Abstract
The Arctic’s winter water cycle is rapidly changing, with implications for snow moisture sources and transport processes. Stable isotope values (δ18O, δ2H, d-excess) of the Arctic snowpack have potential to provide proxy records of these processes, yet it is unclear how well the isotope values of individual snowfall events are preserved within snow profiles. Here, we present water isotope data from multiple taiga and tundra snow profiles sampled in Arctic Alaska and Finland, respectively, during winter 2018–2019. We compare the snowpack isotope stratigraphy with meteoric water isotopes (vapor and precipitation) during snowfall days, and combine our measurements with satellite observations and reanalysis data. Our analyses indicate that synoptic-scale atmospheric circulation and regional sea ice coverage are key drivers of the source, amount, and isotopic composition of Arctic snowpacks. We find that the western Arctic tundra snowpack profiles in Alaska preserved the isotope values for the most recent storm; however, post depositional processes modified the remaining isotope profiles. The overall seasonal evolution in the vapor isotope values were better preserved in taiga snow isotope profiles in the eastern Arctic, where there is significantly less wind-driven redistribution than in the open Alaskan tundra. We demonstrate the potential of the seasonal snowpack to provide a useful proxy for Arctic winter-time moisture sources and propose future analyses.
1. Introduction
Since the mid-1990s, Arctic surface air temperatures (SATs) have warmed at twice the global mean rate [1]. This amplification of the Arctic is driving pronounced changes in the hydrological cycle, including shifting ocean and atmospheric circulation, altered precipitation and humidity patterns, large-scale permafrost degradation, and precipitous ice-mass loss from glacierized regions throughout the Arctic [2,3,4,5]. In particular, the rapid loss of sea ice [6] has been linked to shifting atmospheric moisture source and transport regimes across the Arctic, with implications for the meridional transport of moisture between mid- and high-latitudes [7,8,9]. These impacts are evident, for example, during atmospheric river events, where plumes of warm water vapor are rapidly transported into the Arctic [10,11], and the advection of moisture from the Arctic to lower latitudes, such as during cold air outbreaks and transient cyclones [12,13]. Consequently, changes in the source, timing, amount, and distribution of snow are evident in western Arctic and are projected to continue [14], and northern Scandinavia in the eastern Arctic is experiencing more extreme heavy winter snow conditions, such as in winter 2019–2020 [4,15,16].
Snow is a key component of the Arctic water cycle: it regulates the surface energy balance [17,18,19] and provides an important source and storage of freshwater during the snow-free seasons [20,21,22,23]. Additionally, snow regulates several Arctic ecosystem processes [24,25], including carbon exchange rates during winter that can affect subsequent summer carbon source–sink relationships [26,27,28]. Within ecohydrology, snowmelt provides a key water source for tundra plants, that in turn regulates leaf gas exchange and, in some instances, increases growth in tundra shrub vegetation [29,30,31,32]. Furthermore, changes to snow properties can have cascading consequences to food webs and ungulate populations [33]. Thus, understanding current Arctic water cycle changes, particularly the shifting moisture sources of snow and the fate and function of snowmelt, is imperative.
Stable water isotopes (18O/16O and 2H/1H) and the secondary parameter deuterium (d-excess) are valuable hydrological tracers across multiple spatial and temporal scales [34]—from synoptic atmospheric moisture transport patterns [35,36,37,38], to the micro-scale movement of water in soil pores and plants [39,40,41]. In particular, stable isotope measurements of precipitation can provide information on moisture provenance [12,42,43], including links to Arctic sea-ice loss on contemporary to millennial timescales [5,7,44,45]. However, although some sites in Arctic Alaska have been collecting event-based snowfall samples for stable isotope analysis over the past 15 years [5,46], historically there has been a paucity of sampling in most Arctic regions. Moreover, although individual precipitation event-based studies can provide detailed atmospheric moisture source and transport tracking at specific locations, proxy records of snow moisture source for an event or seasonal scale across multiple Arctic sites has not been considered.
The seasonal snowpack could provide such proxy, assuming that atmospheric moisture provenance and transport processes associated with individual snowfall events are sequentially preserved in the snow profile [47,48]. However, while many studies have investigated site-specific controls on local precipitation isotopes [7,35,36,43], few consider if/how the snowpack distorts the original vapor and snowfall isotope signal [49,50]. Post-depositional processes, such as snow sublimation [51,52,53,54,55], isotope exchange in vapor flow [56,57,58] and canopy interception [59,60], can each modify the snowpack isotope composition from individual precipitation events. However, the cumulative influence of these isotope fractionation processes on snowpack isotope stratigraphy over winter is poorly known [61,62,63,64], with studies focusing on meltwater percolation in the snowpack [65,66,67] or isotope diffusion in firn profiles [47,68]. Consequently, whilst a handful of studies have explored near-surface isotope exchange processes between snow and vapor [54,69,70], comparison of snow isotope stratigraphy with the meteoric water (precipitation or water vapor) sourcing the snowfall has remained relatively unexplored, particularly for regions other than Greenland [49,50]. Studies from different snow environments are needed to better understand isotope variability and fractionation in seasonal snowpacks, and their potential use as an isotope record of moisture sources.
To address this knowledge gap, we conducted atmospheric moisture, snowfall, and snowpit isotope sampling at two long-term research sites at the same latitude (~68.5° N), but on opposite sides of the Arctic: Imnavait Creek research catchment on the North Slope of Alaska (U.S.A) and Pallas research catchment in sub-arctic Lapland (Finland) (Figure 1). The sites differ in their snow conditions, with typical tundra at Imnavait Creek and taiga at Pallas [71]. We paired the snow isotope stratigraphy recorded in snowpits with continuous in situ measurement of atmospheric water vapor isotope composition and opportunistic event-based snowfall isotope sampling. Our key questions were:
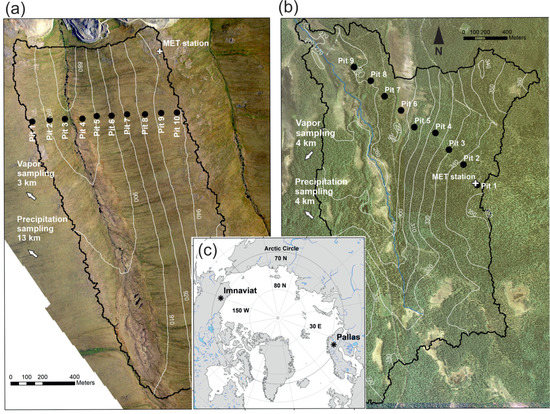
Figure 1.
Locations of snowpit sampling, meteorological stations, and indication of precipitation and vapor sampling locations in the (a) Imnavait and (b) Pallas study sites. Subfigure (c) shows the site locations at the opposite sites of the Arctic.
- Do the isotope profiles in late winter seasonal snowpack reflect individual precipitation events and their different winter atmospheric moisture sources?
- Is post-deposition isotope fractionation over winter distinguishable in snowpack isotope profiles?
- Do snowpacks in the western and eastern Arctic record air mass tracks and post-depositional isotopic fractionation in similar manners?
2. Methods
2.1. Study Sites
2.1.1. Imnavait Creek, Alaska, Western Arctic
Imnavait Creek is located in the northern foothills of the Alaskan Brooks Range (U.S.A.) at an elevation of 844–960 m above sea level (a.s.l.) (68.6° N, 149.3° W) (Figure 1a). It is a long-term monitoring site for permafrost hydrology [72,73,74] and tundra snowpack processes [75,76,77], with over 30 years of snow depth and snow water equivalent measurements [14].
The long-term mean annual SAT is −7.7 °C and annual total precipitation is 334 mm (1985–2017) [78]. The snow cover season typically lasts from October to May [14], and the long-term mean end-of-winter snow-water equivalent and snow depth are 124 mm and 50 cm, respectively. Climate data for this study were obtained from the snow telemetry and snow course data network meteorological station (SNOTEL Station ID 968, Figure 1 and Figure 2).
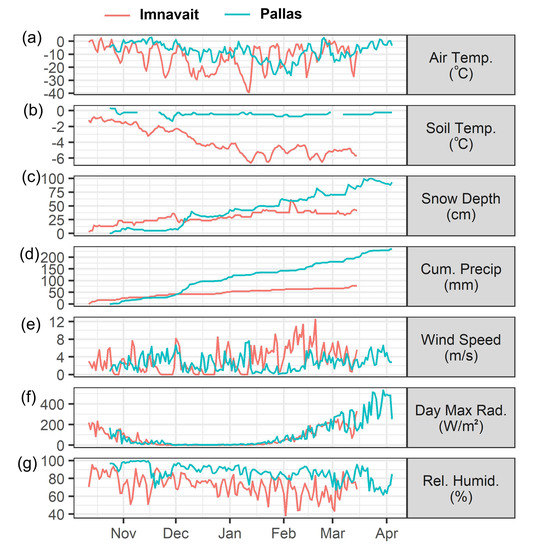
Figure 2.
Key meteorological variables for daily (a) mean air temperature, (b) mean soil temperature, (c) maximum snow depth, (d) cumulative precipitation, (e) mean wind speed, (f) maximum short wave radiation (g) mean relative humidity for winter 2018–2019 at the study sites, with Imnavait in red and Pallas in blue.
The Imnavait site is in the continuous permafrost region. Soils are clay-rich glacial till with a well-developed organic layer. Treeless tundra vegetation at the site is dominated by tussock sedge and dwarf shrub tundra [79]. The variable microtopography in tussock tundra results in high small-scale variability in snow depths [14]. The regional landscape topography comprises rolling hills and river valleys, where the open, treeless terrain with strong winds enhances the redistribution and sublimation of deposited snow [75]. These processes typically result in areas of relatively deep snow on the slopes west of the creek, and relatively shallow snow on the slopes east of the creek that are highly wind scoured (Figure 1) [76].
2.1.2. Pallas, Finnish Lapland, Eastern Arctic
The Pallas site is located in Finnish Lapland at an elevation range of 270–360 m a.s.l (68.0° N, 24.2° E) (Figure 1b). The infrastructure has been utilized as a meteorological monitoring site for over 80 years, with intensive development in atmospheric and ecological research since the 1990s [80], and catchment ecohydrology since 2014.
The annual mean SAT and annual precipitation are 0.4 °C (2002–2019) and 639 mm (2008–2019), respectively. On average, the snow season starts in mid-October and ends in May, with automated snow gauging measurements recording a mean maximum snow depth of 105 cm during the 2007 to 2019 period. Regular snow surveys for snow water equivalent measurements started in 2018 along the same transect as snowpits in this study (Figure 1). Maximum annual values in 2018, 2019, and 2020 were 279, 153, and 325 mm, respectively. Climate data for this study were recorded at the Finnish Meteorological Institute (FMI) Kenttärova weather station (Station ID 101987, Figure 1 and Figure 2).
Despite its high latitude, the site is not underlain by permafrost and is frozen only seasonally with complete thaw soon after snowmelt. Soils on the hillslopes consist of glacial till, overlain by organic peat soils up to 3 m deep at the valley bottom peatland. Conifer stands of Norway spruce and Scots pine cover most of the site, except for treeless peatlands dominated by mosses and low sedges.
Snow research at the site does not have the long-term historical data as in Imnavait, but some differences in snow conditions between the sites are evident. First, the tree canopy at Pallas largely inhibits wind transport within the forest, though it does occur on the open mire. The tree canopy also shelters the snow from solar incidence and intercepts falling snow. Second, both snow depth and water equivalent are approximately double at Pallas compared to Imnavait.
2.2. Snow Sampling and Stable Isotope Analysis
2.2.1. Snowfall
Imnavait precipitation samples were captured using an open container (25 cm3) and collected the morning following a snowfall event. Precipitation sampling was conducted 13 km west of the snowpit site at the Toolik field station (68.6611° N, −149.3705° E), and at an altitude of 843 m a.s.l. that is approximately 40 m lower than the lowest elevation snowpit (Figure 1b). Samples were collected from 12 snowfall events out of the 23 days with precipitation recorded at Imnavait meteorological station from the start of snow accumulation to snowpit sampling. The largest data gap occurred between late December 2018 and mid-January 2019.
Pallas precipitation samples were collected using the same equipment setup as for Imnavait, but more opportunistically due to limited field personnel. Sampling was conducted at the field station (68.0257° N, 24,1602° E) 4 km northwest of the snowpit sampling site (Figure 1a), at approximately the same altitude as snowpit 9. We were able to collect 14 samples out of 104 days with recorded snowfall at the Kenttärova meteorological station (Figure 1a) from the start of snow accumulation to snowpit sampling.
2.2.2. Snowpits
Snowpits were sampled in the late 2018–2019 snow season when the majority of the anticipated snowfall had occurred. Sampling was conducted 14–15 March 2019 at Imnavait, and 3–4 April 2019 at Pallas. Different sampling strategies were employed at the two sites due to contrasting snowpack conditions. At Imnavait the sampling protocol was based on snowpit stratigraphy, i.e., samples taken from each visually distinct layer. The Pallas sampling used fixed-depth increments of the snow profile, because a taiga snowpack contains mainly depth hoar (i.e., typically 4–10 mm large, striated, cup-shaped crystals formed within the snowpack by grain-to-grain vapor diffusion; see [81]), which limits the ability to identify individual snow layers, i.e., snowfall events. Therefore, incremental sampling at Pallas facilitated the comparison of profiles between pits.
