The Diurnal Cycle of Precipitation over Lake Titicaca Basin Based on CMORPH
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data Sets
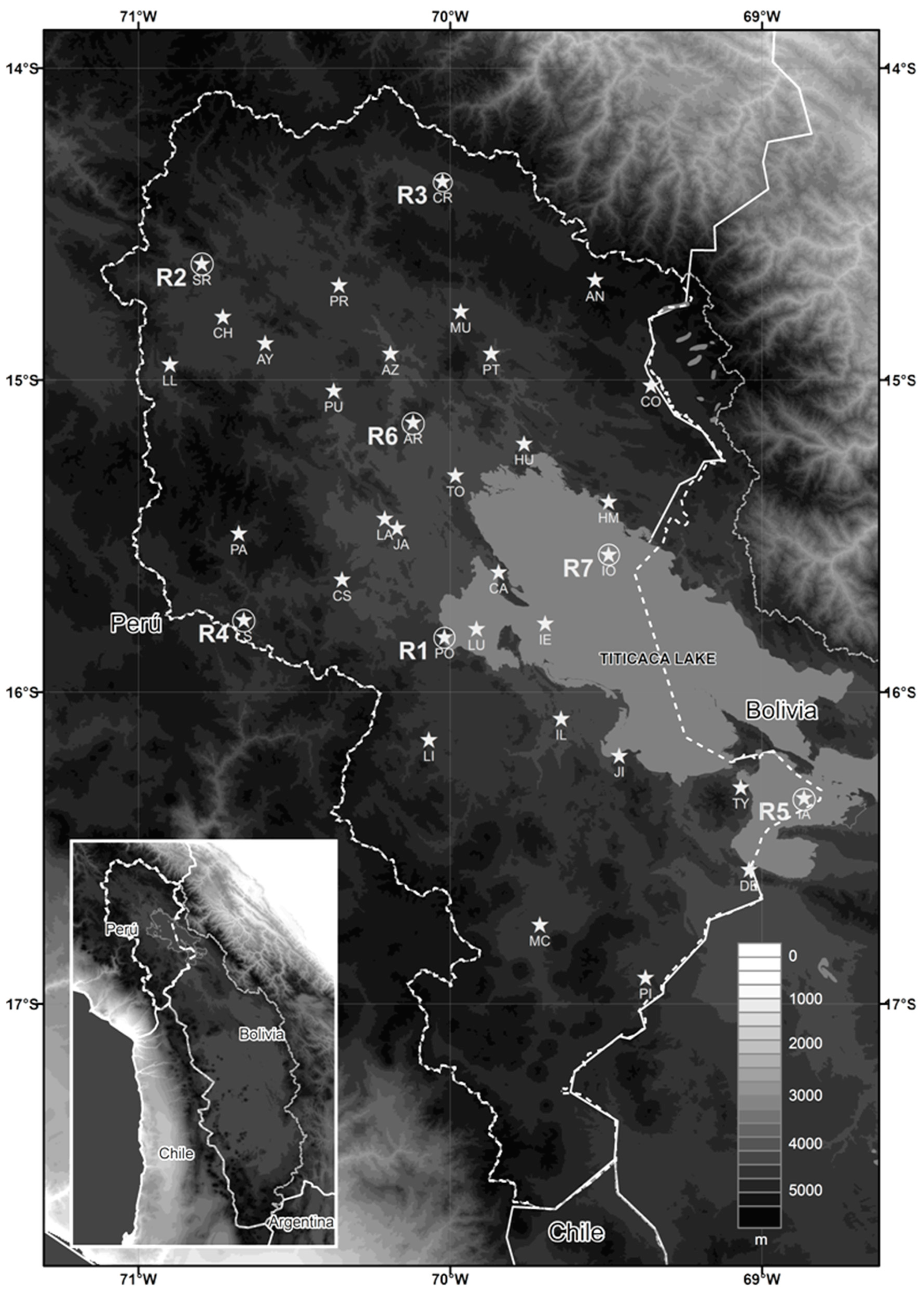
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Set
2.2.1. Gauge Precipitation Data
2.2.2. CMORPH
3. Methods
3.1. Statistical Measures
