Dependence Analysis of PM2.5 Concentrations in 295 Chinese Cities in the Winter of 2019–2020
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data
3. Methodology
3.1. Model of First-Order Binary Markov Chain
3.2. Method of Dependence Analysis
3.3. Procedure for Dependence Analysis
4. Results and Discussion
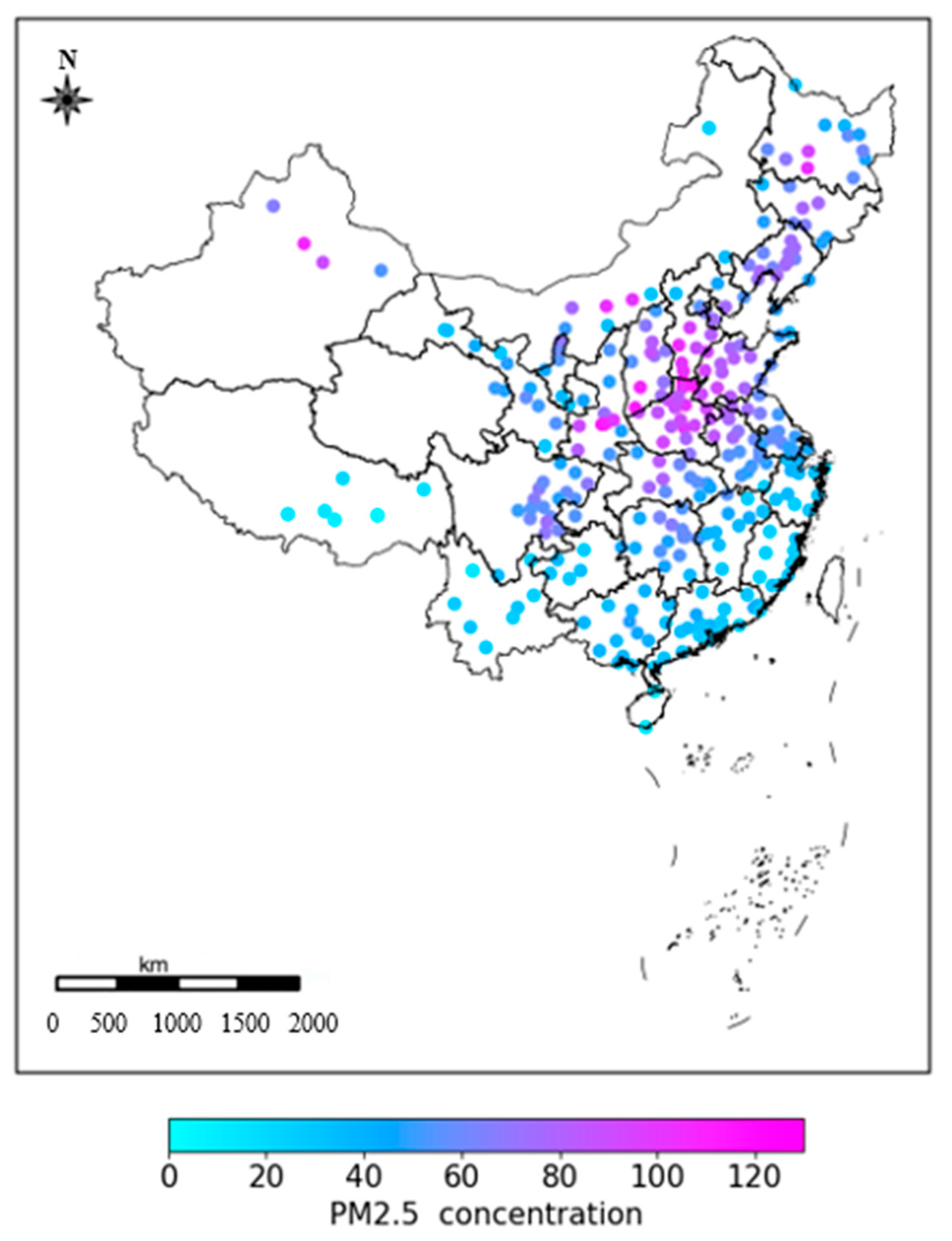
4.1. Overview of the Distribution of PM2.5 Concentration
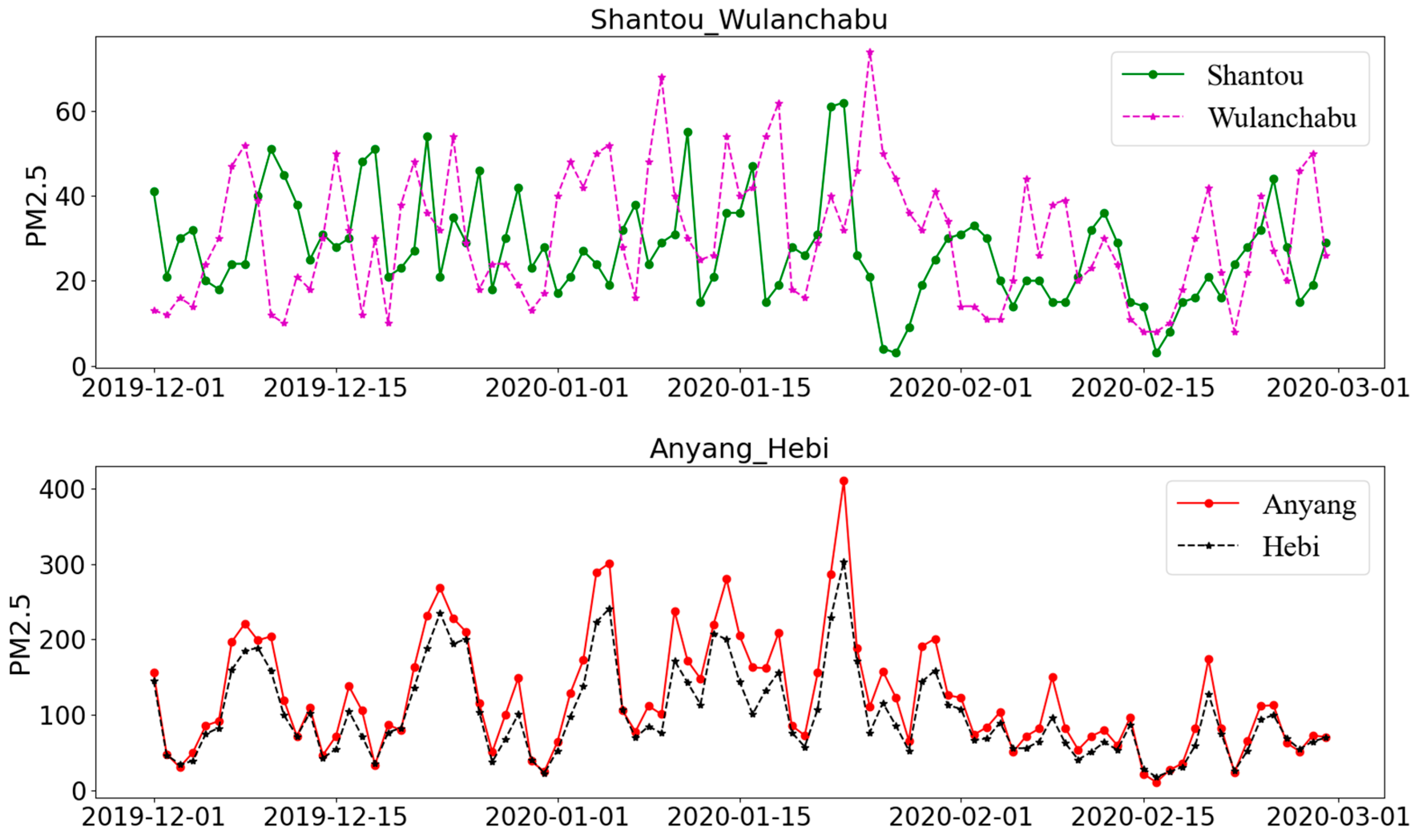
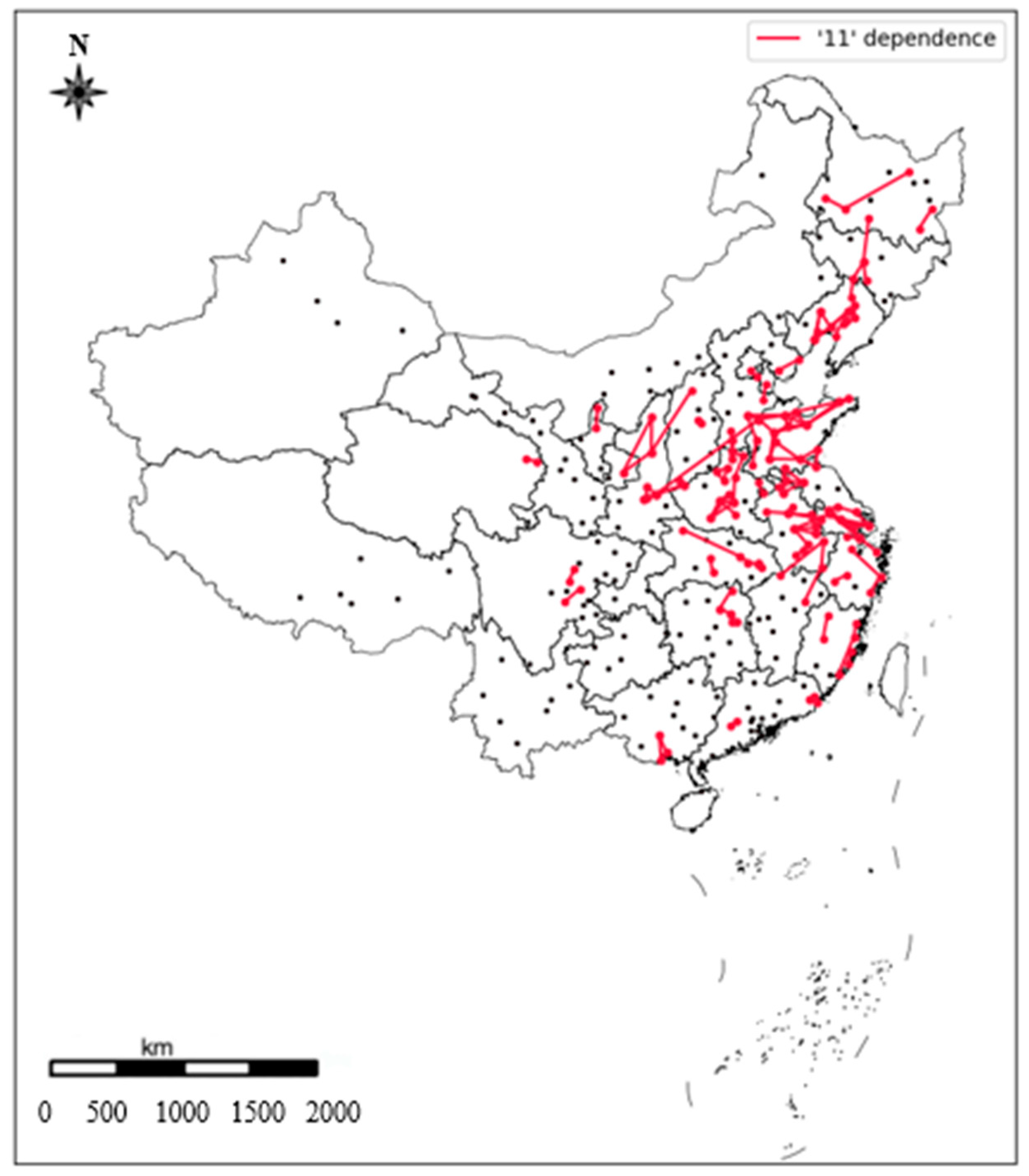
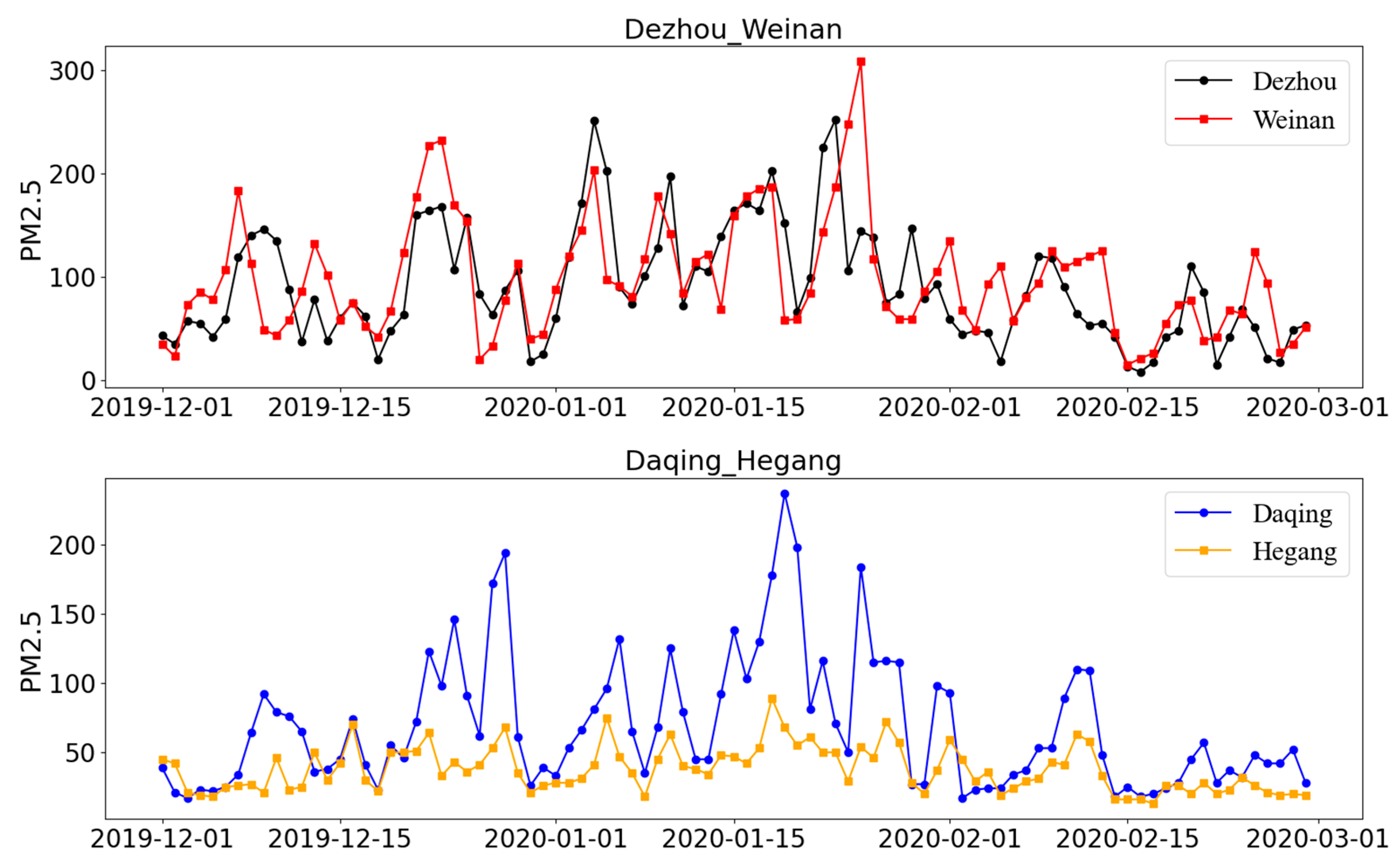
4.2. Dependence Analysis of PM2.5 Concentration
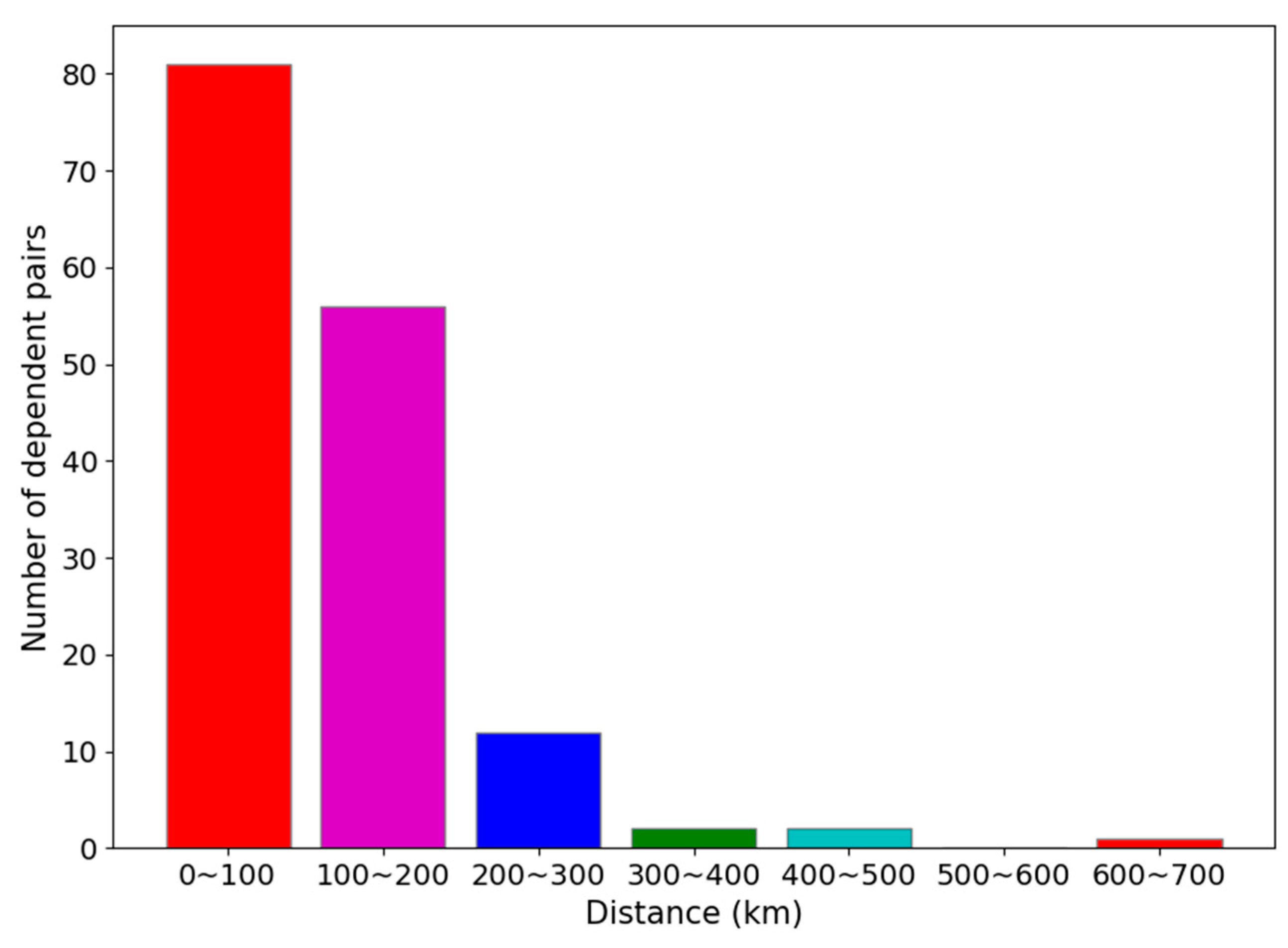
4.3. Distance of Dependent City Pairs
4.4. Topography of Dependent City Pairs
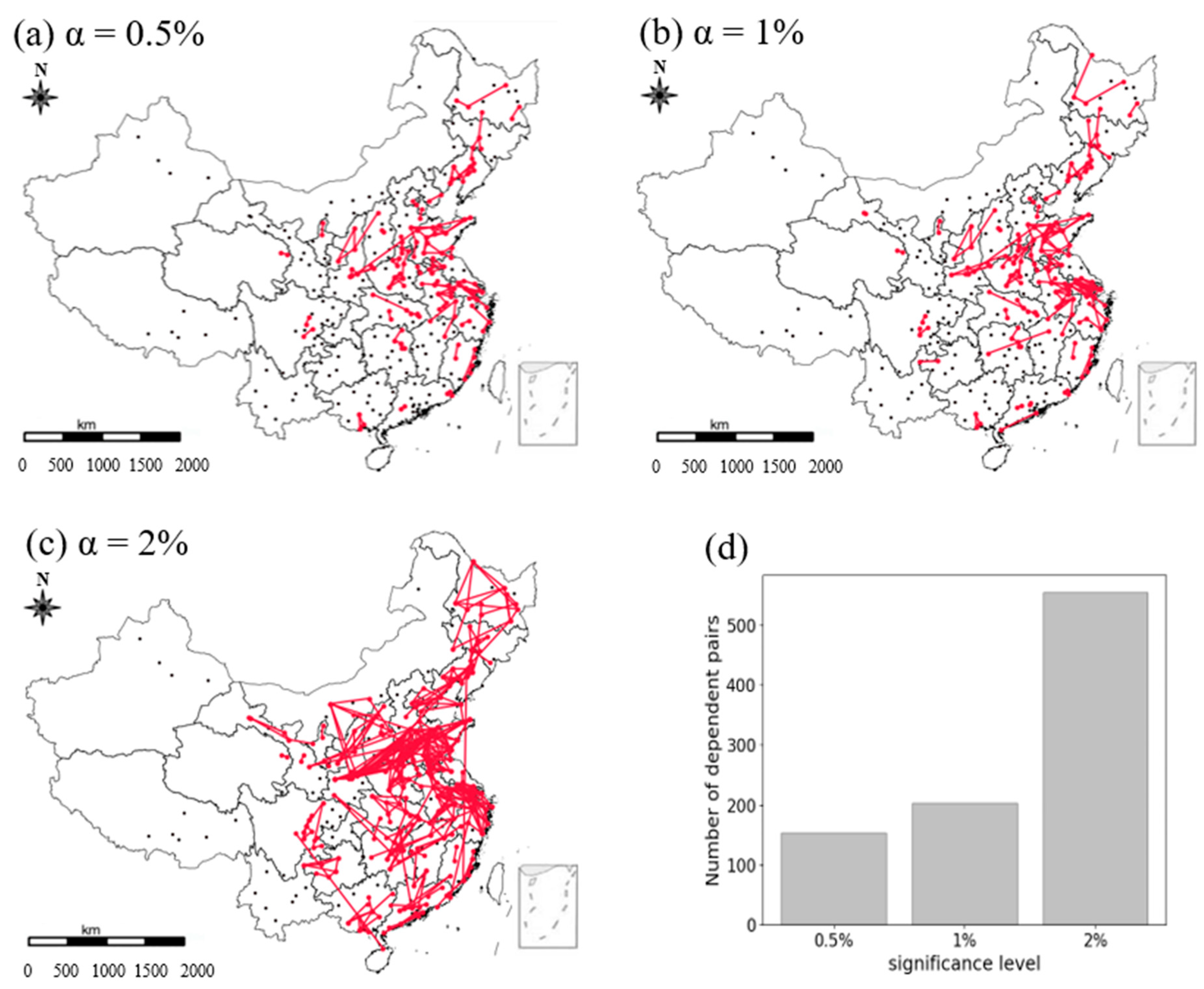
4.5. Impact of Significance Level
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lei, Y.; Davies, G.M.; Jin, H.; Tian, G.; Kim, G. Scale-dependent effects of urban greenspace on particulate matter air pollution. Urban For. Urban Green. 2021, 61, 127089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Niu, X.; Liu, Z. Effects of PM2.5 on health and economic loss: Evidence from Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region of China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 257, 120605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Chen, X.; Zhong, R.; Liu, M. Influence and prediction of PM2.5 through multiple environmental variables in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 849, 157910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, G.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Xue, T.; Zhao, H.; Tong, D.; Zheng, B.; Li, M.; Liu, F.; Hong, C.; et al. Drivers of PM2.5 air pollution deaths in China 2002–2017. Nat. Geosci. 