At Imnavait, ten snowpits were analyzed and sampled. The sampling was conducted along a long-term snow survey monitoring transect [14]. The transect ran perpendicular to valley orientation, starting from the hill crest on the west (Pit 1), crossing the valley bottom, and climbing a west-facing slope to finish atop a water divide on the eastern side of the catchment (Pit 10) (Figure 1). The sampling targeted individual stratigraphic layers in the snow profile that were identified by hand hardness test (subjective, horizontal resistance test of each snowpack layer; see [82]), texture, and visual appearance (e.g., the wind-packed layers appear more bright white and opaque than the coarser glass-like depth hoar layers that are typically found in the bottom). To characterize each layer, we measured the density using density cutters of a 1000 cm3 or 250 cm3 volume (Pedersen et al. [83]) and identified the grain form (i.e., the shape of the snow grain/crystal) per layer according to the international classification of seasonal snow on the ground [81].
After the profile was characterized, depth-integrated samples were taken from each layer using a plastic coring tube. The sampling progressed from top to bottom in the snowpack. At Pallas, nine snowpits were sampled and analyzed. The snowpits were dug along the snow-survey monitoring transect, starting from the hilltop at the Kenttärova station (Pit 1) and ending at the valley bottom (Pit 9) (Figure 1b). The pits were dug at roughly 200 m apart spanning the elevation gradient in the study catchment. The sampling protocol consisted of taking incremental 5 cm snow layer samples using a cubic-shaped 5 cm-deep metal snow sampler. Gaps in the Pallas profiles (Figure 3) are caused by a batch of samples lost in sample processing. Example images of snow pit stratigraphy and sampling strategy for both sites are presented in the Appendix A, Figure A7.
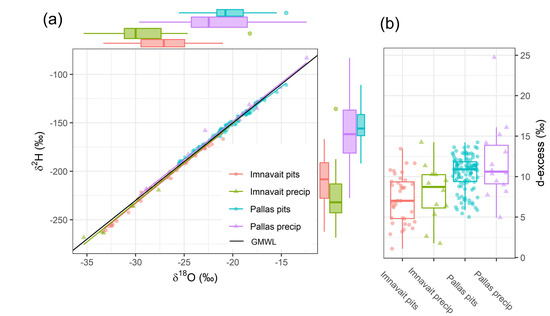
Figure 3.
(a) Dual isotope plot with side panel boxplots and regression lines, and (b) boxplots for d-excess values for snow pit and precipitation samples for Imnavait and Pallas. Note how water line plots depict the generally colder conditions in North Alaska and the lower isotope composition compared to those at Pallas. Slopes and standard errors for regression equations are Imnavait pits: 8.14 ± 0.14, Imnavait precip: 8.13 ± 0.28, Pallas pits: 7.46 ± 0.07, Pallas precip: 7.95 ± 0.28.
2.2.3. Snow Stable Isotope Analysis
All snowfall and snowpit samples were stored initially in the field in zip-lock airtight plastic bags. The bags were transported frozen to the laboratory facility where they were left at room temperature until all snow was melted, typically overnight. The liquid water samples with organic particles were filtered, then transferred to plastic 5 or 15 mL vials, and stored refrigerated at +4 °C until analysis.
Stable isotopes of water were measured at the University of Oulu using laser Cavity Ring-Down Spectroscopy (CRDS) analyzers: Picarro L2130-i and Picarro L2140-i. The Picarro system is composed of an autosampler, a high-precision vaporizer, and a laser CRDS analyzer. Picarro L2130-i and Picarro L2140-i analyzers have guaranteed precision of 0.1 and 0.025‰ for 18O and 0.5 and 0.1‰ for 2H, respectively, satisfied by repeated measurements of standards. All samples were calibrated with two standards USGS45 (−2.2 18O and −10.3 2H) and USGS46 (−29.8 18O and −235.8 2H), and three in-house standards (Hawaii (−0.3 18O and −1 2H), Local Tap Water (−11.2 18O and −84.5 2H), and Viro (−21 18O and −156 2H)) using the post-processing software in L2130-i and L2140-i Picarro analyzers, respectively. In addition to δ-values, we also utilize the secondary parameter deuterium excess (d-excess) calculated as: d-excess = δ2H − 8 × δ18O [84].
2.3. Atmospheric Water Vapor Analysis
Atmospheric water vapor isotope measurements were conducted at both sites simultaneously during winter 2018–2019. At Imnavait, data were retrieved from the on-site National Ecological Observatory Network (NEON) eddy tower at Toolik station (68.66109° N, 149.37047° W, 832 m a.s.l.). The tower sampled ambient air at four heights (10, 20, 30, and 40 m), and here we utilize data from the top collection height for the best estimate of the isotopic composition of the free troposphere prior to (or after) its interaction with the snowpack. At Pallas, measurements were conducted at the FMI Sammaltunturi station (565 m a.s.l., ~280 m above lowest snowpit), approximately 4 km southwest from the snowpit transect (67.9733° N, 24.1157° E). Detailed descriptions of the instrument setup, sampling, and data calibration protocols at each site are presented in Appendix A.
Stable isotope ratios (δ18O and δ2H) were measured at both sites using a Picarro L2130-i Isotope and Gas Concentration Analyzer (herein analyzer) with a Standards Delivery Module (SDM). In summary, ambient air was pumped continuously to the analyzers where isotopic ratios were measured approximately every second (1 Hz). Isotope data were then calibrated using established multi-step protocols [85,86]. First, the humidity-isotope response of each instrument was established in the field to correct for potential analytical bias [86,87,88]. Using an integrated dry air system, the vapor streams of standard waters with a known isotopic composition were measured across a range of controlled humidity injections (Toolik: ~600 to 24,500 ppmv, Pallas: ~400 to 10,000 ppmv) that encompass the range of ambient humidity values during the campaign. Results of the humidity experiments are shown in Figure A1 and Figure A2. A non-linear regression was used to determine the isotope correction as a function of cavity humidity, and applied to the ambient data to remove the humidity bias. Second, ambient measurements were corrected and standardized to the Vienna Standard Mean Ocean Water (VSMOW2) scale. Approximately every 12 h at Pallas and 24 h at Toolik, water standards with a known isotopic composition were injected by the SDM and analyzed to calibrate and monitor for potential instrument drift. At both sites, the analyzer remained stable during the measurement period, with relatively small drifts between successful standard runs that were substantially smaller than the natural variations examined in this study. All ambient and standard measurements were corrected for the humidity concentration dependence, and at both sites, the standard error was estimated at <0.3‰ for δ18O and <1.0‰ for δ2H and d-excess.
Extreme outliers were excluded from our analyses, including d-excess values less than −15‰ and greater than 70‰. Data contaminated by the dry air system used for standard runs (i.e., isotopic values clearly outside the natural range) were also excluded. At Toolik, this included two longer periods between 21 December 2018–4 January 2019 and 29 January–1 February 2019. The 1 Hz isotopic measurements were initially aggregated to 1 min values at Toolik and 5 min values at Pallas. Daily mean isotope values were also calculated at each site for comparing with precipitation isotope data. For full details see Appendix A.
2.4. Synoptic Climatology Analyses
We used the NCEP/NCAR reanalysis dataset [89] to evaluate the broad synoptic-scale atmospheric conditions during the winter 2018–2019 measurement campaign. NCEP/NCAR reanalysis comprises data with 2.5° horizontal grid spacing on 45 vertical levels and are available at 4 h intervals. Here, we used the daily mean 850 mb geopotential heights (i.e., average of the 0z–18z 4 h data) to construct composite maps during all snowfall events sampled at Imnavait and Pallas between 30 October 2018 and 13 March 2019 (Table A1). Daily mean 850 mb vector winds were also used to evaluate the atmospheric transport patterns associated with each individual snowfall event (Appendix A.1, Figure A3 and Figure A4). Additionally, daily mean Arctic sea-ice concentration grids (25 km2 resolution), derived from the Special Sensor Microwave Imager/Sounder (SSMIS), were obtained from the National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC) [90] and used to construct composite sea ice concentration map during the snowfall sampling days.
2.5. Data Analysis and Visualization
Snowpit isotope data are presented as vertical isotope stratigraphy (Figure 4 and Figure 5), where zero represents the base of the snowpack, i.e., the snow–ground interface. To facilitate comparison of vertical isotope variability in snowpits within sites, the snow layer depths were normalized to the total snow depth in each pit. This results in the relative depth of the snow layer within the snowpack (0–100%).
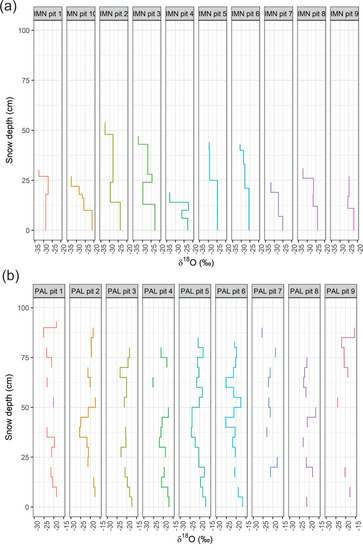
Figure 4.
δ18O profiles for individual snowpits at (a) Imnavait and (b) Pallas. Zero on the y-axis represents the base of the snowpack.
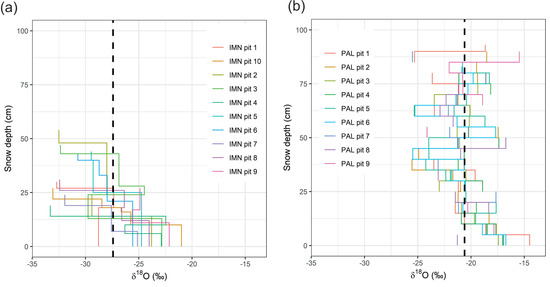
Figure 5.
Snow δ18O and profiles for the sampled snowpits at (a) Imnavait and (b) Pallas. δ18O value in each sample is represented by a vertical line spanning the sampling depth. The dashed line indicates the mean δ18O value of all samples.
To facilitate comparison between precipitation and snowpack, the plotting position for precipitation on the y-axis is calculated as the relative contribution of amount of each snowfall event to the total snow amount. The depth of each precipitation event is recorded as mm snow water equivalent, which is used as the unit of summation. For example, the first two sampled storm events were each 5 mm in magnitude and captured by one snowfall sample (Figure 8a). Each event was comprised of 6.5% of the total 77 mm of accumulated precipitation during the observation period.
The whole profile was normalized to cumulative snowfall, which gives the relative depth of each snowfall event (0–100%) with respect to accumulated snowfall until the sampling. Start and end plotting position of each precipitation sample on the y-axis are given by Equations (1) and (2), respectively.
where:
- ppstart is the y-axis start plotting position in the beginning of the sample i
- ppend is the y-axis end plotting position in the beginning of the sample i
- p is the precipitation amount in sample i (mm)
- n is the number of precipitation events
For vapor data, the plotting position was calculated using the same procedure. The mean vapor value of each day was assigned to the precipitation amount during days with snowfall.
3. Results
3.1. Climate and Snow Conditions at Imnavait and Pallas
At Imnavait, mean air temperature was −12.1 °C during the study period (12 October 2018–15 March 2019). Daily mean values ranged between 2.6 °C and −40.0 °C, and the minimum occurred on 12 January 2019 (Figure 2a). Pallas mean air temperature was −7.7 °C and had fewer extreme variations, with values ranging from 3.0 °C to −26.0 °C, with the temperature minima occurring on 5 February 2019. Air temperature at both sites typically remained below freezing, with a few exceptions in the early snow season in late February 2019 at both sites. Based on snow depth and snowpit data, the few days above 0 °C did not result in significant snowmelt.
Soil temperatures at 5 cm depth showed marked differences between sites (Figure 2b). At Imnavait, soil temperature decreased linearly from −1.0 °C in October to −6.5 °C in mid-January, after which it varied between −6.5 °C and −4.0 °C, and with a seasonal mean value of −3.9 °C. At Pallas, the mean soil temperature was warmer (−0.5 °C) and remained consistent throughout winter. These differences in soil temperature reflect colder air temperature at Imnavait (Figure 2a), coupled with deeper snow cover at Pallas from December onwards (Figure 2c) that effectively insulated and decoupled the soil from cold air temperatures.
We observed a typical snow depth pattern at Imnavait, which is persistently similar between years as reported in previous studies [14,76]. The deeper snow occurred within depositional areas in the bottom of the catchment, whereas shallower snowpacks covered the wind-scoured hillslopes. The snow gauge recorded a depth of 41 cm during the snowpit sampling in April 2019 (Figure 2c), whereas the average across all 10 pits was 34.6 cm (min 19 cm, max 54 cm). The values are below the long-term snow survey value of 50 cm (1985–2017), which is, however, done later in the snow season allowing more snow accumulation [14]. At Pallas, the gauge-recorded snow depth during sampling was 93 cm, below the long-term mean annual maximum snow depth (105 cm, 2007 to 2019). Mean snow depth in pits was 85.1 cm (min 75 cm, max 93 cm). High-resolution snow depth mapping at the site by Meriö et al. [personal communication] showed that snow depth at the automated gauge is consistently higher than that of the rest of the study area, as recorded in the snowpits.
