COVID-19 and Air Pollution: Measuring Pandemic Impact to Air Quality in Five European Countries
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
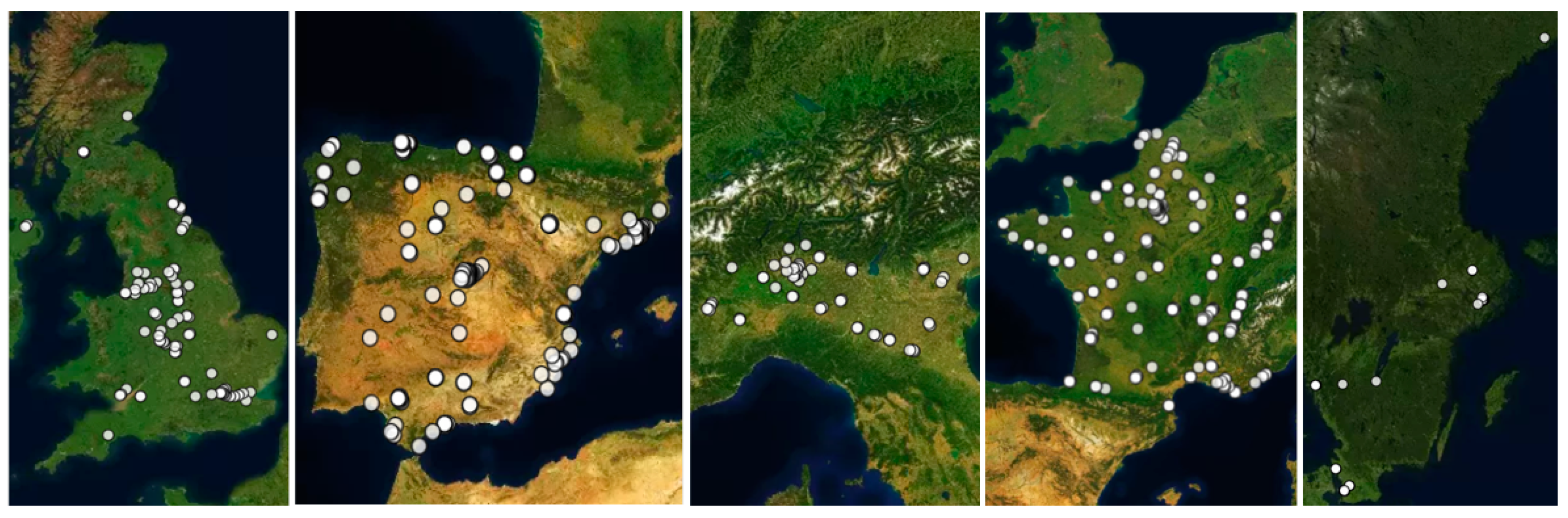
2.1. Analysis Sample, Data, and Limitations
2.2. Mann–Kendall Test
2.3. Sen’s Slope Estimator
3. Results
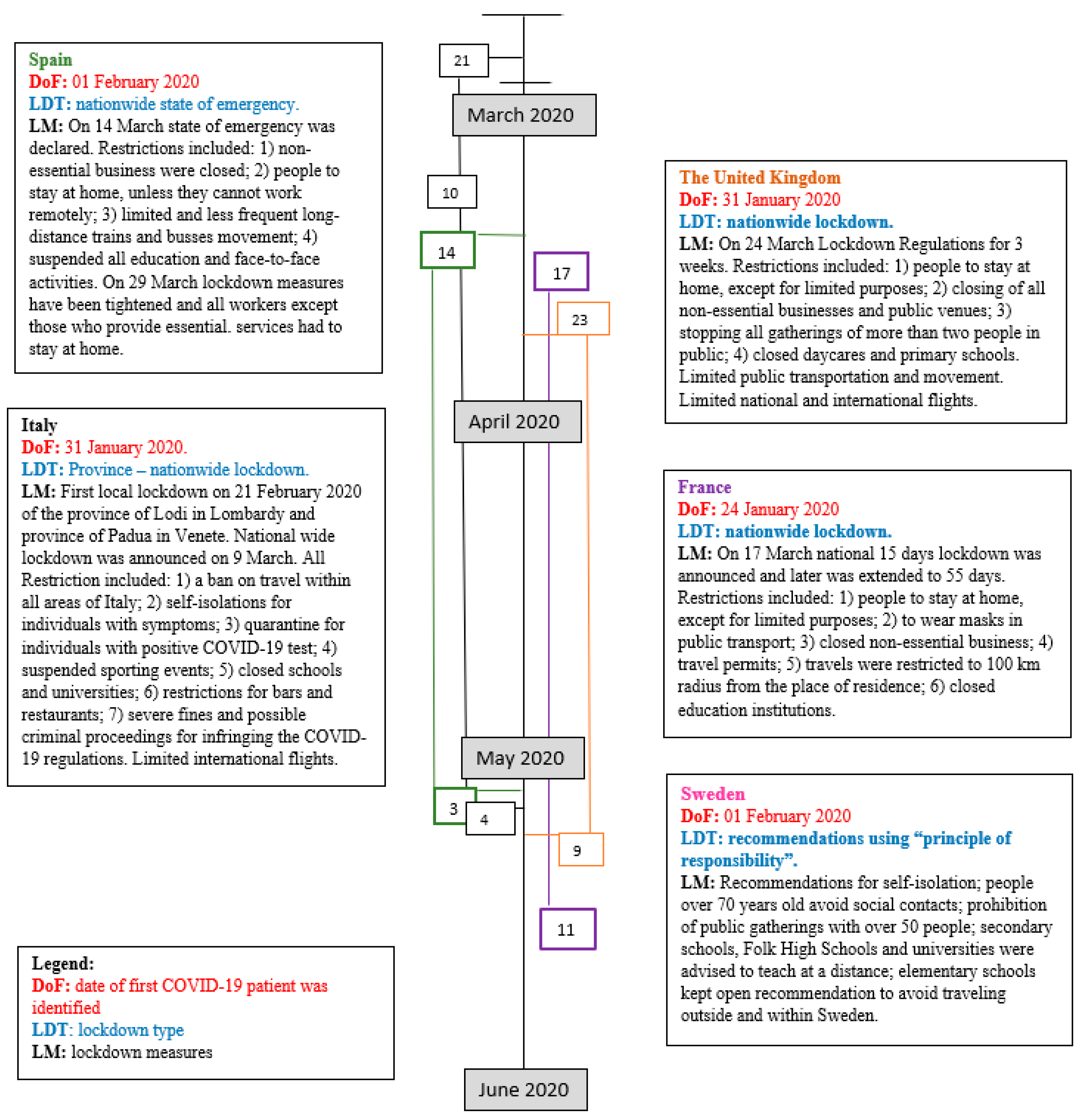
3.1. Review of Country-Based COVID-19 Lockdown Measures
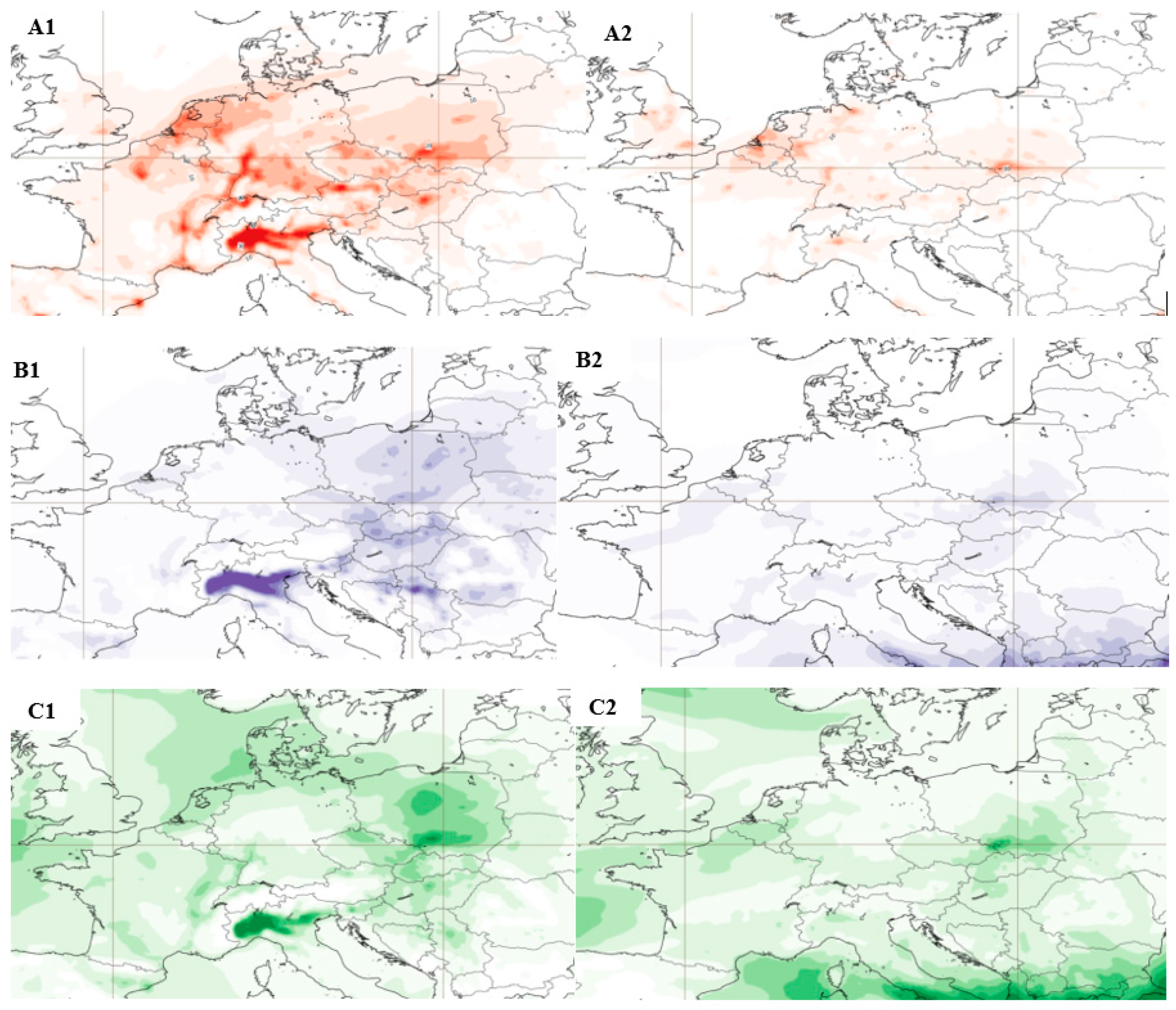
3.2. Air Pollution Analysis in the Context of Production Reduction
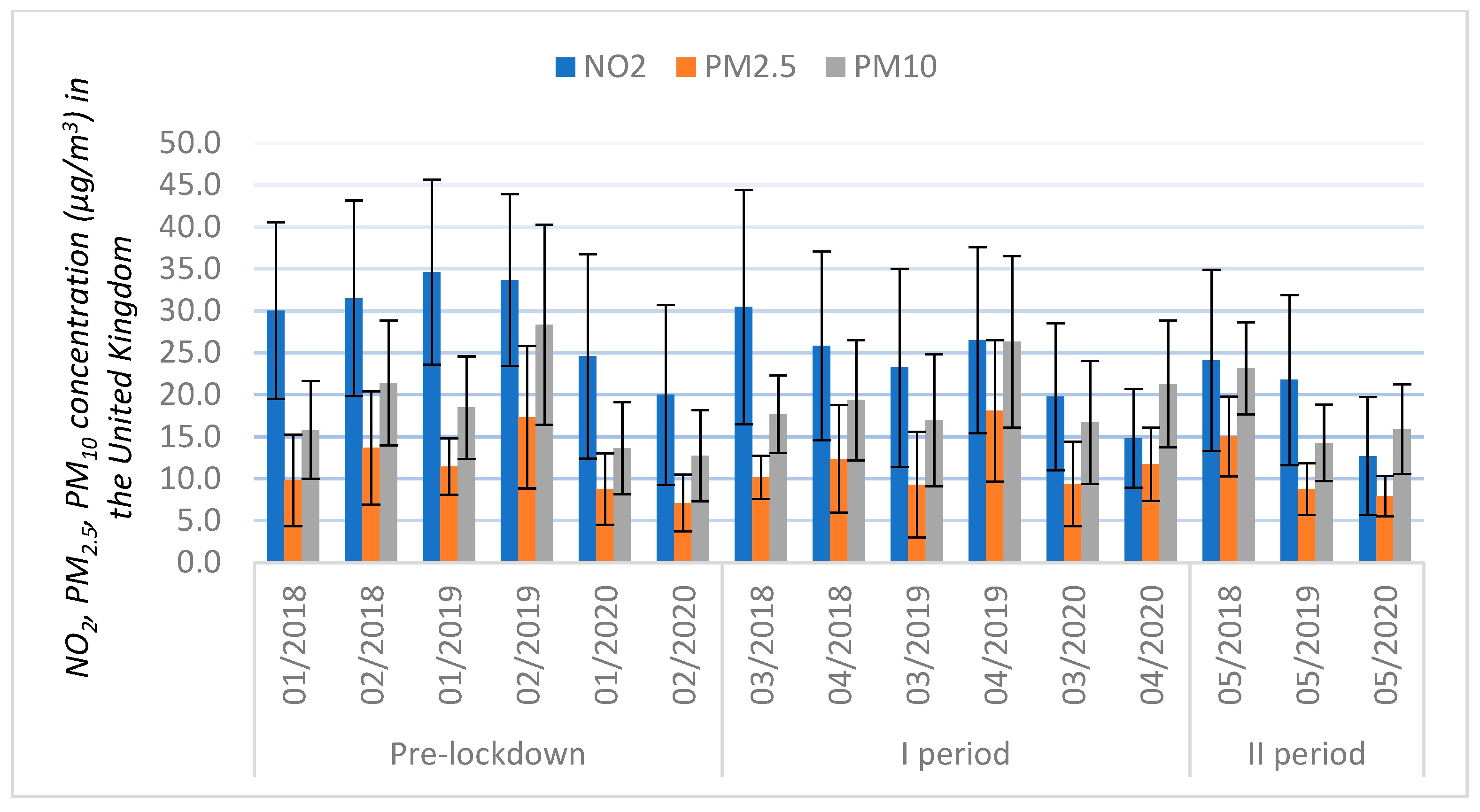
3.3. Trends in the Pollution Variables
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chan, J.F.W.; Yuan, S.; Kok, K.H.; To, K.K.W.; Chu, H.; Yang, J.; Xing, F.; Liu, J.; Yip, C.C.Y.; Poon, R.W.S.; et al. A Familial Cluster of Pneumonia Associated with the 2019 Novel Coronavirus Indicating Person-to-Person Transmission: A Study of a Family Cluster. Lancet 2020, 395, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Nowel Coronavirus (19-nCoV) Situation Report—1. 21 January 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/20200121-sitrep-1-2019-ncov.pdf?sfvrsn=20a99c10_4 (accessed on 8 May 2020).
- Zhu, Y.; Xie, J.; Huang, F.; Cao, L. Association between Short-Term Exposure to Air Pollution and COVID-19 Infection: Evidence from China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 727, 138704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cucinotta, D.; Vanelli, M. WHO Declares COVID-19 a Pandemic. Acta Biomed. 2020, 91, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical Features of Patients Infected with 2019 Novel Coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, C.-H.; Chen, B.; Kraemer, M.U.G.; Li, B.; Cai, J.; Xu, B.; Yang, Q.; et al. An Investigation of Transmission Control Measures during the First 50 Days of the COVID-19 Epidemic in China. Science 2020, 368, 638–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Weekly Epidemiological Update—15 December 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-epidemiological-update---15-december-2020 (accessed on 19 December 2020).
