The Temporal and Spatial Changes of Ship-Contributed PM2.5 Due to the Inter-Annual Meteorological Variation in Yangtze River Delta, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
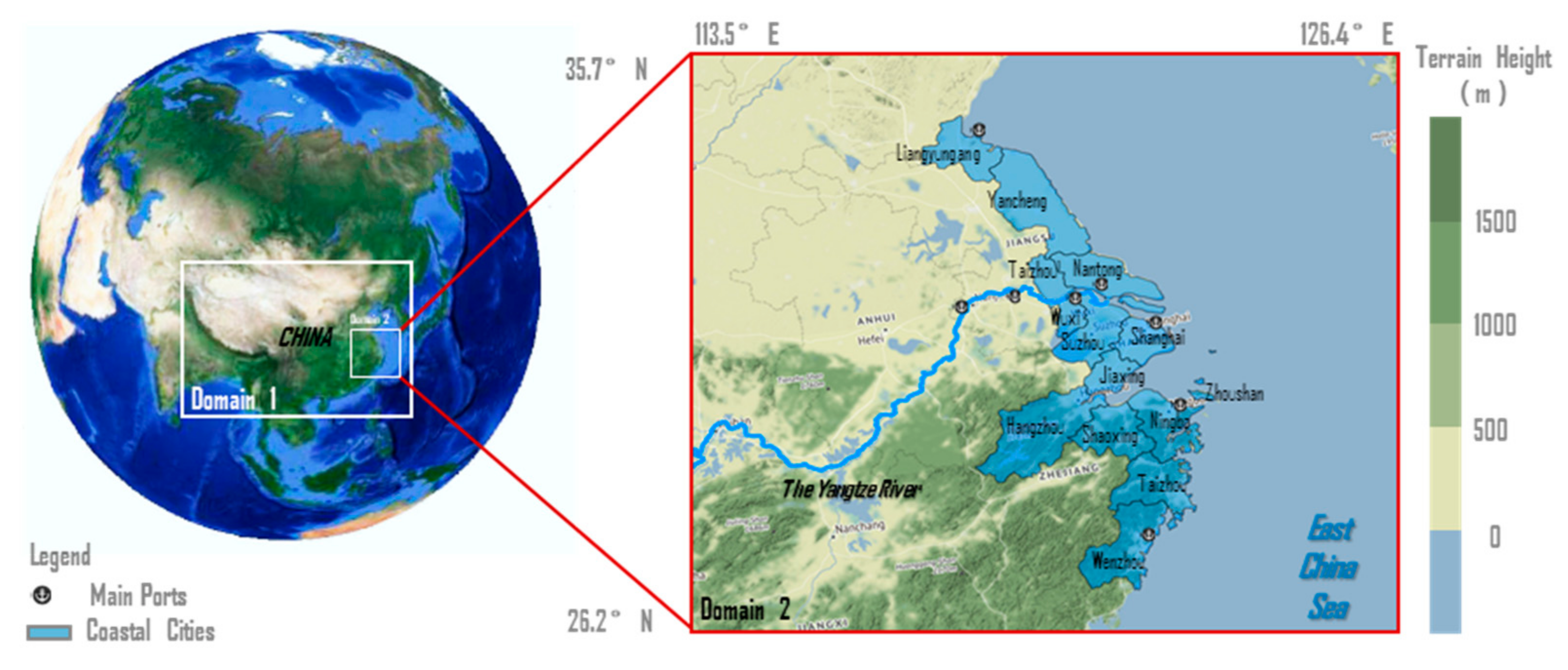
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Climate and Air Quality of the Study Area
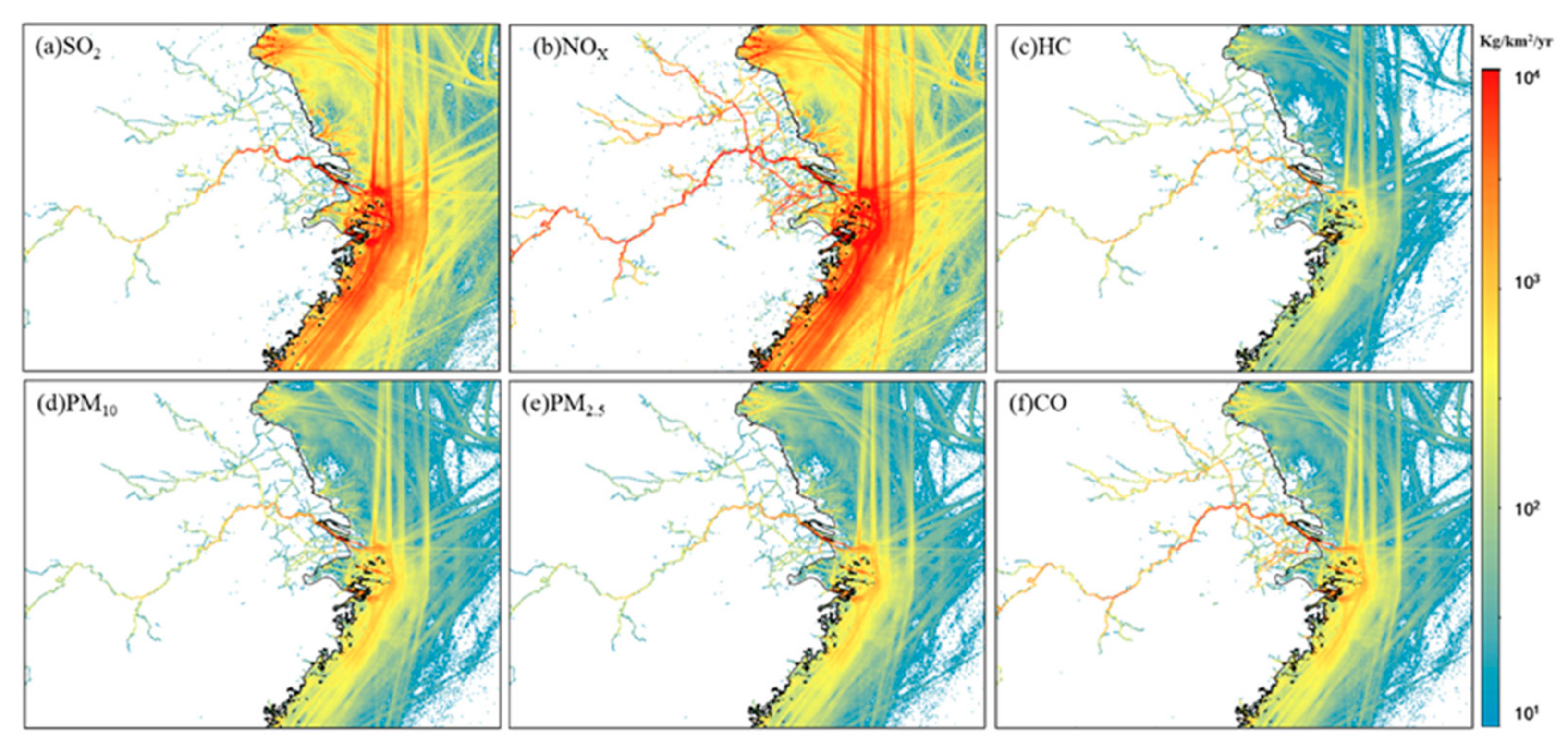
