Using Mobile Monitoring and Atmospheric Dispersion Modeling for Capturing High Spatial Air Pollutant Variability in Cities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
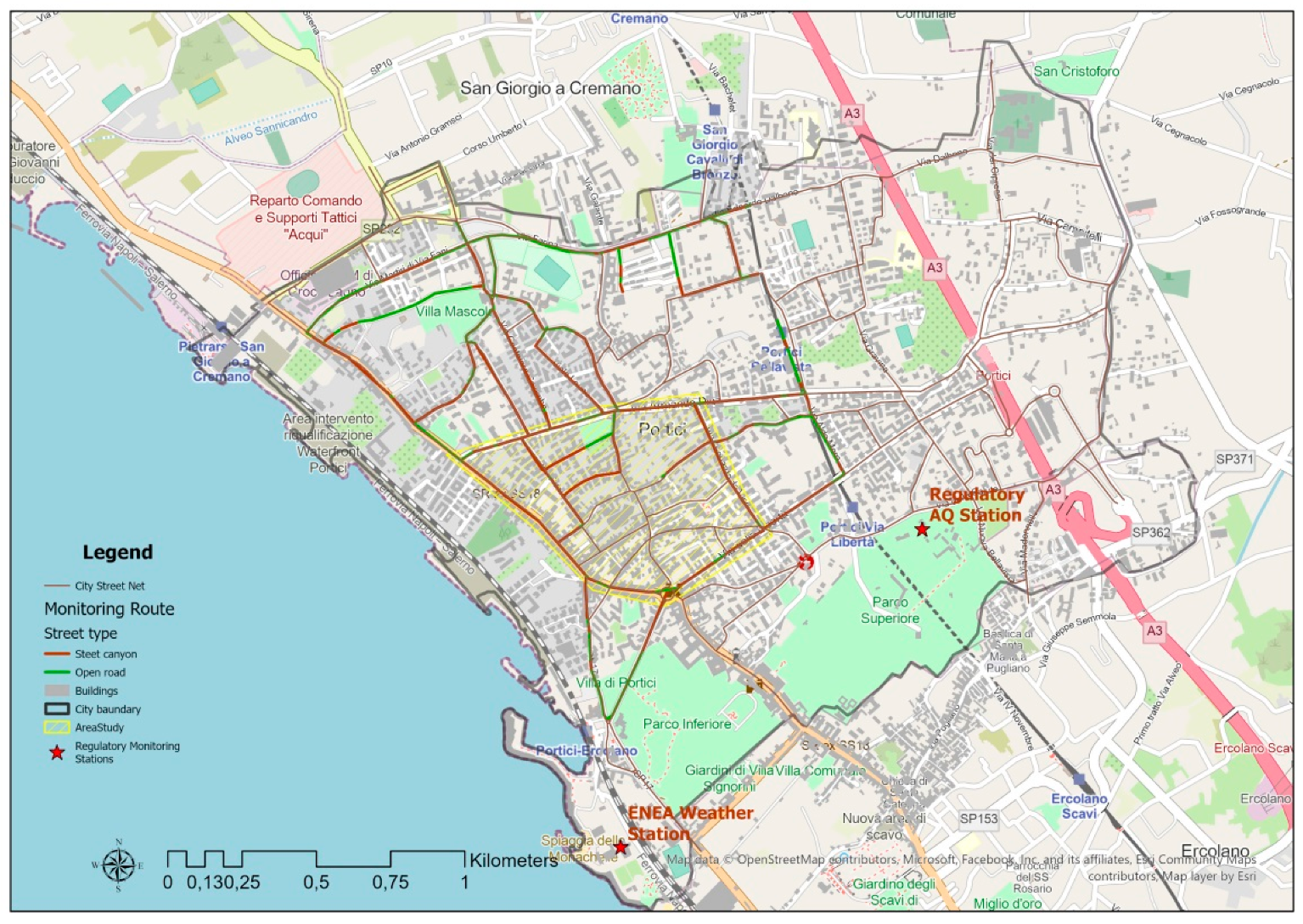
2.1. The Case Study
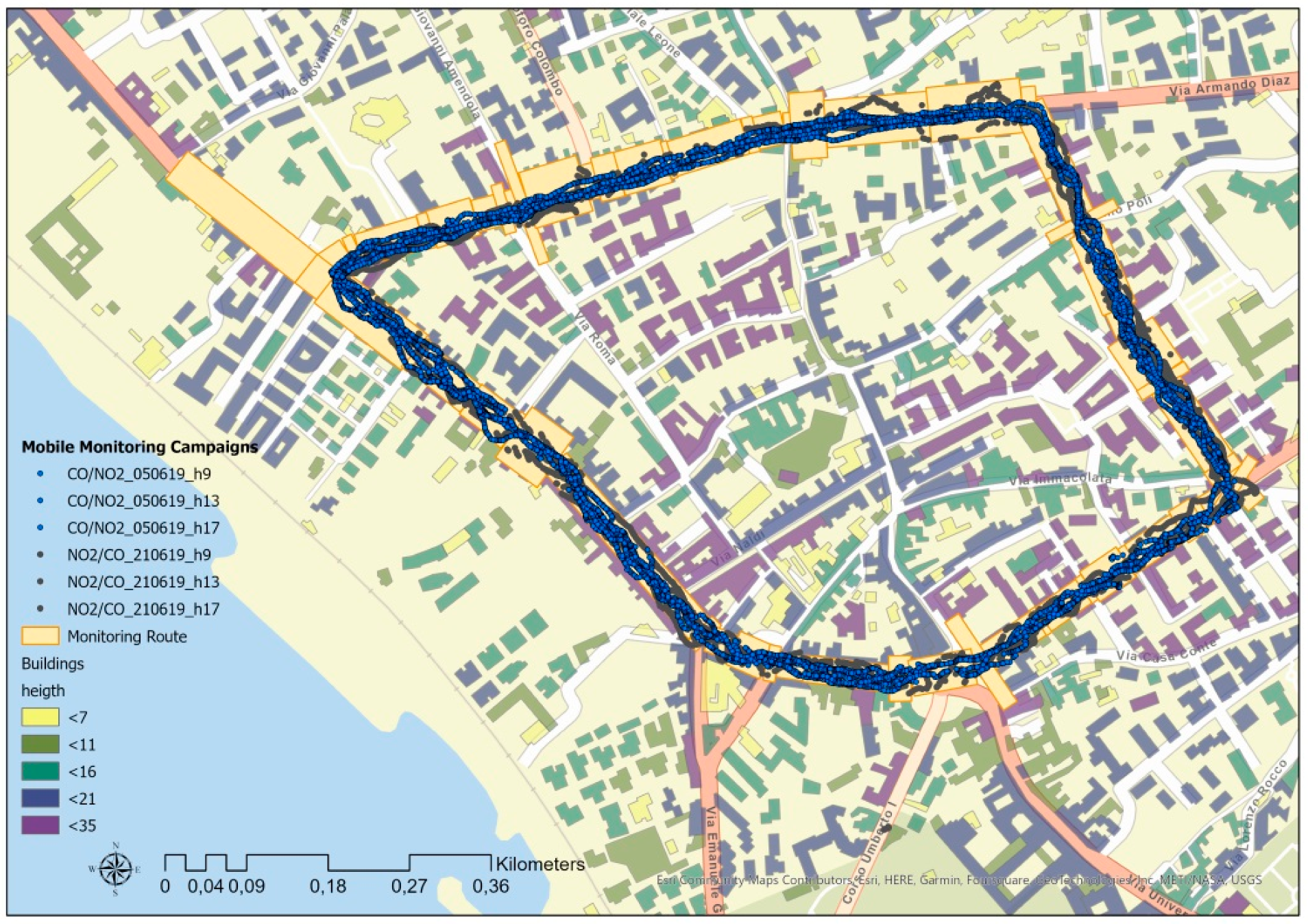
2.2. Mobile Monitoring Campaigns
2.3. Traffic Vehicular Campaigns
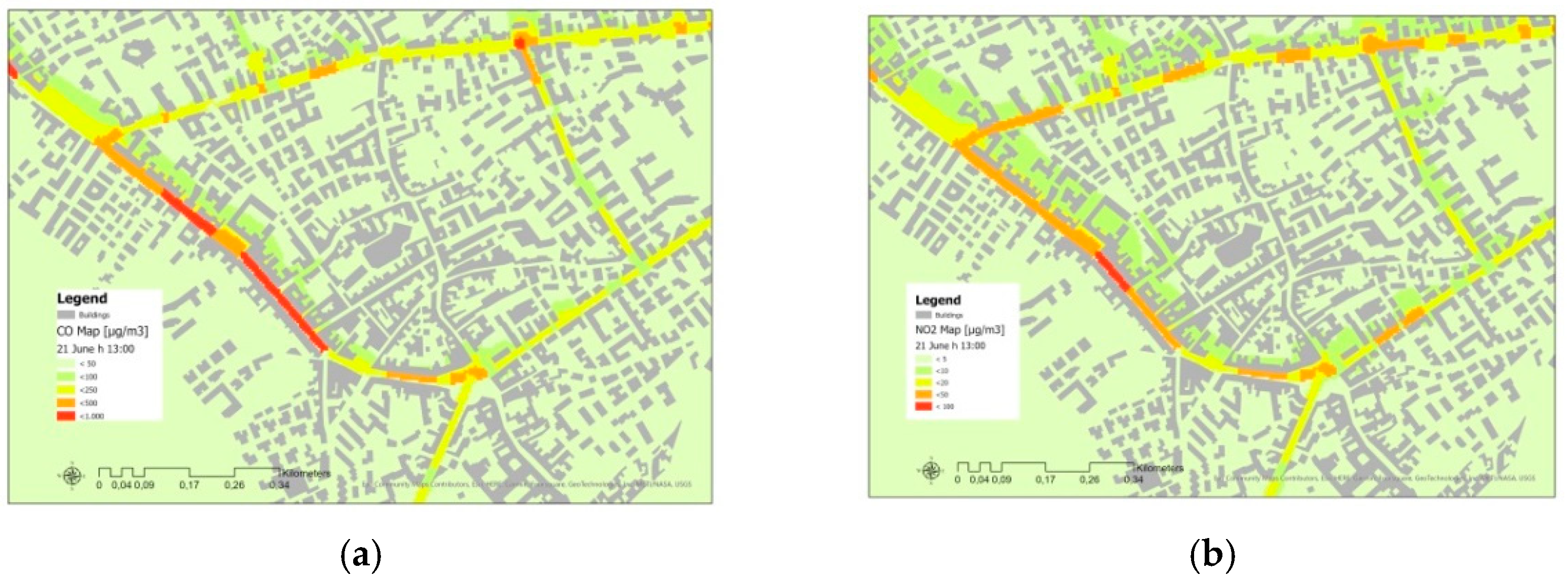
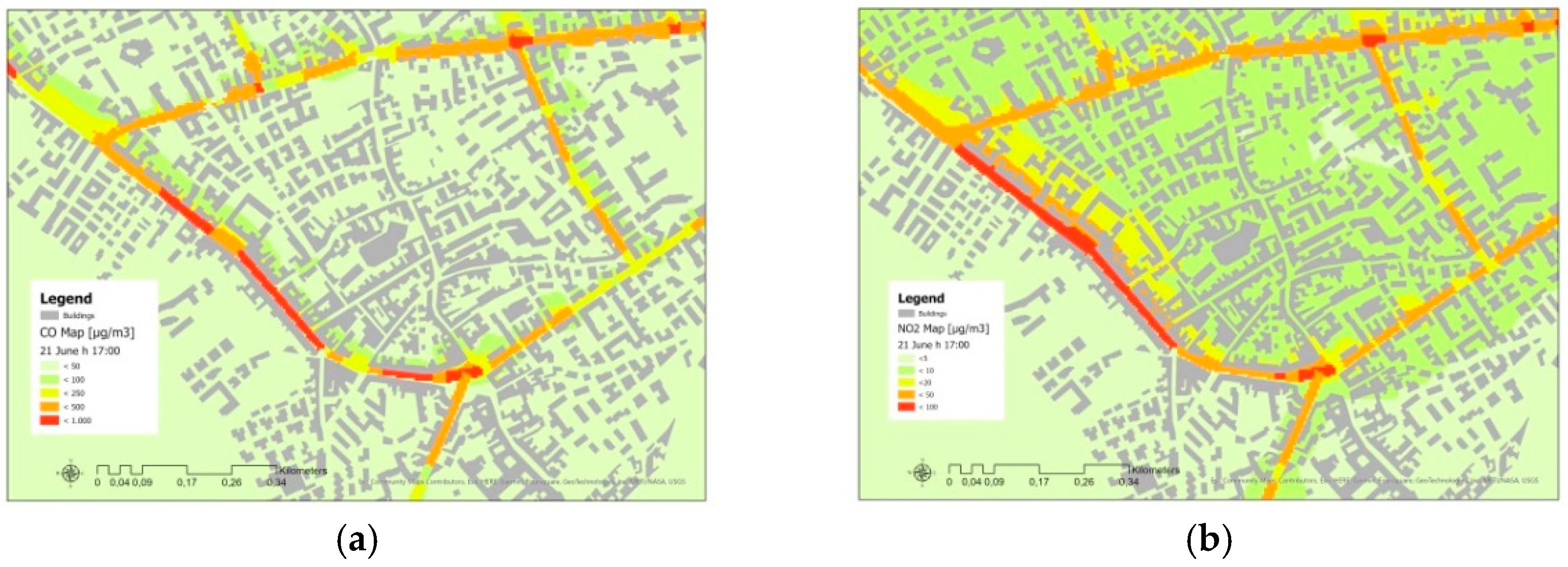
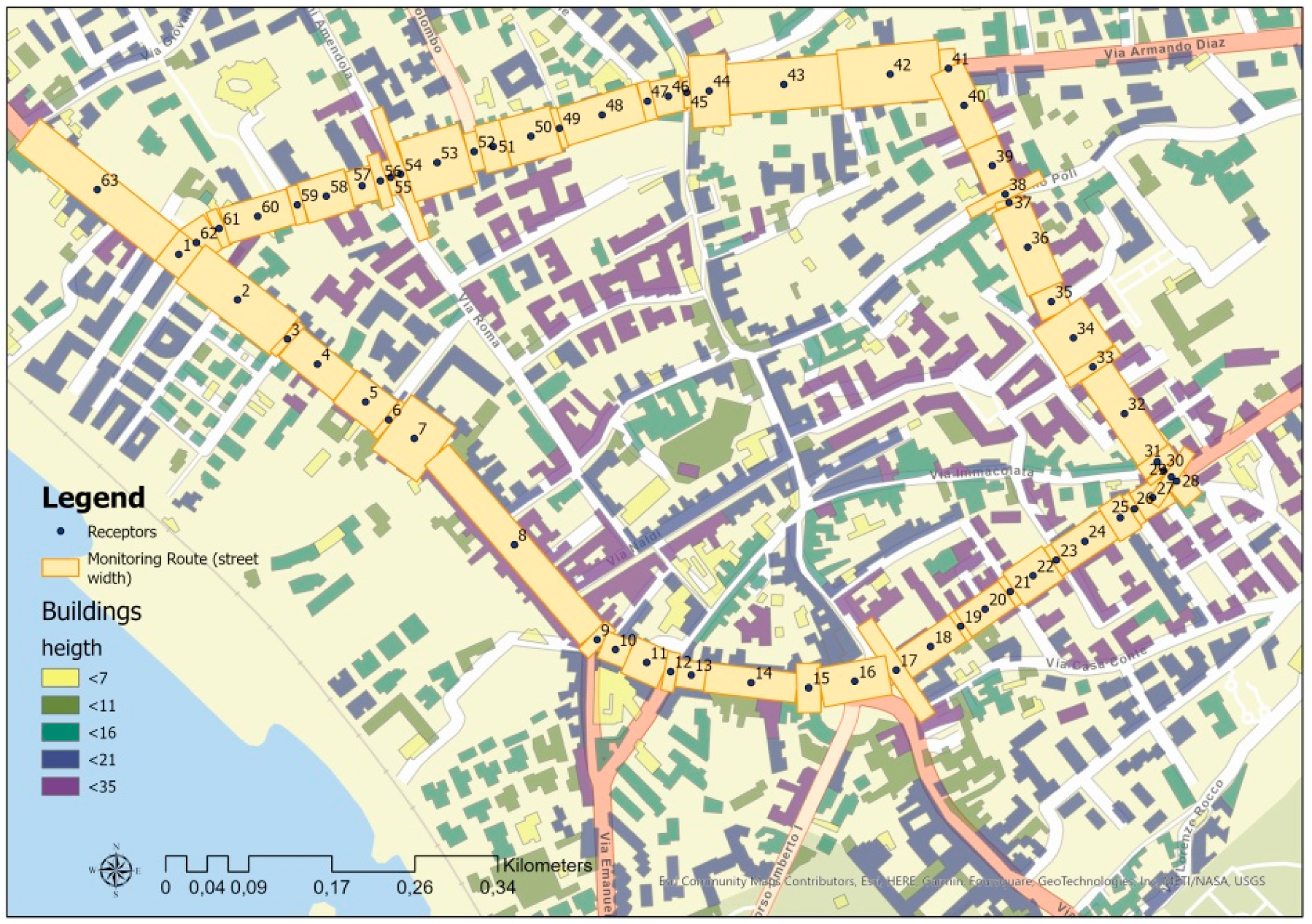
2.4. SIRANE Air Pollution Maps
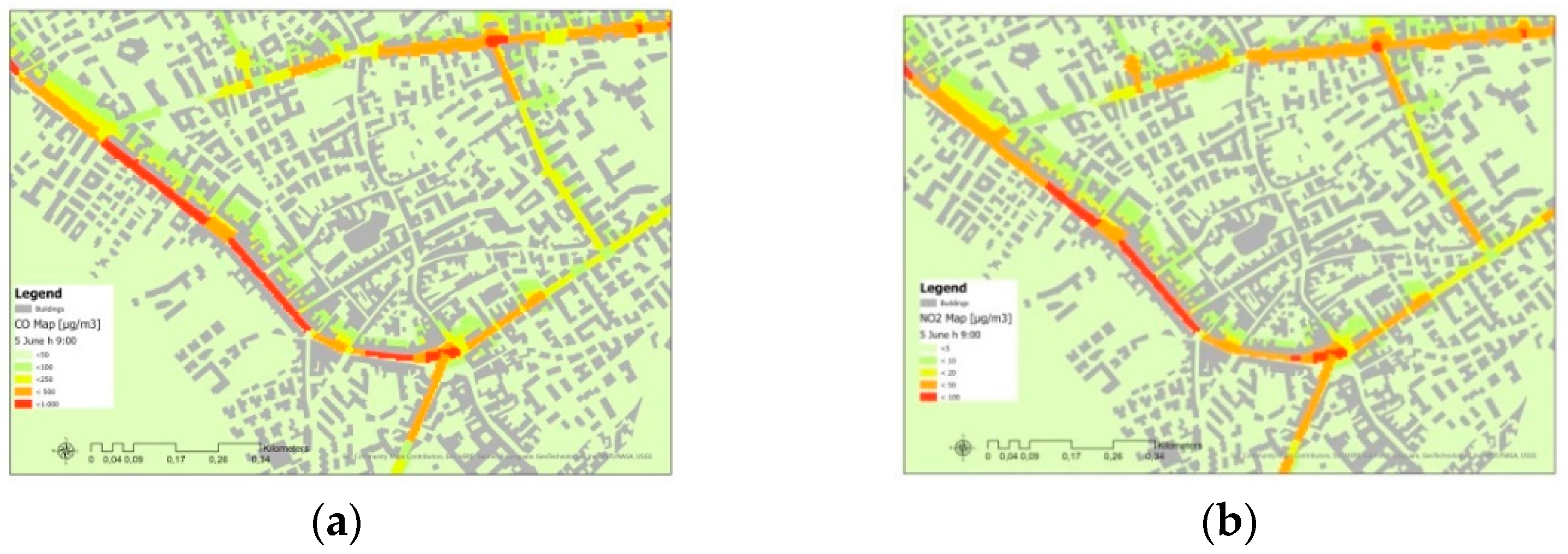
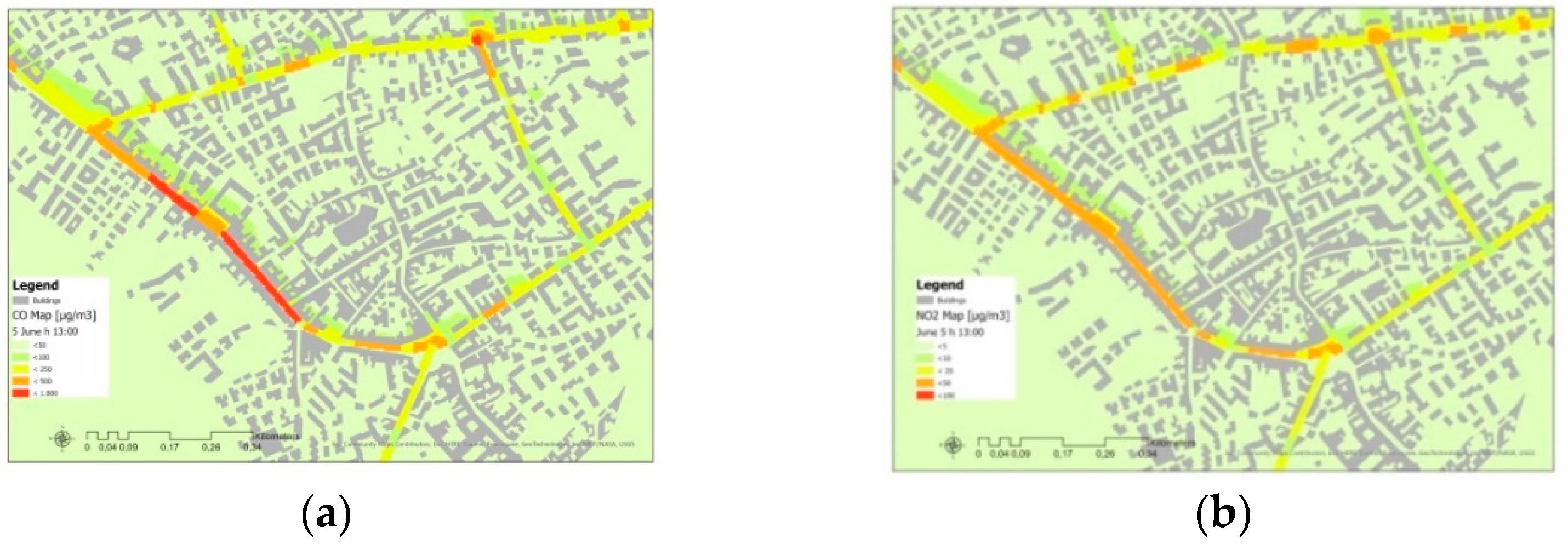
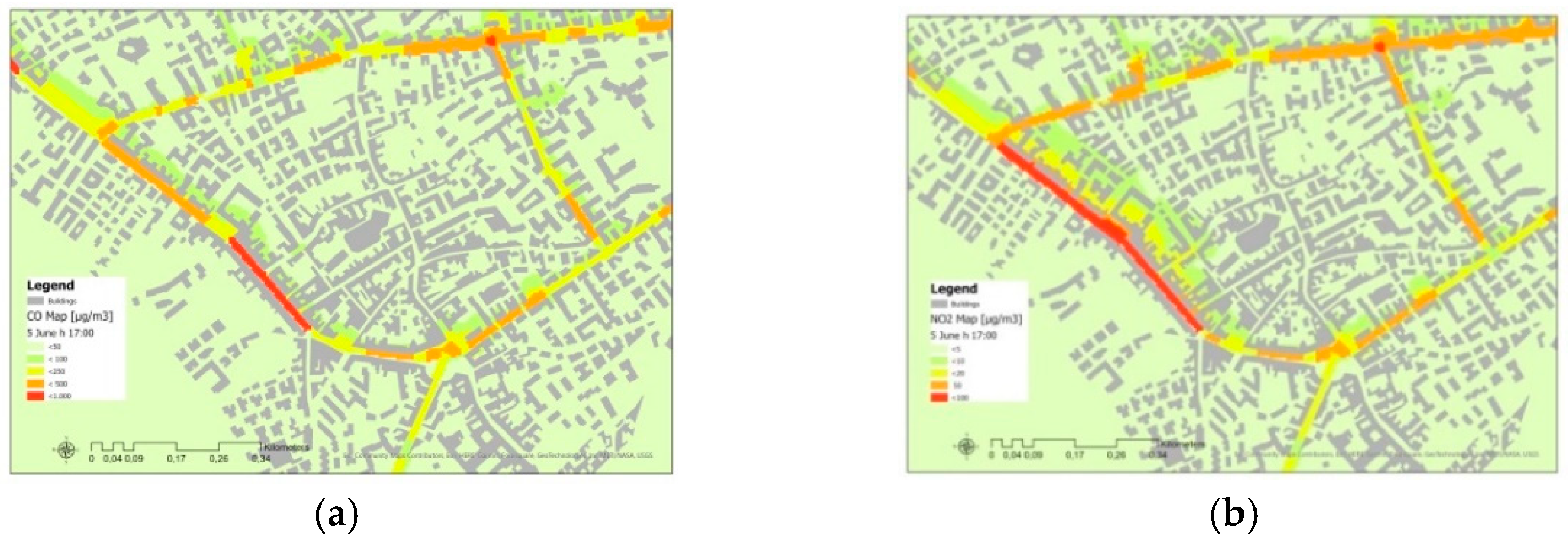
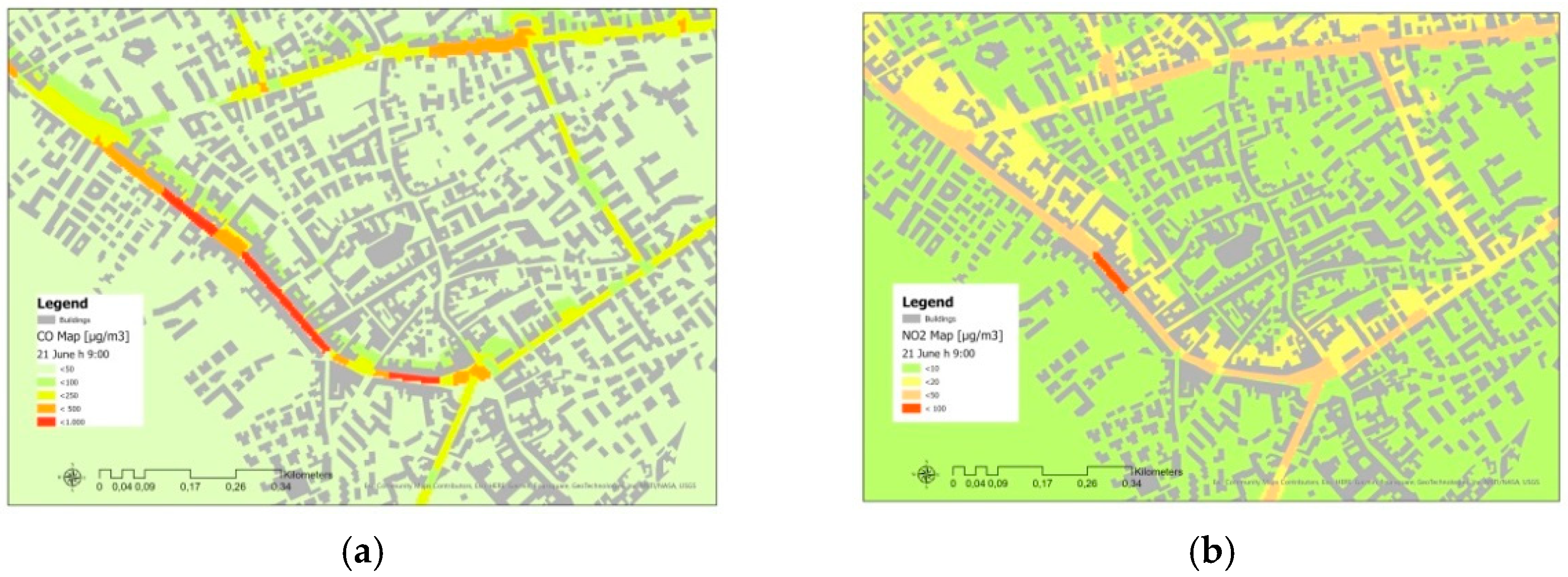
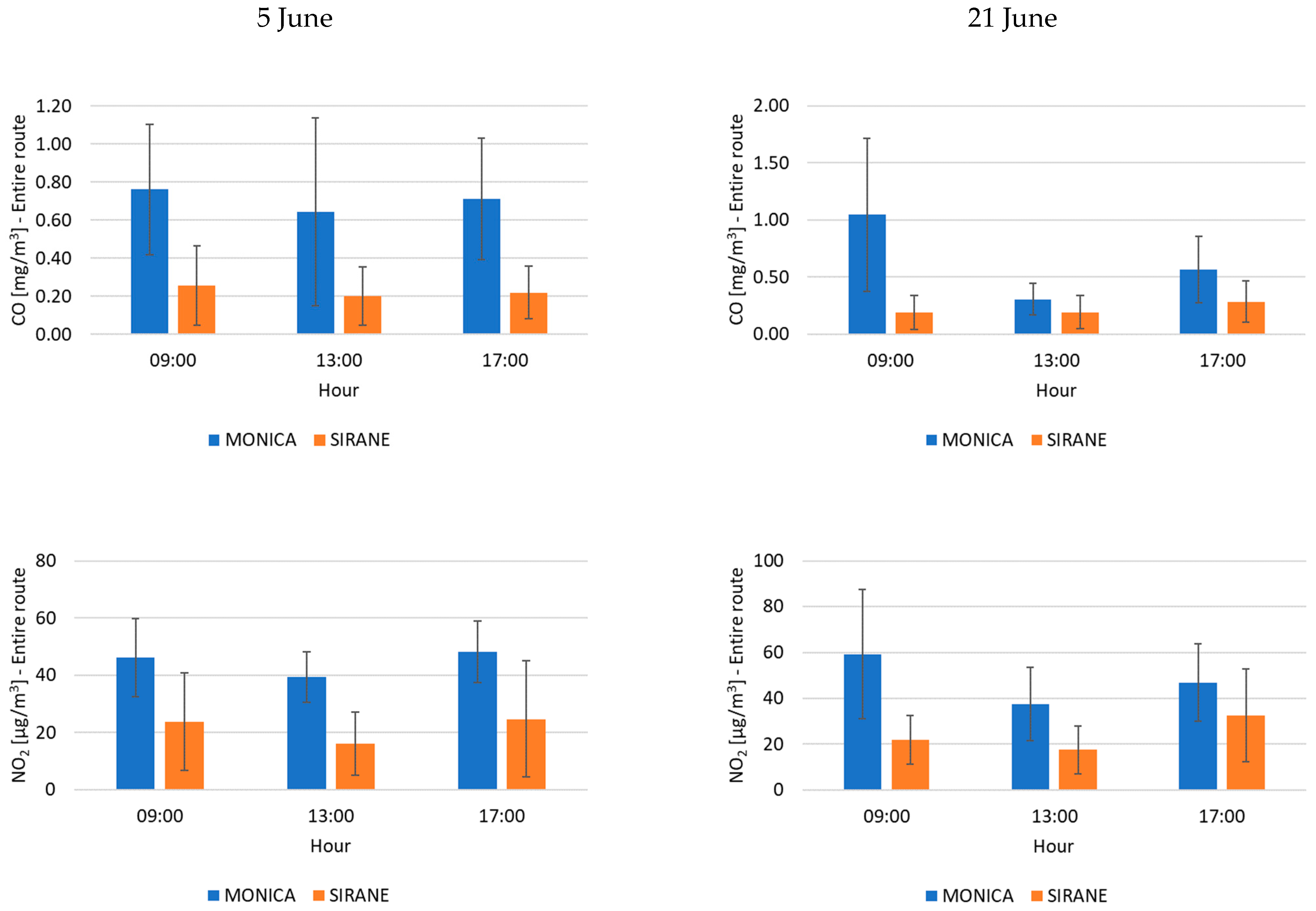
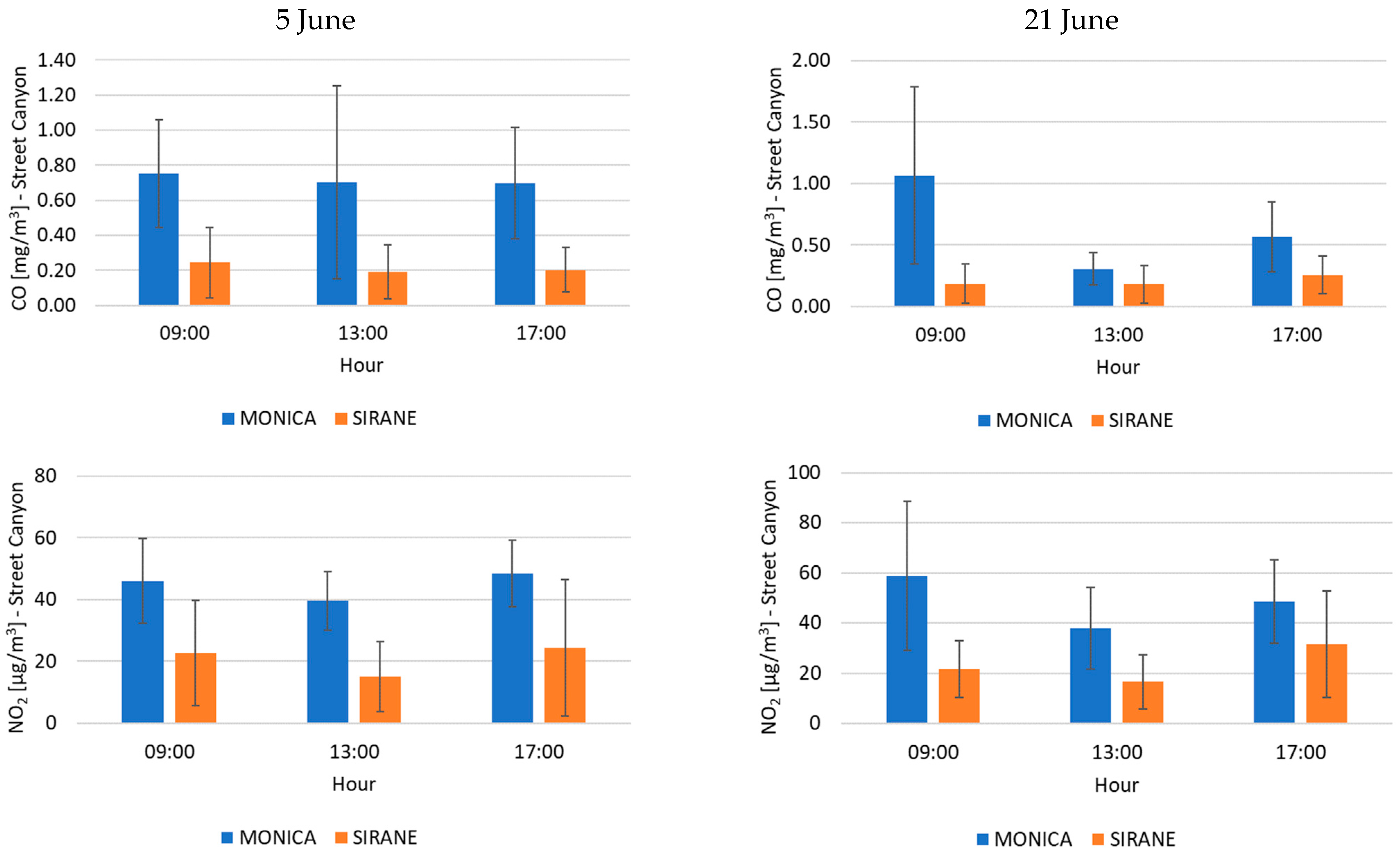
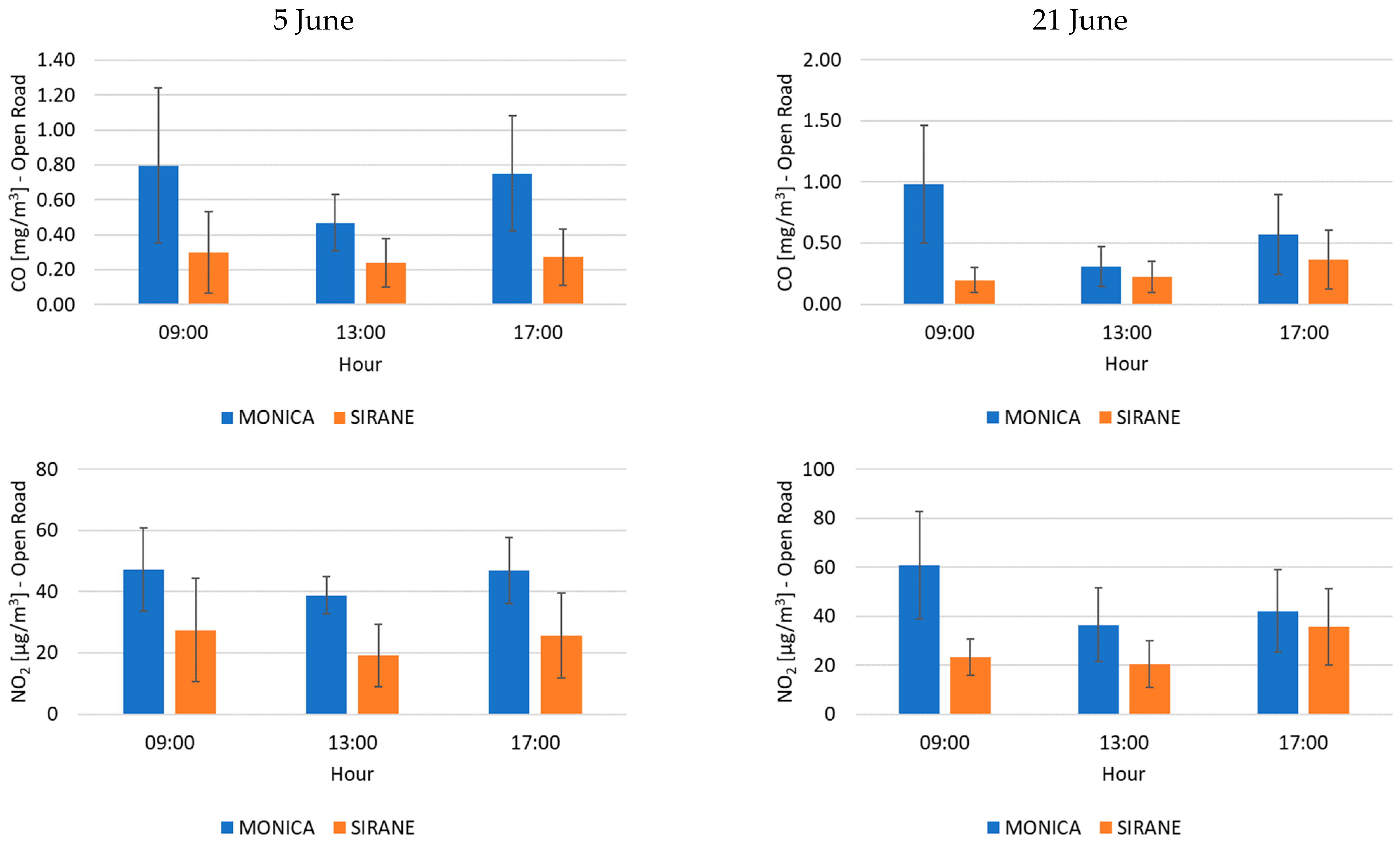
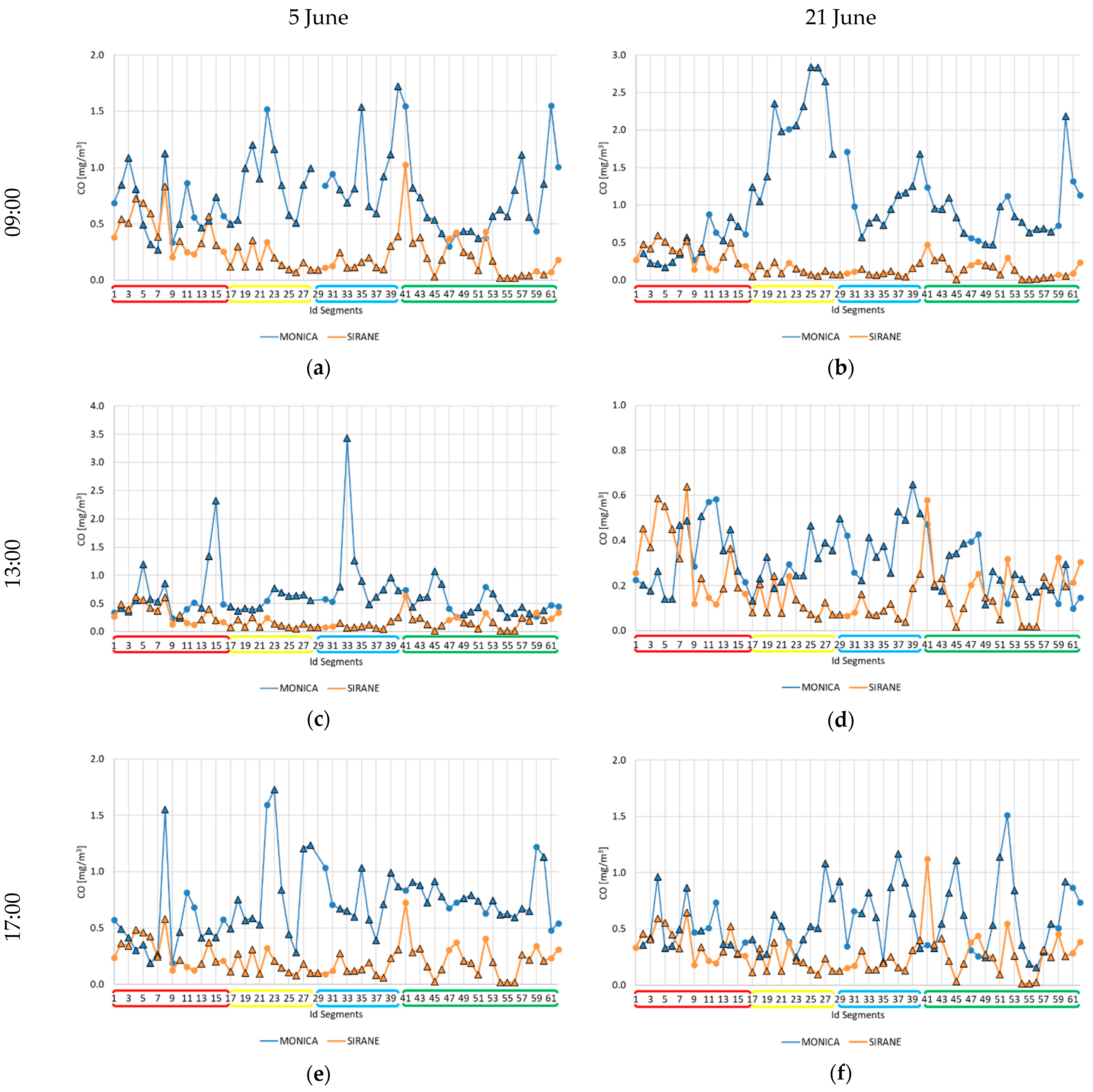