- World Health Organization. Updated WHO Advice for International Traffic in Relation to the Outbreak of the Novel Coronavirus 2019-NCoV; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Updated WHO Recommendations for International Traffic in Relation to COVID-19 Outbreak. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/articles-detail/updated-who-recommendations-for-international-traffic-in-relation-to-covid-19-outbreak (accessed on 24 May 2020).
- Muhammad, S.; Long, X.; Salman, M. COVID-19 Pandemic and Environmental Pollution: A Blessing in Disguise? Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission. Covid-19 Guidelines for Border Management Measures to Protect Health and Ensure the Availability of Goods and Essential Services 2020/C 86 I/01. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX:52020XC0316(03) (accessed on 24 May 2020).
- IATA. Interactive Coronavirus (Covid-19) Travel Regulations Map (Powered by Timatic). Available online: https://www.iatatravelcentre.com/international-travel-document-news/1580226297.htm (accessed on 24 May 2020).
- Kumari, P.; Toshniwal, D. Impact of Lockdown on Air Quality over Major Cities across the Globe during COVID-19 Pandemic. Urban Clim. 2020, 34, 100719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Monetary Fund. Global Financial Stability Report: Bridge to Recovery. Available online: https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/GFSR/Issues/2020/10/13/global-financial-stability-report-october-2020#Chapter1 (accessed on 27 January 2021).