2.3. Model Configuration and Input Data
2.4. Model Evaluation
3. Results
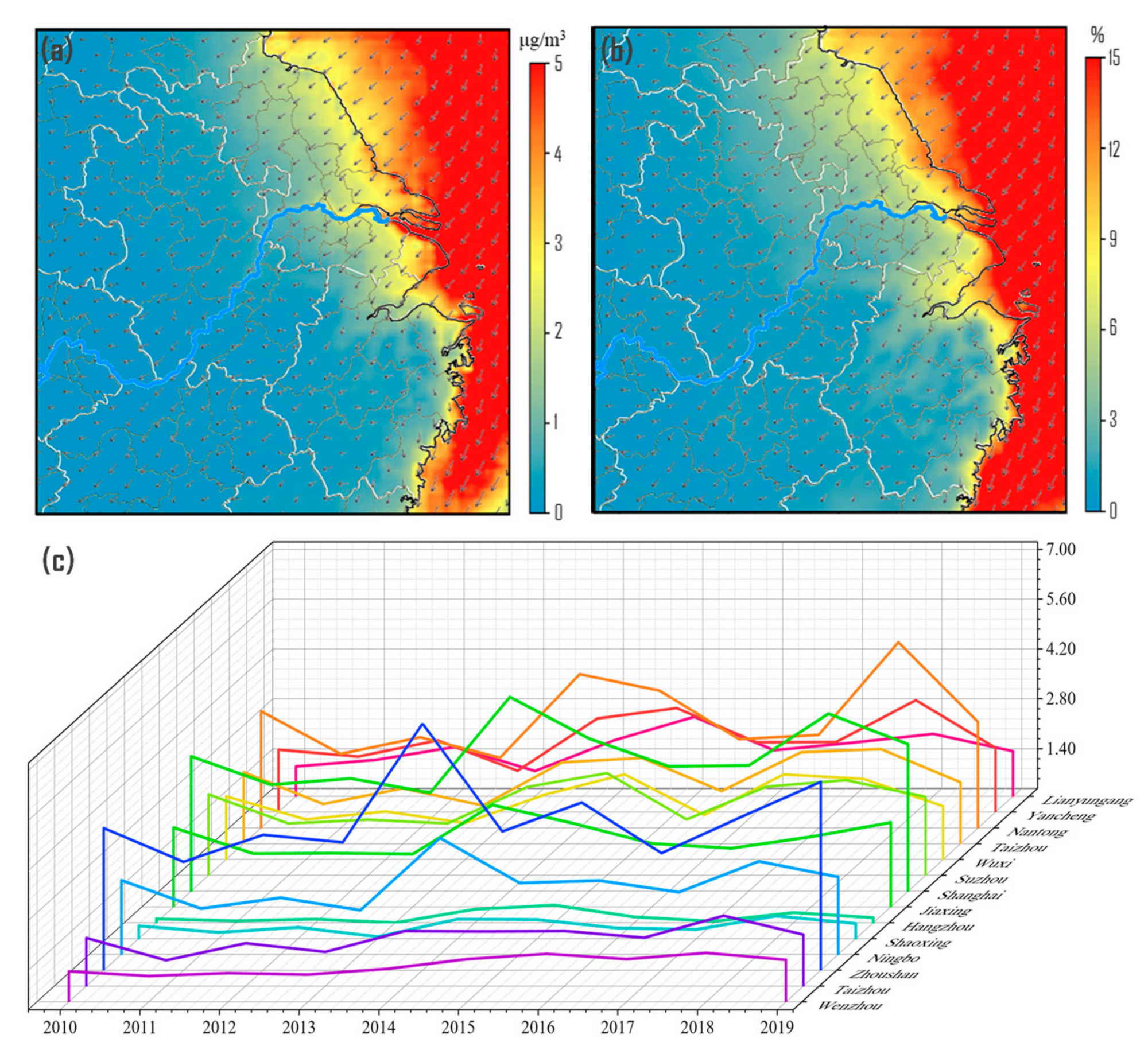
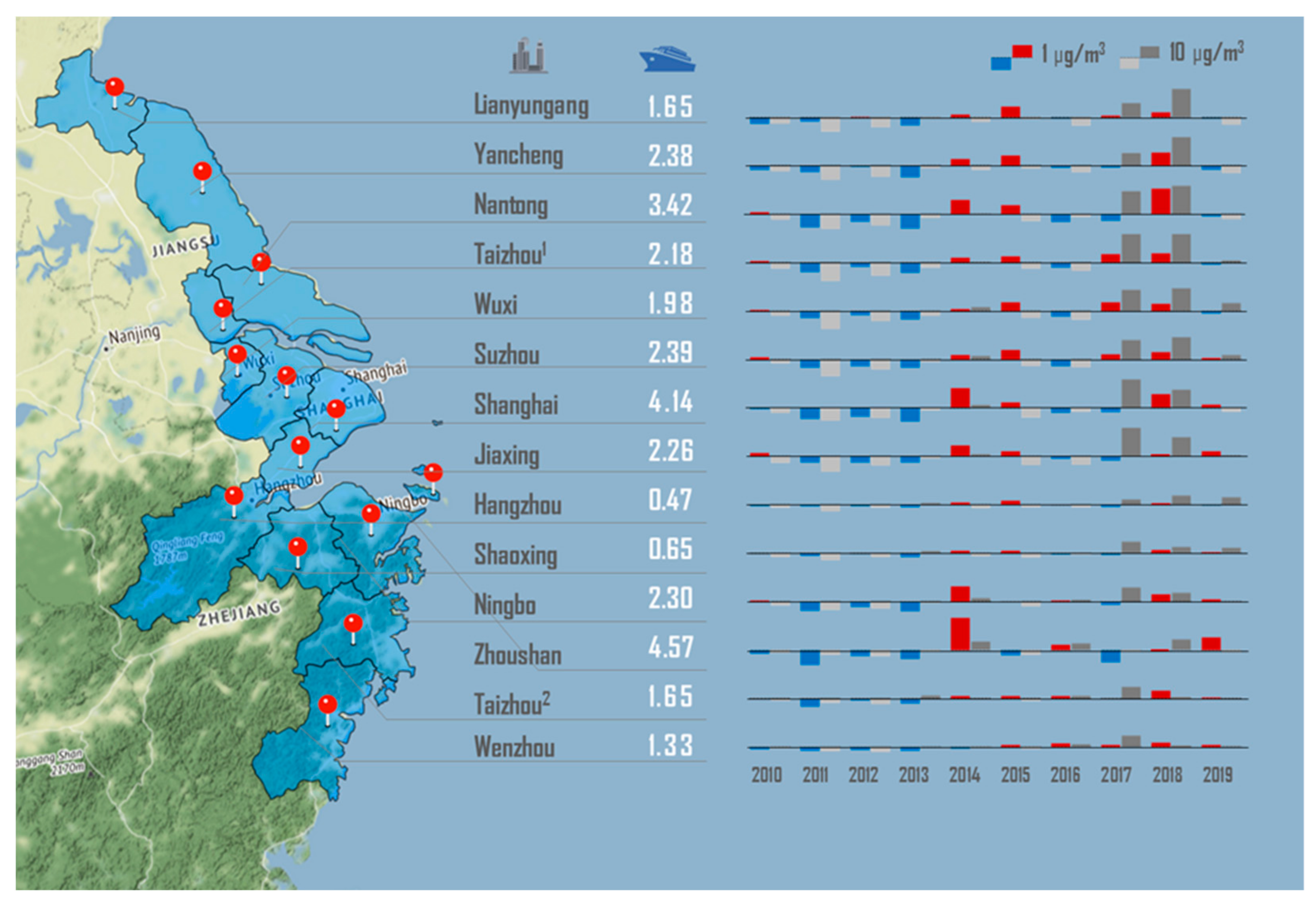
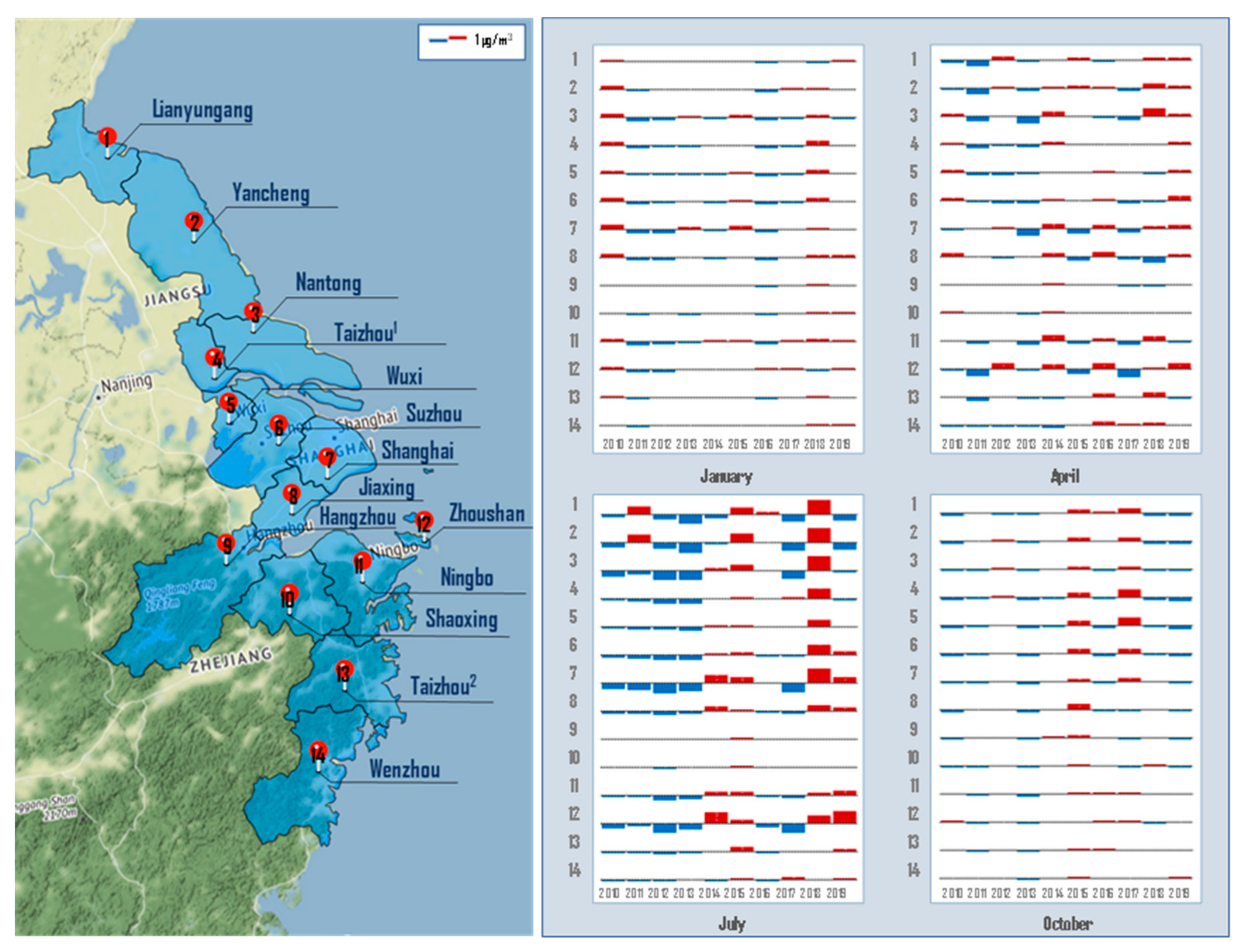
3.1. Annual Changes of Ship-Contributed PM2.5
3.2. Seasonal Changes of Ship-Contributed PM2.5
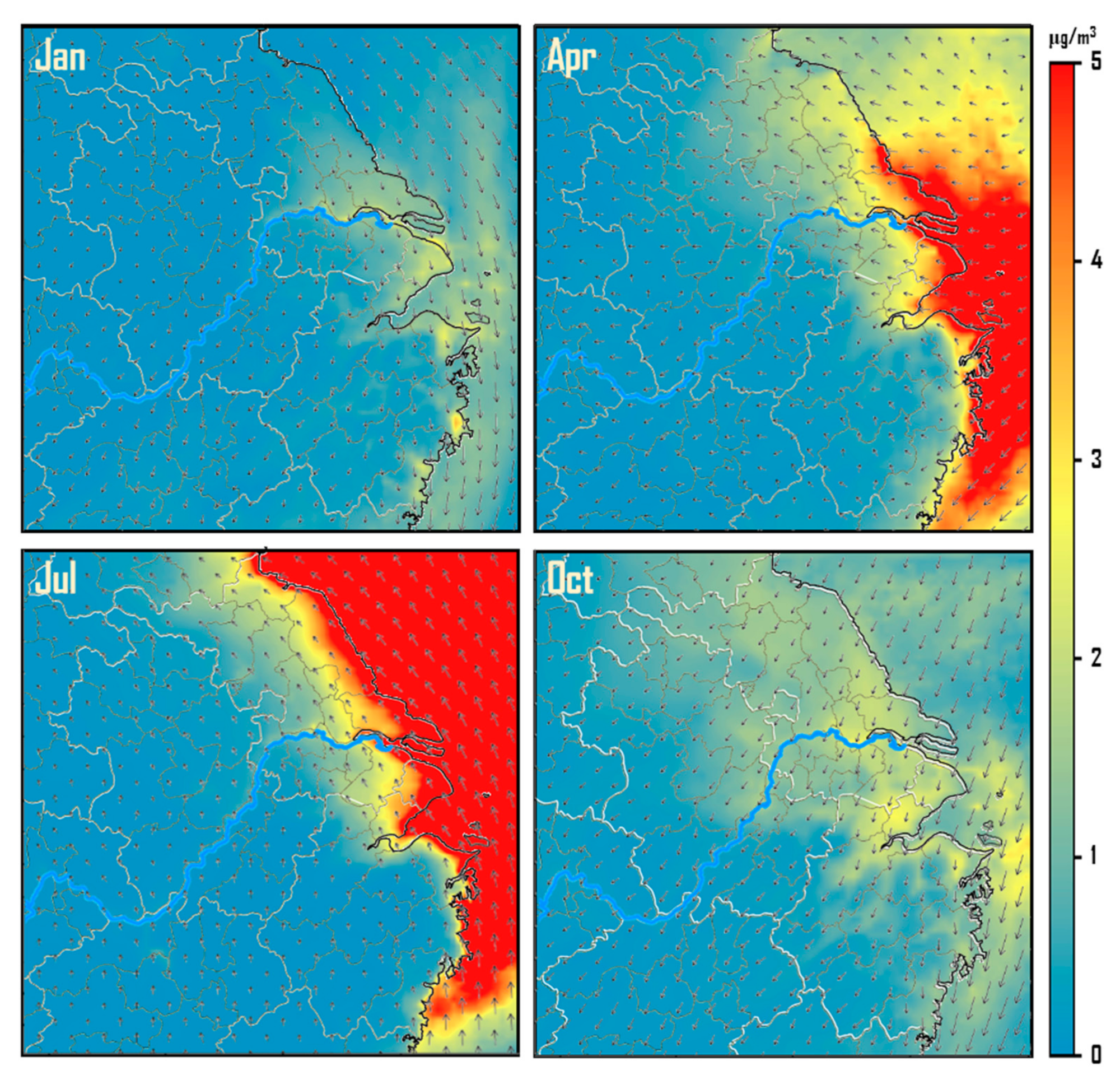
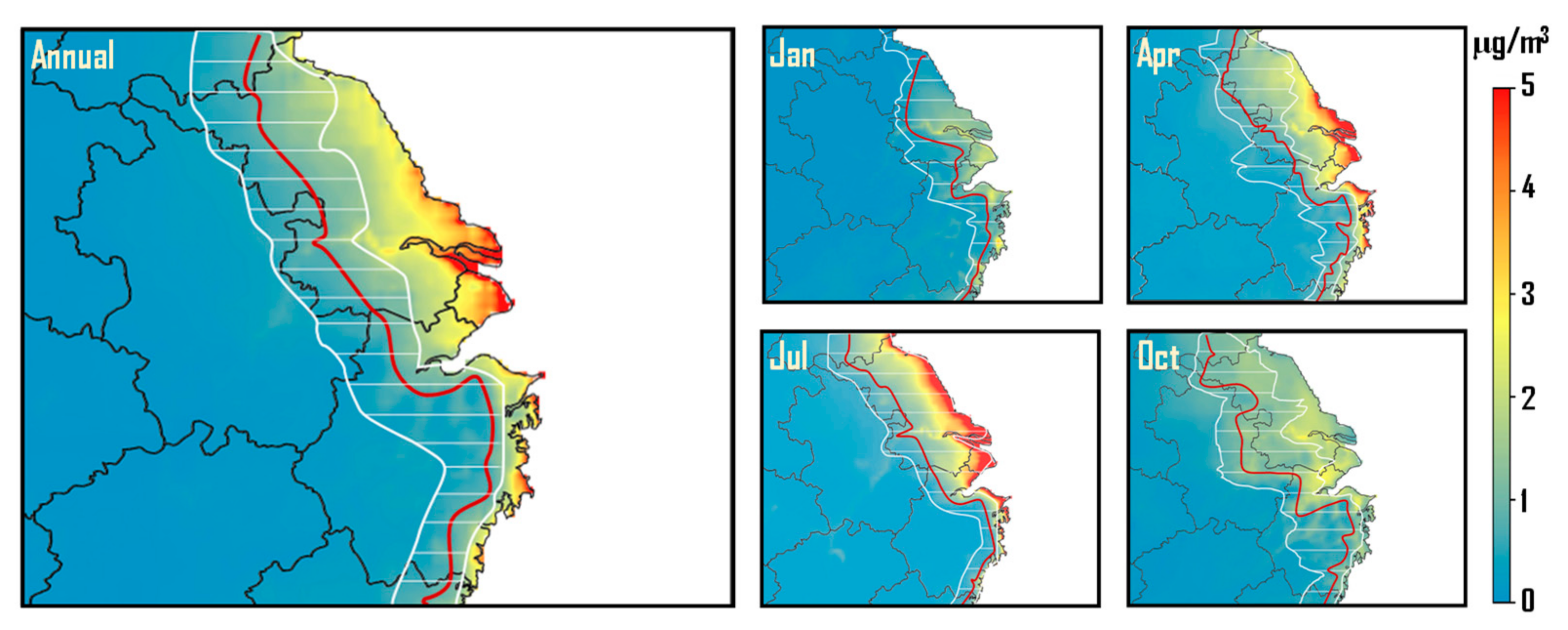
3.3. Changes in the Spatial Distribution
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sorte, S.; Rodrigues, V.; Borrego, C.; Monteiro, A. Impact of harbour activities on local air quality: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 257, 113542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramacher, M.; Lin, T.; Moldanova, J.; Matthias, V.; Johansson, L. The impact of ship emissions on air quality and human health in the Gothenburg area -Part II: Scenarios for 2040. Atmos. Chem. Physics. 2020, 20, 10667–10686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNCTAD. Review of Maritime Transport 2019. Available online: https://unctad.org/system/files/official-document/rmt2019_en.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2020).