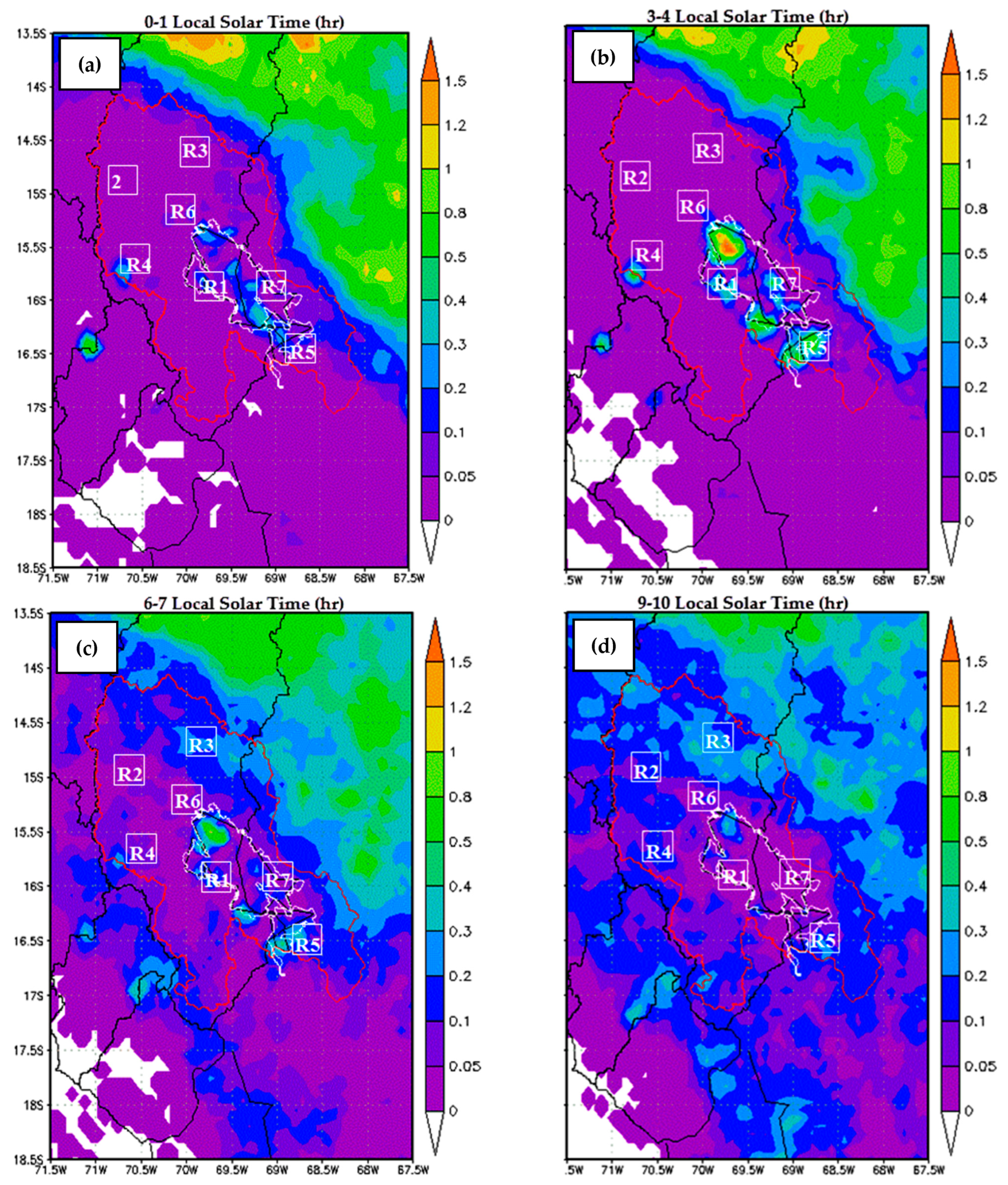
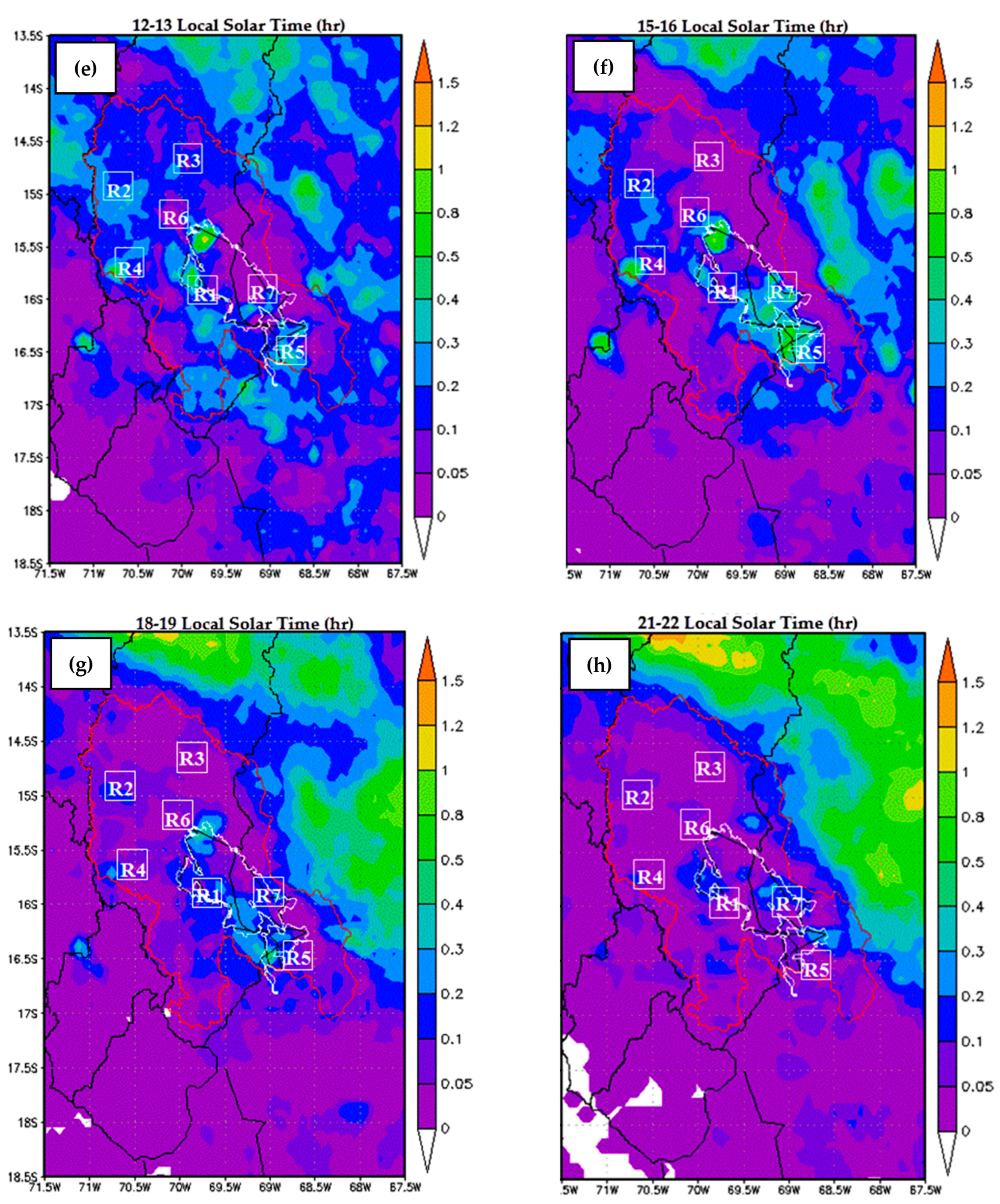
3.2. Analysis of Diurnal Cycle of Precipitation
4. Results
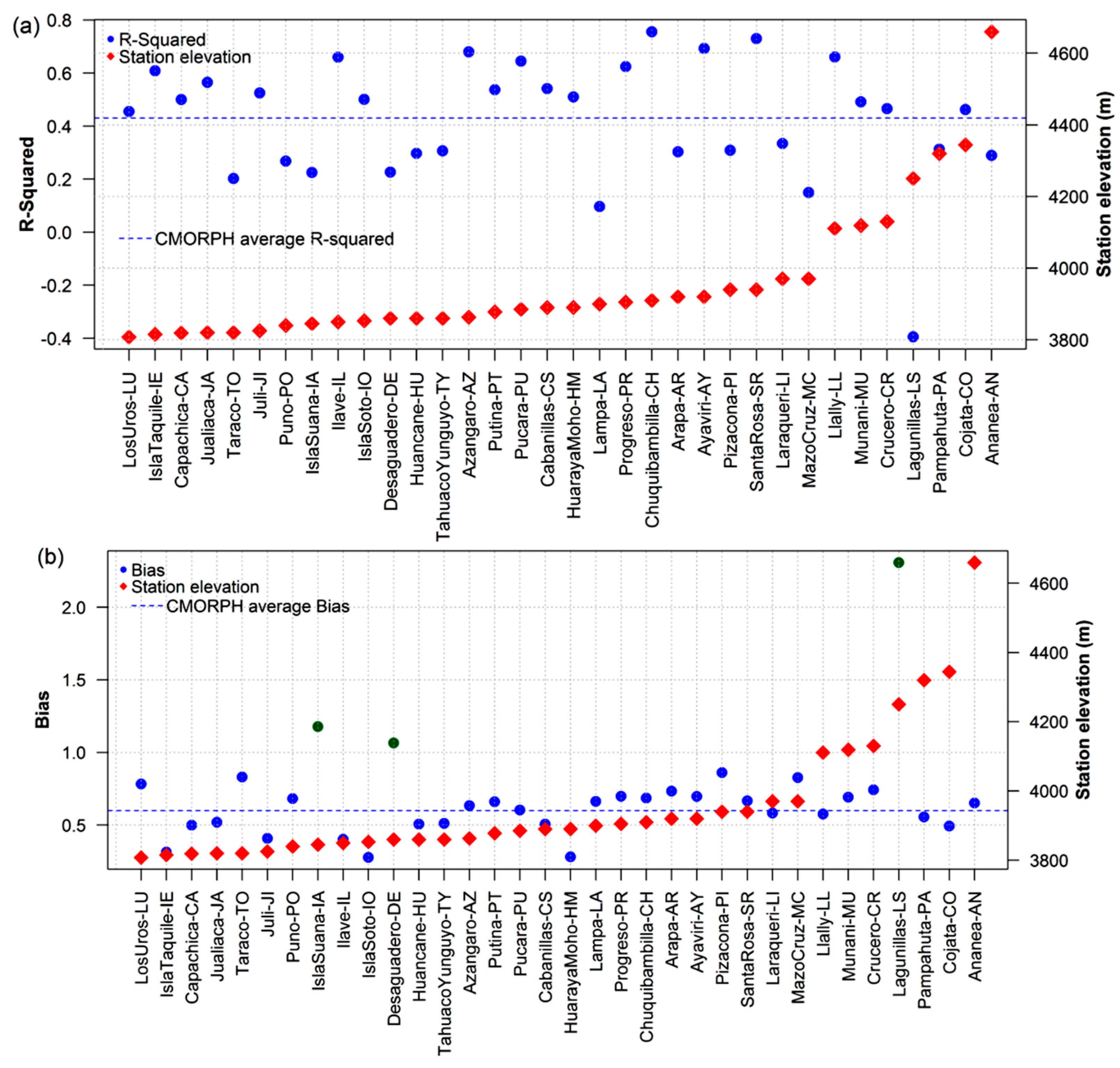
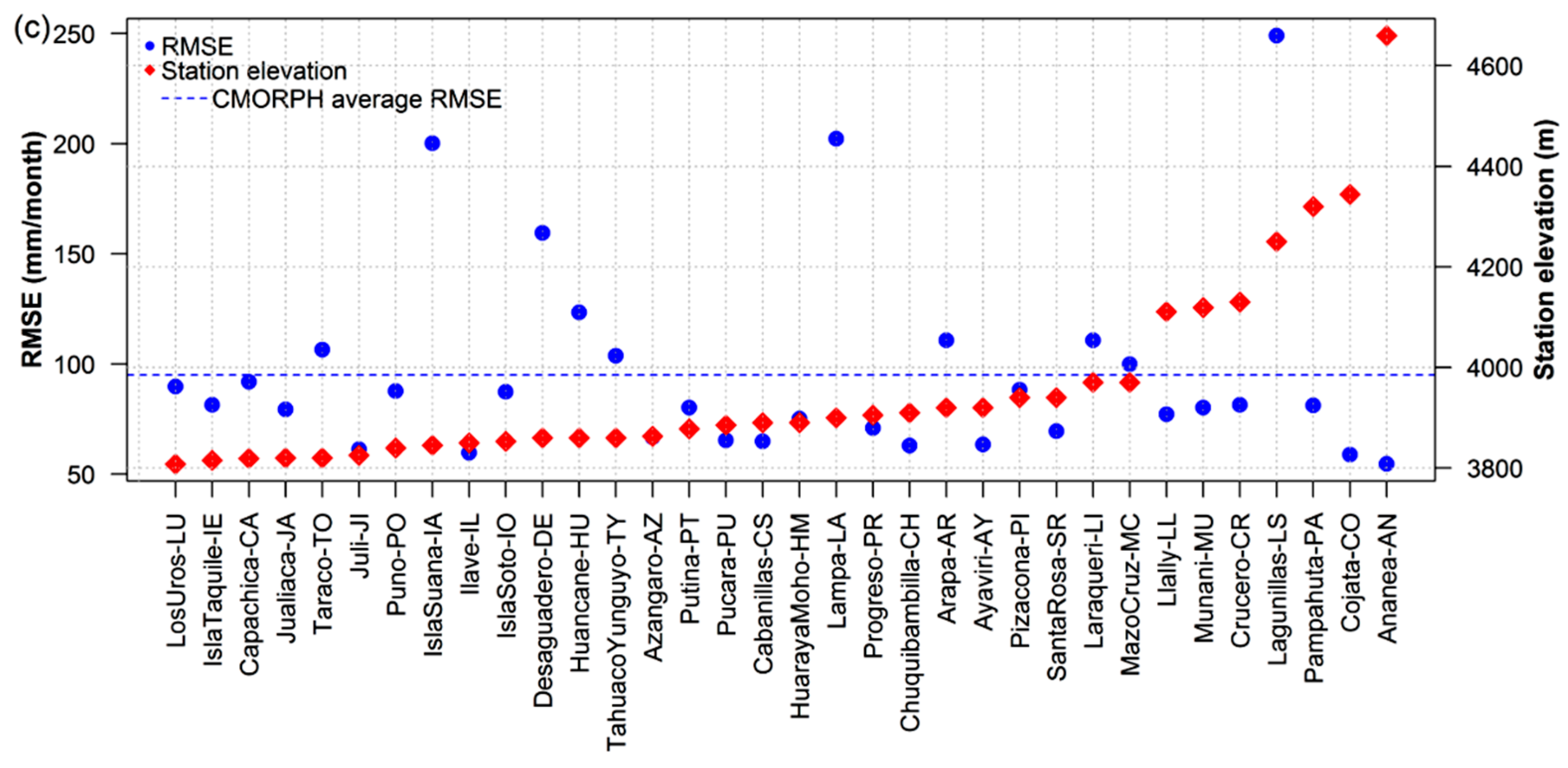
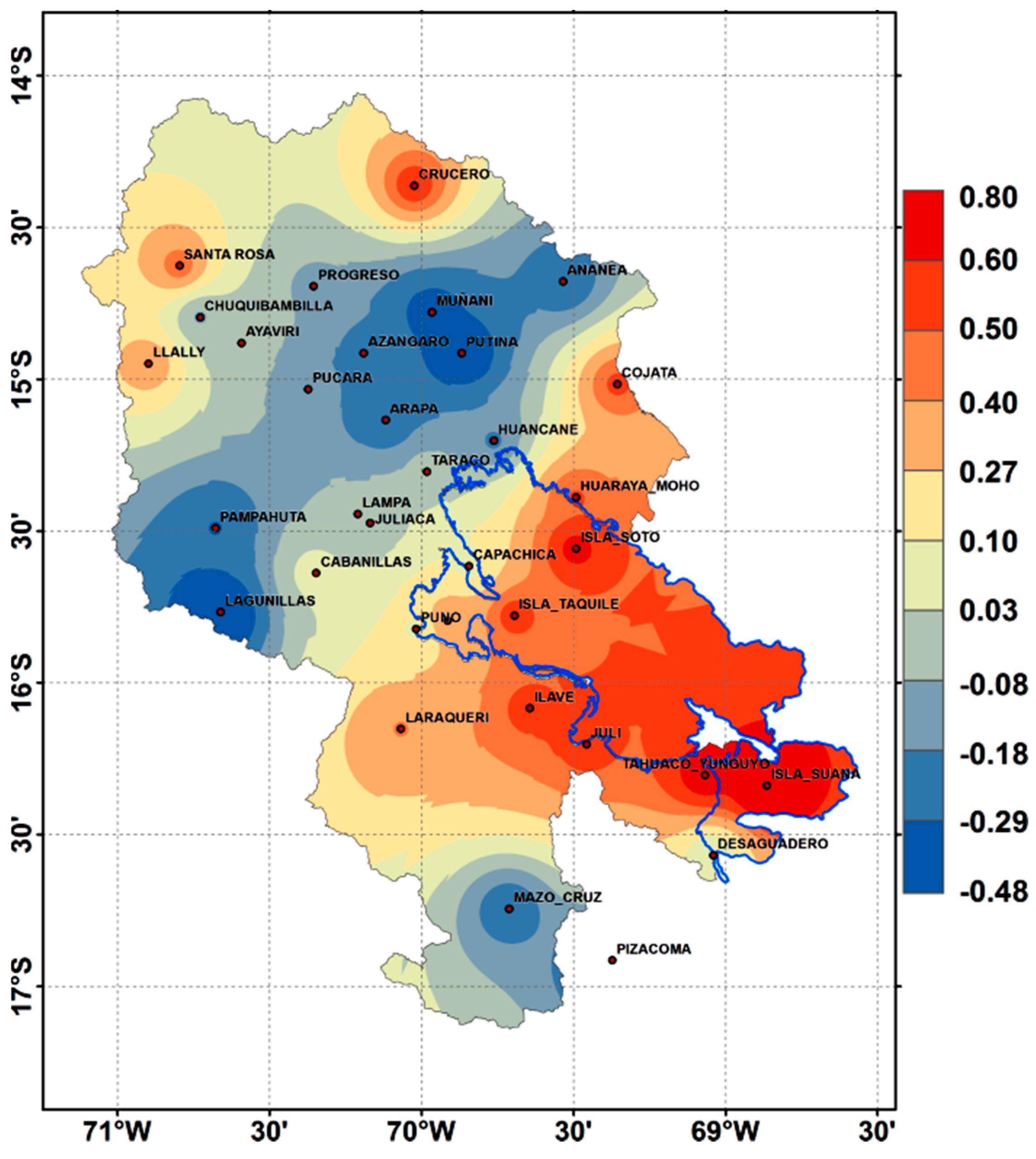
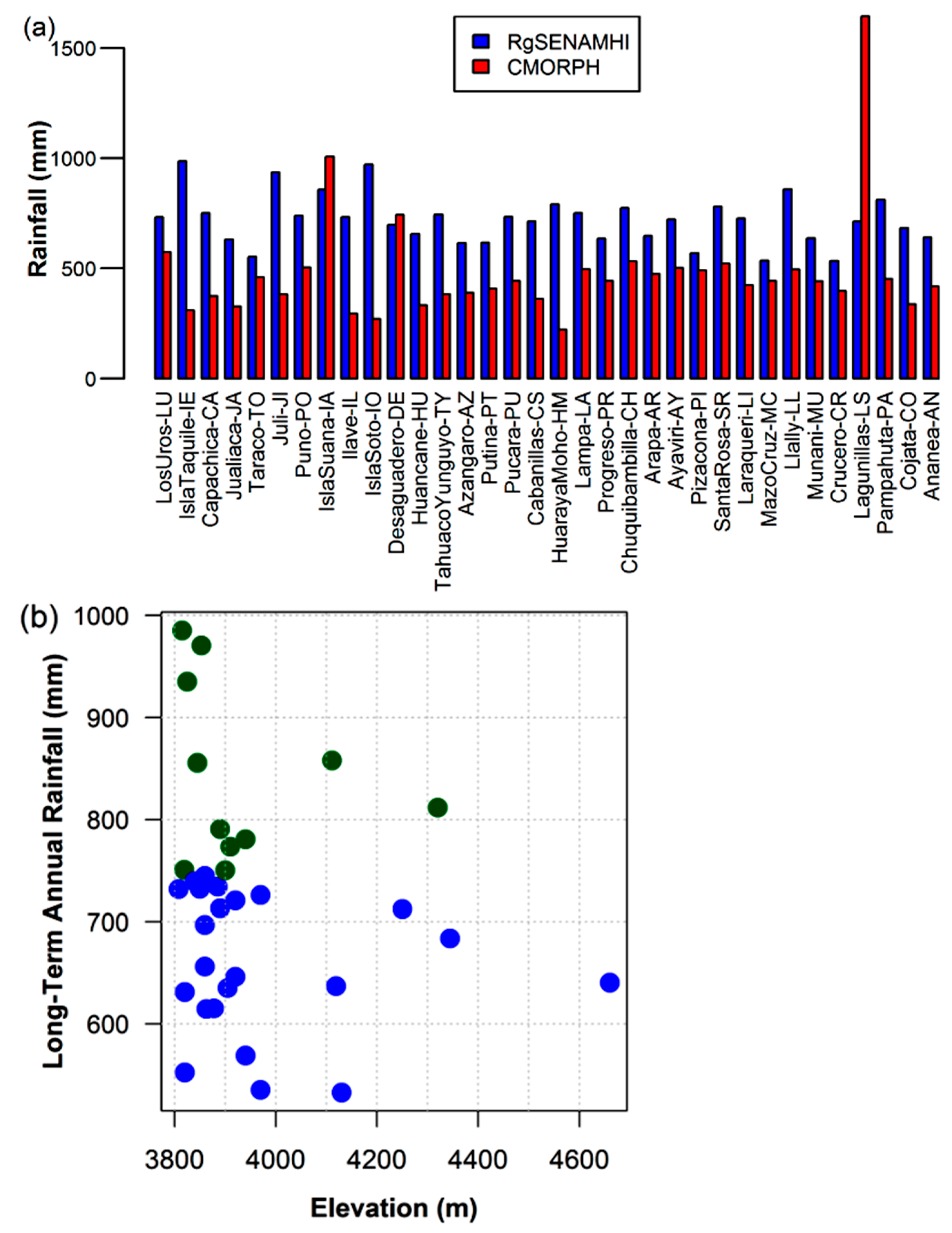
