Characterization of Aerosol Sources and Optical Properties in Siberia Using Airborne and Spaceborne Observations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Description of the Aircraft Campaign and the Data Set
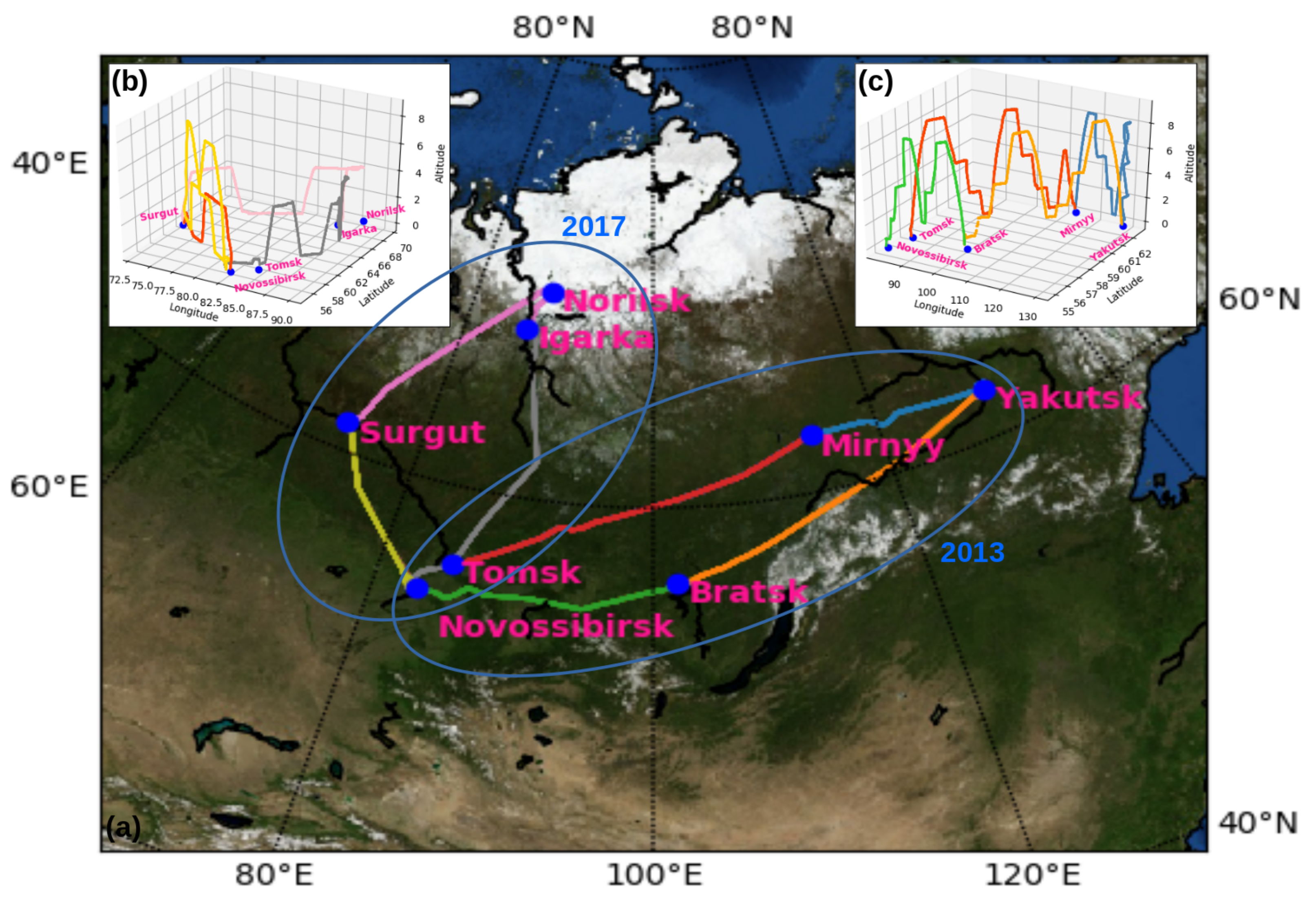
2.1. Campaign Description
2.2. Airborne Lidar System
2.3. In-Situ Measurements
2.4. CALIOP Dataset
3. Methodology of the Aircraft Data Analysis
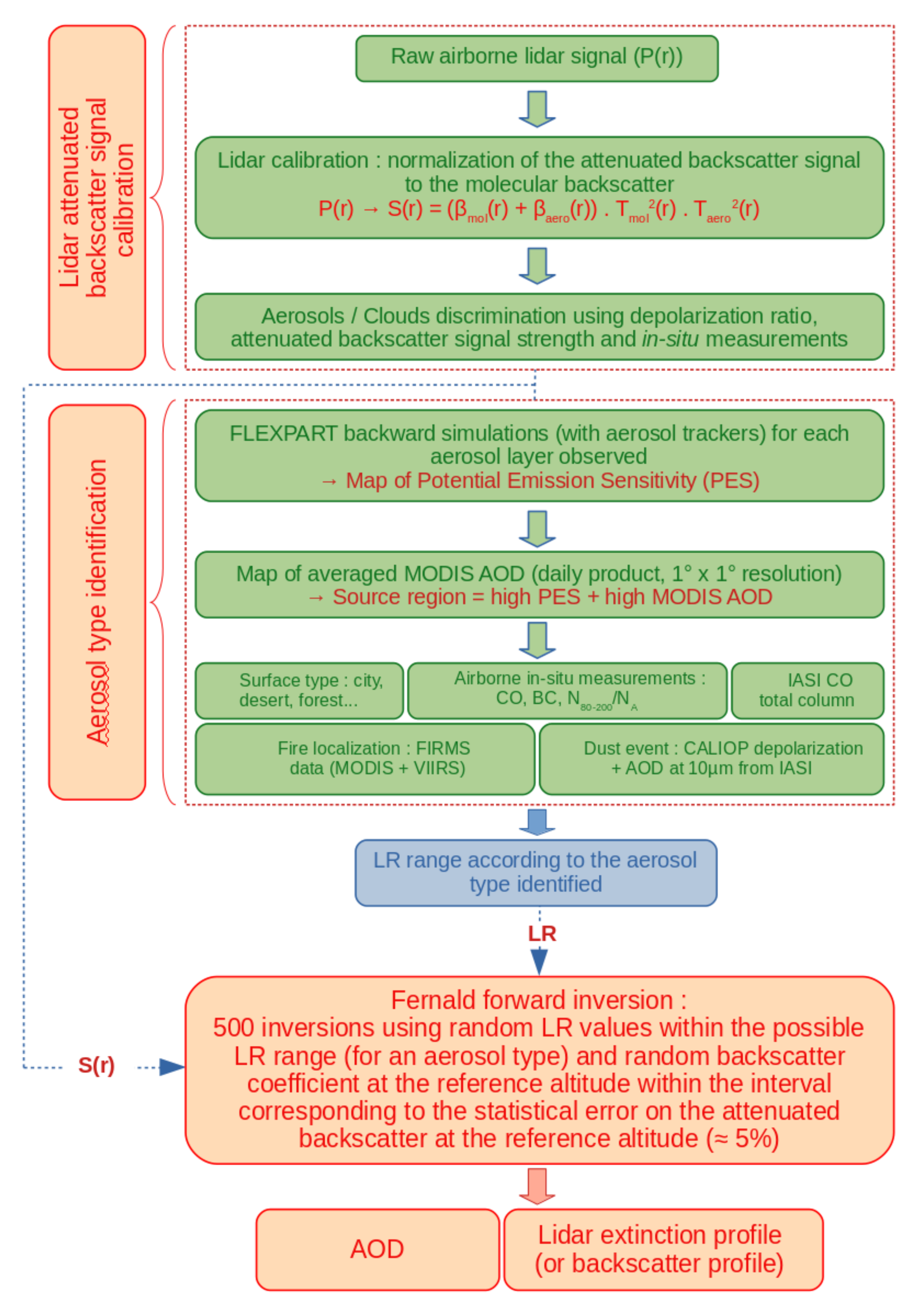
3.1. Aircraft Data Processing
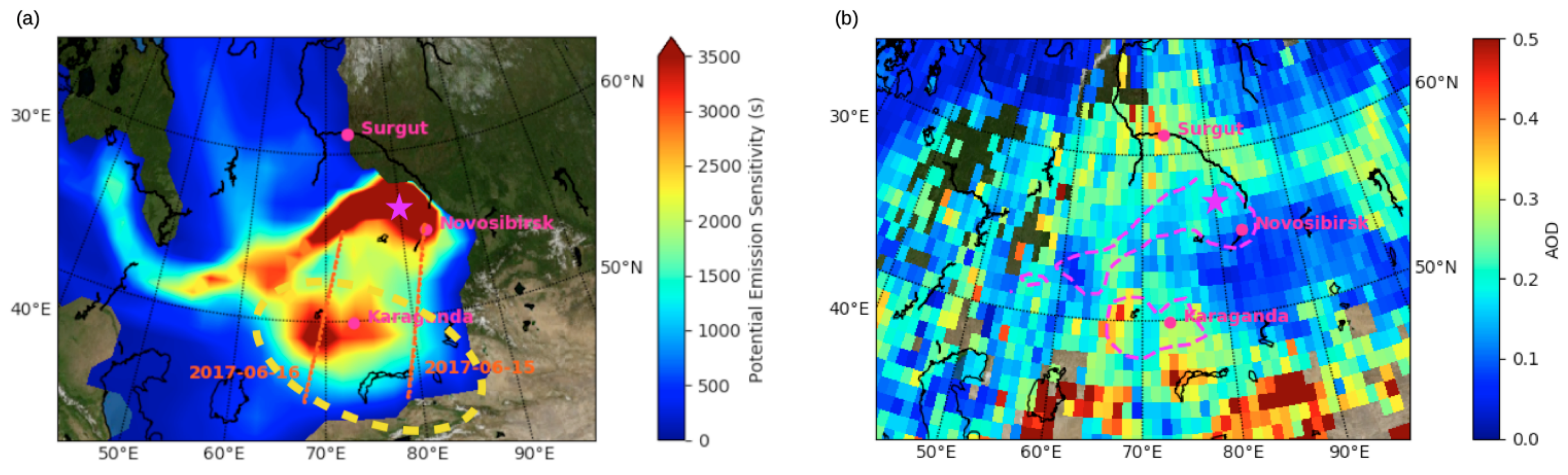
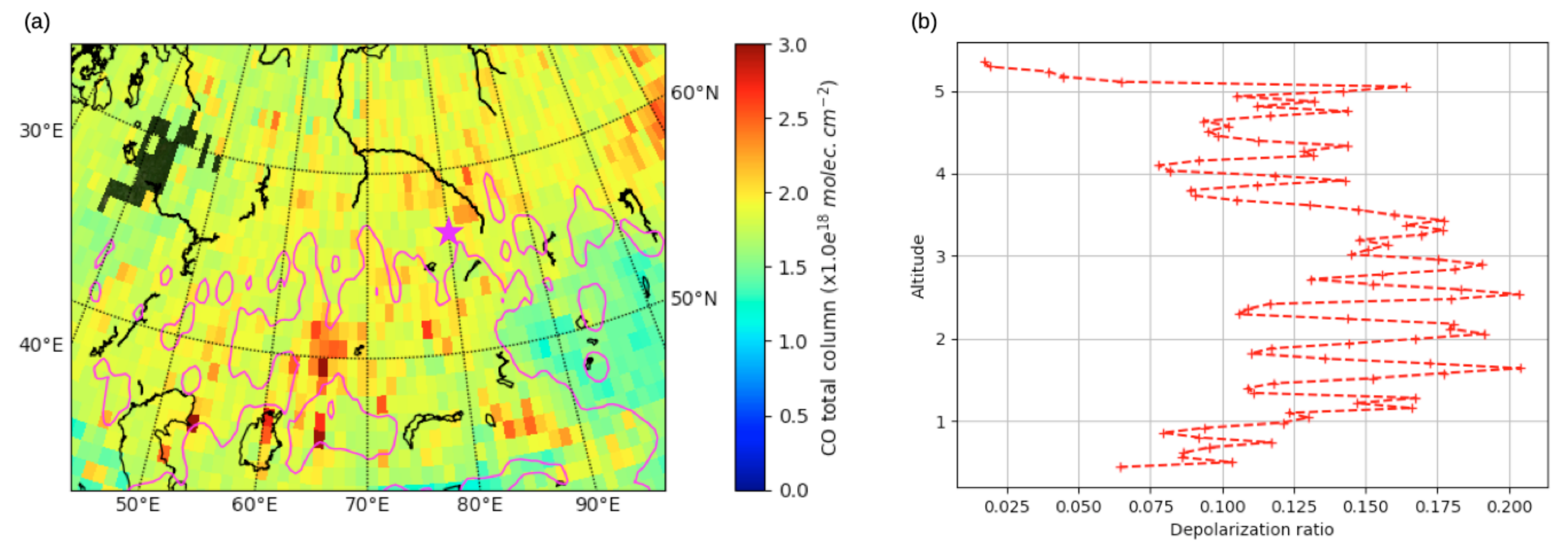
3.2. Identification of the Aerosol Sources
4. Aircraft Campaign Data Analysis
4.1. Dusty Aerosol Mixture
4.2. Ob Valley Gas Flaring Emissions
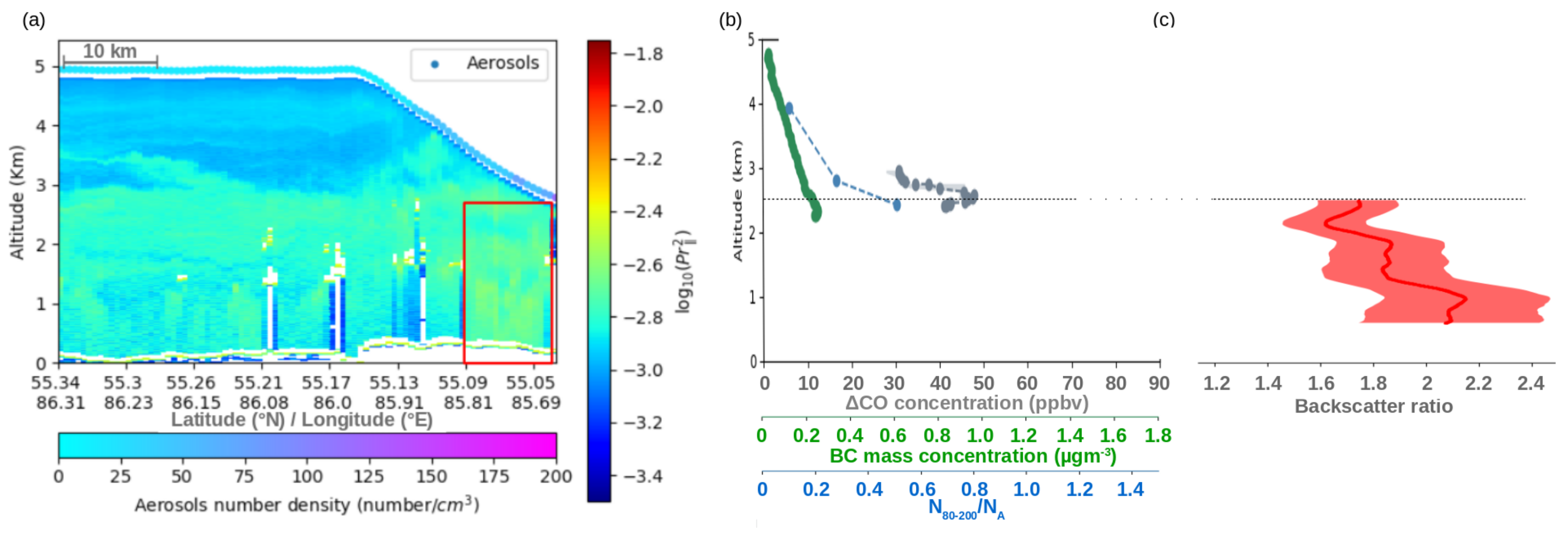
4.3. Fresh Forest Fire Plume
4.4. Aged Forest Fires
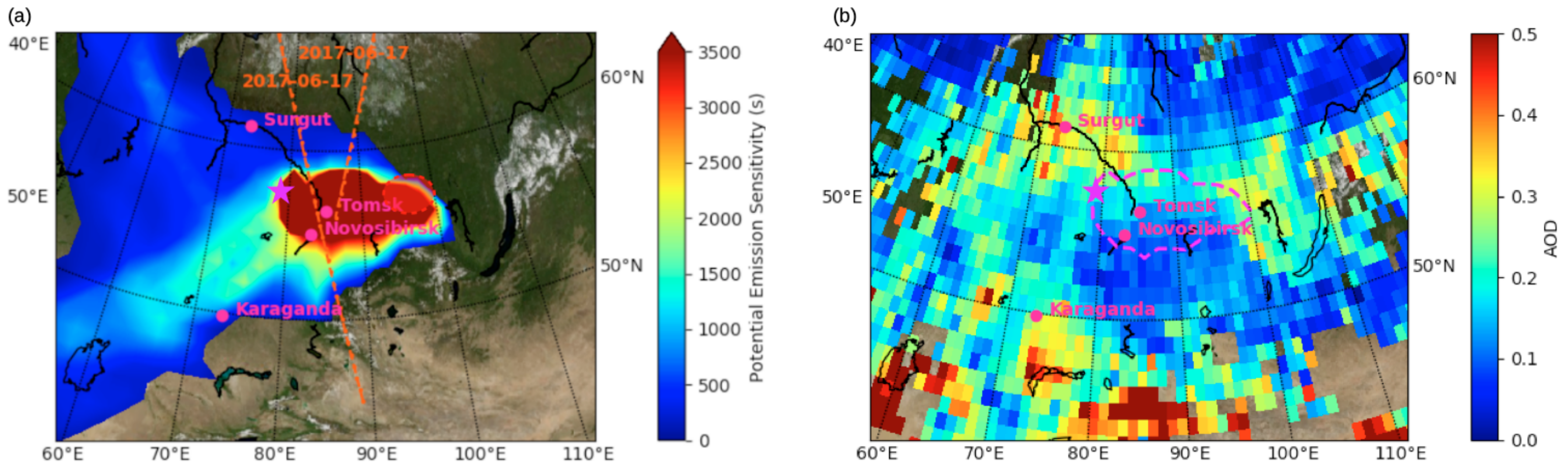
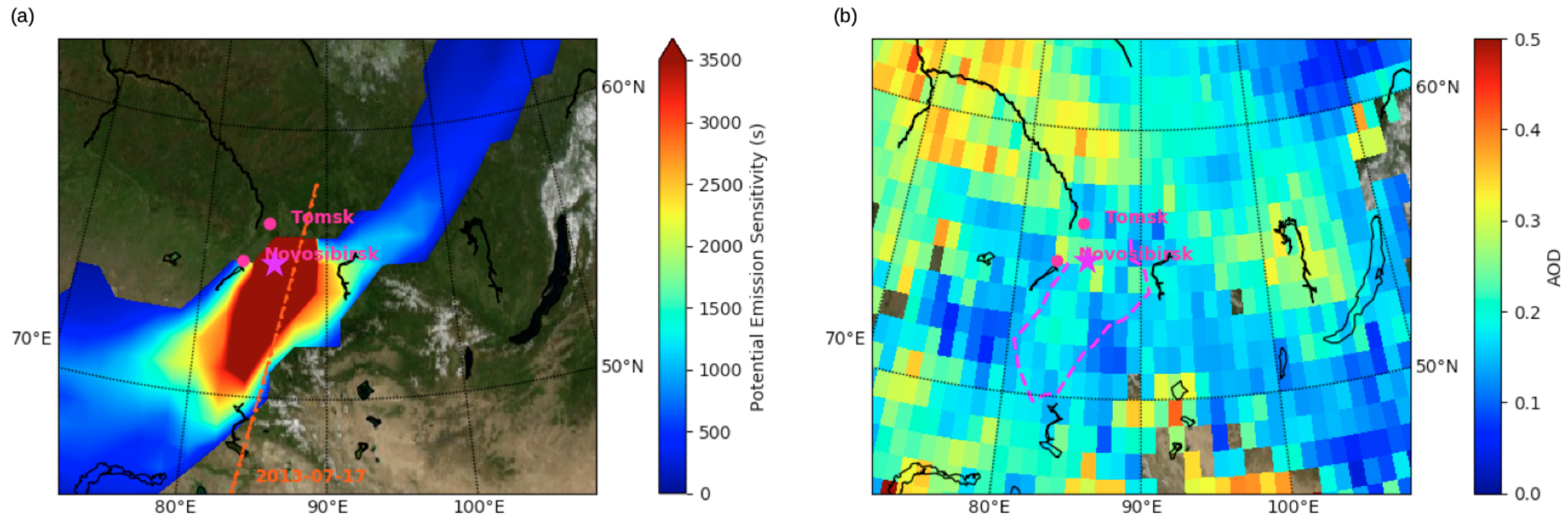
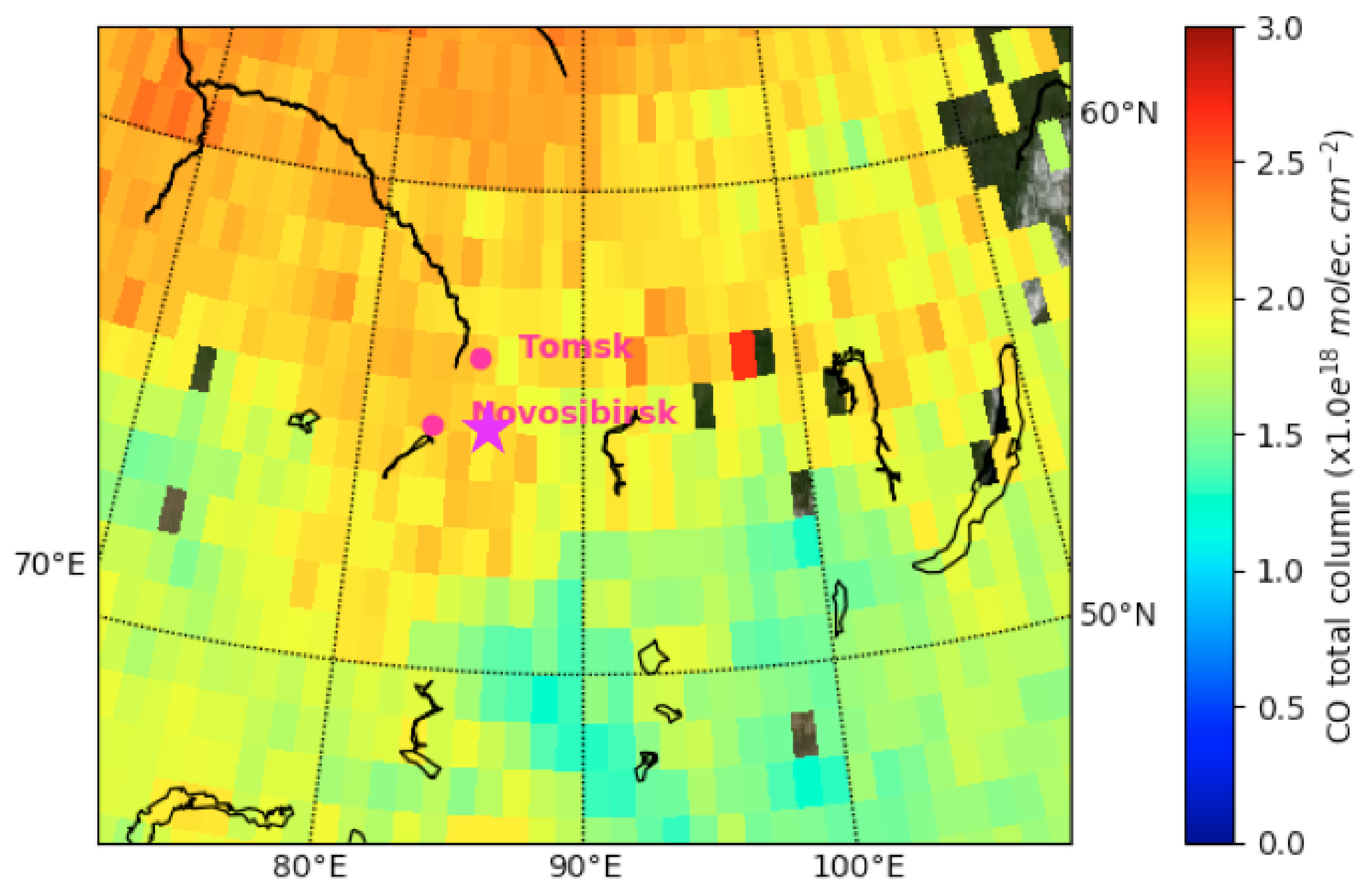
4.5. Siberian Urban and Industrial Emissions
4.6. Long Range Transport of Northern China Emissions
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Chỳlek, P.; Coakley, J.A. Aerosols and climate. Science 1974, 183, 75–77. [Google Scholar]
- Stocker, T.F.; Qin, D.; Plattner, G.K.; Tignor, M.; Allen, S.K.; Boschung, J.; Nauels, A.; Xia, Y.; Bex, V.; Midgley, P.M. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of IPCC the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavoué, D.; Liousse, C.; Cachier, H.; Stocks, B.J.; Goldammer, J.G. Modeling of carbonaceous particles emitted by boreal and temperate wildfires at northern latitudes. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2000, 105, 26871–26890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, J.D.; Stohl, A.; Nédélec, P.; Arshinov, M.Y.; Panchenko, M.; Shmargunov, V.; Law, K.S.; Belan, B.; Ciais, P. Wildfire smoke in the Siberian Arctic in summer: Source characterization and plume evolution from airborne measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 9315–9327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stohl, A.; Klimont, Z.; Eckhardt, S.; Kupiainen, K.; Shevchenko, V.P.; Kopeikin, V.; Novigatsky, A. Black carbon in the Arctic: The underestimated role of gas flaring and residential combustion emissions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 8833–8855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, T.C.; Doherty, S.J.; Fahey, D.; Forster, P.; Berntsen, T.; DeAngelo, B.; Flanner, M.; Ghan, S.; Kärcher, B.; Koch, D.; et al. Bounding the role of black carbon in the climate system: A scientific assessment. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 5380–5552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Fu, J.S.; Prikhodko, V.Y.; Storey, J.M.; Romanov, A.; Hodson, E.L.; Cresko, J.; Morozova, I.; Ignatieva, Y.; Cabaniss, J. Russian anthropogenic black carbon: Emission reconstruction and Arctic black carbon simulation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, J.D.; Ciais, P.; Nédélec, P.; Ramonet, M.; Belan, B.; Arshinov, M.Y.; Golitsyn, G.; Granberg, I.; Stohl, A.; Cayez, G.; et al. The YAK-AEROSIB transcontinental aircraft campaigns: New insights on the transport of CO2, CO and O3 across Siberia. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2008, 60, 551–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, J.D.; Arshinov, M.Y.; Ciais, P.; Belan, B.D.; Nedelec, P. Large-scale aircraft observations of ultra-fine and fine particle concentrations in the remote Siberian troposphere: New particle formation studies. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 1302–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieudonné, E.; Chazette, P.; Marnas, F.; Totems, J.; Shang, X. Lidar profiling of aerosol optical properties from Paris to Lake Baikal (Siberia). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 5007–5026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samoilova, S.; Balin, Y.S.; Kokhanenko, G.; Penner, I. Investigation of the vertical distribution of tropospheric aerosol layers from multifrequency laser sensing data. Part 2: The vertical distribution of optical aerosol characteristics in the visible region. Atmos. Ocean. Opt. 2010, 23, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samoilova, S.; Balin, Y.S.; Kokhanenko, G.; Penner, I. Investigation of the vertical distribution of tropospheric aerosol layers using the data of multiwavelength lidar sensing. Part 3. Spectral peculiarities of the vertical distribution of the aerosol optical characteristics. Atmos. Ocean. Opt. 2012, 25, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancellet, G.; Penner, I.E.; Pelon, J.; Mariage, V.; Zabukovec, A.; Raut, J.C.; Kokhanenko, G.; Balin, Y.S. Aerosol monitoring in Siberia using an 808 nm automatic compact lidar. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 147–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, S.; Ferrare, R.; Hostetler, C.; Hair, J.; Rogers, R.; Obland, M.; Butler, C.; Cook, A.; Harper, D.; Froyd, K. Aerosol classification using airborne High Spectral Resolution Lidar measurements–methodology and examples. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2012, 5, 73–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, S.; Ferrare, R.; Vaughan, M.; Omar, A.; Rogers, R.; Hostetler, C.; Hair, J. Aerosol classification from airborne HSRL and comparisons with the CALIPSO vertical feature mask. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 1397–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groß, S.; Esselborn, M.; Weinzierl, B.; Wirth, M.; Fix, A.; Petzold, A. Aerosol classification by airborne high spectral resolution lidar observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 2487–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelon, J.; Flamant, C.; Chazette, P.; Leon, J.F.; Tanré, D.; Sicard, M.; Satheesh, S. Characterization of aerosol spatial distribution and optical properties over the Indian Ocean from airborne LIDAR and radiometry during INDOEX’99. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2002, 107, INX2-28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winker, D.M.; Vaughan, M.A.; Omar, A.; Hu, Y.; Powell, K.A.; Liu, Z.; Hunt, W.H.; Young, S.A. Overview of the CALIPSO mission and CALIOP data processing algorithms. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 2310–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierro, M.D.; Jaeglé, L.; Anderson, T. Satellite observations of aerosol transport from East Asia to the Arctic: Three case studies. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 2225–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devasthale, A.; Tjernström, M.; Omar, A.H. The vertical distribution of thin features over the Arctic analysed from CALIPSO observations: Part II: Aerosols. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2011, 63, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancellet, G.; Pelon, J.; Blanchard, Y.; Quennehen, B.; Bazureau, A.; Law, K.S.; Schwarzenboeck, A. Transport of aerosol to the Arctic: Analysis of CALIOP and French aircraft data during the spring 2008 POLARCAT campaign. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 8235–8254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Biagio, C.; Pelon, J.; Ancellet, G.; Bazureau, A.; Mariage, V. Sources, Load, Vertical Distribution, and Fate of Wintertime Aerosols North of Svalbard From Combined V4 CALIOP Data, Ground-Based IAOOS Lidar Observations and Trajectory Analysis. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 1363–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, A.H.; Winker, D.M.; Vaughan, M.A.; Hu, Y.; Trepte, C.R.; Ferrare, R.A.; Lee, K.P.; Hostetler, C.A.; Kittaka, C.; Rogers, R.R.; et al. The CALIPSO automated aerosol classification and lidar ratio selection algorithm. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 1994–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.H.; Omar, A.H.; Tackett, J.L.; Vaughan, M.A.; Winker, D.M.; Trepte, C.R.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Poole, L.R.; Pitts, M.C.; et al. The CALIPSO version 4 automated aerosol classification and lidar ratio selection algorithm. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 6107–6135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, D.; Ansmann, A.; Mattis, I.; Tesche, M.; Wandinger, U.; Althausen, D.; Pisani, G. Aerosol-type-dependent lidar ratios observed with Raman lidar. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balin, Y.; Bairashin, G.; Kokhanenko, G.; Penner, I.; Samoilova, S. LOSA-M2 aerosol Raman lidar. Quantum Electron. 2011, 41, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penner, I.E.; Balin, Y.S.; Kokhanenko, G.P.; Belan, B.D.; Arshinov, M.Y.; Chernov, D.G.; Kozlov, V.S. Detection of aerosol plumes from associated gas flaring by laser sensing. In 21st International Symposium Atmospheric and Ocean Optics: Atmospheric Physics; Romanovskii, O.A., Ed.; International Society for Optics and Photonics, SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2015; Volume 9680, pp. 919–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedelec, P.; Cammas, J.P.; Thouret, V.; Athier, G.; Cousin, J.M.; Legrand, C.; Abonnel, C.; Lecoeur, F.; Cayez, G.; Marizy, C. An improved infrared carbon monoxide analyser for routine measurements aboard commercial Airbus aircraft: Technical validation and first scientific results of the MOZAIC III programme. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2003, 3, 3713–3744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchenko, M.; Kozlov, V.; Terpugova, S.; Shmargunov, V.; Burkov, V.; Simultaneous measurements of submicron aerosol and absorbing substance in the height range up to 7 km. In Tenth ARM Science Team Meeting Proceeding, San Antonio, TX, USA, 13–17 March 2000; pp. 13–17. Available online: https://armweb0-stg.ornl.gov/publications/proceedings/conf10/extended_abs/panchenko_mv.pdf (accessed on 3 February 2021).
