Abstract
In this study, nine different statistical models are constructed using different combinations of predictors, including models with and without projected predictors. Multiple machine learning (ML) techniques are employed to optimize the ensemble predictions by selecting the top performing ensemble members and determining the weights for each ensemble member. The ML-Optimized Ensemble (ML-OE) forecasts are evaluated against the Simple-Averaging Ensemble (SAE) forecasts. The results show that for the response variables that are predicted with significant skill by individual ensemble members and SAE, such as Atlantic tropical cyclone counts, the performance of SAE is comparable to the best ML-OE results. However, for response variables that are poorly modeled by individual ensemble members, such as Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico major hurricane counts, ML-OE predictions often show higher skill score than individual model forecasts and the SAE predictions. However, neither SAE nor ML-OE was able to improve the forecasts of the response variables when all models show consistent bias. The results also show that increasing the number of ensemble members does not necessarily lead to better ensemble forecasts. The best ensemble forecasts are from the optimally combined subset of models.
1. Introduction
Tropical cyclones (TC), known as hurricanes in the Atlantic Ocean and Eastern Pacific, are extreme weather systems on Earth that have far reaching adverse impacts on the human society [1,2] and are the costliest natural disasters in the United States [3]. Governmental agencies and nongovernmental organizations dealing with TC disaster preparedness planning and post-disaster humanitarian relief efforts, and industries dealing with the potential impacts from TCs rely on skillful seasonal predictions of TC activities for their preseason decisions. Hurricane experts have started issuing preseason TC predictions since 1984 [4], and the methodologies currently used to produce preseason TC forecasts include multivariate regression [5,6,7,8], dynamic models [9], and statistical dynamical approaches [10,11,12,13]. The reliability and utility of such long-range forecasts have met some skepticism from the public [14]. Findings from several studies also showed that the skills of preseason forecasts issued by various groups were marginal [15,16,17]. Thus, there is a clear gap between the current skills of preseason TC forecasts and the public demand for such information. Only when such technological gap is bridged, the potential economic values of seasonal hurricane prediction can be fully realized [18].
Ensemble techniques have been widely used in weather and climate prediction to reduce forecast uncertainty [19,20]. Applications of artificial intelligence in weather and climate prediction have emerged in recent years [21,22]. Combination of ensemble forecasting approaches with machine learning (ML) techniques has also been explored. Rasp and Lerch [23] and Krasnopolsky and Lin [24] applied neural network (NN) in postprocessing of ensemble weather forecasting and found NN technique can improve ensemble forecasts over traditional ensemble approaches. With regard to seasonal hurricane prediction, Jagger and Elsner [25] demonstrated the benefit of using multimodel consensus in seasonal hurricane prediction. Richmana et al. [26] published an article showing ML techniques can improve seasonal hurricane prediction over traditional regression models. However, combining ML and ensemble forecasting has yet to gain wide adoption in the preseason prediction of hurricanes. In this study, we present a novel approach to seasonal TC prediction based on the optimization of multimodel ensemble forecasts using machine learning techniques. The goal is to improve preseason prediction of Atlantic hurricane activity by identifying response variables and scenarios which are likely to benefit from ML-based optimization of ensemble forecasting.
The ensemble members used in the optimization include nine statistical models and a suite of models based on machine learning. The rest of the article is organized as follows. In Section 2, data and methods used in this study are described, followed by a detailed presentation of results in Section 3. Section 4 discusses the results. Conclusions are summarized in Section 5.
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Data
The number of tropical cyclones (TCs) in the past seasons was obtained by combining the historical database known as HURDAT (HURricane DATabase) [27]) and the archived best track seasonal maps compiled by the National Hurricane Center (NHC). TC counts were manually determined by region and then further categorized by its peak strength within each region based on the Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale. Forecasts are made for three categories TC, HU and MH: TC includes tropical storms, hurricanes (categories 1–2) and major hurricanes (category 3 and higher); HU includes hurricanes and major hurricanes; MH includes major hurricanes only. The three regions are the Gulf of Mexico, the Caribbean Sea, and the whole North Atlantic Basin (Figure 1). Therefore, for clarity, nine response variables are listed in Table 1.
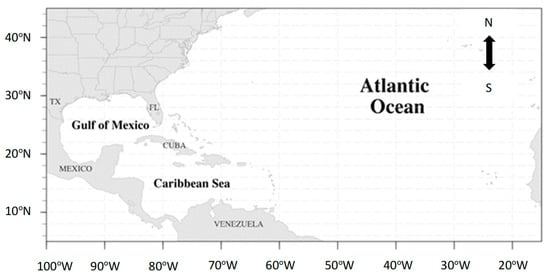
Figure 1.
Three regions for forecast: Gulf of Mexico (bounded by the Gulf coast of the United States, from the southern tip of Florida to Texas; on the southwest and south by Mexico; and on the southeast by Cuba), Caribbean Sea (bordered by the Yucatan Peninsula and the central America on the west and southwest; on the south by Venezuela; and the West Indies); the whole Atlantic Basin is composed of the Atlantic Ocean, the Gulf of Mexico, and the Caribbean Sea.

Table 1.
Definition of response variables.