- Endresen, Y.; Srgrd, E.; Sundet, J.K.; Dalsren, S.B.; Isaksen, I.; Berglen, T.F.; Gravir, G. Emission from international sea transportation and environmental impact. J. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108, 4560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbett, J.J.; Fischbeck, P. Emissions from ships. Science 1997, 278, 823–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capaldo, K.; Corbett, J.J.; Kasibhatla, P.; Fischbeck, P.; Pandis, S.N. Effects of ship emissions on sulphur cycling and radiative climate forcing over the ocean. Nature 1999, 400, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofiev, M.; Winebrake, J.J.; Johansson, L.; Carr, E.W.; Prank, M.; Soares, J.; Vira, J.; Kouznetsov, R.; Jalkanen, J.P.; Corbett, J.J. Cleaner fuels for ships provide public health benefits with climate tradeoffs. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Z.; Liu, H.; Ying, Q.; Fu, M.; Meng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wei, W.; Gong, H.; He, K. Impacts of shipping emissions on PM2.5 pollution in China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 15811–15824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bie, S.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Q.; Li, J.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, X.; Wang, P.; Wang, W. Source appointment of PM2.5 in Qingdao Port, East of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, M.G.; Crutzen, P.J. Influence of NOx emissions from ships on tropospheric photochemistry and climate. Nature 1999, 402, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyring, V.; Isaksen, I.S.; Berntsen, T.; Collins, W.J.; Corbett, J.J.; Endresen, O.; Grainger, R.G.; Moldanova, J.; Schlager, H.; Stevenson, D.S. Transport impacts on atmosphere and climate: Ship. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 4735–4771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Fu, M.; Jin, X.; Shang, Y.; Shindell, D.; Faluvegi, G.; Shindell, C.; He, K. Health and climate impacts of oceangoing vessels in East Asia. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2016, 6, 1037–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, J.A.; Virts, K.S.; Holzworth, R.H.; Mitchell, T.P. Lightning enhancement over major oceanic ship lanes. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 9102–9111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, L.; Jalkanen, J.-P.; Kukkonen, J. Global assessment of ship emissions in 2015 on a high spatial and temporal resolution. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 167, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, D.; Li, C.-T.; Mulvaney, K.M.; Selin, N.E.; Karplus, V.J. Air quality cobenefits of carbon pricing in China. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2018, 8, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yi, W.; Lv, Z.; Deng, F.; Zheng, S.; Xu, H.; Zhao, J.; Liu, H.; He, K. Annual changes of ship emissions around China under gradually promoted control policies from 2016 to 2019. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2021. [preprint] in review. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonson, J.E.; Gauss, M.; Schulz, M.; Jalkanen, J.-P.; Fagerli, H. Effects of global ship emissions on European air pollution levels. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 11399–11422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, M.; Hammingh, P.; Colette, A.; Querol, X.; Degraeuwe, B.; de Vlieger, I.; van Aardenne, J. Impact of maritime transport emissions on coastal air quality in Europe. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 90, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyring, V.; Kohler, H.W.; Van Aardenne, J.; Lauer, A. Emissions from international shipping: 1. The last 50 years. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2005, 110, 1984–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Meng, Z.H.; Shang, Y.; Lv, Z.F.; Jin, X.X. Shipping emission forecasts and cost-benefit analysis of China ports and key regions’ control. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 236, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Jin, X.; Wu, L.; Wang, X.; Fu, M.; Lv, Z.; Morawska, L.; Huang, F.; He, K. The impact of marine shipping and its DECA control on air quality in the Pearl River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 625, 1476–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNCTAD. Review of Maritime Transport 2020. Available online: https://unctad.org/webflyer/review-maritime-transport-2020 (accessed on 10 March 2021).
- World Shipping Council. Available online: https://www.worldshipping.org/ (accessed on 10 March 2021).