The data indicate that snowfall and snow accumulation started earlier at Imnavait and were consistently increasing during October and November (Figure 2c). From February 2019 onward, the snow depth at Imnavait remained at approximately 40 cm, whereas the snow depth at Pallas increased from 50 to 100 cm between early February and the end of March 2019. Accordingly, a similar evolution was observed for snowfall. Total water equivalent of snowfall received during the observation period was 23.5 mm at Pallas and 77 mm at Imnavait.
3.2. Isotopic Composition of Snowpack and Precipitation
The snow and precipitation δ18O values at Imnavait were lower compared to Pallas (Figure 3a and Table A1). The differences for both δ18O and d-excess were statistically significant between sites (Imnavait and Pallas), but not between snowpit and precipitation samples at either Imnavait or Pallas (Tukey’s post hoc test, p = 0.05). The δ18O composition of snowpit samples at Imnavait were slightly higher (the mean −27.4‰, standard error of the mean ±0.6‰) compared to precipitation (−29.0, ± 1.3‰), but the range in snowpit and precipitation samples was similar (−35 to −20‰) (Figure 3a). At Pallas, the mean δ18O values for snowpit (−20.6, ± 0.2‰) and precipitation (−20.5 ± 1.3‰) were similar, but the range was larger in precipitation (−30 to −12.5‰) than in snowpack (−25 to −15‰). This is despite fewer precipitation samples (n = 14) compared to the number of snow samples (n = 111).
Regression lines (R2 > 0.98) of Imnavait snowpit and precipitation and Pallas precipitation were close to the global meteoric water line (GMWL, δ2H = 8 × δ18O) (Figure 3a), with slopes ± 7.95 to 8.14), whereas the Pallas snowpit regression slope of 7.45 was slightly lower than the GMWL. Both sites exhibited a positive correlation between air temperature and δ18O values (Appendix A, Figure A6). At Pallas we observed a temperature-δ18O slope of 0.60‰/°C for vapor and 0.68‰/°C for snowfall. At Imnavait the temperature-δ18O slopes were lower, with 0.47‰/°C for vapor and 0.09‰/°C for snowfall.
The d-excess values at Imnavait ranged between 0 and 15‰ in both the snowpack and precipitation, with mean values of 7.3 and 8.0‰, respectively. However, the median d-excess was lower in the pit samples compared with precipitation with an offset of 1.7‰ (Figure 3b). At Pallas, mean snowpack and precipitation d-excess values were 10.4 and 11.2‰, respectively, and collectively ranged between 5 and 17‰. Overall, the Pallas d-excess values median and range between precipitation and pits were similar, with an offset of 0.3‰.
3.3. Isotope Stratigraphy in the Snowpits
Figure 4 illustrates the high variability in δ18O between the snowpit profiles at both Imnavait and Pallas. Snow depth at Imnavait was lower and more variable among individual pits compared to at Pallas. The δ2H values in snowpit profiles are shown in Appendix A, Figure A5. Because δ18O and δ2H values are closely correlated (Figure 3a) and visually difficult to find any differences in the profile plots, we present only the δ18O and d-excess values in the subsequent plots.
To facilitate comparison within and among sites, in Figure 5 we also present combined snowpit profiles. At both sites we found an overall lowering δ18O trend with increasing depth (Figure 5). At Pallas, the typical range in isotope variability between pits at all depths is ~5‰, with higher variability observed closer to the top in the snow profiles (above 50 cm snow depth). At Imnavait, the first 10 cm at the base of the profiles has consistently higher δ18O values compared to the top of the snowpack. Variability in δ18O values increases above the snow depth of ~10 cm, without any clear patterns or trend as a function of snow depth.
Isotope stratigraphy of snow pits at Imnavait is highlighted by plotting snowpack isotope samples in each snowpit relative to the maximum snow depth of the pit and visualizing snow density (Figure 6a), and grouping samples based on their snow grain type (Figure 7). The top of the snowpack (~75–100% of total depth) comprised low-density snow (~100 kg m−3) with low δ18O values, most less than −30‰ (Figure 6a). The middle of the snowpack (~25–75% of total depth) consisted of a high density (~300–400 kg m−3) layer where the δ18O values varied between −25 and −30‰. The base of the snowpack (~0–25% of total depth) consisted of a moderate dense (~200 kg m−3) layer, where the snow δ18O values were higher relative to layers above it, with most samples ranging between −20 to −25‰. One of the key factors that appears to explain the δ18O values of snow is the grain type (Figure 7). For instance, at Imnavait rounded-grain snow crystals found in the upper layers of the snowpack had typically low δ18O values compared to those in lower layers of the snowpack (“wind packed” or “depth hoar”), differing by up to 20‰. Plots of the snow profile isotopes relative to total depth at Pallas (Figure 6b) did not reveal much more consistency in the layering compared to absolute snow depth (Figure 5b).
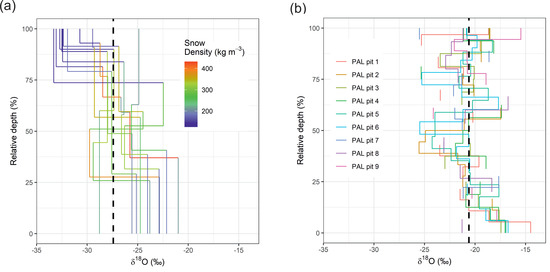
Figure 6.
Snow layer δ18O as a function of relative depth in each snowpit for (a) Imnavait and (b) Pallas. Snow density in layers is visualized for Imnavait. Dashed line indicates the mean δ18O value for all samples.
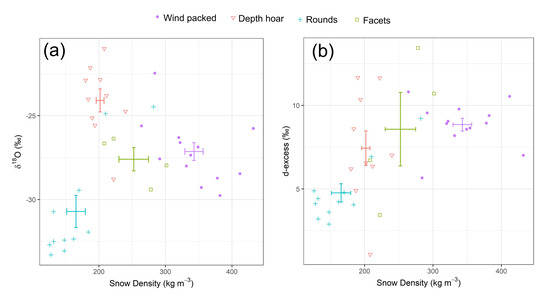
Figure 7.
(a) δ18O and (b) d-excess for Imnavait snowpack samples as a function of snow density, grouped by snow grain type. The error bars display the mean, and the standard error of the mean, for each group.Examining snow layer d-excess values as a function of normalized snow depth (Figure 8), in addition to grain type and density (Figure 7b), indicates that at Imnavait there is less consistency in d-excess values at different depths of the snow profile compared to δ18O (Figure 8a). Only the top layer in the snowpack shows consistent d-excess values. However, when the data are grouped by grain type and plotted in density–d-excess space (Figure 7b), it becomes apparent that the recent storm (rounds) and the high-density wind packed layer are clustered between 3–5‰ and 8–11‰ in d-excess, respectively. To the contrary, the metamorphosed snow layers (depth hoar, facets) are more variable in their d-excess and equally distributed between 0 and 13‰ (Figure 7b). At Pallas, there is higher variability in d-excess values at the base (0–25%) and top (75–100%) of the snow profiles, with d-excess values more uniform in the middle of the snowpack (25–75%). This stratigraphic pattern contrasts with the δ18O variability in the profile, where values at the base of the snowpack were the most consistent (Figure 6b).
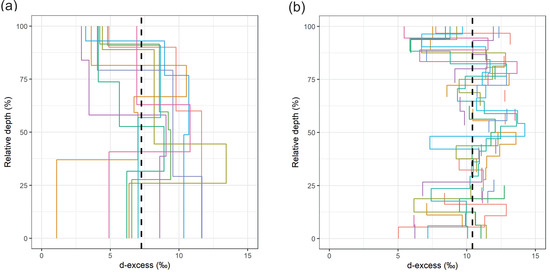
Figure 8.
Snow layer d-excess as a function of relative depth for (a) Imnavait and (b) Pallas. Dashed lines indicate the mean d-excess value for all samples.
At Imnavait the early season precipitation (30% of total snowfall, occurring between October and December 2018) had δ18O values that ranged between −26 and −30‰ (Figure 9a). However, the corresponding snowpit samples at the base of the snowpack exhibit higher δ18O values (−20 and −25‰). Gaps in precipitation sampling in the middle of the season, corresponding to the wind-packed snow layers in the middle of the snowpack, did not allow reliable comparison between precipitation and snow layers. The two storms which were sampled (~40–50% of total snowfall) were characterized by lower δ18O values relative to the corresponding snow layers, similarly to the early season storms. Snow sampled from the top of the snowpack on 14–15 March 2018 exhibited δ18O values between −33 and −30‰, consistent with snowfall δ18O values (−33.3‰) sampled from a precipitation event on the 11 and 12 March (Figure 9a).
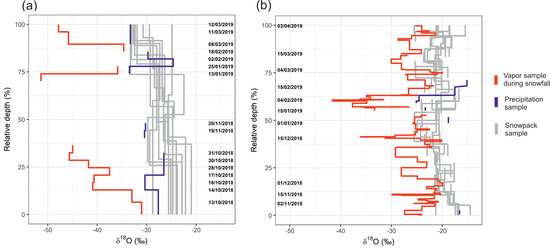
Figure 9.
Accumulated vapor δ18O composition (red) during days with snowfall and accumulated precipitation δ18O profiles (blue) superimposed on the snowpack δ18O profiles (gray). Gaps in the precipitation and vapor records are indicative of snowfall events in the meteorological record, which were not sampled. Dates on the vertical axes for (a) Imnavait specify days when precipitation or vapor samples were collected and for (b) Pallas indicate the timeline of snow accumulation and vapor sampling approximately every two weeks.
Imnavait atmospheric vapor δ18O values were low relative to the corresponding daily precipitation and snowpack values, with mean values of −40.8, −29.4, and −27.4‰ respectively (Figure 9a). In the early snow season (~<30% of total snowfall), the vapor δ18O composition showed a gradual lowering trend from −30 to −45‰ (Figure 9a). The vapor δ18O composition during the most recent snowfall (12 and 13 March) was among the lowest measured during the campaign (~−48‰), as was precipitation (~−34‰).
Due to logistical constraints, Pallas precipitation samples were only collected during mid-winter (events that contributed 40–65% of the total cumulative snowfall) (Figure 8b). The δ18O composition of these events was comparable to values observed in the middle of the Pallas snowpack, but with higher variability in the precipitation samples. The few precipitation samples over the season precluded rigorous comparison with the rest of snow isotope profiles. The Pallas vapor δ18O composition was consistently lower compared to the precipitation and snowpack, (respective means −28.0, −20.4, and −20.6‰, Figure 9b). Unlike Imnavait, the vapor and snow δ18O values were less offset, at some points overlapping with the snow profile. The snow profiles and vapor record showed similar isotope dynamics. Both transitioned from relatively high to low δ18O values from early to mid-season (0–60% of normalized snow profiles and vapor composition of snowfall days). In the top profile (60–100%), both the snow and vapor isotope composition remain variable but relatively constant vertically.
The method for comparing the snowpack, atmospheric water vapor, and precipitation d-excess values presented in Figure 10, is defined in Equation (1). At Imnavait, the range of d-excess values was similar in both precipitation and the snow profile. Only the top layer in the snowpack clearly reflects the d-excess values in the most recent precipitation event on 13 March 2019 (Figure 10a). The d-excess values in the vapor were distinctly offset from both snowpit and precipitation samples, particularly for the most recent event where precipitation and snow d-excess values ranged between 0 and 5‰, and vapor between 30 and 33‰.
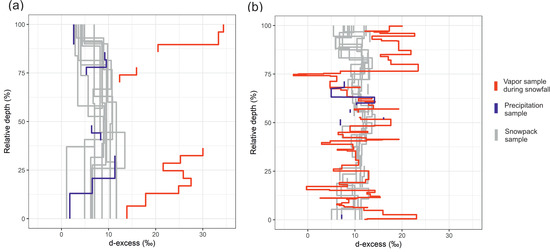
Figure 10.
Accumulated atmospheric vapor d-excess composition (red) during days with snowfall and accumulated precipitation isotope profiles (blue) superimposed on the snowpack isotope profiles (gray) for (a) Imnavait and (b) Pallas.
At Pallas, a few precipitation samples exhibited d-excess values similar to those recorded in the snowpack at corresponding depths (Figure 10b). Moreover, we found that the snowpack d-excess profile from 0 to 75% of snow depth closely followed the vapor isotope composition during snowfall days. Even though the overall trends were similar, the snowpack samples were less variable than the corresponding storm day vapor composition. Vapor d-excess composition during snowfall events that comprised 75–100% of the total snowfall (corresponding to events after the beginning of March) was between 12 and 24‰, which were higher compared to the top 75–100% of the snowpack, with values between 5 and 13‰.