A variety of climate-related global and regional monthly predictors are taken into account for the forecast of the forthcoming hurricane season. Most of these candidate predictors come from the NOAA Earth System Research Laboratory Division (https://psl.noaa.gov/data/climateindices/list/, accessed on 18 April 2021), including Atlantic and Pacific SST-related climate indices, El Nino Southern Oscillation (ENSO) related indices, and atmospheric and teleconnection indices. In addition, measures taken over the main development region (MDR, 10°–20° N, 80°–20° W) are incorporated as well. All of the MDR indices are derived from the NCEP–NOAA Reanalysis dataset at https://psl.noaa.gov/cgi-bin/data/timeseries/timeseries1.pl, accessed on 18 April 2021 [28]. Data obtained from the same source are the surface latent heat flux (LHF), which is used to compute the Empirical Orthogonal Functions (EOF) for only the winter season. Global (GGST), North-Hemisphere (NGST) and South-Hemisphere (SGST) mean land–ocean temperature index, based on the GISS Surface Temperature Analysis Ver-4, are also considered as predictors. A total of 34 monthly indices are listed in Table 2. Detailed definitions of these climate indices are referred to Córdoba et al. [29]. The use of these climatic indices as candidate predictors in seasonal hurricane prediction has been previously discussed in Keith and Xie [8] and Córdoba et al. [29].

Table 2.
Nine sets of training data consisting of different combinations of covariates over different time domains.
The statistical model was constructed with data after 1951, since hurricane data after 1951 are considered more reliable and the predictor variables are consistently available after 1951. For the forecast of 2020 hurricane season, there are 69 annual counts. Moreover, only storms originating over the tropical waters from June 1 to November 30 are considered, excluding subtropical and extratropical storms.
2.2. Methods for Forecasting TC Counts
2.2.1. List of Statistical Models as Ensemble Members
A generalized linear model with Lasso regularization is adopted. It assumes that the logarithm of the expected TC counts in each region is linearly related to the candidate predictors and performs a variable selection procedure using a shrinkage parameter, to identify the combination of indices that has the best predictive ability. Lasso’s ability to handle the cases where there are a large number of features (covariates) against the limited observations of TC counts (response) per year is especially useful.
However, given that most of the predictors are highly correlated with each other, in which case Lasso has limitations, a preprocessing hierarchical clustering analysis [30] is carried out before applying Lasso. It allows us to group covariates into clusters based on the distances of the covariates correlation matrix, therefore identifies the primary covariates in each cluster. Specifically, the algorithm selects ten clusters first and then chooses the variable with the highest correlation with the response variable in each cluster. The reason to consider ten clusters is that it covers a large enough number of covariates to provide sufficient information, and in the meantime, it retains a sufficiently small number of covariates to have enough residual degree of freedom. For comparison, the result using only hierarchical clustering analysis is given in the next section as well.
The sliding window cross validation (SWCV) method was introduced by Córdoba et al. [29] to evaluate the performance of the model. In the SWCV, data are partitioned into w windows, and in each window, there are years of training data to construct the model to forecast the immediate succeeding year. The calculation of w and should guarantee that the sample size of windows and years within each window is not smaller than 30. Specifically, the first step is to construct the model with data from 1951–1980, and then forecast 1981. Since there are 69 years, this process can be repeated 39 times. The final 39th process is to predict 2019 with the model constructed using 1989–2018. Compared to the regular leave-one-out cross-validation (LOOCV), SWCV respects the chronological order of the data and allows for a more reasonable procedure.
Nine sets of predictors are used as training data (Table 2), and each set of the predictors are paired with nine response variables to construct nine sets of statistical models. Therefore, a total of 9 × 9 regression models are analyzed in this study. F1X, F2X, and F3X, where x represents B, N, L, respectively, represent different groupings of observed and projected predictors. Under each scenario, there are three groups of predictors that are designed to investigate whether it is worth incorporating the forecasts of future ENSO index and the EOF value of winter LHF. For example, F1 models use only predictors observed in January and February, so they can be used to make forecasts as early as March, whereas F2 models use predictors observed from January to April, so predictions can only be made in or after May. F3 models use January observed predictors and projected predictors. For each training set , we model the count with a Poisson distribution: , with . Here, we try to minimize the following function:
where:
where is the Lasso shrinkage parameter, is the intercept, and index j are the regression coefficients and the selected indices, respectively, which are specific to each region and strength category of TC (i = 1, 2…9).
The forecast value from F is compared with the observed value through the logarithm score (LS) which is defined as the logarithm of the probability estimate of the value. LS has the advantage of respecting the probabilistic nature of the forecast value, and therefore would be a proper scoring rule to evaluate the forecasts generated from probabilistic models. For a certain year, the likelihood skill score (H) is computed using the following formula:
where represents climatology. It is used here as a reference to evaluate the efficiency of our proposed models, defined as:
We then take the average of H among all of the windows, with a positive value indicating superior skill of models against climatology.
For clarity, the procedure for the forecast of 2020 hurricane season can be described as follows:
- Partition data into windows, w = 39 for SWCV and no window for LOOCV (used here as the baseline);
- In each window, carry out the hierarchical clustering analysis and select the ten primary predictors; construct the model with Lasso using the ten covariates selected;
- Calculate the logarithm scores between the forecast and observed values;
- Compare scores with climatology using the mean likelihood skill score ().
Readers are referred to Córdoba et al. [29] for more detailed information.
2.2.2. Machine Learning Based Linear Combination of Statistical Models to Produce Ensemble Models
The first way to take advantage of the ensemble of models is to do a weighted combination of their outputs. Specifically, the ensemble model we explored in this part is as follows:
where is the ith statistical model output, is the ith weight parameter, ŷ is the predicted count. The overall training and validation methodology follows (for SWCV):
- Divide the data into 39 windows with 31 years in each window. The first 30 years are used for training and validation is performed on the 31st year.
