Abstract
In recent years, ozone (O3) concentration has shown a decreasing trend in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei (BTH) region in China. However, O3 pollution remains a prominent problem. Accurate estimation of O3 exposure levels can provide support for epidemiological studies. A total of 13 variables were combined to estimate short- and long-term O3 exposure levels using the geographically weighted regression (GWR) model in the BTH region with a spatial resolution of 1 × 1 km from 2017 to 2020. Five variables were left in the GWR model. O3 concentration was positively correlated with temperature, wind speed, and SO2, whereas is was negatively correlated with precipitation and NO2. Results showed that the model performed well. Leave-one-out cross-validation (LOOCV) R2 for short- and long-term simulation results were 0.91 and 0.71, and the values for RMSE were 11.14 and 3.49 μg/m3, respectively. The annual maximum 8 h average O3 concentration was the highest in 2018 and the lowest in 2020. Decreasing concentrations of major precursors of O3 due to the regional joint prevention and control may be the reason. O3 concentration was high in the southeast of the BTH region, including in Hengshui, Handan, Xingtai and Cangzhou.
1. Introduction
Ground-level ozone (O3) is mainly produced by nitrogen oxides (NOx) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) through complex photochemical reactions [1]. O3 formation is influenced by the emission of precursors, photochemical transformations and meteorological conditions. O3 is a typical secondary pollutant, which not only damages the ecological environment and affects the growth of plants and animals, but also poses a certain threat to public health [2,3,4,5,6]. Epidemiological studies had indicated that short- and long-term exposure to severe O3 pollution may cause many diseases, including asthma, lung function decrements, respiratory infection, heart failure, impaired heart function, and so on [7,8,9,10]. Meanwhile, exposure to O3 pollution can lead to premature deaths [11,12]. It is estimated that there were 156,173 (95% confidence interval (CI): 79,562–303,843), 104,051 (95% CI: 35,824–200,055), and 33,456 (95% CI: 0–70,548) cases of all-cause, cardiovascular as well as respiratory death led by long-term exposure to O3 in 331 Chinese cities in 2020 [13].
According to air quality report released by Ministry of Environmental Protection for the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei (BTH) region and surrounding areas, the number of polluted days with O3 as a dominating pollutant accounted for 41%, 46%, 48.2%, and 46.6% of the total polluted days from 2017 to 2020, respectively. Meanwhile, the daily maximum 8 h average O3 concentrations were 193, 199, 196, and 180 μg/m3 during the four years, respectively [14,15,16,17]. None of them meet Class II standard (160 μg/m3) in Ambient Air Quality Standards (GB 3095-2012). Accurate estimation of O3 exposure level and reasonable analysis of the spatiotemporal distribution characteristics are significant for preventing and controlling air pollution and assessing the impact on human health [18].
At present, multiple data and methods were used to estimate the O3 concentration. Ground measurement can provide accurate O3 concentration values at monitoring sites [1,19]. However, it cannot meet the large-scale analysis of spatio-temporal distribution of O3, and the site maintenance requires a lot of human effort and material resources. Remote sensing techniques are applied to simulate O3 concentration at large spatial scales. Satellite remote sensing data can provide large-scale spatial and temporal distribution information of O3, but it is limited by atmospheric climate conditions such as clouds [20]. Chemical transport models (CTMs) can also be used to predict O3 concentration, such as Weather Research and Forecasting Community Multiscale Air Quality (WRF-CMAQ) model. Such models provide complete spatio-temporal coverage by taking into account emission patterns, meteorological conditions as well as atmospheric chemical reactions. However, there are some drawbacks including high computational costs and incorrect specification of physical processes and initial/boundary state [18,21,22]. In addition, many statistical models have been applied to pollutant concentration estimation. Kriging interpolation estimates pollutant concentrations based on Tobler’s First Law of Geography [23]. Ordinary kriging (OK) is one of the kriging interpolation techniques, which performs well in predicting air quality levels in areas where only several monitoring sites are available [24]. OK assumes a stationary mean of the variable within the search window [25]. However, the observations of O3 show high spatial heterogeneity in O3 concentrations [26]. The land use regression (LUR) model uses pollutant monitoring data and spatial predictor variables to estimate the pollutant concentration, which can reflect small-scale spatial distribution of pollutant concentrations. Multiple linear regression (MLR) establishes the global relationship between several independent variables and a dependent variable. However, it neglects the spatial variability of air pollutants [27]. To cope with deficiencies of the above model, geographically weighted regression (GWR) was proposed [28]. GWR is a local spatial statistical method with spatial variability coefficients. It incorporates data location information to predict air pollutant concentrations on a large scale. The model can provide a quantitative spatially varying relationship between air pollutant concentrations and multiple predictor variables. Moreover, the local parameter estimates obtained by the model can show a high spatial variability, compensating for the weakness of the global regression methods. The GWR model has been used in several recent studies to explore air pollutant exposure levels. By the calibration of GWR, Stowell et al. [29] simulated daily PM2.5 concentration in Southern California, and the results showed that the model performed well (cross-validation coefficient of determination (R2) = 0.80). Based on the GWR model, Shen et al. [30] simulated concentrations of NO2, O3, PM10, and PM2.5 across Europe from 2000 to 2019, and the mean R2 values were 0.67, 0.57, 0.61, and 0.77, respectively.