2021, 14, 645–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, J.; Wei, Y.; Yitshak-Sade, M.; Di, Q.; Dominici, F.; Zanobetti, A. A national difference in difference analysis of the effect of PM2.5 on annual death rates. Environ. Res. 2021, 194, 110649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, M.; Sun, C.; Chen, W.; Jin, G.; Gong, J.; Zhu, M.; Yuan, J.; Dai, J.; Wang, M.; Pan, Y. Personal exposure to PM2.5, genetic variants and DNA damage: A multi-center population-based study in Chinese. Toxicol. Lett. 2015, 235, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Lin, Y.; Lin, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Yu, H.; Huang, Y.; Yang, J.; Cai, Y.; Liu, F.; Li, Y.; et al. PM2.5 induces pulmonary microvascular injury in COPD via METTL16-mediated m6A modification. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 303, 119115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Chen, J.; An, X.; Liu, F.; Liang, F.; Tang, X.; Qu, P. The impact of PM2.5 on children’s blood pressure growth curves: A prospective cohort study. Environ. Intern. 2022, 158, 107012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, I.; Khare, M.; Gargava, P.; Khan, A.A. Effect of PM2.5 chemical constituents on atmospheric visibility impairment. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2018, 68, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Fan, Q.; Liao, Z.; Xie, J.; Xu, X.; Fan, S. Spatial-temporal characteristics of the air quality in the Guangdong-HongKong-Macau Greater Bay Area of China during 2015–2017. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 210, 14–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; An, J.; Liu, M.