- In each window, construct a model: use the predictions from 9 statistical models for each of the 30 years as training set and apply the optimization techniques to learn weight parameters. Predict count for the 31st year using the trained ensemble model.
- Compare scores against climatology using the mean H value.
For LOOCV, we used the same methods but instead of 39 windows, for each of the 69 years one year was the validation year while the remaining 68 years were used as the training set. The baseline method we used for the weighted combination is simple averaging of the output of models; all weights have value 0.11. We will refer to this simple averaging method as SAE from now on. We then used several optimization techniques for optimizing the weights in the ensemble model, with all initial weights set to 0.11. These methods include the ridge regression, lasso regression, linear regression, and gradient descent and for every method before optimization begins, the initial weights are equal to that of the SAE model. The objective function of each optimization method is listed with as the true count and as the ensemble output.
- Lasso optimization:where is the Lasso shrinkage parameter and is the norm of the weights in the ensemble model.
- Ridge optimization:where is the ridge shrinkage parameter and is the norm of the weights in the ensemble model.
- Linear regression:where is the true count for training years, of shape , is a matrix of shape where each row corresponds to the output counts of nine statistical models and is the weight vector of shape . For SWCV, in each window, whereas for LOOCV, . The minimum value for the objective function will be 0 if , but it is not always possible that will be in the column space of , and hence the linear regression method finds the orthogonal projection of into the column space of . Let the orthogonal projection of in the column space of be , then will be the weight that gives a minimum value for the given objective function such that no other weights can give a lower value for the function. In this way, we obtain the weights .
- Gradient descent:
The function to minimize is the same as in the linear regression case. The differences are on how to determine the weights. In this method, we use the gradients of the objective function with respect to weights for updating weight values. A gradient of the objective function determines the direction in which the objective function is increasing the most, and so at each step we move in the direction opposite to that of the gradient. Learning rate is a hyperparameter that is multiplied by the gradient at each update of weights to control by how much the weight is updated. The gradient of the objective function with respect to the weights for a year is obtained as:
Gradient of the objective function with respect to a weight :
where are the weights and is the output of nine ensemble member models for year .
The algorithm for optimizing weights for a window with SWCV using gradient descent is:
For epochs from 1 to 200 is:
For year from 1 to 30 is:
where is the learning rate, which is empirically selected among the values 0.001, 0.0001, and 0.00001.
Besides experimenting with different optimization methods, we also experiment with the composition of the ensemble. Instead of using all nine statistical models, we tried to pick the top models, The quality of the model was determined based on the mean H value among all validation years in 39 windows for SWCV and among all 69 validation years for LOOCV.
3. Results
3.1. Results from Emsemble Members
3.1.1. Results from Regression Models
Before proceeding to examine the results obtained through the ensemble optimization techniques, the performances of the nine statistical models are discussed first. For each response over three regions, three comparisons are made: the first compares the performances of two cross-verification methods (SWCV and LOOCV), the second compares the models constructed using Lasso and those generated using only the hierarchical clustering algorithm in the process of variable selection, and the final compares the proposed models against climatology to see if there is any improvement and efficiency.
Mean squared errors (MSE) and mean H values are used to measure the difference between models with the SWCV or LOOCV method applied. Take the tropical cyclone of the Atlantic Basin as an example, Figure 2a gives the difference of MSE between climatology and each model F, along with the percentage of change presented within the curly brackets. It shows that at least one model F with the SWCV method has lower MSE than climatology. The largest percentage of improvement comes from model F3B with a 22.3% improvement, in this case. Compared to SWCV, all models with LOOCV method show much lower MSEs than climatology. Correspondingly, Figure 2b shows the mean H values of each model validated using SWCV (bottom panel) and LOOCV (upper panel). The mean H value is slightly higher using LOOCV than using SWCV, suggestion LOOCV is a less strict method since LOOCV allows the use of future data to evaluate the forecasts of past seasons during the cross-validation process, which differs from the real-world scenario. In contrast, SWCV avoids assessing the past forecasts with future data and presents a more realistic scenario in the forecast procedure. Therefore, the following comparisons are made among the models using SWCV validation.
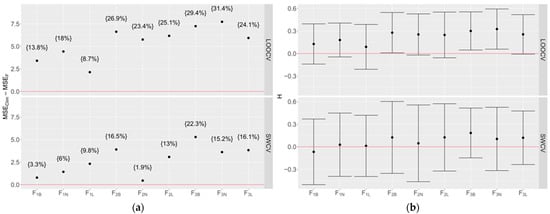
Figure 2.
(a) Differences of MSE between climatology and each model F for the forecast of tropical cyclones in the Atlantic Basin for the SWCV or LOOCV method. The nondimensional percentage of MSE change, computed as (MSEClim − MSEF)/MSEClim, is given in the curly brackets. (b) H values averaged among all the verification years for SWCV and LOOCV methods. Positive values denote the superior skill of model F with Lasso applied, compared to the climatology.
Since candidate indices are highly correlated with each other, we use Lasso to select the primary covariates in the process of variable selection. As a comparison, Figure 3 gives the mean H values for the responses between the models constructed with Lasso and those without Lasso (using hierarchical clustering analysis only). Positive values indicate significantly better skill for models with the clustering algorithm. As stated earlier, the validation of the given models is accomplished with SWCV. For all the responses considered, the negative H-scores clearly state that models with Lasso demonstrate better predictive skill than models in which clustering analysis is applied.