This study attempts to estimate short- and long-term O3 exposure levels in the BTH region, China, based on GWR model by fusing air pollutant data, meteorological data and the second Modern-Era Retrospective analysis for Research and Applications (MERRA-2) data. In addition, we evaluated the accuracy of the prediction results.
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Study Domain
The BTH region (36°05′–42°40′ N, 113°27′–119°50′ E) is located on the eastern coast of China and covers an area of 218,000 km2. The topography is dominated by plains and plateaus, which is high in the northwest and low in the southeast. It comprises Beijing, Tianjin and Hebei Province. The region is not only one of the most economically developed area, but is also a densely populated region. Figure 1 displays the distributions of monitoring sites, meteorological stations and topography in the BTH region.
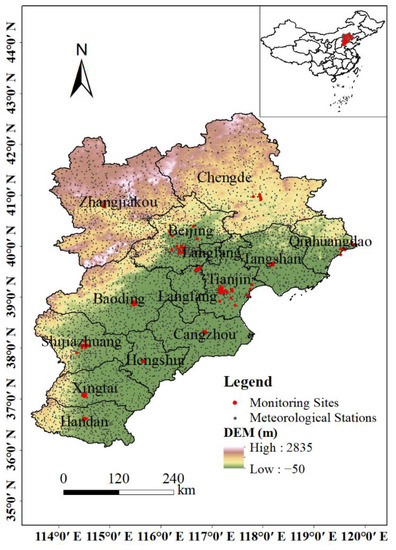
Figure 1.
Distribution of O3 monitoring sites, meteorological stations and topography in the BTH region.
2.2. Data Collection and Processing
2.2.1. Air Pollutant Datasets
Air pollutant datasets were obtained from the China National Environmental Monitoring Centre (CNEMC) (http://beijingair.sinaapp.com/, accessed on 24 September 2022), including the hourly values of O3, PM2.5, PM10, CO, NO2, and SO2 from 2017 to 2020. Calculated daily maximum 8 h average O3 concentration demands at least 20 maximum 8 h O3 concentrations during a day, and the calculation of the 24 h average for the other air pollutants demands at least 20 hourly average values during a day. A monitoring site used to calculate annual maximum 8 h average was retained when it was recording for at least 324 daily maximum 8 h average values during a year. Otherwise, this monitoring site was considered invalid. There were 90 O3 monitoring sites. Based on these criterions, 86 sites with valid daily values and 81 sites with valid annual values were reserved for the O3 concentration estimation from 2017 to 2020, respectively. The 4-year average annual O3 concentration was regarded as the dependent variable for GWR model development. The distribution of 90 monitoring sites is shown in Figure 1.
2.2.2. Meteorological Data
The meteorological data were derived from China Meteorological Administration (http://data.cma.cn/, accessed on 24 September 2022), containing daily air pressure, wind speed, temperature, relative humidity as well as precipitation of 6887 meteorological stations from 2017 to 2020. Figure 1 also shows the distribution of meteorological stations.
2.2.3. MERRA-2 Reanalysis Data
MERRA-2 is released by NASA’s Global Modeling and Assimilation Office (GMAO) and provides data beginning in 1980. The spatial resolution is 0.5 × 0.625°, and the temporal resolutions are 1 h, 3 h, and 1 month. It provides data for a total of 72 vertical layers from the ground to 80 km altitude. Aerosol optical depth (AOD), planetary boundary layer height (PBLH), and atmospheric temperature data at 10 m, 1000 hPa, and 975 hPa in the BTH region from 1 January 2017 to 31 December 2020 were used in the study. In this paper, atmospheric temperature data at 10 m from the ground, 1000 hPa, and 975 hPa were used to calculate the strength of the temperature inversion. The air pressure was converted to altitude according to Equation (1).
where H represents altitude, P represents air pressure and P0 is standard atmospheric pressure (0 °C, 101.325 kPa). Then, 1000 and 975 hPa were converted to altitudes of 110 and 323 m, respectively. When the upper layer temperature is higher than the lower, the inversion temperature occurs. The strength of the temperature inversion refers to the ratio of the temperature difference to thickness of the inverse temperature layer, which is calculated by Equation (2).
where TI refers to the temperature inversion in units of °C/100 m. H1 < H2. T1 and T2 refer to the temperatures at the height of H1 and H2, respectively. TI is calculated when T1 < T2.
Since the predictor variables included in this paper have different sources and resolutions, all variables were interpolated to the grids with spatial resolutions of 1 km based on ArcGIS 10.2 using kriging, and then, the interpolated variables were matched with the O3 monitoring data. Meanwhile, to assess the importance of these predictor variables, data were standardized by z-score before performing GWR according to the following formula:
where z represents the standardized variable value, x is the actual value of the sample data, and μ and σ represent the average value and standard deviation of the sample data, respectively.
2.3. GWR Model Building
By establishing a local point-by-point regression model using ArcGIS 10.2, GWR reveals the relationship between independent and dependent variables. It allows regression coefficients to change in space, which can effectively explore the spatial non-stationary of variables. The calculation equation is as follows, where (ui,vi) refers to location information of the ith monitoring site, and ak(ui,vi) represents the realization of the continuous function ak(ui,vi) at the ith monitoring site.
