Haze Level Evaluation Using Dark and Bright Channel Prior Information
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Background
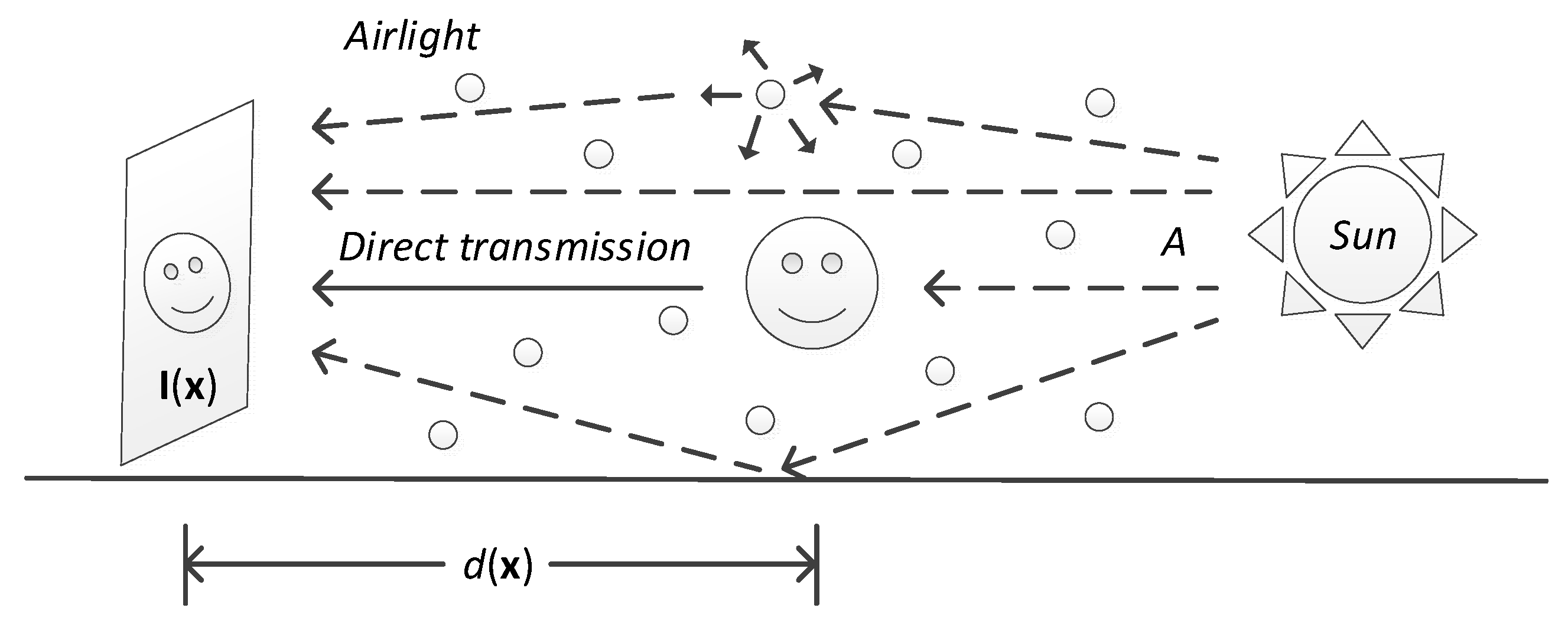
2.1. Physical Model
2.2. Dark Channel Prior
2.3. Bright Channel Prior
3. Methodology
3.1. Motivation
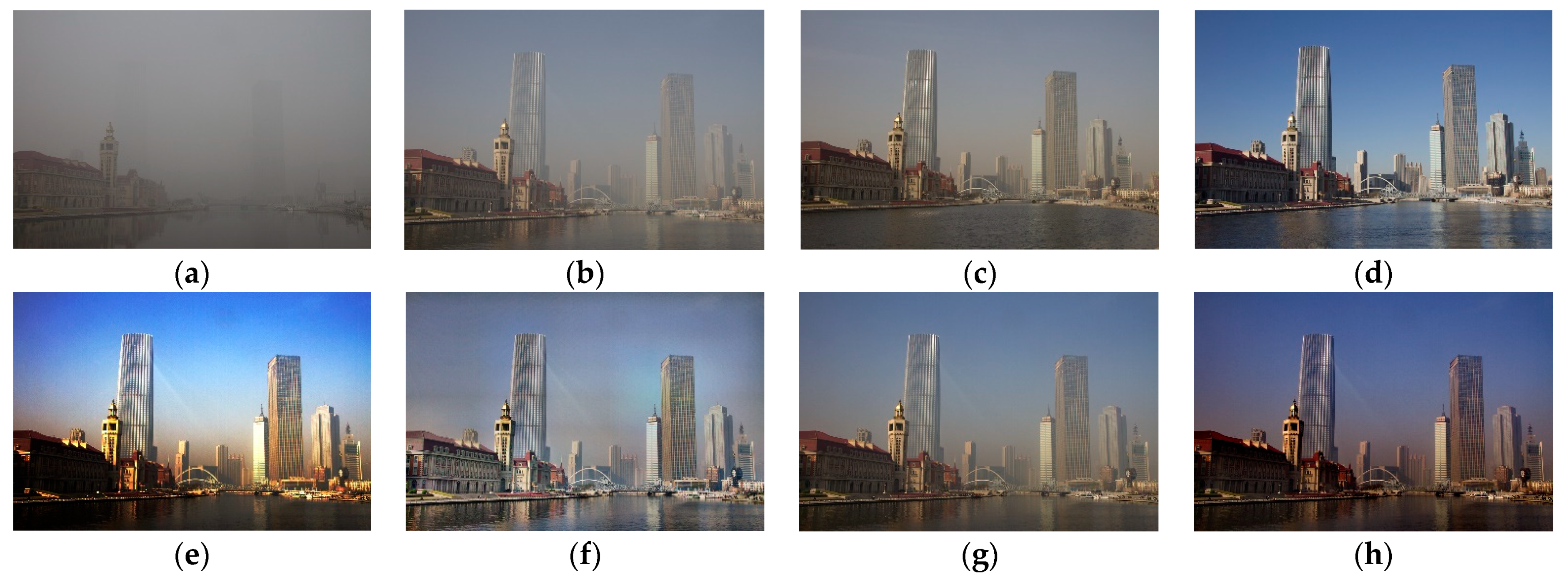
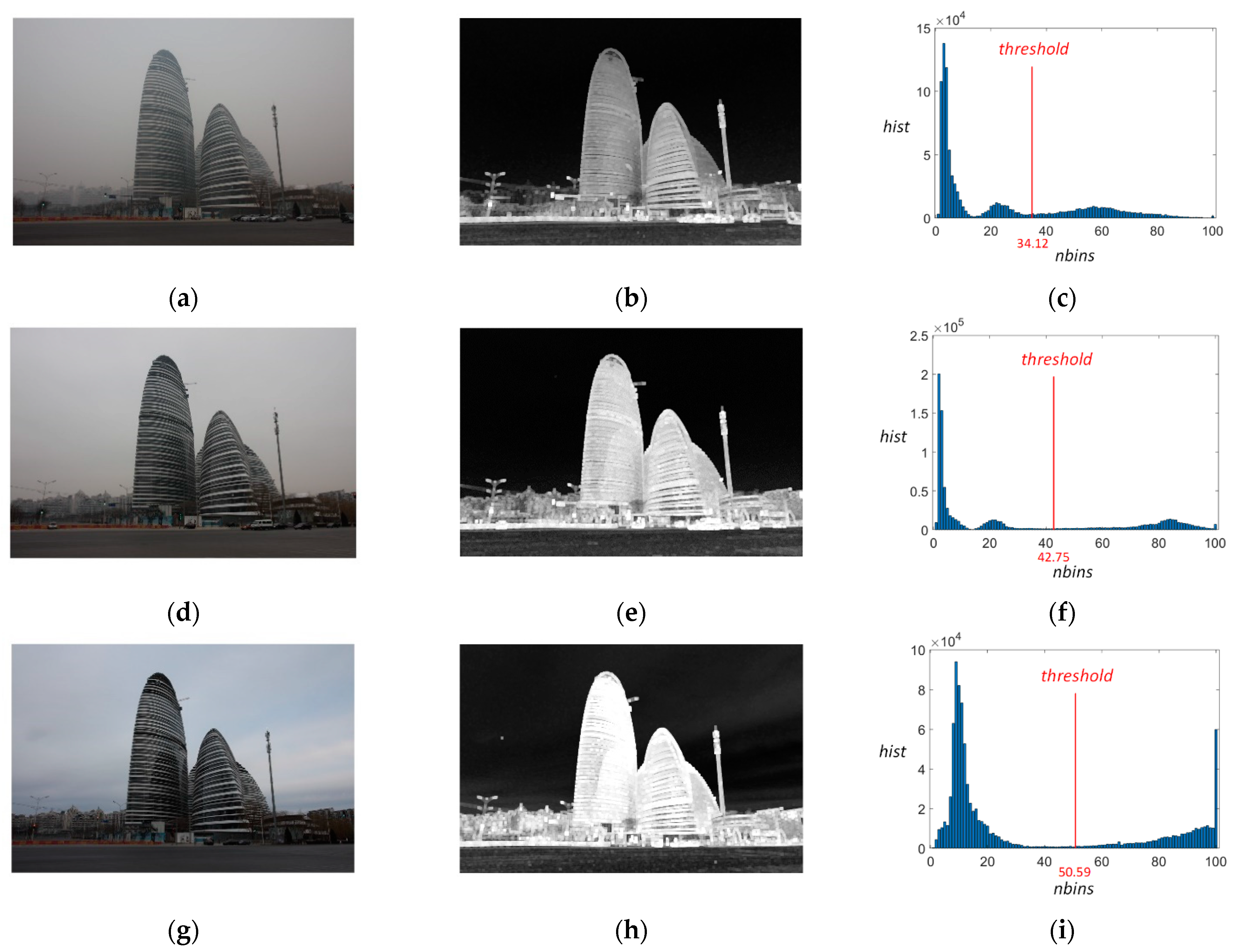
3.2. DBCP-I
3.3. DBCP-II
3.4. DBCP-III
4. Experimental Results and Discussion
4.1. Evaluation Index
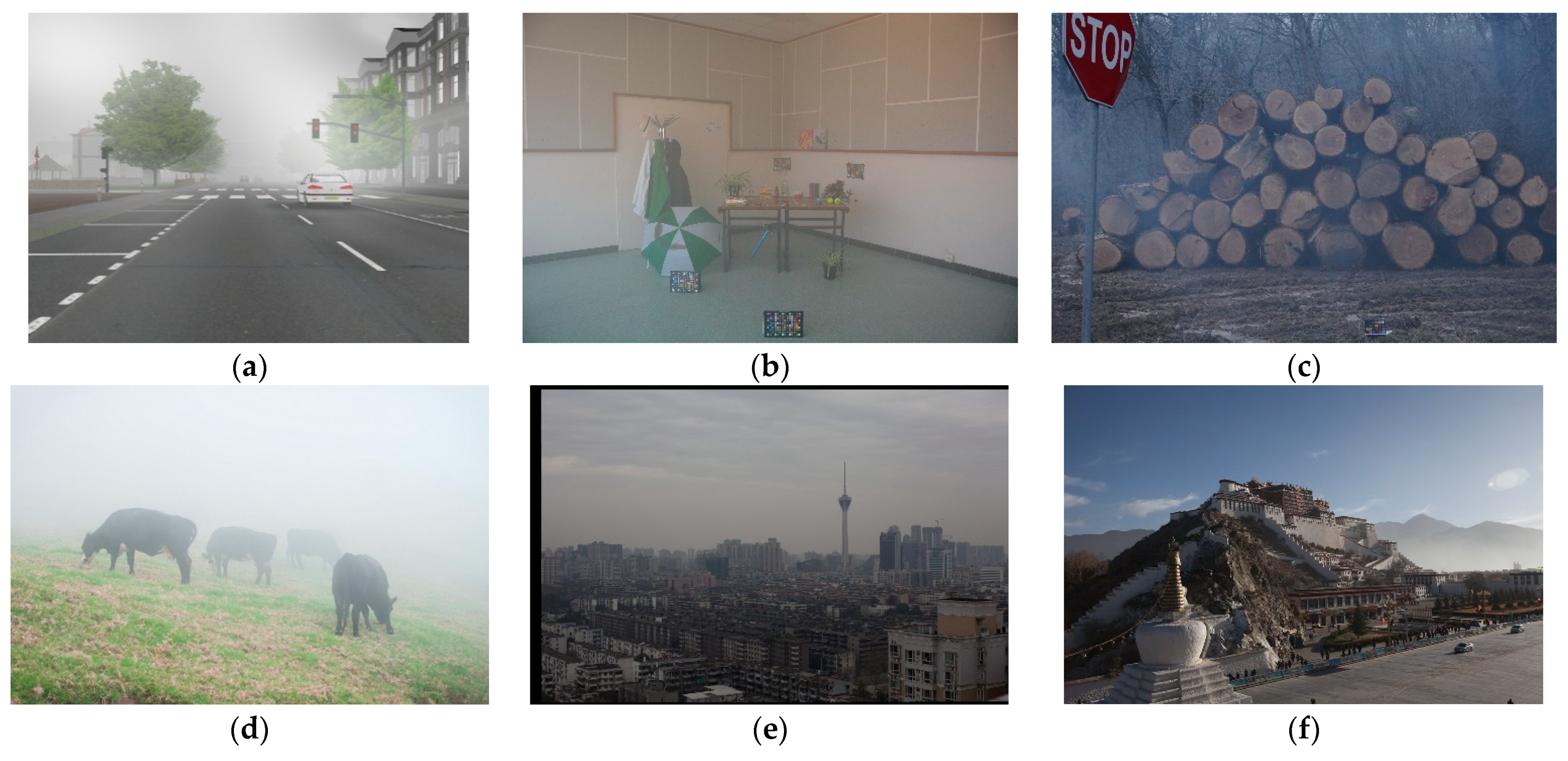
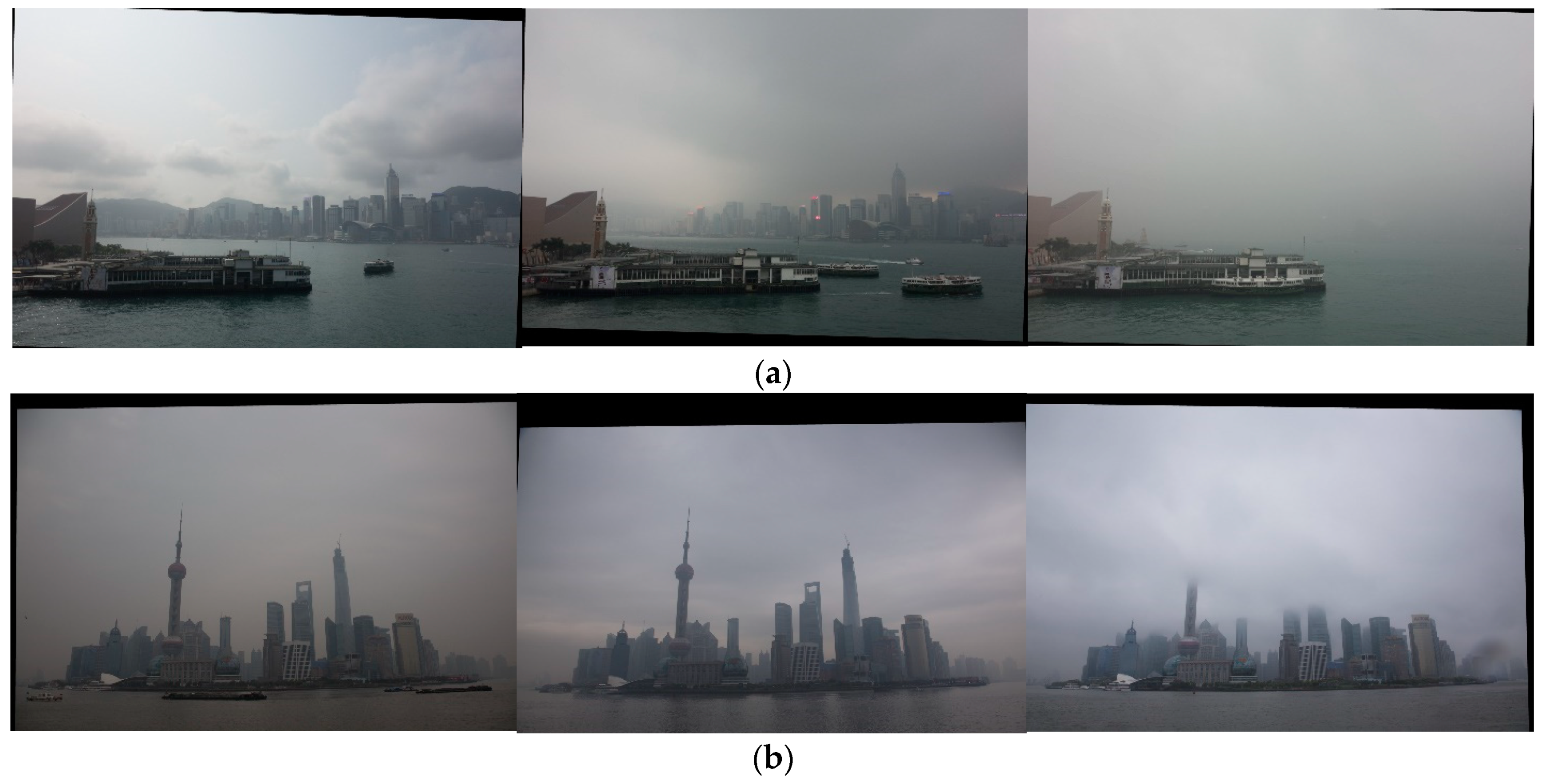
4.2. Datasets
4.3. Performance Comparison
4.3.1. Implementation Details
4.3.2. Experiment Results on RHID_AQI
4.3.3. Experiment Results on exBeDDE
4.4. Performance Analysis
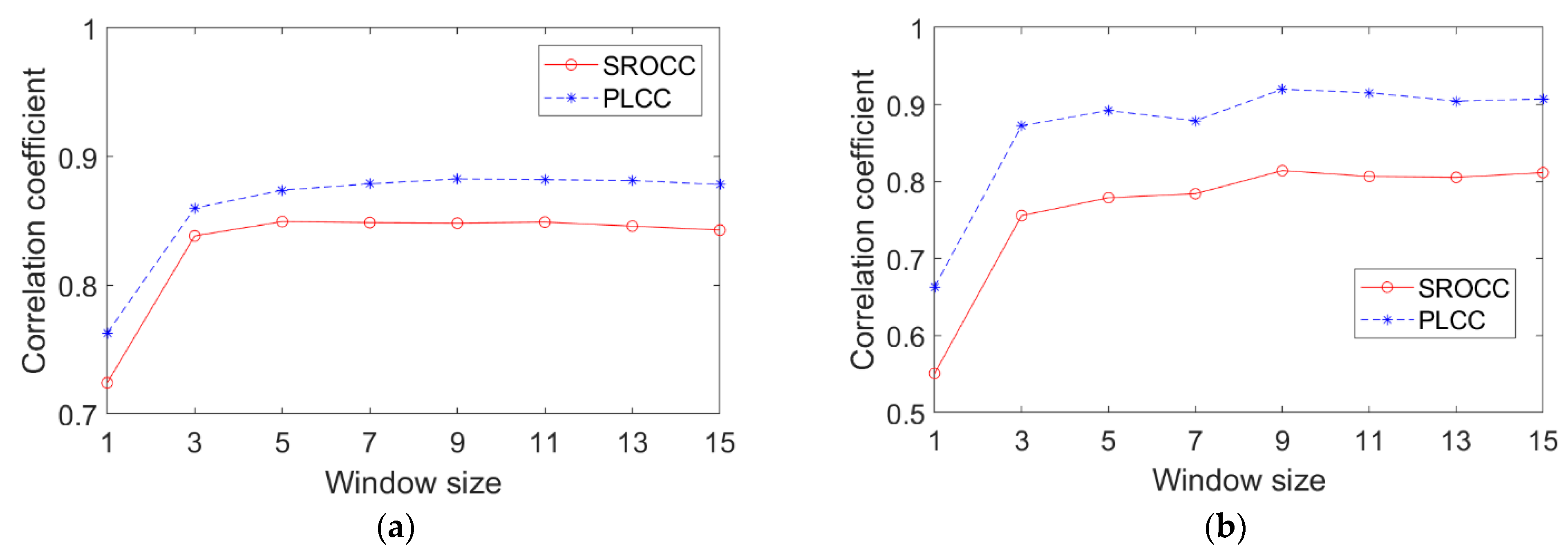
4.5. Effect of Window Size
4.6. Computation Cost
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, G.-H.; Yang, C.-L.; Po, L.-M.; Xie, S.-L. Edge-based structural similarity for image quality assessment. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics Speed and Signal Processing Proceedings, Toulouse, France, 14–19 May 2006; Volume 2, p. 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, G.-H.; Yang, C.-L.; Xie, S.-L. Gradient-based structural similarity for image quality assessment. In Proceedings of the 2006 International Conference on Image Processing, Atlanta, GA, USA, 8–11 October 2006; pp. 2929–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Mou, X. RFSIM: A feature based image quality assessment metric using Riesz transforms. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Hong Kong, China, 26–29 September 2010; pp. 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Mou, X.; Zhang, D. FSIM: A feature similarity index for image quality assessment. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2011, 20, 2378–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Sheikh, H.; Bovik, A. No-reference perceptual quality assessment of JPEG compressed images. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Image Processing, Rochester, NY, USA, 22–25 September 2002; Volume 1, pp. I-477–I-480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Simoncelli, E.P.; Bovik, A.C. Multiscale structural similarity for image quality assessment. In Proceedings of the Thrity-Seventh Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems & Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 9–12 November 2003; Volume 2, pp. 1398–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, J.; Li, Q.; Erlebacher, G. Hybrid no-reference natural image quality assessment of noisy, blurry, JPEG2000, and JPEG images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2011, 20, 2089–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, W.; Mou, X.; Zhang, L.; Bovik, A.; Feng, X. Blind image quality assessment using joint statistics of gradient magnitude and laplacian features. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2014, 23, 4850–4862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simoncelli, E.P. Statistical models for images: Compression, restoration and synthesis. In Proceedings of the Conference Record of the Thirty-First Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers (Cat. No.97CB36136), Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 2–5 November 1997; pp. 673–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoncelli, E.P. Modeling the joint statistics of images in the wavelet domain. In Proceedings of the International Society for Optical Engineering, Denver, CO, USA, 19–23 July 1999; Volume 3813, pp. 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoncelli, E.P.; Schwartz, O. Modeling surround suppression in V1 neurons with a statistically-derived normalization model. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 1999, 11, 153–159. [Google Scholar]