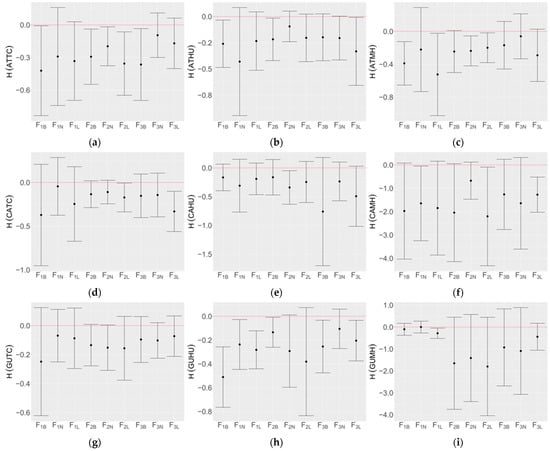
Figure 3.
Mean H values with SWCV applied between Lasso and clustering models by response: (a) ATTC, (b) ATHU, (c) ATMH, (d) CATC, (e) CAHU, (f) CAMH, (g) GUTC, (h) GUHU, and (i) GUMH. Positive values denote the superior skill of model F with clustering analysis, compared to the models with Lasso applied.
The primary variables selected among each window are different; therefore, it is necessary to analyze the percentage of times a variable is selected for a specific response and model. Figure 4 and Figure 5 give a summary of the top twenty variables selected from the total 39 windows with Lasso or clustering analysis per response and for SWCV. NINO variables are highlighted with bold lines. It is intriguing to note that the forecast NINO variables are selected as a predictor in the clustering models only for the prediction of ATTC and ATHU. In contrast, forecast JAS NINO variables are chosen in most Lasso models, except for the response of ATMH, CAHU, and CAMH. All models selecting JAS NINO variables come from F3X, suggesting the tight correlation between the number of storms and the hurricane-season ENSO condition. Additionally, it is worth noting that different predictors make different contributions to each response variable in different models. Certain predictors are consistently selected for some responses of the same region across all Lasso models. TNA in February is chosen in the forecasts of TC and HU in the Atlantic Basin. When predicting the 2020 season in the Caribbean, SOI of March and AO of April are selected across all F for TC, HU, and MH. February TNA is selected for TC and HU only in the same region. In the Gulf of Mexico, SOI of January and the second EOF value of the winter LHF (LHF.win2) are consistently picked out across all models for predictions of all three responses. In addition, MDROLR of February is selected for TC and MH of the Gulf of Mexico region.
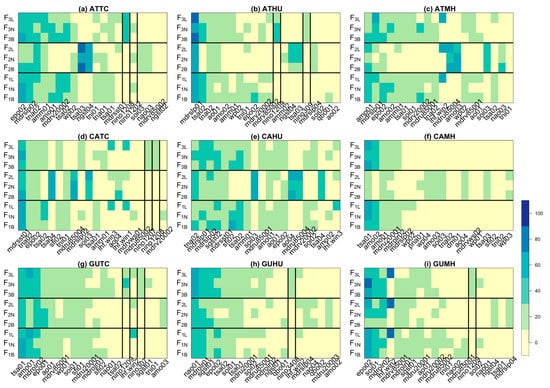
Figure 4.
Percentage of times a variable is selected across all 39 windows (unit: %) in the model F with Lasso and SWCV per response: (a) ATTC, (b) ATHU, (c) ATMH, (d) CATC, (e) CAHU, (f) CAMH, (g) GUTC, (h) GUHU, and (i) GUMH. NINO variables are highlighted in bold lines.
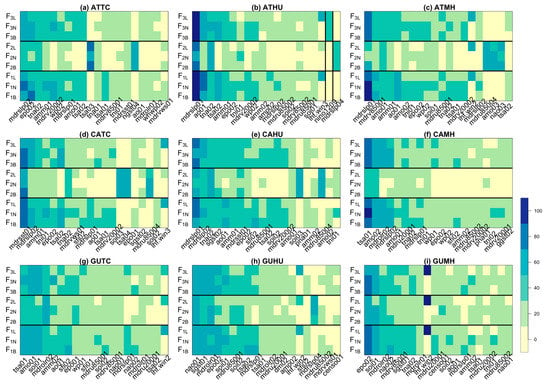
Figure 5.
Same as Figure 4, but for models with clustering algorithm. (a) ATTC, (b) ATHU, (c) ATMH, (d) CATC, (e) CAHU, (f) CAMH, (g) GUTC, (h) GUHU, and (i) GUMH.
To further illustrate the selection of significant predictors, the top five most selected predictors by Lasso and clustering algorithm are shown in Table 3 and Table 4, respectively. For brevity, only predictor-selection for ATTC is presented. The percentage of times each variable is selected is calculated across all 39 windows. Predictor selections for other response variables are presented in Figure 4 and Figure 5 and discussed earlier.

Table 3.
Five most selected variables with Lasso and SWCV, for ATTC per model. Percentage of times a variable is selected is calculated across all 39 windows and given in the curly brackets (unit: %). NINO variables are highlighted in bold.

Table 4.
Same as Table 3, but for models with clustering algorithm.
Our final goal is to compare model F with SWCV and Lasso against the climatology and see if there is improvement. Mean H values are given in Figure 6, and the positive values indicate significant difference from the climatology and there are skills brought by the specific F. For each response, there is at least one model F that has a better skill than the climatology, except for the hurricane in the Atlantic basin and Gulf of Mexico, and for major hurricanes in the Atlantic basin and Caribbean.
