Model Uncertainty in the Projected Indian Summer Monsoon Precipitation Change under Low-Emission Scenarios
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Datasets and Models
2.1. Model Simulations and Outputs
2.2. Method
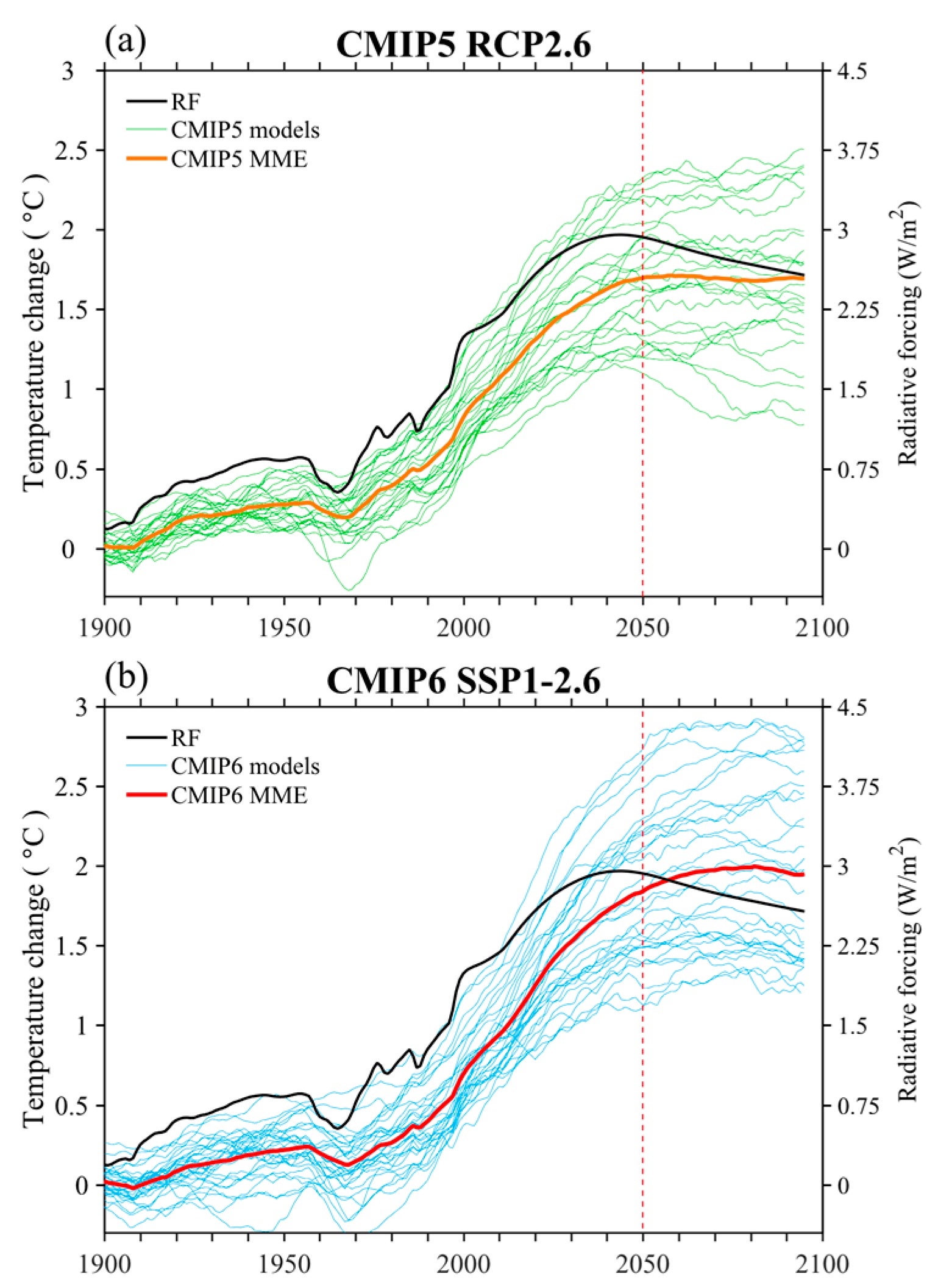
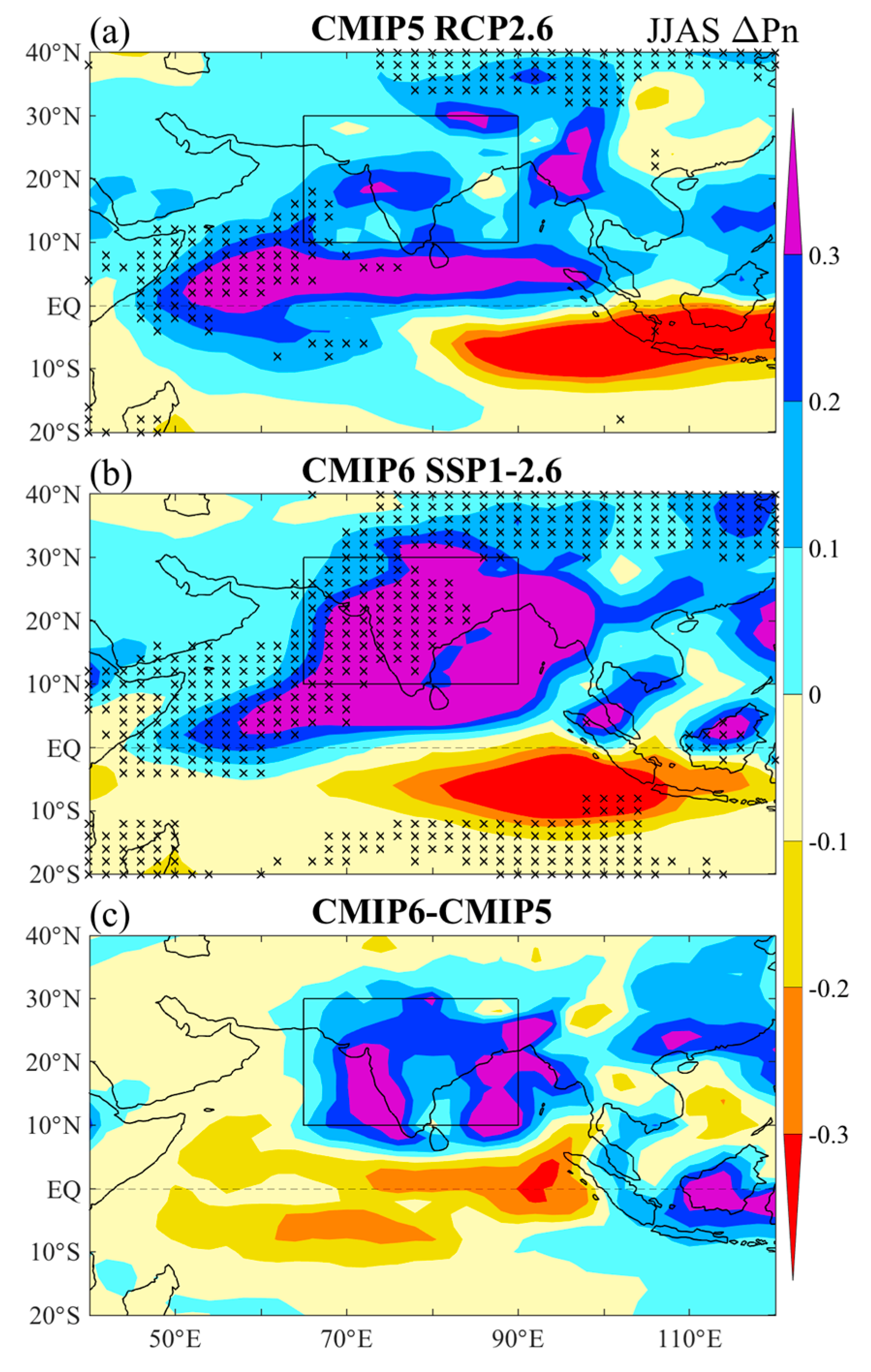
3. ISM Precipitation Change
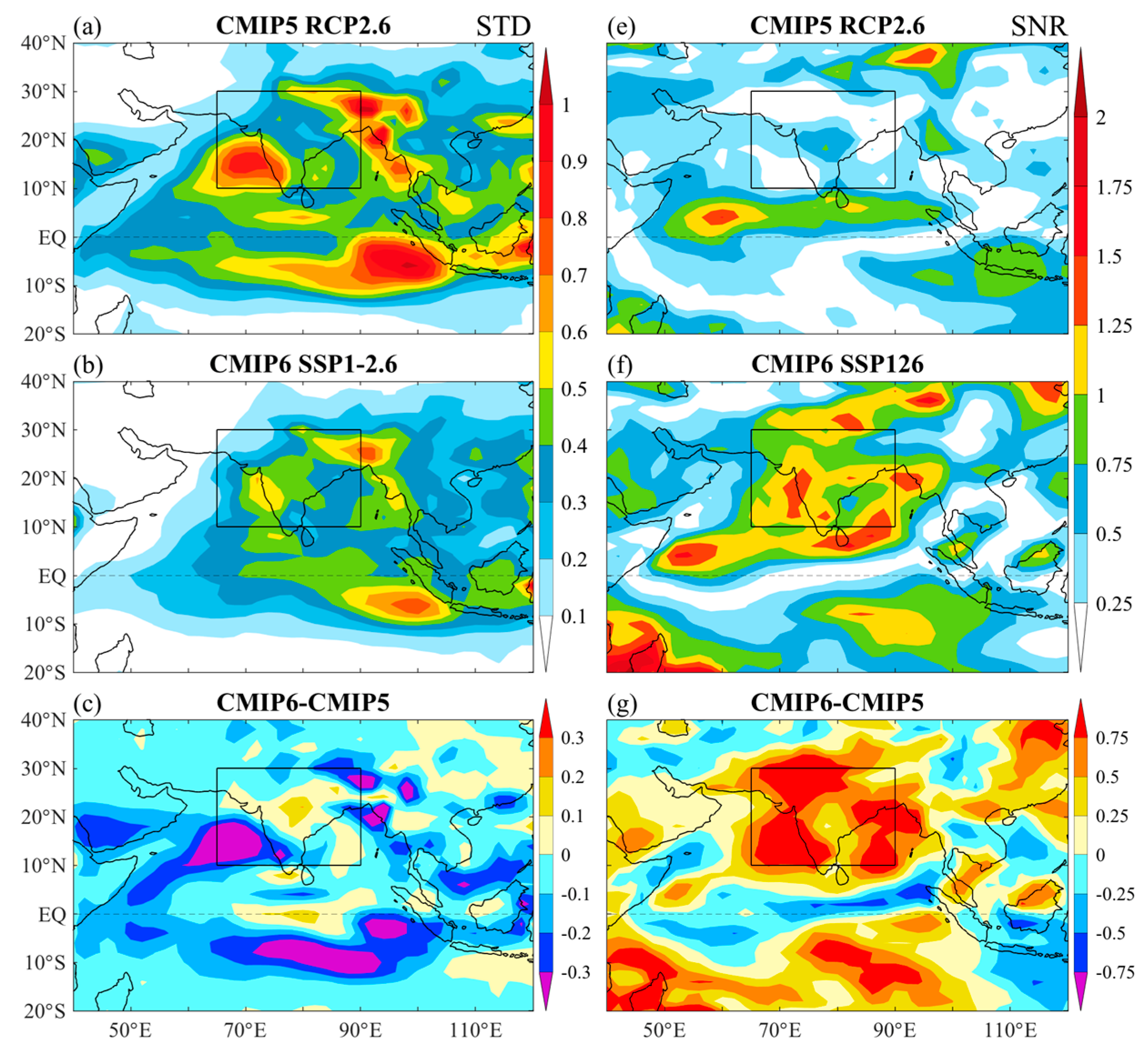
4. Model Uncertainty in ISM Precipitation Change
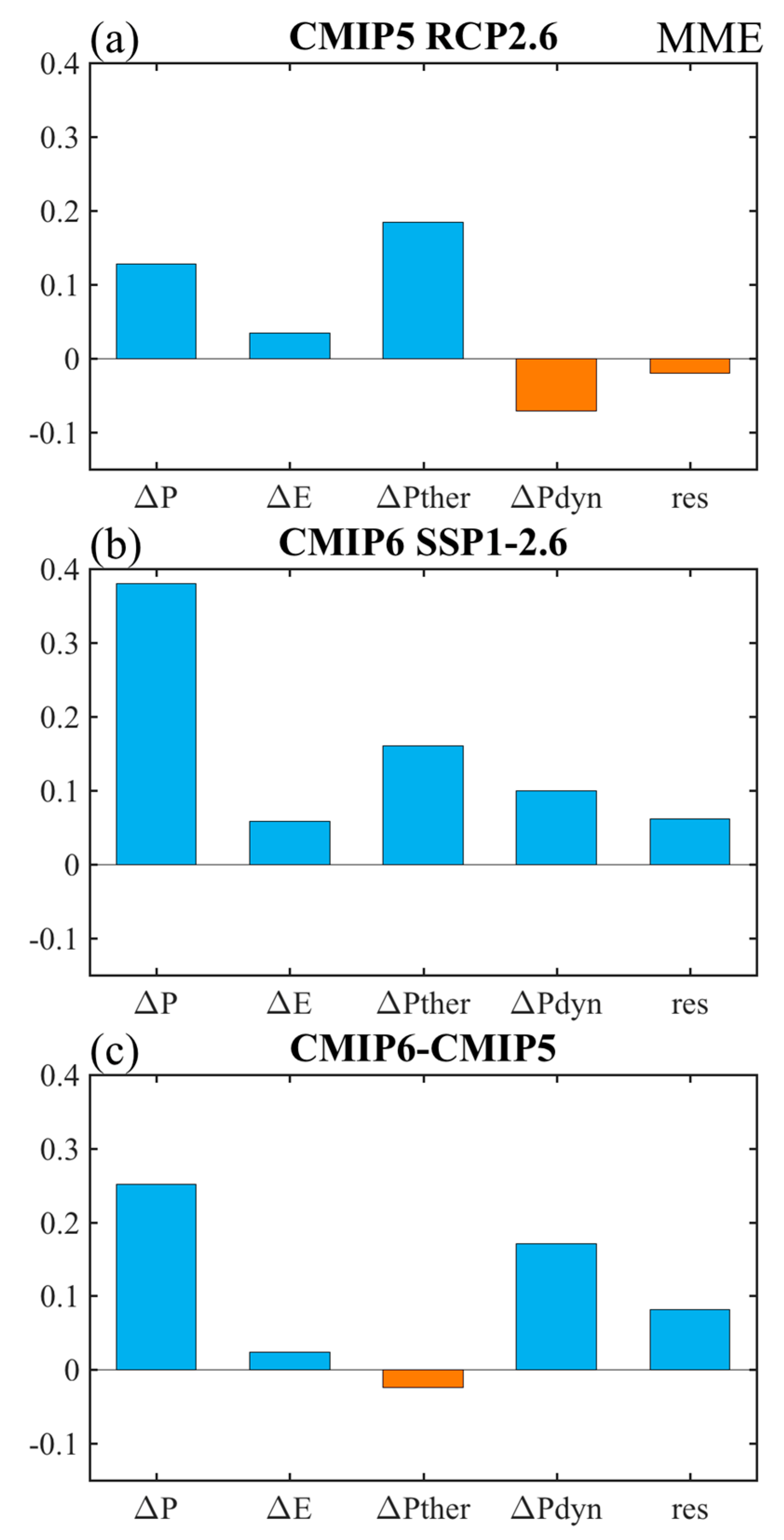
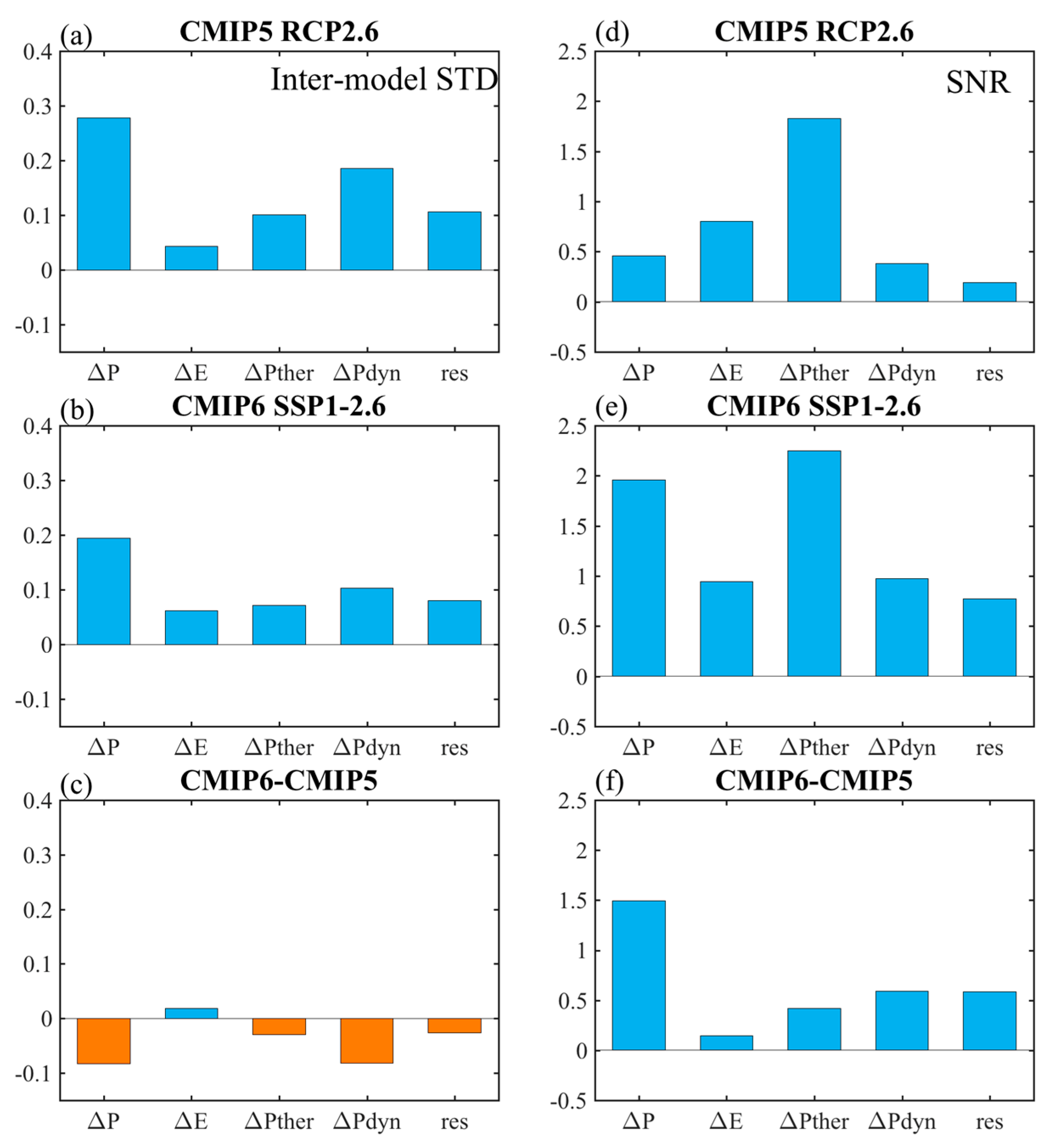
4.1. Sources of the Model Uncertainty
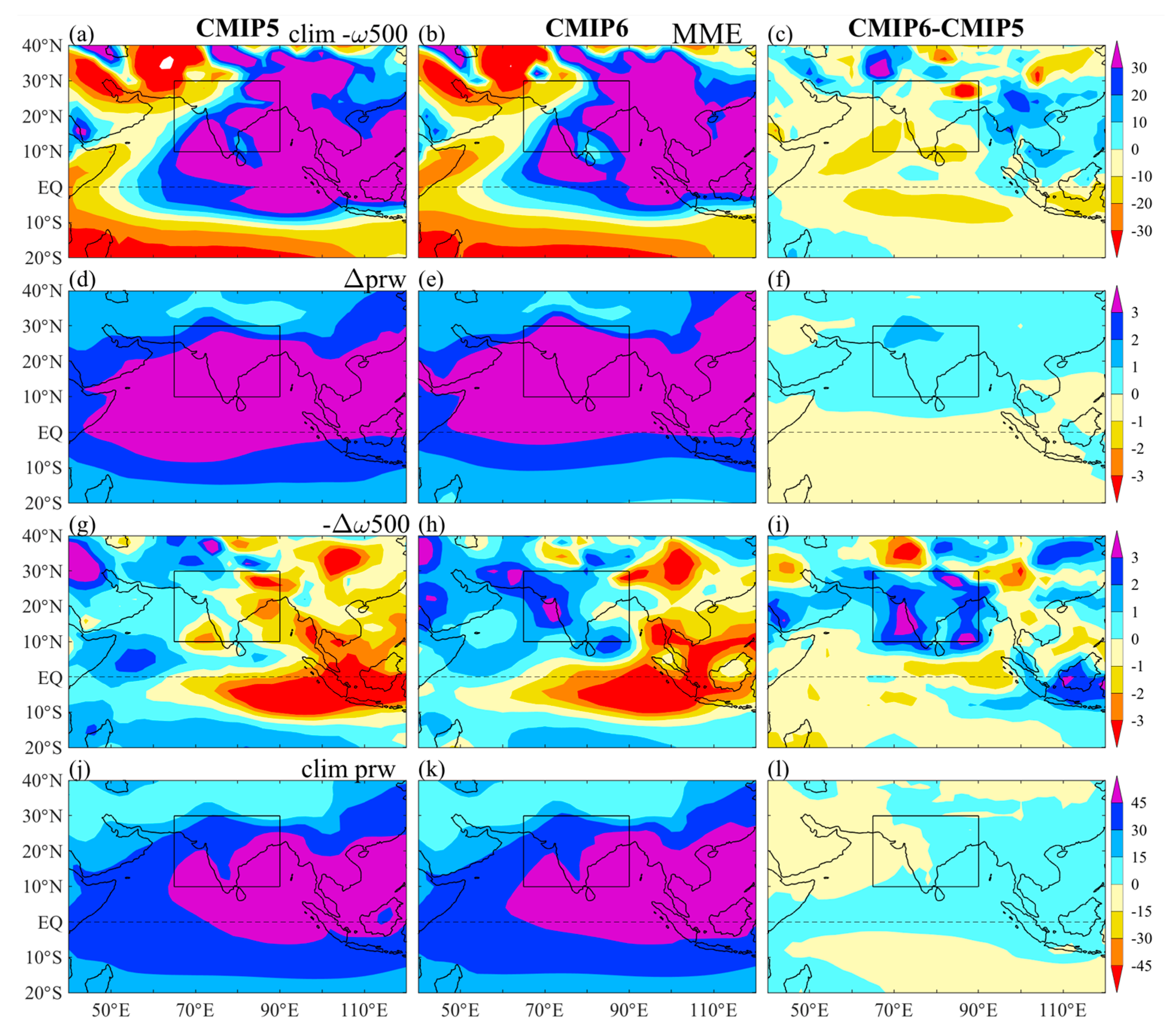
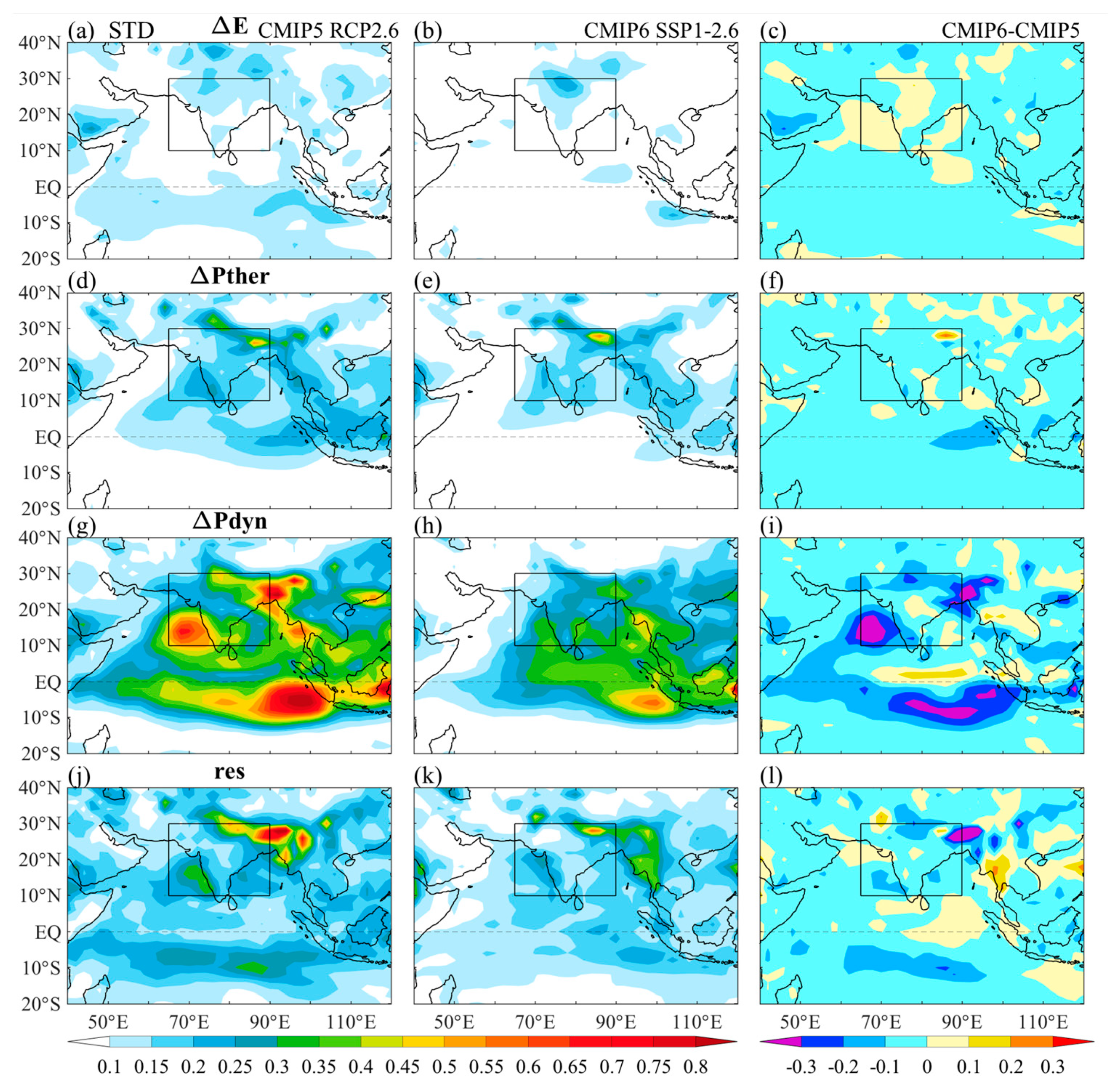
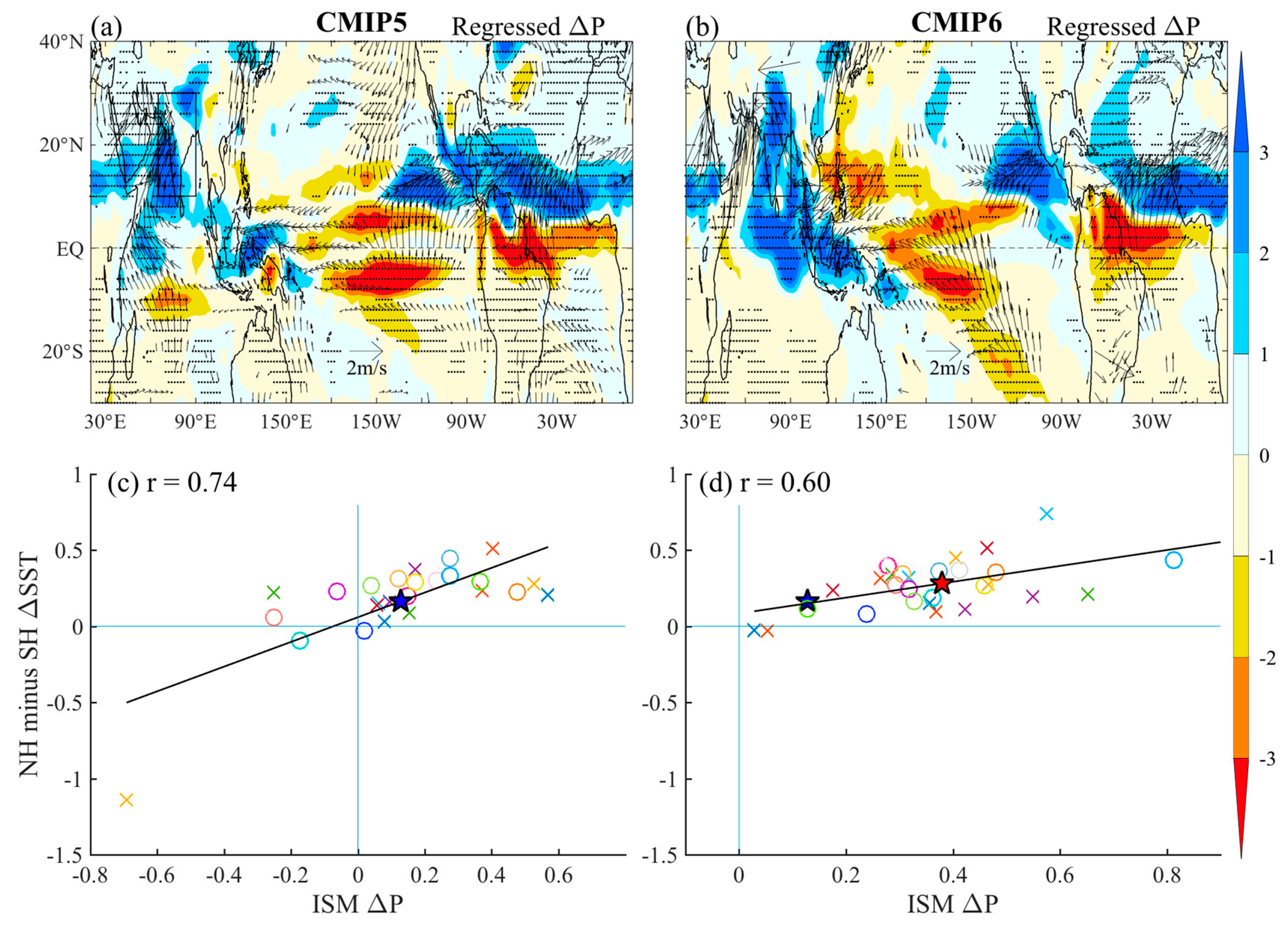
4.2. Physical Processes for the Model Uncertainty
5. Summary and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Turner, A.G.; Slingo, J.M. Uncertainties in future projections of extreme precipitation. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2009, 10, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.G.; Annamalai, H. Climate change and the South Asian summer monsoon. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis; UK Cambridge Univ. Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhou, T. Distinct effects of global mean warming and regional sea surface warming pattern on projected uncertainty in the South Asian summer monsoon. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 9433–9439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, S.-M.; Xie, S.-P. Intermodel variations in projected precipitation change over the North Atlantic: Sea surface temperature effect. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 4158–4165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.-P.; Deser, C.; Vecchi, G.A.; Collins, M.; Delworth, T.L.; Hall, A.; Hawkins, E.; Johnson, N.C.; Cassou, C.; Giannini, A.; et al. Towards predictive understanding of regional climate change. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2015, 5, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, S.-M.; Xie, S.-P.; Liu, W. Uncertainty in tropical rainfall projections: Atmospheric circulation effect and the Ocean Coupling. J. Clim. 2016, 29, 2671–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Huang, G.; Huang, P. Changes in the East Asian summer monsoon rainfall under global warming: Moisture budget decompositions and the sources of uncertainty. Clim. Dyn. 2018, 51, 1363–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabeerali, C.T.; Rao, S.A.; Dhakate, A.R.; Salunke, K.; Goswami, B.N. Why ensemble mean projection of south Asian monsoon rainfall by CMIP5 models is not reliable? Clim. Dyn. 2015, 45, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgi, F.; Francisco, R. Evaluating uncertainties in the prediction of regional climate change. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2000, 27, 1295–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, E.; Sutton, R. The potential to narrow uncertainty in regional climate predictions. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2009, 90, 1095–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, E.; Sutton, R. The potential to narrow uncertainty in projections of regional precipitation change. Clim. Dyn. 2011, 37, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowell, D.P. Sources of uncertainty in future changes in local precipitation. Clim. Dyn. 2012, 39, 1929–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Huang, G.; Huang, P. A bias-corrected projection for the changes in East Asian summer monsoon rainfall under global warming. Clim. Dyn. 2020, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deser, C.; Phillips, A.; Bourdette, V.; Teng, H. Uncertainty in climate change projections: The