Hygroscopicity of Fresh and Aged Salt Mixtures from Saline Lakes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
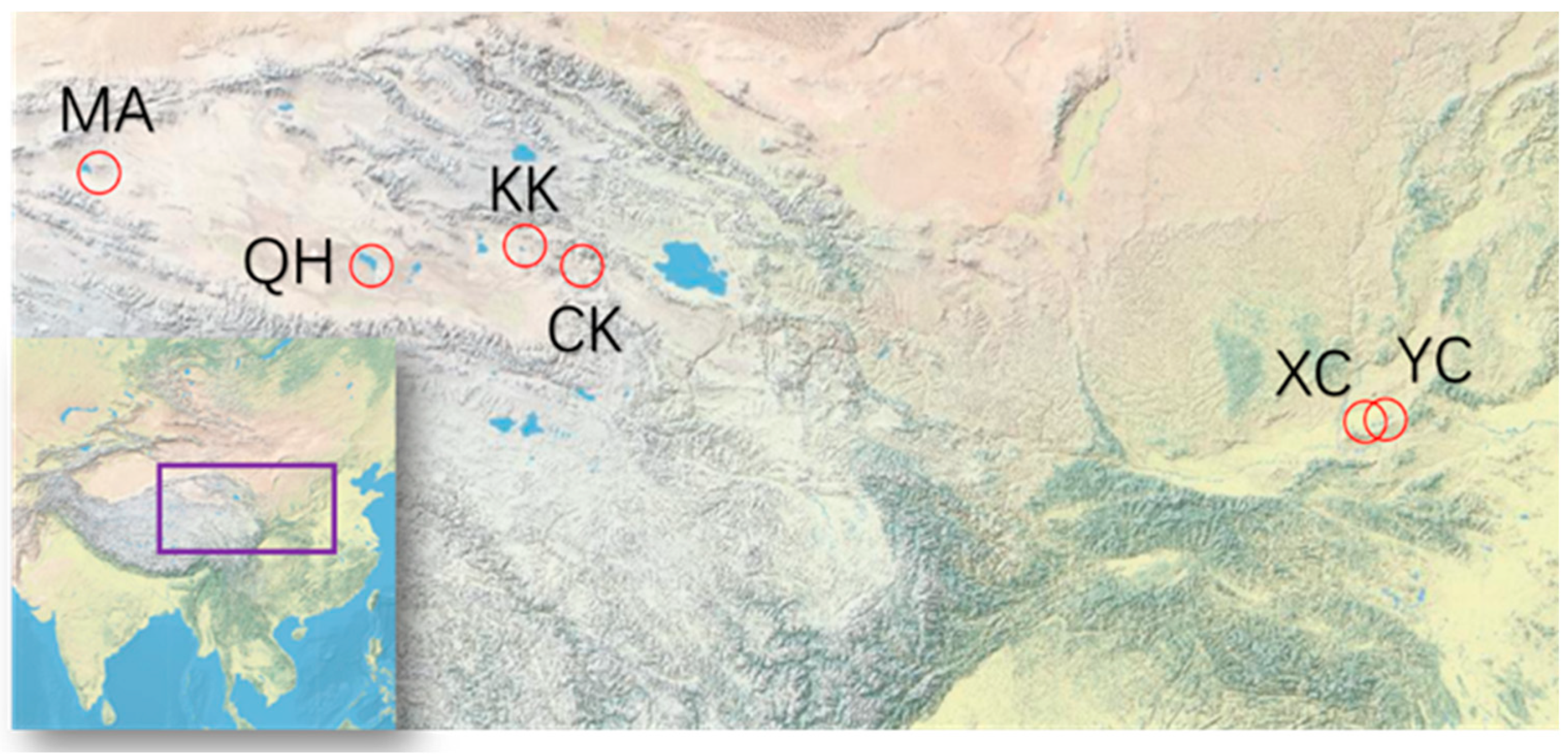
2.1. Sampling Sites
2.1.1. Two Lakes (XC and YC) in Shanxi Province
2.1.2. Four Lakes (CK, KK, QH and MA) in Qaidam Basin
2.2. Ion Chromatography
2.3. Brine Crystallization
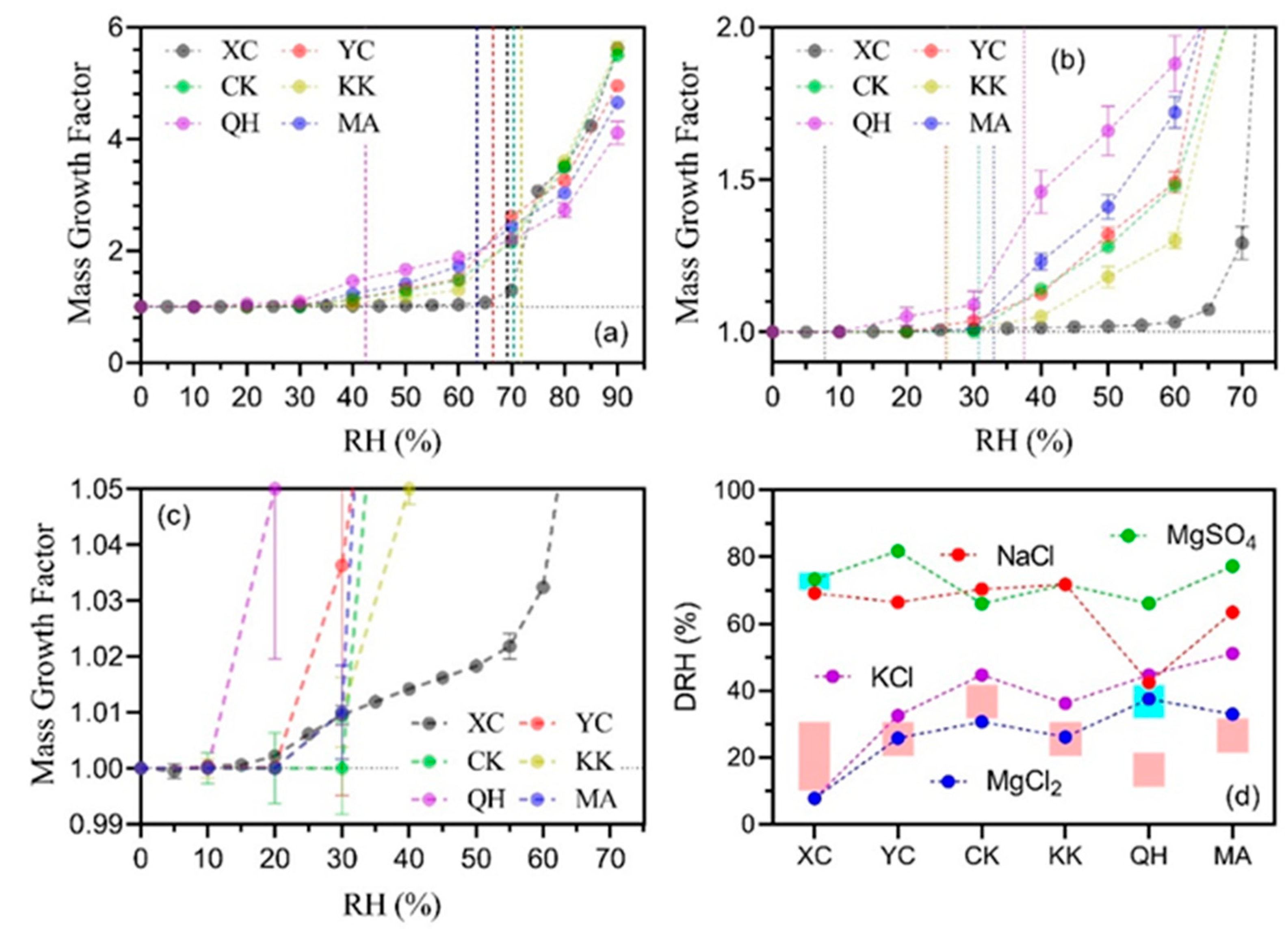
2.4. Hygroscopicity Measurements
2.5. Thermodynamic Model
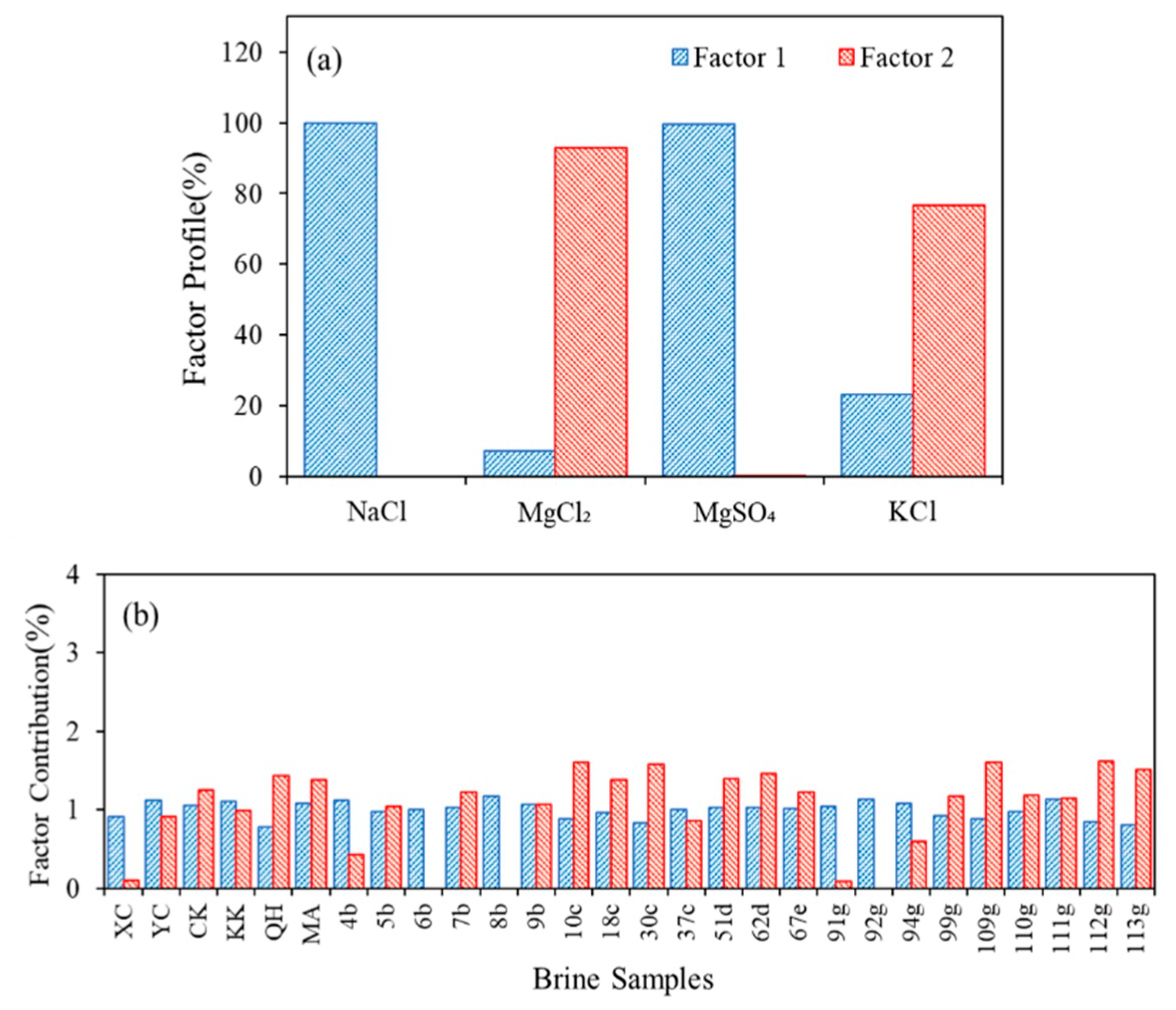
2.6. Positive Matrix Factorization Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Saline Lake Brines
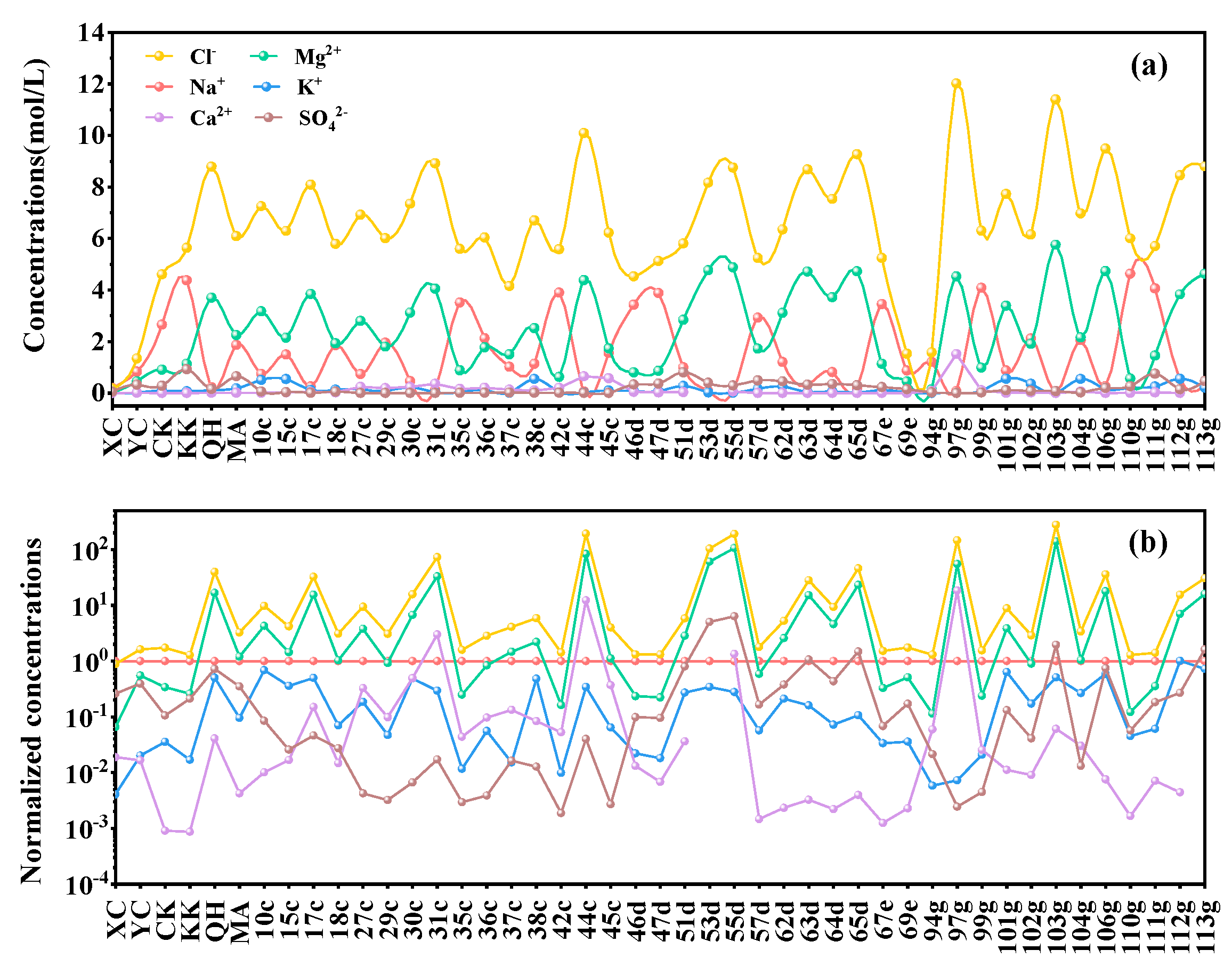
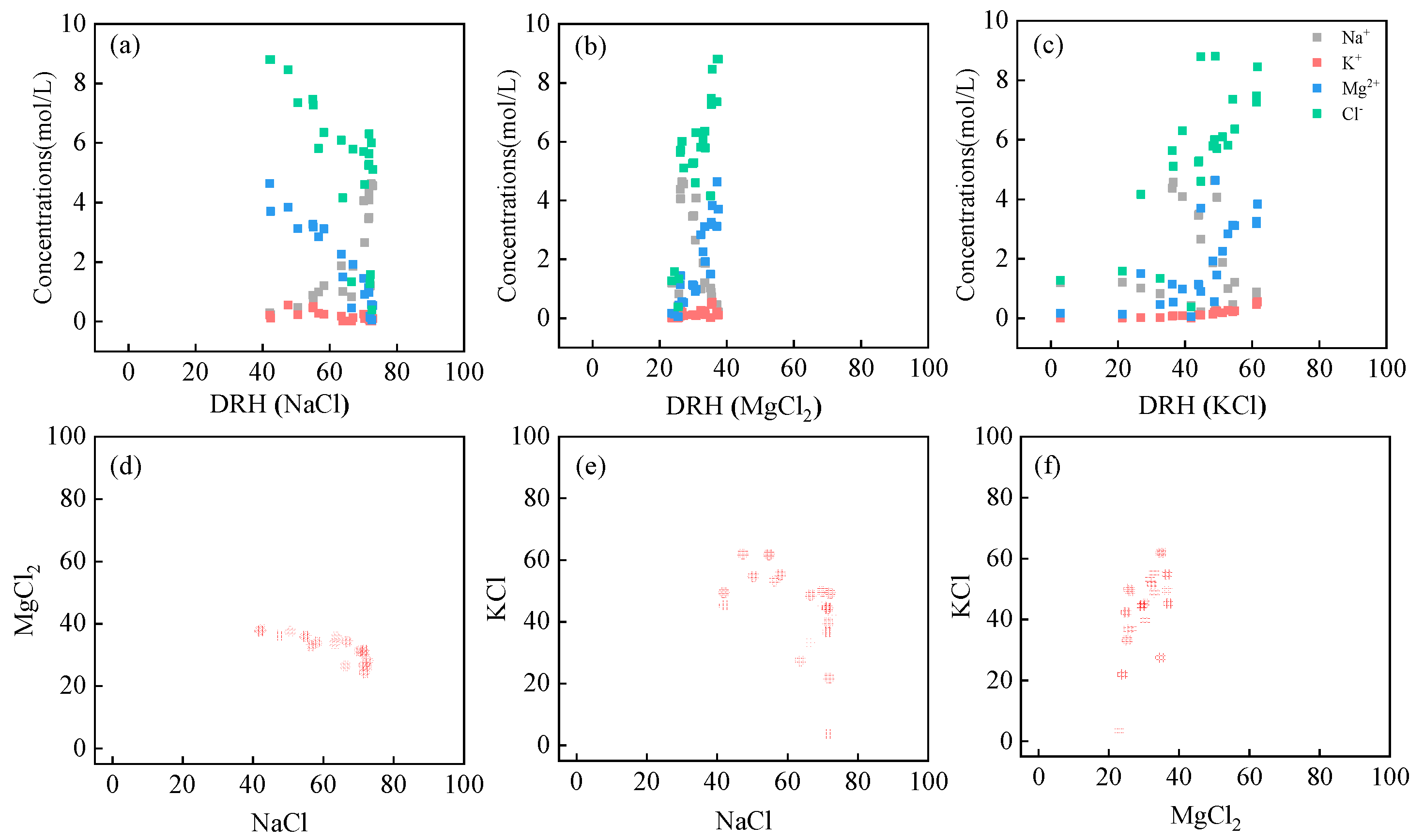
3.1.1. Ionic Concentrations
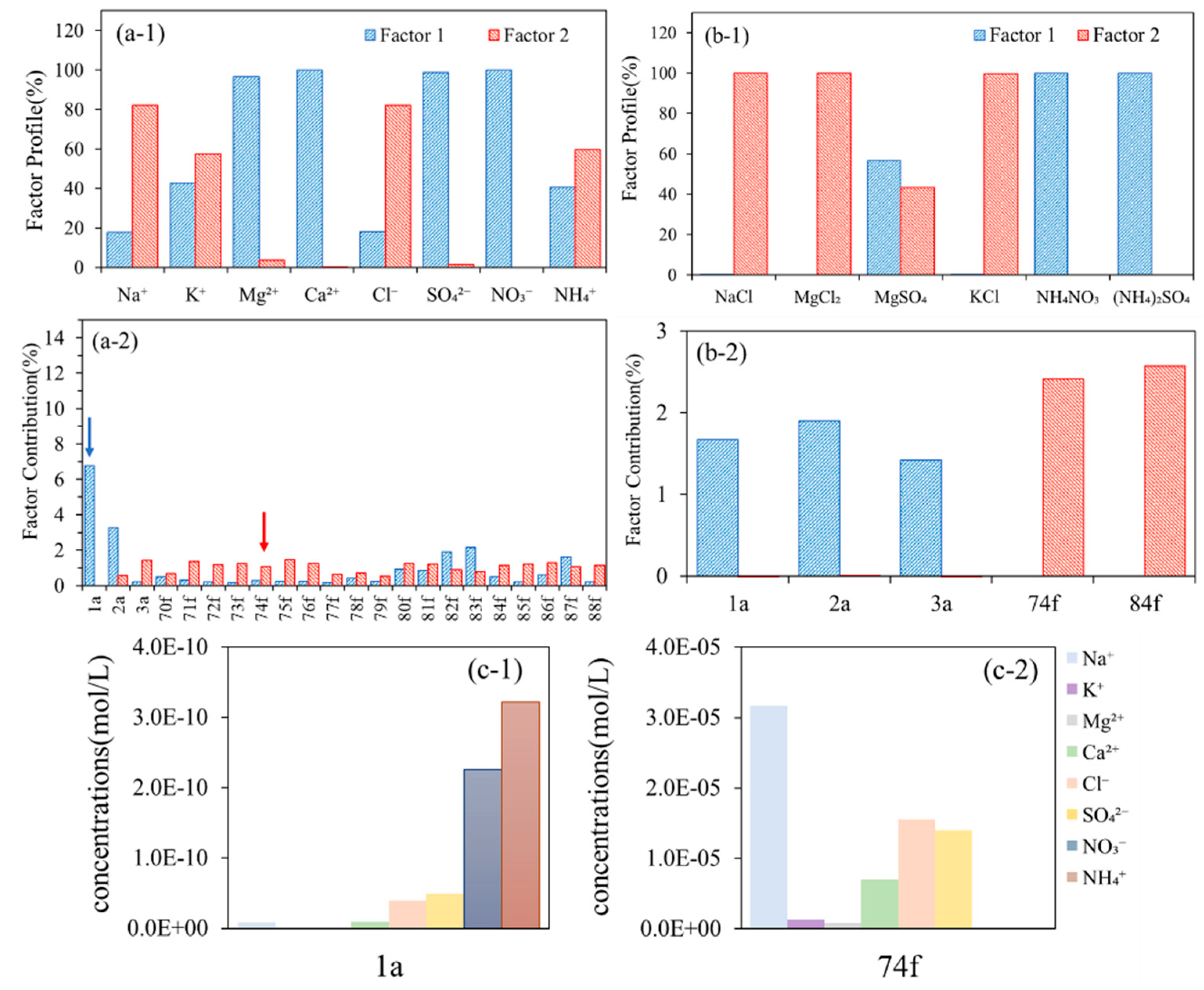
3.1.2. PMF Analysis of Ionic Concentrations
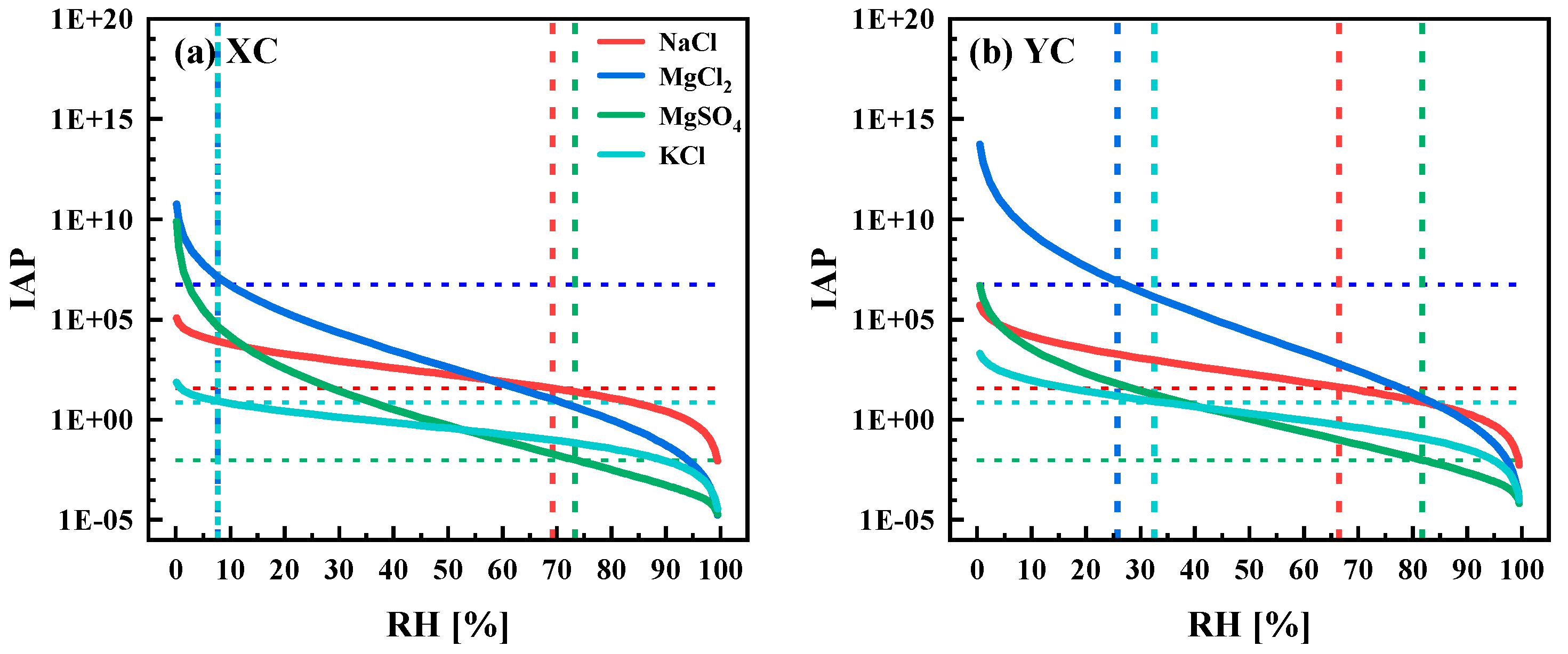
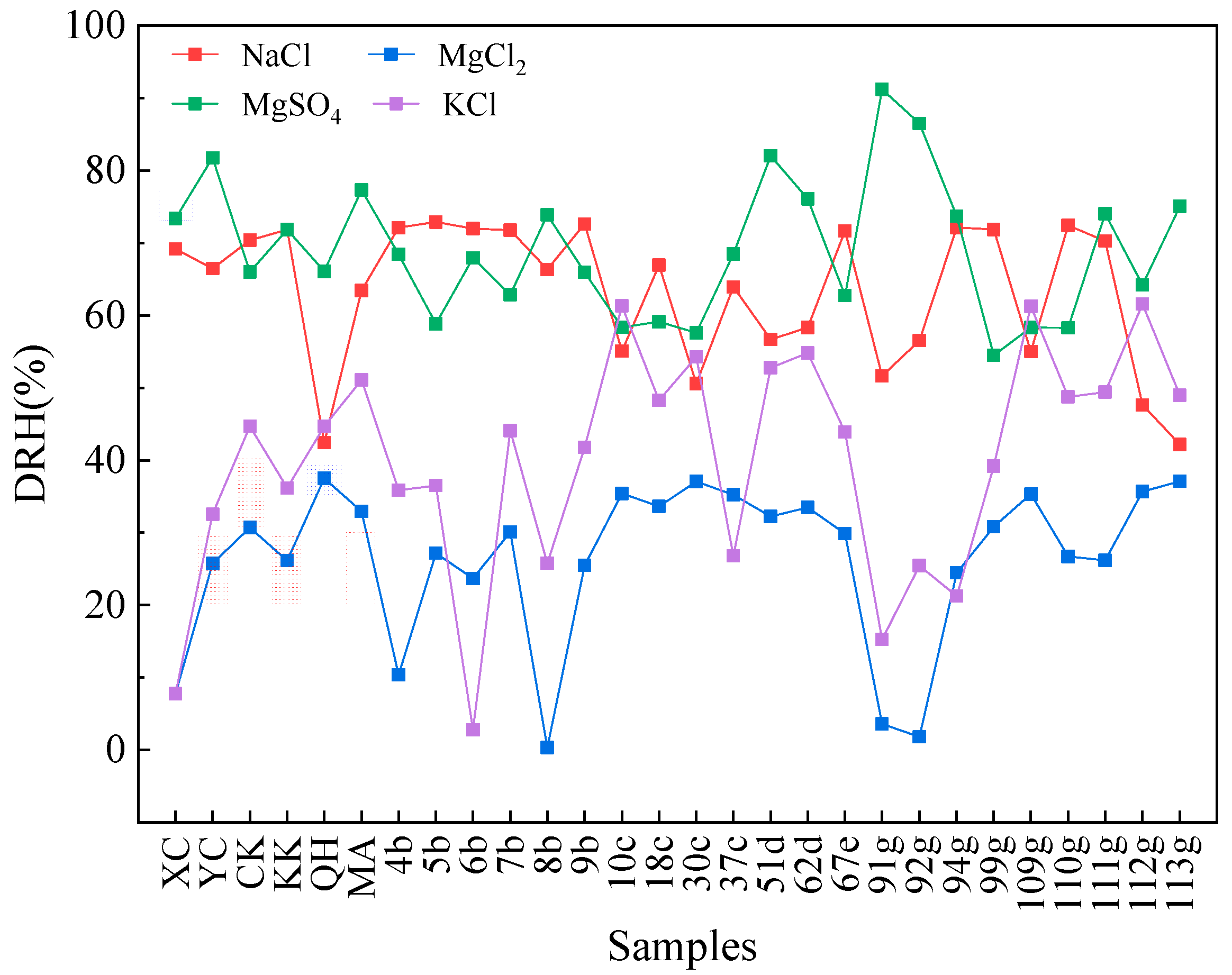
3.1.3. Deliquescence RH
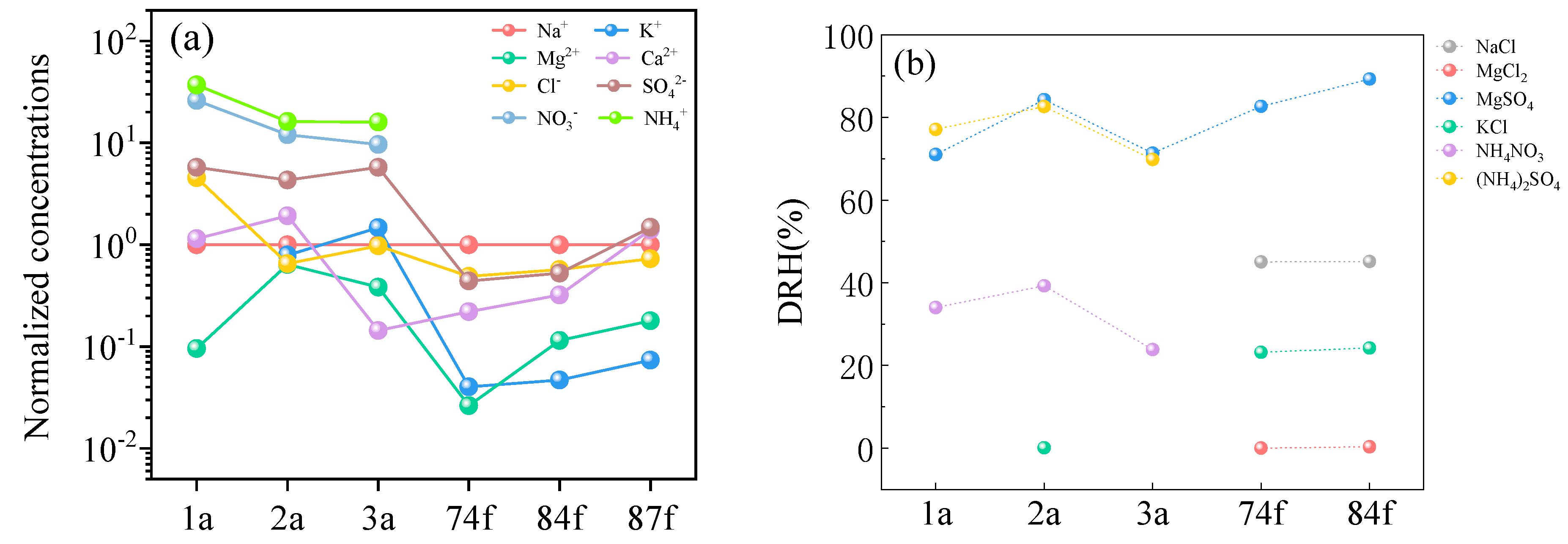
3.1.4. Aged Salt Aerosol Particles
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Lee, W.; Diner, D.J.; Garay, M.J.; Jiang, J.; Wang, Y.; Yu, J.; Kalashnikova, O.V. Evaluation of sea salt aerosols in climate systems: Global climate modeling and observation-based analyses. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 034047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbatt, J.P.; Benz, S.; Cziczo, D.J.; Kanji, Z.; Lohmann, U.; Mohler, O. Solid ammonium sulfate aerosols as ice nuclei: A pathway for cirrus cloud formation. Science 2006, 313, 1770–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cziczo, D.J.; Froyd, K.D.; Hoose, C.; Jensen, E.J.; Diao, M.; Zondlo, M.A.; Smith, J.B.; Twohy, C.H.; Murphy, D.M. Clarifying the dominant sources and mechanisms of cirrus cloud formation. Science 2013, 340, 1320–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoose, C.; Möhler, O. Heterogeneous ice nucleation on atmospheric aerosols: A review of results from laboratory experiments. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 9817–9854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grythe, H.; Ström, J.; Krejci, R.; Quinn, P.; Stohl, A. A review of sea-spray aerosol source functions using a large global set of sea salt aerosol concentration measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 1277–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Hua, T.; Zhang, C.; Lang, L.; Wang, H. Aeolian salts in Gobi deserts of the western region of Inner Mongolia: Gone with the dust aerosols. Atmos. Res. 2012, 118, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, C.; Ristovski, Z.; Milic, A.; Gu, Y.; Islam, M.S.; Wang, S.; Hao, J.; Zhang, H.; He, C.; et