- Liu, Z.; Lu, X.; Feng, J.; Fan, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X. Influence of Ship Emissions on Urban Air Quality: A Comprehensive Study Using Highly Time-Resolved Online Measurements and Numerical Simulation in Shanghai. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Patton, A.; Ma, W.C.; Kan, H.D.; Wu, L.B.; Fung, F.; Wang, S.X.; Ding, D.; Walker, K. Projection of ship emissions and their impact on air quality in 2030 in Yangtze River delta, China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Brown, R.; Yang, L.; Morawska, L.; Ristovski, Z.; Fu, Q.; Huang, C. Shipping emissions and their impacts on air quality in China. Total Environ. 2017, 581, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, M.; Liu, H.; Jin, X.; He, K. National- to port-level inventories of shipping emissions in China. Environ. Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 114024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Shen, Y.; Lin, Y.; Pan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Louie, P.K.; Li, M.; Fu, Q. Atmospheric pollution from ships and its impact on local air quality at a port site in Shanghai. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 6315–6330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamoudou, I.; Zhang, F.; Chen, Q.; Wang, P.; Chen, Y. Characteristics of PM2.5 from ship emissions and their impacts on the ambient air: A case study in Yangshan Harbor, Shanghai. Total Environ. 2018, 640–641, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, W.; Fu, Q.; Xin, Y.; Li, C.; Zhou, B.; Qi, Y.; Chen, L. Characteristics and ship traffic source identification of air pollutants in China’s largest port. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 64, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.L.; Ding, Y.; Ge, Y.S.; Yu, L.X.; Yin, H.; Ye, W.T.; Liang, B. Real-world emissions of inland ships on the Grand Canal, China. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 81, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, W.; Ma, H.; Feng, J.; Yu, Q.; Yang, X.; Ng, S.K.; Fu, Q.; Chen, L. Spatial and seasonal dynamics of ship emissions over the Yangtze river delta and east China sea and their potential environmental influence. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 1322–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.S.; Tian, X.X.; Lang, J.L.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Guo, X.R.; Wang, W.L.; Liu, B. The impact of ship emissions on PM2.5 and the deposition of nitrogen and sulfur in Yangtze River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 1609–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Shanshan, L.; Mao, J.; Patton, A.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, W.; Liu, C.; Shen, Y.; Fu, Q.; et al. The influence of spatiality on shipping emissions, air quality and potential human exposure in the Yangtze River Delta/Shanghai, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 6167–6183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, S.; Daniel, J.J.; Wang, X.; Shen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Gui, K.; Zhao, T.; Liao, L.; Zhai, S. Fine particulate matter (PM2.5) trends in China, 2013–2018: Separating contributions from anthropogenic emissions and meteorology. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 11031–11041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Xue, W.; Lei, Y.; Huang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Cheng, S.; Ren, Z.; Wang, J. Spatiotemporal variation in the impact of meteorological conditions on PM2.5 pollution in China from 2000 to 2017. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 223, 117215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghude, S.; Chate, D.; Jena, C.; Beig, G.; Kumar, R.; Barth, M.; Pfister, G.; Fadnavis, S.; Pithani, P. Premature mortality in India due to PM2.5 and ozone exposure. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 4650–4658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, A.; Hixson, M.; Kleeman, M.J. Quantifying population exposure to airborne particulate matter during extreme events in California due to climate change. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 7453–7463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. Air Quality Criteria for Ozone and Related Photochemical Oxidants; US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Hu, J.; Qi, Y.; Hu, X.M. Relationships between meteorological parameters and criteria air pollutants in three megacities in China. Environ. Res. 2015, 140, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Ma, Q.; Zhao, B.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y. Winter haze over North China Plain from 2009 to 2016: Influence of emission and meteorology. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 1308–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, F.; Chen, D.C.; Guo, X.R.; Lang, J.L.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Fu, X.Y. Impact of Sea Breeze Circulation on the Transport of Ship Emissions in Tangshan Port, China. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Meteorological Administration. Available online: http://data.cma.cn/ (accessed on 10 May 2021).
- Liao, Z.; Gao, M.; Sun, J.; Fan, S. The impact of synoptic circulation on air quality and pollution-related human health in the Yangtze River Delta region. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607, 838–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daoyi, G.; Jinhong, Z.; Shaowu, W. The Influence of Siberian High on Large-Scale Climate over Continental Asia. Plateau Meteorol. 2002, 21, 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Shanghai Environmental Protection Bureau. Available online: https://sthj.sh.gov.cn/hbzhywpt1143/hbzhywpt1144/index.html (accessed on 10 May 2021).
- Ministry of Ecology and Environmental of the People’s Republic. Ecological and Environmental Bulletin. Available online: http://www.mee.gov.cn/hjzl/ (accessed on 10 May 2021).
- Kang, H.; Zhu, B.; Gao, J.; He, Y.; Wang, H.; Su, J.; Pan, C.; Zhu, T.; Yu, B. Potential impacts of cold frontal passage on air quality over the Yangtze River Delta, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 3673–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, H.L.A.; Wang, T.; Ding, A.; Blake, D.R.; Nam, J.C. Impact of Asian continental outflow on the concentrations of O3, CO, NMHCs and halocarbons on Jeju Island, South Korea during March 2005. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 2933–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, T.; Ding, A.; Blake, D.R.; Zahorowski, W.; Poon, C.N.; Li, Y.S. Chemical characterization of the boundary layer outflow of air pollution to Hong Kong during February-April 2001. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 8787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Ma, J.; Xu, J.; Zhong, Q.; Mao, Z.; Zhou, W. Application of meteorological air pollution index in Shanghai. Meteorol. Mon. 2018, 44, 704–712. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Caiyanlin, Z.Z.F. Numerical Simulations of an Advection Fog Event over Shanghai Pudong International Air-port with the WRF Model. J. Meteorol. Res. 2017, 31, 874–889. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, W.; Shi, X.; Yan, G.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; Tang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Lei, Y. Impacts of meteorology and emission variations on the heavy air pollution episode in North China around the 2020 Spring Festival. China Earth Sci. 2021, 64, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaali, M.; Moranl, D.M.; Bouchet, V.S.; Pavlovic, R.; Cousineau, S.; Sassi, M. On the influence of chemical initial and boundary conditions on annual regional air quality model simulations for North America. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 4873–4885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, R. Effects of atmospheric circulations on the interannual variation in PM2.5 concentrations over the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region in 2013–2018. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 7667–7682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, F.; Chen, J.; Sun, J.; Wang, S.; Zou, Z.; Zhou, J.; Yu, Q.; Ma, W.; et al. Simulating the impacts of ship emissions on coastal air quality: Importance of a high-resolution emission inventory relative to cruise- and land-based observations. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Cai, S.; Wang, S.; Zhao, B.; Chang, X.; Hao, J. Development of a unit-based industrial emission inventory in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region and resulting improvement in air quality modelling. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 3447–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Cheng, S.; Yao, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J. Multiple perspectives for modelling regional PM2.5 transport across cities in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region during haze episodes. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 212, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wu, Q.; Zhao, R.; Cheng, H.; He, H.; Ma, Q.; Wang, L.; Luo, H. New method for evaluating winter air quality: PM2.5 assessment using Community Multi-Scale Air Quality Modelling (CMAQ) in Xi’an. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 211, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Farley, R.; Orville, H. Bulk Parameterization of the snow field in a cloud model. Clim. Appl. Meteorol. 1983, 22, 1065–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewari, M.; Chen, F.; Wang, W.; Dudhia, J.; LeMone, M.A.; Mitchell, K.; Ek, M.; Gayno, G.; Wegiel, J.; Cuenca, R.H. Implementation and Verification of the Unified NOAH Land Surface Model in the WRF Model. In Proceedings of the 20th Conference on Weather Analysis and Forecasting/16th Conference on Numerical Weather Prediction, Seattle, WA, USA, 10 January 2004; pp. 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, S.-Y.; Yign, N.; Jimy, D. A new vertical diffusion package with an explicit treatment of entrainment processes. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2006, 134, 2318–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, M.D.; Suarez, M.J.; Liang, X.Z.; Yan, M.M.H. A thermal infrared radiation parameterization for atmospheric studies. NASA Tech. Memo. 2001, 19, 1–68. [Google Scholar]
- Stephen., F.B.; Schwarzkopf, M.D. An efficient, accurate algorithm for calculating CO2 15 µm band cooling rates. Geophys. Res. 1981, 86, 1205–1232. [Google Scholar]
- Sarwar, G.; Luecken, D.; Yarwood, G.; Whitten, G.Z.; Carter, W.P.L. Impact of an updated carbon bond mechanism on predictions from the CMAQ modeling system: Preliminary assessment. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2008, 47, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitten, G.Z.; Heo, G.; Kimura, Y.; McDonald-Buller, E.; Allen, D.T.; Carter, W.P.L.; Yarwood, G. A new condensed toluene mechanism for Carbon Bond: CB05-TU. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 5346–5355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarwood, G.; Jung, J.; Heo, G.; Whitten, G.Z.; Mellberg, J.; Estes, M. CB06-version 6 of the carbon bond mechanism. In Proceedings of the 2010 CMAS Conference, Chapel Hill, NC, USA, 11 October 2010. [Google Scholar]
- NCEP. Available online: https://rda.ucar.edu/datasets/ds083.2/ (accessed on 12 February 2020).