3.4. Synoptic-Scale Moisture Transport and Isotope Hydrology
Composite maps depicting the mean synoptic climatology during the sampled snowfall events are presented in Figure 11, and individual event-based maps are shown in Figure A3 and Figure A4. In the western Arctic, daily composited 850 mb geopotential heights indicate a large, elongated region of low pressure centered over the Bering Sea region during the Imnavait snowfall events (Figure 11). The net result was strong westerly and southwesterly winds that typically tracked from the North Pacific and across the Gulf of Alaska or Bering Sea, from where air masses transited across continental Alaska to Imnavait (Figure A3). Individual event-based wind vector analyses indicate that these circulation patterns were associated with snowfall characterized by a range of isotope values between −18.2 and −35.3‰ for δ18O, and 1.8 and 14.2‰ for d-excess (Table A1). The final snowfall event sampled at Imnavait on 13 March 2019 reflected the convergence of strong southerly airflow with northeasterly winds from the Beaufort Sea (Figure A3). The event was associated with snowfall characterized by δ18O and d-excess values of −33.3 and 2.6‰, respectively. Overall, we found that mean sea ice concentration in the western Arctic was high during the 2018–2019 measurement campaign, with mean ice cover in the Beaufort and Chukchi Seas at 93 and 60%, respectively, during the snowfall sampling days at Imnavait (Figure 11).
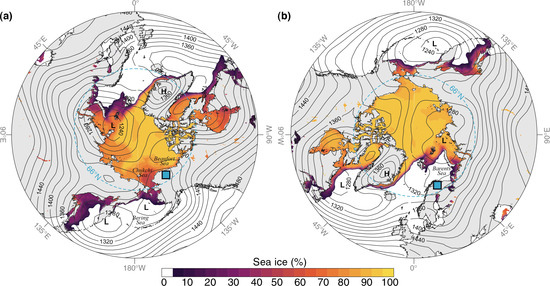
Figure 11.
Daily mean climatology composites of the snowfall sampling days at (a) Imnavait and (b) Pallas (blue squares) during the winter 2018–2019 measurement campaign. Contour lines depict mean 850 mb geopotential heights with the dominant low (L) and high (H) pressure centers [89], and the shaded region represents daily mean composited sea ice concentration during the corresponding snowfall sampling days [90]. The dashed blue circle depicts the Arctic Circle at ~66° N. Sampling dates used to construct the composite maps are given in Table A1.
In the eastern Arctic we observed a different synoptic configuration during the snowfall events sampled at Pallas. Daily composited 850 mb geopotential heights indicate a large area of low pressure centered over the Barents-Kara Sea region coupled with relatively high surface pressure in the North Atlantic (Figure 11). This configuration resulted in prevailing west-southwesterly and southerly airflow that transported air masses to Pallas from the North Atlantic region (~80% of the snowfall events) (Figure A4). Additionally, ~20% of the winter 2018–2019 snowfall events we sampled derived from cyclonic north-northwesterly air masses that flowed across the Norwegian and Barents Seas (Figure A4). Individual event-based wind vector analyses indicate that Pallas winter snowfall events deriving from Atlantic air masses were characterized by mean δ18O and d-excess values of −20.9 and 9.8‰, respectively, whereas the northerly air masses delivered snowfall with relatively higher mean δ18O and d-excess values of −17.6 and 20.4‰, respectively (Table A1). Overall, compared to the western Arctic we found that regional sea ice concentration in the eastern Arctic was relatively low during the 2018–2019 measurement campaign, with ~22% mean ice coverage in the Barents Sea during the snowfall sampling days (Figure 11).
4. Discussion
4.1. Isotope Fractionation in the Snowpack
We found that the atmospheric vapor δ18O at the sites was low relative to the corresponding daily precipitation and snowpack values. The average differences between vapor and precipitation were 11.4 and 7.6‰, and vapor and snowpack were 13.4 and 7.4‰ for Imnavait and Pallas, respectively (Figure 4), and consistent with those observed in other regions of the Arctic [12,91]. These differences reflect equilibrium fractionation during phase change, which results in isotopic enrichment in heavy isotopes in the solid phase relative to vapor. Modeled equilibrium vapor-ice fractionation at Imnavait and Pallas average air temperatures (−12.1 and −7.7 °C) using fractionation factors 1.0166 and 1.0159 [92], respectively, results in average vapor-ice fractionation of 16.1‰ at Imnavait and 15.4‰ at Pallas. The observed differences are lower than the modeled ones, for Pallas in particular, suggesting non-equilibrium conditions during condensation, post-depositional isotope modification, or both.
There are both similarities and differences in post-depositional isotope modification between the western and the eastern Arctic. At both sites there is a general tendency that the base of the snowpack has higher δ18O values compared to the top (Figure 5 and Figure 6). This pattern is likely in part due to the seasonality effect [84]; temperatures of snowfall early in the winter (October and November) occur under warmer temperatures and from moisture sources with warmer water temperatures compared to mid- and late winter (December, January, February and March) when snowfall occurs at lower temperatures (Figure 2) [5]. The seasonality effect is corroborated by the positive correlation between air temperature and isotope values in both precipitation and vapor samples at both sites (Figure A6). The seasonality effect is evident at the Pallas site in particular, when comparing the snow isotope profile with atmospheric vapor isotopes during days of snowfall (Figure 9b). Both snowpack and vapor isotope composition gradually shift from higher to lower δ18O values as the winter advances. This enforces the observation that snowpack may provide an isotope proxy of seasonality in moisture sources in seasonal snowpacks.
At Imnavait, samples of early season precipitation enabled direct comparison of precipitation with the base of snowpack (Figure 9a). The comparison showed that the snowpack base was characterized by higher δ18O values compared to the corresponding precipitation events. This suggests that the seasonal isotope signal was not preserved within the snowpack, and there was post-depositional enrichment of the heavy isotopes over winter. Heavy isotope enrichment of basal snow layers has previously been attributed to soil water diffusion into the snowpack over winter, and molecular diffusion in vapor transport through the snowpack. Friedman [58] and Sturm and Benson [56] showed how preventing soil water from diffusing into the snowpack resulted in lower isotope values at the base of the snowpack compared to a undisturbed reference snowpack. Sinclair and Marshall [47] found that the base of snowpacks on a glacial moraine had higher isotope values compared with snowpacks on the glaciers, and attributed this to soil water availability of the moraine snowpacks. At Imnavait, the shallow tundra snowpack had strong temperature gradients between soil and air (Figure 2) inducing vapor movement through the snowpack [56], as evidenced by the depth hoar layers (Figure 6 and Figure 7). It is therefore very likely that the higher isotope values at the base of the Imnavait snowpack are not only explained solely by seasonality, but also isotope modification and interaction with soil water over the winter. In the boreal snowpack at Pallas, such comparison was not available due to paucity of data (Figure 9b), but the two sampled early season snowfall samples did not indicate a clear shift like that in Imnavait tundra snow.
At Imnavait, the snowpack is characterized by higher δ18O values relative to snowfall at the site, and more so than at Pallas (Figure 3). In addition to the discussed potential soil water–snowpack interaction in tundra snow, the differences between snowfall and snowpack can be indicative of sublimation and evaporation isotope fractionation. In general, conditions become more favorable for sublimation in high wind speeds, low air relative humidity, and higher solar insolation [93]. When comparing the two sites (Figure 2), Imnavait experienced higher wind speeds (mean 3.3 m/s, standard error of the mean ± 0.2 m/s) compared to Pallas (2.7 ± 0.1 m/s), and a more variable wind regime with more days of both low and high winds (Figure 2e). Wind transport is known to intensively redistribute snow at the site [75,76]. Relative humidity was on average higher at Pallas (86.8 ± 0.7%) in comparison to Imnavait (72.4 ± 0.9%) (Figure 2g). The Pallas site is dominated by conifer canopies, which reduces wind transport, provides shading from solar insolation, and increases relative humidity at the snow-atmosphere interface.
The most recent precipitation event prior to snowpit sampling at Imnavait provided key insights to potential snow isotope fractionation due to snow sublimation during wind transport. Surface snow in all pits had δ18O values that were consistently higher compared to the precipitation event less than two days prior to the snowpit sampling (Figure 9a). One explanation is that sublimation, enhanced by wind transport, immediately fractionated the fresh snow during the two days between the storm and the pit sampling. At Pallas, isotope values of the most recent snow event of ~6 mm (2–3 April 2019, i.e., one day before snowpit sampling) was not clearly identifiable at the top of snow pits. This may be due to different sampling strategies between the sites. At Pallas the constant sampling interval of 5 cm was likely to capture snow also from earlier storms. At Imnavait the sampling was based on stratigraphy, where the most recent storm created a low-density layer that was sampled as whole (see Figure A7).
Snowpack samples at both sites lie close to the GMWL, with a δ2H–δ18O slope near 8 (Figure 3). Experimental and field studies have found δ2H–δ18O slopes of ~5–6 in snowpacks undergoing kinetic sublimation fractionation [9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95], whereas the slope in our snow samples was close to 8, resembling the GMWL. Only the Pallas snowpit samples had a slope lower than the GMWL, which could indicate kinetic fractionation. The lack of kinetic fractionation signal was particularly surprising at Imnavait tundra snowpack, where modeling by Liston and Sturm (1998) estimated 9–22% of the Imnavait snowfall precipitation input to sublime, with higher sublimation rates on wind-scoured hillslopes. The lack of kinetic fractionation signal in Imnavait snow samples could be explained by whole-grain ice-vapor transition in blowing snow [58], in which the whole snow grain sublimates and does not leave a residual higher δ18O in the remaining snowpack. This would result in isotope values similar to equilibrium fractionation, i.e., proportional change in both δ2H and δ18O isotope, as suggested by the Imnavait surface snow layer and snowfall comparison.
4.2. Contrasting d-excess Values in Snowpack and Vapor between Sites
Comparing d-excess values between vapor, precipitation, and snowpack provided an additional tracer to understand the isotope fractionation processes in the seasonal snowpack. Condensation of vapor to rain or snowfall is generally considered an equilibrium fractionation process [84]. Even though equilibrium fractionation results in enrichment in heavy isotopes from vapor to liquid/solid phase, the d-excess parameter should remain largely unchanged from vapor to precipitation and snowpack. This model generally seemed to be the case at Pallas (Figure 10b), but surprisingly not at Imnavait (Figure 10a).
At Imnavait, the vapor d-excess values were substantially higher compared to snowpack and precipitation d-excess values. Precipitation d-excess values had a similar range as the snowpack samples (Figure 10a), but individual snow layers d-excess values did not clearly resemble those in the precipitation. Only the top of the snowpack clearly reflected d-excess values from the recent snowfall event (as for δ18O in Figure 9a). One possible reason for the difference between vapor to precipitation and snow is that the strong winds at the Imnavait site caused some fractionation in the precipitated snow before the actual sampling.
At Pallas, vapor d-excess was more variable compared to snowpits or precipitation profiles but, unlike at Imnavait, the trend and central values in vapor d-excess resembled the snowpack d-excess remarkably well between 0 and 75% of the total snow depth (Figure 10b). Interestingly, the d-excess values in vapor during snowfall days were higher compared to the snowpack profile in the late winter (>75% of total snowfall/precipitation). Shortwave radiation at the site increases rapidly at the sites in late winter, and the Pallas sampling was conducted three weeks later in spring 2019 (Figure 3f). Increased radiation load can enhance snow sublimation with kinetic isotope fractionation, leading to lower d-excess values in the remaining snowpack [51,96], which may in part explain the difference in Pallas vapor and snowpack d-excess in the late winter.
4.3. Regional Drivers of Snow Amount and Snowpack Isotope Signatures
Collectively, our analyses indicate that synoptic-scale atmospheric circulation is a key driver of the source, amount, and isotopic composition of accumulated snowfall in Arctic snowpacks. Overall, Pallas received approximately twice as much snow compared to Imnavait in winter 2018–2019 (Figure 2). We propose this phenomenon can be partly attributed to regional differences in sea ice cover and thus the availability of open (ice-free) sources of atmospheric moisture. For example, the Beaufort and Chukchi Seas that surround northern Alaska were ice-covered for the duration of our winter 2018–2019 measurement campaign, thus limiting the availability and transport of atmospheric vapor from the north [12]. Consequently, our atmospheric transport analyses indicate that all snowfall events collected at Imnavait were associated with prevailing southerly air masses from the North Pacific region (Figure 11). To the contrary, in the western Arctic, large areas of the Barents Sea to the north of Scandinavia remained ice-free throughout winter 2018–2019 and, together with the Norwegian Sea, provided a constant source of evaporative moisture that could be transported to Pallas and condense as snowfall [13,97,98]. Such differences are also evident when comparing the winter 2018–2019 relative humidity data between sites, with Imnavait characterized by considerably lower relative humidity, overall, compared to Pallas (Figure 2g). These major differences in the distribution of Arctic sea-ice, and thus the availability of evaporative sources of atmospheric moisture for precipitation, are becoming increasingly evident [7,44,91,99], and reflect complex patterns of atmospheric moisture transport into, within, and out of the Arctic [100].