- Ankilow, A.; Baklanov, A.; Mavliev, R.; Eremenko, S.; Reischl, G.; Majerowicz, A. Comparison ofthe Novosibirsk automated diffusion battery with the Vienna electro mobility spectrometer. J. Aerosol Sci. 1991, 22, S325–S328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankilov, A.; Baklanov, A.; Colhoun, M.; Enderle, K.H.; Gras, J.; Julanov, Y.; Kaller, D.; Lindner, A.; Lushnikov, A.; Mavliev, R.; et al. Particle size dependent response of aerosol counters. Atmos. Res. 2002, 62, 209–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankilov, A.; Baklanov, A.; Colhoun, M.; Enderle, K.H.; Gras, J.; Julanov, Y.; Kaller, D.; Lindner, A.; Lushnikov, A.; Mavliev, R.; et al. Intercomparison of number concentration measurements by various aerosol particle counters. Atmos. Res. 2002, 62, 177–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernald, F.G. Analysis of atmospheric lidar observations: Some comments. Appl. Opt. 1984, 23, 652–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dee, D.P.; Uppala, S.M.; Simmons, A.; Berrisford, P.; Poli, P.; Kobayashi, S.; Andrae, U.; Balmaseda, M.; Balsamo, G.; Bauer, D.P.; et al. The ERA-Interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 553–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stohl, A.; Seibert, P. Accuracy of trajectories as determined from the conservation of meteorological tracers. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 124, 1465–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stohl, A.; Eckhardt, S.; Forster, C.; James, P.; Spichtinger, N.; Seibert, P. A replacement for simple back trajectory calculations in the interpretation of atmospheric trace substance measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 4635–4648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibert, P.; Frank, A. Source-receptor matrix calculation with a Lagrangian particle dispersion model in backward mode. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2004, 4, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giglio, L.; Descloitres, J.; Justice, C.O.; Kaufman, Y.J. An enhanced contextual fire detection algorithm for MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 87, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, W.; Oliva, P.; Giglio, L.; Csiszar, I.A. The New VIIRS 375 m active fire detection data product: Algorithm description and initial assessment. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 143, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clerbaux, C.; Chazette, P.; Hadji-Lazaro, J.; Mégie, G.; Müller, J.F.; Clough, S. Remote sensing of CO, CH4, and O3 using a spaceborne nadir-viewing interferometer. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1998, 103, 18999–19013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadji-Lazaro, J.; Clerbaux, C.; Thiria, S. An inversion algorithm using neural networks to retrieve atmospheric CO total columns from high-resolution nadir radiances. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1999, 104, 23841–23854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurtmans, D.; Coheur, P.F.; Wespes, C.; Clarisse, L.; Scharf, O.; Clerbaux, C.; Hadji-Lazaro, J.; George, M.; Turquety, S. FORLI radiative transfer and retrieval code for IASI. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2012, 113, 1391–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clerbaux, C. Daily IASI/Metop-A ULB-LATMOS Carbon Monoxide (CO) L2 Product (Total Column). 2018. Available online: https://doi.org.10.25326/16 (accessed on 3 February 2021).