- Chen, D.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Lang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhao, Y. High-spatiotemporal-resolution ship emission inventory of China based on AIS data in 2014. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 609, 776–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Streets, D.G.; Carmichael, G.R.; He, K.B.; Huo, H.; Kannari, A.; Klimont, Z.; Park, I.S.; Reddy, S.; Fu, J.S.; et al. Asian emissions in 2006 for the NASA INTEX-B mission. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 5131–5153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, Q.; Streets, D.G.; He, K.B.; Cheng, Y.F.; Emmons, L.K.; Huo, H.; Kang, S.C.; Lu, Z.; Shao, M. Mapping Asian anthropogenic emissions of non-methane volatile organic compounds to multiple chemical mechanisms. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 5617–5638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Huo, H.; Zhang, Q.; Yao, Z.L.; Wang, X.T.; Yang, X.F.; Liu, H.; He, K.B. High–resolution mapping of vehicle emissions in China in 2008. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 9787–9805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhang, Q.; Tong, D.; Zheng, B.; Li, M.; Huo, H.; He, K.B. High-resolution inventory of technologies, activities, and emissions of coal-fired power plants in China from 1990 to 2010. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 13299–13317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xing, X.; Lang, J.; Chen, D.; Cheng, S.; Wei, L.; Wei, X.; Liu, C. A comprehensive biomass burning emission inventory with high spatial and temporal resolution in China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 2839–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.S.; Cheng, S.Y.; Li, J.B.; Chen, T.; Zhao, X.Y.; Guo, X.R.; Hu, H.L.; Yu, T. Application of LIDAR Technique and MM5-CMAQ Modeling Approach for the Assessment of Winter PM10 Air Pollution: A Case Study in Beijing, China. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2007, 181, 409–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.S.; Cheng, S.Y.; Liu, L.; Chen, T.; Guo, X.R. An integrated MM5–CMAQ modeling approach for assessing trans-boundary PM10 contribution to the host city of 2008 Olympic summer games-Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 1237–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.S.; Cheng, S.Y.; Liu, L.; Lei, T.; Guo, X.R.; Zhao, X.Y. Assessment of the Integrated ARPS-CMAQ Modeling System through Simulating PM10 Concentration in Beijing. China. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2008, 25, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Cheng, S.; Zhou, Y.; Guo, X.; Fan, S.; Wang, H. Impact of Road Fugitive Dust on Air Quality in Beijing. China. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2010, 27, 825–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.S.; Wang, X.T.; Nelson, P.; Li, Y.; Zhao, N.; Zhao, Y.H.; Lang, J.L.; Zhou, Y.; Guo, X.R. Ship emission inventory and its impact on the PM2.5 air pollution in Qingdao Port, North China. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 166, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.S.; Liu, X.X.; Lang, J.L.; Zhou, Y.; Wei, L.; Wang, X.T.; Guo, X.R. Estimating the contribution of regional transport to PM2.5 air pollution in a rural area on the North China Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 583, 280–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.S.; Zhao, N.; Lang, J.L.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.T.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.H.; Guo, X.R. Contribution of ship emissions to the concentration of PM2.5: A comprehensive study using AIS data and WRF/Chem model in Bohai Rim Region, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610, 1476–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Fu, X.; Guo, X.; Lang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, B.; Wang, W. The impact of ship emissions on nitrogen and sulfur deposition in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 708, 124636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Zhang, Y.; Lang, J.; Ying, Z.; Li, Y.; Guo, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, B. Evaluation of different control measures in 2014 to mitigate the impact of ship emissions on air quality in the Pearl River Delta, China. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 216, 116911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Zhang, M.; Skorokhod, A.; Kou, X. Modeling dry deposition of reactive nitrogen in China with RAMS-CMAQ. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 166, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zhang, M.; Chen, L.; Kou, X.; Skorokhod, A. CMAQ simulation of atmospheric CO2 concentration in East Asia: Comparison with GOSAT observations and ground measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 160, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wei, Z.; Wei, W.; Fu, J.S.; Meng, C.; Ma, S. Source apportionment of PM2.5 in top polluted cities in Hebei, China using the CMAQ model. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 122, 723–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantinidou, K.; Hadjinicolaou, P.; Zittis, G.; Lelieveld, J. Performance of Land Surface Schemes in the WRF Model for Climate Simulations over the MENA-CORDEX Domain. Earth Syst. Environ. 2020, 4, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCEI. Available online: https://gis.ncdc.noaa.gov/maps/ncei/cdo/hourly/ (accessed on 20 July 2020).