role of internal variability. Clim. Dyn. 2012, 38, 527–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusain, A.; Ghosh, S.; Karmakar, S. Added value of CMIP6 over CMIP5 models in simulating Indian summer monsoon rainfall. Atmos. Res. 2020, 232, 104680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, S.-M.; Li, G.; Hu, K.; Ying, J. Origins of the IOD-like Biases in CMIP Multimodel Ensembles: The Atmospheric Component and Ocean–Atmosphere Coupling. J. Clim. 2020, 33, 10437–10453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kripalani, R.H.; Oh, J.H.; Kulkarni, A.; Sabade, S.S.; Chaudhari, H.S. South Asian summer monsoon precipitation variability: Coupled climate model simulations and projections under IPCC AR4. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Xie, S.-P.; Du, Y. Monsoon-induced biases of climate models over the tropical Indian Ocean. J. Clim. 2015, 28, 3058–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Xie, S.-P.; Du, Y. Climate model errors over the South Indian Ocean thermocline dome and their effect on the basin mode of interannual variability. J. Clim. 2015, 28, 3093–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Xie, S.-P.; Du, Y. A robust but spurious pattern of climate change in model projections over the tropical Indian Ocean. J. Clim. 2016, 29, 5589–5608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, G.; Yang, S. Origin of Indian summer monsoon rainfall biases in CMIP5 multimodel ensemble. Clim. Dyn. 2018, 51, 755–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Qian, Y.; Song, F.; Leung, L.R.; Wu, P.; Guo, Z.; Lu, Y.; Huang, A. Better monsoon precipitation in coupled climate models due to bias compensation. NPJ Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2019, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annamalai, H.; Hamilton, K.; Sperber, K.R. The