4.1. Point-to-Grid Comparison
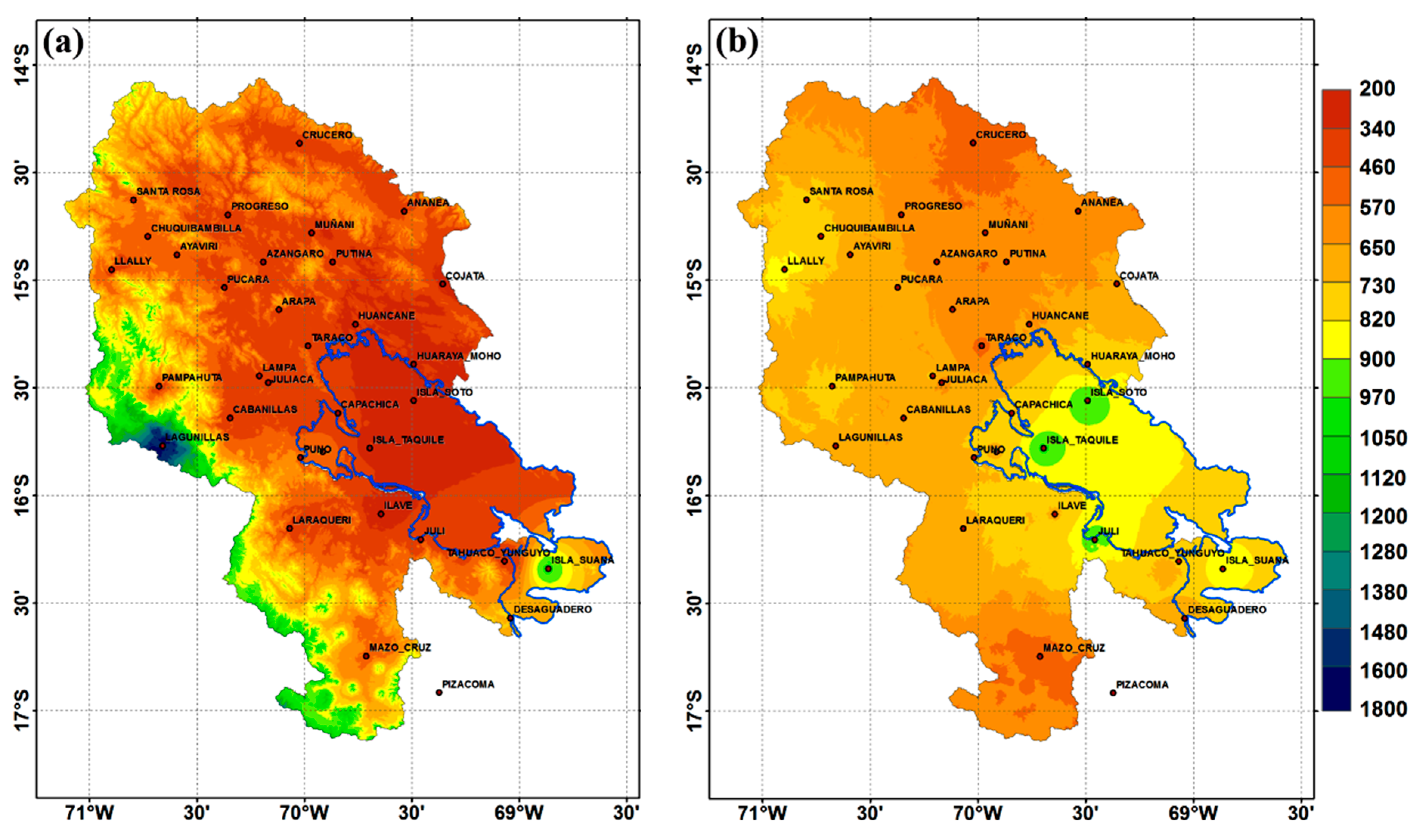
4.2. Areal Comparison
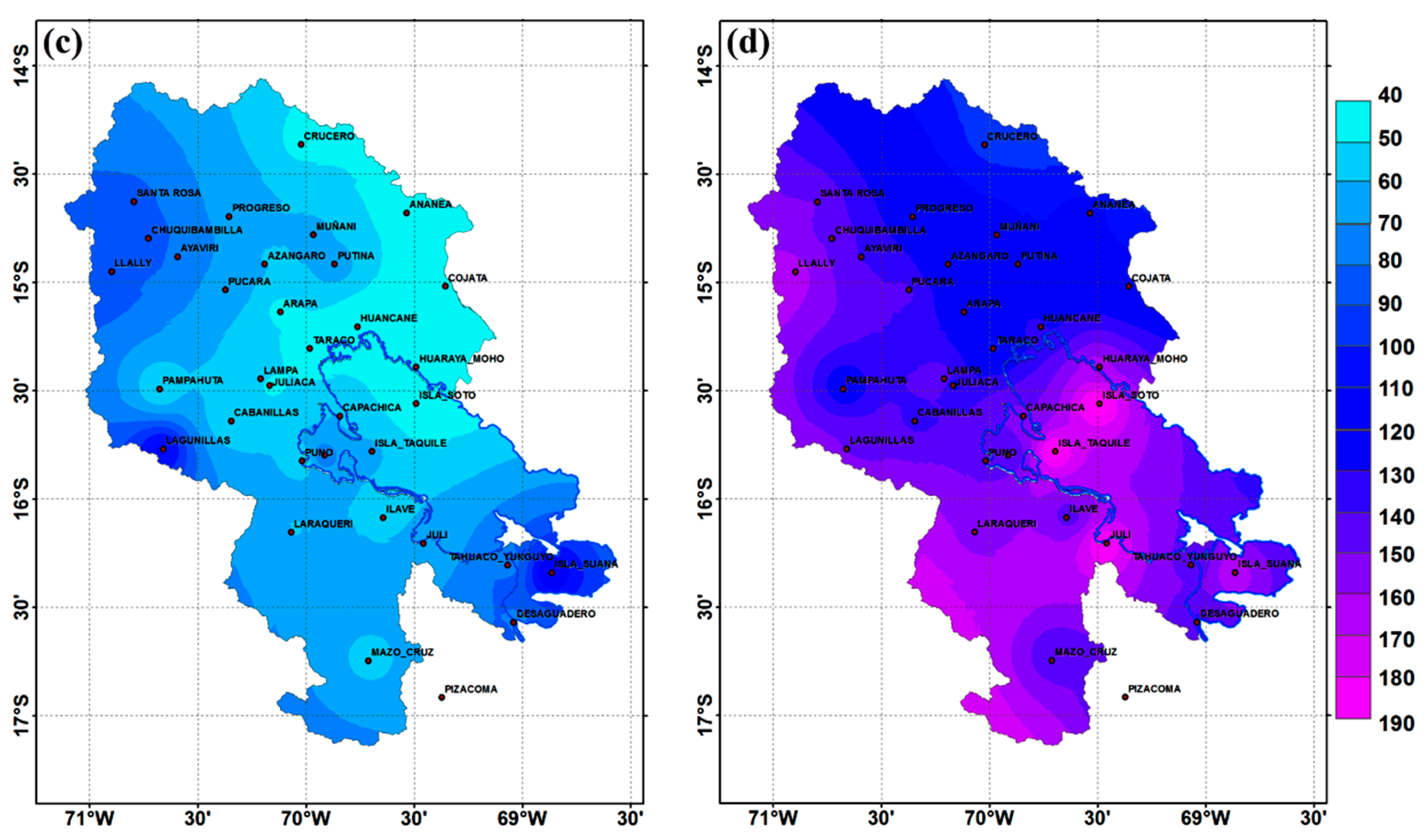
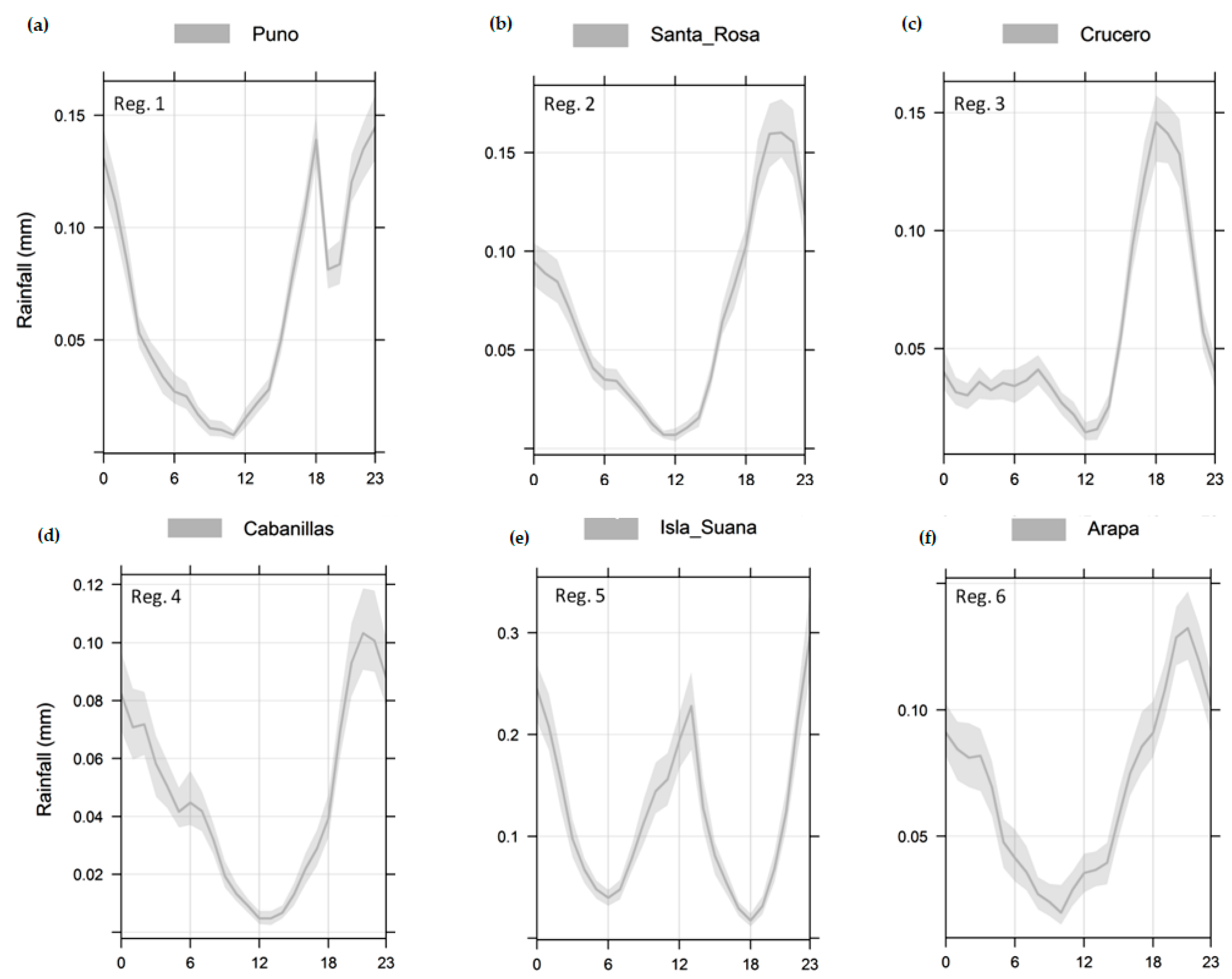
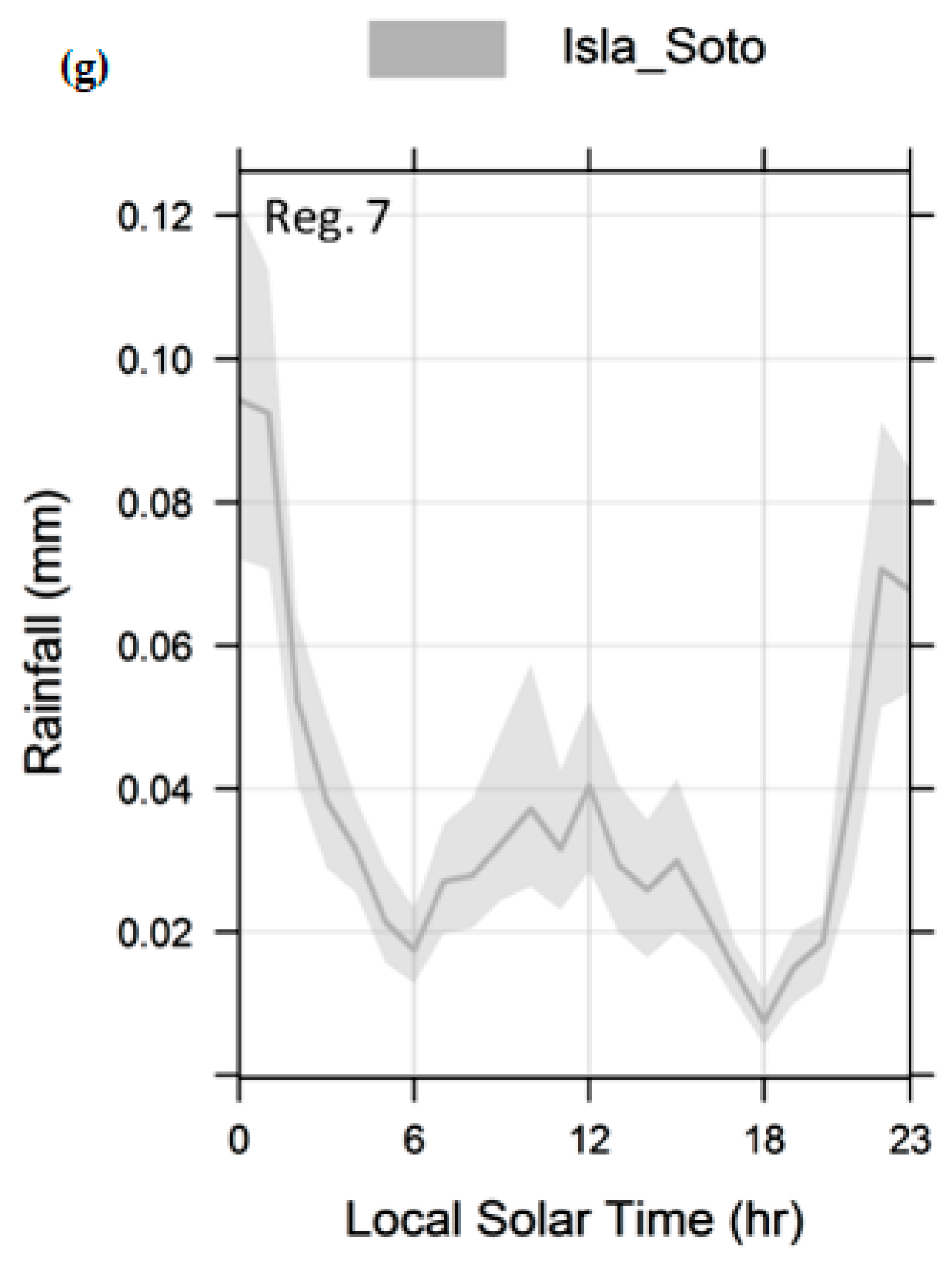
4.3. Diurnal Cycle of Precipitation Using Data from CMORPH
5. Conclusions
- The CMORPH estimates exhibit remarkable accordance with the RgSENAMHI data in terms of their precipitation patterns and captured daily rainfall frequency better that rainfall amounts over the LTb. The precipitation maximum mainly exist over two regions: Lake Titicaca and the surrounding terrain. However, the magnitude and extent of the maximum of the CMORPH rainfall were smaller than those of the RgSENAMHI rainfall. On the other hand, rainfall occurrences are underestimated over most of the LTb, but there are differences over some areas (e.g., Lagunillas, Isla Suana, and Desaguaderos stations) where rainfall is overestimated.