- Boylan, J.W.; Russell, A.G. PM and light extinction model performance metrics, goals, and criteria for three-dimensional air quality models. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 4946–4959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhu, B.; Kang, H.; Hou, X.; Gao, J.; Kuang, X.; Yan, S.; Shi, S.; Fang, C.; Pan, C.; et al. Stable and transport indices applied to winter air pollution over the Yangtze River Delta, China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 272, 115954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, P.J.; Magana, V.O.; Palmer, T.N.; Shukla, J.; Tomas, R.A.; Yanai, M.; Yasunari, T. Monsoons: Processes, predictability, and the prospects for prediction. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 103, 14451–14510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zeng, Q.A. Unified monsoon index. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 29, 1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zeng, Q.A. A new monsoon index and the geographical distribution of the global monsoons. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2003, 20, 299–302. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Zeng, Q.A. A new monsoon index, its interannual variability and relation with monsoon precipitation. Clim. Environ. Res. 2005, 10, 351–365. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Du, Y.; Wen, Z. Seasonal, Interannual, and Interdecadal Variations of the East Asian Summer Monsoon: A Diurnal-Cycle Perspective. J. Clim. 2021, 34, 4403–4421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.H.; Chen, J.L.; Wang, L.; Lin, Z.D. Characteristics, processes, and causes of the spatio-temporal variabilities of the East Asian monsoon system. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2012, 29, 910–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.H.; Gu, L.; Xu, Y.H.; Zhang, Q.L.; Wu, S.S.; Cao, J. Characteristics of the interannual variations of onset and advance of the East Asian summer monsoon and their associations with thermal states of the tropical western Pacific. Chin. Atmos. Sci. 2005, 29, 20–36. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Liao, H.; Li, J. Impacts of Asian summer monsoon on seasonal and interannual variations of aerosols over eastern China. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, D00K05. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Zhao, T.; Gong, S.; Xu, X.; Han, Y.; Yin, Y.; Tang, L.; He, H.; He, J. Implications of East Asian summer and winter monsoons for interannual aerosol variations over central-eastern China. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 129, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Species | Month | AVG-obs 1 | AVG-sim 2 | MAE 3 | R 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T2 | January | 6.22 | 5.61 | 1.28 | 0.84 |
| ℃ | April | 15.42 | 13.86 | 1.99 | 0.81 |
| July | 27.23 | 26.49 | 1.46 | 0.78 | |
| October | 19.79 | 18.89 | 1.38 | 0.87 | |
| RH2 | January | 70.31 | 71.11 | 8.27 | 0.75 |
| % | April | 76.28 | 80.62 | 8.36 | 0.83 |
| July | 82.94 | 89.95 | 7.57 | 0.72 | |
| October | 72.22 | 77.60 | 8.20 | 0.73 | |
| WS10 | January | 2.78 | 3.12 | 0.86 | 0.72 |
| m/s | April | 3.23 | 3.43 | 2.46 | 0.75 |
| July | 2.85 | 3.32 | 0.95 | 0.74 | |
| October | 3.08 | 3.31 | 0.89 | 0.78 |
| Species | Month | MAE | NMB 5 (%) | NME 6 (%) | MFB 7 (%) | MFE 8 (%) | R |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM2.5 | January | 21.19 | −9.33 | 25.29 | −5.89 | 17.27 | 0.84 |
| µg/m3 | April | 12.81 | −4.37 | 17.49 | −3.15 | 12.14 | 0.81 |
| July | 13.22 | −10.23 | 32.03 | −10.80 | 26.51 | 0.75 | |
| October | 14.15 | −27.70 | 29.29 | −21.96 | 23.32 | 0.78 | |
| PM10 | January | 22.09 | −8.63 | 18.87 | −5.92 | 15.22 | 0.83 |
| µg/m3 | April | 15.38 | −3.21 | 18.66 | −2.20 | 13.68 | 0.73 |
| July | 16.93 | −4.65 | 24.85 | −6.06 | 20.40 | 0.76 | |
| October | 16.25 | −5.60 | 19.27 | −6.00 | 15.84 | 0.82 | |
| SO2 | January | 9.77 | 3.00 | 31.67 | 1.60 | 23.47 | 0.76 |
| µg/m3 | April | 5.67 | 1.62 | 28.15 | 1.84 | 19.69 | 0.77 |
| July | 3.74 | −2.58 | 26.49 | −4.35 | 20.64 | 0.72 | |
| October | 6.06 | −4.30 | 29.21 | −6.73 | 23.47 | 0.77 | |
| NO2 | January | 10.13 | 1.83 | 19.94 | 2.52 | 14.51 | 0.78 |
| µg/m3 | April | 8.90 | −6.54 | 20.01 | −6.45 | 16.34 | 0.76 |
| July | 8.49 | −17.65 | 27.09 | −17.38 | 24.28 | 0.77 | |
| October | 10.56 | −6.38 | 24.88 | −7.22 | 21.75 | 0.76 | |
| O3 | January | 9.04 | −4.42 | 15.30 | −4.00 | 11.39 | 0.76 |
| µg/m3 | April | 11.64 | −4.77 | 11.35 | −4.40 | 8.77 | 0.74 |
| July | 22.04 | −11.05 | 18.20 | −6.73 | 13.71 | 0.82 | |
| October | 19.63 | −8.08 | 15.97 | −6.82 | 12.58 | 0.74 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, D.; Liang, D.; Li, L.; Guo, X.; Lang, J.; Zhou, Y. The Temporal and Spatial Changes of Ship-Contributed PM2.5 Due to the Inter-Annual Meteorological Variation in Yangtze River Delta, China. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 722. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12060722
Chen D, Liang D, Li L, Guo X, Lang J, Zhou Y. The Temporal and Spatial Changes of Ship-Contributed PM2.5 Due to the Inter-Annual Meteorological Variation in Yangtze River Delta, China. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(6):722. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12060722
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Dongsheng, Dingyue Liang, Lei Li, Xiurui Guo, Jianlei Lang, and Ying Zhou. 2021. "The Temporal and Spatial Changes of Ship-Contributed PM2.5 Due to the Inter-Annual Meteorological Variation in Yangtze River Delta, China" Atmosphere 12, no. 6: 722. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12060722
APA StyleChen, D., Liang, D., Li, L., Guo, X., Lang, J., & Zhou, Y. (2021). The Temporal and Spatial Changes of Ship-Contributed PM2.5 Due to the Inter-Annual Meteorological Variation in Yangtze River Delta, China. Atmosphere, 12(6), 722. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12060722