South Asian summer monsoon and its relationship with ENSO in the IPCC AR4 simulations. J. Clim. 2007, 20, 1071–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Qian, Y.; Wu, T.; Huang, A.; Fang, Y. Parametric sensitivity analysis for the Asian summer monsoon precipitation simulation in the Beijing Climate Center AGCM, version 2.1. J. Clim. 2015, 28, 5622–5644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seager, R.; Naik, N.; Vecchi, G.A. Thermodynamic and dynamic mechanisms for large-scale changes in the hydrological cycle in response to global warming. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 4651–4668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Held, I.M.; Soden, B.J. Robust responses of the hydrological cycle to global warming. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 5686–5699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadwick, R.; Boutle, I.; Martin, G. Spatial patterns of precipitation change in CMIP5: Why the rich do not get richer in the tropics. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 3803–3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Xie, S.-P.; Hu, K.; Huang, G.; Huang, R. Patterns of the seasonal response of tropical rainfall to global warming. Nat. Geosci. 2013, 6, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, W. Simulated changes of the Indian summer monsoon under enhanced greenhouse gas conditions in a global time-slice experiment. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherchi, A.; Alessandri, A.; Masina, S.; Navarra, A. Effects of increased CO2 levels on monsoons. Clim. Dyn. 2011, 37, 83–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, H.; Kitoh, A. Thermodynamic and dynamic effects on regional monsoon rainfall changes in a warmer climate. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 1704–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, H.; Iwai, A.; Kuwako, K.; Hori, M.E. Impact of anthropogenic forcing on the Asian summer monsoon as simulated by eight GCMs. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L06703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, W. The sensitivity of the Indian summer monsoon to a global warming of 2°C with respect to pre-industrial times. Clim. Dyn. 2011, 37, 1843–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Xie, S.-P.; He, C.; Chen, Z. Western Pacific emergent constraint lowers projected increase in Indian summer monsoon rainfall. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2017, 7, 708–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Special Report on Global Warming of 1.5°C; UK Cambridge Univ. Press: Cambridge, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palter, J.B.; Frölicher, T.L.; Paynter, D.; John, J.G. Climate, ocean circulation, and sea level changes under stabilization and overshoot pathways to 1.5K warming. Earth Syst. Dyn. 2018, 9, 817–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Huang, G. Different multi-year mean temperature in mid-summer of South China under different 1.5 °C warming scenarios. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Zhou, T.; Zou, L.; Zhang, L.; Chen, X. Reduced exposure to extreme precipitation from 0.5 °C less warming in global land monsoon regions. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Qu, X.; Huang, G.; Gong, Y. Projections of East Asian summer monsoon under 1.5 °C and 2 °C warming goals. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2019, 137, 2187–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, S.-M.; Xie, S.-P.; Du, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zheng, X.