Evaluation of the Barrier Effect of Polylactic Acid-Modified Membrane on Odours at the Excavated Soil Interface of a Pesticide-Contaminated Site
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Overview
2.2. Polylactic Acid-Modified Membrane
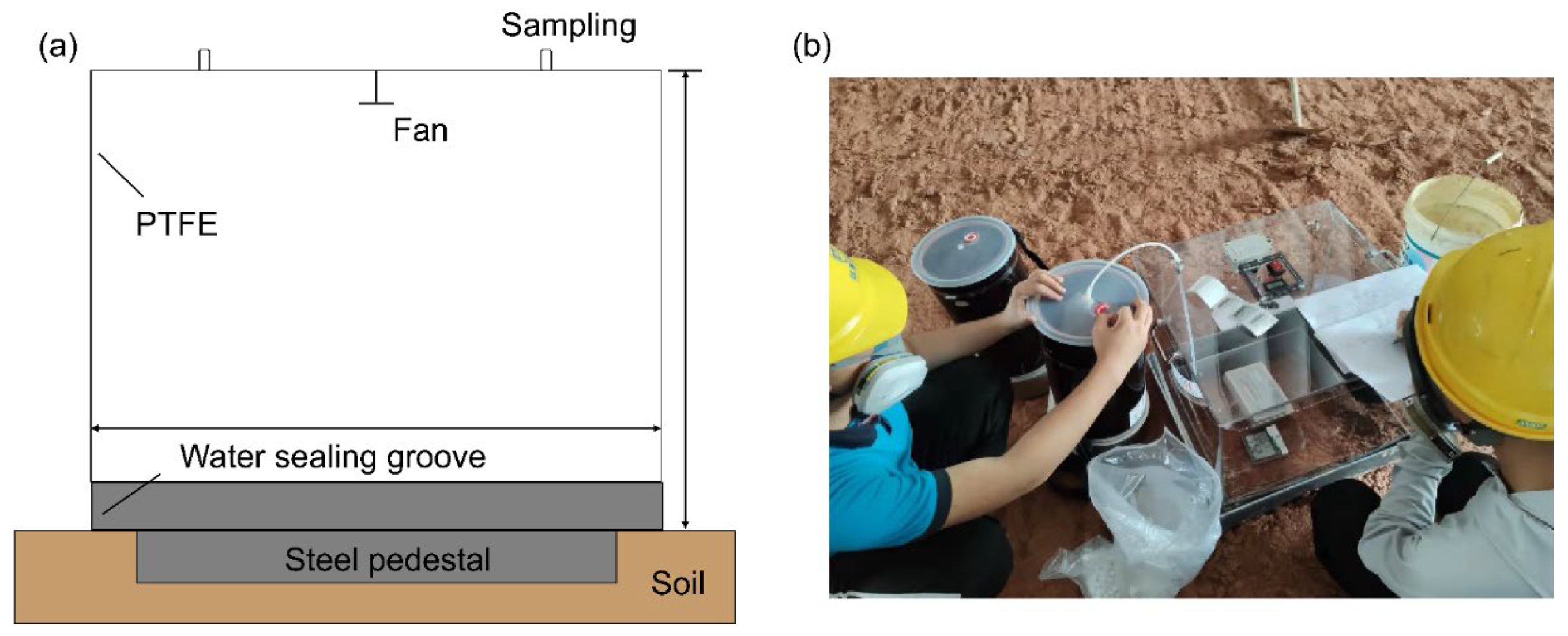
2.3. Collection and Analysis of Gas Samples
2.4. Evaluation Methods
2.4.1. Diffusion Flux Calculation
2.4.2. Theoretical Odour Concentration
2.4.3. Health Risk Assessment
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Main Odours
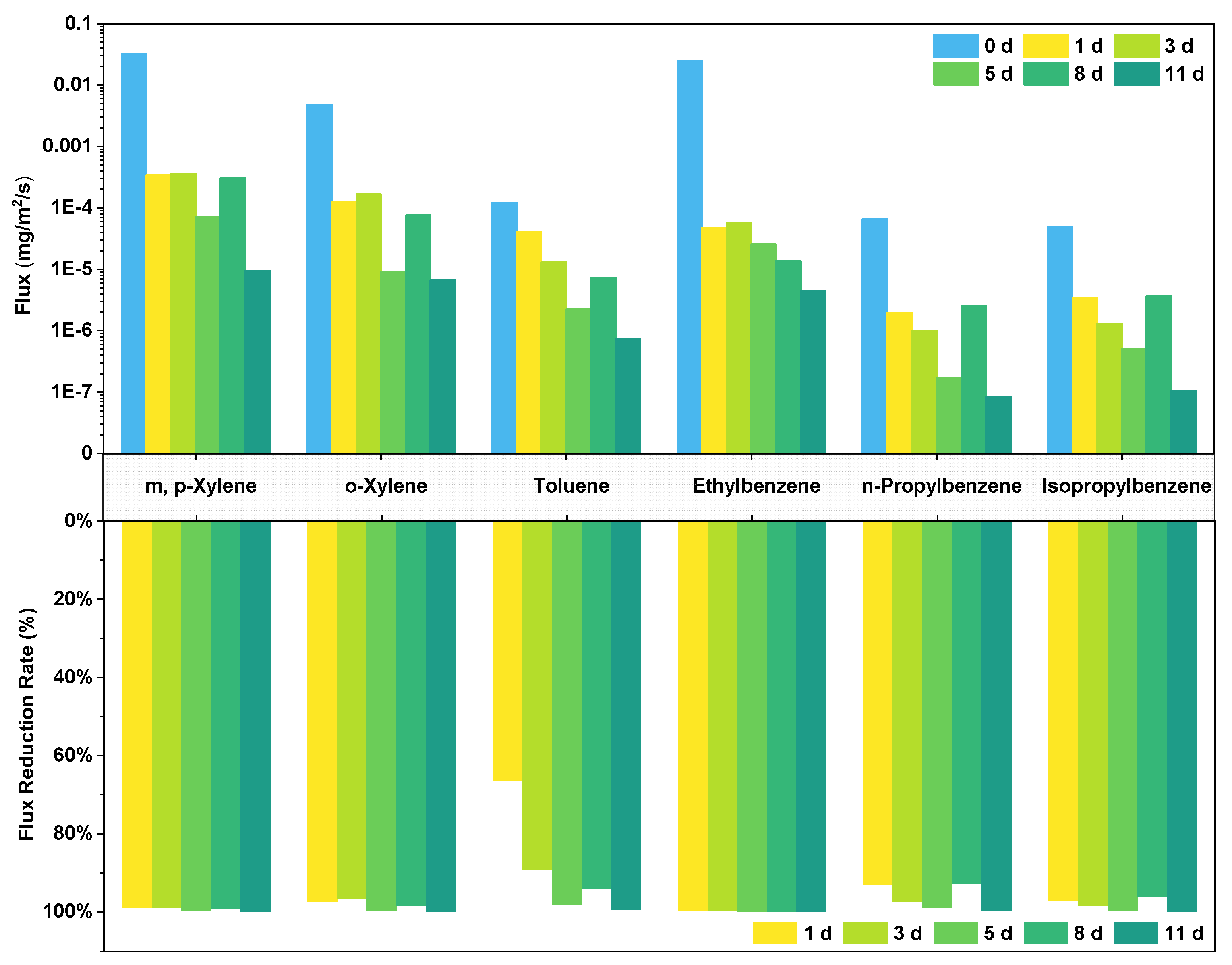
3.2. Diffusion Flux of Odours
3.3. Concentrations of Odours
3.4. Health Risk Level
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, K.; Wang, C.; Xue, S.; Li, W.; Liu, J.; Li, L. The identification, health risks and olfactory effects assessment of VOCs released from the wastewater storage tank in a pesticide plant. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 184, 109665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grung, M.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, H.; Steen, A.O.; Huang, J.; Zhang, G.; Larssen, T. Pesticide levels and environmental risk in aquatic environments in China—A review. Environ. Int. 2015, 81, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, L.; Ma, Y.; Li, F. Using Isomeric and Metabolic Ratios of DDT To Identify the Sources and Fate of DDT in Chinese Agricultural Topsoil. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 1990–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Bai, L.; Man, C.; Liang, W.; Li, F.; Meng, X. DDT Vertical Migration and Formation of Accumulation Layer in Pesticide-Producing Sites. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 9084–9091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, F.; Song, J.; Chen, M.; Wei, J.; Pan, Y.; Yu, H. Risk assessment of manufacturing equipment surfaces contaminated with DDTs and dicofol. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zheng, H.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, F.; Yao, J.; Zhao, W.; Du, X. Screening and Distribution Characteristics of Odorous Substances in Soil of Typical Pesticide-Contaminated Site. Res. Environ. Sci. 2022, 35, 1482–1489. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?doi=10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2022.02.05 (accessed on 8 September 2022). (In Chinese).