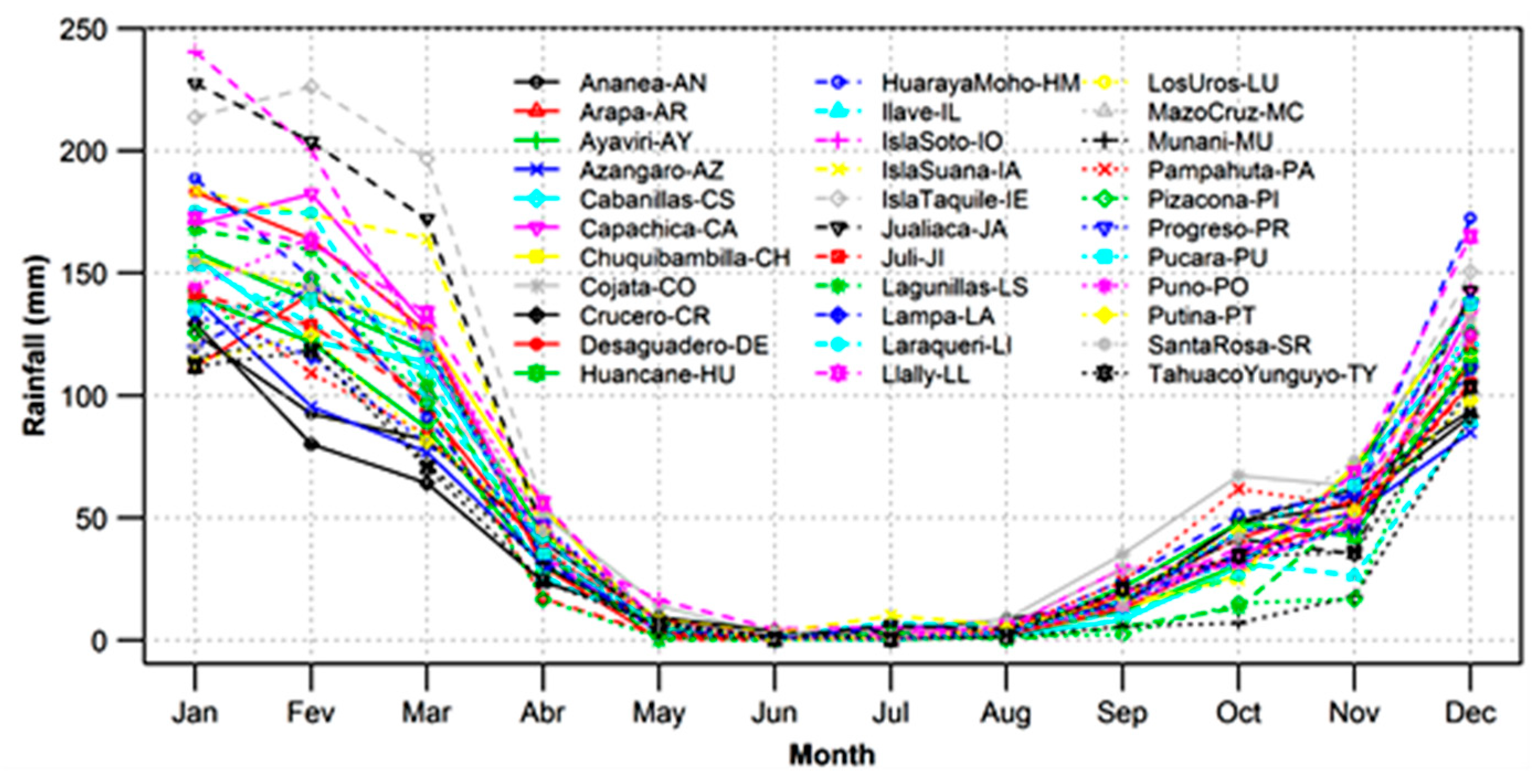
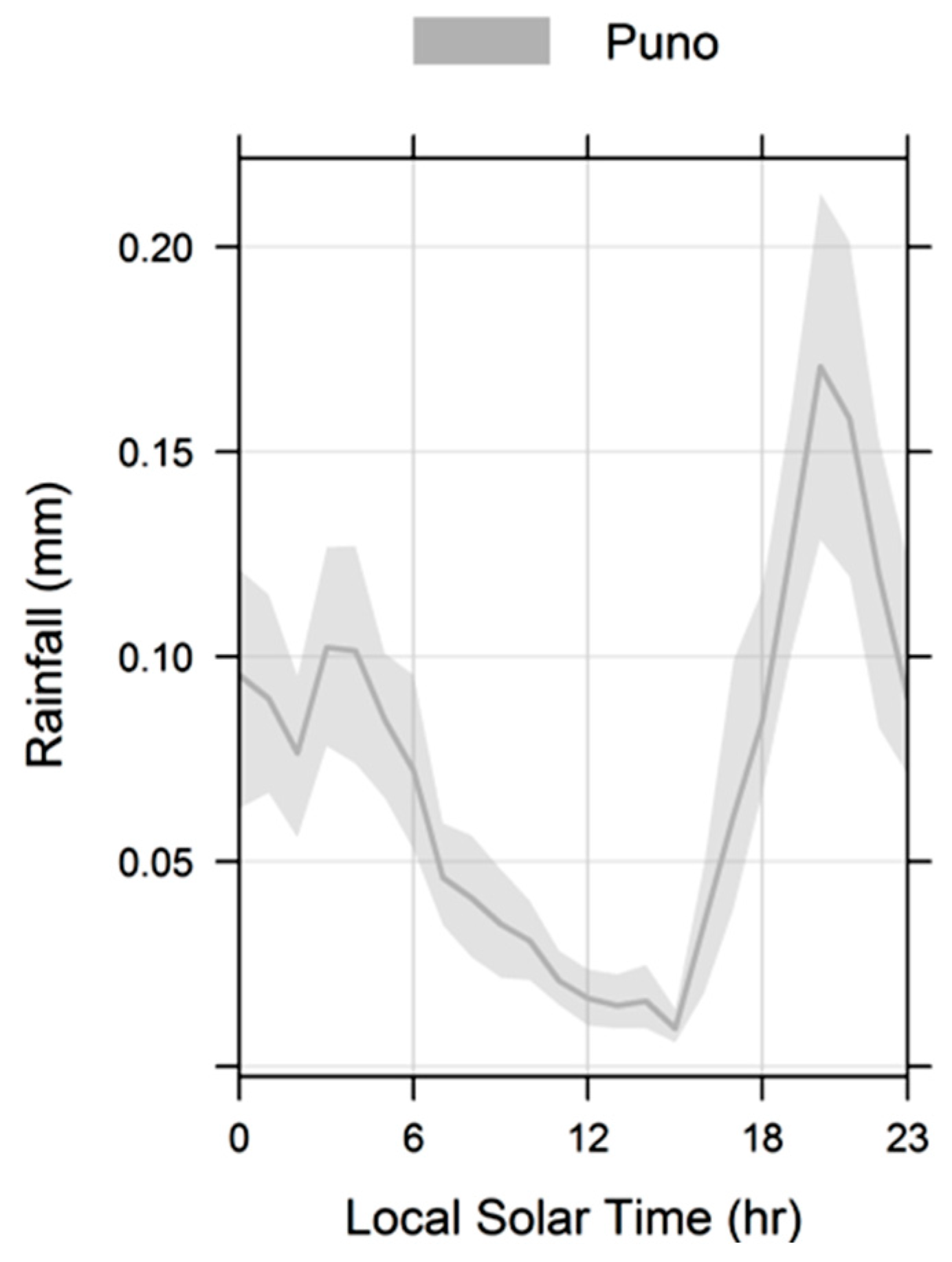
- Precipitation over our study domain showed diurnal cycles with obvious regional differences. Over the surrounding lake area, the plateau, and high mountain areas, precipitation peaks are in the late afternoon, while over low areas, such as the valleys (near to lake) and Lake Titicaca, it peaks around midnight to early morning. This result suggests that the diurnal cycle of precipitation is closely related to the local circulation resulting from solar radiation and the complex orography.
