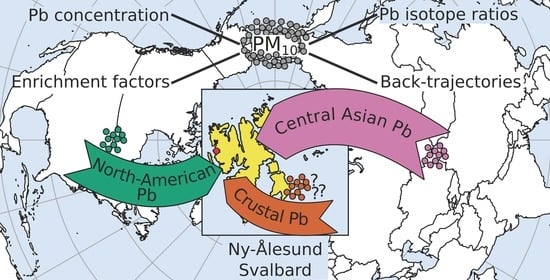
Potential Source Areas for Atmospheric Lead Reaching Ny-Ålesund from 2010 to 2018
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Sampling
2.2. Sample Analysis
2.3. Data Analysis
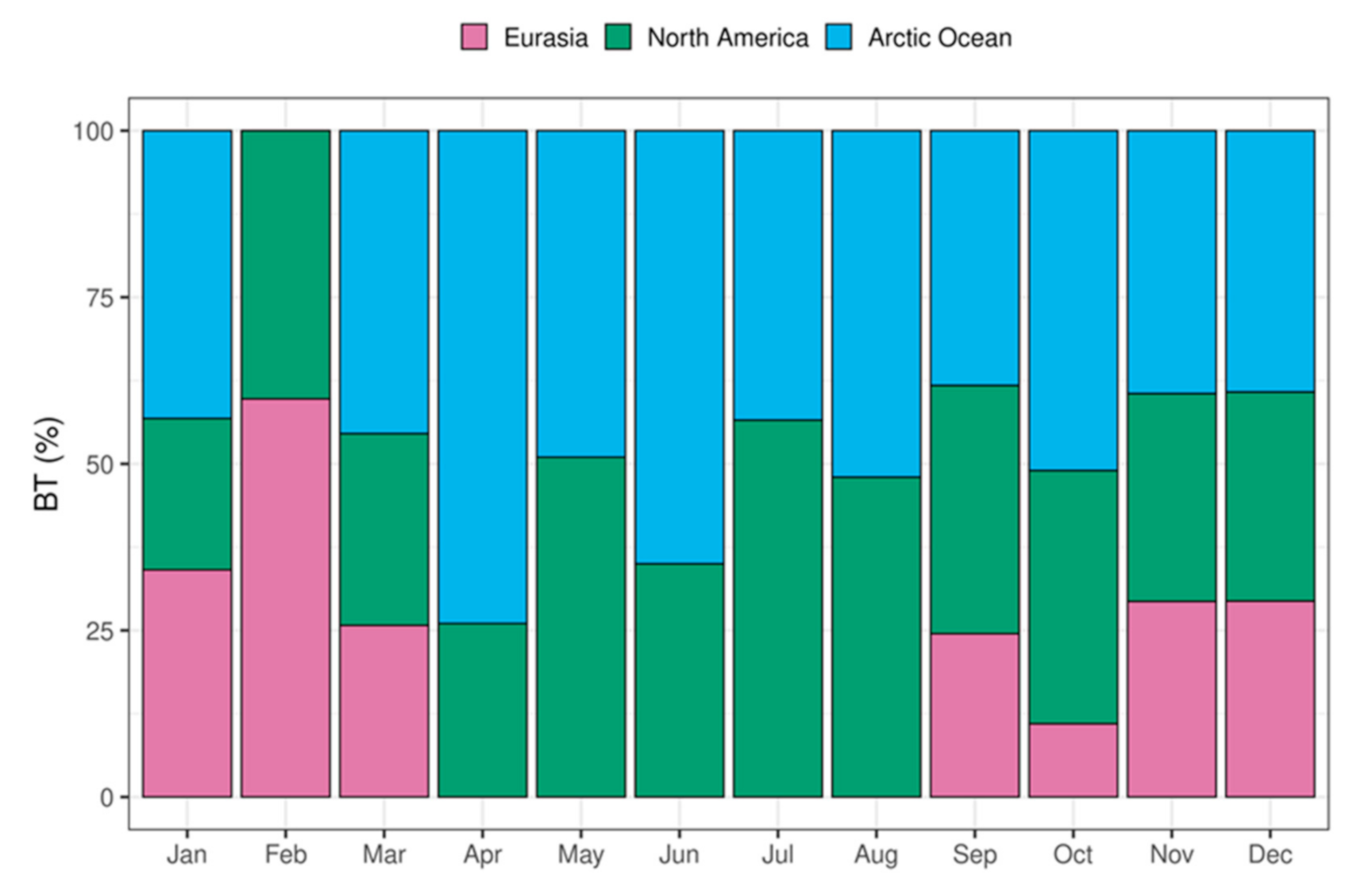
2.4. Back Trajectory Analysis
3. Results
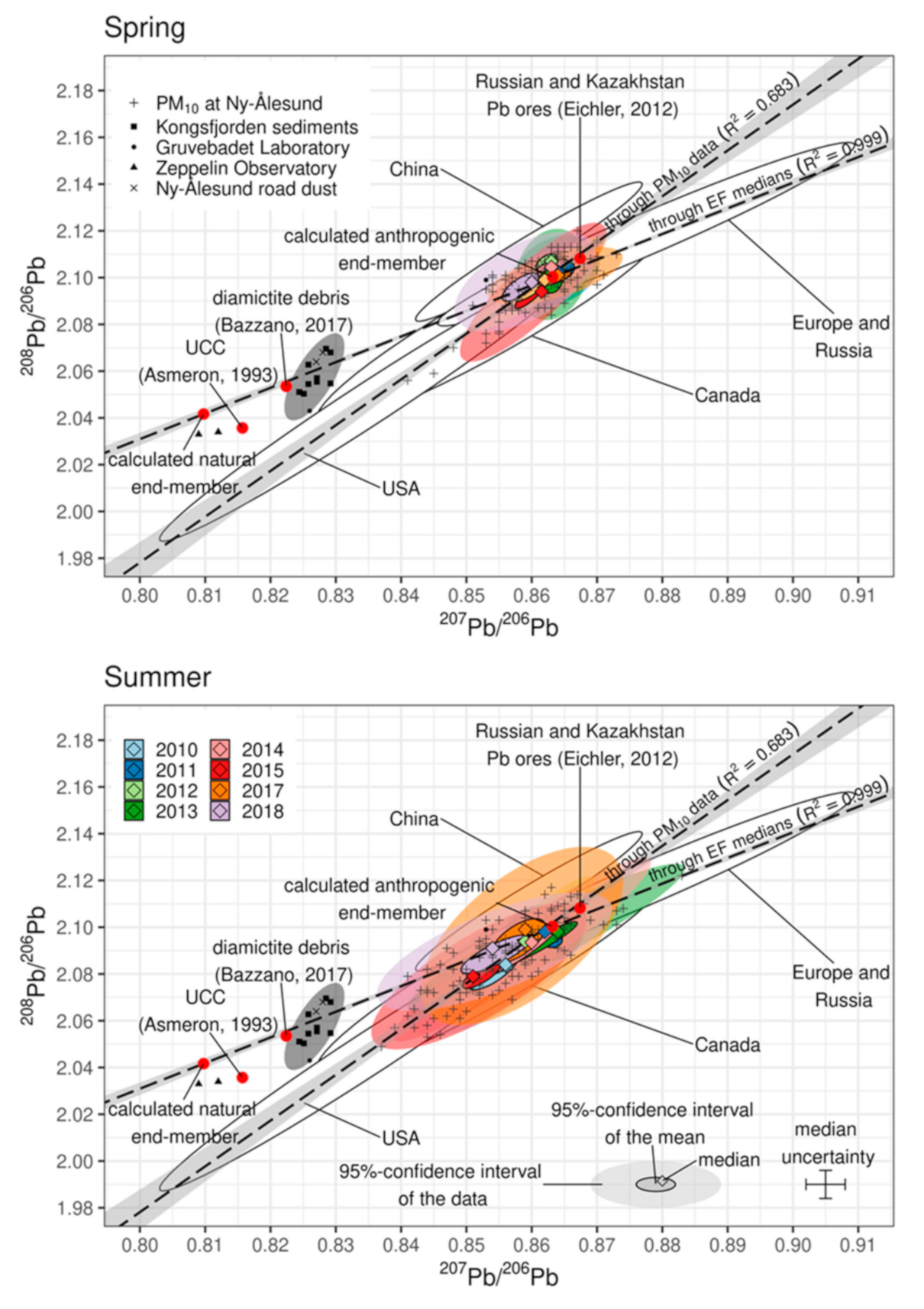
3.1. Lead Concentration, Enrichment, and Isotopic Composition
3.2. Natural Contribution to Atmospheric Lead
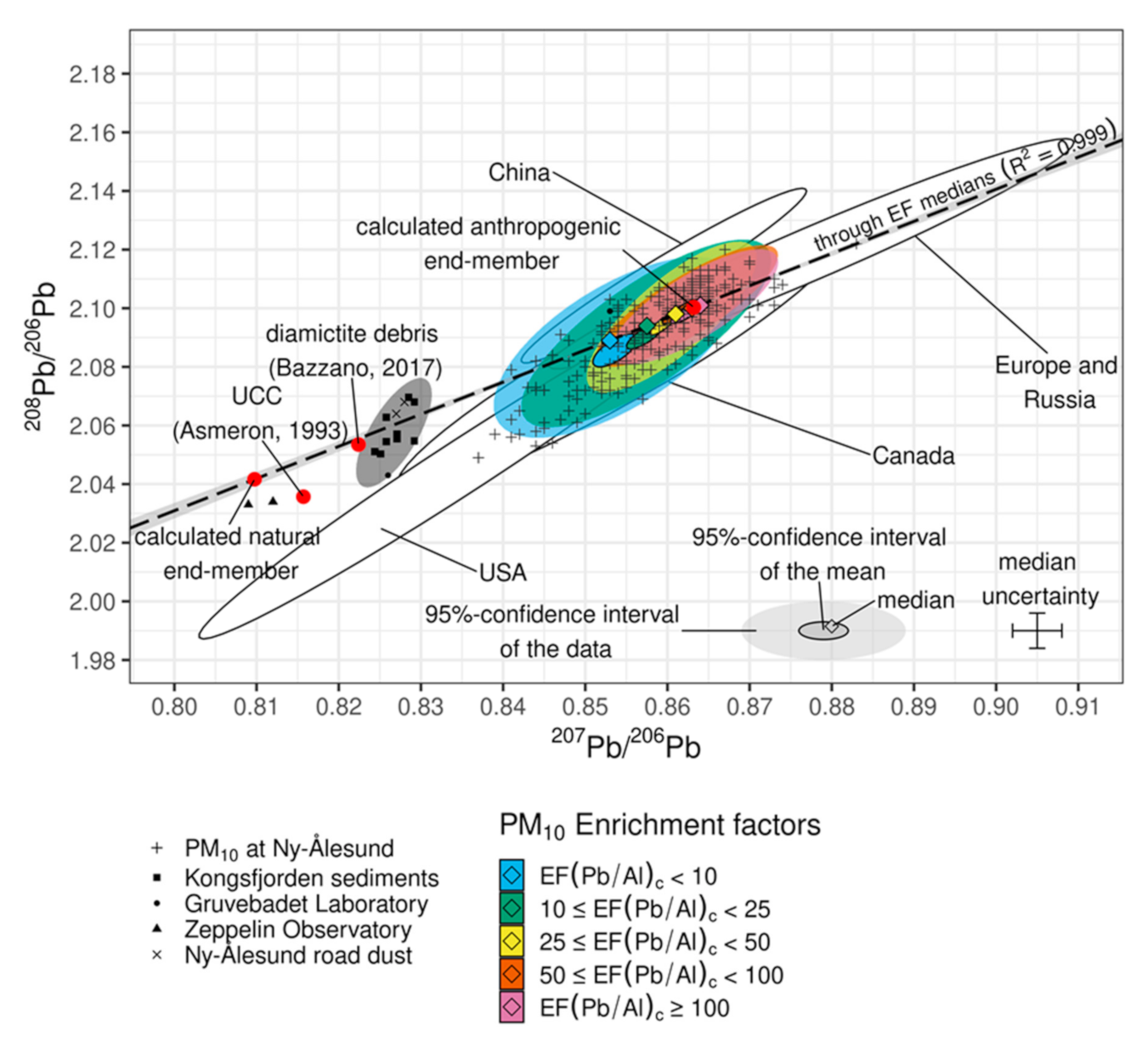
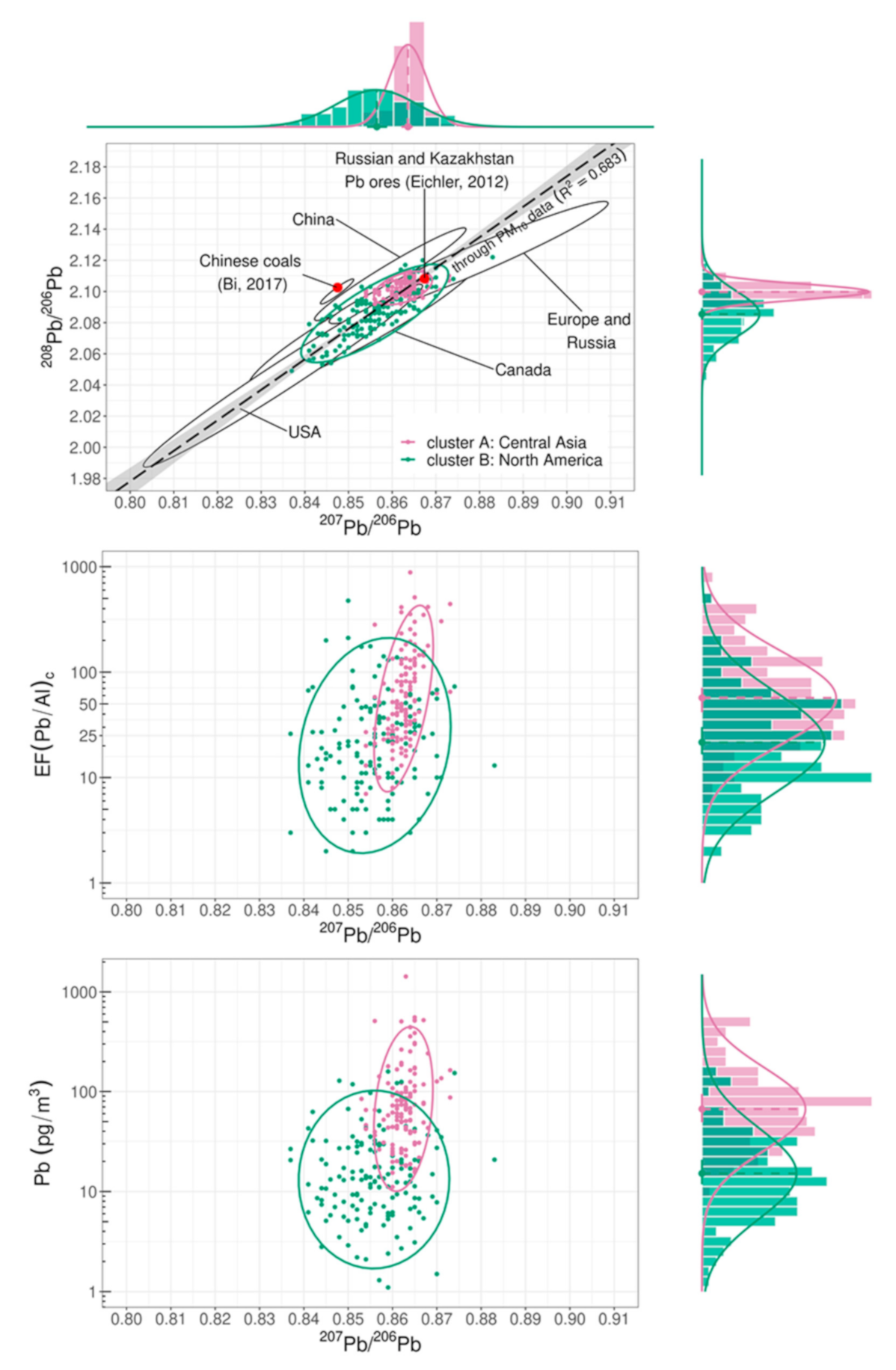
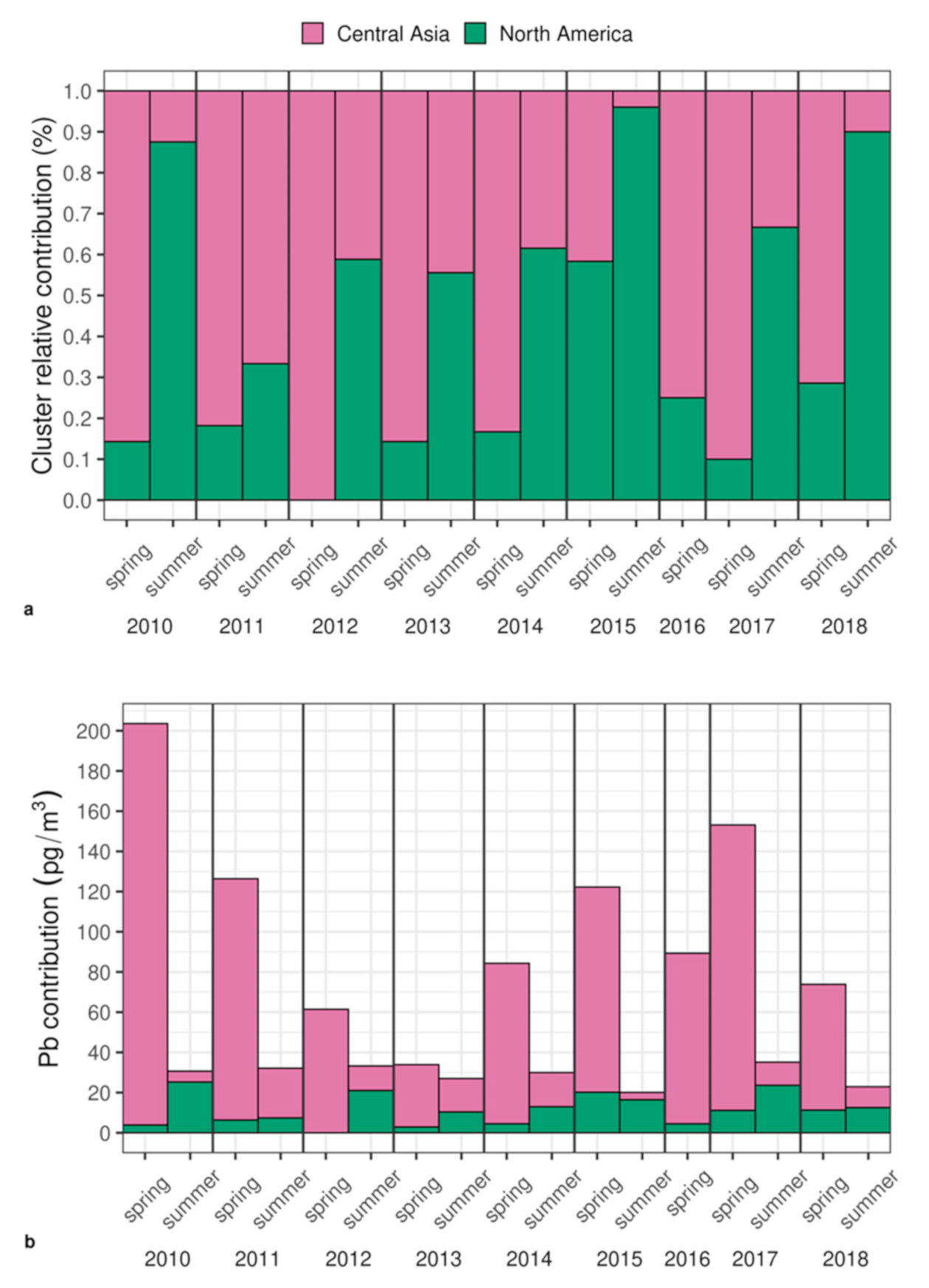
3.3. Disentangling Anthropogenic Contributions to Atmospheric Lead
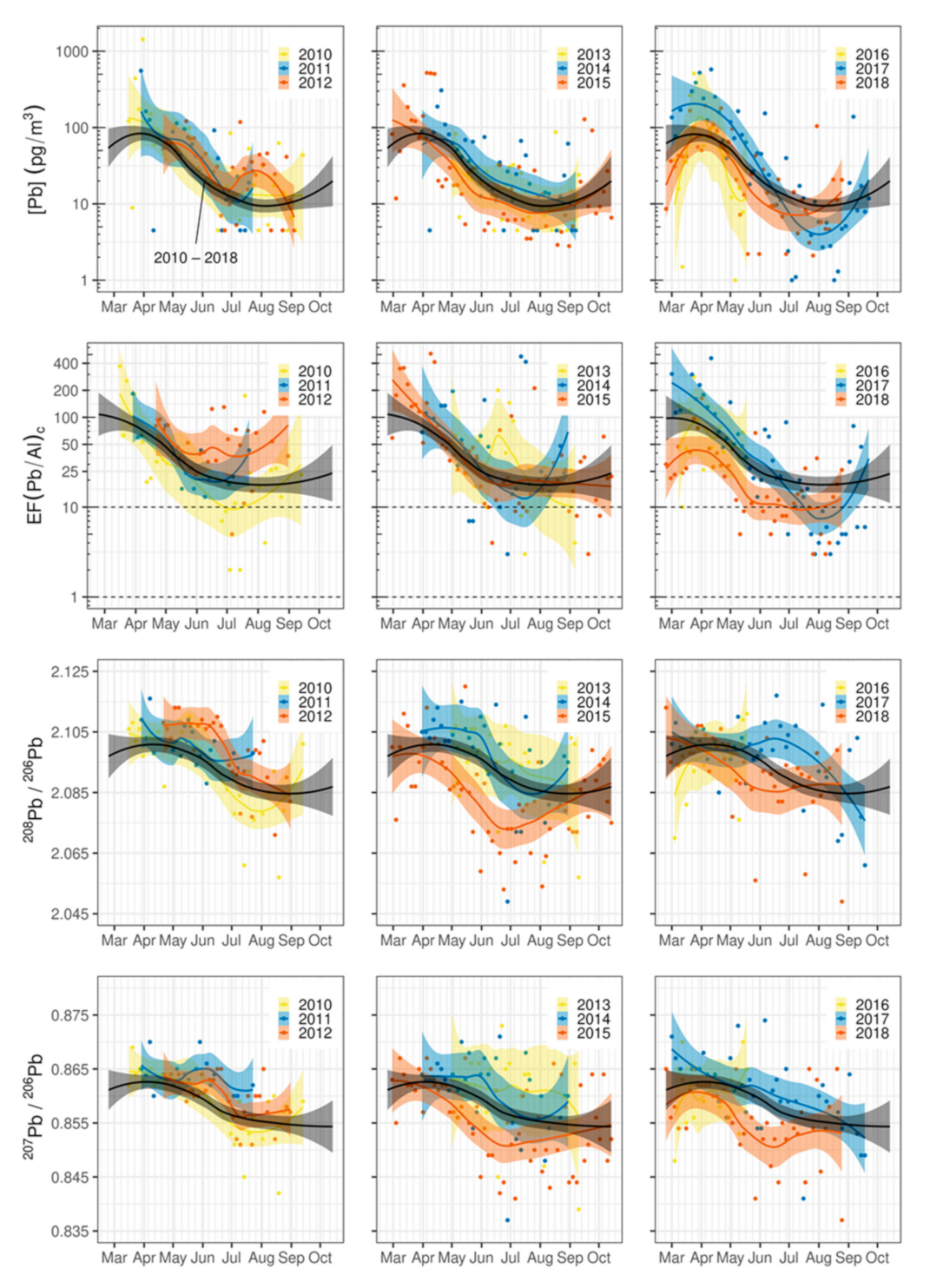
3.4. Temporal Variations in Lead Concentration, Enrichment and Isotopic Composition
3.5. Back-Trajectory Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IPPC. Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Solomon, S., Quin, D., Manning, M., Marquis, M., Averyt, K., Tignor, M., LeRoy Miller, H., Jr., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Serreze, M.C.; Francis, J.A. The Arctic Amplification Debate. Clim. Chang. 2006, 76, 241–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, W.N.; Hovelsrud, G.K.; van Oort, B.E.H.; Key, J.R.; Kovacs, K.M.; Michel, C.; Haas, C.; Granskog, M.A.; Gerland, S.; Perovich, D.K.; et al. Arctic Sea Ice in Transformation: A Review of Recent Observed Changes and Impacts on Biology and Human Activity. Rev. Geophys. 2014, 52, 185–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmermans, M.-L.; Jayne, S.R. The Arctic Ocean Spices Up. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2016, 46, 1277–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blunden, J.; Arndt, D.S.; Hartfield, G. State of the Climate in 2017. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2018, 99, Si–S310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, R.W.; Barrie, L.A.; Bidleman, T.F.; Diamond, M.L.; Gregor, D.J.; Semkin, R.G.; Strachan, W.M.J.; Li, Y.F.; Wania, F.; Alaee, M.; et al. Contaminants in the Canadian Arctic: 5 Years of Progress in Understanding Sources, Occurrence and Pathways. Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 254, 93–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muir, D.; Braune, B.; DeMarch, B.; Norstrom, R.; Wagemann, R.; Lockhart, L.; Hargrave, B.; Bright, D.; Addison, R.; Payne, J.; et al. Spatial and Temporal Trends and Effects of Contaminants in the Canadian Arctic Marine Ecosystem: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 1999, 230, 83–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muir, D.C.G.; Wagemann, R.; Hargrave, B.T.; Thomas, D.J.; Peakall, D.B.; Norstrom, R.J. Arctic Marine Ecosystem Contamination. Sci. Total Environ. 1992, 122, 75–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AMAP. AMAP Assessment 2002: Heavy Metals in the Arctic; Arctic Monitoring and Assessment Programme (AMAP): Oslo, Norway, 2004; p. xvi. [Google Scholar]
- Ramanathan, V.; Ramana, M.V.; Roberts, G.; Kim, D.; Corrigan, C.; Chung, C.; Winker, D. Warming Trends in Asia Amplified by Brown Cloud Solar Absorption. Nature 2007, 448, 575–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udisti, R.; Bazzano, A.; Becagli, S.; Bolzacchini, E.; Caiazzo, L.; Cappelletti, D.; Ferrero, L.; Frosini, D.; Giardi, F.; Grotti, M.; et al. Sulfate Source Apportionment in the Ny-Ålesund (Svalbard Islands) Arctic Aerosol. Rend. Lincei 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winiger, P.; Andersson, A.; Eckhardt, S.; Stohl, A.; Gustafsson, Ö. The Sources of Atmospheric Black Carbon at a European Gateway to the Arctic. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.H.; Jang, E.; Yoon, Y.J.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, T.-W.; Becagli, S.; Caiazzo, L.; Cappelletti, D.; Krejci, R.; Eleftheriadis, K.; et al. Influence of Biogenic Organics on the Chemical Composition of Arctic Aerosols. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2019, 33, 1238–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, P.K.; Shaw, G.; Andrews, E.; Dutton, E.G.; Ruoho-Airola, T.; Gong, S.L. Arctic Haze: Current Trends and Knowledge Gaps. Tellus Ser. B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2007, 59, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, P.K.; Miller, T.L.; Bates, T.S. A 3-Year Record of Simultaneously Measured Aerosol Chemical and Optical Properties at Barrow, Alaska. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107, 4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzano, A.; Ardini, F.; Becagli, S.; Traversi, R.; Udisti, R.; Cappelletti, D.; Grotti, M. Source Assessment of Atmospheric Lead Measured at Ny-Ålesund, Svalbard. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 113, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.L.; Barrie, L.A. Trends of Heavy Metal Components in the Arctic Aerosols and Their Relationship to the Emissions in the Northern Hemisphere. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 342, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komárek, M.; Ettler, V.; Chrastný, V.; Mihaljevič, M. Lead Isotopes in Environmental Sciences: A Review. Environ. Int. 2008, 34, 562–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardini, F.; Bazzano, A.; Grotti, M. Lead Isotopic Ratios in the Arctic Environment. Environ. Chem. 2020, 17, 213–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flament, P.; Bertho, M.L.; Deboudt, K.; Véron, A.; Puskaric, E. European Isotopic Signatures for Lead in Atmospheric Aerosols: A Source Apportionment Based upon 206Pb/207Pb Ratios. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 296, 35–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollhöfer, A.; Rosman, K.J.R. The Temporal Stability in Lead Isotopic Signatures at Selected Sites in the Southern and Northern Hemispheres. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2002, 66, 1375–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollhöfer, A.; Rosman, K.J.R. Isotopic Source Signatures for Atmospheric Lead: The Northern Hemisphere. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2001, 65, 1727–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzano, A.; Cappelletti, D.; Udisti, R.; Grotti, M. Long-Range Transport of Atmospheric Lead Reaching Ny-Ålesund: Inter-Annual and Seasonal Variations of Potential Source Areas. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 139, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzano, A.; Ardini, F.; Grotti, M.; Malandrino, M.; Giacomino, A.; Abollino, O.; Cappelletti, D.; Becagli, S.; Traversi, R.; Udisti, R. Elemental and Lead Isotopic Composition of Atmospheric Particulate Measured in the Arctic Region (Ny-Ålesund, Svalbard Islands). Rend. Lincei 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzola, M.; Viola, A.P.; Lanconelli, C.; Vitale, V. Atmospheric Observations at the Amundsen-Nobile Climate Change Tower in Ny-Ålesund, Svalbard. Rend. Lincei 2016, 27, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Scrucca, L.; Fop, M.; Murphy, T.B.; Raftery, A.E. Mclust 5: Clustering, Classification and Density Estimation Using Gaussian Finite Mixture Models. R J. 2016, 8, 289–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Organization for Nuclear Research, OpenAIRE, Zenodo: CERN, Geneva (CH). 2013. Available online: https://www.zenodo.org/ (accessed on 16 March 2021). [CrossRef]
- Stein, A.F.; Draxler, R.R.; Rolph, G.D.; Stunder, B.J.B.; Cohen, M.D.; Ngan, F. NOAA’s HYSPLIT Atmospheric Transport and Dispersion Modeling System. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 2059–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freud, E.; Krejci, R.; Tunved, P.; Leaitch, R.; Nguyen, Q.T.; Massling, A.; Skov, H.; Barrie, L. Pan-Arctic Aerosol Number Size Distributions: Seasonality and Transport Patterns. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 8101–8128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conca, E.; Abollino, O.; Giacomino, A.; Buoso, S.; Traversi, R.; Becagli, S.; Grotti, M.; Malandrino, M. Source Identification and Temporal Evolution of Trace Elements in PM10 Collected near to Ny-Ålesund (Norwegian Arctic). Atmos. Environ. 2019, 203, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedepohl, K.H. The Composition of the Continental Crust. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 58A, 959–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bory, A.J.M.; Abouchami, W.; Galer, S.J.G.; Svensson, A.; Christensen, J.N.; Biscaye, P.E. A Chinese Imprint in Insoluble Pollutants Recently Deposited in Central Greenland as Indicated by Lead Isotopes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 1451–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shotyk, W.; Zheng, J.; Krachler, M.; Zdanowicz, C.; Koerner, R.; Fisher, D. Predominance of Industrial Pb in Recent Snow (1994–2004) and Ice (1842–1996) from Devon Island, Arctic Canada. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmerom, Y.; Jacobsen, S.B. The Pb Isotopic Evolution of the Earth: Inferences from River Water Suspended Loads. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1993, 115, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzano, A.; Rivaro, P.; Soggia, F.; Ardini, F.; Grotti, M. Anthropogenic and Natural Sources of Particulate Trace Elements in the Coastal Marine Environment of Kongsfjorden, Svalbard. Mar. Chem. 2014, 163, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroni, B.; Arnalds, O.; Dagsson-Waldhauserová, P.; Crocchianti, S.; Vivani, R.; Cappelletti, D. Mineralogical and Chemical Records of Icelandic Dust Sources Upon Ny-Ålesund (Svalbard Islands). Front. Earth Sci. 2018, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carignan, J.; Simonetti, A.; Gariépy, C. Dispersal of Atmospheric Lead in Northeastern North America as Recorded by Epiphytic Lichens. Atmos. Env. 2002, 36, 3759–3766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollhöfer, A.; Rosman, K.J.R. Lead Isotopic Ratios in European Atmospheric Aerosols. Phys. Chem. Earth Part B Hydrol. Ocean Atmos. 