- Jia, J.; Wang, B.; Wu, Y.; Niu, Z.; Ma, X.; Yu, Y.; Hou, P. Environmental Risk Controllability and Management of VOCs during Remediation of Contaminated Site. Soil Sediment Contam. 2016, 25, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Liu, S.; Wang, S.; Zhao, M.; Jia, J. Health risk assessment and distribution of VOCs during excavation processes for the remediation of contaminated sites. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2019, 25, 2073–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Sun, Z.; Zhu, S.; Lou, Z.; Zhu, N.; Feng, L. The identification and health risk assessment of odor emissions from waste landfilling and composting. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 1038–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadyan, M.; Baharfar, Y. Control of workers’ exposure to xylene in a pesticide production factory. Int. J. Occup. Environ. Health. 2015, 21, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yang, J.; Pan, H.; Su, Q.; Liu, Y.; Shi, Y. Abatement of malodorants from pesticide factory in dielectric barrier discharges. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 177, 908–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashothaman, A.; Sudha, J.; Senthilkumar, N. A comprehensive review on biodegradable polylactic acid polymer matrix composite material reinforced with synthetic and natural fibers. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Han, Y.; Yan, X.; Liu, J. H2S removal and bacterial structure along a full-scale biofilter bed packed with polyurethane foam in a landfill site. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 147, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ning, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Cui, H.; Meng, J.; Teng, C.; Wang, G.; Shang, X. Impact assessment of odor nuisance, health risk and variation originating from the landfill surface. Waste Manag. 2021, 126, 771–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Li, P.; Li, X.; Liao, C.; Li, X.; Zuo, Y. Effect of silane coupling agent on compatibility interface and properties of wheat straw/polylactic acid composites. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 182, 2108–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taleb, K.; Pillin, I.; Grohens, Y.; Saidi Besbes, S. Polylactic acid/Gemini surfactant modified clay bio-nanocomposites: Morphological, thermal, mechanical and barrier properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 177, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, D.B.; De Carvalho, J.S.; De Oliveira, S.A.; Rosa, D.D.S. A new approach for flexible PBAT/PLA/CaCO3 films into agriculture. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, J.P.; Bacigalupe, A.; Maggi, J.; Eisenberg, P. Biodegradable PLA/PBAT/Clay Nanocomposites: Morphological, Rheological and Thermomechanical Behavior. J. Renew. Mater. 2016, 4, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiecien, I.; Adamus, G.; Jiang, G.; Radecka, I.; Baldwin, T.C.; Khan, H.R.; Johnston, B.; Pennetta, V.; Hill, D.; Bretz, I.; et al. Biodegradable PBAT/PLA Blend with Bioactive MCPA-PHBV Conjugate Suppresses Weed Growth. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Zhou, Y.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Gong, R.; Xu, J. Optimizing Interfacial Adhesion in PBAT/PLA Nanocomposite for Biodegradable Packaging Films. Food Chem. 2020, 334, 127487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, X.; Li, X.; Yu, Y.; Pan, H.; Yang, J.; Wang, D.; Yang, H.; Zhang, H.; Dong, L. The mechanical, thermal, rheological and Morphological properties of PLA/PBAT blown films by Using bis(tert-butyl dioxy isopropyl) benzene as crosslinking agent. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2019, 59, E227–E236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Feng, M.; Lin, K.; Bai, X. A Kind of Polylactic Acid-Based Nano-Modified Membrane and Its Preparation Method and Application. Patent ZL202110157534.5, 2 September 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Yilmaz, M.; Tinjum, J.M.; Acker, C.; Marten, B. Transport mechanisms and emission of landfill gas through various cover soil configurations in an MSW landfill using a static flux chamber technique. J. Environ. Manage. 