- The bias underestimation was observed over most of the LTb areas and overestimation (e.g., Lagunillas, Isla Suana, and Desaguadero stations). The total bias decreases when approaching the lake attaining its minimum value over the mountains [4,5]. In addition, the high resolution of the CMORPH data can depict finer regional details, such as a less coherent phase pattern over a few regions (e.g., Isla Suana).
- The CMORPH and RgSENAMHI rainfall amounts show weak to moderate correlations (41% and 59%), respectively. Higher correlations were observed over the lake (>0.6). Based on the period and study area, there was a distinct difference between the accuracy of the CMORPH and RgSENAMHI. It was also observed that the accuracy of the CMORPH in the LTb shows large spatial variability [4,5]. On the other hand, efforts should be devoted toward applying spatially and temporally-varying bias correction to the CMORPH product and evaluating the implications of such adjustments for water resource applications in the study area [8].
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CMORPH | CPC MORPHing technique |
| LTb | Lake Titicaca basin |
| LST | Local Solar Time |
| RgSENAMHI | Rain gauge SENAMHI |
References
- Canedo, C.; Pillco, R.Z.; Berndtsson, R. Role of Hydrological Studies for the Develompent of the TDPS System. Water 2016, 8, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Heap, A.D. Spatial Interpolation Methods: A Review for Environmental Scientists; Geoscience Australia: Canberra, Australia, 2008. Available online: https://www.ga.gov.au/corporate_data/68229/Rec2008_023.pdf (accessed on 20 July 2019).
- Scheel, M.L.M.; Rohrer, M.; Huggel, C.; Santos Villar, D.; Silvestre, E.; Huffman, G.J. Evaluation of TRMM Multi-satellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA) performance in the Central Andes region and its dependency on spatial and temporal resolution. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 2649–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haile, A.T.; Yan, T.; Habib, E. Accuracy of the CMORPH satellite-rainfall product over Lake Tana Basin in Eastern Africa. Atmos. Res. 2015, 163, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-X.; Bi, X.-Q.; Kong, X.-H. Observed Diurnal Cycle of Summer Precipitation over South Asia and East Asia Based on CMORPH and TRMM Satellite Data. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. Lett. 2015, 8, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinku, T.; Connor, S.J.; Ceccato, P. Comparation of CMORPH and TRMM-3B42 over Mountainous Regions of Africa and South America. In Satellite Rainfall Applications for Surface Hydrology; Gebremichael, M., Hossain, F., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, F.A.J.; Carbone, R.E.; Janowiak, J.E.; Arkin, P.; Joyce, R.; Hallak, R.; Ramos, C.G.M. Satellite rainfall estimates over South America—Possible applicability to the water management of large watersheds. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2010, 46, 344–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, F.A.J.; Vemado, F.; Vemado, G.; Gomes, V.R.F.A.; Do Carmo, G.L.; Irineu, C.R.; Dos Santos, C.C.; Sampaio, L.E.S.; Fischer, G.M.; Tadashi, O.A.; et al. A Step towards Integrating CMORPH Precipitation Estimation with Rain Gauge Measurements. Adv. Meteorol. 2018, 2018, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, J.J. Evaluation of different methodologies for precipitation estimates calibration-cmorph-over South America. Rev. Bras. Meteorol. 2009, 24, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapriano, M.R.P.; Arkin, P.A. An Intercomparison and Validation of High-Resolution Satellite Precipitation Estimates with 3-Hourly Gauge Data. J. Hydrometeorol. 2019, 10, 149–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinku, T.; Chidzambwa, S.; Ceccato, P.; Connor, S.J.; Ropelewski, C.F. Validation of high-resolution satellite rainfall products over complex terrain. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 4097–4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satgé, F.; Bonnet, M.-P.; Gosset, M.; Molina, J.; Yuque, L.W.H.; Pillco, Z.R.; Timouk, F.; Garnier, J. Assessment of satellite rainfall products over the Andean plateau. Atmos. Res. 2016, 167, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satgé, F.; Ruelland, D.; Bonnet, M.-P.; Gosset, M.; Molina, J.; Pillco, Z.R. Consistency of satellite-based precipitation products in space and over time compared with gauge observations and snow-hydrological modelling in the Lake Titicaca region. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 23, 595–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, A.; Lin, X.; Hsu, K.-L. The frequency, intensity, and diurnal cycle of precipitation in surface and satellite observations over low- and mid-latitudes. Clim. Dyn. 2007, 29, 727–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janowiak, J.E.; Arkin, P.A.; Morrissey, M. An examination of the diurnal cycle in oceanic tropical rainfall using satellite and in situ data. Mon. Weather. Rev. 1994, 122, 2296–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, A.T.C.; Chiu, L.S.; Yang, G. Diurnal cycle of oceanic precipitation from SSM/I data. Mon. Weather. Rev. 1995, 123, 3371–3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorooshian, S.; Gao, X.; Maddox, R.A.; Hon, Y.; Imam, B. Diurnal variability of tropical rainfall retrieved from combined GOES and TRMM satellite information. J. Clim. 2002, 15, 983–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesbitt, S.W.; Zipser, E.J. The diurnal cycle of rainfall and convective intensity according to three years of TRMM measurements. J. Clim. 2003, 16, 1456–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, K.P.; Collier, J.C.; North, G.R.; Wu, Q.Y.; Ha, E.H.; Hardin, J. Diurnal cycle of tropical precipitation in Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite and ocean buoy rain gauge data. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, D21104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Hsu, K.L.; Sorooshian, S.; Gao, X.G. Improved representation of diurnal variability of rainfall retrieved from the Tropical Rainfall Measurement Mission Microwave Imager adjusted Precipitation Estimation From Remotely Sensed Information Using Artificial Neural Networks (PERSIANN) system. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, D06102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Smith, E.A. Mechanisms for diurnal variability of global tropical rainfall observed from TRMM. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 5190–5226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, J.; Srivatsan, V.R.; Ngoc, S.N.; Shie-Yui, L. Evaluation of High-Resolution Satellite rainfall data over Singapure. Procedia Eng. 2016, 154, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, H.; Letu, H.; Nakajima, T.Y.; Wang, Z.; Ma, R.; Wang, T.; Lei, Y.; Ji, D.; Li, S.; Shi, J. Diurnal cycle and seasonal variation of cloud cover the Tibetan Plateau as determined from Himawari-8 new-generation geostationary satellite data. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, P.; Liang, L.; Zhang, S. Evaluation of precipitation from CMORPH, GPCP-2, TRMM 3B43, GPCC and ITPCAS with ground-based measurements in the Qinling-Daba Mountains, China. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, A. Global Precipitation and Thunderstorm Frequencies. Part I: Seasonal and Interannual Variations. J. Clim. 2000, 14, 1092–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Rotunno, R. Diurnal Cycle of Rainfall and Winds near the South Coast of China. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2018, 75, 2065–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watters, D.; Battaglia, A. The Summertime Diurnal Cycle of Precipitation Derived from IMERG. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garreaud, R.; Vuille, M.; Clement, A. The climate of the Altiplano: Observed current conditions and mechanisms of past changes. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2003, 194, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T. Mechanism of Orographic Precipitation around the Meghalaya Plateau Associated with Intraseasonal Oscillation and the Diurnal Cycle. Mon. Weather Rev. 2013, 141, 3049–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minder, J.; Letcher, T.W. The Evolution of Lake-Effect Convection during Landfall and Orographic Uplift as Observerd by Profiling Radars. Mon. Weather Rev. 2015, 143, 4422–4442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veals, P.G.; Steenburgh, W.J.; Campell, L.S. Factors Affeting the Inland and Orographic Enhancement of Lake-Effect Precipitation over the Tug Hill Plateau. Mon. Weather Rev. 2018, 146, 1745–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, S.E.; Hartman, A.T.; Klaust, D.A. On the Diurnal Cycle of Rainfall and Convection over Lake Victoria and Its Catchment. Part II: Meteorological Factors in the Diurnal and Seasonal Cycles. J. Hydrometeorol. 2021, 22, 3049–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garreaud, R. Intraseasonal Variability of Misture and Rainfall over the South American Altiplano. Mon. Weather Rev. 2000, 128, 3337–3346. [Google Scholar]