We propose that the higher variability in δ18O values at Pallas (Figure 3a) reflects these differences in air mass transport trajectories, together with a wider variety of oceanic vapor source regions that feed continental precipitation. For example, at Pallas the winter snowfall events during 2018–2019 are sourced from air masses transported across the Barents, Norwegian, Atlantic, and Baltic Seas, and continental areas of Eurasia (Appendix A, Figure A4). Alternatively, in Alaska our analyses indicate that nearly all air masses derived from the North Pacific/Gulf of Alaska region. Thus, moisture transported by the air mass to Imnavait is characterized by less isotopic variability, but there is also significant isotopic fractionation along this storm track.
These differences in air mass transport regimes are reflected in the overall tendency for Imnavait vapor and snowfall to be characterized by moisture with δ18O values ~5‰ lower than at Pallas. This includes (1) south to north fractionation effects with this snow delivery pathway over the Alaskan landmass (continental effect) [12,35,42,43,101], and (2) moisture transport with further altitudinal fractionation over the Alaska Range (altitudinal effect). To the contrary, the relatively close proximity of the Barents and Norwegian Seas to Pallas, coupled with the overall lower topography of Scandinavia compared to Alaska, means that moist air masses are subject to less rain-out and distillation effects during transit, and thus the Pallas vapor, snowfall, and snowpack are all characterized by relatively higher δ18O values compared to those at Imnavait (Figure 9).
4.4. Uncertainties and Wider Implications
The ranges of typical snow δ18O values between the different snowpits at any given depth were 2–5‰ for Pallas and 5–10‰ for Imnavait (Figure 5 and Figure 6). Most existing studies have used a single or a few snow profiles to characterize the regions’ snowpack isotopically [56,65,66,102]. However, our analyses indicate that this limited sampling may be misleading. By sampling multiple snowpits, as in our study, common patterns in the regional snow isotope profiles start to emerge, but there is still pronounced spatial variability among pits (Figure 6). The 5 cm incremental sampling at Pallas allowed better vertical isotope resolution for comparison between pits, which was lost in layer-based sampling at Imnavait. High-frequency incremental sampling with detailed physical snow layer analysis would be the optimal strategy, however, it is work-intensive to sample multiple pits. For a reliable comparison of snowpit isotope stratigraphy with vapor or precipitation records in Arctic snowpacks, we recommend sampling multiple snowpits. Challenging field conditions and remote locations of our Arctic study sites produced unfortunate gaps in both precipitation time series and snowpit profiles. Complete records of vapor, precipitation, and snow profiles are needed to further validate some of our findings.
Our data showed significant isotope variability in snow profiles at short 1–2 km proximity. In contrast, Sinclair and Marshall [47] showed fair agreement in snow isotope stratigraphy in two snowpits 160 km apart in the Canadian Rocky Mountains. Their high-altitude maritime snowpacks had approximately five times the snow compared to Pallas, making the isotope stratigraphy deposited from each large synoptic snowfall event more distinguishable. Guided by their findings, depositional areas of snow might prove useful for sampling snowpack isotope profiles for proxy moisture sources. In tundra snowpacks experiencing significant wind transport, such areas could be natural (lee slopes) or manmade (snow fences).
Our vapor–precipitation–snowpack comparison is complicated by the implicit assumption in Equation (1) that each deposited snow layer preserved its depth over the winter. In reality, snowpack densification is likely to compact the lower snowpack layers relative to the top [56]. This could be addressed by simulating snow layer evolution with physically based snowpack modeling in which snow layer densification is explicitly represented [103]. Frequent storms depositing the snow layers at Pallas (Figure 2d, Figure 9a) and the marked spatial variability in total snow depth and layering at Imnavait (Figure 4a) would complicate any explicit snow layer simulations and layer identification, but this should be further explored.
Isotope diffusion models offer another potential simulation tool to make snowpit and atmospheric isotope data more comparable [48]. The paleoclimate community has highlighted the importance of post-depositional processes modifying the original snow isotope signature in ice and firn profiles [104,105,106]. These isotope modifications may cascade into uncertainties in ice core isotope profiles used for paleoclimate reconstruction. Isotope diffusion models have been successfully used to reproduce the observed diffusive smearing in the multi-season firn and ice-water isotope profile [47,68]. However, model equations and boundary conditions are designed for deep firn and ice profiles (meters to tens of meters). The applicability of firn isotope diffusion models to tundra or taiga snowpacks with high temperature gradients and additional water source from underlying soil needs to be tested.
Post-depositional modification of water isotopes in natural snowpacks has been simulated from the perspective of ice-water isotope exchange (hydrological scope, see, e.g., [53,65,107]) and ice-vapor isotope exchange (paleoclimate scope, see e.g., [47,48,68]. However, the existing models are not suited to capture key processes causing isotope evolution in Arctic seasonal snow layers: vapor diffusion from soil to snowpack, and isotope fractionation during sublimation. A way forward could be the introduction of isotope simulation routines into physically based snow models already characterizing the water fluxes (vapor flow, sublimation) and snow densification [103,107,108].
As the New Arctic is upon us, with shifting moisture source transport, the use of isotope stratigraphy in snowpacks as seasonal reservoirs of water isotopes can help to document how these shifts are manifested across the north. Robust moisture source trajectory modeling coupled with a pan-Arctic snowpack isotope dataset could help understand the differential influence of important factors, such as sea ice retreat on water movement across the Arctic. Snowpack isotope sampling in the late snow season could allow moisture proxies over larger spatial gradients than possible with fixed liquid and vapor water isotope sample locations.
5. Conclusions
Our analyses indicate that both the total amount of snow and isotope values in Arctic snowpacks are influenced by synoptic-scale atmospheric circulation. Our atmospheric transport analyses associated western Arctic tundra snow with prevailing southerly air masses from the Gulf of Alaska region, and eastern Arctic taiga snowpack with more variable transport regimes, and thus more variable sources of atmospheric moisture. The differences in source areas were seen in the relatively higher δ18O in the eastern Arctic snow.
Our intensive in situ atmospheric vapor isotope monitoring allowed comparison of snowpit isotope stratigraphy and meteoric isotope values. The analysis suggested the variability atmospheric moisture sources over winter were to some extent recorded in our eastern Arctic taiga snow profile. Our western Arctic tundra snowpack profile experienced more post-depositional isotope modification, complicating the use of tundra snow profiles as a proxy for seasonal evolution in moisture sources. We propose that isotope studies in tundra snow could be further advanced by using different sampling strategies and numerical modeling.
Whilst these findings also have critical implications for proxy-based studies that assume isotopic preservation within individual snow/firn layers, our analyses suggest that the isotopic composition of seasonal snowpacks in spring may still provide insight to understanding winter snow processes. Overall, our results present the potential seasonal snowpack isotope records for moisture source attribution in remote regions, where continuous sampling of precipitation or atmospheric vapor is not feasible.
This interdisciplinary study is laying the foundation for a completely new era in the Arctic earth sciences because it couples programs in Atmospheric circulation patterns, sea Ice traits, moisture transport pathways, Snow pack structure, and snow’s ability to record these processes in its water Isotope properties (AISI). The degree to which these AISI interactions are stored in snow packs, and can be retrospectively recovered across the Arctic, will require a coordinated, synchronized pan-Arctic program of research that would allow validation and model development. AISI interactions would include sampling in permanent snow fields that records multiple years of winter and samples from glaciers on Svalbard, in Alaska, and on the Greenland Ice Sheet. These comparative studies would benefit from in situ water vapor isotope measurements [55,99,109] and event-based sampling of snow across the entire Arctic [110].
Author Contributions
All authors contributed intellectually to the framework, interpretation of the data and the manuscript writing and editing. Collected and processed the snow pit data in Imnavait Alaska, compiled the snow isotope dataset, led the isotope data analysis and manuscript writing, P.A.-a.; conceptualized the study, designed the sampling setup, collected precipitation isotope samples, J.M.W.; performed atmospheric and sea ice analyses, H.B.; organized the Alaska winter field program, S.H.P.; installed Pallas atmospheric vapor instrumentation, E.K.; provided water vapor isotope data for N Alaska, B.K.; measured precipitation isotope samples, M.M.; organized Pallas snow precipitation data collection and atmospheric vapor analysis, K.-R.M.; conducted field sampling of snow isotopes in Finland, K.N.; organized snow isotope data collection in Finland, H.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by an Academy of Finland grants 316349 and 316014 awarded to P. Ala-aho and J.M. Welker, respectively. In addition, support was provided by the NSF Arctic System Science project (1604249) and the University of the Arctic (UArctic) Research Chairship awarded to J.M.W.
Data Availability Statement
Climate data for the study sites are available in the publicly accessible repository cited in the paper. Isotope data are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge Juha Hatakka and the Finnish Meteorological Institute and staff working at the stations in Pallas-Yllästunturi National Park. Valtteri Hyöky helped maintain the Picarro vapor instrumentation at Pallas and assisted with the humidity-isotope calibrations. Tarja Törmänen and Aino Erkinaro assisted with sample analysis at the University of Oulu. Kaj Lynoe and Jari-Pekka Nousu assisted in snowpit field campaigns. This material is based in part upon work supported by the National Science Foundation through the NEON (National Ecological Observatory Network) Program. A special thanks to Chris Florian, Natchaya Durden, and Hongyan Luo for their support on NEON instrument quality control and data processing.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Appendix A
This Appendix includes a description of the atmospheric stable isotope analyses at Imnavait and Pallas, in addition to Figure A1, Figure A2, Figure A3, Figure A4, Figure A5, Figure A6 and Figure A7 and Table A1 related to the supporting text and the main manuscript.
Appendix A.1. Imnavait, U.S.A.
Water vapor isotope composition was measured as a part of the National Ecological Observatory Network (NEON). A Picarro L2130-i has been operated nearly continuously at the Toolik field station since the beginning of September 2017. The analyzer is connected to a network of tubing on the eddy tower that enables ambient air to be sampled at four heights—10, 20, 30, and 40 m. For the analysis presented in this study, we examined only the isotopic measurements from the top collection height of 40 m. By limiting data to this height, we attempted to obtain a best estimate of the isotopic composition of the free troposphere prior to (or after) its interaction with the snow pack. At regular intervals, the L2130-i switches between sampling mode, which samples the ambient air, and field validation mode, which uses a set of known liquid water standards to ensure consistency and accuracy in the measurements. During sampling mode, air is pumped for 9 min. One minute between each measurement is used for solenoid switching and purging the instrument, and for stabilization of the instrument. A Standards Delivery Module (SDM) regularly injects three water standards into the L2130-i to validate isotopic measurements that cover much of the range of natural variability. Standards for validating isotope measurements were: Low (δ18O = −27.77‰ and δD = −217.67), Med (δ18O = −18.38‰ and δ2H = −136.52), and High (δ18O = −4.22‰ and δ2H = −29.18). The standards were run approximately every 24 h. A dry air system is connected to the SDM to dilute water vapor concentrations to replicate natural concentrations. Although instrument drift does not have a significant impact on the instrument measurements, it is well known that there is an instrument bias presented by the humidity of the air being measured, particularly at low humidity values [86,87,88]. Because of this effect, isotopic measurements must be corrected based on their humidity.
NEON personnel conducted humidity bias experiments on the Toolik Picarro on 5 September 2019 using the Med standard (δ18O = −18.38‰ and δ2H = −136.52). The standard water was injected for 5 min into dry air of 13 different flow rates to measure standard values across a range from 600 to 24,500 ppmv. These water vapor concentrations were computed from the NEON output variable “rtioMoleWetH2o”, which is the equivalent to the Picarro measured water vapor ppmv/1,000,000. The 1Hz measurements of H2O concentration, δ18O, and δ2H were aggregated to 1-min resolution, and the standard deviation of these 1 Hz measurements was also calculated for each 1-min window. Because it takes time for the instrument to stabilize following a change of the input gas, we used these standard deviation values to ensure a proper stabilization was reached. These criteria include the 1-min H2O concentration standard deviation being less than 25 ppmv and the change of the log10(H2O) ppmv from one minute to the next being less than 0.02. Data that meet those criteria are plotted in Figure A1, where we show the relationship between δ18O vs. log10(H2O) (Figure A1a) and δ2H vs. log10(H2O) (Figure A1b). Strongly significant relationships are observed for each isotope ratio, and it can be seen that there is significant bias in the low humidity measurements, whereas when the humidity decreases, the δ18O and δ2H measurements become artificially depleted. The 2nd order polynomial equation fitted in Figure A1 was applied to the ambient air measurements to remove the humidity bias. This experiment was conducted from ~600 to 24,500 ppm. Although it is possible that the humidity bias changed over time, this pattern is quite common across Picarro devices, thus we assume that a correction based on this experiment is reasonable for the full dataset and does not introduce new sources of significant error (i.e., these errors are not larger than the humidity bias itself).