In the GWR model, for each sample, the other samples are given different weights according to their different spatial relationships with that sample, so that the regression coefficients are no longer constant but vary with the samples. The calculation formula is as follows:
where W(ui,vi) refers to an N × N weight matrix at sample point i. The weighting functions are mainly divided into adaptive kernel function and fixed kernel function. Adaptive kernel function was chosen due to the uneven distribution of O3 monitoring sites.
Spatial weighting function is core of the GWR model. There are numerous methods for selecting the spatial weighting function, among which the distance threshold method is simple. However, this method suffers from the problem of discontinuity. As a sample for which parameters are estimated varies in space, the weights could change suddenly as other samples move into or out of the circular buffer around the sample. One obvious way to combat this is the Gaussian method, which uses a continuous monotone decreasing function to represent the relationship between the weight wij and the distance dij. The Gaussian function is shown in Equation (6).
where β denotes the bandwidth, which refers to the non-negative decay parameter of the function between weight and distance.
Akaike information criterion (AIC) method was used to determine the bandwidth. The method uses two parameters to estimate the model and is a standard to measure the goodness of fit of the statistical model. The AIC value is expressed as:
where is the maximum likelihood estimate of standard deviation of the random error, and S represents the hat matrix of O3.
The stepwise regression approach was used to select the variables to be included in the GWR model. First, the regression equations of each predictor variable on O3 concentration were established in turn. The variable that has the largest adjusted R2 was selected as the first factor to be included in the model. The rest of the variables were then entered. Those with the potential to further improve the model performance (adjusted R2 increased by at least 1%) were contained in the model in turn. The pattern lasted until no more variables satisfied the requirements.
Variance inflation factor (VIF) is an important indicator of multicollinearity among multiple variables in regression analysis. It is considered that there is no multicollinearity among the variables included in the model when VIF ≤ 3. Therefore, variables with p value > 0.1 or VIF > 3 were removed in the final step, and the model accuracy was reassessed [18].
2.4. Cross-Validation
The accuracy of the GWR model was assessed by the leave-one-out cross-validation (LOOCV) method. O3 monitoring data were divided into n portions according to the number of the monitoring sites. O3 monitoring data from one monitoring site was chosen as a validation set. Then, the model was trained using data from the remaining n − 1 monitoring sites, and the model accuracy was verified using the data from the validation set. The above steps were repeated n times until the O3 monitoring data from all monitoring sites, which were used as a validation set. The predictive performance of the model was evaluated by the R2 and the root mean square error (RMSE). The calculation formulas are as follows:
where yi represents O3 monitoring value, is average value of O3 concentration, refers to simulated value of O3, and n is the sample number.
3. Result
3.1. Exploratory Data Analysis
The variables in the dataset included O3, PM2.5, PM10, CO, NO2, SO2, precipitation, air pressure, relative humidity, temperature, wind speed, AOD, PBLH, and TI. The statistics of daily maximum 8 h average O3 concentration are shown in Table 1 and Table 2. The mean values of daily maximum 8 h average O3 concentrations in the BTH area from 2017 to 2020 were 93.64, 95.98, 92.25, and 90.49 μg/m3, respectively, which increased first, and then decreased. The maximum values were 476.63, 314.33, 319.5, and 366.58 μg/m3, which occurred on 6 July 2017, 6 June 2018, 1 August 2019, and 25 June 2020, respectively. The statistics of daily values for the predictor variables from 2017 to 2020 are shown in Table 2, including the mean, minimum, maximum values and standard deviation for all variables.

Table 1.
Statistics of daily maximum 8 h average O3 concentration.

Table 2.
Descriptive statistics of daily values for the predictor variables from 2017 to 2020.
Figure 2 shows the variation characteristics of the O3 monitoring data from 2017 to 2020. Hourly O3 concentration was kept at a high level from 12:00 to 20:00 and reached its maximum at 16:00 p.m. (110.09 μg/m3). Seasonal maximum 8 h average O3 concentration peaked in summer, followed by spring, autumn, and winter. Annual maximum 8 h average O3 concentrations were 92.82, 95.98, 92.11, and 89.06 μg/m3, respectively, and the corresponding standard deviations were 9.78, 6.22, 6.11, and 10.89 μg/m3 in 2017, 2018, 2019, and 2020, respectively. The 4-year average O3 concentration was 92.42 μg/m3.
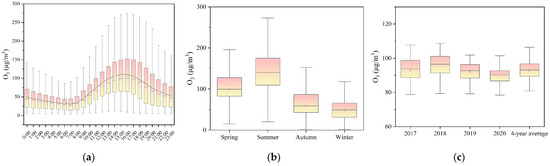
Figure 2.
Variation characteristics of O3 monitoring data from 2017 to 2020. (a) Hourly O3 concentration, (b) seasonal maximum 8 h average O3 concentration, and (c) annual maximum 8 h average O3 concentration.
3.2. Model Fitting and Cross Validation
Table 3 presents the predicted variables for the 4-year average GWR model. The five variables were included in the GWR model, which were precipitation, temperature, NO2, wind speed, and SO2. The VIF of all five variables was less than 3 and ensured that there were no redundant independent variables in the model. The regression coefficients of predictors in the GWR model for the simulation of 4-year average O3 concentration indicated that temperature, wind speed, and SO2 were positively correlated with the O3 concentrations, whereas precipitation and NO2 were negatively correlated with O3 concentrations.