2020, 280, 111677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; McHugh, T.; Beckley, L.; DeVaull, G.; Lahvis, M.; Jiang, L. Vapor intrusion investigations and decision-making: A critical review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 7050–7069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikezawa, H.; Nagumo, Y.; Hattori, M.; Nonaka, M.; Ohyama, T.; Harada, N. Suppressive effect of the deep placement of lime nitrogen on N2O emissions in a soybean field. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 804, 150246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.; Xu, R.; Yu, J.; Li, F.; Wei, D.; Borjigidai, A. Nitrogen deposition accelerates greenhouse gas emissions at an alpine steppe site on the Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 765, 144277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S. Odor Characteristics and Concentration of Malodorous Chemical Compounds Emitted from a Combined Sewer System in Korea. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capelli, L.; Sironi, S.; Del-Rosso, R.; Céntola, P.; Il-Grande, M. A comparative and critical evaluation of odour assessment methods on a landfill site. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 7050–7058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lu, W.; Wang, H.; Huang, Q.; Gao, X. Odor impact assessment of trace sulfur compounds from working faces of landfills in Beijing, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 220, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokowa, A.; Diaz, C.; Koziel, J.A.; McGinley, M.; Barclay, J.; Schauberger, G.; Guillot, J.-M.; Sneath, R.; Capelli, L.; Zorich, V.; et al. Summary and Overview of the Odour Regulations Worldwide. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brancher, M.; Hieden, A.; Baumann-Stanzer, K.; Schauberger, G.; Piringer, M. Performance evaluation of approaches to predict sub-hourly peak odour concentrations. Atmos. Environ. X 2020, 7, 100076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martí, V.; Jubany, I.; Pérez, C.; Rubio, X.; De Pablo, J.; Giménez, J. Human Health Risk Assessment of a landfill based on volatile organic compounds emission, immission and soil gas concentration measurements. Appl. Geochem. 2014, 49, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Liu, J.; Zhao, P.; Li, W.; Yan, L.; Piringer, M.; Schauberger, G. Evaluation of the chemical composition and correlation between the calculated and measured odour concentration of odorous gases from a landfill in Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 164, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; McHugh, T.; Eklund, B. Flux Chamber Measurements Should Play a More Important Role in Contaminated Site Management. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 11645–11647. Available online: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/acs.est.0c04078 (accessed on 8 September 2022). [CrossRef]
- Bastuck, M.; Baur, T.; Richter, M.; Mull, B.; Schütze, A.; Sauerwald, T. Comparison of ppb-level gas measurements with a metal-oxide semiconductor gas sensor in two independent laboratories. Sens. Actuators B 2018, 273, 1037–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, J.; Qi, S.; Yamauchi, Y.; Shi, R.; Fang, R.; Ishida, Y.; Wang, S.; Tomsia, A.P.; et al. Layered nanocomposites by shear-flow-induced alignment of nanosheets. Nature 2020, 580, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Yan, F.; Ding, Z.; Zhao, J. Effects and mechanisms of calcium peroxide on purification of severely eutrophic water. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 2796–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmeri, H.; Alaie, E.; Shavandi, M.; Dastgheib, S.M.M.; Tasharrofi, S. Bioremediation of benzene from groundwater by calcium peroxide (CaO2) nanoparticles encapsulated in sodium alginate. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 78, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndjou’ou, A.-C.; Cassidy, D. Surfactant production accompanying the modified Fenton oxidation of hydrocarbons in soil. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 1610–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Chen, J. Performance and properties of nanoscale calcium peroxide for toluene removal. Chemosphere 2013, 91, 717–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madan, S.S.; Upwanshi, W.A.; Wasewar, K.L. Adsorption of α-toluic acid by calcium peroxide nanoparticles. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 16507–16513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 14554-1993; Emission Standards of Odours Pollutants. China National Environmental Protection Agency: Beijing, China, 1993.