Based on examination of the data and the typical low water content of the air at Toolik (mean H2O concentration for this measurement period was 2200 ppm), we also exclude the first of the nine minutes of a given measurement height to account for extra necessary stabilization time. The 1 Hz isotopic measurements area initially aggregated to 1-min values. The humidity bias correction determined in Figure A1 was applied to this data, which has the effect of increasing δ18O and δ2H values at low H2O concentrations. Extreme d-excess outliers were excluded from this analysis at this point, including values less than −15‰ and greater than 70‰. Data that were clearly contaminated by the dry air system used for standard runs (i.e., isotopic values clearly outside the natural range) were also excluded from this analysis. This included two longer periods (21 December 2018–4 January 2019, 29 January 2019–1 February 2019) and several short-term intervals (i.e., several minutes/hours).
After quality assurance and controls, this 1-min data was aggregated to a daily average. Typically, over 300 min of sampling that was distributed evenly across the day in the series of 9-min intervals was compiled in a given day, providing a relatively robust approximation of the daily average. The standard error of daily aggregated data was generally <0.2‰ for δ18O and <1‰ for δ2H and d-excess. The humidity correction was only calibrated to measurements down to 600 ppm, so isotopic measurements at H2O concentrations below that exhibit additional possible uncertainty. Given the strength of the relationship in Figure A1, it is likely that this uncertainty is still rather low compared to the natural variability, but it should be considered possible that there are unknown uncertainties at these low humidity time periods. Due to a number of instrument issues and the challenges of setting up the large number and spatially diverse NEON sites, standard runs did not occur consistently across the measurement period, particularly for the window of this study (October 2018–March 2019). However, when standards were run, it can be observed that the Picarro L2130-i was quite stable over the measurement period, with relatively small drifts between successful standard runs. These drift values were substantially smaller than the natural variations examined in this study.
Appendix A.2. Pallas, Finland
At Pallas, atmospheric vapour isotopes and mixing ratios were measured at the FMI Sammaltunturi station (67.973° N, 24.116° E; 565 m asl). The Picarro L2130-i and SDM has been installed inside the station building since mid-December 2017 and is connected to the FMI common sampling line. Ambient air was sampled via 12 m length stainless steel tubing (56 mm) connected to a composite polyethylene–aluminium tube extending 3 m above the station roof (7 m above ground level). To limit residence time the air was pumped through the line at a flow rate of 3 L m−1, giving a residence time of ~5 s from the inlet to the analyzer. A low energy heating cable (5 W m−1) was wrapped around the inlet to prevent freezing, and a shield was used to stop precipitation from entering the sampling line. Temperature inside the building was maintained at 20 °C throughout the measurement campaign, aiding instrument stability and preventing condensation in the line.
Stable isotope ratios (δ18O and δ2H) were measured approximately every second by the analyzer and calibrated using standard protocols employed at Toolik. First, we established the humidity-isotope response of the instrument in the field to correct for potential analytical bias [85,86]. Using an integrated dry air cylinder (HiQ zero air 5.0), the vapor stream of two standard waters (United States Geological Survey (USGS) 45 and 46) were measured across a range of controlled humidity injections from 400 to 10,000 ppmv that encompass the range of ambient humidity values during the winter 2018–2019 field campaign. The standard waters approximately span the isotopic range of ambient measurements during this period (USGS-45; δ18O: −2.2 ± 0.01‰; δ2H: −10.3 ± 0.40‰ and USGS-46; δ18O: −29.8 ± 0.03; δ2H: −235.8 ± 0.70‰). Standards were measured for 12 min at each humidity level, and a non-linear regression was performed on the δX-mixing ratio relationship, where δX is either δ18O or δ2H. The nonlinear regression was of the form:
where δXcorr is the difference between the observed isotopic value and the actual standard isotopic value, q is the water vapor mixing ratio, and a and b are constants. The best-fit curve was used to determine the isotope correction as a function of cavity humidity (Figure A2). Second, ambient measurements were standardised to the Vienna-Standard Mean Ocean Water (VSMOW2) scale. Every 12 h, two USGS standards were automatically injected by the SDM at a constant flow rate and analysed for 20 min to calibrate and monitor for potential instrument drift. All ambient and standard measurements were corrected for the humidity concentration dependence, and based on the uncertainty of both corrections, the measurement accuracy was estimated at ±0.2‰ for δ18O and ±0.6‰ for δ2H. Measurement precision, estimated from the standard deviation of calibration measurements at a constant humidity level, was ±0.3 and ±0.8‰ for δ18O and δ2H, respectively, at humidity levels > 2000 ppmv.
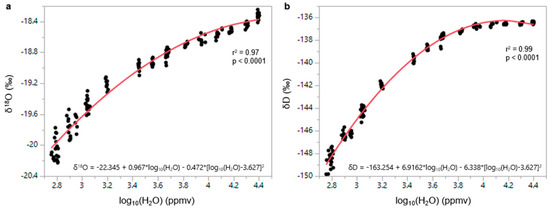
Figure A1.
Imnavait humidity response calibrations for (a) δ18O and (b) δ2H (δD) against the log10 of the H2O concentration (ppmv) as measured by the Picarro L2130-i. Each data point is the 1-min average value, and the 2nd order polynomial best fit equation was used to correct isotopic measurements used in this analysis.
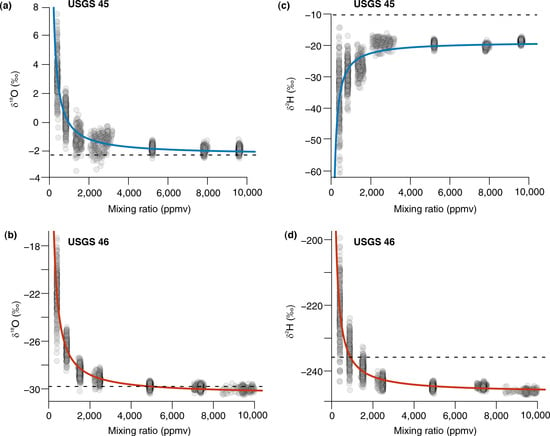
Figure A2.
Pallas humidity response calibrations for (a,b) δ18O and (c,d) δ2H of USGS standards 45 (blue) and 46 (red). Grey circles represent individual 1-s measurements, and the solid line shows the non-linear regression used to correct ambient isotope data as a function of cavity humidity. Dashed line shows the known isotopic value of the standard water.
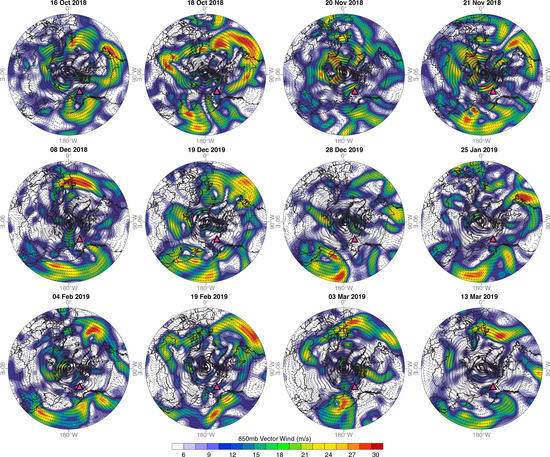
Figure A3.
Northern Hemisphere (35 to 90° N) daily mean 850 mb vector winds during snowfall events sampled at Imnavait (triangle) in winter 2018–2019, from National Centers for Environmental Prediction (NCEP) and the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) NCEP/NCAR reanalysis [89].
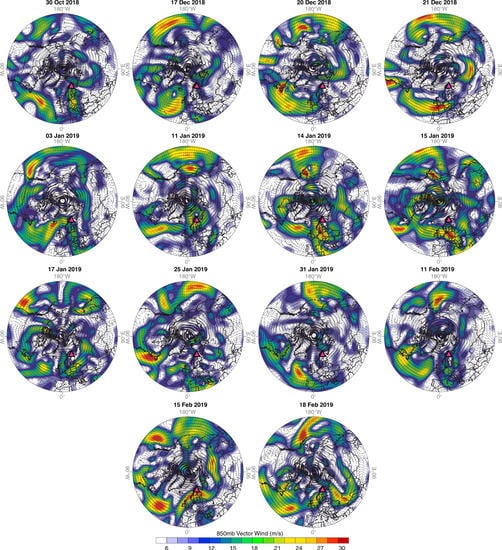
Figure A4.
Northern Hemisphere (35 to 90° N) daily mean 850 mb vector winds during snowfall events sampled at Pallas (triangle) in winter 2018–2019, from NCEP/NCAR reanalysis [89].
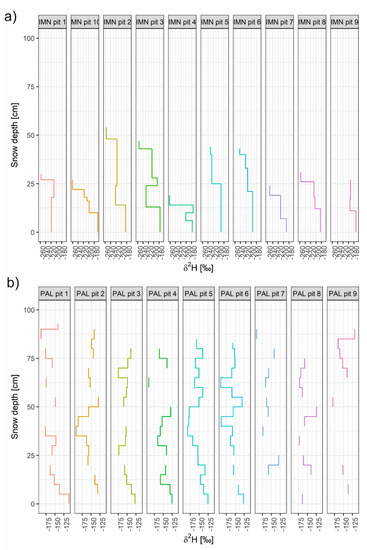
Figure A5.
δ2H profiles for individual snowpits at (a) Imnavait and (b) Pallas. Zero on the y-axis represents the base of the snowpack.
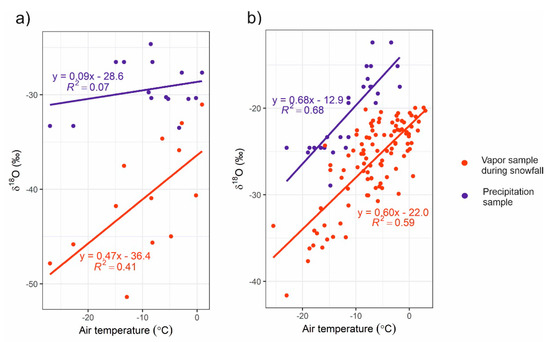
Figure A6.
δ18O values in snowfall samples and vapor samples during snowfall events as a function of daily average air temperature at (a) Pallas and (b) Imnavait.
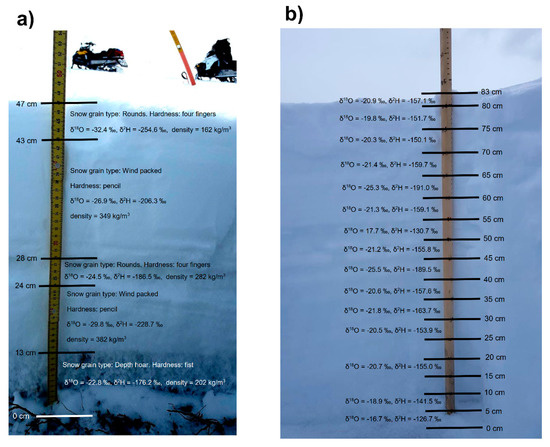
Figure A7.
Snow pit stratigraphy and sampling intervals with associated isotope values at (a) Imnavait pit three and (b) Pallas pit six (see Figure 1). For the Imnavait hand hardness test, snow grain type and snow density data are also presented.

Table A1.
Winter 2018–2019 Imnavait and Pallas snowfall samples and stable isotope data.
Table A1.
Winter 2018–2019 Imnavait and Pallas snowfall samples and stable isotope data.
| Pallas, Finland | Imnavait, USA | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample Date | δ18O (‰) | δ2H (‰) | d-Excess (‰) | Sample Date | δ18O (‰) | δ2H (‰) | d-Excess (‰) |
| 30 October 2018 | −16.6 | −125.6 | 7.2 | 16 Oct 2018 | −27.6 | −219.4 | 1.8 |
| 17 December 2018 | −19.4 | −145.1 | 10.0 | 18 Oct 2018 | −30.3 | −236.2 | 6.5 |
| 17 December 2018 | −18.9 | −139.3 | 11.5 | 20 Nov 2018 | −30.4 | −235.2 | 8.3 |
| 20 December 2018 | −18.3 | −131.2 | 15.2 | 21 Nov 2018 | −30.3 | −235.6 | 6.4 |
| 21 December 2018 | −22.1 | −165.4 | 11.5 | 08 Dec 2018 | −35.3 | −268.4 | 14.2 |
| 03 January 2019 | −18.8 | −143.4 | 6.9 | 19 Dec 2018 | −28.4 | −217.2 | 10.2 |
| 03 January 2019 | −19.9 | −149.4 | 9.4 | 28 Dec 2018 | −26.5 | −200.9 | 11.3 |
| 11 January 2019 | −12.4 | −83.1 | 16.1 | 25 Jan 2019 | −33.5 | −262.6 | 5.3 |
| 14 January 2019 | −29.6 | −227.6 | 9.4 | 04 Feb 2019 | −24.6 | −187.5 | 9.5 |
| 15 January 2019 | −22.9 | −172.6 | 10.5 | 19 Feb 2019 | −29.7 | −228.7 | 9.2 |
| 17 January 2019 | −23.3 | −177.7 | 9.0 | 03 Mar 2019 | −18.2 | −135.6 | 10.3 |
| 25 January 2019 | −22.8 | −158.0 | 24.7 | 13 Mar 2019 | −33.3 | −263.7 | 2.6 |
| 31 January 2019 | −25.1 | −190.5 | 10.4 | ||||
| 11 February 2019 | −24.6 | −182.4 | 14.1 | ||||
| 15 February 2019 | −17.5 | −135.1 | 5.0 | ||||
| 18 February 2019 | −15.1 | −113.3 | 7.7 | ||||
| Mean: | −20.5 | −152.5 | −11.2 | Mean: | −29.0 | −224.3 | −8.0 |
References
- Overland, J.E.; Hanna, E.; Hanssen-Bauer, I.; Kim, S.J.; Walsh, J.E.; Wang, M.; Bhatt, U.S.; Thoman, R.L.; Ballinger, T.J. Surface Air Temperature. 2020. Available online: https://arctic.noaa.gov/Report-Card/Report-Card-2019/ArtMID/7916/ArticleID/835/Surface-Air-Temperature (accessed on 22 January 2021).