- Wainwright, M.J.; Simoncelli, E.P. Scale mixtures of gaussians and the statistics of natural images. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2000, 12, 855–861. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, K.; Liu, W.; Wang, Z. Perceptual evaluation of single image dehazing algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 27–30 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ancuti, C.; Codruta, A.; Vleeschouwer, C. D-HAZY: A dataset to evaluate quantitatively dehazing algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 25–28 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Mansouri, A.; Nouboud, F.; Chalifour, A.; Mammass, D.; Meunier, J.; Elmoataz, A. A color image database for haze model anddehazing methods evaluation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Image and Signal Processing, Trois-Rivieres, QC, Canada, 30 May–1 June 2016; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. Chapter 12. pp. 109–117. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Ren, W.; Fu, D.; Tao, D.; Feng, D.; Zeng, W.; Wang, Z. Benchmarking single-image dehazing and beyond. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 28, 492–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Ding, L.; Sharma, G. HazeRD: An outdoor scene dataset and benchmark for single image dehazing. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Beijing, China, 17–20 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Min, X.; Zhai, G.; Gu, K.; Yang, X.; Guan, X. Objective quality evaluation of dehazed images. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2018, 20, 2879–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, X.; Zhai, G.; Gu, K.; Zhu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Guo, G.; Yang, X.; Guan, X.; Zhang, W. Quality evaluation of image dehazing methods using synthetic hazy images. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2019, 21, 2319–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancuti, C.O.; Ancuti, C.; Timofte, R. NH-HAZE: An image dehazing benchmark with non-homogeneous hazy and haze-free images. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, L.; Huang, S.; Shen, Y.; Zhao, S. Dehazing evaluation: Real-world benchmark datasets, criteria, and baselines. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 6947–6962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Land, E.H. The Retinex. In Ciba Foundation Symposium-Colour Vision: Physiology and Experimental Psychology; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1965; pp. 217–227. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Sun, J.; Tang, X. Guided image filtering. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2013, 35, 1397–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, W.; Liu, S.; Zhang, H.; Pan, J.; Cao, X.; Yang, M.H. Single image dehazing via multi-scale convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8–16 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Fu, Y.; Yu, H. Haze image database and preliminary assessments. In Proceedings of the Fully3D Conference, Xi’an, China, 18–23 June 2017; pp. 825–830. [Google Scholar]
- Fattal, R. Single image dehazing. ACM Trans. Graph. 2008, 27, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Sun, J.; Tang, X. Single image haze removal using dark channel prior. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2011, 33, 2341–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narasimhan, S.; Nayar, S. Chromatic framework for vision in bad weather. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Hilton Head, SC, USA, 15 June 2000; Volume 1, pp. 598–605. [Google Scholar]
- Narasimhan, S.G.; Nayar, S.K. Vision and the atmosphere. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2002, 48, 233–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narasimhan, S.G.; Nayar, S.K. Contrast restoration of weather degraded images. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2003, 25, 713–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, R.T. Visibility in bad weather from a single image. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Anchorage, AK, USA, 23–28 June 2008; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Lin, Q.; Guo, W.; Ding, X.; Huang, Y. Single image de-haze under non-uniform illumination using bright channel prior. J. Theor. Appl. Inf. Technol. 2013, 48, 1843–1848. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.T.; Zhuo, S.J.; Tao, D.P.; Bu, J.J.; Li, N. Automatic local exposure correction using bright channel prior for under-exposed images. Signal Process. 2013, 93, 3227–3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Zhang, R.; Wu, Q.; Wu, Y. A new haze image database with detailed air quality information and a novel no-reference image quality assessment method for haze images. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Shanghai, China, 20–25 March 2016; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 1095–1099. [Google Scholar]
- Otsu, N. A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1979, 9, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- VQEG. Final Report from the Video Quality Experts Group on the Validation of Objective Models of Video Quality Assessment—Phase II. 2003. Available online: http://www.vqeg.org (accessed on 20 April 2022).