- Zambrano-Monserrate, M.A.; Ruano, M.A.; Sanchez-Alcalde, L. Indirect Effects of COVID-19 on the Environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.; Wang, J.; Li, T.; Fang, C. Pollution Characteristics, Transport Pathways, and Potential Source Regions of PM2.5 and PM10 in Changchun City in 2018. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepe, E.; Bajardi, P.; Gauvin, L.; Privitera, F.; Lake, B.; Cattuto, C.; Tizzoni, M. COVID-19 outbreak response, a dataset to assess mobility changes in Italy following national lockdown. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galeazzi, A.; Cinelli, M.; Bonaccorsi, G.; Pierri, F.; Schmidt, A.L.; Scala, A.; Pammolli, F.; Quattrociocchi, W. Human Mobility in Response to COVID-19 in France, Italy and UK. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.06341. [Google Scholar]
- European Environment Agency. Air Quality in Europe—2020 Report; European Environment Agency: Luxembourg, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Lozhkina, O.; Lozhkin, V.; Nevmerzhitsky, N.; Tarkhov, D.; Vasilyev, A. Motor Transport Related Harmful PM2.5 and PM10: From Onroad Measurements to the Modelling of Air Pollution by Neural Network Approach on Street and Urban Level. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series; Institute of Physics Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2016; Volume 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omri, A. CO2 Emissions, Energy Consumption and Economic Growth Nexus in MENA Countries: Evidence from Simultaneous Equations Models. Energy Econ. 2013, 40, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Hao, Y.; Lu, Z.-N.; Wu, H.; Ran, Q. Do Economic Activities Cause Air Pollution? Evidence from China’s Major Cities. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 49, 101593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Special Eurobarometer 468: Attitudes of European Citizens towards the Environment. Available online: http://data.europa.eu/euodp/en/data/dataset/S2156_88_1_468_ENG (accessed on 26 January 2021).