2001, 26, 835–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukai, H.; Tanaka, A.; Fujii, T.; Zeng, Y.; Hong, Y.; Tang, J.; Guo, S.; Xue, H.; Sun, Z.; Zhou, J.; et al. Regional Characteristics of Sulfur and Lead Isotope Ratios in the Atmosphere at Several Chinese Urban Sites. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 1064–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzano, A.; Ardini, F.; Terol, A.; Rivaro, P.; Soggia, F.; Grotti, M. Effects of the Atlantic Water and Glacial Run-off on the Spatial Distribution of Particulate Trace Elements in the Kongsfjorden. Mar. Chem. 2017, 191, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grotti, M.; Soggia, F.; Ardini, F.; Bazzano, A.; Moroni, B.; Vivani, R.; Cappelletti, D.; Misic, C. Trace Elements in Surface Sediments from Kongsfjorden, Svalbard: Occurrence, Sources and Bioavailability. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichler, A.; Tobler, L.; Eyrikh, S.; Gramlich, G.; Malygina, N.; Papina, T.; Schwikowski, M. Three Centuries of Eastern European and Altai Lead Emissions Recorded in a Belukha Ice Core. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 4323–4330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukai, H.; Machida, T.; Tanaka, A.; Vera, Y.P.; Uematsu, M. Lead Isotope Ratios in the Urban Air of Eastern and Central Russia. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 2783–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.-H.; Hwang, H.; Han, C.; Hur, S.D.; Kim, S.-J.; Hong, S. Pb Concentrations and Isotopic Record Preserved in Northwest Greenland Snow. Chemosphere 2017, 187, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, X.-Y.; Li, Z.-G.; Wang, S.-X.; Zhang, L.; Xu, R.; Liu, J.-L.; Yang, H.-M.; Guo, M.