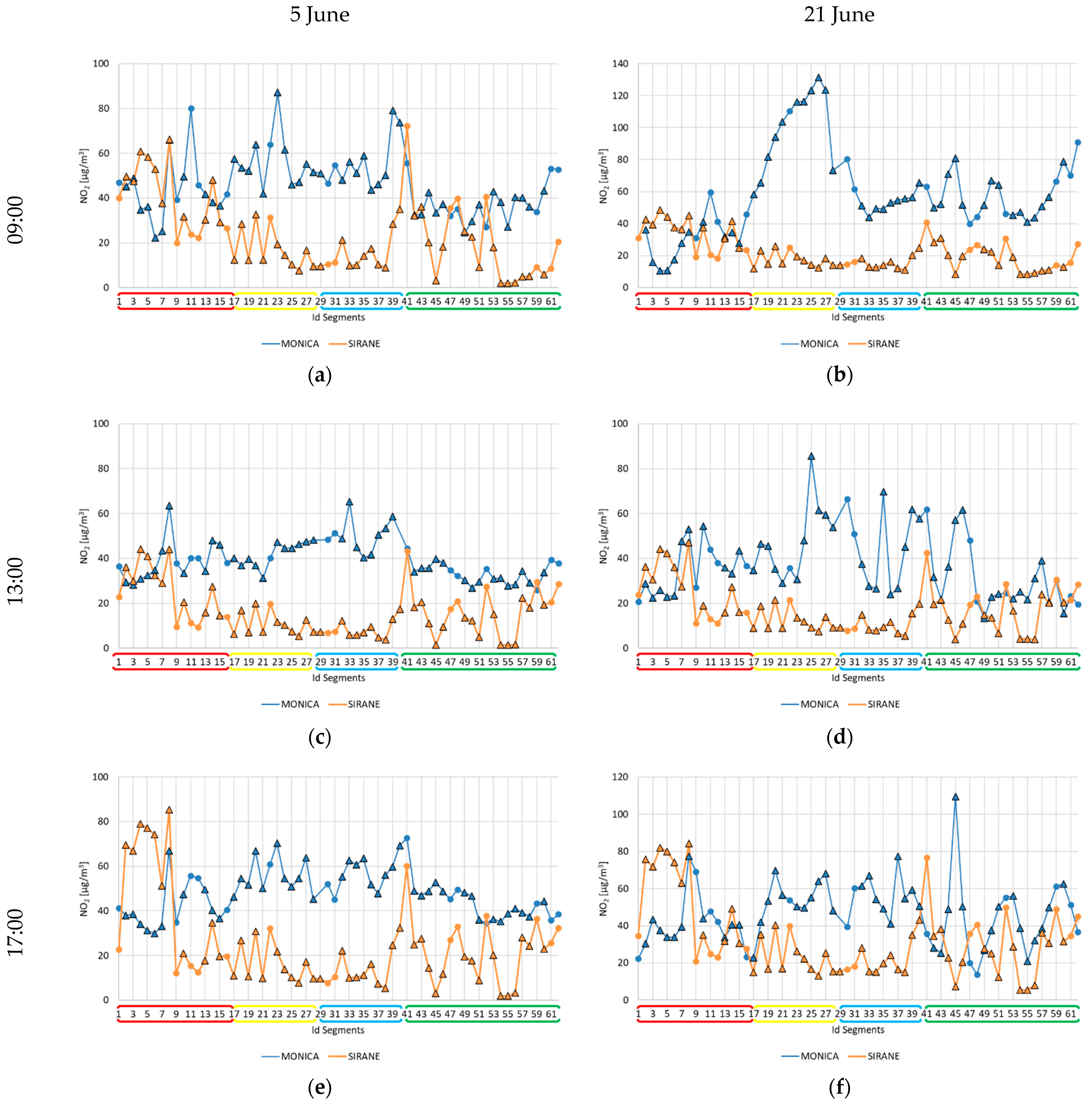
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- European Environment Agency. Europe’s Air Quality Status 2020 Report. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/status-of-air-quality-in-Europe-2022 (accessed on 31 October 2022).
- Toscano, D.; Murena, F. The historical trend of air pollution and its impact on human health in Campania region (Italy). Atmosphere 2021, 12, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardoulakis, S.; Solazzo, E.; Lumbreras, J. Intra-urban and street scale variability of BTEX, NO2 and O3 in Birmingham, UK: Implications for exposure assessment. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 5069–5078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, J.; Van den Bossche, J.; Reggente, M.; Van Poppel, M.; De Baets, B.; Theunis, J. Cyclist exposure to UFP and BC on urban routes in Antwerp, Belgium. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 92, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murena, F.; Prati, M.V. Spatial variability of fine particle number concentration in an urban area. In Proceedings of the Seventh International Conference on Environmental Management, Engineering, Planning and Economics (CEMEPE 2019) and SECOTOX Conference, Mykonos Island, Greece, 19–24 May 2019; pp. 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, J.G.; Kingham, S.; Pearce, J.; Sturman, A.P. A review of intraurban variations in particulate air pollution: Implications for epidemiological research. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 6444–6462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattoruso, G.; Nocerino, M.; Toscano, D.; Pariota, L.; Sorretino, G.; Manna, V.; De Vito, S.; Carteni, A.; Fabbricino, M.; Di Francia, G. Site suitability analysis for low-cost sensor networks for urban spatially dense air pollution monitoring. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apte, J.S.; Messier, K.P.; Gani, S.; Brauer, M.; Kirchstetter, T.W.; Lunden, M.M.; Marshall, J.D.; Portier, C.J.; Vermeleu, R.C.H.; Hamburg, S.P. High-resolution air pollution mapping with Google street view cars: Exploiting big data. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6999–7008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steffens, J.; Kimbrough, S.; Baldauf, R.; Isakov, V.; Brown, R.; Powell, A.; Deshmukh, P. Near-port air quality assessment utilizing a mobile measurement