- The World Bank. Earth Day 2020: Could COVID-19 Be the Tipping Point for Transport Emissions? Available online: https://www.worldbank.org/en/news/feature/2020/04/22/earth-day-2020-could-covid-19-be-the-tipping-point-for-transport-emissions (accessed on 29 May 2020).
- Shi, X.; Brasseur, G.P. The Response in Air Quality to the Reduction of Chinese Economic Activities during the COVID-19 Outbreak. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL088070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rugani, B.; Caro, D. Impact of COVID-19 Outbreak Measures of Lockdown on the Italian Carbon Footprint. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 139806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattorini, D.; Regoli, F. Role of the Chronic Air Pollution Levels in the Covid-19 Outbreak Risk in Italy. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 264, 114732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameletti, M. The Effect of Corona Virus Lockdown on Air Pollution: Evidence from the City of Brescia in Lombardia Region (Italy). Atmos. Environ. 2020, 239, 117794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyche, K.P.; Nichols, M.; Parfitt, H.; Beckett, P.; Gregg, D.J.; Smallbone, K.L.; Monks, P.S. Changes in Ambient Air Quality and Atmospheric Composition and Reactivity in the South East of the UK as a Result of the COVID-19 Lockdown. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaymon, I.D.; Zhang, Y.; Hopke, P.K.; Zhang, Y.; Hua, J.; Mei, X. COVID-19 Pandemic in Wuhan: Ambient Air Quality and the Relationships between Criteria Air Pollutants and Meteorological Variables before, during, and after Lockdown. Atmos. Res. 2021, 250, 105362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menut, L.; Bessagnet, B.; Siour, G.; Mailler, S.; Pennel, R.; Cholakian, A. Impact of Lockdown Measures to Combat Covid-19 on Air Quality over Western Europe. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 140426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filonchyk, M.; Hurynovich, V.; Yan, H. Impact of Covid-19 Lockdown on Air Quality in the Poland, Eastern Europe. Environ. Res. 2020, 110454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, T.; Xie, M.; Li, S.; Zhuang, B.; Fu, Q.; Zhao, M.; Wu, H.; Liu, J.; Saikawa, E.; et al. Drivers for the Poor Air Quality Conditions in North China Plain during the COVID-19 Outbreak. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 246, 118103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Xu, X.; Wang, S.; He, S.; He, P. Heterogeneous Effects of COVID-19 Lockdown Measures on Air Quality in Northern China. Appl. Energy 2021, 282, 116179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.; An, C.; Chen, Z.; Tian, Z. Assessing the Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on Urban Transportation and Air Quality in Canada. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 765, 144270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gama, C.; Relvas, H.; Lopes, M.; Monteiro, A. The Impact of COVID-19 on Air Quality Levels in Portugal: A Way to Assess Traffic Contribution. Environ. Res. 2021, 193, 110515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldasano, J.M. COVID-19 Lockdown Effects on Air Quality by NO2 in the Cities of Barcelona and Madrid (Spain). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 140353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Hao, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, F. Have Traffic Restrictions Improved Air Quality? A Shock from COVID-19. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 279, 123622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coccia, M. How Do Low Wind Speeds and High Levels of Air Pollution Support the Spread of COVID-19? Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 12, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coccia, M. Effects of the Spread of COVID-19 on Public Health of Polluted Cities: Results of the First Wave for Explaining the Dejà vu in the Second Wave of COVID-19 Pandemic and Epidemics of Future Vital Agents. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coccia, M. How (Un)Sustainable Environments Are Related to the Diffusion of COVID-19: The Relation between Coronavirus Disease 2019, Air Pollution, Wind Resource and Energy. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coccia, M. An Index to Quantify Environmental Risk of Exposure to Future Epidemics of the COVID-19 and Similar Viral Agents: Theory and Practice. Environ. Res. 2020, 191, 110155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putaud, J.-P.; Pozzoli, L.; Pisoni, E.; Dos Santos, S.M.; Lagler, F.; Lanzani, G.; Dal Santo, U.; Colette, A. Impacts of the COVID-19 Lockdown on Air Pollution at Regional and Urban Background Sites in Northern Italy. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2020, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Environment Agency. The Challenge of Reducing Industrial Pollution. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/signals/signals-2020/articles/the-challenge-of-reducing-industrial-pollution (accessed on 1 February 2021).
- Italy Industrial Production Index. Available online: https://www.investing.com/economic-calendar/italian-industrial-production-951 (accessed on 30 December 2020).
- France—Industrial Production Index. Available online: https://countryeconomy.com/business/industrial-production/france (accessed on 30 December 2020).
- Sweden—Industrial Production Index. Available online: https://countryeconomy.com/business/industrial-production/sweden (accessed on 30 December 2020).
- Office for National Statistics. Available online: https://www.ons.gov.uk/economy/economicoutputandproductivity/output/bulletins/indexofproduction/previousReleases?:uri=economy/economicoutputandproductivity/output/bulletins/indexofproduction/previousReleases&:uri=economy/economicoutputandproductivi-ty/output/bulletins/indexofproduction/previousReleases&:uri=economy/economicoutputandproductivity/output/bulletins/indexofproduc-tion/previousReleases&:uri=economy/economicoutputandproductivity/output/bulletins/indexofproduction/previousReleases&:uri=economy/economicoutputandproductivity/output/bulletins/indexofproduction/previousReleases&page=1 (accessed on 30 December 2020).