-T.; Huang, G.; Hu, K.M.; Ying, J. Effects of Ocean Slow Response under Low Warming Targets. J. Clim. 2020, 33, 477–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Vuuren, D.P.; Edmonds, J.; Kainuma, M.; Riahi, K.; Thomson, A.; Hibbard, K.; Hurtt, G.C.; Kram, T.; Krey, V.; Jean-Francois Lamarque, J.-F.; et al. The representative concentration pathways: An overview. Clim. Chang. 2011, 109, 5–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, B.M.; O’Neill, B.C.; Tebaldi, C. What would it take to achieve the Paris temperature targets? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 7133–7142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Ramanathan, V. Well below 2 °C: Mitigation strategies for avoiding dangerous to catastrophic climate changes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 10315–10323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, K.E.; Stouffer, R.J.; Meehl, G.A. An overview of CMIP5 and the experiment design. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2012, 35, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyring, V.; Bony, S.; Meehl, G.A.; Senior, C.A.; Stevens, B.; Stouffer, R.J.; Taylor, K.E. Overview of the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 6 (CMIP6) experimental design and organization. Geosci. Model Dev. 2016, 9, 1937–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelinka, M.D.; Myers, T.A.; McCoy, D.T.; Po-Chedley, S.; Caldwell, P.M.; Ceppi, P.; Stephen, A.K.; Karl, E.T. Causes of higher climate sensitivity in CMIP6 models. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2019GL085782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Xie, S.-P.; Kosaka, Y. Mechanisms for tropical tropospheric circulation change in response to global warming. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 2979–2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.-P.; Deser, C.; Vecchi, G.A.; Ma, J.; Teng, H.; Wittenberg, A.T. Global warming pattern formation: Sea surface temperature and rainfall. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 966–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzenberger, A.; Schewe, J.; Pongratz, J.; Levermann, A. Robust increase of Indian monsoon rainfall and its variability under future warming in CMIP-6 models. Earth Syst. Dyn. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, V.; Chung, C.; Kim, D.; Bettge, T.; Buja, L.; Kiehl, J.T.; Washington, W.M.; Fu, Q.; Sikka, D.R.; Wild, M. Atmospheric brown clouds: Impacts on South Asian climate and hydrologic cycle. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 5326–5333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.-M.; Kim, K.-M. Observational relationships between aerosol and Asian monsoon rainfall, and circulation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L21810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.; Ramanathan, V. Relationship between trends in land precipitation and tropical SST gradient. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roxy, M.K.; Ritika, K.; Terray, P.; Murtugudde, R.; Ashok, K.; Goswami, B.N. Drying of Indian subcontinent by rapid Indian Ocean warming and a weakening land-sea thermal gradient. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; He, B.; Bao, Q.; Duan, A.; Jin, F.F. Thermal controls on the Asian summer monsoon. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, K.-M.; Kim, K.-M.; Leuna, R. Changing circulation structure and precipitation characteristics in Asian monsoon regions: Greenhouse warming vs. aerosol effects. Geosci. Lett. 2017, 4, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| CMIP5 (25) | CMIP6 (30) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | bcc-csm1-1-m | 16 | HadGEM2-ES | 1 | ACCESS-CM2 | 16 | GISS-E2-1-G |
| 2 | bcc-csm1-1 | 17 | IPSL-CM5A-LR | 2 | ACCESS-ESM1-5 | 17 | HadGEM3-GC31-LL |