-Z. Lead Isotopic Compositions of Selected Coals, Pb/Zn Ores and Fuels in China and the Application for Source Tracing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 13502–13508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonetti, A.; Gariépy, C.; Carignan, J. Pb and Sr Isotopic Compositions of Snowpack from Québec, Canada: Inferences on the Sources and Deposition Budgets of Atmospheric Heavy Metals. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2000, 64, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, L.S.; Blum, J.D.; Dvonch, J.T.; Gratz, L.E.; Landis, M.S. The Use of Pb, Sr, and Hg Isotopes in Great Lakes Precipitation as a Tool for Pollution Source Attribution. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 502, 362–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosman, K.J.R.; Chisholm, W.; Boutron, C.F.; Candelone, J.P.; Hong, S. Isotopic Evidence to Account for Changes in the Concentration of Lead in Greenland Snow between 1960 and 1988. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1994, 58, 3265–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinnes, E.; Berg, T.; Uggerud, H.T. Three Decades of Atmospheric Metal Deposition in Norway as Evident from Analysis of Moss Samples. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 412–413, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law, K.S.; Stohl, A. Arctic Air Pollution: Origins and Impacts. Science 2007, 315, 1537–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Pb (pg/m3) | 207Pb/206Pb | 208Pb/206Pb | EF(Pb/Al)c | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 59 | 0.859 | 2.094 | 65 |
| Std. Dev | 119 | 0.007 | 0.014 | 97 |
| Min | 1.0 | 0.837 | 2.049 | 2.0 |
| Q1 | 8.2 | 0.855 | 2.087 | 15 |
| Median | 24 | 0.861 | 2.098 | 33 |
| Q3 | 64 | 0.864 | 2.103 | 68 |
| Max | 1428 | 0.883 | 2.122 | 883 |
| MAD | 28 | 0.006 | 0.012 | 33 |
| IQR | 55 | 0.009 | 0.016 | 53 |
| Skewness | 6.2 | −0.6 | −0.9 | 3.9 |
| n > LoQ | 300 | 286 | 286 | 287 |