- Instituto National de Estadística. Available online: https://www.ine.es/en/prensa/ipi_prensa_en.htm (accessed on 30 December 2020).
- Coccia, M. The Effects of Atmospheric Stability with Low Wind Speed and of Air Pollution on the Accelerated Transmission Dynamics of COVID-19. Int. J. Environ. Stud. 2021, 78, 1802937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coker, E.S.; Cavalli, L.; Fabrizi, E.; Guastella, G.; Lippo, E.; Parisi, M.L.; Pontarollo, N.; Rizzati, M.; Varacca, A.; Vergalli, S. The Effects of Air Pollution on COVID-19 Related Mortality in Northern Italy. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2020, 76, 611–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Environment Agency. Air Quality and COVID-19. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/themes/air/air-quality-and-covid19 (accessed on 18 June 2020).
- Gilbert, R. Statistical Methods for Environmental Pollution Monitoring; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- COVID-19 Health System Response Monitor. Available online: https://www.covid19healthsystem.org/countries/unitedkingdom/countrypage.aspx (accessed on 23 December 2020).
- Jephcote, C.; Hansell, A.L.; Adams, K.; Gulliver, J. Changes in Air Quality during COVID-19 ‘Lockdown’ in the United Kingdom. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 272, 116011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Statistica. Coronavirus (COVID-19) Outbreak in Spain—Statistics & Facts. Available online: https://www.statista.com/topics/6118/coronavirus-covid-19-outbreak-in-spain/ (accessed on 7 February 2021).
- Our World in Data. Data on COVID-19 (Coronavirus) by Our World in Data. 2020. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/coronavirus-data (accessed on 20 December 2020).
- OECD. Data on Country Response Measures to COVID-19. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/download-data-response-measures-covid-19 (accessed on 19 December 2020).
- Lovarelli, D.; Conti, C.; Finzi, A.; Bacenetti, J.; Guarino, M. Describing the Trend of Ammonia, Particulate Matter and Nitrogen Oxides: The Role of Livestock Activities in Northern Italy during Covid-19 Quarantine. Environ. Res. 2020, 191, 110048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitzer, D.; Martinier, S.; Shannon, D. France: The French Government Response to the COVID-19: Highlights of Measures Taken. Available online: https://www.mondaq.com/france/operational-impacts-and-strategy/926220/the-french-government-response-to-the-covid-19-highlights-of-measures-taken (accessed on 16 June 2020).
- Chadwick, L. France Approves Release of Controversial COVID-19 Tracking App. Available online: https://www.euronews.com/2020/05/27/france-s-controversial-covid-19-tracking-phone-app-approved-by-lower-house-of-parliament (accessed on 16 June 2020).
- Deloite. EU Countries Measures on COVID-19 under Magnifying Glass. Available online: https://www2.deloitte.com/ro/en/pages/business-continuity/articles/EU-countries-measures-on-COVID-19-under-magnifying-glass.html (accessed on 13 June 2020).
- European Commission. Travel Restrictions. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/info/live-work-travel-eu/health/coronavirus-response/travel-and-transportation-during-coronavirus-pandemic/travel-and-eu-during-pandemic_en (accessed on 13 June 2020).
- European Space Agency. Air Pollution Remains Low as Europeans Stay at Home. Available online: http://www.esa.int/Applications/Observing_the_Earth/Copernicus/Sentinel-5P/Air_pollution_remains_low_as_Europeans_stay_at_home (accessed on 13 June 2020).
- Cantini, F.; Niccoli, L.; Matarrese, D.; Nicastri, E.; Stobbione, P.; Goletti, D. Baricitinib Therapy in COVID-19: A Pilot Study on Safety and Clinical Impact. J. Infect. 2020, 81, 318–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatti, R.C.; Velichevskaya, A.; Tateo, A.; Amoroso, N.; Monaco, A. Machine Learning Reveals that Prolonged Exposure to Air Pollution Is Associated with SARS-CoV-2 Mortality and Infectivity in Italy. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domingo, J.L.; Marquès, M.; Rovira, J. Influence of Airborne Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 on COVID-19 Pandemic. A Review. Environ. Res. 2020, 188, 109861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinoudis, G.; Padellini, T.; Bennett, J.; Davies, B.; Ezzati, M.; Blangiardo, M. Long-Term Exposure to Air-Pollution and COVID-19 Mortality in England: A Hierarchical Spatial Analysis. Environ. Int. 2021, 146, 106316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Copernicus Sentinel-5P Tropospheric Nitrogen Dioxide. Available online: https://maps.s5p-pal.com/no2/ (accessed on 13 June 2020).
- Évaluation de L’impact du Deconfinement sur la Qualité de L’air en Île-de-France. Available online: http://www.airparif.asso.fr/actualite/detail/id/286 (accessed on 23 December 2020).
- Wijfferlaars. COVID-19 Has a Devastating Impact on Italy’s Economy. Available online: https://economics.rabobank.com/publications/2020/july/covid-19-devastating-impact-on-italy-economy/ (accessed on 20 December 2020).