approach. Atmos Pollut Res. 2017, 8, 1023–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Gu, P.; Li, H.Z.; Robinson, E.S.; Lipsky, E.; Kaltsonoudis, C.; Lee, A.K.Y.; Apte, J.S.; Robinson, A.L.; Sullivan, R.C.; et al. Spatial variability of sources and mixing state of atmospheric particles in a metropolitan area. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 6807–6815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, E.; De Vito, S.; Salvato, M.; Fattoruso, G.; Di Francia, G. Computational intelligence for smart air quality monitors calibration. In Computational Science and Its Applications; LNCS; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 10406, pp. 443–454. [Google Scholar]
- Zwack, L.M.; Hanna, S.R.; Spengler, J.D.; Levy, J.I. Using advanced dispersion models and mobile monitoring to characterize spatial patterns of ultrafine particles in an urban area. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 4822–4829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merbitz, H.; Fritz, S.; Schneider, C. Mobile measurements and regression modeling of the spatial particulate matter variability in an urban area. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 438, 389–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulhac, L.; Salizzoni, P.; Cierco, F.X.; Perkins, R. The model SIRANE for atmospheric urban pollutant dispersion; PART I, presentation of the model. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 7379–7395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CERC. ADMS-Urban. 2016. Available online: http://www.cerc.co.uk/ADMS-Urban (accessed on 31 October 2022).