| n | 331 | 331 | 331 | 331 |
| Parameters | Cluster A: Central Asia | Cluster B: North America |
|---|---|---|
| Mean | 208Pb/206Pb = 2.1019 207Pb/206Pb = 0.8623 log(EF) = 1.76 log(Pb) = 1.82 | 208Pb/206Pb = 2.0870 207Pb/206Pb = 0.8563 log(EF) = 1.33 log(Pb) = 1.80 |
| Standard deviation | 208Pb/206Pb = 0.0052 207Pb/206Pb = 0.0036 log(EF) = 0.43 log(Pb) = 0.41 | 208Pb/206Pb = 0.0151 207Pb/206Pb = 0.0079 log(EF) = 0.47 log(Pb) = 0.45 |
| Covariance | 208Pb/206Pb, 207Pb/206Pb = 1.1 × 10−5 208Pb/206Pb, log(EF) = 6.5 × 10−4 208Pb/206Pb, log(Pb) = 4.2 × 10−4 207Pb/206Pb, log(EF) = 6.7 × 10−4 207Pb/206Pb, log(Pb) = 3.6 × 10−4 log(EF), log(Pb) = 0.11 | 208Pb/206Pb, 207Pb/206Pb = 9.6 × 10−5 208Pb/206Pb, log(EF) = 7.8 × 10−4 208Pb/206Pb, log(Pb) = 5.1 × 10−4 207Pb/206Pb, log(EF) = 8.0 × 10−4 207Pb/206Pb, log(Pb) = 4.3 × 10−4 log(EF), log(Pb) = 0.13 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bazzano, A.; Bertinetti, S.; Ardini, F.; Cappelletti, D.; Grotti, M. Potential Source Areas for Atmospheric Lead Reaching Ny-Ålesund from 2010 to 2018. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 388. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12030388
Bazzano A, Bertinetti S, Ardini F, Cappelletti D, Grotti M. Potential Source Areas for Atmospheric Lead Reaching Ny-Ålesund from 2010 to 2018. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(3):388. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12030388
Chicago/Turabian StyleBazzano, Andrea, Stefano Bertinetti, Francisco Ardini, David Cappelletti, and Marco Grotti. 2021. "Potential Source Areas for Atmospheric Lead Reaching Ny-Ålesund from 2010 to 2018" Atmosphere 12, no. 3: 388. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12030388
APA StyleBazzano, A., Bertinetti, S., Ardini, F., Cappelletti, D., & Grotti, M. (2021). Potential Source Areas for Atmospheric Lead Reaching Ny-Ålesund from 2010 to 2018. Atmosphere, 12(3), 388. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12030388