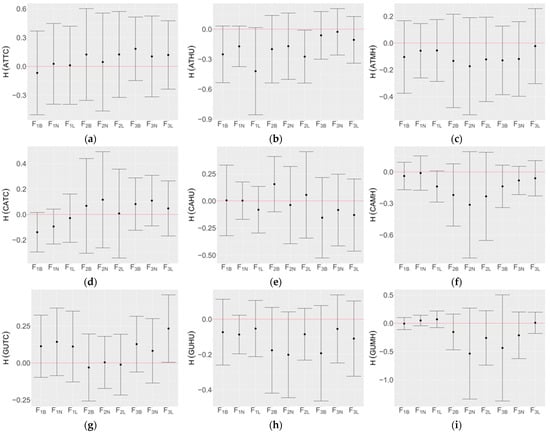
Figure 6.
Mean H values between model F with Lasso and SWCV applied, and the climatology by response: (a) ATTC, (b) ATHU, (c) ATMH, (d) CATC, (e) CAHU, (f) CAMH, (g) GUTC, (h) GUHU, and (i) GUMH. Positive values denote the significant improvement of model F, compared to the climatology.
3.1.2. Potential Benefits of Multimodel Ensemble
To evaluate whether preseason Atlantic hurricane count predictions would benefit from multimodel ensemble forecasts using existing regression models, the average of the predictions from the top three models ranked by the positive mean H-scores are computed for the period of 2005–2019. Among all top three models, F3L (32%) and F2N (29.5%) are the most selected models, followed by F1L and F3N (11.4%). The difference of MSE between climatology and model prediction is 3.08 and 18.16, respectively for TC in the Atlantic basin from the best individual model (with the highest positive H-score) and the top three model ensemble. It is apparent that both the best model and the ensemble results show skills over climatology. Forecasts based on the top three model ensemble improve further, leading to about 41% improvement against the climatology. Additionally, for each year, the H-score was calculated and its mean and standard error for the 2005–2019 period were computed using bootstrap with replacement (B = 1000). A similar conclusion was reached from the H-score, which showed that the best individual model and the ensemble prediction performed better than climatology, with an average H-score of 0.21 and 0.65, respectively. This demonstrates that if one can correctly identify the top performing models prior to issuing the preseason Atlantic hurricane prediction, the multimodel ensemble based on a subset of the top performing models has the potential to significantly improve the preseason prediction. The mean H-scores (0.65) of the ensemble forecasts based on the averaging of top three models for Atlantic TC counts are in line with those reported by Colorado State University (0.60) and the tropical Storm Risk group (0.77) for the period of 2005–2019.
3.2. Comparison of Forecasts Using Simple Average Ensemble (SAE)
As discussed in Section 2.2.2, we also created SAE models using the top 2, 4, 5 … 9 models based on the ranks of models, as shown in Table 5 for SWCV and Table 6 for LOOCV. In general, SAE predictions using 2–5 models are in line with the top three model SAE, but six or more model SAE performed worse. Figure 7 shows the results for the mean H-scores using ensemble of the top three models for SWCV. We can see that the SAE of the top three models gives a better performance for all responses than the nine model SAE (Figure 8). For example, the mean H-score from the average ensemble of the top three models for Gulf of Mexico Tropical Cyclones (GUTC) is 0.2 while the mean H-score obtained by the nine model SAE is 0.13.

Table 5.
Rank of nine individual models with SWCV validation.

Table 6.
Rank of nine individual models with LOOCV validation.
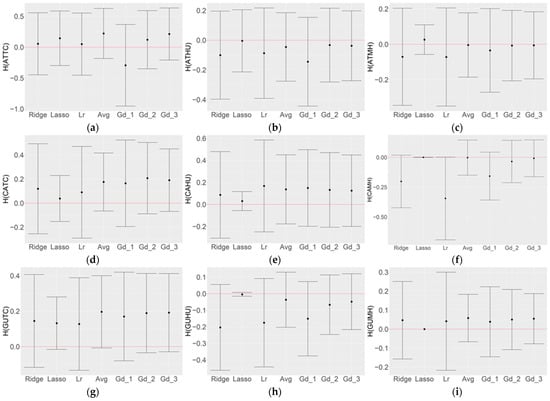
Figure 7.
Mean H values between ensemble models of top three models using different optimizations with SWCV and the climatology by response: (a) ATTC, (b) ATHU, (c) ATMH, (d) CATC, (e) CAHU, (f) CAMH, (g) GUTC, (h) GUHU, and (i) GUMH. Positive values denote superior skill of the ensemble model over climatology. Lr represents the ensemble model with optimization using linear regression. Avg represents the average of all selected models and Gd_1 represents the ensemble model with gradient descent optimization with a learning rate of 0.001. Gd_2 represents the ensemble model with gradient descent optimization with a learning rate of 0.0001. Gd_3 represents the ensemble model with gradient descent optimization with a learning rate of 0.00001.
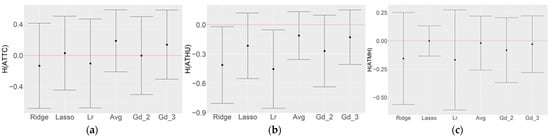
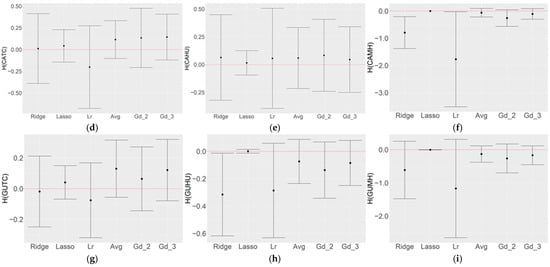
Figure 8.
