Comparisons between Mean and Turbulent Parameters of Aircraft-Based and Ship-Based Measurements in the Marine Atmospheric Boundary Layer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Instrumented Aircraft
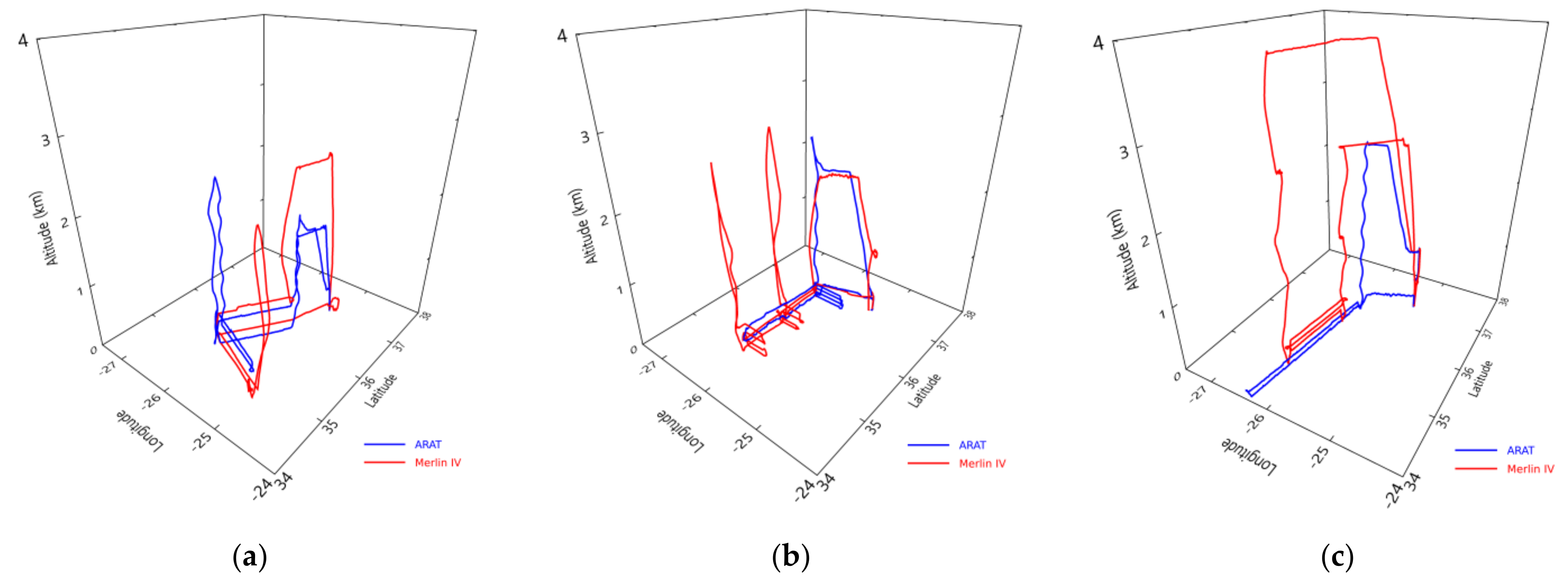
2.2. Flight Plans
2.3. Data from Aircraft
2.4. Infrared (IR) Flux Divergence
3. Results
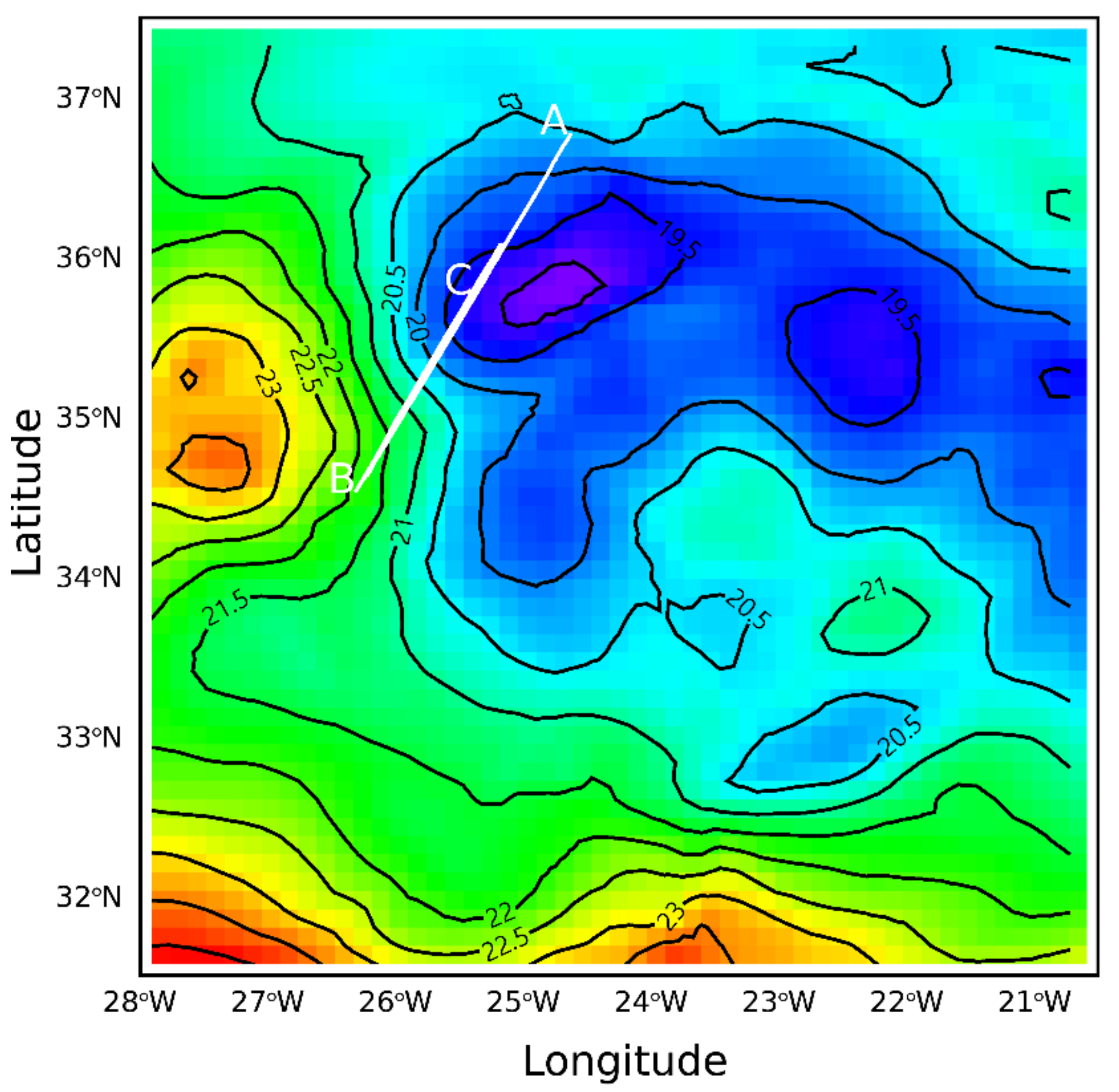
3.1. SST Field
3.2. Comparison of the Data from the Two Aircrafts
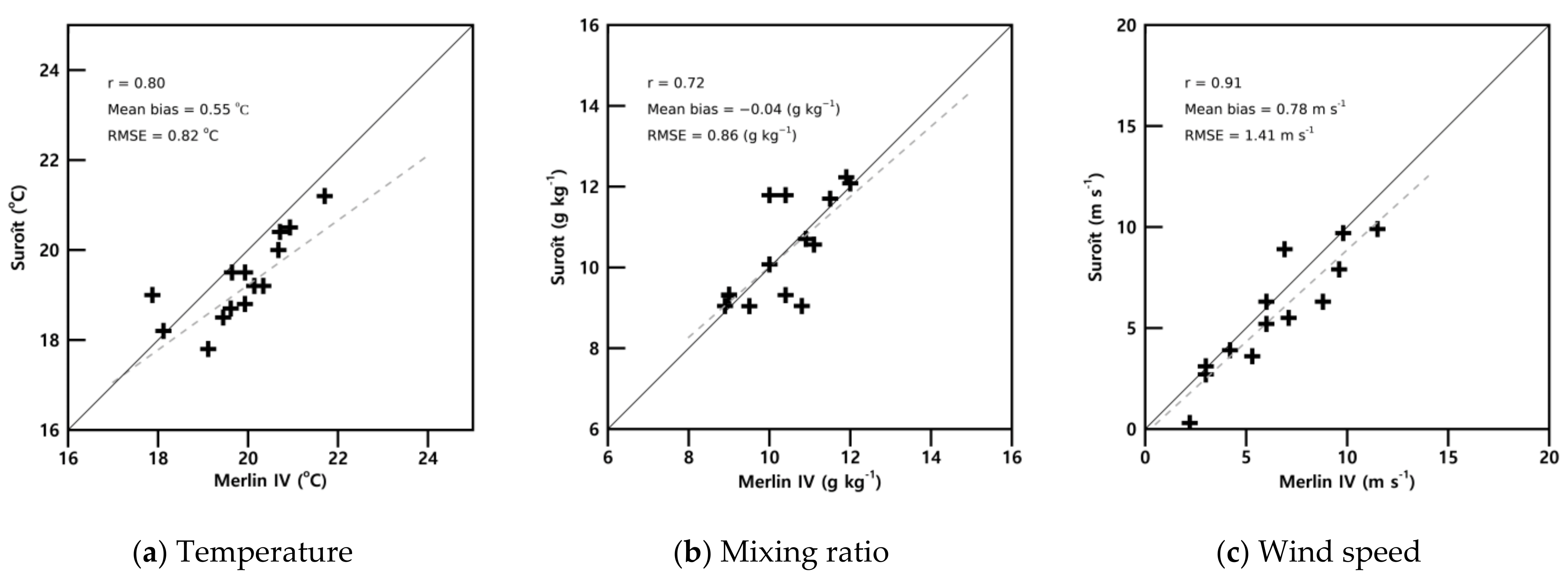
3.2.1. Air Temperature
3.2.2. Wind Speed and Mixing Ratio
3.2.3. Turbulence Parameters
3.3. Comparison between the Aircraft and the Ship
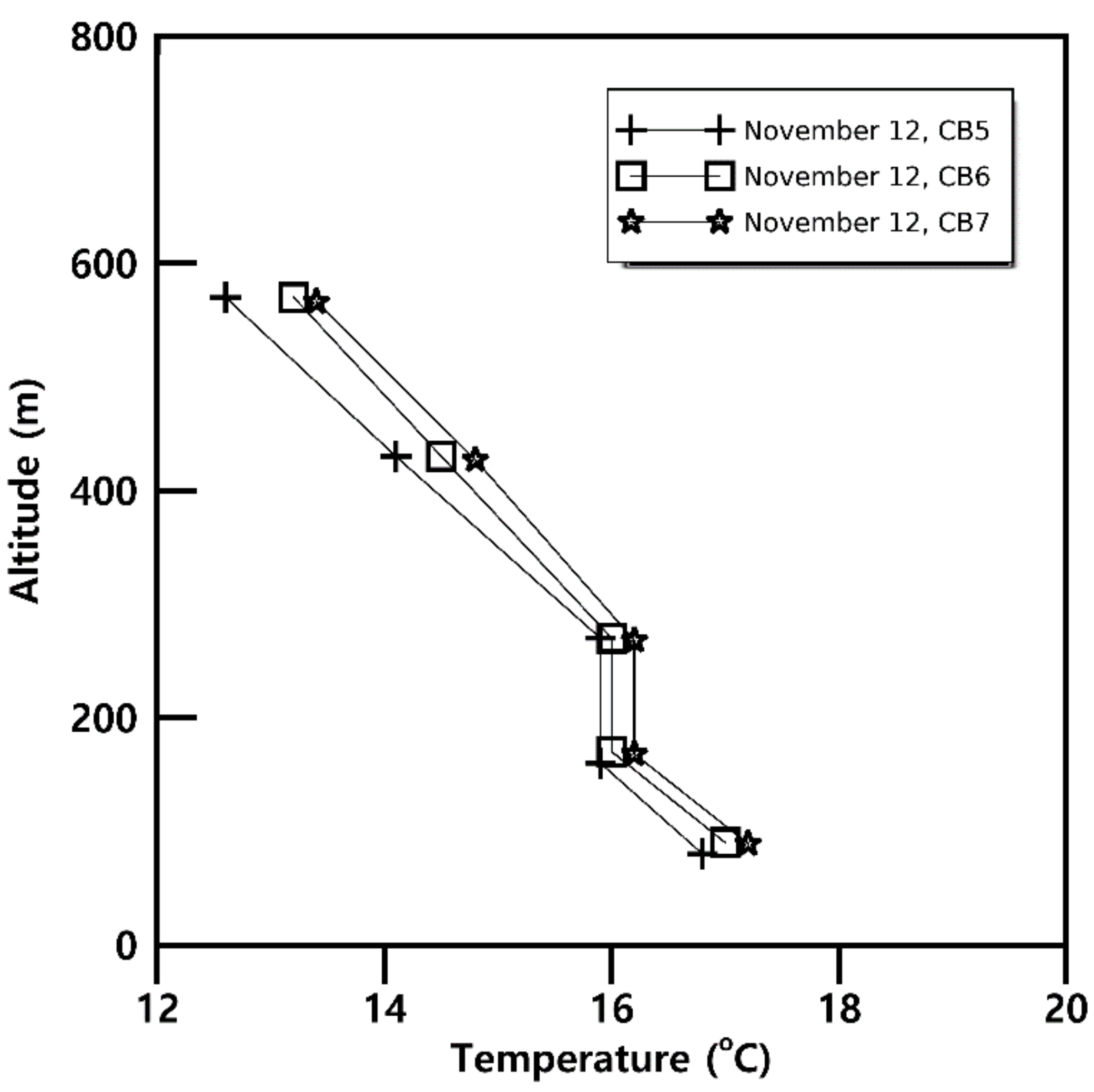
3.3.1. Temperature and Mixing Ratio
3.3.2. Wind Speed
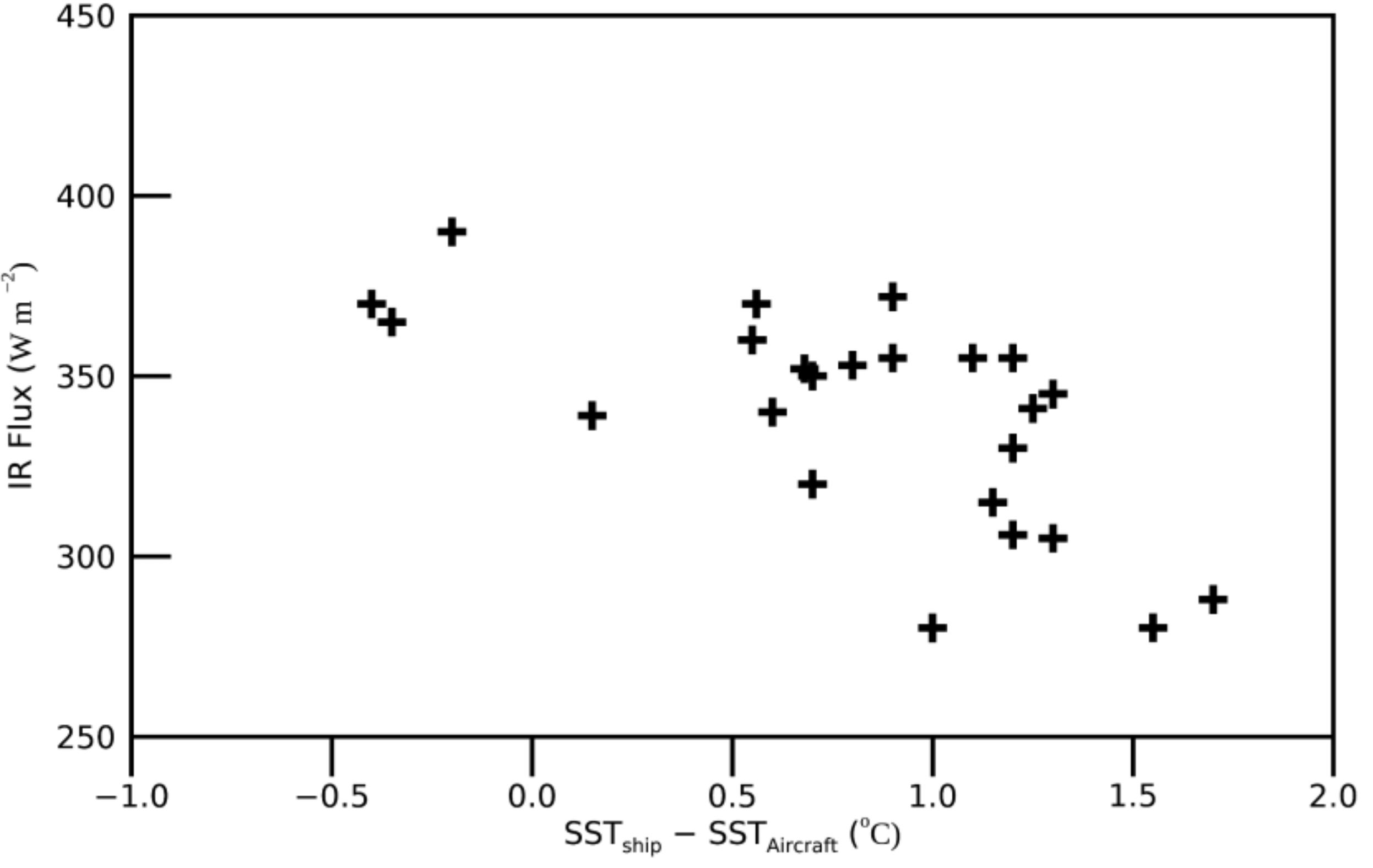
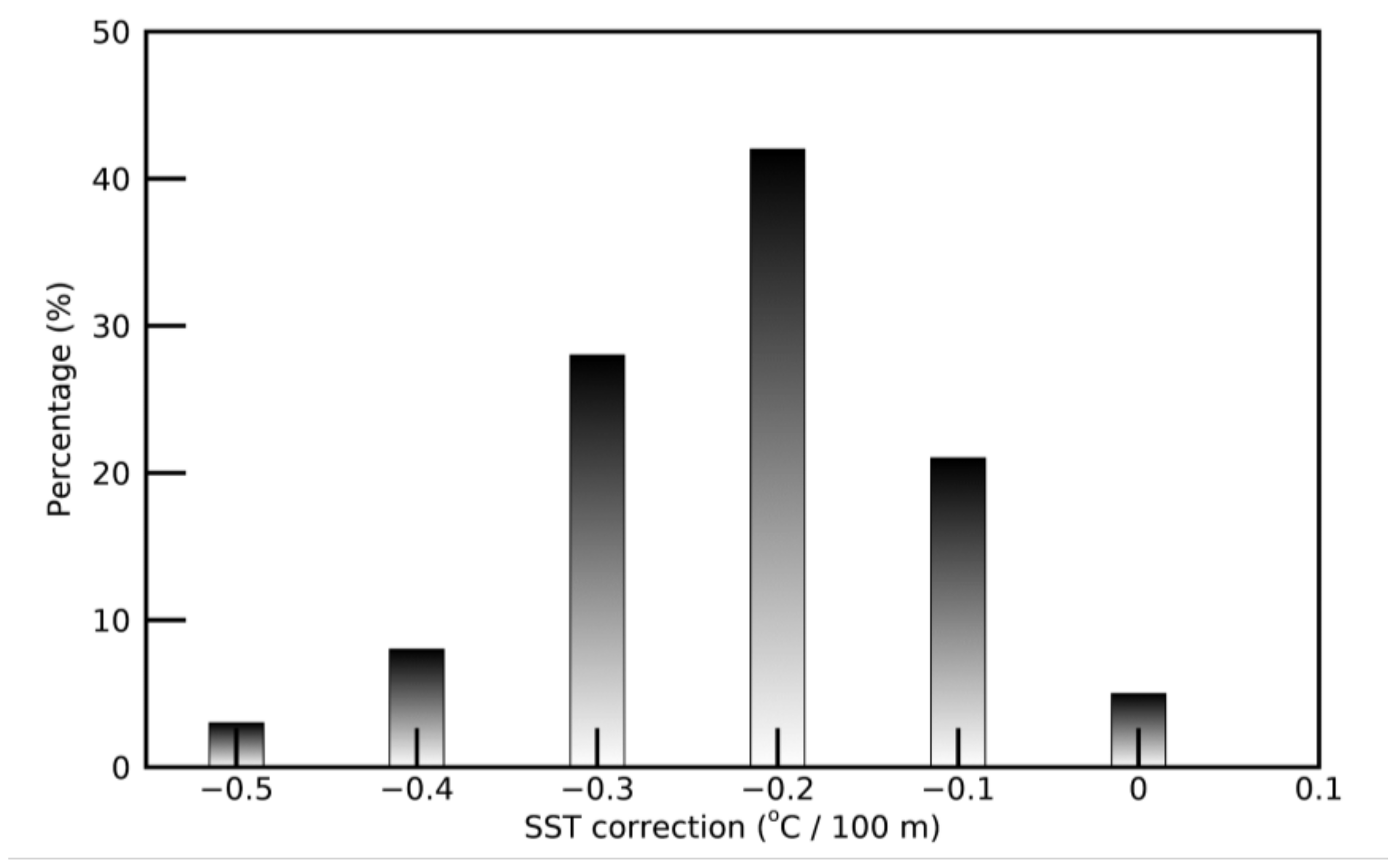
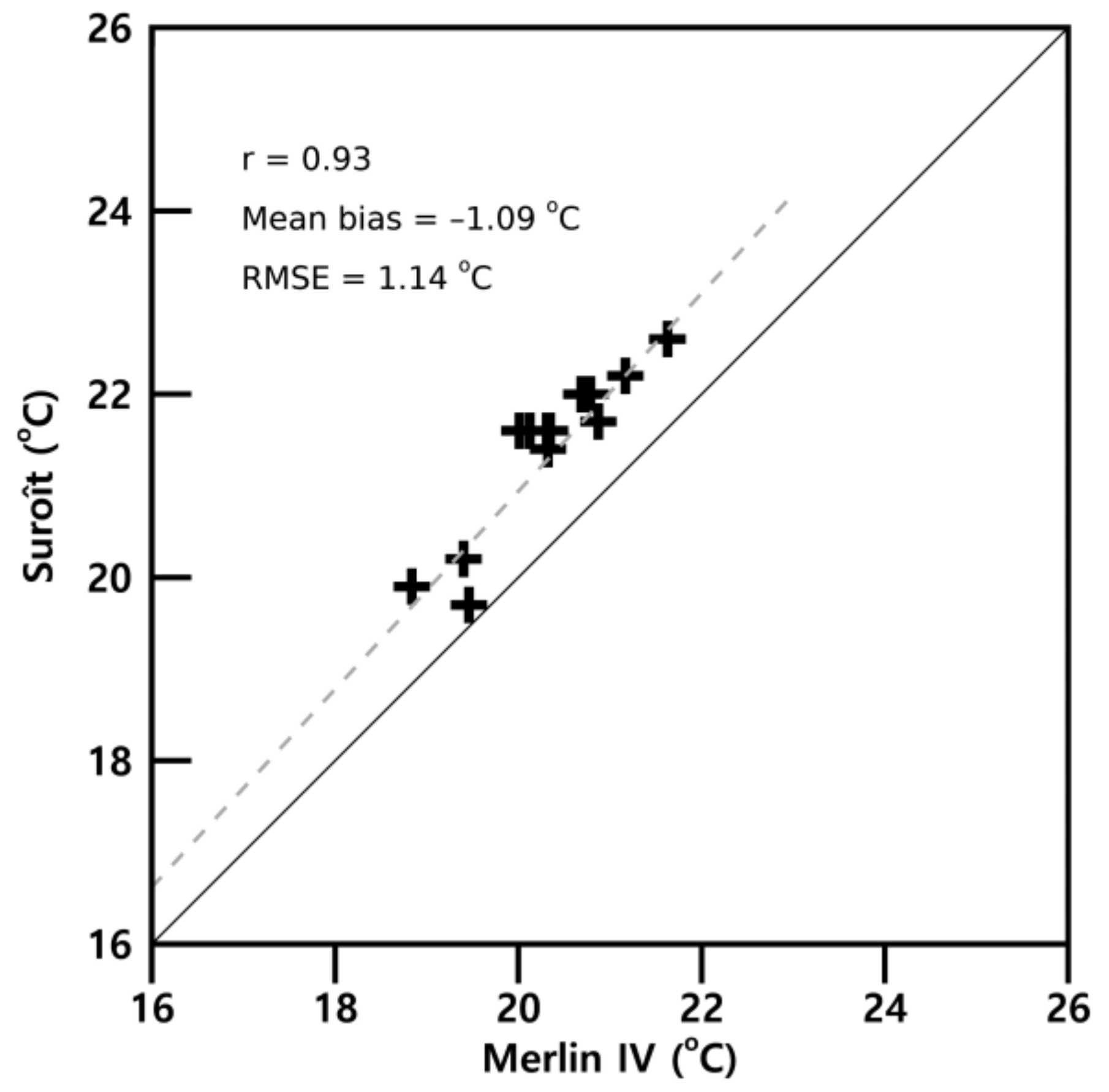
3.3.3. SST
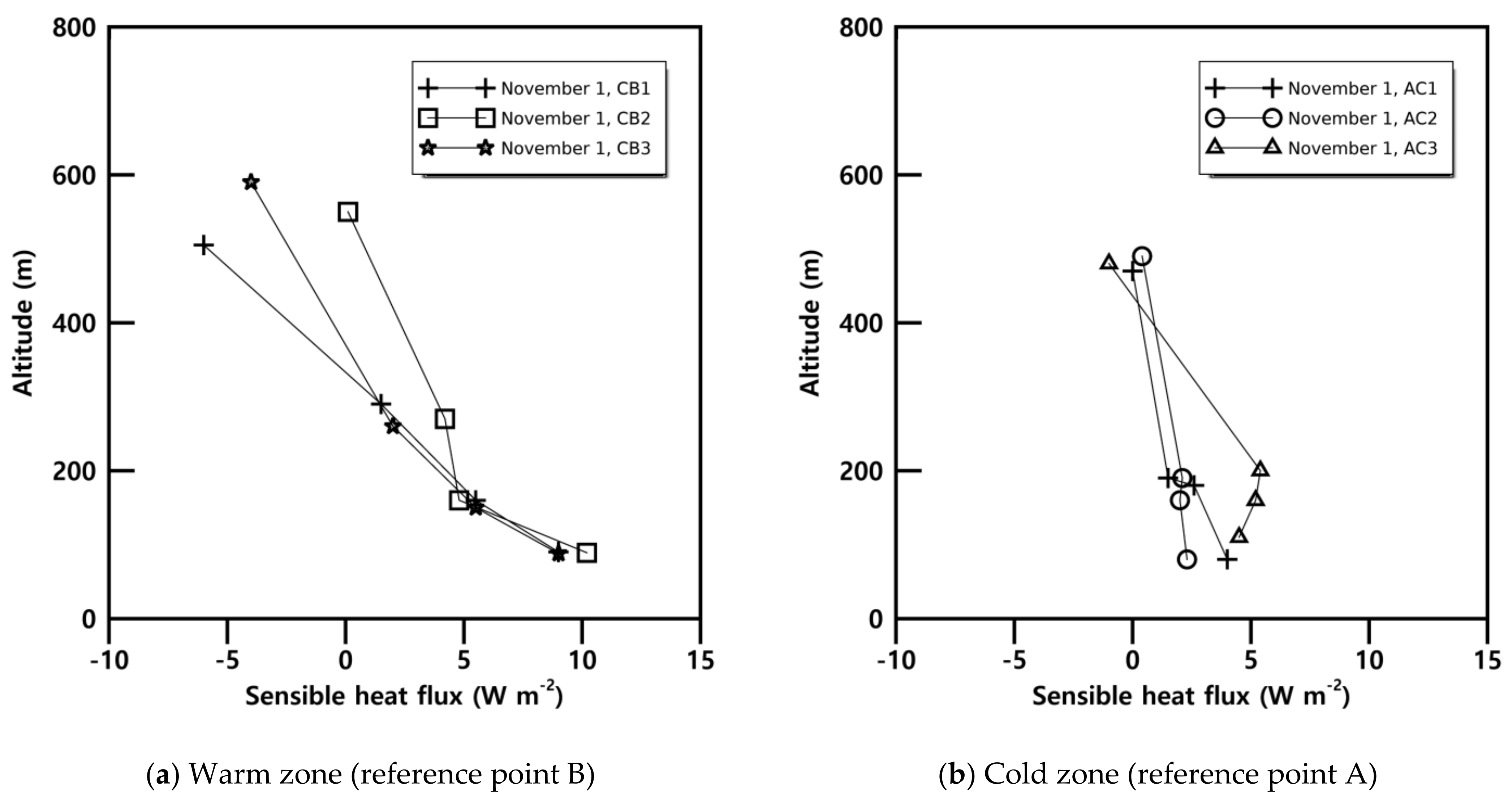
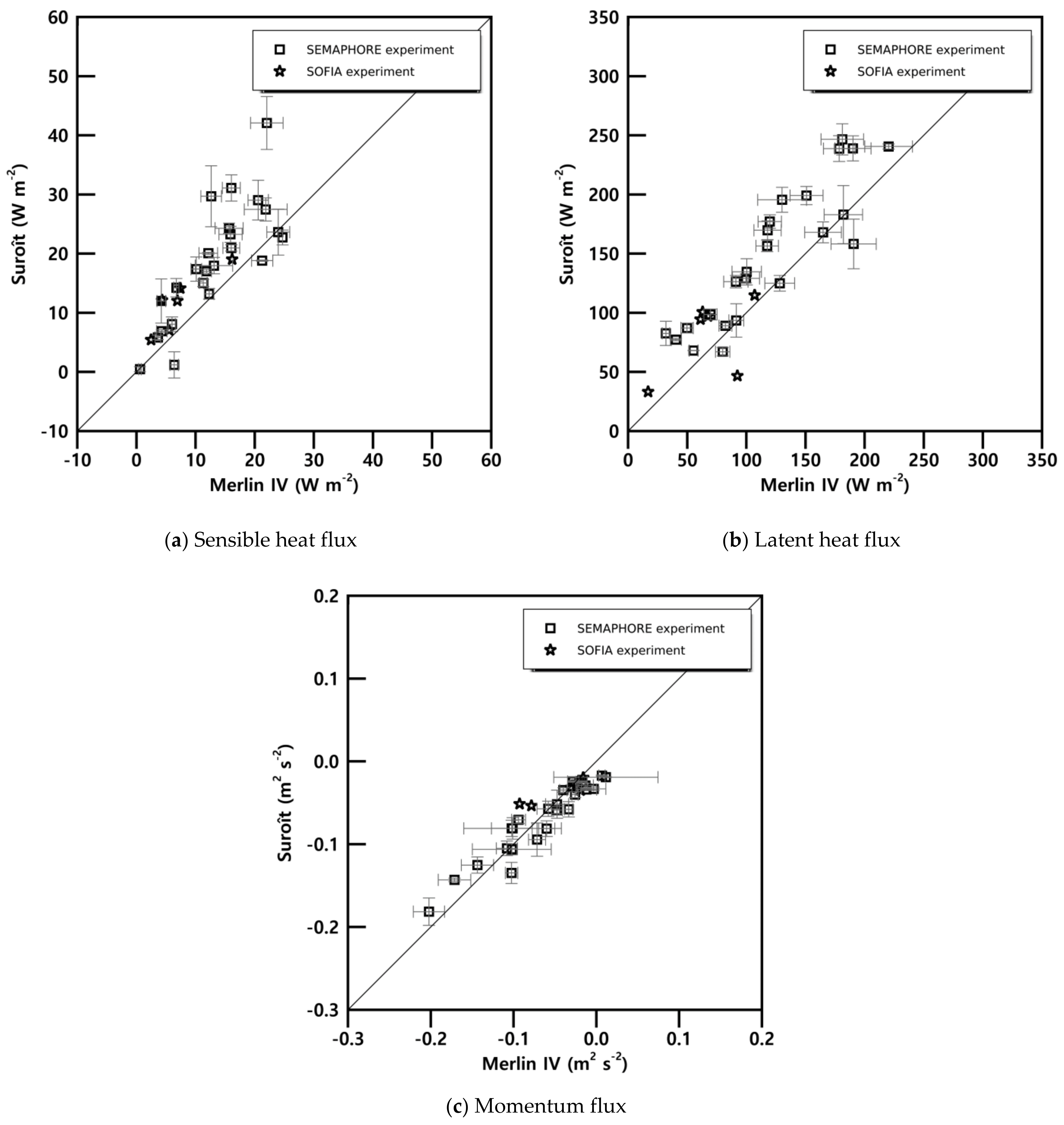
3.3.4. Turbulence Parameters
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kalogiros, J.; Wang, Q. Aircraft Observations of Sea-Surface Turbulent Fluxes Near the California Coast. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2011, 139, 283–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairall, C.W.; Bradley, E.F.; Hare, J.E.; Grachev, A.A.; Edson, J.B. Bulk parameterization of air-sea fluxes: Updates and verification for the COARE algorithm. J. Clim. 2003, 16, 571–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreas, E.L.; Mahrt, L.; Vickers, D. A new drag relation for aerodynamically rough flow over the ocean. J. Atmos. Sci. 2012, 69, 2520–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, S. Aircraft observations of the ekman layer during the joint air-sea interaction experiment. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1985, 111, 391–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, N.C.; Raman, S. Observations of a mesoscale circulation over the Gulf Stream region. Glob. Atmos. Ocean 1994, 2, 21–39. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, N.C.; Raman, S. Validity of similarity relations over the Gulf Stream. Tellus Ser. A Dyn. Meteorol. Oceanogr. 1996, 48, 368–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rogers, D.P. The marine boundary layer in the vicinity of an ocean front. J. Atmos. Sci. 1989, 46, 2044–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Friehe, C.A. Air-sea fluxes and surface layer turbulence around a sea surface temperature front. J. Geophys. Res. 1991, 96, 8593–8609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, M.D.; Vickery, P.J.; Reinhold, T.A. Reduced drag coefficient for high wind speeds in tropical cyclones. Nature 2003, 422, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persson, P.O.G.; Hare, J.E.; Fairall, C.W.; Otto, W.D. Air–sea interaction processes in warm and cold sectors of extratropical cyclonic storms observed during FASTEX. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2005, 131, 877–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.A.; Black, P.G.; French, J.R.; Drennan, W.M. First direct measurements of enthalpy flux in the hurricane boundary layer: The CBLAST results. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L14813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, G.N.; Renfrew, I.A. Aircraft-based observations of air–sea fluxes over Denmark Strait and the Irminger Sea during high wind speed conditions. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2009, 135, 2030–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Siems, S.T.; Manton, M.J.; Hande, L.B.; Haynes, J.M. The structure of low-altitude clouds over the Southern Ocean as seen by CloudSat. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 2535–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, S.C.H.; Huang, Y.; Lang, F.; Messmer, M.; Simmonds, I.; Siems, S.T.; Manton, M.J. A Climatology of the Marine Atmospheric Boundary Layer over the Southern Ocean from Four Field Campaigns During 2016–2018. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, e2020JD033214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, K.D.; Bodas-Salcedo, A.; Déqué, M.; Fermepin, S.; Medeiros, B.; Watanabe, M.; Jakob, C.; Klein, S.A.; Senior, C.A.; Williamson, D.L. The transpose-AMIP II Experiment and Its Application to the Understanding of Southern Ocean cloud Biases in Climate Models. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 3258–3274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hande, L.B.; Siems, S.T.; Manton, M.J.; Belusic, D. Observations of wind shear over the Southern Ocean. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, F.; Huang, Y.; Siems, S.T.; Manton, M.J. Characteristics of the Marine Atmospheric Boundary Layer Over the Southern Ocean in Response to the Synoptic Forcing. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 7799–7820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, B.H.; Bénech, B.; Lambert, D.; Durand, P.; Druilhet, A.; Giordani, H.; Planton, S. Structure of the marine atmospheric boundary layer over an oceanic thermal front: SEMAPHORE experiment. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1998, 103, 25159–25180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eymard, L.; Planton, S.; Durand, P.; Le Visage, C.; Le Traon, P.Y.; Prieur, L.; Weill, A.; Hauser, D.; Rolland, J.; Pelon, J.; et al. Study of the air-sea interactions at the mesoscale: The SEMAPHORE experiment. Ann. Geophys. 1996, 14, 986–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordani, H.; Planton, S.; Bénech, B.; Kwon, B.H. Monitoring the atmospheric and surface variability during the SEMAPHORE campaign: A data re-analysis with the ARPEGE operational system. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 103, 25047–25060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, D.; Durand, P. The marine atmospheric boundary layer during SEMAPHORE. Part I: Mean vertical structure and non-axisymmetry of turbulence. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1999, 125, 495–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, D.; Durand, P. Aircraft to aircraft intercomparison during SEMAPHORE. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1998, 103, 25109–25123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, B.H. Structure de la Couche Limite Atmospherique Marine en Presence d’un Front Oceanique (Experience Semaphore). Ph.D. Thesis, Paul Sabatier Universiry, Toulouse, France, 1997; p. 200. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, E.N.; Friehe, C.A.; Lenschow, D.H. Use of Pressure Fluctuations on the Nose of an Aircraft for Measuring Air Motion. J. Clim. Appl. Meteorol. 1983, 22, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenschow, D.H. Aircraft Measurements in the Boundary Layer. In Probing the Atmospheric Boundary Layer; American Meteorological Society: Boston, MA, USA, 1986; pp. 39–55. [Google Scholar]
- Mahrt, L. Heat and Moisture Fluxes over the Pine Forest in HAPEX. In Land Surface Evaporation; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 261–273. [Google Scholar]
- Giordani, H.; Planton, S.; Benech, B.; Kwon, B.-H. Atmospheric boundary layer response to sea surface temperatures during the SEMAPHORE experiment. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1998, 103, 25047–25060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Käse, R.H.; Siedler, G. Meandering of the subtropical front south-east of the Azores. Nature 1982, 300, 245–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Käse, R.H.; Price, J.F.; Richardson, P.L.; Zenk, W. A quasi-synoptic survey of the thermocline circulation and water mass distribution within the Canary Basin. J. Geophys. Res. 1986, 91, 9739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guymer, T.H.; Businger, J.A.; Katsaros, K.B.; Shaw, W.J.; Taylor, P.K.; Large, W.G.; Payne, R.E. Transfer processes at the air-sea interface. Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. London 1983, 308, 253–273. [Google Scholar]