- Wallace, J.; Corr, D.; Deluca, P.; Kanaroglou, P.; McCarry, B. Mobile monitoring of air pollution in cities: The case of Hamilton, Ontario, Canada. J Environ Monitor. 2009, 11, 998–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwack, L.M.; Paciorek, C.J.; Spengler, J.D.; Levy, J.I. Characterizing local traffic contributions to particulate air pollution in street canyons using mobile monitoring techniques. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 2507–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Bossche, J.; Peters, J.; Verwaeren, J.; Botteldooren, D.; Theunis, J.; De Baets, B. Mobile monitoring for mapping spatial variation in urban air quality: Development and validation of a methodology based on an extensive dataset. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 105, 148–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasenfratz, D.; Saukh, O.; Walser, C.; Hueglin, C.; Fierz, M.; Arn, T.; Beutel, J.; Thiele, L. Deriving high-resolution urban air pollution maps using mobile sensor nodes. Pervasive Mob Comput. 2015, 16, 268–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Bossche, J.; Theunis, J.; Elen, B.; Peters, J.; Botteldooren, D.; De Baets, B. Opportunistic mobile air pollution monitoring: A case study with city wardens in Antwerp. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 141, 408–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vito, S.; Esposito, E.; Massera, E.; Formisano, F.; Fattoruso, G.; Ferlito, S.; Del Giudice, A.; D’Elia, G.; Salvato, M.; Polichetti, T.; et al. Crowdsensing IoT architecture for pervasive air quality and exposome monitoring: Design, development, calibration, and long-term validation. Sensors 2021, 21, 5219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vito, S.; Fattoruso, G.; D’Elia, G.; Esposito, E.; Ferlito, S.; Del Giudice, A.; Massera, E.; Loffredo, G.; Di Francia, G. Hyper resoluted air quality maps in urban environment with crowdsensed data from intelligent low cost sensors. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Symposium on Olfaction and Electronic Nose (ISOEN), 29 May–1 June 2022; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Peruzzi, C.; Ramel-Delobel, M.; Coudon, T.; Fervers, B.; De Vito, S.; Fattoruso, G.; Salizzoni, P. Air pollution measurements during commuting in Lyon (No. EGU22-13150). In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly 2022, Vienna, Austria, 23–27 May 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ntziachristos, L.; Gkatzoflias, D.; Kouridis, C.; Samaras, Z. COPERT: A European road transport emission inventory model. In Information Technologies in Environmental Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 491–504. [Google Scholar]
- Soulhac, L.; Salizzoni, P.; Mejean, P.; Perkins, R.J. Parametric laws to model urban pollutant dispersion with a street network approach. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 67, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulhac, L.; Perkins, R.J.; Salizzoni, P. Flow in a street canyon for any external wind direction. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 2008, 126, 365–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulhac, L.; Garbero, V.; Salizzoni, P.; Mejean, P.; Perkins, R.J. Flow and dispersion in street intersections. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 2981–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salizzoni, P.; Soulhac, L.; Mejean, P. Street canyon ventilation and atmospheric turbulence. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 5056–5067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulhac, L.; Salizzoni, P.; Mejean, P.; Didier, D.; Rios, I. The model SIRANE for atmospheric urban pollutant dispersion; PART II, validation of the model on a real case study. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 49, 320–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulhac, L.; Nguyen, C.V.; Volta, P.; Salizzoni, P. The model SIRANE for atmospheric urban pollutant dispersion. PART III: Validation against NO2 yearly concentration measurements in a large urban agglomeration. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 167, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biemmi, S.; Gaveglio, R.; Salizzoni, P.; Boffadossi, M.; Casadei, S.; Bedogni, M.; Carbero, V.; Soulhac, L. Estimate of boundary layer parameters and background concentrations for pollutant dispersion modeling in urban areas. In Proceedings of the 31st NATO/SPS International Technical Meeting on Air Pollution Modelling and its Application, Torino, Italy, 27 September–1 October 2010; p. 27. [Google Scholar]
- Castagnetti, F.B.; Salizzoni, P.; Garbero, V.; Genon, G.; Soulhac, L. Atmospheric pollution modelling in urban areas at local scale: An example of the application to a neighborhood in Turin. Geoing Ambient E Min. 2008, 124, 63–76. [Google Scholar]