- Bring, A.; Fedorova, I.; Dibike, Y.; Hinzman, L.; Mård, J.; Mernild, S.H.; Prowse, T.; Semenova, O.; Stuefer, S.L.; Woo, M. Arctic Terrestrial Hydrology: A Synthesis of Processes, Regional Effects, and Research Challenges. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2016, 121, 621–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biskaborn, B.K.; Smith, S.L.; Noetzli, J.; Matthes, H.; Vieira, G.; Streletskiy, D.A.; Schoeneich, P.; Romanovsky, V.E.; Lewkowicz, A.G.; Abramov, A.; et al. Permafrost is Warming at a Global Scale. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulliainen, J.; Luojus, K.; Derksen, C.; Mudryk, L.; Lemmetyinen, J.; Salminen, M.; Ikonen, J.; Takala, M.; Cohen, J.; Smolander, T. Patterns and Trends of Northern Hemisphere Snow Mass from 1980 to 2018. Nature 2020, 581, 294–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, E.S.; Welker, J.M. Influence of Sea Ice on Ocean Water Vapor Isotopes and Greenland Ice Core Records. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 12475–12483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroeve, J.; Notz, D. Changing State of Arctic Sea Ice Across all Seasons. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 103001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puntsag, T.; Mitchell, M.J.; Campbell, J.L.; Klein, E.S.; Likens, G.E.; Welker, J.M. Arctic Vortex Changes Alter the Sources and Isotopic Values of Precipitation in Northeastern US. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nygård, T.; Naakka, T.; Vihma, T. Horizontal Moisture Transport Dominates the Regional Moistening Patterns in the Arctic. J. Clim. 2020, 33, 6793–6807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vihma, T.; Screen, J.; Tjernström, M.; Newton, B.; Zhang, X.; Popova, V.; Deser, C.; Holland, M.; Prowse, T. The Atmospheric Role in the Arctic Water Cycle: A Review on Processes, Past and Future Changes, and their Impacts. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2016, 121, 586–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattingly, K.S.; Mote, T.L.; Fettweis, X. Atmospheric River Impacts on Greenland Ice Sheet Surface Mass Balance. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 8538–8560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nusbaumer, J.; Alexander, P.M.; LeGrande, A.N.; Tedesco, M. Spatial Shift of Greenland Moisture Sources Related to Enhanced Arctic Warming. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 14723–14731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, E.S.; Cherry, J.E.; Young, J.; Noone, D.; Leffler, A.J.; Welker, J.M. Arctic Cyclone Water Vapor Isotopes Support Past Sea Ice Retreat Recorded in Greenland Ice. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papritz, L.; Sodemann, H. Characterizing the Local and Intense Water Cycle during a Cold Air Outbreak in the Nordic Seas. Mon. Weather Rev. 2018, 146, 3567–3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuefer, S.L.; Kane, D.L.; Dean, K.M. Snow Water Equivalent Measurements in Remote Arctic Alaska Watersheds. Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, e2019WR025621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faranda, D. An Attempt to Explain Recent Changes in European Snowfall Extremes. Weather Clim. Dyn. 2020, 1, 445–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, Z.D.; Perlwitz, J.; Butler, A.H.; Manney, G.L.; Newman, P.A.; Lee, S.H.; Nash, E.R. The Remarkably Strong Arctic Stratospheric Polar Vortex of Winter 2020: Links to Record-Breaking Arctic Oscillation and Ozone Loss. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, e2020JD033271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, D.; Dozier, J. Climate and Energy Exchange at the Snow Surface in the Alpine Region of the Sierra Nevada: 2. Snow Cover Energy Balance. Water Resour. Res. 1992, 28, 3043–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groisman, P.Y.; Karl, T.R.; Knight, R.W. Observed Impact of Snow Cover on the Heat Balance and the Rise of Continental Spring Temperatures. Science 1994, 263, 198–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiegler, C.; Lund, M.; Christensen, T.R.; Mastepanov, M.; Lindroth, A. Two Years with Extreme and Little Snowfall: Effects on Energy Partitioning and Surface Energy Exchange in a High-Arctic Tundra Ecosystem. Cryosphere 2016, 10, 1395–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, S.T.; Kirchner, J.W.; Braun, S.; Siegwolf, R.T.; Goldsmith, G.R. Seasonal Origins of Soil Water used by Trees. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 23, 1199–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchner, J.W.; Allen, S.T. Seasonal Partitioning of Precipitation between Streamflow and Evapotranspiration, Inferred from End-Member Splitting Analysis. In Proceedings of the AGU Fall Meeting, San Francisco, CA, USA, 9–13 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Meriö, L.; Ala-aho, P.; Linjama, J.; Hjort, J.; Kløve, B.; Marttila, H. Snow to Precipitation Ratio Controls Catchment Storage and Summer Flows in Boreal Headwater Catchments. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 4096–4109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetzlaff, D.; Buttle, J.; Carey, S.K.; McGuire, K.; Laudon, H.; Soulsby, C. Tracer-based Assessment of Flow Paths, Storage and Runoff Generation in Northern Catchments: A Review. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 3475–3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokhorst, S.; Pedersen, S.H.; Brucker, L.; Anisimov, O.; Bjerke, J.W.; Brown, R.D.; Ehrich, D.; Essery, R.L.; Heilig, A.; Ingvander, S. Changing Arctic Snow Cover: A Review of Recent Developments and Assessment of Future Needs for Observations, Modelling, and Impacts. Ambio 2016, 45, 516–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callaghan, T.V.; Johansson, M.; Brown, R.D.; Groisman, P.Y.; Labba, N.; Radionov, V.; Bradley, R.S.; Blangy, S.; Bulygina, O.N.; Christensen, T.R. Multiple Effects of Changes in Arctic Snow Cover. Ambio 2011, 40, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanc-Betes, E.; Welker, J.M.; Sturchio, N.C.; Chanton, J.P.; Gonzalez-Meler, M.A. Winter Precipitation and Snow Accumulation Drive the Methane Sink Or Source Strength of Arctic Tussock Tundra. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2016, 22, 2818–2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupascu, M.; Czimczik, C.I.; Welker, M.C.; Ziolkowski, L.A.; Cooper, E.J.; Welker, J.M. Winter Ecosystem Respiration and Sources of CO2 from the High Arctic Tundra of Svalbard: Response to a Deeper Snow Experiment. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2018, 123, 2627–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natali, S.M.; Watts, J.D.; Rogers, B.M.; Potter, S.; Ludwig, S.M.; Selbmann, A.; Sullivan, P.F.; Abbott, B.W.; Arndt, K.A.; Birch, L. Large Loss of CO 2 in Winter Observed Across the Northern Permafrost Region. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2019, 9, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturm, M.; Schimel, J.; Michaelson, G.; Welker, J.M.; Oberbauer, S.F.; Liston, G.E.; Fahnestock, J.; Romanovsky, V.E. Winter Biological Processes could Help Convert Arctic Tundra to Shrubland. Bioscience 2005, 55, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jespersen, R.G.; Leffler, A.J.; Oberbauer, S.F.; Welker, J.M. Arctic Plant Ecophysiology and Water Source Utilization in Response to Altered Snow: Isotopic (Δ 18 O and Δ 2 H) Evidence for Meltwater Subsidies to Deciduous Shrubs. Oecologia 2018, 187, 1009–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welker, J.M.; Rayback, S.; Henry, G.H. Arctic and North Atlantic Oscillation Phase Changes are Recorded in the Isotopes (δ18O and δ13C) of Cassiope Tetragona Plants. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2005, 11, 997–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welker, J.M.; THE Heaton; Spiro, B.; Callaghan, T.V. Indirect Effects of Winter Climate on the D13C and the DD Characteristics of Annual Growth Segments in the Long-Lived Arctic Plant Cassiope Tetragona: A Preliminary Analysis. Paleoclimatological Res. 1995, 15, 105–120. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, B.B.; Lorentzen, J.R.; Welker, J.M.; Varpe, Ø.; Aanes, R.; Beumer, L.T.; Pedersen, Å.Ø. Reindeer Turning Maritime: Ice-locked Tundra Triggers Changes in Dietary Niche Utilization. Ecosphere 2019, 10, e02672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, G.J.; Cai, Z.; Fiorella, R.P.; Putman, A.L. Isotopes in the Water Cycle: Regional-to Global-Scale Patterns and Applications. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2019, 47, 453–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vachon, R.W.; Welker, J.M.; White, J.; Vaughn, B.H. Monthly Precipitation Isoscapes (δ18O) of the United States: Connections with Surface Temperatures, Moisture Source Conditions, and Air Mass Trajectories. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akers, P.D.; Welker, J.M.; Brook, G.A. Reassessing the Role of Temperature in Precipitation Oxygen Isotopes Across the Eastern and Central U Nited S Tates through Weekly Precipitation-day Data. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 7644–7661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjostrom, D.J.; Welker, J.M. The Influence of Air Mass Source on the Seasonal Isotopic Composition of Precipitation, Eastern USA. J. Geochem. Explor. 2009, 102, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, H.L.; Kaufman, D.S.; Henderson, A.C.; Leng, M.J. Synoptic Scale Controls on the δ18O in Precipitation Across Beringia. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 4608–4616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprenger, M.; Leistert, H.; Gimbel, K.; Weiler, M. Illuminating Hydrological Processes at the Soil-vegetation-atmosphere Interface with Water Stable Isotopes. Rev. Geophys. 2016, 54, 674–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penna, D.; Hopp, L.; Scandellari, F.; Allen, S.T.; Benettin, P.; Beyer, M.; Dawson17, J.W. Tracing Ecosystem Water Fluxes using Hydrogen and Oxygen Stable Isotopes: Challenges and Opportunities from an Interdisciplinary Perspective. Biogeosci. Discuss. 2018, 15, 6399–6415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welker, J.M.; Fahnestock, J.T.; Sullivan, P.F.; Chimner, R.A. Leaf Mineral Nutrition of Arctic Plants in Response to Warming and Deeper Snow in Northern Alaska. Oikos 2005, 109, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welker, J.M. Isotopic (δ18O) Characteristics of Weekly Precipitation Collected Across the USA: An Initial Analysis with Application to Water Source Studies. Hydrol. Process. 2000, 14, 1449–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, H.L.; Klein, E.S.; Welker, J.M. Synoptic and Mesoscale Mechanisms Drive Winter Precipitation δ18O/δ2H in South-central Alaska. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 4252–4266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopec, B.G.; Feng, X.; Michel, F.A.; Posmentier, E.S. Influence of Sea Ice on Arctic Precipitation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charles, C.D.; Rind, D.V.; Jouzel, J.; Koster, R.D.; Fairbanks, R.G. Glacial-Interglacial Changes in Moisture Sources for Greenland: Influences on the Ice Core Record of Climate. Science 1994, 263, 508–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniels, W.C.; Russell, J.M.; Giblin, A.E.; Welker, J.M.; Klein, E.S.; Huang, Y. Hydrogen Isotope Fractionation in Leaf Waxes in the Alaskan Arctic Tundra. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2017, 213, 216–236. [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair, K.E.; Marshall, S.J. Post-Depositional Modification of Stable Water Isotopes in Winter Snowpacks in the Canadian Rocky Mountains. Ann. Glaciol. 2008, 49, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Helsen, M.M.; Van de Wal, R.; Van den Broeke, M.R.; Masson-Delmotte, V.; Meijer, H.; Scheele, M.P.; Werner, M. Modeling the Isotopic Composition of Antarctic Snow using Backward Trajectories: Simulation of Snow Pit Records. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111, 111. [Google Scholar]
- Grootes, P.M.; Stuiver, M. Oxygen 18/16 Variability in Greenland Snow and Ice with 10− 3-to 105-year Time Resolution. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1997, 102, 26455–26470. [Google Scholar]