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Tao, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, F.; Zheng, D.; Gao, Q.; et al. Spatiotemporal variations and influencing factors of PM2.5 concentrations in Beijing, China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 262, 114276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Zhang, M.; Song, Y.; Huang, B. Spatiotemporal assessment of PM2.5 concentrations and exposure in China from 2013 to 2017 using satellite-derived data. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 286, 124965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Zhong, R.; Liu, M.; Ye, C.; Chen, X. Spatiotemporal distribution characteristics of PM2.5 concentration in China from 2000 to 2018 and its impact on population. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 323, 116273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Wong, T.W.; Dong, G.H.; Ho, K.F.; Yang, Y.; Yim, S.H.L. Impacts of sectoral emissions in China and the implications: Air quality, public health, crop production, and economic costs. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 084008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Shao, C.; Zhao, R.; Guan, Y.; Chen, C. Spatio-temporal variation and driving factors analysis of PM2.5 health risks in Chinese cities. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 107937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhong, S.; Bian, X.; Yu, L. Impact of 2015–2016 EI Nino and 2017–2018 La Nina on PM2.5 concentrations across China. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 208, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Chen, H. Impact of urban morphology on the spatial and temporal distribution of PM2.5 concentration: A numerical simulation with WRF/CMAQ model in Wuhan, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 290, 