Same as Figure 7, but for the ensemble model of all nine models. (a) ATTC, (b) ATHU, (c) ATMH, (d) CATC, (e) CAHU, (f) CAMH, (g) GUTC, (h) GUHU, and (i) GUMH.
Figure 9 shows the comparison between the top three model SAE and the nine model SAE for SWCV. Except for the Atlantic hurricanes, the top three model SAE performs better than the nine model SAE.
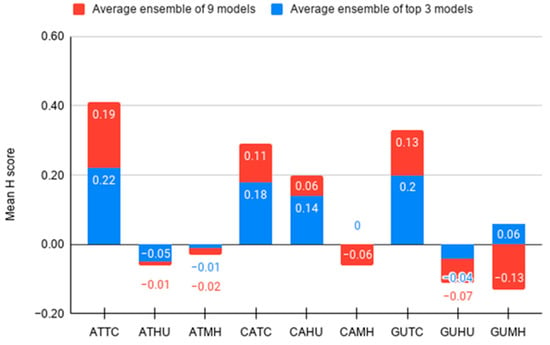
Figure 9.
Comparisons between average ensemble with top three models and that with all nine models.
3.3. Optimization of Top Three Model Ensemble
Figure 7 shows the different ensemble models obtained by performing various optimizations discussed in Section 2.2.2 using top three model weighted ensemble for SWCV, which are shown in Table 5. In some cases, the machine-learning-based optimizations for the top three model weighted average (ML-OP predictions) led to a higher mean H-score than the corresponding SAE predictions. More detailed comparisons are shown in Figure 10.
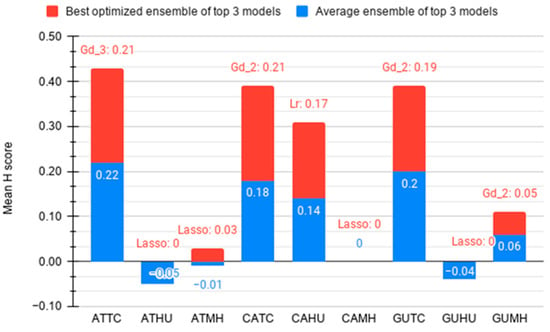
Figure 10.
Comparisons between average ensemble of top three models with best optimized top three ensemble models obtained using the methods described in Section 2.2.2. Gd_3 represents the model with gradient descent optimization having learning rate 0.00001. Lasso represents the model with Lasso optimization. Gd_2 represents the model with gradient descent optimization having learning rate 0.0001. Lr represents the model with linear regression optimization.
Figure 10 shows the comparison of the scores of the top three model SAE with that of the best optimized ensemble of top three models (ML-OP) for each category. We see that for CATC, the gradient descent optimization with a learning rate of 0.0001 improved the mean H-score by 0.03 over the SAE; for CAHU linear regression optimization improved the mean H-score by 0.03 over the SAE; for ATMH Lasso optimization improved the mean H-score by 0.04 over the SAE; and for GUHU Lasso optimization improved the mean H-score by 0.04 over the SAE.
4. Discussion
The performance of individual and various combinations of ensemble forecasts are summarized in Table 7. Mean H-scores are used to measure the performance of individual and ensemble models using SWCV validation. The left column lists the nine categories of response variables (ATTC, ATHU, ATMH, CATC, CATHU, CAMH, GUTC, GUHU, GUMH). The other columns show the best H-score for individual models. The column index (1-9) indicates the number of top performing models used in the ensemble. Index 1 means the best performing individual model. Index 2 means best two-model ensemble forecast, etc. Numbers in bold indicate the best H-score. Numbers in italic are H-scores of ensemble forecasts that are better than the best individual model forecast. Numbers highlighted in gray are H-scores using simple average ensembles. It is evident that except for Gulf of Mexico tropical storm counts (GUTC), ensemble forecasts score higher than the best individual models. For example, the H-scores for all ensemble forecasts of Atlantic TC counts (0.19–0.23) are better than the best individual model forecasts (0.18). Ensembles using the top two to five models generally perform better than using six or more models. For Atlantic TC counts and Gulf of Mexico TC counts, ensemble forecasts using simple averaging of the forecasts of ensemble members perform as good as or better than using more complex machine learning algorithms. For major hurricane counts over the entire Atlantic or Gulf of Mexico, and for TC and hurricane counts in the Caribbean Sea, optimized ensemble forecasts using machine learning algorithms perform better than ensembles derived from simple averaging. For Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico hurricane counts and Caribbean Sea major hurricane counts, no model or model ensemble shows any skill compared with climatology when validated using SWCV. The lack of prediction skill for Caribbean Sea major hurricane count by all models could be due to the small sample size in the relatively small study region.

Table 7.
Mean H-scores for individual and ensemble models using SWCV validation. The left column lists the nine categories of response variables (ATTC, ATHU, ATMH, CATC, CAHU, CAMH, GUTC, GUHU, GUMH). The other columns show the best H-score for individual models. The column index (1–9) indicates the number of top performing models used in the ensemble. Index 1 means the best performing individual model. Index 2 means the best two-model ensemble forecast, etc. Numbers in bold indicate the best H-score. Numbers in italic are the H-scores of ensemble forecasts that are better than the best individual model forecast. Numbers highlighted in gray are H-scores using simple average ensembles.