Table 3.
Four-year average GWR model of O3 concentration based on 81 monitoring sites.
The daily and 4-year average annual maximum 8 h average values of 81 monitoring sites across the BTH region were matched with the GWR model simulations at the corresponding sites. Figure 3 shows the fitting scatter plots of the GWR model for the short- and long-term cross validation results, respectively. The LOOCV R2 for the short- and long-term simulation results were 0.91 and 0.71, and the values for RMSE were 11.14 and 3.49 μg/m3, respectively.
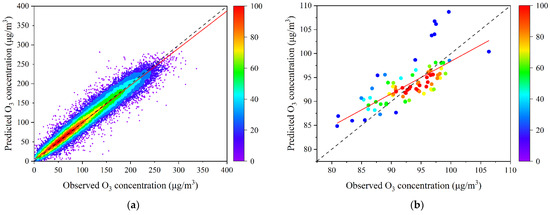
Figure 3.
Fitting scatter plots of the GWR model cross-validation results for the short- (a) and long-term (b).
3.3. Spatio-Temporal Distribution of O3 Concentration
The short-term O3 exposure levels were estimated from 2017 to 2020. Figure 4 showed the spatio-temporal distribution of the short-term O3 exposure levels based on the GWR model with a spatial resolution of 1 × 1 km in the BTH region for the first day of each month in 2020. The maximum value of daily maximum 8 h average O3 concentration was 224.84 μg/m3 on 7 June 2020, and the lowest value was 18.85 μg/m3 on 5 January 2020. Short-term O3 exposure level was high in southern Hebei, such as Hengshui, Cangzhou and Handan, and low in Chengde and Qinhuangdao.
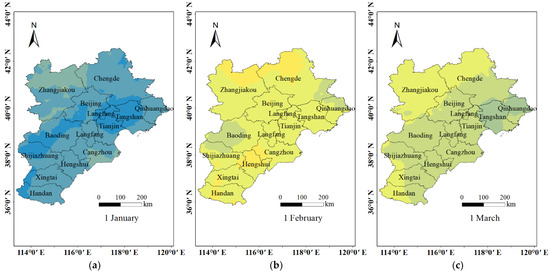
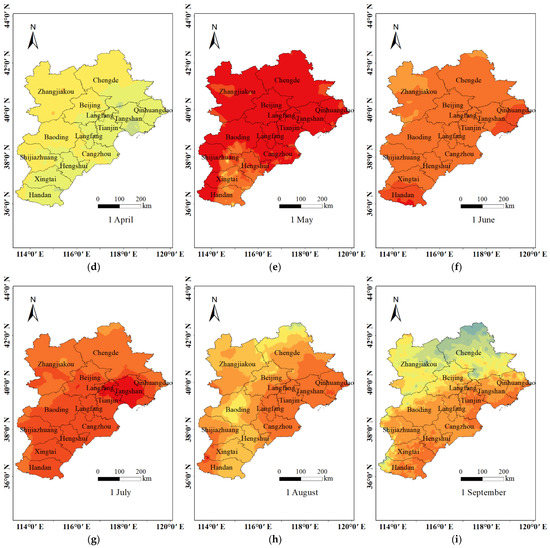
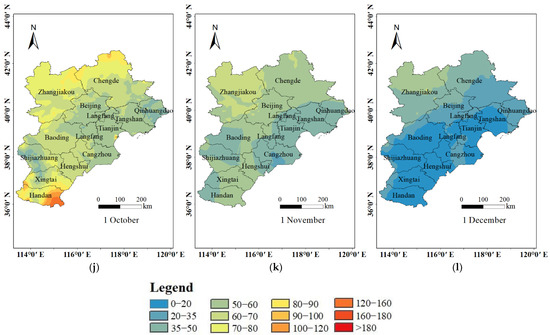
Figure 4.
Short-term O3 exposure levels based on GWR model for the first day of every month in the BTH region in 2020. (a) 1 January, (b) 1 February, (c) 1 March, (d) 1 April, (e) 1 May, (f) 1 June, (g) 1 July, (h) 1 August, (i) 1 September, (j) 1 October, (k) 1 November, and (l) 1 December, respectively.
Figure 5 displayed the seasonal average O3 concentrations and the percentages of O3 exceedance days. The variation of O3 concentrations showed an obvious seasonal characteristic in the BTH region. O3 concentration was the highest in summer with an average value of 140.36 μg/m3, followed by spring (109.48 μg/m3), autumn (70.24 μg/m3) and winter (51.73 μg/m3). In both spring and summer, O3 concentrations did not meet the Class I standard of Ambient Air Quality Standards of China (100 μg/m3). From the exceedance rate of each season, it can be revealed that the percentage of O3 exceedance days ranged from 0% to 90.22%. The percentage of O3 exceedance days in summer was the highest, which were 87.78%, 87.36%, 85.23%, and 90.22% from 2017 to 2020, respectively, while the lowest was in winter, meeting the standard in all four years.
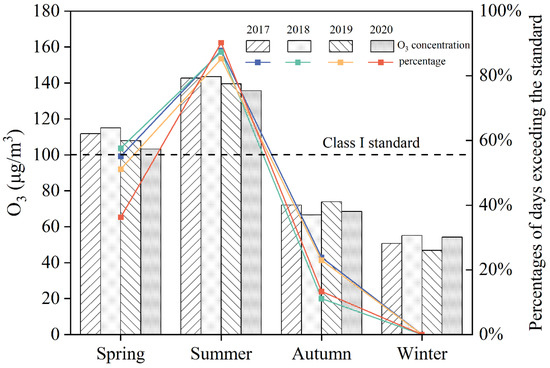
Figure 5.