222427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Jin, X.; Liu, M.; Ma, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, Y. Analysis of spatiotemporal variation of PM2.5 and its relationship to land use in China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2021, 12, 101151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Yuan, Q.; Yue, L.; Li, T. Investigation of the spatially varying relationships of PM2.5 with meteorology, topography, and emissions over China in 2015 by using modified geographically weighted regression. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 262, 114257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Liu, Y.M. The influential factors of urban PM2.5 concentrations in China: A spatial econometric analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 1443–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.H.; Ryu, J.; Choi, Y.; Jeon, S.W.; Lee, W.K. Understanding global PM2.5 concentrations and their drivers in recent decades (1998–2016). Environ. Intern. 2020, 144, 106011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Zhang, M.; Ding, Y. Exploring the effect of economic and environment factors on PM2.5 concentration: A case study of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 268, 110703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Ren, X.; Xiong, K.; Li, L.; Bi, X.; Wu, Q. Analysis of the driving factors of PM2.5 concentration in the air: A case study of the Yangtze River Delta, China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 110, 105889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shuai, C.; Bian, J.; Chen, X.; Wu, Y.; Shen, L. Socioeconomic factors of PM2.5 concentrations in 152 Chinese cities: Decomposition analysis using LMDI. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 218, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Feng, Y.J.; Liang, H.Y. The impact of meteorological factors on PM2.5 variations in Hong Kong. Earth Environ. Sci. 2017, 78, 012003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Du, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Xia, L.; Liu, J.; Pei, F. Analysis and interpretation of the particulate matter (PM10 and PM2.5) concentrations at the subway stations in Beijing, China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 45, 366–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Lei, Y.; Shi, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Li, L.; Zhang, Z. Evolution of the spatiotemporal pattern of PM2.5 concentrations in China—A case study from the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 183, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shi, G.; Zhan, Y.; Zhou, L.; Yang, F. Characteristics of PM2.5 spatial distribution and influencing meteorological conditions in Sichuan Basin, southwestern China. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 253, 118364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Zhao, C.; Yang, Y. A comprehensive analysis of the spatio-temporal variation of urban air pollution in China during 2014–2018. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 220, 117066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Jiao, M.; Huang, G.; Xia, B. Spatial-temporal heterogeneity of air pollution and its relationship with meteorological factors in the Pearl River delta, China. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 254, 118415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Zhang, P.; Liu, D. Spatiotemporal variations and influencing factors analysis of PM2.5 concentrations in Jilin province, Northeast China. Chin. Geo. Sci. 2018, 28, 810–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Yuan, Q.; Li, T.; Shen, H.; Zhang, L. The relationships between PM2.5 and meteorological factors in China: Seasonal and regional variations. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, D.; Xie, X.; Cai, J.; Zhuang, Y.; Cheng, N.; He, B.; Gao, B. Spatial self-aggregation effects and national division of city-level PM2.5 concentrations in China based on spatiotemporal clustering. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 207, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Duan, Y.; Li, L.; Xu, L.; Yang, Y. Spatiotemporal trends of PM2.5 concentrations and typical regional pollutant transport during 2015–2018 in China. Urban Clim. 2020, 34, 100710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Du, P.; Samat, A.; Xia, J.; Che, M.; Xue, Z. Spatiotemporal pattern of PM2.5 concentrations in mainland China and analysis of its influencing factors using geographically weighted regression. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, D.; Gozolchiani, A.; Ashkenazy, Y.; Havlin, S. Teleconnection paths via climate network direct link detection. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 115, 268501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boers, N.; Goswami, B.; Rheinwalt, A.; Bookhagen, B.; Hoskins, B.; Kurths, J. Complex networks reveal global pattern of extreme-rainfall teleconnections. Nature 2019, 566, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michele, C.D.; Meroni, V.; Rahimi, L.; Deidda, C.; Ghezzi, A. Dependence types in a binarized precipitation network. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsonis, A.A.; Swanson, K.L.; Roebber, P.J. What do networks have to do with climate? Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2006, 87, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsonis, A.A.; Swanson, K.L. Topology and predictability of EI Nino and La Nina networks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 228502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Yu, Y.; Yin, D.; He, J.; Liu, N.; Qu, J.; Xiao, J. Annual and diurnal variations of gaseous and particulate pollutants in 31 provincial capital cities based on in situ air quality monitoring data from China National Environmental Monitoring Center. Environ. Int. 2016, 86, 92–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilks, D.S. Statistical Methods in the Atmospheric Sciences; Elsevier Academic Press Publications: San Diego, CA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, R. Effects of atmospheric circulations on the interannual variation in PM2.5 concentrations over the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region in 2013–2018. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 7667–7682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Cai, X.; Yu, M.; Wang, X.; Song, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, T. Regional PM2.5 pollution confined by atmospheric internal boundaries in the North China Plain: Analysis based on surface observations. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 841, 156728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
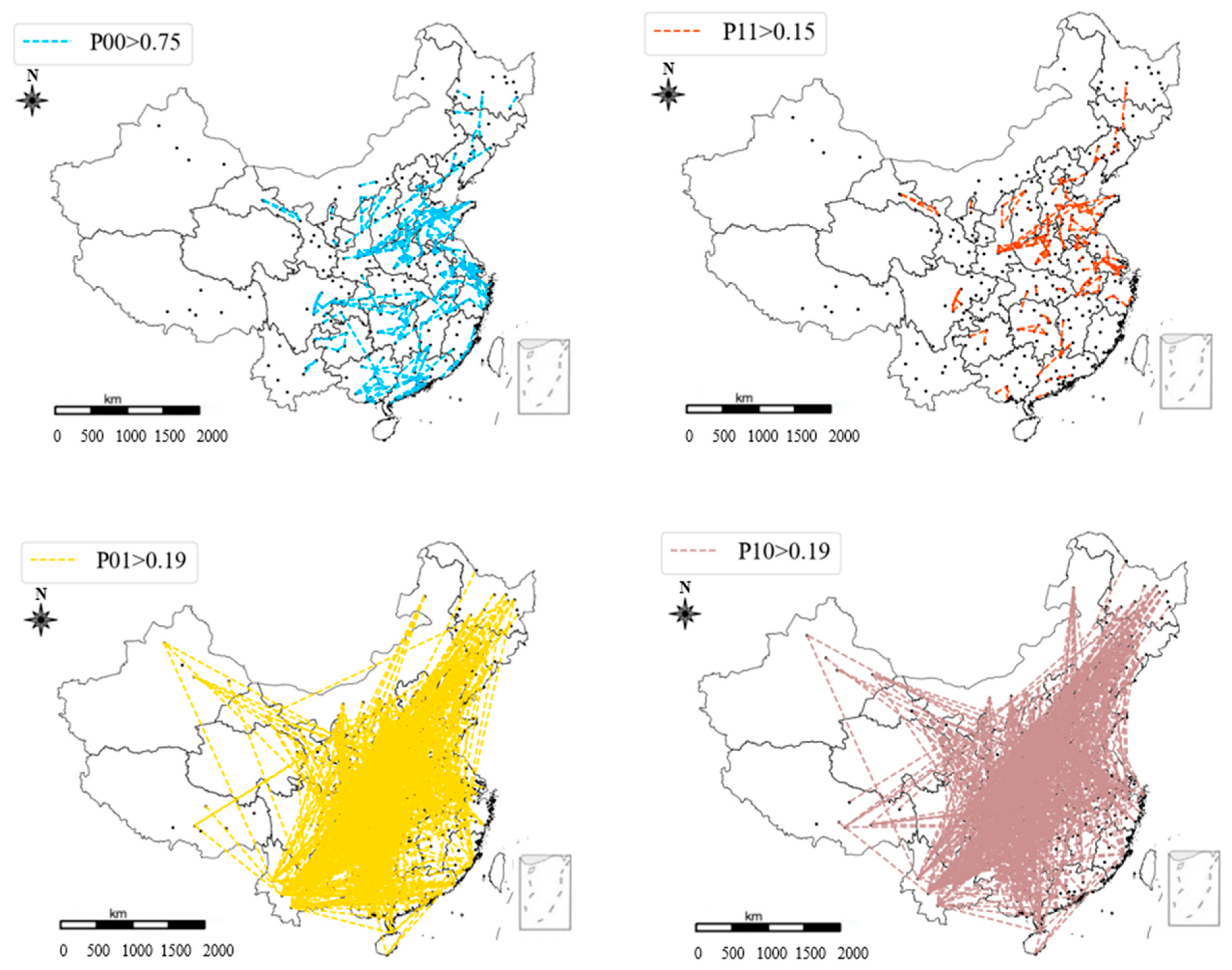
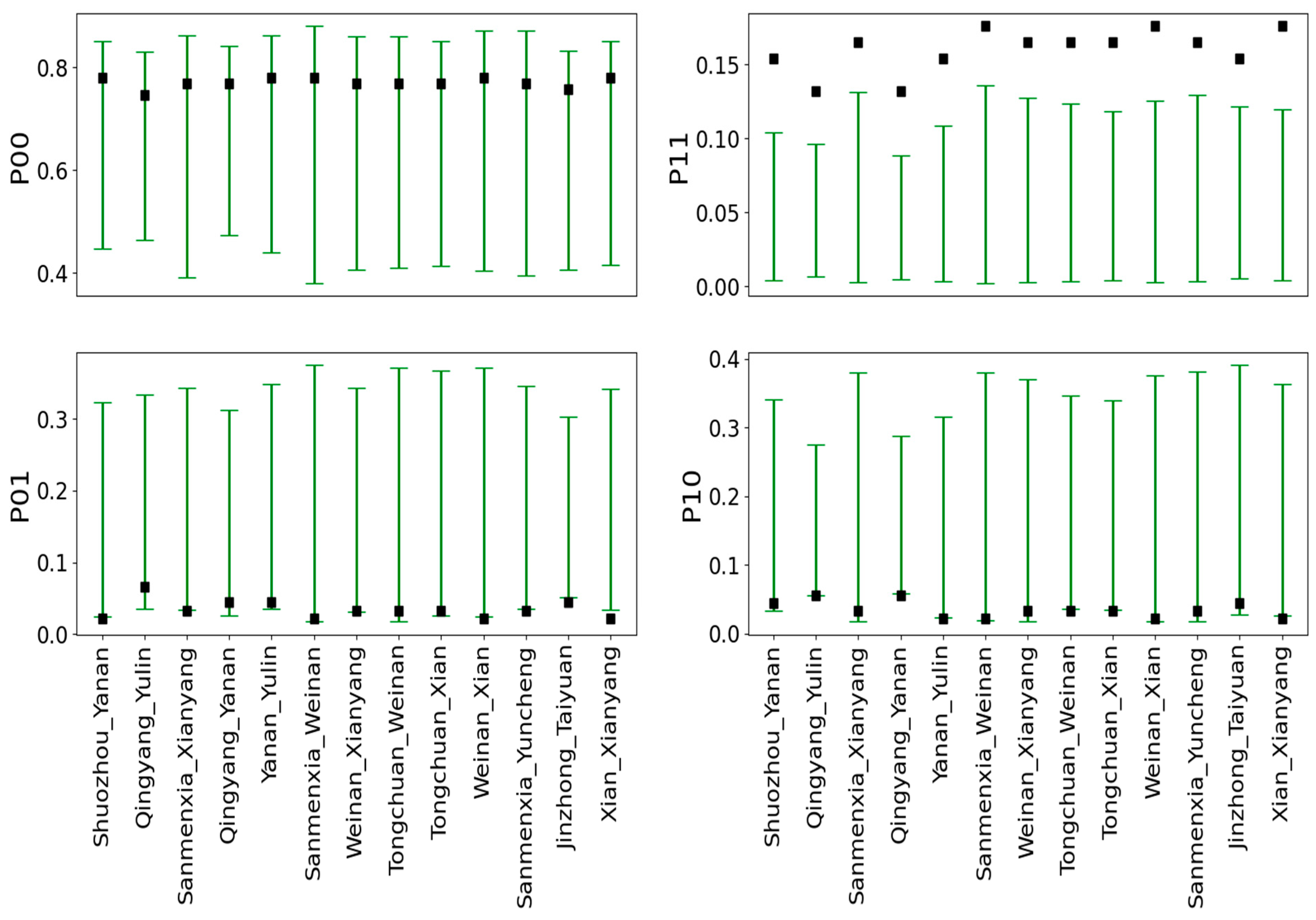
| Dependence Type | Definition |
|---|---|
| “00” | Co-occurrence of PM2.5 non-extreme for city i and PM2.5 non-extreme for city j |
| “01” | Co-occurrence of PM2.5 non-extreme for city i and PM2.5 extreme for city j |
| “10” | Co-occurrence of PM2.5 extreme for city i and PM2.5 non-extreme for city j |
