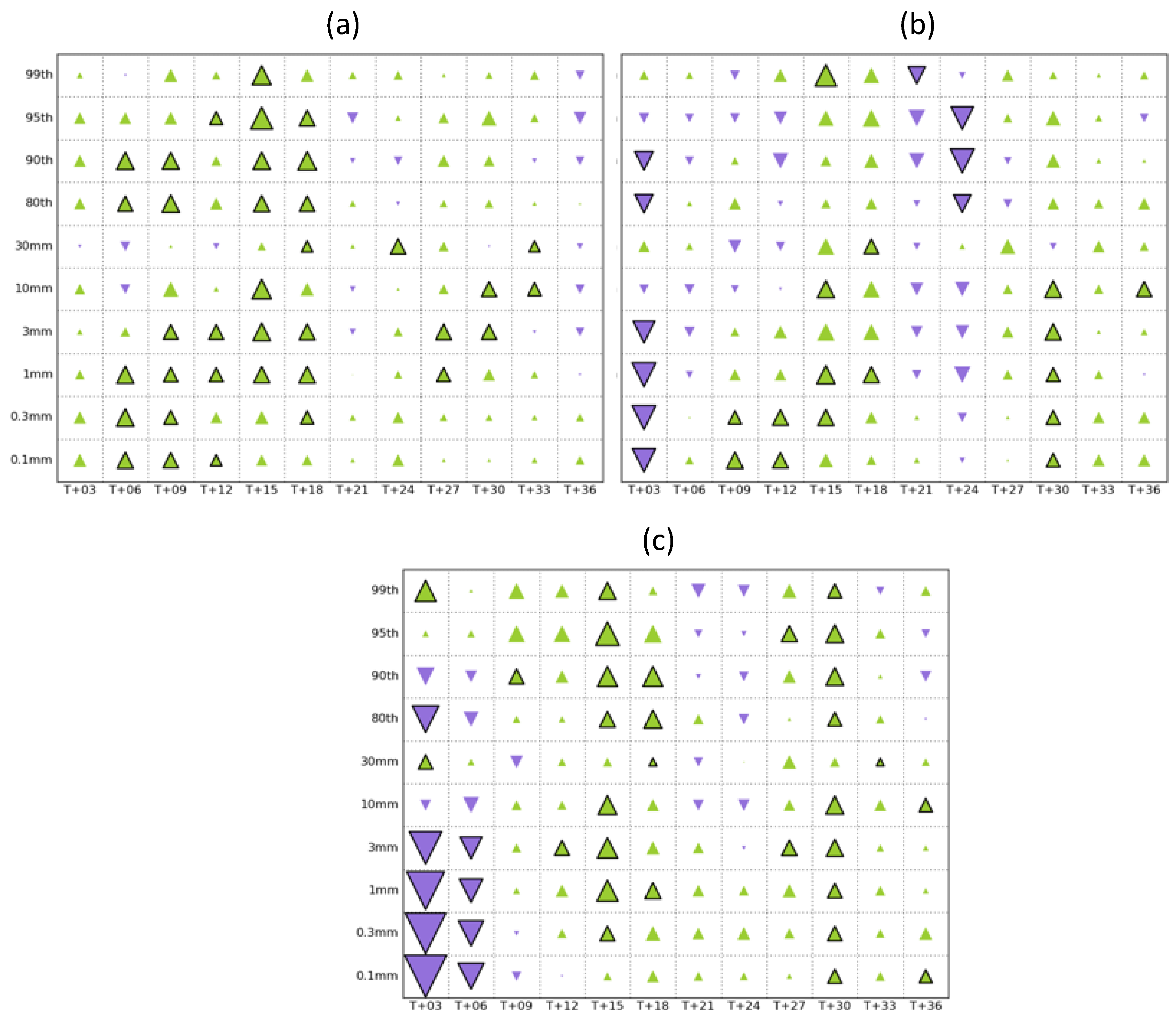
4.2. Forecast Verification
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Warner, T.T.; Peterson, R.A.; Treadon, R.E. A Tutorial on Lateral Boundary Conditions as a Basic and Potentially Serious Limitation to Regional Numerical Weather Prediction. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1997, 78, 2599–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- von Storch, H.; Langenberg, H.; Feser, F. A Spectral Nudging Technique for Dynamical Downscaling Purposes. Mon. Weather Rev. 2000, 128, 3664–3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidard, V.; Fischer, C. Introducing the coupling information in a limited-area variational assimilation. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2008, 134, 723–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalnay, E. Atmospheric Modeling, Data Assimilation and Predictability; Cambridge University Press (CUP): Cambridge, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X. Background blending using a spatial filter. HIRLAM Newsl. 2005, 49, 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Trier, S.B.; Xiao, Q.; Weisman, M.L.; Wang, H.; Ying, Z.; Xu, M.; Zhang, Y. Sensitivity of 0–12-h Warm-Season Precipitation Forecasts over the Central United States to Model Initialization. Weather Forecast. 2012, 27, 832–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, P.; Huang, X.-Y. Initialization of the HIRLAM Model Using a Digital Filter. Mon. Weather Rev. 1992, 120, 1019–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brožkovà, R.; Klarić, D.; Ivatek-Šahdan, S.; Geleyn, J.-F.; Casse, V.; Širokà, M.; Radnoti, G.; Janoušek, M.; Stadlbacher, K.; Seidl, H. DFI Blending: An Alternative Tool for Preparation of the Initial Conditions for LAM; WMO CAS/JSC WGNE Report; Ritchie, H., Ed.; World Meteorological Organization-Publications-Wmo Td: Geneva, Switzerland, 2001; Volume 31, Chapter 1.7–1.8. [Google Scholar]