It is possible to pick the best performing ensemble forecast options for each response variable based on the results presented above, but the performance of ensemble forecasts optimized by using machine learning techniques is limited by the skills of the ensemble members. When the ensemble members have common weaknesses, then such weaknesses cannot be overcome using ensemble optimization. In such a scenario, as in the case of Atlantic hurricane counts (ATHU), all existing models suffer from systematic biases, new models or modeling approaches should be considered instead of attempting to optimize sub-ensembles of existing biased models.
In a closer look at the predictions of individual models (Figure 11), we found that large forecast errors occurred in all models in a very small number of years, such as 1995 and 2005. The year 1995 saw a hyperactive Atlantic hurricane season with 19 named storms, 11 hurricanes, and 5 major hurricanes. It was considered the start of the transition from less active to highly active decadal periods. The year 2005 was the busiest season on record prior to its time, with 27 named storms, 15 hurricanes and 7 major hurricanes. In both seasons, none of the publicly published seasonal hurricane prediction models were able to predict the level of activity. These are considered outliers in a statistical sense. Removing these two years from the training and validation data significantly improves the forecast skill of individual models as well as the ensemble. For example, the H-scores for the top ranked individual and ensemble models turned positive using SWCV. This suggests that extreme events such as 1995 and 2005 might need to be dealt with separately from the other years by using different approaches.
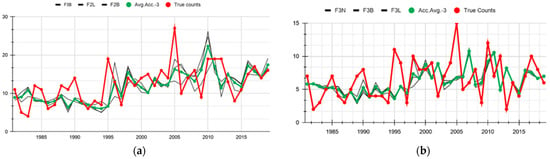
Figure 11.
Predictions for (a) ATTC counts and (b) ATHU counts by different models for Atlantic hurricanes over the years. Avg.Acc.-3 refers to the average ensemble of top three models obtained using the methodology described in Section 2.2.2. F3N, F3B, and F3L are the actual top three models whose average ensemble is formed.
5. Conclusions
In this study, nine different statistical models are constructed using different combinations of predictors, including models with and without projected El Nino indices. Multiple machine learning (ML) techniques are employed to optimize the ensemble prediction by selecting the top performing ensemble members and determining the weights for each ensemble member. The ML-Optimized Ensemble (ML-OE) forecasts are evaluated against the benchmark of Simple-Averaging Ensemble (SAE) forecasts. The results show that for response variables that are handled well by individual ensemble members, such as tropical cyclone counts over the entire Atlantic basin, the performance of SAE is comparable to the best ML-OE results. However, for response variables which are poorly modeled by individual ensemble members, such as major hurricane counts or hurricane counts in smaller sub-basins, ML-OE predictions show consistently higher skill score than individual model and the SAE prediction. The results also show that increasing the number of ensemble members does not necessarily lead to better ensemble forecasts. The best ensemble forecasts are from the optimally combined small subset of top performing models. The results further indicate that for response variables that are predicted with large systematic biases of the same sign by a majority of or all the ensemble members, ensemble techniques cannot produce better forecasts. A closer look at the years when systematic forecast biases occurred shows that these are hyperactive record-breaking seasons. Predictions of such extreme events might need to be dealt with different modeling approaches.
There are several directions worth future explorations. The first is the application of more sophisticated machine learning algorithms, including some traditional nonlinear ML models (e.g., random forests) and LSTM or Transformers or other Deep Neural Networks (DNN) that have shown some promising results in predicting sequences of data. The applications of DNNs require large volumes of data, for which high-resolution temporal records can be useful. The second direction is the application of fine-grained time series analysis, such as Dynamic Time Warping (DTW), which can be used to get similarity measures between years for temporal data analysis. The third direction is to deal with extreme anomalies and the rest of the data separately using different approaches. Ultimately, one needs to address the issue of predictability, i.e., with the limitations of available data for the response and predictor variables, what is the upper limit of preseason hurricane forecast accuracy? What is the maximum forecast lead time for skillful preseason hurricane predictions?
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.X. and X.S. (Xipeng Shen); methodology, L.X. and X.S. (Xipeng Shen); software, X.S. (Xia Sun) and S.U.S.; validation, all; formal analysis, all; investigation, all; resources, L.X. and X.S. (Xipeng Shen); data curation, X.S. (Xia Sun); writing—original draft preparation, all; writing—review and editing, L.X. and X.S. (Xipeng Shen); visualization, X.S. (Xia Sun) and S.U.S.; supervision, L.X. and X.S. (Xipeng Shen); project administration, L.X.; funding acquisition, L.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study is funded by the National Science Foundation’s Center for Accelerated Real-Time Analytics (CARTA) through award #2020-2696.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data used in this study are available upon request.