al. A review of biomass burning: Emissions and impacts on air quality, health and climate in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 1000–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Hua, T.; Zhang, C.; Qian, G.; Luo, W. Salts in the clay playas of China’s arid regions: Gone with the wind. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 68, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, T.E. Eolian sediments generated by anthropogenic disturbance of playas: Human impacts on the geomorphic system and geomorphic impacts on the human system. Geomorphology 1996, 17, 207–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formenti, P. Chemical composition of mineral dust aerosol during the Saharan Dust Experiment (SHADE) airborne campaign in the Cape Verde region, September 2000. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, D18:3–1–D18:3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhuang, G.; Yuan, H.; Rahn, K.A.; Wang, Z.; An, Z. Aerosol particles from dried salt-lakes and saline soils carried on dust storms over Beijing. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 2009, 20, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Abuduwaili, J.; Gabchenko, M.V.; Junrong, X. Eolian transport of salts—A case study in the area of Lake Ebinur (Xinjiang, Northwest China). J. Arid. Environ. 2008, 72, 1843–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prospero, J.M. Environmental characterization of global sources of atmospheric soil dust identified with the NIMBUS 7 Total Ozone Mapping Spectrometer (TOMS) absorbing aerosol product. Rev. Geophys. 2002, 40, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaston, C.J.; Pratt, K.A.; Suski, K.J.; May, N.W.; Gill, T.E.; Prather, K.A. Laboratory studies of the cloud droplet activation properties and corresponding chemistry of saline playa dust. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 1348–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, K.A.; Twohy, C.H.; Murphy, S.M.; Moffet, R.C.; Heymsfield, A.J.; Gaston, C.J.; DeMott, P.J.; Field, P.R.; Henn, T.R.; Rogers, D.C.; et al. Observation of playa salts as nuclei in orographic wave clouds. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, D15301:1–D15301:17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Zhang, S.; Wang, G.; Lv, S.; Li, D.; Liu, L.; Li, J.; Liu, S.; Du, W.; Meng, J.; et al. Efficient heterogeneous formation of ammonium nitrate on the saline mineral particle surface in the atmosphere of East Asia during dust storm periods. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 15622–15630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Cheng, C.; Huang, Y.; Tao, J.; Ren, Y.; Wu, F.; Meng, J.; Li, J.; Cheng, Y.; Cao, J.; et al. Evolution of aerosol chemistry in Xi’an, inland China, during the dust storm period of 2013—Part 1: Sources, chemical forms and formation mechanisms of nitrate and sulfate. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 11571–11585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, V.; Crutzen, P.J.; Kiehl, J.T.; Rosenfeld, D. Aerosols, climate, and the hydrological cycle. Science 2001, 294, 2119–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.; Chen, H.; Kukulies, J.; Ou, T.; Chen, D. Regionalization of seasonal precipitation over the Tibetan Plateau and associated large-scale atmospheric systems. J. Clim. 2021, 34, 2635–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Kuang, Y.; Liang, L.; He, Y.; Cheng, H.; Bian, Y.; Tao, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, P.; Ma, N.; et al. Dust-dominated coarse particles as a medium for rapid secondary organic and inorganic aerosol formation in highly polluted air. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 15710–15721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitroo, D.; Gill, T.E.; Haas, S.; Pratt, K.A.; Gaston, C.J. ClNO2 Production from N2O5 uptake on saline playa dusts: New insights into potential inland sources of ClNO2. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 7442–7452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Zhang, H.; Gu, W.; Gao, J.; Jian, X.; Shi, G.; Zhu, B.; Xie, L.; Guo, L.; Gao, X.; et al. Hygroscopic properties of saline mineral dust from different regions in China: Geographical variations, compositional dependence, and atmospheric implications. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 10844–10857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Li, J.; Gu, W.; Santos, L.F.E.D.; Boman, J.; Zhang, X.; Tang, M.; Wang, S.; Kong, X. Chemical and hygroscopic characterization of surface salts in the Qaidam Basin: Implications for climate impacts on Planet Earth and Mars. ACS Earth Space Chem. 2021, 5, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobo, Y.; Zhang, D.; Matsuki, A.; Iwasaka, Y. Asian dust particles converted into aqueous droplets under remote marine atmospheric conditions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 17905–17910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laskin, A.; Iedema, M.J.; Ichkovich, A.; Graber, E.R.; Taraniuk, I.; Rudich, Y. Direct observation of completely processed calcium carbonate dust particles. Faraday Discuss. 2005, 130, 453–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, M.; Cziczo, D.J.; Grassian, V.H. Interactions of water with mineral dust aerosol: Water adsorption, hygroscopicity, cloud condensation, and ice nucleation. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 4205–4259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D. Impact of climate change on sensitive marine and extreme terrestrial ecosystems: Recent progresses and future challenges: This article belongs to Ambio’s 50th Anniversary Collection. Theme: Climate change impact. Ambio 2021, 50, 1141–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, X. Climate changes in the Qaidam Basin in NW China over the past 40 kyr. Palaeogeogr. Palaeocl. 2020, 551, 109679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frie, A.L.; Dingle, J.H.; Ying, S.C.; Bahreini, R. The effect of a receding saline lake (the Salton Sea) on airborne particulate matter composition. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 8283–8292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peckham, S.; Grell, G.A.; McKeen, S.A.; Barth, M.; Pfister, G.; Wiedinmyer, C.; Fast, J.D.; Gustafson, W.I.; Zaveri, R.; Easter, R.C.; et al. WRF-Chem Version 3.3 User’s Guide; NOAA Technical Memo: Boulder, CO, USA, 2011; p. 99.