- Short, C.J.; Petch, J. Reducing the spin-up of a regional NWP system without data assimilation. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2022, 148, 1623–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlgren, P.; Gustafsson, N. Assimilating host model information into a limited area model. Tellus A Dyn. Meteorol. Oceanogr. 2012, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vendrasco, E.P.; Sun, J.; Herdies, D.L.; de Angelis, C.F. Constraining a 3DVAR Radar Data Assimilation System with Large-Scale Analysis to Improve Short-Range Precipitation Forecasts. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2016, 55, 673–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Huang, X.-Y.; Xu, D.; Liu, J. A scale-dependent blending scheme for WRFDA: Impact on regional weather forecasting. Geosci. Model Dev. 2014, 7, 1819–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, X. Analysis blending using a spatial filter in grid-point model coupling. HIRLAM Newsl. 2005, 48, 49–55. [Google Scholar]
- Hsiao, L.-F.; Huang, X.-Y.; Kuo, Y.-H.; Chen, D.-S.; Wang, H.; Tsai, C.-C.; Yeh, T.-C.; Hong, J.-S.; Fong, C.-T.; Lee, C.-S. Blending of Global and Regional Analyses with a Spatial Filter: Application to Typhoon Prediction over the Western North Pacific Ocean. Weather Forecast. 2015, 30, 754–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y. A Dynamic Blending Scheme to Mitigate Large-Scale Bias in Regional Models. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clayton, A. UK Met Office, Personal Communications.