Seasonal average O3 concentrations and the percentages of O3 exceedance days.
The estimation results of annual and 4-year average annual O3 exposure levels from 2017 to 2020 are shown in Figure 6 and Figure 7. The annual maximum 8 h average values in the BTH region from 2017 to 2020 were 93.58, 96.60, 92.66, and 91.21 μg/m3, respectively, which showed a clear trend of increasing from 2017 to 2018 and subsequently decreasing from 2018 to 2020. High O3 concentration areas were gathered in the southern BTH region in 2018, including Hengshui, Cangzhou, Handan, and Xingtai. The O3 concentrations in these cities all failed to meet the Class I standard (100 μg/m3). In terms of the variation of pollution areas, the O3 pollution area gradually expanded from the west and southeast to the entire southern region from 2017 to 2018. However, the pollution area has shrunk to Shijiazhuang and Hengshui in the southern part of the BTH from 2018 to 2020. The 4-year average O3 concentration estimation results presenting the O3 concentration in the southeast and western regions of BTH were high, and the concentration in the northeast region was relatively low. The center of high O3 concentrations appeared in Hengshui (97.62 μg/m3), followed by Handan and Xingtai, while lower O3 concentrations were shown in Chengde and Qinhuangdao.
Figure 6.
Estimation of annual O3 exposure level from 2017 to 2020. (a) 2017, (b) 2018, (c) 2019, and (d) 2020, respectively.
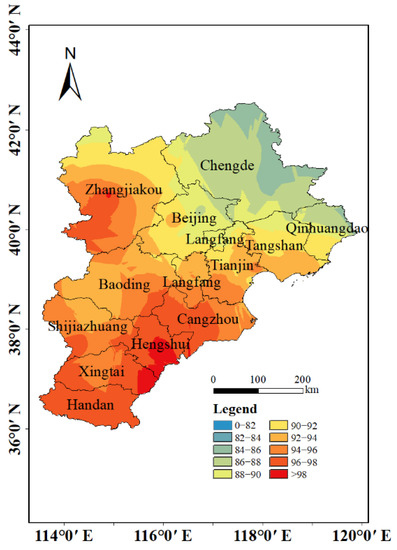
Figure 7.
Estimation of 4-year average O3 exposure level.
4. Discussion
The GWR model constructed in this study has achieved higher model performance than those of other comparable studies. Ma et al. [31] built a high-performance random forest (RF) model in the BTH region and estimated daily maximum 8 h average O3 concentrations, and the R2 value was 0.84. Lyu et al. [32] not only analyzed spatial and temporal variations of air pollutions but also predicted O3 concentrations based on machine learning (ML) algorithms across the BTH region, and ML algorithms including RF and decision tree regression showed the R2 values as 0.83 and 0.73, respectively. The GWR model constructed in this study has better prediction accuracy, with LOOCV R2 of 0.91 and 0.71 for the short- and long-term O3 exposure levels, respectively. In addition, O3 exposure levels estimated in our study have a relatively high spatial and temporal resolution compared to other similar studies. Hu et al. [33] combined the Weather Research and Forecasting with Chemistry (WRF-Chem) model and extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost) algorithm to predict the near-surface O3 concentrations with a resolution of 0.1 × 0.1° in the BTH region. Wei et al. [34] integrated multi-source datasets and used space-time extremely randomized trees (STET) to estimate surface O3 concentrations at the resolution of 10 × 10 km across the BTH region. Xue et al. [35] combined the WRF-Chem and RF models to simulate O3 concentrations with a horizontal resolution of 9 km across the BTH region. Compared with the above research studies, we attempted to predict O3 concentrations at the spatial resolution of 1 × 1 km. Masri et al. [36] built an LUR model to simulate O3 concentration spatial distributions in summer and winter in Tianjin, China, while we predicted O3 exposure levels at temporal resolutions of 1 day, 1 year and 4 years.
Solar radiation is an essential condition for O3 generation. Strong solar radiation increases temperature, and high temperature can make the photochemical reactions of O3 formation active, which increases O3 concentration. In addition, summer temperature is higher than winter temperature, which contributes to the high O3 concentration in summer [37]. Wind speed was positively correlated with O3 in the BTH region in this study, which is in line with the result of Wang et al. [38]. In general, high wind speed favors the diffusion of pollutants when there are only local sources of pollution, resulting in the reduction of O3 concentration. The higher the wind speed, the higher the O3 concentration, indicating that the influence of external pollution sources cannot be ignored [39]. Wang et al. [40] built the regional transport matrix of O3 in the BTH region. The result suggested that the transport source was the major contributor for O3, which provided the supporting evidence. Rainfall had a negative correlation with O3 concentration. It can accelerate wet deposition by scavenging O3 and its soluble precursors, e.g., NO2, resulting in the reduction of O3 concentration [41,42]. In addition, there may be a negative correlation between NO2 and O3 at fine scales, because NO emitted from motor vehicles near the road reacts rapidly to generate NO2. At the same time, O3 is reduced and other compounds are formed. This process is referred to as NOx titration.