- Tarel, J.-P.; Hautiere, N.; Caraffa, L.; Cord, A.; Halmaoui, H.; Gruyer, D. Vision enhancement in homogeneous and heterogeneous fog. IEEE Intell. Transp. Syst. Mag. 2012, 4, 6–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Huang, J.; Luo, J. Using user generated online photos to estimate and monitor air pollution in major cities. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Internet Multimedia Computing and Service, Zhangjiajie, China, 19 August 2015; pp. 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ancuti, C.; Ancuti, C.O.; Timofte, R.; De Vleeschouwer, C. I-HAZE: A dehazing benchmark with real hazy and haze-free indoor images. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Advanced Concepts for Intelligent Vision Systems, Poitiers, France, 24–27 September 2018; Volume 11182, pp. 620–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ancuti, C.O.; Ancuti, C.; Timofte, R.; De Vleeschouwer, C. O-HAZE: A dehazing benchmark with real hazy and haze-free outdoor images. In Proceedings of the 31st Meeting of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 867–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ancuti, C.O.; Ancuti, C.; Sbert, M.; Timofte, R. Dense-haze: A benchmark for image dehazing with dense-haze and haze-free images. In Proceedings of the 26th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Taipei, Taiwan, 22–25 September 2019; pp. 1014–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ITU-T, Geneva, Switzerland: Methodology for the Subjective Assessment of the Quality of Television Pictures. Recommendation ITU-R BT.500-11. Available online: https://www.itu.int/rec/R-REC-BT.500 (accessed on 20 April 2022).
- CHsieh, C.-H.; Horng, S.-C.; Huang, Z.-J.; Zhao, Q. Objective haze removal assessment based on two-objective optimization. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 8th International Conference on Awareness Science and Technology, Taichung, Taiwan, 8–10 November 2017; pp. 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wen, S.; Ma, J.; Keung, L.H.; Wang, H. Image defogging based on combination of image bright and dark channels. Guangxue Xuebao (Acta Opt. Sin.) 2018, 38, 1115004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, L.K.; You, J.; Bovik, A. Referenceless prediction of perceptual fog density and perceptual image defogging. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2015, 24, 3888–3901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, W.; Zhang, L.; Mou, X. Learning without human scores for blind image quality assessment. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013; pp. 995–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mittal, A.; Soundararajan, R.; Bovik, A. Making a ‘completely blind’ image quality analyzer. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2013, 20, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Li, H. A highly efficient method for blind image quality assessment. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 27–30 September 2015; pp. 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Bovik, A. A feature-enriched completely blind image quality evaluator. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2015, 24, 2579–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, J.; Ye, P.; Li, Q.; Du, H.; Liu, Y.; Doermann, D.S. Blind image quality assessment based on high order statistics aggregation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2016, 25, 4444–4457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, K.; Liu, W.; Liu, T.; Wang, Z.; Tao, D. dipIQ: Blind image quality assessment by learning-to-rank discriminable image pairs. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 26, 3951–3964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Min, X.; Ma, K.; Guangtao, Z.; Zhai, G.; Wang, Z.; Lin, W. Unified blind quality assessment of compressed natural, graphic, and screen content images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 26, 5462–5474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, K.; Lin, W.; Zhai, G.; Yang, X.; Zhang, W.; Chen, C.W. No-reference quality metric of contrast-distorted images based on information maximization. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2017, 47, 4559–4565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, X.; Gu, K.; Zhai, G.; Liu, J.; Yang, X.; Chen, C.W. Blind quality assessment based on pseudo-reference image. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2018, 20, 2049–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, X.; Zhai, G.; Gu, K.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X. Blind image quality estimation via distortion aggravation. IEEE Trans. Broadcast. 2018, 64, 508–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, K.; Tao, D.; Qiao, J.-F.; Lin, W. Learning a no-reference quality assessment model of enhanced images with big data. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2018, 29, 1301–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, K.; Liu, W.; Zhang, K.; Duanmu, Z.; Wangmeng, Z.; Zuo, W. End-to-end blind image quality assessment using deep neural networks. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 27, 1202–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, L.; Ye, P.; Li, Y.; Doermann, D. Convolutional neural networks for no-reference image quality assessment. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 1733–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bosse, S.; Maniry, D.; Muller, K.-R.; Wiegand, T.; Samek, W. Deep neural networks for no-reference and full-reference image quality assessment. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 27, 206–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Van De Weijer, J.; Bagdanov, A.D. RankIQA: Learning from rankings for no-reference image quality assessment. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 1040–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| IQA Model | SROCC | PCC |
|---|---|---|
| [35] | 0.71 | 0.79 |
| [39] | 0.21 | 0.49 |
| [33] | 0.71 | 0.81 |
| [44] | 0.24 | 0.49 |
| [45] | 0.09 | 0.17 |
| [45] | 0.40 | 0.46 |
| [45] | 0.65 | 0.70 |
| [46] | 0.77 | 0.82 |
| QAC [47] | 0.31 | 0.72 |
| NIQE [48] | 0.48 | 0.69 |
| LPSI [49] | 0.35 | 0.57 |
| IL-NIQE [50] | 0.52 | 0.64 |
| HOSA [51] | 0.42 | 0.58 |
| dipIQ [52] | 0.10 | 0.51 |
| UCA [53] | 0.04 | 0.36 |
| NIQMC [54] | 0.67 | 0.76 |
| BPRI(p) [55] | 0.33 | 0.53 |
| BPRI(c) [55] | 0.30 | 0.49 |
| BMPRI [56] | 0.07 | 0.53 |
| BIQME [57] | 0.82 | 0.84 |
| MEON [58] | 0.30 | 0.57 |
| CNN [59] | 0.87 | 0.85 |
| DIQaM-NR [60] | 0.90 | 0.93 |
| DBCP-I | 0.86 | 0.88 |
| DBCP-II | 0.93 | 0.93 |
| DBCP-III | 0.90 | 0.92 |
| IQA Model | Beijing | Hangzhou | Kunming | Lasa | Shijiazhuang | Taiyuan | Tianjin | Wuhan | Hit Count |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [35] | 0.85 | 0.88 | 0.53 | 0.44 | 0.41 | 0.15 | 0.77 | 0.78 | 0 |
| [39] | 0.72 | 0.37 | 0.55 | 0.54 | 0.43 | 0.26 | 0.84 | 0.16 | 0 |
| [33] | 0.96 | 0.86 | 0.62 | 0.41 | 0.70 | 0.51 | 0.98 | 0.90 | 2 |
| [44] | 0.72 | 0.43 | 0.56 | 0.54 | 0.44 | 0.26 | 0.86 | 0.20 | 0 |
| [45] | 0.50 | 0.25 | 0.42 | 0.45 | 0.28 | 0.36 | 0.59 | 0.28 | 0 |
| [45] | 0.02 | 0.57 | 0.37 | 0.18 | 0.69 | 0.22 | 0.29 | 0.66 | 0 |
| [45] | 0.62 | 0.30 | 0.49 | 0.03 | 0.49 | 0.03 | 0.48 | 0.38 | 0 |
| [46] | 0.96 | 0.85 | 0.73 | 0.59 | 0.61 | 0.18 | 0.94 | 0.91 | 2 |
| QAC [47] | 0.48 | 0.27 | 0.45 | 0.09 | 0.41 | 0.38 | 0.79 | 0.76 | 0 |
| NIQE [48] | 0.71 | 0.20 | 0.01 | 0.06 | 0.60 | 0.25 | 0.76 | 0.24 | 0 |
| LPSI [49] | 0.03 | 0.74 | 0.28 | 0.26 | 0.27 | 0.37 | 0.33 | 0.73 | 0 |
| IL-NIQE [50] | 0.40 | 0.43 | 0.32 | 0.16 | 0.70 | 0.58 | 0.81 | 0.50 | 0 |
| HOSA [51] | 0.34 | 0.51 | 0.17 | 0.21 | 0.49 | 0.24 | 0.69 | 0.20 | 0 |
| dipIQ [52] | 0.68 | 0.28 | 0.17 | 0.07 | 0.62 | 0.31 | 0.02 | 0.36 | 0 |
| UCA [53] | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.08 | 0.00 | 0.10 | 0.11 | 0.08 | 0.26 | 0 |
| NIQMC [54] | 0.78 | 0.35 | 0.37 | 0.06 | 0.55 | 0.32 | 0.76 | 0.54 | 0 |
| BPRI(p) [55] | 0.74 | 0.33 | 0.24 | 0.22 | 0.62 | 0.27 | 0.87 | 0.53 | 0 |
| BPRI(c) [55] | 0.40 | 0.33 | 0.12 | 0.21 | 0.69 | 0.27 | 0.80 | 0.44 | 0 |
| BMPRI [56] | 0.91 | 0.67 | 0.28 | 0.41 | 0.54 | 0.12 | 0.02 | 0.47 | 0 |
| BIQME [57] | 0.81 | 0.58 | 0.72 | 0.18 | 0.49 | 0.10 | 0.74 | 0.52 | 0 |
| MEON [58] | 0.64 | 0.36 | 0.45 | 0.38 | 0.71 | 0.06 | 0.76 | 0.45 | 0 |
| CNN [59] | 0.92 | 0.72 | 0.83 | 0.73 | 0.69 | 0.87 | 0.96 | 0.78 | 3 |
| DIQaM-NR [60] | 0.91 | 0.89 | 0.85 | 0.76 | 0.79 | 0.79 | 0.88 | 0.79 | 5 |
| DBCP-I | 0.91 | 0.84 | 0.82 | 0.84 | 0.77 | 0.21 | 0.88 | 0.70 | 2 |
| DBCP-II | 0.97 | 0.93 | 0.82 | 0.77 | 0.71 | 0.05 | 0.92 | 0.85 | 3 |
| DBCP-III | 0.98 | 0.91 | 0.84 | 0.64 | 0.74 | 0.74 | 0.95 | 0.94 | 7 |