| 3 | BNU-ESM | 18 | MIROC-ESM | 3 | BCC-CSM2-MR | 18 | INM-CM4-8 |
| 4 | CanESM2 | 19 | MIROC-ESM-CHEM | 4 | CanESM5 | 19 | INM-CM5-0 |
| 5 | CCSM4 | 20 | MIROC5 | 5 | CanESM5-CanOE | 20 | IPSL-CM6A-LR |
| 6 | CESM1-CAM5 | 21 | MPI-ESM-LR | 6 | CAMS-CSM1-0 | 21 | KACE-1-0-G |
| 7 | CNRM-CM5 | 22 | MPI-ESM-MR | 7 | CESM2 | 22 | MIROC-ES2L |
| 8 | CSIRO-Mk3-6-0 | 23 | MRI-CGCM3 | 8 | CESM2-WACCM | 23 | MIROC6 |
| 9 | FGOALS-g2 | 24 | NorESM1-M | 9 | CNRM-CM6-1 | 24 | MPI-ESM1-2-LR |
| 10 | FIO-ESM | 25 | NorESM1-ME | 10 | CNRM-CM6-1-HR | 25 | MPI-ESM1-2-HR |
| 11 | GFDL-CM3 | 11 | CNRM-ESM2-1 | 26 | MRI-ESM2-0 | ||
| 12 | GFDL-ESM2M | 12 | EC-Earth3 | 27 | NESM3 | ||
| 13 | GFDL-ESM2G | 13 | EC-Earth3-Veg | 28 | NorESM2-MM | ||
| 14 | GISS-E2-H | 14 | FGOALS-g3 | 29 | NorESM2-LM | ||
| 15 | GISS-E2-R | 15 | GFDL-ESM4 | 30 | UKESM1-0-LL | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Long, S.-M.; Li, G. Model Uncertainty in the Projected Indian Summer Monsoon Precipitation Change under Low-Emission Scenarios. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12020248
Long S-M, Li G. Model Uncertainty in the Projected Indian Summer Monsoon Precipitation Change under Low-Emission Scenarios. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(2):248. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12020248
Chicago/Turabian StyleLong, Shang-Min, and Gen Li. 2021. "Model Uncertainty in the Projected Indian Summer Monsoon Precipitation Change under Low-Emission Scenarios" Atmosphere 12, no. 2: 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12020248
APA StyleLong, S.-M., & Li, G. (2021). Model Uncertainty in the Projected Indian Summer Monsoon Precipitation Change under Low-Emission Scenarios. Atmosphere, 12(2), 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12020248