- Ide, K.; Coutier, P.; Ghil, M.; Lorenc, A.C. Unified notation for data assimilation: Operational, sequential and variational. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 1997, 75, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.Y.; Barker, D.; Webster, S.; Dipankar, A.; Lock, A.; Mittermaier, M.; Sun, X.; North, R.; Darvell, R.; Boyd, D.; et al. SINGV–the Convective-Scale Numerical Weather Prediction System for Singapore. ASEAN J. Sci. Technol. Dev. 2019, 36, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dipankar, A.; Webster, S.; Sun, X.; Sanchez, C.; North, R.; Furtado, K.; Wilkinson, J.; Lock, A.; Vosper, S.; Huang, X.-Y.; et al. SINGV: A convective-scale weather forecast model for Singapore. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 4131–4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, M.; Allen, T.; Bain, C.; Boutle, I.; Edwards, J.; Finnenkoetter, A.; Franklin, C.; Hanley, K.; Lean, H.; Lock, A.; et al. The first Met Office Unified Model–JULES Regional Atmosphere and Land configuration, RAL1. Geosci. Model Dev. 2020, 13, 1999–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heng, B.C.P.; Tubbs, R.; Huang, X.-Y.; MacPherson, B.; Barker, D.; Boyd, D.F.A.; Kelly, G.; North, R.; Stewart, L.; Webster, S.; et al. SINGV-DA: A data assimilation system for convective-scale numerical weather prediction over Singapore. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1923–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raymond, W.H. High-Order Low-Pass Implicit Tangent Filters for Use in Finite Area Calculations. Mon. Weather Rev. 1988, 116, 2132–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, S.; Jun-Ichi, H.; Tauhid, Y.I.; Yamanaka, M.D.; Okamoto, N.; Murata, F.; Sakurai, N.; Hashiguchi, H.; Sribimawati, T. Diurnal Land–Sea Rainfall Peak Migration over Sumatera Island, Indonesian Maritime Continent, Observed by TRMM Satellite and Intensive Rawinsonde Soundings. Mon. Weather Rev. 2004, 132, 2021–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dipankar, A.; Webster, S.; Huang, X.-Y.; Doan, V.Q. Understanding Biases in Simulating the Diurnal Cycle of Convection over the Western Coast of Sumatra: Comparison with Pre-YMC Observation Campaign. Mon. Weather Rev. 2019, 147, 1615–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skofronick-Jackson, G.; Petersen, W.A.; Berg, W.; Kidd, C.; Stocker, E.F.; Kirschbaum, D.B.; Kakar, R.; Braun, S.; Huffman, G.J.; Iguchi, T.; et al. The Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Mission for Science and Society. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc. 2017, 98, 1679–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, N.M.; Lean, H.W. Scale-Selective Verification of Rainfall Accumulations from High-Resolution Forecasts. Mon. Weather Rev. 2008, 136, 78–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinton, G.E.; Shallice, T. Lesioning an attractor network: Investigations of acquired dyslexia. Psychol. Rev. 1991, 98, 74–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bremner, F.J.; Gotts, S.J.; Denham, D.L. Hinton diagrams: Viewing connection strengths in neural networks. Behav. Res. Methods Instruments Comput. 1994, 26, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilks, D.S. Statistical Methods in the Atmospheric Sciences, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 162–166. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.C.K.; Dipankar, A.; Huang, X.-Y. On the Sensitivity of the Simulated Diurnal Cycle of Precipitation to 3-Hourly Radiosonde Assimilation: A Case Study over the Western Maritime Continent. Mon. Weather Rev. 2021, 149, 3449–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Notations | Meaning | Notations | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| State vector | Analysis increment | ||
| Filtered (low-pass) state vector | Large-scale corrected analysis | ||
| Driving model state vector | Large-scale correction | ||
| Blended state vector | Kalman gain | ||
| Analysis vector | Observations | ||
| Background state vector | Observation operator | ||
| Δ | Grid size | B | Background error covariance matrix |
| Lc | Cut-off length scale for low-pass filter | ε | Filtering parameter (see Equation (13)) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dipankar, A.; Huang, X.-Y.; Heng, P. On Applying Large-Scale Correction to Limited-Area Numerical Weather Prediction Models. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1142. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13071142
Dipankar A, Huang X-Y, Heng P. On Applying Large-Scale Correction to Limited-Area Numerical Weather Prediction Models. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(7):1142. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13071142
Chicago/Turabian StyleDipankar, Anurag, Xiang-Yu Huang, and Peter Heng. 2022. "On Applying Large-Scale Correction to Limited-Area Numerical Weather Prediction Models" Atmosphere 13, no. 7: 1142. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13071142
APA StyleDipankar, A., Huang, X.-Y., & Heng, P. (2022). On Applying Large-Scale Correction to Limited-Area Numerical Weather Prediction Models. Atmosphere, 13(7), 1142. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13071142