- Villue, M.; Keimig, F. Interannual Variability of Summertime Convective Cloudiness and Precipitation in the Central Derived from ISCCP-B3 Data. J. Clim. 2004, 17, 3334–3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OEA (Organización de los Estados Americanos)/PNUMA (Programa de las Naciones Unidas para el Medio Ambiente). Diagnóstico Ambiental del Sistema Titicaca-Desaguadero-Poopó-Salar de Copaisa (Sistema TDPS) Bolivia-Perú; OEA: Washington, DC, USA, 1996; p. 192. [Google Scholar]
- Heidinger, H.; Yarlequé, C.; Posadas, A.; Quiroz, R. TRMM rainfall correction over the Andean Plateau using wavelet multi-resolution analysis. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 4583–4602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torre-Batlló, J.; Martí-Cardona, B.; Pillco-Zolá, R. Mapping long-term evapotranspiration losses in the catchment of the shrinking Lake Poopó. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019. preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamuriano, M.; Martynov, A.; Panziera, L.; Bronnimann, S. Characteristics of a Hailstorm over the Andean La Paz Valley. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2019. preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blacutt, L.A.; Herdies, D.L.; De Gonçalves, L.G.G.; Vila, D.A.; Andrade, M. Precipitation comparison for the CFSR, MERRA, TRMM3B42 and Combined Scheme datasets in Bolivia. Atmos. Res. 2015, 163, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebere, S.B.; Alamirew, T.; Merkel, B.J. Performance of High-Resolution Satellite Rainfall Products over Data Scarse Parts of Eastern Ethiopia. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 11639–11663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, R.J.; Janowiak, J.E.; Arkin, P.A.; Xie, P. CMORPH: A Method that Produces Global Precipitation Estimates from Passive Microware and Infrared Data at High Spatial and Temporal Resolution. J. Hydrometeorol. 2004, 5, 487–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joice, R.J.; Xie, P.; Yarosh, Y.; Janowiak, J.E.; Arkin, P.A. CMORPH: A “Morphing” Approach for High Resolution Precipitation Product Generation. In Satellite Rainfall Applications for Surface Hydrology; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rais, A.F.; Yunita, R. Main Diurnal Cycle Pattern of Rainfall in East Java. AIP Conf. Proc. 2017, 1876, 020057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Meng, Z.; Zhang, F.; Markowski, P.M. The influence of sea and land-breeze circulations on the diurna variability in preciptation over a tropical island. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 13213–13232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, Y.; Satgé, H.; Hussain, M.B.; Martinez-Carvajal, H.; Bonnet, M.-P.; Cárdenas-Soto, M.; Roig, H.L.; Akther, G. Performance of CMOPRH, TMPA, and PERSIANN rainfall datasets oven plain, mountainous and glacial regions of Pakistan. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2018, 131, 1119–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janowiak, J.E.; Kousky, V.E.; Joyce, R.J. Diurnal cycle of precipitation determined from the CMORPH high spatial and temporal resolution global precipitation analyses. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, D23105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, J.A.; Ruscia, R.C.; Menéndez, C.G. The diurnal cycle of precipitation over South America represented by five gridded datasets. Int. J. Climatol. 2019, 40, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh-Tuan, L.; Matsumoto, J.; Ngo-Duc, T.; Nodzu, M.I.; Inoue, T. Evaluation of satellite precipitation products over Central Vietnan. Prog. Earth Planet. Sci. 2019, 6, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TDPS: Climatología del Sistema de los Lagos Titicaca, Desaguadero, Poopó y Salares Coipasa y Uyuni (TDPS); Comisión de Comunidades de Europeas, Repúblicas del Perú y Bolivia: La Paz, Bolivia, 1993.
- Revollo, M.M. Management issues in the Lake Titicaca and Lake Poopo System: Importance of developing a water budget. Lake Reserv. 2001, 6, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, M.A.; Bourges, J.; Cortes, J.; Mattos, R. Climatology and hydrology of the Lake Titicaca basin. In Lake Titicaca. A Synthesis of Limnological Knowledge; Dejoux, C., Litis, A., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1992; pp. 63–88. [Google Scholar]
- Hunziker, S.; Gubler, S.; Calle, J.; Moreno, I.; Andrade, M.; Velarde, F.; Ticona, L.; Carrasco, G.; Castellón, Y.; Oria, C.; et al. Identifying, attributing, and overcoming common data quality is-sues of manned station observations. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 4131–4145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quevedo, K.; Sánchez, K. Comparison of two interpolation methods to estimate air temperature applying geostatistical techniques. Rev. Peru. Geo-Atmos. 2009, 1, 90–107. [Google Scholar]
- Worqlul, A.W.; Maathuis, A.; Adem, A.A.; Demissie, S.S.; Langan, S.; Steenhuis, T.S. Comparison of rainfall estimations by TRMM 3B42, MPEG and CFSR with ground-observed data for the Lake Tana basin in Ethiopia. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 4871–4881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budyko, M.I. Climate and life. In International Geophysics Series; Miller, D.H., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1974; Volume 18, 508p. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, S.; Loeb, N.G.; Rosse, F.G.; Doelling, D.R.; Rutan, D.A.; Caldwell, T.E.; Yu, L.; Weller, R.A. Surface irradiances consistent with CERES-derived top-of-atmosphere shortwave and longwave irradiances. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 2719–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gálvez, J.M.; Douglas, M.W. Modulation of rainfall by Lake Titicaca using the WRF Model. In Proceedings of the 8th ICSHMO, Foz do Iguaçu, Brazil, 24–28 April 2006; pp. 745–752. [Google Scholar]
- Zaratti, F.; Forno, R.N.; García, J.F. Erythemally weighted UV variations at two high-altitude locations. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canedo, R.C.; Hochrainer-Stigler, S.; Pflug, G.; Condori, B.; Berndtsson, R. Early warning and drought risk assessment for the Bolivian Altiplano agriculture using high resolution satellite imagery data. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2018. preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canedo, R.C.; Hochrainer -Stigler, S.; Pflug, G.; Condori, B.; Berndtsson, R. Drought risk in the Bolivian Altiplano associated with El Niño Southern Oscillation using satellite imagery data. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 21, 995–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Dataset Name (Reference) | Spatial–Temporal Resolution and Coverage | Data Sources and Merging Method | Online Documentation |
|---|---|---|---|
| CMORPH (Joyce et al., 2004) [41] | 0.07275° grid, 60° S–60° N, 180° W–180° E; 30 min, 12/2002-present. | Microwave estimates from the DMSP 13, 14, and 15 (SSM/I); the NOAA-15, 16, and 17 (AMSU-B); and the TRMM (TMI) satellites are propagated by motion vectors derived from geostationary satellite infrared data. | (http://www.cpc.ncep.noaa.gov/products/janowiak/cmorph_description.html). Accessed on 10 September 2019 |
| Rain gauges (SENAMHI) (Hunziker et al., 2017) [52] | 14° S–18° S, 71° W–69° W 1964–2013 | Daily reports from 34 rain gauges were used to derive the gridded data. | (http://www.geography.unibe.ch/research/climatology group/research_projects/decade/index_eng.html). Accessed on 21 July 2019 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chuchón Angulo, E.; Pereira Filho, A.J. The Diurnal Cycle of Precipitation over Lake Titicaca Basin Based on CMORPH. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 601. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13040601
Chuchón Angulo E, Pereira Filho AJ. The Diurnal Cycle of Precipitation over Lake Titicaca Basin Based on CMORPH. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(4):601. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13040601
Chicago/Turabian StyleChuchón Angulo, Eleazar, and Augusto Jose Pereira Filho. 2022. "The Diurnal Cycle of Precipitation over Lake Titicaca Basin Based on CMORPH" Atmosphere 13, no. 4: 601. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13040601
APA StyleChuchón Angulo, E., & Pereira Filho, A. J. (2022). The Diurnal Cycle of Precipitation over Lake Titicaca Basin Based on CMORPH. Atmosphere, 13(4), 601. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13040601