During these four years, annual O3 concentrations in the BTH region peaked in 2018 and then began to decrease. Regional joint prevention and control and the decreasing concentrations of major precursors of O3 may be the reasons. Although a series of stringent air pollution control strategies has been issued over the past few years, for example, Air Pollution Prevention and Control Action Plan, O3 concentrations were able to decrease until the integrated management of the O3 precursor (VOCs) was first proposed in the important policy of governance for controlling O3 in the winter of 2018. The policy had achieved initial improvements in 2019 [43]. O3 concentration in the BTH region had a seasonal variation. The concentrations were highest in summer, followed by spring, autumn, and winter. In general, high temperature and strong solar radiation levels in summer can stimulate active photochemical reactions, which lead to high O3 concentrations [44]. Although the temperature in spring was lower than summer, dry and rainless meteorological conditions also contribute to O3 production [45]. In autumn and winter, O3 concentrations decreased due to weakened solar radiation and lower temperatures. In terms of spatial variation, O3 concentrations were higher in the southeastern region, including in Hengshui, Handan, Xingtai and Cangzhou, and were lower in Chengde. The southeastern part of BTH region was dominated by heavy industries, and these polluting industries have high precursors emissions, which are more conducive to O3 generation [46]. In addition, the number of civil vehicles in Beijing, Tianjin, and Hebei province is gradually rising, which increases emissions from vehicle exhaust and thus worsens O3 pollution [47,48,49].
There are some limitations in our study. The variables used in the GWR model including air pollutants and meteorology, as well as more variables such as traffic, population, and pollutant emission, should be considered in future studies to make more accurate estimations. In addition, there may not be enough samples for the regions lacking monitoring sites to accurately capture O3 exposure levels. With the continuous development of the national air quality monitoring network, the performance of our model will be continuously improved.
5. Conclusions
Short- and long-term O3 exposure levels were estimated based on the GWR model at the spatial resolution of 1 × 1 km in the BTH region from 2017 to 2020. The cross-validation results indicated that simulated concentrations were well consistent with observed O3 concentrations. By estimating the parameters of each location, the GWR model constructed in this study showed a high ability to simulate O3 concentration at different spatial and temporal scales. The temperature, wind speed, and SO2 were positively related with O3 concentrations, whereas precipitation and NO2 were negatively correlated with O3 concentrations. We found that O3 concentration increased with wind speed, and the possible reason was that the contribution of the transport source was greater than the contribution of the local source. Compared with long-term O3 exposure level, short-term O3 exposure level obtained a better simulated performance. The estimations based on the GWR model showed spatio-temporal variation of O3 concentrations across the BTH region. In summary, the model could accurately estimate O3 exposure levels, which could be helpful for epidemiological studies and health risk assessment in the future.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.C.; Data curation, Z.Q., C.C., M.S., S.X. and K.M.; Methodology, M.S. and L.C.; Resources, Y.L. (Yusi Liu); Software, Z.Q. and Y.T.; Supervision, Z.M.; Visualization, H.Z. and Y.S.; Writing—original draft, Z.Q.; Writing—review & editing, C.C., Y.L. (Yaxin Liu), L.C. and S.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program (Grants No. 2016YFC0201700).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
China National Environmental Monitoring Centre. China Air Quality Data. Available online: http://beijingair.sinaapp.com/ (accessed on 23 September 2022); China Meteorological Administration. Meteorological Data. Available online: http://data.cma.cn/ (accessed on 23 September 2022); the second Modern-Era Retrospective analysis for Research and Applications. Available online: https://disc.gsfc.nasa.gov/datasets/M2I3NPASM_5.12.4/summary; https://disc.gsfc.nasa.gov/datasets/M2I1NXASM_5.12.4/summary; https://disc.gsfc.nasa.gov/datasets/M2T1NXFLX_5.12.4/summary; https://disc.gsfc.nasa.gov/datasets/M2I3NXGAS_5.12.4/summary (accessed on 23 September 2022).