Acknowledgments
This study is funded by the National Science Foundation’s Center for Accelerated Real-Time Analytics (CARTA) through award #2020-2696. We appreciate the support from CARTA center management.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Grinsted, A.; Ditlevsen, P.; Christensen, J.H. Normalized US hurricane damage estimates using area of total destruction, 1900-2018. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 23942–23946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doocy, S.; Dick, A.; Daniels, A.; Kirsch, T.D. The human impact of tropical cyclones: A historical review of events 1980-2009 and systematic literature review. PLOS Curr. Disasters 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.B.; Katz, R.W. US billion-dollar weather and climate disasters: Data sources, trends, accuracy and biases. Nat. Hazards 2013, 67, 387–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, W.M. Summary of 1984 Atlantic Seasonal Tropical Cyclone Activity and Verification of Author’s Forecast (PDF) (Report); Colorado State University: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gray, W.M. Atlantic seasonal hurricane frequency, Part I: El Niño and 30 mb quasi-biennial influence. Mon. Weather Rev. 1984, 112, 1649–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, W.M. Atlantic seasonal hurricane frequency, Part II: Forecasting its variability. Mon. Weather Rev. 1984, 112, 1669–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landsea, C.W.; Gray, W.M.; Mielke, P.W., Jr.; Berry, K.J. Seasonal forecasting of Atlantic hurricane activity. Weather 1994, 49, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, E.; Xie, L. Predicting Atlantic Tropical Cyclone Seasonal Activity in April. Weather Forecast. 2009, 24, 436–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, S.J.; Wing, A.A. Tropical cyclones in climate models. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Clim. Chang. 2005, 7, 211–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klotzbach, P.J.; Caron, L.-P.; Bell, M.M. A statistical/dynamical model for North Atlantic seasonal hurricane prediction. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecchi, G.A.; Zhao, M.; Wang, H.; Villarini, G.; Rosati, A.; Kumar, A.; Held, I.M.; Gudgel, R. Statistical–dynamical predictions of seasonal North Atlantic hurricane activity. Mon. Weather Rev. 2011, 139, 1070–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-M.; Webster, P.J. Extended-range seasonal hurricane forecasts for the North Atlantic with a hybrid dynamical-statistical model. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L21705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Schemm, J.-K.E.; Wang, W.; Long, L.; Chelliah, M.; Bell, G.D.; Peng, P. Statistical Forecast Model for Atlantic Seasonal Hurricane Activity Based on the NCEP Dynamical Seasonal Forecast. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 4481–4500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- How Accurate are Pre-Season Hurricane Landfall Forecasts? Available online: https://www.washingtonpost.com/news/capital-weather-gang/wp/2013/04/23/how-accurate-are-pre-season-hurricane-landfall-forecasts/ (accessed on 26 February 2021).
- Klotzbach, P.J.; Saunders, M.A.; Bell, G.D.; Blake, E.S. North Atlantic Seasonal Hurricane Prediction. In Climate Extremes: Patterns and Mechanisms, Geophysical Monograph 226; Wang, S.-S., Yoon, J.-H., Funk, C.C., Gillies, R.R., Eds.; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, E.B.; Gibney, E.J.; Brown, D.P.; Mainelli, M.; Franklin, J.L.; Kimberlain, T.B.; Hammer, G.R. Tropical Cyclones of the eastern North Pacific Ocean, 1949–2006. In Historical Climatology Series; National Climatic Data Center: Miami, FL, USA, 2008; Volume 2–6, in publication. [Google Scholar]
- Klotzbach, P.J.; Gray, W.M. Updated 6–11-Month Prediction of Atlantic Basin Seasonal Hurricane Activity. Weather Forecast. 2004, 19, 917–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Emanuel, K.; Fondriest, F.; Kossin, J. Potential Economic Value of Seasonal Hurricane Forecasts. Weather Clim. Soc. 2012, 4, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, T.N. Predicting uncertainty in forecasts of weather and climate. Rep. Prog. Phys. 1999, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slingo, J.; Palmer, T. Uncertainty in weather and climate prediction. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A. 2011, 369, 4751–4767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewage, P.; Trovati, M.; Pereira, E.; Behera, A. Deep learning-based effective fine-grained weather forecasting model. Pattern Anal. Appl. 2021, 24, 343–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scher, S.; Messori, G. Predicting weather forecast uncertainty with machine learning. Q. J. R Meteorol. Soc. 2018, 144, 2830–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasp, S.; Lerch, S. Neural Networks for Postprocessing Ensemble Weather Forecasts. Mon. Weather Rev. 2021, 146, 3885–3900. Available online: https://journals.ametsoc.org/view/journals/mwre/146/11/mwr-d-18-0187.1.xml (accessed on 26 February 2021).
- Krasnopolsky, V.M.; Lin, Y. A Neural Network Nonlinear Multimodel Ensemble to Improve Precipitation Forecasts over Continental US. Adv. Meteorol. 2018, 2012, 649450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagger, T.H.; Elsner, J.B. A Consensus Model for Seasonal Hurricane Prediction. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 6090–6099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richmana, M.B.; Lesliea, L.M.; Ramsay, H.A.; Klotzbach, P.J. Reducing Tropical Cyclone Prediction Errors Using Machine Learning Approaches. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvinen, B.R.; Neumann, C.J.; Davis, M.A.S. A Tropical Cyclone Data Tape for the North Atlantic Basin, 1886–1983: Contents, Limitations, and Uses; NOAA Technical Memorandum NWS NHC 22: Coral Gables, FL, USA, 1984; p. 21.
- Leetmaa, A.; Reynolds, R.; Jenne, R.; Josepht, D. The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc. 1996, 77, 437–470. [Google Scholar]
- Córdoba, M.A.; Fuentes, M.; Guinness, J.; Xie, L. Verification of Statistical Seasonal Tropical Cyclone Forecast. Zenodo 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtagh, F.; Legendre, P. Ward’s hierarchical agglomerative clustering method: Which algorithms implement Ward’s criterion? J. Classif. 2014, 31, 274–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).