- Zelinka, M.D.; Hartmann, D.L. Climate feedbacks and their implications for poleward energy flux changes in a warming climate. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 608–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyder, P.; Edwards, J.M.; Allan, R.P.; Hewitt, H.T.; Bracegirdle, T.J.; Gregory, J.M.; Wood, R.A.; Meijers, A.J.S.; Mulcahy, J.; Field, P.; et al. Critical Southern Ocean climate model biases traced to atmospheric model cloud errors. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Schuddeboom, A.; Varma, V.; McDonald, A.J.; Morgenstern, O.; Harvey, M.; Parsons, S.; Field, P.; Furtado, K. Cluster-Based Evaluation of Model Compensating Errors: A Case Study of Cloud Radiative Effect in the Southern Ocean. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 3446–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brilouet, P.; Durand, P.; Canut, G. The marine atmospheric boundary layer under strong wind conditions: Organized turbulence structure and flux estimates by airborne measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 2115–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenschow, D.H.; Stankov, B.B. Length scales in the convective boundary layer. J. Atmos. Sci. 1986, 43, 1198–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druilhet, A.; Guédalia, D.; Noilhan, J.; Charpentier, C. moyens aéroportés utilisés durant l’expérience COCAGNE. J. Rech. Atmos. 1985, 19, 369–398. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, W.J.; Businger, J.A. Intermittency and the organization of turbulence in the near-neutral marine atmospheric boundary layer. J. Atmos. Sci. 1985, 28, 918–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Arya, P. Introduction to Micrometeorology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Panofsky, H.A.; Dutton, J.A. Atmospheric Turbulence, Model and Methods for Engineering Application; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Dupuis, H.; Taylor, P.K.; Weill, A.; Katsaros, K. Inertial dissipation method applied to derive turbulent fluxes over the ocean during the Surface of the ocean, Fluxes and Interaction with the Atmosphère/Atlantic Stratocumulus Transition Experiment (SOFA/ASTEX) and Structure des Echanges Mer-Atmosphère. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1997, 102, 21115–21129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betts, A.K.; Desjardins, R.L.; Macpherson, J.I.; Kelly, R.D. Boundary-layer heat and moisture budgets from fife. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 1990, 50, 109–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weill, A.; Baudin, F.; Dupuis, H.; Eymard, L.; Frangi, J.; Gérard, É.; Durand, P.; Bénech, B.; Dessens, J.; Druilhet, A.; et al. SOFIA 1992 experiment during ASTEX. Glob. Atmos. Ocean. Syst. 1995, 3, 355–395. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, P.A.; Renfrew, I.A. Aircraft-based observations of air-sea turbulent fluxes around the British Isles. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 141, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gioli, B.; Miglietta, F.; De Martino, B.; Hutjes, R.W.A.; Dolman, H.A.J.; Lindroth, A.; Schumacher, M.; Sanz, M.J.; Manca, G.; Peressotti, A.; et al. Comparison between tower and aircraft-based eddy covariance fluxes in five European regions. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2004, 127, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, M.-S.; Kwon, B.H.; Goo, T.-Y. Comparisons between Mean and Turbulent Parameters of Aircraft-Based and Ship-Based Measurements in the Marine Atmospheric Boundary Layer. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1088. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12091088
Kim M-S, Kwon BH, Goo T-Y. Comparisons between Mean and Turbulent Parameters of Aircraft-Based and Ship-Based Measurements in the Marine Atmospheric Boundary Layer. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(9):1088. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12091088
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Min-Seong, Byung Hyuk Kwon, and Tae-Young Goo. 2021. "Comparisons between Mean and Turbulent Parameters of Aircraft-Based and Ship-Based Measurements in the Marine Atmospheric Boundary Layer" Atmosphere 12, no. 9: 1088. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12091088
APA StyleKim, M.-S., Kwon, B. H., & Goo, T.-Y. (2021). Comparisons between Mean and Turbulent Parameters of Aircraft-Based and Ship-Based Measurements in the Marine Atmospheric Boundary Layer. Atmosphere, 12(9), 1088. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12091088