| “11” | Co-occurrence of PM2.5 extreme for city i and PM2.5 extreme for city j |
| City_Pairs | Distance (km) | Dependence Type |
|---|---|---|
| Dezhou_Weinan | 697.218 | “11” |
| Daqing_Hegang | 402.310 | “11” |
| Shuozhou_Yanan | 402.272 | “11” |
| Shiyan_Xiaogan | 350.414 | “11” |
| Qingyang_Yulin | 341.317 | “11” |
| Xuancheng_Jiujiang | 298.152 | “11” |
| Weihai_Weifang | 277.361 | “11” |
| Dongying_Yantai | 244.838 | “11” |
| Huludao_Shenyang | 244.575 | “11” |
| Harbin_Changchun | 240.657 | “11” |
| Sanmenxia_Xianyang | 233.391 | “11” |
| Weifang_Yantai | 219.554 | “11” |
| Hangzhou_Taizhou | 217.661 | “11” |
| Fuzhou_Xiamen | 214.872 | “11” |
| Hengshui_Binzhou | 206.768 | “11” |
| Zhenjiang_Jiaxing | 204.263 | “11” |
| Huangshan_Yingtan | 203.517 | “11” |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bai, C.; Yan, P. Dependence Analysis of PM2.5 Concentrations in 295 Chinese Cities in the Winter of 2019–2020. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1847. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13111847
Bai C, Yan P. Dependence Analysis of PM2.5 Concentrations in 295 Chinese Cities in the Winter of 2019–2020. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(11):1847. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13111847
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Chunmei, and Ping Yan. 2022. "Dependence Analysis of PM2.5 Concentrations in 295 Chinese Cities in the Winter of 2019–2020" Atmosphere 13, no. 11: 1847. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13111847
APA StyleBai, C., & Yan, P. (2022). Dependence Analysis of PM2.5 Concentrations in 295 Chinese Cities in the Winter of 2019–2020. Atmosphere, 13(11), 1847. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13111847