- Hu, M.; Chen, Z.; Cui, H.; Wang, T.; Zhang, C.; Yun, K. Air Pollution and Critical Air Pollutant Assessment during and after COVID-19 Lockdowns: Evidence from Pandemic Hotspots in China, the Republic of Korea, Japan, and India. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 12, 316–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Gao, W.; Song, T.; Sun, Y.; Li, L.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; et al. Exploring the Regional Pollution Characteristics and Meteorological Formation Mechanism of PM2.5 in North China during 2013–2017. Environ. Int. 2020, 134, 105283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Naeher, L.P. A Review of Traffic-Related Air Pollution Exposure Assessment Studies in the Developing World. Environ. Int. 2006, 32, 106–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vultaggio, M.; Varrica, D.; Alaimo, M.G. Impact on Air Quality of the Covid-19 Lockdown in the Urban Area of Palermo (Italy). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collivignarelli, M.C.; Abbà, A.; Bertanza, G.; Pedrazzani, R.; Ricciardi, P.; Carnevale Miino, M. Lockdown for CoViD-2019 in Milan: What Are the Effects on Air Quality? Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 732, 139280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
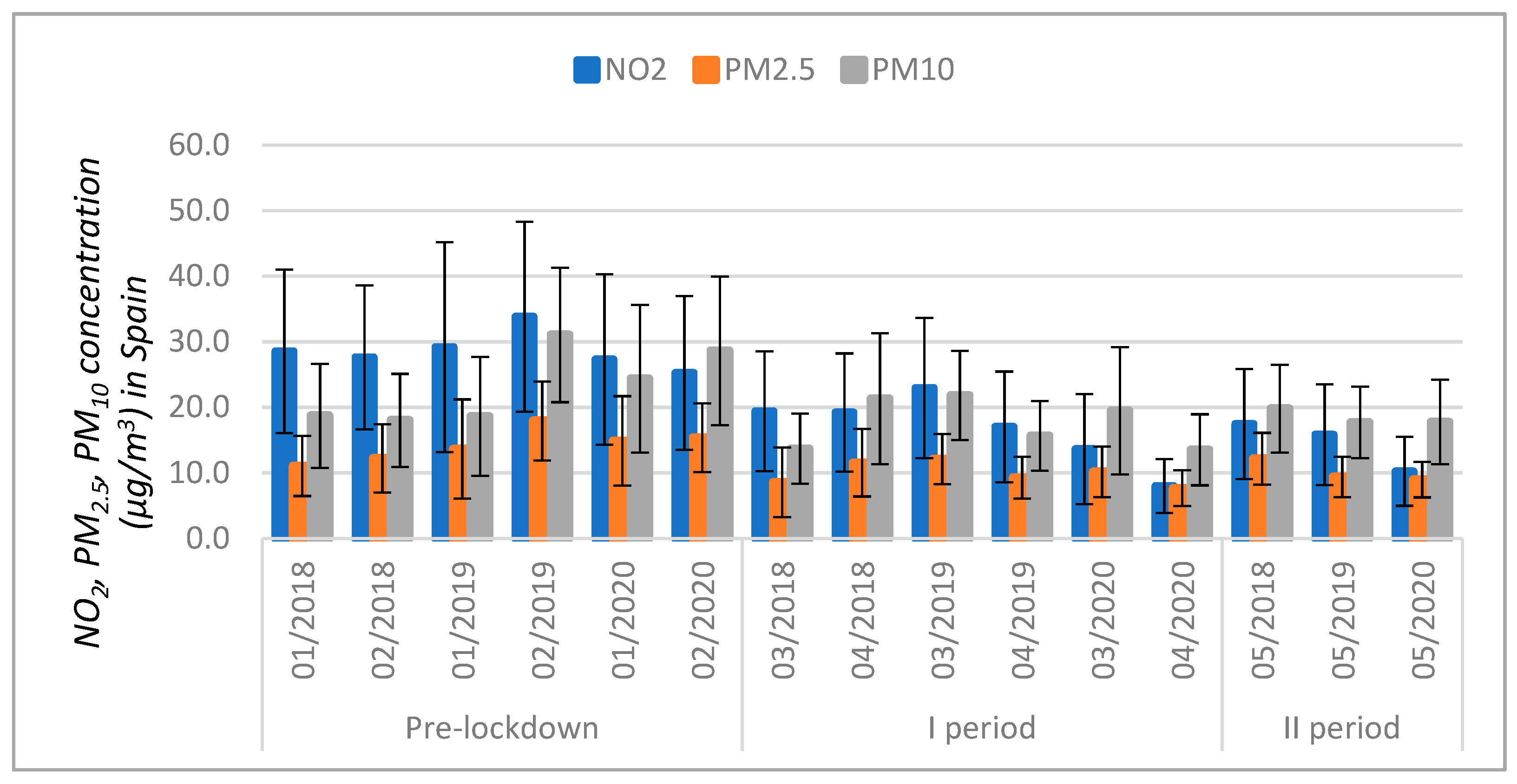
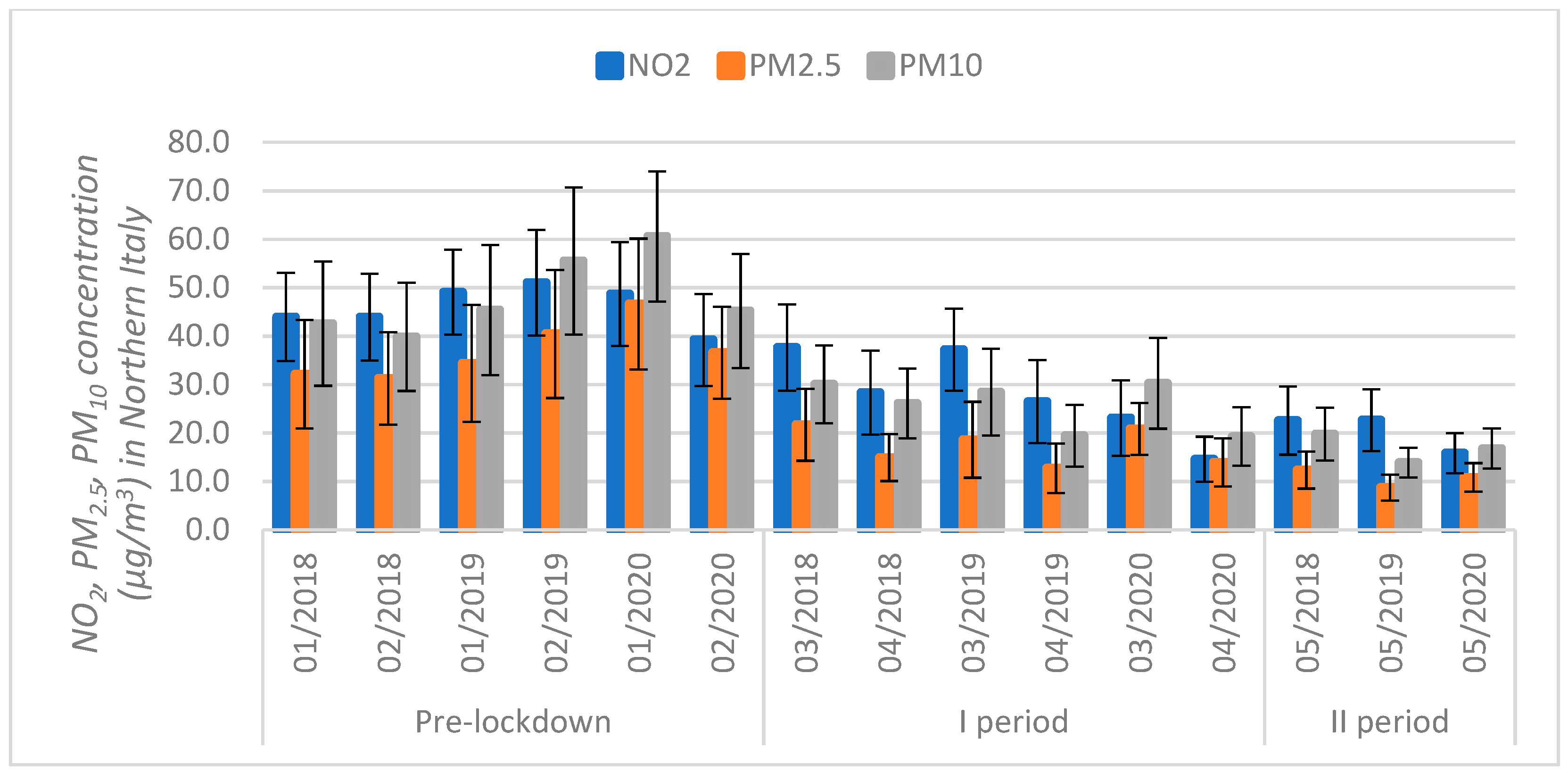
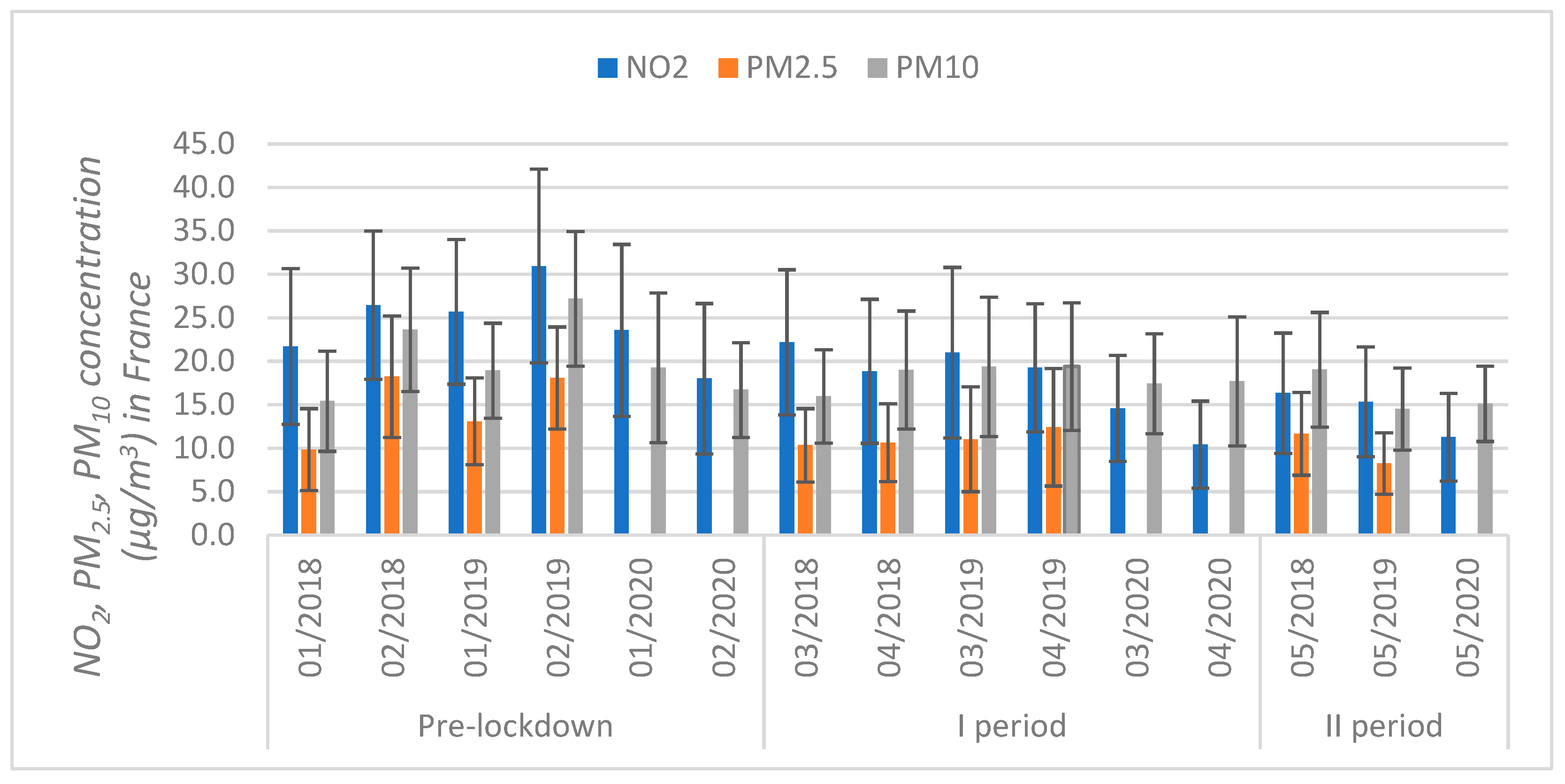
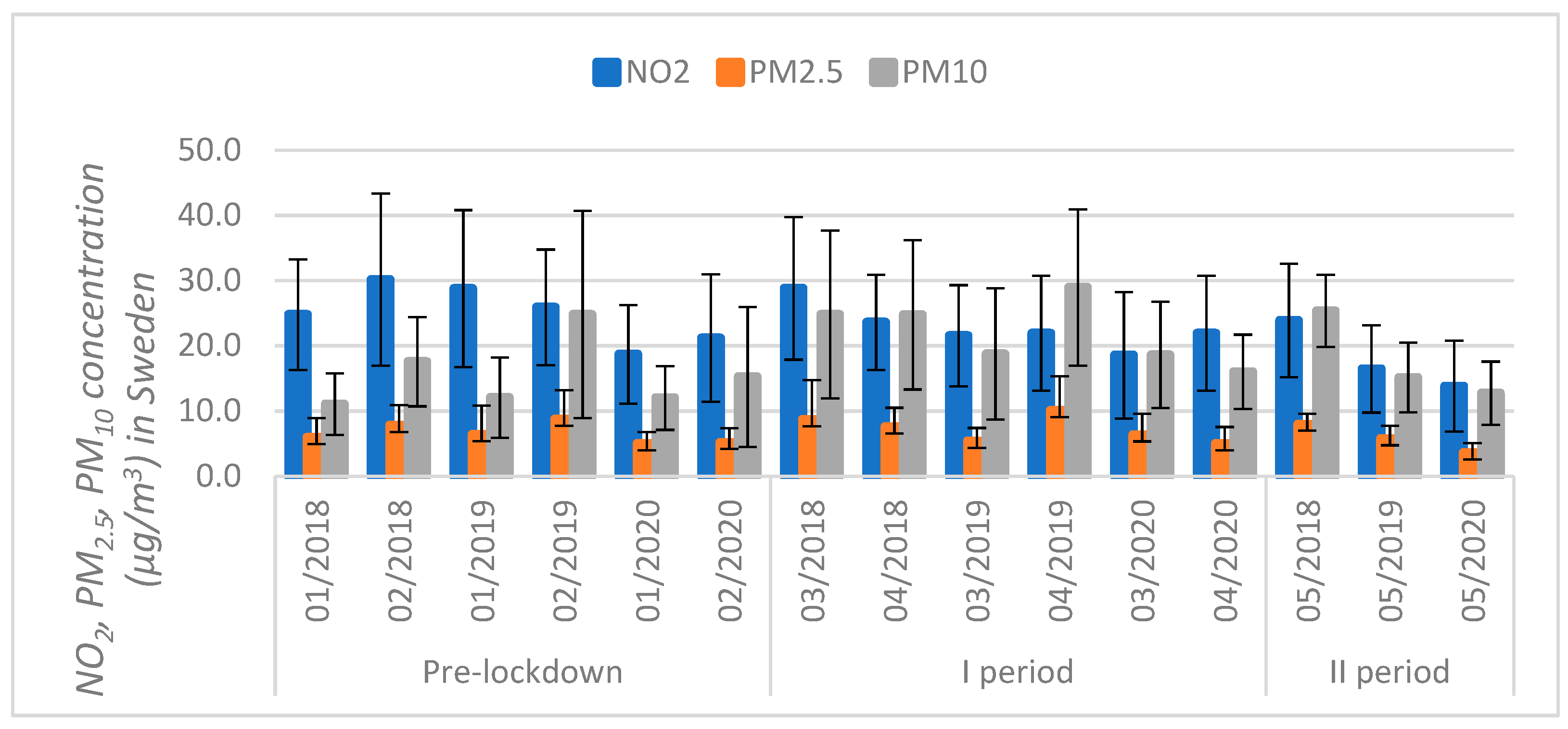
| Countries | NO2 | PM2.5 | PM10 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pearson Correlation Coefficient (p) | The United Kingdom | 0.038 | 0.303 | 0.075 |
| Spain | 0.025 | 0.017 | 0.014 | |
| Northern Italy | 0.046 | 0.077 | 0.085 | |
| France | 0.045 | - | 0.643 | |
| Sweden | 0.646 | 0.191 | 0.726 |
| Countries | Pollutants | Kendall’s Tau | p-Value | S-Value | Interpretation | Sen’s Slope |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The United Kingdom | NO2 | −0.657 | 0.001 | −69.000 | Accept H1 | −1.167 |
| PM2.5 | −0.287 | 0.137 | −30.000 | Accept H0 | −0.200 | |
| PM10 | −0.219 | 0.255 | −23.000 | Accept H0 | −0.282 | |
| Spain | NO2 | −0.486 | 0.012 | −51.000 | Accept H1 | −1.036 |
| PM2.5 | −0.096 | 0.620 | −10.000 | Accept H0 | −0.073 | |
| PM10 | −0.019 | 0.921 | −2.000 | Accept H0 | −0.018 | |
| Northern Italy | NO2 | −0.394 | 0.042 | −41.000 | Accept H1 | −1.783 |
| PM2.5 | −0.200 | 0.299 | −21.000 | Accept H0 | −0.783 | |
| PM10 | −0.257 | 0.181 | −27.000 | Accept H0 | −1.180 | |
| France | NO2 | −0.505 | 0.009 | −53.000 | Accept H1 | −0.840 |