- Nie, E.; Zheng, G.; Shao, Z.; Yang, J.; Chen, T. Emission characteristics and health risk assessment of volatile organic compounds produced during municipal solid waste composting. Waste Manag. 2019, 79, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Fu, X.; Guo, H.; Meng, R.; Lu, W.; Zhao, M.; Wang, H. Health risk impacts analysis of fugitive aromatic compounds emissions from the working face of a municipal solid waste landfill in China. Environ. Int. 2016, 97, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Liu, J.; Liu, S.; Li, W.; Yan, L.; Shu, M.; Zhao, P.; Zhou, P.; Cao, W. Assessment of the health risks and odor concentration of volatile compounds from a municipal solid waste landfill in China. Chemosphere 2018, 202, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bari, M.A.; Kindzierski, W.B. Concentrations, sources and human health risk of inhalation exposure to air toxics in Edmonton, Canada. Chemosphere 2016, 173, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| S. No. | Malodourous Substances | Concentration (mg/m3) | Olfactory Threshold (mg/m3) | Odour Activity Value | Cumulative Odour Contribution (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | M, p-xylene | 2500.00 | 0.19 | 13,157.89 | 63.86 |
| 2 | N-propyl benzene | 57.90 | 0.02 | 2895.00 | 77.91 |
| 3 | Ethylbenzene | 2000.00 | 0.81 | 2469.14 | 89.89 |
| 4 | Toluene | 800.00 | 1.36 | 588.24 | 92.75 |
| 6 | Cumene | 20.00 | 0.05 | 400.00 | 94.69 |
| 5 | O-xylene | 700.00 | 1.80 | 388.89 | 96.58 |
| 7 | 2-Hexone | 30.00 | 0.11 | 279.55 | 97.93 |
| 8 | Styrene | 40.00 | 0.16 | 250.00 | 99.15 |
| 9 | 1,2,4-Trimethylbenzene | 90.60 | 0.64 | 141.56 | 99.83 |
| 10 | 1,3,5-Trimethylbenzene | 31.20 | 0.91 | 34.29 | 100.00 |
| 11 | Benzene | 0.02 | 2.70 | 0.01 | 100.00 |
| Total | 20,604.56 |
| Time (d) | Target HQ | Target Risk | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m, p-Xylene | o-Xylene | Toluene | Ethylbenzene | n-Propylbenzene | Isopropylbenzene | Ethylbenzene | |
| 0 | 2.48 × 100 | 3.66 × 10−1 | 1.84 × 10−4 | 1.89 × 10−1 | 1.23 × 10−3 | 9.42 × 10−4 | 1.62 × 10−4 |
| 1 | 2.60 × 10−2 | 9.67 × 10−3 | 6.19 × 10−5 | 3.58 × 10−4 | 3.74 × 10−5 | 6.56 × 10−5 | 3.07 × 10−7 |
| 3 | 2.74 × 10−2 | 1.26 × 10−2 | 1.97 × 10−5 | 4.41 × 10−4 | 1.90 × 10−5 | 2.48 × 10−5 | 3.78 × 10−7 |
| 5 | 5.45 × 10−3 | 6.98 × 10−4 | 3.42 × 10−6 | 1.94 × 10−4 | 3.28 × 10−6 | 9.51 × 10−6 | 1.66 × 10−7 |
| 8 | 2.31 × 10−2 | 5.76 × 10−3 | 1.10 × 10−5 | 1.04 × 10−4 | 4.76 × 10−5 | 6.89 × 10−5 | 8.88 × 10−8 |
| 11 | 7.19 × 10−4 | 5.07 × 10−4 | 1.14 × 10−6 | 3.38 × 10−5 | 1.59 × 10−6 | 2.01 × 10−6 | 2.90 × 10−8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, H.; Ma, Y.; Du, X.; Zhang, M.; Shi, Y.; Yao, J.; Zhao, W. Evaluation of the Barrier Effect of Polylactic Acid-Modified Membrane on Odours at the Excavated Soil Interface of a Pesticide-Contaminated Site. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1695. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13101695
Zheng H, Ma Y, Du X, Zhang M, Shi Y, Yao J, Zhao W. Evaluation of the Barrier Effect of Polylactic Acid-Modified Membrane on Odours at the Excavated Soil Interface of a Pesticide-Contaminated Site. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(10):1695. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13101695
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Hongguang, Yan Ma, Xiaoming Du, Meng Zhang, Yi Shi, Juejun Yao, and Weiguang Zhao. 2022. "Evaluation of the Barrier Effect of Polylactic Acid-Modified Membrane on Odours at the Excavated Soil Interface of a Pesticide-Contaminated Site" Atmosphere 13, no. 10: 1695. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13101695
APA StyleZheng, H., Ma, Y., Du, X., Zhang, M., Shi, Y., Yao, J., & Zhao, W. (2022). Evaluation of the Barrier Effect of Polylactic Acid-Modified Membrane on Odours at the Excavated Soil Interface of a Pesticide-Contaminated Site. Atmosphere, 13(10), 1695. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13101695