- Li, C.; Gao, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y. Impact of anthropogenic activities on the enrichment of fluoride and salinity in groundwater in the Yuncheng Basin constrained by Cl/Br ratio, δ18O, δ2H, δ13C and δ7Li isotopes. J. Hydrol. 2019, 579, 124211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Gao, X. Assessment of groundwater quality at Yuncheng Basin: Denotation for the water management in China. Ground Water 2019, 57, 492–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Guo, Q. Enrichment of fluoride in groundwater under the impact of saline water intrusion at the salt lake area of Yuncheng Basin, northern China. Environ. Geol. 2007, 53, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kezao, C.; Bowler, J.M. Late Pleistocene evolution of salt lakes in the Qaidam Basin, Qinghai province, China. Palaeogeogr. Palaeocl. 1986, 54, 87–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Dong, Z.; Cui, X.; Bao, F. Pattern analysis of simple transverse dunes in China’s Qaidam Basin, north of the Kunlun Mountains. Environ. Earth. Sci. 2016, 75, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Gu, W.; Ma, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhong, C.; Li, S.; Yin, X.; Huang, R.; He, H.; Wang, X. Water adsorption and hygroscopic growth of six anemophilous pollen species: The effect of temperature. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 2247–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Gu, W.; Peng, C.; Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Zong, T.; Tang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Lin, Q.; Ge, M.; et al. A comprehensive study of hygroscopic properties of calcium- and magnesium-containing salts: Implication for hygroscopicity of mineral dust and sea salt aerosols. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 2115–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.; Li, Y.; Zhu, J.; Jia, X.; Lin, Q.; Zhang, G.; Ding, X.; Song, W.; Bi, X.; Wang, X.; et al. Investigation of water adsorption and hygroscopicity of atmospherically relevant particles using a commercial vapor sorption analyzer. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 3821–3832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuend, A.; Marcolli, C.; Booth, A.M.; Lienhard, D.M.; Soonsin, V.; Krieger, U.K.; Topping, D.O.; McFiggans, G.; Peter, T.; Seinfeld, J.H. New and extended parameterization of the thermodynamic model AIOMFAC: Calculation of activity coefficients for organic-inorganic mixtures containing carboxyl, hydroxyl, carbonyl, ether, ester, alkenyl, alkyl, and aromatic functional groups. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 9155–9206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuend, A.; Marcolli, C.; Luo, B.P.; Peter, T. A thermodynamic model of mixed organic-inorganic aerosols to predict activity coefficients. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 4559–4593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, G.; Duvall, R.; Brown, S.; Bai, S. EPA Positive Matrix Factorization (PMF) 5.0 Fundamentals and User Guide; EPA/600/R-14/108 (NTIS PB2015-105147); U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2014.
- Wu, C.; Tuo, J.; Chen, R.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Y. Relationships between source inputs and lipid geochemistry of lake sediments on the Northern Tibetan Plateau, China. Geomicrobiol. J. 2020, 37, 702–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Fan, Q.; Wei, H.; Qin, Z.; Zhang, X.; Du, Y.; Shan, F. Sulfur isotope constraints on the formation of MgSO4-deficient evaporites in the Qarhan salt Lake, western China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2020, 189, 104160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Lowenstein, T.K.; Wei, H.; Yuan, Q.; Qin, Z.; Shan, F.; Ma, H. Sr isotope and major ion compositional evidence for formation of Qarhan Salt Lake, western China. Chem. Geol. 2018, 497, 128–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Mao, J.; Ren, Y.; Li, Y.; Lin, Y.; Power, I.M.; Luo, Y. Salt crystallization sequences of nonmarine brine and their application for the formation of potassium deposits. Aquat. Geochem. 2018, 24, 209–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Long, Q.; Chen, L.; Liu, D.; Zhu, D. Microbial community structure and diversity within hypersaline Keke Salt Lake environments. Can. J. Microbiol. 2017, 63, 895–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P. Saline Lakes of Qaidam Basin; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Lowenstein, T.K.; Spencer, R.J.; Pengxi, Z. Origin of ancient potash evaporites: Clues from the modem nonmarine qaidam basin of Western china. Science 1989, 245, 1090–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H.; Park, Y.; Hwang, H.; Kang, S.; Ro, C.U. Elevated nitrogen-containing particles observed in Asian dust aerosol samples collected at the marine boundary layer of the Bohai Sea and the Yellow Sea. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 6933–6947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Na+ | K+ | Mg2+ | Ca2+ | Cl− | SO42− | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na+ | 1.00 | |||||
| K+ | −0.06 | 1.00 | ||||
| Mg2+ | −0.55 | 0.24 | 1.00 | |||
| Ca2+ | −0.07 | −0.21 | 0.16 | 1.00 | ||
| Cl− | −0.13 | 0.29 | 0.86 | 0.35 | 1.00 | |
| SO42− | 0.25 | −0.02 | 0.11 | −0.33 | 0.05 | 1.00 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Liu, W.; Li, L.; Gu, W.; Zhang, X.; Hallquist, M.; Tang, M.; Wang, S.; Kong, X. Hygroscopicity of Fresh and Aged Salt Mixtures from Saline Lakes. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1203. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12091203
Li J, Liu W, Li L, Gu W, Zhang X, Hallquist M, Tang M, Wang S, Kong X. Hygroscopicity of Fresh and Aged Salt Mixtures from Saline Lakes. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(9):1203. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12091203
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jun, Wanyu Liu, Linjie Li, Wenjun Gu, Xiying Zhang, Mattias Hallquist, Mingjin Tang, Sen Wang, and Xiangrui Kong. 2021. "Hygroscopicity of Fresh and Aged Salt Mixtures from Saline Lakes" Atmosphere 12, no. 9: 1203. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12091203
APA StyleLi, J., Liu, W., Li, L., Gu, W., Zhang, X., Hallquist, M., Tang, M., Wang, S., & Kong, X. (2021). Hygroscopicity of Fresh and Aged Salt Mixtures from Saline Lakes. Atmosphere, 12(9), 1203. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12091203