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the National Key Research and Development Program (grant no. 2016YFC0201700).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wang, T.; Xue, L.K.; Brimblecombe, P.; Lam, Y.F.; Li, L.; Zhang, L. Ozone pollution in China: A review of concentrations, meteorological influences, chemical precursors, and effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 1582–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefohn, A.S.; Malley, C.S.; Simon, H.; Wells, B.; Xu, X.B.; Zhang, L.; Wang, T. Responses of human health and vegetation exposure metrics to changes in ozone concentration distributions in the European Union, United States, and China. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 152, 123–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefohn, A.S.; Malley, C.S.; Smith, L.; Wells, B.; Hazucha, M.; Simon, H.; Naik, V.; Mills, G.; Schultz, M.G.; Paoletti, E.; et al. Tropospheric ozone assessment report: Global ozone metrics for climate change, human health, and crop/ecosystem research. Elem. Sci. Anthr. 2018, 6, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuvolone, D.; Petri, D.; Voller, F. The effects of ozone on human health. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 8074–8088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.F.; Wei, Y.J.; Fang, Z.F. Ozone Pollution: A Major Health Hazard Worldwide. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, S.; Xue, B.R.; Lv, Z.F.; Meng, Z.H.; Yang, X.F.; Xue, T.; Yu, Q.; He, K.B. Ground-level ozone pollution and its health impacts in China. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 173, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Wang, W.; Chen, C.; Ban, J.; Xu, D.; Zhu, P.; He, M.Z.; Li, T. Acute effect of multiple ozone metrics on mortality by season in 34 Chinese counties in 2013–2015. J. Intern. Med. 2018, 283, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Li, X.L.; Teng, Y.; Fu, H.C.; Chen, L.; Mao, J.; Zhang, H.; Gao, S.; Sun, Y.L.; Ma, Z.X.; et al. Estimation of health and economic benefits based on ozone exposure level with high spatial-temporal resolution by fusing satellite and station observations. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, Y.M.; Zhang, N.N.; Chu, C.J. Assessing the health impacts attributable to PM2.5 and ozone pollution in 338 Chinese cities from 2015 to 2020. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 287, 117623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.Y.; Huang, X.J.; Guo, Y.H. Spatiotemporal variation of ozone pollution and health effects in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 57808–57822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, M.L.; Peng, R.D.; Dominici, F. The exposure-response curve for ozone and risk of mortality and the adequacy of current ozone regulations. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 532–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, M.C.; Jerrett, M.; Pope, C.A.; Krewski, D.; Gapstur, S.M.; Diver, W.R.; Beckerman, B.S.; Marshall, J.D.; Su, J.; Crouse, D.L.; et al. Long-Term Ozone Exposure and Mortality in a Large Prospective Study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 193, 1134–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.X.; Cheng, C.X.; Zhao, H. A Health Impact and Economic Loss Assessment of O3 and PM2.5 Exposure in China from 2015 to 2020. Geohealth 2022, 6, e2021GH000531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China. Bulletin of the State of the Environment in China for Year 2017. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/hjzl/sthjzk/zghjzkgb/201805/P020180531534645032372.pdf (accessed on 23 September 2022).
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China. Bulletin of the State of the Environment in China for Year 2018. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/hjzl/sthjzk/zghjzkgb/201905/P020190619587632630618.pdf (accessed on 23 September 2022).
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China. Bulletin of the State of the Environment in China for Year 2019. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/hjzl/sthjzk/zghjzkgb/202006/P020200602509464172096.pdf (accessed on 23 September 2022).
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China. Bulletin of the State of the Environment in China for Year 2020. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/hjzl/sthjzk/zghjzkgb/202105/P020210526572756184785.pdf (accessed on 23 September 2022).
- Chen, L.; Liang, S.; Li, X.L.; Mao, J.; Gao, S.; Zhang, H.; Sun, Y.L.; Vedal, S.; Bai, Z.P.; Ma, Z.X.; et al. A hybrid approach to estimating long-term and short-term exposure levels of ozone at the national scale in China using land use regression and Bayesian maximum entropy. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 141780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.N.; Cheng, T.H.; Gu, X.F.; Chen, H.; Guo, H.; Wang, Y.; Bao, F.W.; Shi, S.Y.; Xu, B.R.; Zuo, X.; et al. Assessing Spatial and Temporal Patterns of Observed Ground-level Ozone in China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.H.; Yang, X.Y.; Li, Z.Q.; Wang, Z.T.; Zhang, Y.H.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, C.Y.; Ma, P.F. Advances of ozone satellite remote sensing in 60 years. Natl. Remote Sens. Bull. 2022, 26, 817–833. [Google Scholar]
- Chianese, E.; Galletti, A.; Giunta, G.; Landi, T.C.; Marcellino, L.; Montella, R.; Riccio, A. Spatiotemporally resolved ambient particulate matter concentration by fusing observational data and ensemble chemical transport model simulations. Ecol. Model. 2018, 385, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akita, Y.; Baldasano, J.M.; Beelen, R.; Cirach, M.; de Hoogh, K.; Hoek, G.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.; Serre, M.L.; de Nazelle, A. Large Scale Air Pollution Estimation Method Combining Land Use Regression and Chemical Transport Modeling in a Geostatistical Framework. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 4452–4459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.M.; Li, Y.X.; Shi, N.F.; Su, J. Spatio-temporal Change Characteristics of Ozone Concentration in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 42, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Zhan, Y.; Li, J.Y.; Chao, C.Y.; Liu, Q.F.; Wang, C.Y.; Jia, S.Q.; Ma, L.; Biswas, P. Using Kriging incorporated with wind direction to investigate ground-level PM2.5 concentration. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 751, 141813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Heap, A.D. Spatial interpolation methods applied in the environmental sciences: A review. Environ. Model. Softw. 2014, 53, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couzo, E.; Olatosi, A.; Jeffries, H.E.; Vizuete, W. Assessment of a regulatory model’s performance relative to large spatial heterogeneity in observed ozone in Houston, Texas. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2012, 62, 696–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayan, T.; Bhattacharya, T.; Chakraborty, S.; Konar, S. Application of Multiple Linear Regression and Geographically Weighted Regression Model for Prediction of PM2.5. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. India Sect. A Phys. Sci. 2022, 92, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunsdon, C.; Fotheringham, A.S.; Charlton, M.E. Geographically weighted regression: A method for exploring spatial nonstationarity. Geogr. Anal. 1996, 28, 281–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stowell, J.D.; Bi, J.Z.; Al-Hamdan, M.Z.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, S.M.; Freedman, F.; Kinney, P.L.; Liu, Y. Estimating PM2.5 in Southern California using satellite data: Factors that affect model performance. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 094004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; de Hoogh, K.; Schmitz, O.; Clinton, N.; Tuxen-Bettman, K.; Brandt, J.; Christensen, J.H.; Frohn, L.M.; Geels, C.; Karssenberg, D.; et al. Europe-wide air pollution modeling from 2000 to 2019 using geographically weighted regression. Environ. Int. 2022, 168, 107485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.M.; Ban, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Yang, Y.; He, M.K.Z.; Li, S.S.; Shi, W.J.; Li, T.T. Random forest model based fine scale spatiotemporal O3 trends in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region in China, 2010 to 2017. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 276, 116635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Y.; Ju, Q.R.; Lv, F.M.; Feng, J.L.; Pang, X.B.; Li, X. Spatiotemporal variations of air pollutants and ozone prediction using machine learning algorithms in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region from 2014 to 2021. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 306, 119420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.M.; Zhang, J.; Xue, W.H.; Zhou, L.H.; Che, Y.F.; Han, T. Estimation of the Near-Surface Ozone Concentration with Full Spatiotemporal Coverage across the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region Based on Extreme Gradient Boosting Combined with a WRF-Chem Model. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Li, Z.Q.; Li, K.; Dickerson, R.R.; Pinker, R.T.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Sun, L.; Xue, W.H.; Cribb, M. Full-coverage mapping and spatiotemporal variations of ground-level ozone (O3) pollution from 2013 to 2020 across China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 270, 112775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.H.; Zhang, J.; Hu, X.M.; Yang, Z.; Wei, J. Hourly Seamless Surface O3 Estimates by Integrating the Chemical Transport and Machine Learning Models in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masri, S.; Hou, H.Y.; Dang, A.; Yao, T.; Zhang, L.W.; Wang, T.; Qin, Z.; Wu, S.Y.; Hang, B.; Chen, J.C.; et al. Development of spatiotemporal models to predict ambient ozone and NOx concentrations in Tianjin, China. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 213, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.M.; Li, J.; Guo, J.P.; Jiang, Z.J.; Chu, Y.Q.; Chang, L.; Yang, Y.; Liao, H. The impact of synoptic patterns on summertime ozone pollution in the North China Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 735, 139559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Zheng, Y.F.; Liu, Y.J.; Li, Q.P.; Ding, Y.H. Characteristics of ozone and its relationship with meteorological factors in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region. China Environ. Sci. 2019, 39, 2689–2698. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Q.; Fan, W.Y.; Huang, H.; Sun, M.L.; Liu, A.X. Variation of surface O3 concentration and its influencing factors in summer in Tianjin. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2009, 18, 12–16. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.L.; Xue, W.B.; Lei, Y.; Wu, W.L. Model-derived source apportionment and regional transport matrix study of ozone in Jingjinji. China Environ. Sci. 2017, 37, 3684–3691. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.M.; Shuo, W.; Zhao, W.X.; Xu, X.Z.; Zhang, W.J.; Arshad, A. Investigating the Relationship between Air Pollutants and Meteorological Parameters Using Satellite Data over Bangladesh. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Wang, L.L.; Lu, C.H.; Liu, J.D.; Li, M.G.; Tang, G.Q.; Ji, D.S.; Zhang, N.; Wang, Y.S. Meteorological mechanism for a large-scale persistent severe ozone pollution event over eastern China in 2017. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 92, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, S.L.; Zhang, W.J.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, S.B.; Li, H.S. Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Urban Air Quality in Beijing-Tianjin Hebei and Its Surrounding Areas (‘2 + 26’ Cities). Res. Environ. Sci. 2021, 34, 172–184. [Google Scholar]
- Adame, J.A.; Lozano, A.; Bolivar, J.P.; De la Morena, B.A.; Contreras, J.; Godoy, F. Behavior, distribution and variability of surface ozone at an arid region in the south of Iberian Peninsula (Seville, Spain). Chemosphere 2008, 70, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Ma, Z.Q.; Hao, T.Y.; Fan, W.Y.; Yang, X.; Tang, Y.X.; Cai, Z.Y.; Han, S.Q. Temporal and spatial distribution characteristics and background concentration estimation of ozone in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. China Environ. Sci. 2021, 41, 4999–5008. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, J.; Zheng, B.; Li, M.; Yu, F.; Chen, C.C.; Liu, F.; Zhou, X.F.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, Q.; He, K.B. A high-resolution air pollutants emission inventory in 2013 for the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, China. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 170, 156–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beijing Bureau of Statistics of China. Beijing Statistical Year Book 2021; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2021. Available online: http://nj.tjj.beijing.gov.cn/nj/main/2021-tjnj/zk/indexch.htm (accessed on 23 September 2022).
- Hebei Bureau of Statistics of China. Hebei Statistical Year Book 2021; China Statistics Press: Hebei, China, 2021. Available online: http://tjj.hebei.gov.cn/hetj/tjnj/2021/zk/indexch.htm (accessed on 23 September 2022).
- Tianjin Bureau of Statistics of China. Tianjin Statistical Year Book 2021; China Statistics Press: Tianjin, China, 2021. Available online: http://stats.tj.gov.cn/nianjian/2021nj/zk/indexch.htm (accessed on 23 September 2022).
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).