- Garbero, V.; Salizzoni, P.; Soulhac, L. Experimental study of pollutant dispersion within a network of streets. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 2010, 136, 457–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giambini, P.; Salizzoni, P.; Soulhac, L.; Corti, A. Air quality modelling system for traffic scenario analysis in Florence: Model validation and identification of critical issues. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Harmonisation within Atmospheric Dispersion Modelling for Regulatory Purposes (HARMO 2010), Paris, France, 1–4 June 2010; pp. 195–199. [Google Scholar]
- Pognant, F.; Bo, M.; Nguyen, C.V.; Salizzoni, P.; Clerico, M. Modelling and evaluation of emission scenarios deriving from wood biomass boilers in alpine valley. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Harmonisation within Atmospheric Dispersion Modelling for Regulatory Purposes (HARMO 2017), Bologna, Italy, 9–12 October 2017; pp. 9–12. [Google Scholar]
- Pognant, F.; Bo, M.; Nguyen, C.V.; Salizzoni, P.; Clerico, M. Design, modelling and assessment of emission scenarios resulting from a network of wood biomass boilers. Environ. Model. Assess. 2018, 23, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, N.B.; Garbero, V.; Salizzoni, P.; Lamaison, G.; Soulhac, L. Modelling pollutant dispersion in a street network. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 2015, 155, 157–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpentieri, M.; Salizzoni, P.; Robins, A.; Soulhac, L. Evaluation of a neighbourhood scale, street network dispersion model through comparison with wind tunnel data. Environ. Model. Softw. 2012, 37, 110–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, M.; Charvolin-Volta, P.; Clerico, M.; Nguyen, C.V.; Pognant, F.; Soulhac, L.; Salizzoni, P. Urban air quality and meteorology on opposite sides of the Alps: The Lyon and Torino case studies. Urban Clim. 2020, 34, 100698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, M.; Salizzoni, P.; Pognant, F.; Mezzalama, R.; Clerico, M. A combined citizen science—Modelling approach for NO2 assessment in Torino urban agglomeration. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murena, F.; Toscano, D. High emitting vehicles and sustainable development of urban areas. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Air Quality—Science and Application, Thessalonik, Greece, 27 June–1 July 2022. [Google Scholar]
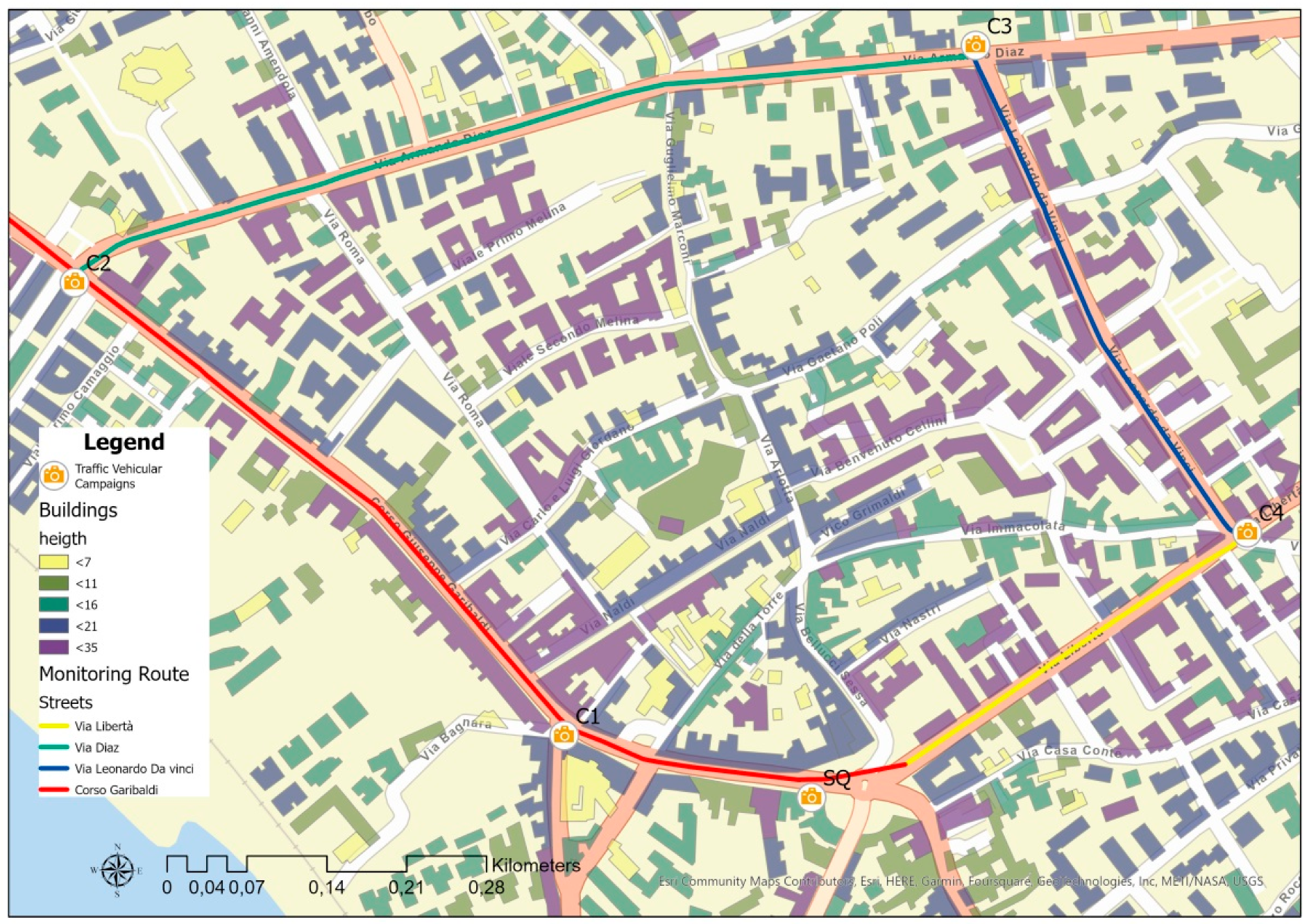
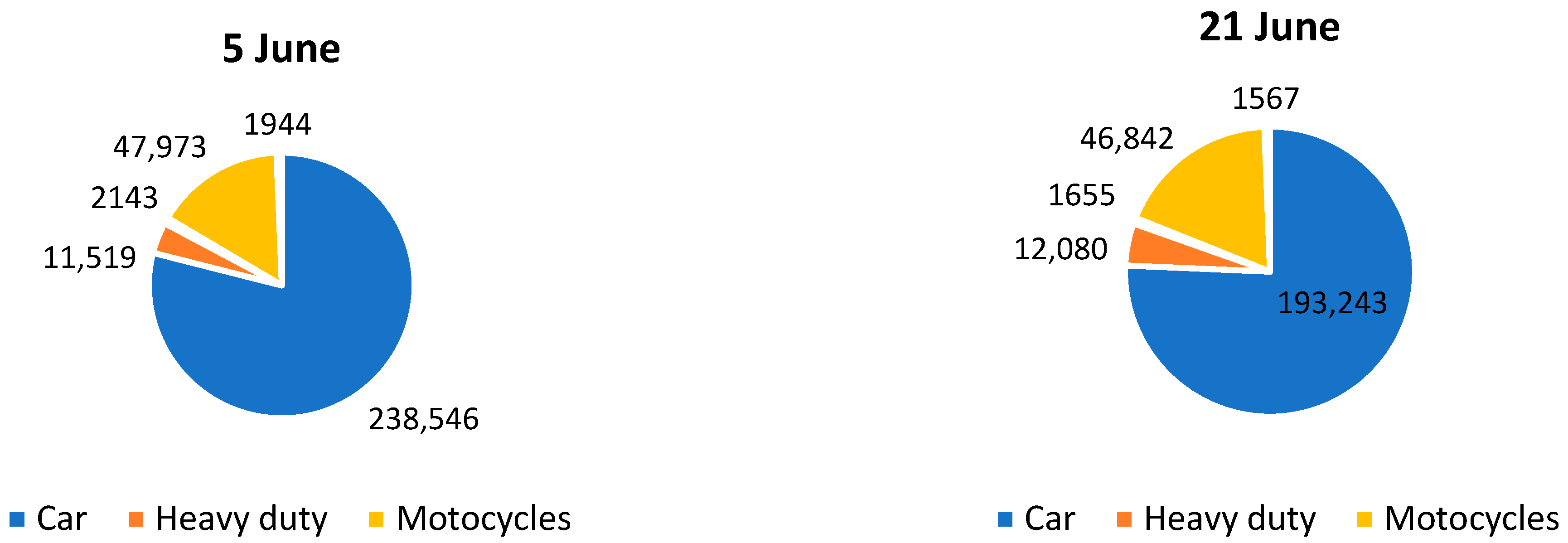
| Street Name | Number of Segments | Street Canyons | Average Width [m] | Average Height of Building [m] | Length [m] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Via Libertà | 12 | 11 | 21.45 | 20.31 | 367.23 |
| Via Diaz | 22 | 15 | 24.82 | 17.62 | 824.89 |
| Via Da Vinci | 12 | 10 | 23.31 | 23.04 | 486.91 |
| Corso Garibaldi | 16 | 11 | 20.45 | 18.53 | 908.18 |
| Total (Vehicles/Hour) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 June | 21 June | |||||
| Street | 09:00 | 13:00 | 17:00 | 09:00 | 13:00 | 17:00 |
| Via Libertà | 23,602 | 19,780 | 23,045 | 14,022 | 15,313 | 16,880 |
| Via Diaz | 28,624 | 31,949 | 32,985 | 28,334 | 30,180 | 31,117 |
| Via da Vinci | 12,376 | 10,360 | 10,638 | 7380 | 7158 | 7846 |
| Corso Garibaldi | 34,889 | 35,006 | 38,871 | 34,632 | 35,959 | 26,566 |
| Total | 99,491 | 97,095 | 105,539 | 84,368 | 88,610 | 82,409 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fattoruso, G.; Toscano, D.; Cornelio, A.; De Vito, S.; Murena, F.; Fabbricino, M.; Di Francia, G. Using Mobile Monitoring and Atmospheric Dispersion Modeling for Capturing High Spatial Air Pollutant Variability in Cities. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1933. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13111933
Fattoruso G, Toscano D, Cornelio A, De Vito S, Murena F, Fabbricino M, Di Francia G. Using Mobile Monitoring and Atmospheric Dispersion Modeling for Capturing High Spatial Air Pollutant Variability in Cities. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(11):1933. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13111933
Chicago/Turabian StyleFattoruso, Grazia, Domenico Toscano, Antonella Cornelio, Saverio De Vito, Fabio Murena, Massimiliano Fabbricino, and Girolamo Di Francia. 2022. "Using Mobile Monitoring and Atmospheric Dispersion Modeling for Capturing High Spatial Air Pollutant Variability in Cities" Atmosphere 13, no. 11: 1933. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13111933
APA StyleFattoruso, G., Toscano, D., Cornelio, A., De Vito, S., Murena, F., Fabbricino, M., & Di Francia, G. (2022). Using Mobile Monitoring and Atmospheric Dispersion Modeling for Capturing High Spatial Air Pollutant Variability in Cities. Atmosphere, 13(11), 1933. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13111933