| PM2.5 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| PM10 | −0.163 | 0.399 | −17.000 | Accept H0 | −0.130 | |
| Sweden | NO2 | −0.580 | 0.003 | −60.000 | Accept H1 | −0.733 |
| PM2.5 | −0.452 | 0.020 | −47.000 | Accept H1 | −0.257 | |
| PM10 | −0.107 | 0.584 | −11.000 | Accept H0 | −0.250 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Skirienė, A.F.; Stasiškienė, Ž. COVID-19 and Air Pollution: Measuring Pandemic Impact to Air Quality in Five European Countries. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 290. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12030290
Skirienė AF, Stasiškienė Ž. COVID-19 and Air Pollution: Measuring Pandemic Impact to Air Quality in Five European Countries. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(3):290. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12030290
Chicago/Turabian StyleSkirienė, Akvilė Feiferytė, and Žaneta Stasiškienė. 2021. "COVID-19 and Air Pollution: Measuring Pandemic Impact to Air Quality in Five European Countries" Atmosphere 12, no. 3: 290. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12030290
APA StyleSkirienė, A. F., & Stasiškienė, Ž. (2021). COVID-19 and Air Pollution: Measuring Pandemic Impact to Air Quality in Five European Countries. Atmosphere, 12(3), 290. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12030290