- Peyridieu, S.; Chédin, A.; Capelle, V.; Tsamalis, C.; Pierangelo, C.; Armante, R.; Crevoisier, C.; Crépeau, L.; Siméon, M.; Ducos, F.; et al. Characterisation of dust aerosols in the infrared from IASI and comparison with PARASOL, MODIS, MISR, CALIOP, and AERONET observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 6065–6082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capelle, V.; Chédin, A.; Siméon, M.; Tsamalis, C.; Pierangelo, C.; Pondrom, M.; Armante, R.; Crevoisier, C.; Crepeau, L.; Scott, N. Evaluation of IASI derived dust aerosols characteristics over the tropical belt. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2013, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capelle, V.; Chédin, A.; Pondrom, M.; Crevoisier, C.; Armante, R.; Crepeau, L.; Scott, N. Infrared dust aerosol optical depth retrieved daily from IASI and comparison with AERONET over the period 2007–2016. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 206, 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesche, M.; Gross, S.; Ansmann, A.; Mueller, D.; Althausen, D.; Freudenthaler, V.; Esselborn, M. Profiling of Saharan dust and biomass-burning smoke with multiwavelength polarization Raman lidar at Cape Verde. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2011, 63, 649–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groß, S.; Tesche, M.; Freudenthaler, V.; Toledano, C.; Wiegner, M.; Ansmann, A.; Althausen, D.; Seefeldner, M. Characterization of Saharan dust, marine aerosols and mixtures of biomass-burning aerosols and dust by means of multi-wavelength depolarization and Raman lidar measurements during SAMUM 2. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2011, 63, 706–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimont, Z.; Kupiainen, K.; Heyes, C.; Purohit, P.; Cofala, J.; Rafaj, P.; Borken-Kleefeld, J.; Schöpp, W. Global anthropogenic emissions of particulate matter including black carbon. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 8681–8723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Elansky, N.; Timofeev, Y.M.; Wang, G.; Golitsyn, G.; Makarova, M.; Rakitin, V.; Shtabkin, Y.; Skorokhod, A.; Grechko, E.; et al. Long-Term Trends of Carbon Monoxide Total Columnar Amount in Urban Areas and Background Regions: Ground-and Satellite-based Spectroscopic Measurements. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2018, 35, 785–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willeke, K.; Whitby, K.T. Atmospheric aerosols: Size distribution interpretation. J. Air Pollut. Control Assoc. 1975, 25, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäumer, D.; Vogel, B.; Versick, S.; Rinke, R.; Möhler, O.; Schnaiter, M. Relationship of visibility, aerosol optical thickness and aerosol size distribution in an ageing air mass over South-West Germany. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 989–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furutani, H.; Dall’osto, M.; Roberts, G.C.; Prather, K.A. Assessment of the relative importance of atmospheric aging on CCN activity derived from field observations. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 3130–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesche, M.; Ansmann, A.; Müller, D.; Althausen, D.; Engelmann, R.; Hu, M.; Zhang, Y. Particle backscatter, extinction, and lidar ratio profiling with Raman lidar in south and north China. Appl. Opt. 2007, 46, 6302–6308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Villiers, R.A.; Ancellet, G.; Pelon, J.; Quennehen, B.; Schwarzenboeck, A.; Gayet, J.F.; Law, K.S. Airborne measurements of aerosol optical properties related to early spring transport of mid-latitude sources into the Arctic. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 5011–5030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chazette, P.; Raut, J.C.; Totems, J. Springtime aerosol load as observed from ground-based and airborne lidars over northern Norway. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 13075–13095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolae, D.; Nemuc, A.; Mueller, D.; Talianu, C.; Vasilescu, J.; Belegante, L.; Kolgotin, A. Characterization of fresh and aged biomass burning events using multiwavelength Raman lidar and mass spectrometry. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 2956–2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, D.; Mattis, I.; Wandinger, U.; Ansmann, A.; Althausen, D.; Stohl, A. Raman lidar observations of aged Siberian and Canadian forest fire smoke in the free troposphere over Germany in 2003: Microphysical particle characterization. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2005, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cape, J.; Coyle, M.; Dumitrean, P. The atmospheric lifetime of black carbon. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 59, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, M.T.; Samset, B.H.; Skeie, R.B.; Watson-Parris, D.; Katich, J.M.; Schwarz, J.P.; Weinzierl, B. Short Black Carbon lifetime inferred from a global set of aircraft observations. Npj Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2018, 1, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murayama, T.; Müller, D.; Wada, K.; Shimizu, A.; Sekiguchi, M.; Tsukamoto, T. Characterization of Asian dust and Siberian smoke with multi-wavelength Raman lidar over Tokyo, Japan in spring 2003. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, Y.M.; Kim, Y.J.; Müller, D. Seasonal characteristics of lidar ratios measured with a Raman lidar at Gwangju, Korea in spring and autumn. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 2208–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Nishizawa, T.; Sugimoto, N.; Matsui, I.; Wang, Z. Characteristics of aerosol optical properties in pollution and Asian dust episodes over Beijing, China. Appl. Opt. 2008, 47, 4945–4951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansmann, A.; Engelmann, R.; Althausen, D.; Wandinger, U.; Hu, M.; Zhang, Y.; He, Q. High aerosol load over the Pearl River Delta, China, observed with Raman lidar and Sun photometer. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heese, B.; Baars, H.; Bohlmann, S.; Althausen, D.; Deng, R. Continuous vertical aerosol profiling with a multi-wavelength Raman polarization lidar over the Pearl River Delta, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 6679–6691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieudonné, E.; Chazette, P.; Marnas, F.; Totems, J.; Shang, X. Raman Lidar Observations of Aerosol Optical Properties in 11 Cities from France to Siberia. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chazette, P.; Randriamiarisoa, H.; Sanak, J.; Couvert, P.; Flamant, C. Optical properties of urban aerosol from airborne and ground-based in situ measurements performed during the Etude et Simulation de la Qualité de l’air en Ile de France (ESQUIF) program. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2005, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, R.; Liu, S.C.; Shiu, C.J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y. Trends in aerosol optical depth in northern China retrieved from sunshine duration data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, H.C.; Chou, C.C.K.; Lee, C.S.L.; Kuo, W.C.; Chang, S.C. Hygroscopic properties and cloud condensation nuclei activity of atmospheric aerosols under the influences of Asian continental outflow and new particle formation at a coastal site in eastern Asia. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 5911–5922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Zhizhin, M.; Baugh, K.; Hsu, F.C.; Ghosh, T. Methods for Global Survey of Natural Gas Flaring from Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite Data. Energies 2016, 9, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster, C.; Wandinger, U.; Wotawa, G.; James, P.; Mattis, I.; Althausen, D.; Simmonds, P.; O’Doherty, S.; Jennings, S.G.; Kleefeld, C.; et al. Transport of boreal forest fire emissions from Canada to Europe. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 22887–22906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petetin, H.; Sauvage, B.; Parrington, M.; Clark, H.; Fontaine, A.; Athier, G.; Blot, R.; Boulanger, D.; Cousin, J.M.; Nédélec, P.; et al. The role of biomass burning as derived from the tropospheric CO vertical profiles measured by IAGOS aircraft in 2002–2017. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 17277–17306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, K.M.; Laing, J.R.; Stevens, R.G.; Jaffe, D.A.; Pierce, J.R. The evolution of biomass-burning aerosol size distributions due to coagulation: Dependence on fire and meteorological details and parameterization. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 7709–7724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quennehen, B.; Schwarzenboeck, A.; Matsuki, A.; Burkhart, J.F.; Stohl, A.; Ancellet, G.; Law, K.S. Anthropogenic and forest fire pollution aerosol transported to the Arctic: Observations from the POLARCAT-France spring campaign. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 6437–6454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

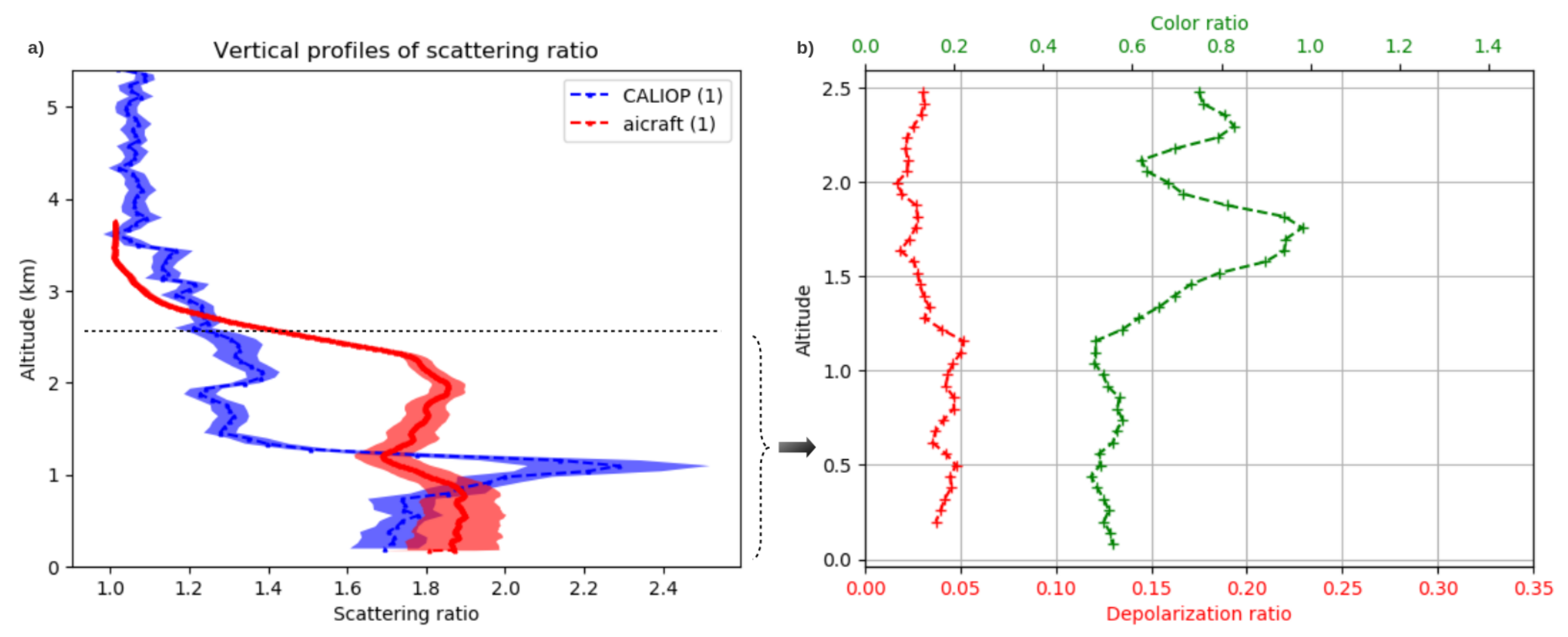
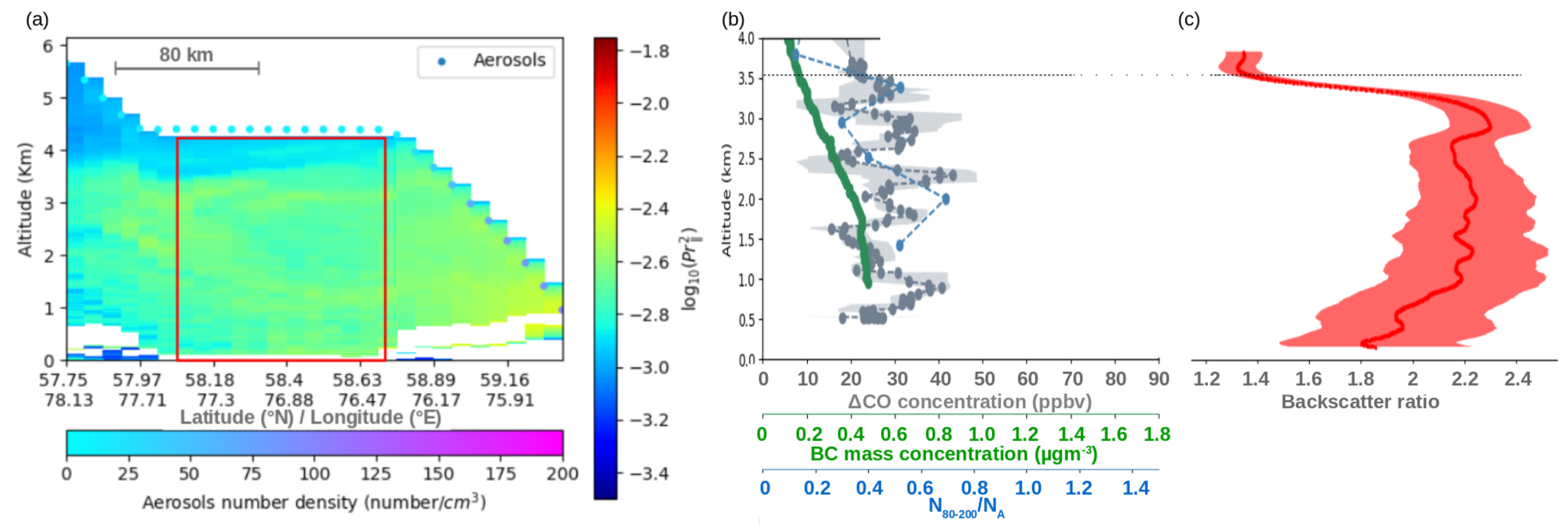

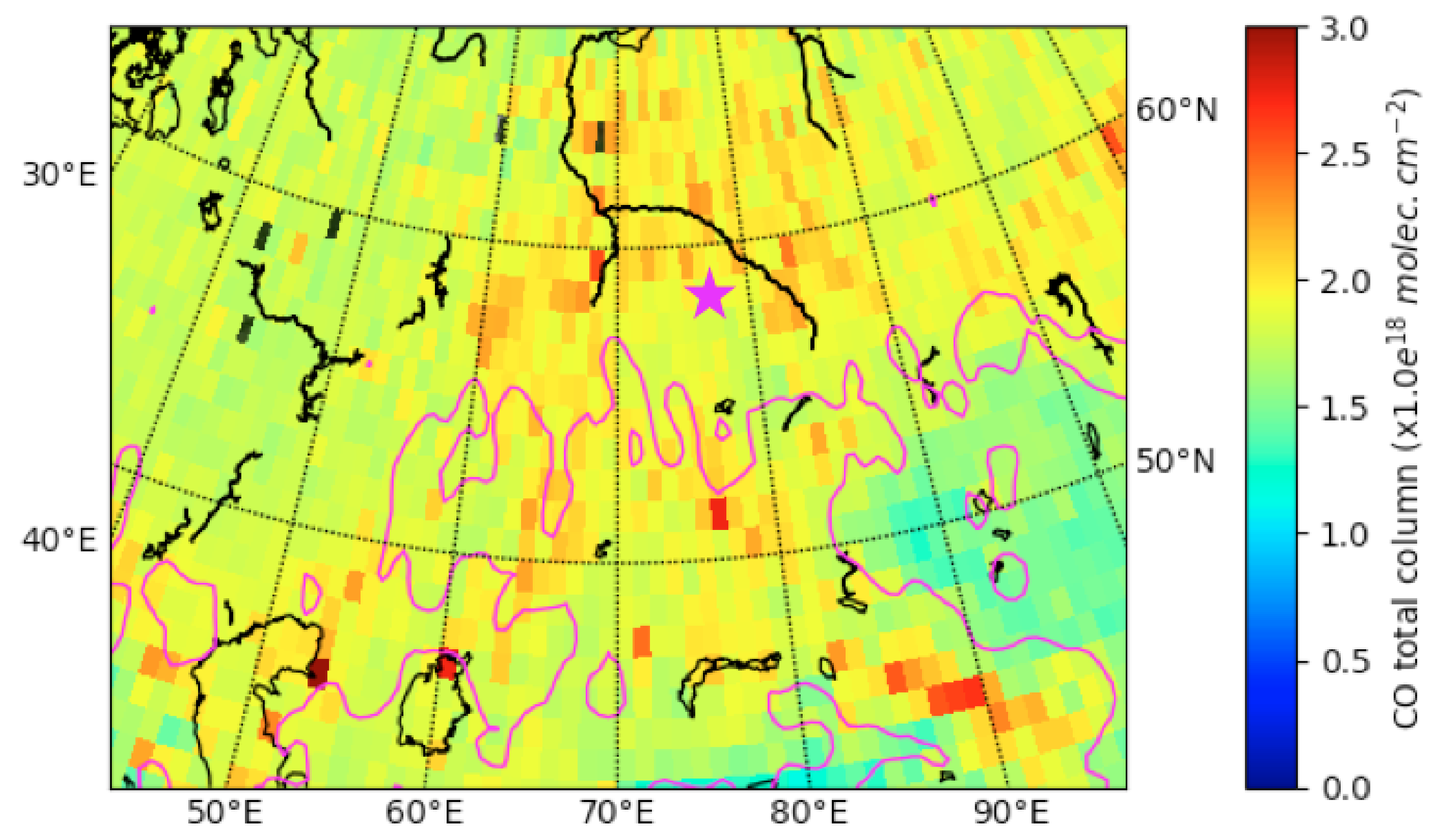




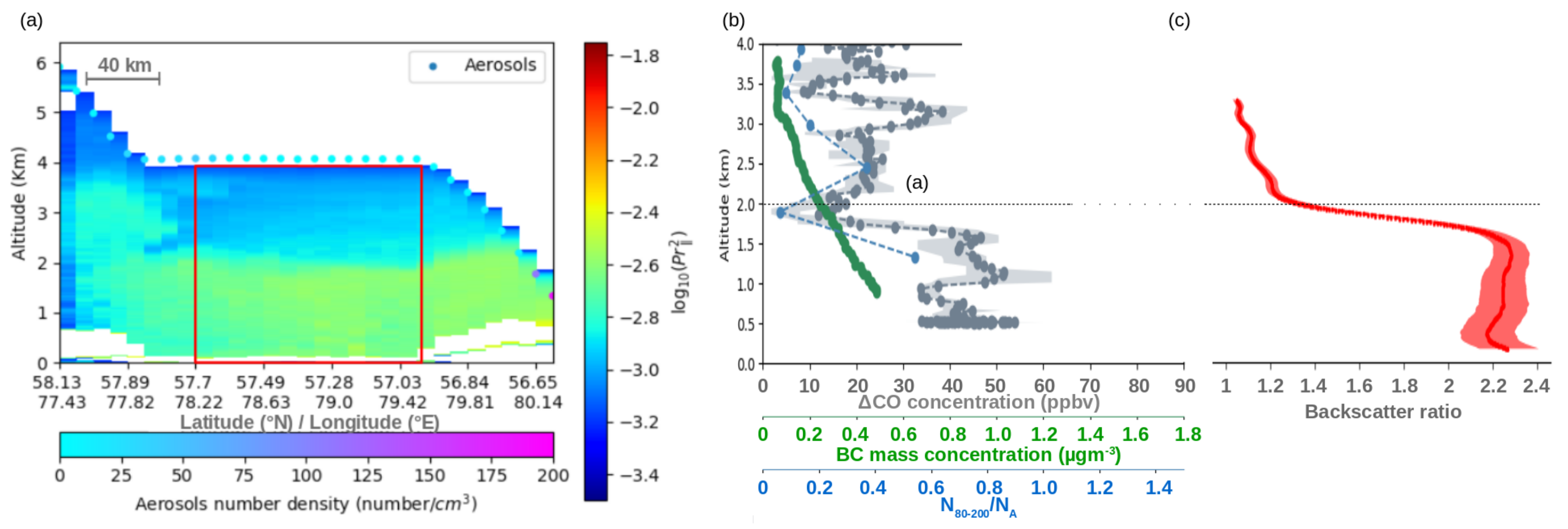


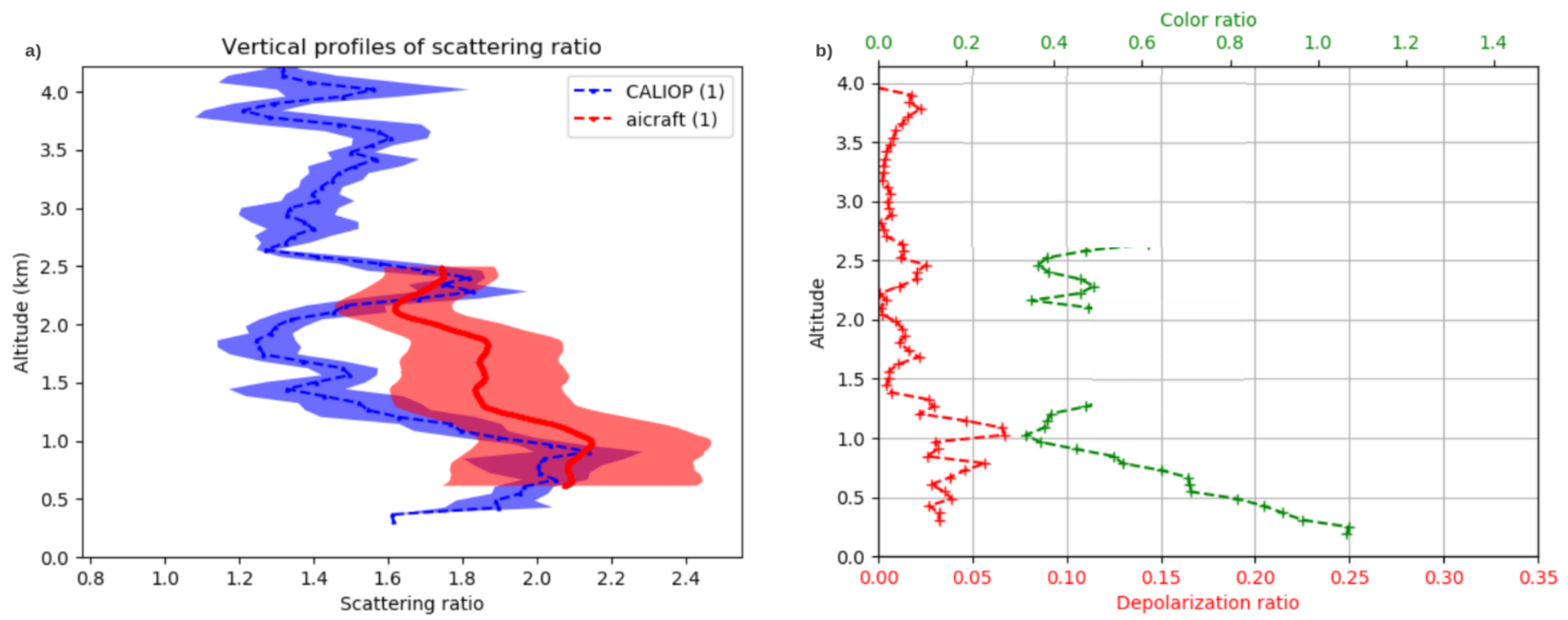

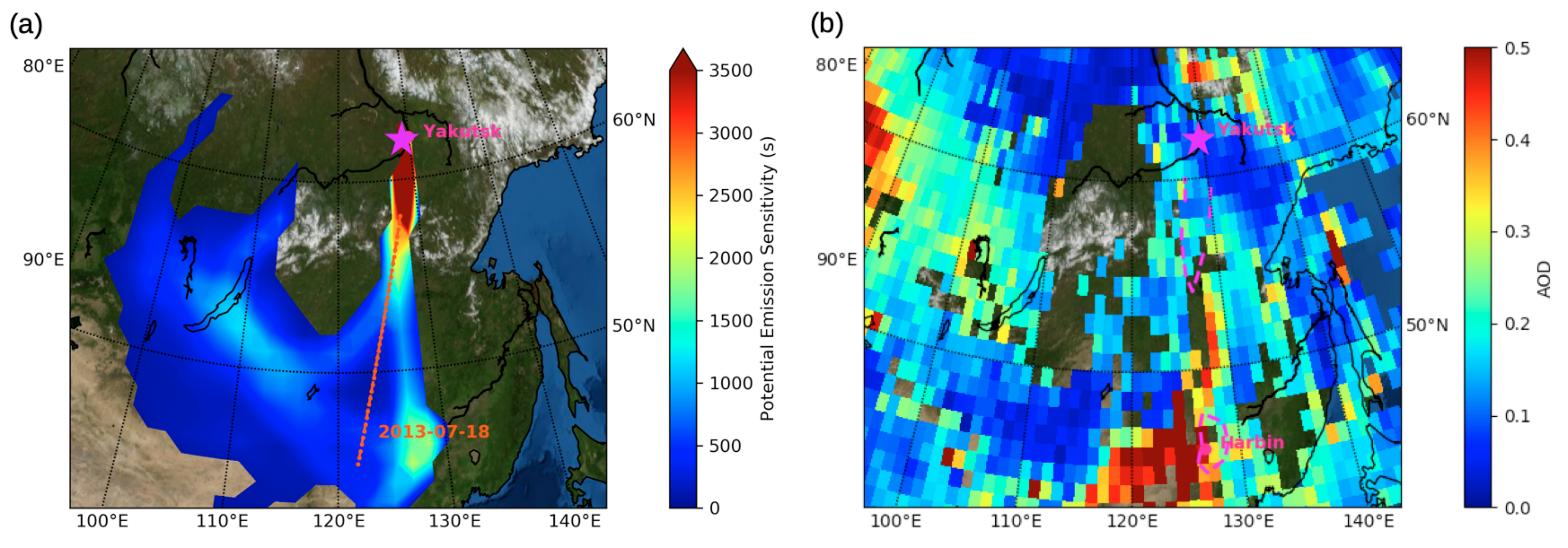

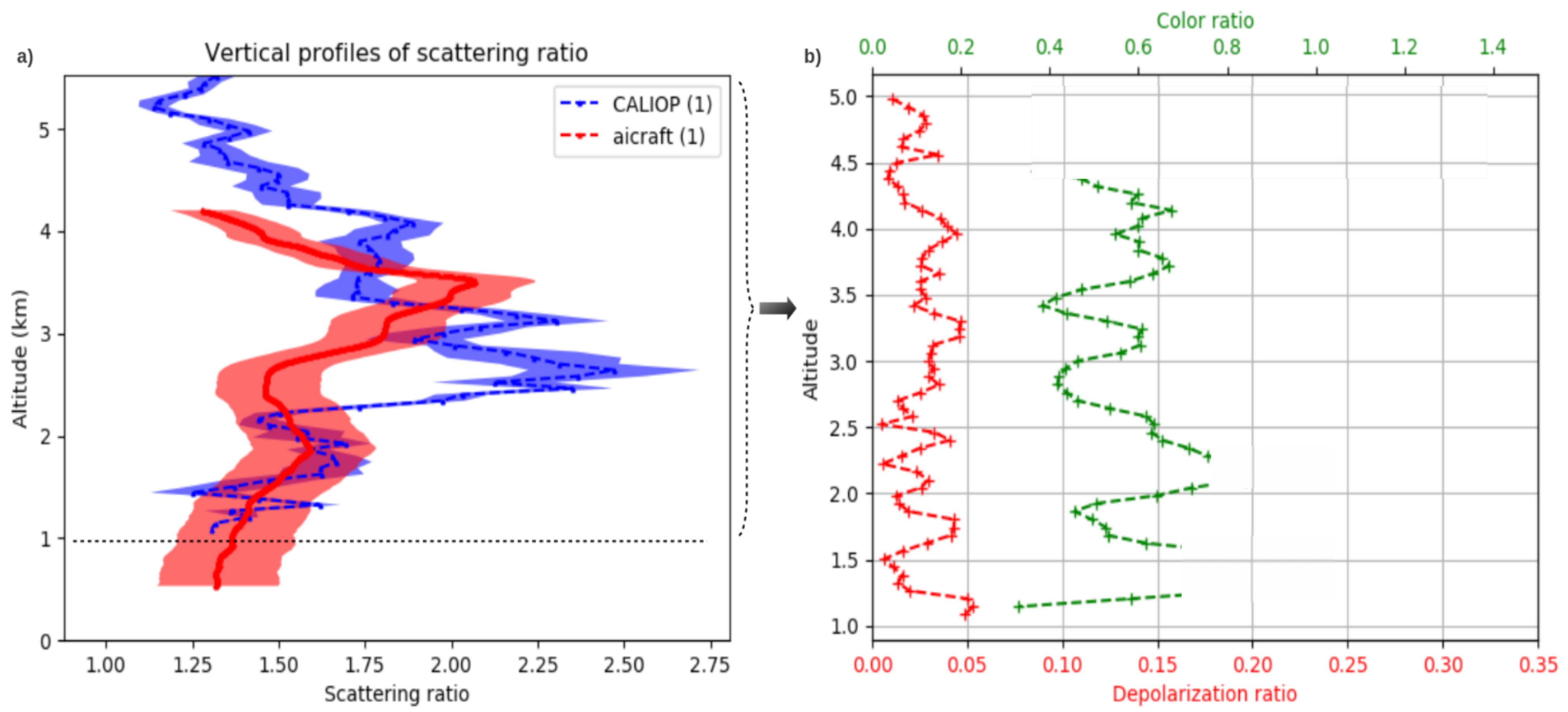
| Aerosol Type | Dust/Smoke | Smoke from | Smoke from | Gas Flaring | Urban | Urban |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Emissions from | Siberian Fires | Siberian Fires | Emissions | Emissions of | Emissions from | |
| Kazakhstan | Siberian Cities | Northern China | ||||
| Layer Altitude | 1.0 (2.0) | 2.2 (3.5) | 0.9 (1.8) | 1.5 (3.2) | 1.5 (3) | 3.0 (4.5) |
| mean (maximum), km | ||||||
| Layer age | Aged | Fresh | Aged | Fresh | Fresh | Aged |
| CO, ppbv | 20 | 35–45 | 45–55 | 30–40 | 50 | 60–80 |
| BC concentration | 0.2–0.4 | 1.5 | 0.4–0.5 | 0.4–0.5 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| in g.m | ||||||
| N/N | - | 0.15 | 0.6 | 0.3–0.6 | 0.5 | 0.8–1.0 |
| Aircraft AOD | 0.1 ± 0.03 | 0.12 ± 0.02 | 0.16 ± 0.03 | 0.21 ± 0.06 | 0.15 ± 0.09 | 0.19 ± 0.01 |
| CALIOP AOD | 0.11 ± 0.04 | 0.11 ± 0.04 | 0.17 ± 0.07 | 0.32 ± 0.09 | 0.18 ± 0.06 | 0.21 ± 0.07 |
| MODIS AOD | 0.11 ± 0.02 * | 0.19 ± 0.02 * | 0.22 ± 0.04 ** | 0.33 ± 0.05 ** | 0.29 ± 0.05 * | - |
| CALIOP Depolarization | 4–5 | 3–10 | 5–12 | 3–5 | 1–5 | 1–5 |
| ratio, % | ||||||
| CALIOP color ratio | 0.5–0.7 | 0.4 | 0.7 | 0.2–0.4 | 0.3–0.5 | 0.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zabukovec, A.; Ancellet, G.; Penner, I.E.; Arshinov, M.; Kozlov, V.; Pelon, J.; Paris, J.-D.; Kokhanenko, G.; Balin, Y.S.; Chernov, D.; et al. Characterization of Aerosol Sources and Optical Properties in Siberia Using Airborne and Spaceborne Observations. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12020244
Zabukovec A, Ancellet G, Penner IE, Arshinov M, Kozlov V, Pelon J, Paris J-D, Kokhanenko G, Balin YS, Chernov D, et al. Characterization of Aerosol Sources and Optical Properties in Siberia Using Airborne and Spaceborne Observations. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(2):244. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12020244
Chicago/Turabian StyleZabukovec, Antonin, Gerard Ancellet, Iwan E. Penner, Mikhail Arshinov, Valery Kozlov, Jacques Pelon, Jean-Daniel Paris, Grigory Kokhanenko, Yuri S. Balin, Dimitry Chernov, and et al. 2021. "Characterization of Aerosol Sources and Optical Properties in Siberia Using Airborne and Spaceborne Observations" Atmosphere 12, no. 2: 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12020244
APA StyleZabukovec, A., Ancellet, G., Penner, I. E., Arshinov, M., Kozlov, V., Pelon, J., Paris, J.-D., Kokhanenko, G., Balin, Y. S., Chernov, D., & Belan, B. D. (2021). Characterization of Aerosol Sources and Optical Properties in Siberia Using Airborne and Spaceborne Observations. Atmosphere, 12(2), 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12020244