| IQA Model | Beijing | Changsha | Chengdu | Hangzhou | Hefei | Hongkong | Lanzhou |
| [35] | 0.39 | 0.33 | 0.96 | 0.55 | 0.90 | 0.69 | 0.58 |
| [39] | 0.50 | 0.05 | 0.89 | 0.08 | 0.22 | 0.05 | 0.16 |
| [33] | 0.96 | 0.48 | 0.99 | 0.91 | 0.75 | 0.40 | 0.83 |
| [44] | 0.51 | 0.05 | 0.89 | 0.05 | 0.33 | 0.05 | 0.11 |
| [45] | 0.28 | 0.05 | 0.71 | 0.35 | 0.65 | 0.12 | 0.11 |
| [45] | 0.43 | 0.33 | 0.84 | 0.45 | 0.63 | 0.69 | 0.05 |
| [45] | 0.17 | 0.33 | 0.82 | 0.17 | 0.88 | 0.61 | 0.24 |
| [46] | 0.97 | 0.07 | 0.98 | 0.79 | 0.72 | 0.35 | 0.89 |
| QAC [47] | 0.20 | 0.36 | 0.45 | 0.68 | 0.62 | 0.75 | 0.67 |
| NIQE [48] | 0.44 | 0.12 | 0.86 | 0.63 | 0.85 | 0.93 | 0.61 |
| LPSI [49] | 0.53 | 0.43 | 0.69 | 0.88 | 0.02 | 0.85 | 0.37 |
| IL-NIQE [50] | 0.57 | 0.86 | 0.77 | 0.71 | 0.63 | 0.79 | 0.65 |
| HOSA [51] | 0.50 | 0.14 | 0.85 | 0.71 | 0.13 | 0.08 | 0.01 |
| dipIQ [52] | 0.47 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.82 | 0.07 | 0.37 | 0.75 |
| UCA [53] | 0.16 | 0.05 | 0.34 | 0.51 | 0.05 | 0.45 | 0.19 |
| NIQMC [54] | 0.16 | 0.52 | 0.77 | 0.17 | 0.73 | 0.60 | 0.28 |
| BPRI(p) [55] | 0.85 | 0.38 | 0.97 | 0.88 | 0.55 | 0.41 | 0.83 |
| BPRI(c) [55] | 0.78 | 0.38 | 0.96 | 0.85 | 0.72 | 0.46 | 0.92 |
| BMPRI [56] | 0.68 | 0.60 | 0.30 | 0.28 | 0.25 | 0.32 | 0.50 |
| BIQME [57] | 0.43 | 0.33 | 0.96 | 0.19 | 0.92 | 0.60 | 0.26 |
| MEON [58] | 0.55 | 0.29 | 0.95 | 0.24 | 0.63 | 0.35 | 0.56 |
| CNN [59] | 0.77 | 0.60 | 0.92 | 0.70 | 0.80 | 0.94 | 0.77 |
| DIQaM-NR [60] | 0.94 | 0.20 | 0.93 | 0.90 | 0.80 | 0.54 | 0.37 |
| DBCP-I | 0.84 | 0.90 | 0.95 | 0.94 | 0.93 | 0.41 | 0.61 |
| DBCP-II | 0.98 | 0.81 | 0.97 | 0.83 | 0.93 | 0.45 | 0.83 |
| DBCP-III | 0.98 | 0.90 | 0.99 | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.47 | 0.80 |
| IQA Model | Nanchang | Shanghai | Shenyang | Tianjin | Wuhan | Average | Hit Count |
| [35] | 0.80 | 0.10 | 0.78 | 0.36 | 0.91 | 0.61 | 0 |
| [39] | 0.56 | 0.46 | 0.79 | 0.36 | 0.38 | 0.37 | 0 |
| [33] | 0.93 | 0.52 | 0.99 | 0.60 | 0.96 | 0.77 | 7 |
| [44] | 0.54 | 0.46 | 0.83 | 0.36 | 0.38 | 0.38 | 0 |
| [45] | 0.30 | 0.56 | 0.64 | 0.24 | 0.61 | 0.38 | 0 |
| [45] | 0.84 | 0.04 | 0.61 | 0.29 | 0.85 | 0.50 | 0 |
| [45] | 0.07 | 0.29 | 0.63 | 0.26 | 0.37 | 0.40 | 0 |
| [46] | 0.90 | 0.52 | 0.96 | 0.43 | 0.94 | 0.71 | 5 |
| QAC [47] | 0.83 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.36 | 0.93 | 0.50 | 0 |
| NIQE [48] | 0.86 | 0.07 | 0.49 | 0.55 | 0.67 | 0.59 | 1 |
| LPSI [49] | 0.56 | 0.41 | 0.64 | 0.24 | 0.86 | 0.54 | 1 |
| IL-NIQE [50] | 0.84 | 0.37 | 0.74 | 0.00 | 0.91 | 0.65 | 0 |
| HOSA [51] | 0.57 | 0.30 | 0.67 | 0.05 | 0.36 | 0.37 | 0 |
| dipIQ [52] | 0.69 | 0.12 | 0.19 | 0.36 | 0.02 | 0.47 | 1 |
| UCA [53] | 0.01 | 0.42 | 0.53 | 0.07 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0 |
| NIQMC [54] | 0.34 | 0.42 | 0.94 | 0.33 | 0.79 | 0.50 | 0 |
| BPRI(p) [55] | 0.88 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.29 | 0.90 | 0.58 | 1 |
| BPRI(c) [55] | 0.91 | 0.14 | 0.26 | 0.31 | 0.90 | 0.63 | 1 |
| BMPRI [56] | 0.15 | 0.75 | 0.40 | 0.45 | 0.39 | 0.42 | 1 |
| BIQME [57] | 0.59 | 0.01 | 0.90 | 0.21 | 0.35 | 0.48 | 0 |
| MEON [58] | 0.90 | 0.83 | 0.93 | 0.74 | 0.15 | 0.59 | 2 |
| CNN [59] | 0.85 | 0.40 | 0.71 | 0.40 | 0.90 | 0.73 | 1 |
| DIQaM-NR [60] | 0.94 | 0.80 | 0.90 | 0.40 | 0.90 | 0.72 | 2 |
| DBCP-I | 0.93 | 0.31 | 0.87 | 0.43 | 0.92 | 0.75 | 5 |
| DBCP-II | 0.74 | 0.05 | 0.86 | 0.63 | 0.74 | 0.74 | 4 |
| DBCP-III | 0.93 | 0.26 | 0.97 | 0.64 | 0.95 | 0.81 | 10 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chu, Y.; Chen, F.; Fu, H.; Yu, H. Haze Level Evaluation Using Dark and Bright Channel Prior Information. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 683. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13050683
Chu Y, Chen F, Fu H, Yu H. Haze Level Evaluation Using Dark and Bright Channel Prior Information. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(5):683. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13050683
Chicago/Turabian StyleChu, Ying, Fan Chen, Hong Fu, and Hengyong Yu. 2022. "Haze Level Evaluation Using Dark and Bright Channel Prior Information" Atmosphere 13, no. 5: 683. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13050683
APA StyleChu, Y., Chen, F., Fu, H., & Yu, H. (2022). Haze Level Evaluation Using Dark and Bright Channel Prior Information. Atmosphere, 13(5), 683. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13050683