- Steen-Larsen, H.C.; Masson-Delmotte, V.; Sjolte, J.; Johnsen, S.J.; Vinther, B.M.; Bréon, F.; Clausen, H.B.; Dahl-Jensen, D.; Falourd, S.; Fettweis, X. Understanding the Climatic Signal in the Water Stable Isotope Records from the NEEM Shallow Firn/Ice Cores in Northwest Greenland. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechler, A.R.; Niemi, N.A. The Influence of Snow Sublimation on the Isotopic Composition of Spring and Surface Waters in the Southwestern United States: Implications for Stable Isotope–based Paleoaltimetry and Hydrologic Studies. Bulletin 2012, 124, 318–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earman, S.; Campbell, A.R.; Phillips, F.M.; Newman, B.D. Isotopic Exchange between Snow and Atmospheric Water Vapor: Estimation of the Snowmelt Component of Groundwater Recharge in the Southwestern United States. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ala-aho, P.; Tetzlaff, D.; McNamara, J.P.; Laudon, H.; Kormos, P.; Soulsby, C. Modeling the Isotopic Evolution of Snowpack and Snowmelt: Testing a Spatially Distributed Parsimonious Approach. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 5813–5830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madsen, M.V.; Steen-Larsen, H.C.; Hörhold, M.; Box, J.; Berben, S.M.P.; Capron, E.; Faber, A.; Hubbard, A.; Jensen, M.F.; Jones, T.R. Evidence of Isotopic Fractionation during Vapor Exchange between the Atmosphere and the Snow Surface in Greenland. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 2932–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopec, B.G.; Akers, P.D.; Klein, E.S.; Welker, J.M. Significant Water Vapor Fluxes from the Greenland Ice Sheet Detected through Water Vapor Isotopic (δ18O, δD, Deuterium Excess) Measurements. Cryosphere Discuss 2020. under review. [Google Scholar]
- Sturm, M.; Benson, C.S. Vapor Transport, Grain Growth and Depth-Hoar Development in the Subarctic Snow. J. Glaciol. 1997, 43, 42–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, T.A.; Albert, M.R.; Lomonaco, R.; Engel, C.; Courville, Z.; Perron, F. Experimental Determination of Snow Sublimation Rate and Stable-Isotopic Exchange. Ann. Glaciol. 2008, 49, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, I.; Benson, C.; Gleason, J. Isotopic Changes during Snow Metamorphism. In Stable Isotope Geochemistry: A Tribute to Samuel Epstein; The Geochemical Society: San Antonio, TX, USA, 1991; pp. 211–221. [Google Scholar]
- Von Freyberg, J.; Bjarnadóttir, T.R.; Allen, S.T. Influences of Forest Canopy on Snowpack Accumulation and Isotope Ratios. Hydrol. Process. 2020, 34, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koeniger, P.; Hubbart, J.A.; Link, T.; Marshall, J.D. Isotopic Variation of Snow Cover and Streamflow in Response to Changes in Canopy Structure in a Snow-dominated Mountain Catchment. Hydrol. Process. Int. J. 2008, 22, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, H.; Stichler, W. Deuterium and Oxygen-18 Contents as an Index of the Properties of Snow Covers. Int. Assoc. Hydrol. Sci. Publ. 1974, 114, 122–135. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, S.L.; Flores, A.N.; Heilig, A.; Kohn, M.J.; Marshall, H.; McNamara, J.P. Isotopic Evidence for Lateral Flow and Diffusive Transport, but Not Sublimation, in a Sloped Seasonal Snowpack, Idaho, USA. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 3298–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unnikrishna, P.V.; McDonnell, J.J.; Kendall, C. Isotope Variations in a Sierra Nevada Snowpack and their Relation to Meltwater. J. Hydrol. 2002, 260, 38–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beria, H.; Larsen, J.R.; Ceperley, N.C.; Michelon, A.; Vennemann, T.; Schaefli, B. Understanding Snow Hydrological Processes through the Lens of Stable Water Isotopes. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Water 2018, 5, e1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, T.; Wang, K.; Kong, Y.; Shi, X.; Kang, S.; Huang, Y.; He, Y.; Wang, S.; Lee, J.; Cuntz, M. Observing and Modeling the Isotopic Evolution of Snow Meltwater on the Southeastern Tibetan Plateau. Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, e2019WR026423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.; Feng, X.; Kirchner, J.W.; Osterhuber, R.; Klaue, B.; Renshaw, C.E. Isotopic Evolution of a Seasonal Snowpack and its Melt. Water Resour. Res. 2001, 37, 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ham, J.; Do Hur, S.; Lee, W.S.; Han, Y.; Jung, H.; Lee, J. Isotopic Variations of Meltwater from Ice by Isotopic Exchange between Liquid Water and Ice. J. Glaciol. 2019, 65, 1035–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsen, S.J.; Clausen, H.B.; Cuffey, K.M.; Hoffmann, G.; Schwander, J.; Creyts, T. Diffusion of Stable Isotopes in Polar Firn and Ice: The Isotope Effect in Firn Diffusion. In Physics of Ice Core Records; HokkaidoUniversityPress: Sapporo, Japan, 2000; pp. 121–140. [Google Scholar]
- Steen-Larsen, H.C.; Masson-Delmotte, V.; Hirabayashi, M.; Winkler, R.; Satow, K.; Prié, F.; Bayou, N.; Brun, E.; Cuffey, K.M.; Dahl-Jensen, D. What Controls the Isotopic Composition of Greenland Surface Snow? Clim. Past 2014, 10, 377–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritter, F.; Steen-Larsen, H.C.; Werner, M.; Masson-Delmotte, V.; Orsi, A.; Behrens, M.; Birnbaum, G.; Freitag, J.; Risi, C.; Kipfstuhl, S. Isotopic Exchange on the Diurnal Scale between Near-Surface Snow and Lower Atmospheric Water Vapor at Kohnen Station, East Antarctica. Cryosphere 2016, 10, 1647–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturm, M.; Holmgren, J.; Liston, G.E. A Seasonal Snow Cover Classification System for Local to Global Applications. J. Clim. 1995, 8, 1261–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinzman, L.D.; Kane, D.L.; Gieck, R.E.; Everett, K.R. Hydrologic and Thermal Properties of the Active Layer in the Alaskan Arctic. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 1991, 19, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamara, J.P.; Kane, D.L.; Hinzman, L.D. An Analysis of Streamflow Hydrology in the Kuparuk River Basin, Arctic Alaska: A Nested Watershed Approach. J. Hydrol. 1998, 206, 39–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, D.L.; Hinzman, L.D.; Benson, C.S.; Everett, K.R. Hydrology of Imnavait Creek, an Arctic Watershed. Ecography 1989, 12, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liston, G.E.; Sturm, M. A Snow-Transport Model for Complex Terrain. J. Glaciol. 1998, 44, 498–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturm, M.; Wagner, A.M. Using Repeated Patterns in Snow Distribution Modeling: An Arctic Example. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raleigh, M.S.; Livneh, B.; Lapo, K.; Lundquist, J.D. How does Availability of Meteorological Forcing Data Impact Physically Based Snowpack Simulations? J. Hydrometeorol. 2016, 17, 99–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, D.L.; Youcha, E.K.; Stuefer, S.L.; Myerchin-Tape, G.; Lamb, E.; Homan, J.W.; Gieck, R.E.; Schnabel, W.E.; Toniolo, H. Hydrology and Meteorology of the Central Alaskan Arctic: Data Collection and Analysis; University of Alaska Fairbanks: Fairbanks, AK, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, D.A.; Binnian, E.; Evans, B.M.; Lederer, N.D.; Nordstrand, E.; Webber, P.J. Terrain, Vegetation and Landscape Evolution of the R4D Research Site, Brooks Range Foothills, Alaska. Ecography 1989, 12, 238–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohila, A.; Penttilä, T.; Jortikka, S.; Aalto, T.; Anttila, P.; Asmi, E.; Aurela, M.; Hatakka, J.; Hellén, H.; Henttonen, H. Preface to the Special Issue on Integrated Research of Atmosphere, Ecosystems and Environment at Pallas. Boreal Environ. Res. 2015, 20, 431–454. [Google Scholar]
- Fierz, C.; Armstrong, R.L.; Durand, Y.; Etchevers, P.; Greene, E.; McClung, D.M.; Nishimura, K.; Satyawali, P.K.; Sokratov, S.A. The International Classification for Seasonal Snow on the Ground; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Greene, E.M.; Birkeland, K.W.; Elder, K.; Johnson, G.; Landry, C.; McCammon, I.; Moore, M.; Sharaf, D.; Sterbenz, C.; Tremper, B. Snow, Weather, and Avalanches: New Observation Guidelines for Avalanche Programs in the United States; American Avalanche Association: Victor, ID, USA, 2016; 104p. [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen, S.H.; Liston, G.E.; Welker, J.M. Snow Depth and Snow Density Measured in Arctic Alaska for Caribou Winter Applications in 2018 and 2019; Arctic Data Center: Mo i Rana, Norway, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Dansgaard, W. Stable Isotopes in Precipitation. Tellus 1964, 16, 436–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aemisegger, F.; Sturm, P.; Graf, P.; Sodemann, H.; Pfahl, S.; Knohl, A.; Wernli, H. Measuring Variations of Δ 18 O and Δ 2 H in Atmospheric Water Vapour using Two Commercial Laser-Based Spectrometers: An Instrument Characterisation Study. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2012, 5, 1491–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steen-Larsen, H.C.; Johnsen, S.J.; Masson-Delmotte, V.; Stenni, B.; Risi, C.; Sodemann, H.; Balslev-Clausen, D.; Blunier, T.; Dahl-Jensen, D.; Ellehøj, M.D. Continuous Monitoring of Summer Surface Water Vapor Isotopic Composition Above the Greenland Ice Sheet. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 4815–4828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastrikov, V.; Steen-Larsen, H.C.; Masson-Delmotte, V.; Gribanov, K.; Cattani, O.; Jouzel, J.; Zakharov, V. Continuous Measurements of Atmospheric Water Vapour Isotopes in Western Siberia (Kourovka). Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 1763–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, A.; Noone, D.; Berkelhammer, M.; Steen-Larsen, H.C.; Sato, P. The Stability and Calibration of Water Vapor Isotope Ratio Measurements during Long-Term Deployments. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 4521–4538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalnay, E.; Kanamitsu, M.; Kistler, R.; Collins, W.; Deaven, D.; Gandin, L.; Iredell, M.; Saha, S.; White, G.; Woollen, J. The NCEP/NCAR 40-Year Reanalysis Project. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1996, 77, 437–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetterer, F.; Knowles, K.; Meier, W.N.; Savoie, M.; Windnagel, A.K. Sea Ice Index, Version 3; National Snow and Ice Data Center: Boulder, CO, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bonne, J.; Meyer, H.; Behrens, M.; Boike, J.; Kipfstuhl, S.; Rabe, B.; Schmidt, T.; Schönicke, L.; Steen-Larsen, H.C.; Werner, M. Moisture Origin as a Driver of Temporal Variabilities of the Water Vapour Isotopic Composition in the Lena River Delta, Siberia. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 10493–10511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellehoj, M.D.; Steen-Larsen, H.C.; Johnsen, S.J.; Madsen, M.B. Ice-vapor Equilibrium Fractionation Factor of Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotopes: Experimental Investigations and Implications for Stable Water Isotope Studies. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2013, 27, 2149–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustafson, J.R.; Brooks, P.D.; Molotch, N.P.; Veatch, W.C. Estimating Snow Sublimation using Natural Chemical and Isotopic Tracers Across a Gradient of Solar Radiation. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Feng, X.; Posmentier, E.S.; Faiia, A.M.; Taylor, S. Stable Isotopic Exchange Rate Constant between Snow and Liquid Water. Chem. Geol. 2009, 260, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hachikubo, A.; Hashimoto, S.; Nakawo, M.; Nishimura, K. Isotopic Mass Fractionation of Snow due to Depth Hoar Formation. Polar Meteorol. Glaciol. 2000, 14, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Stichler, W.; Schotterer, U.; Fröhlich, K.; Ginot, P.; Kull, C.; Gäggeler, H.; Pouyaud, B. Influence of Sublimation on Stable Isotope Records Recovered from High-altitude Glaciers in the Tropical Andes. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 22613–22620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, H.; Hubbard, A.; Klein, E.S.; Mustonen, K.; Akers, P.D.; Mattila, H.; Welker, J.M. Arctic sea-ice loss fuels extreme European snowfall. Nat. Geosci. 2020. (provisionally accepted). [Google Scholar]
- Bintanja, R.; Selten, F.M. Future Increases in Arctic Precipitation Linked to Local Evaporation and Sea-Ice Retreat. Nature 2014, 509, 479–482. [Google Scholar]
- Nygård, T.; Graversen, R.G.; Uotila, P.; Naakka, T.; Vihma, T. Strong Dependence of Wintertime Arctic Moisture and Cloud Distributions on Atmospheric Large-Scale Circulation. J. Clim. 2019, 32, 8771–8790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winnick, M.J.; Chamberlain, C.P.; Caves, J.K.; Welker, J.M. Quantifying the Isotopic ‘continental Effect’. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2014, 406, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judy, C.; Meiman, J.R.; Friedman, I. Deuterium Variations in an Annual Snowpack. Water Resour. Res. 1970, 6, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liston, G.E.; Polashenski, C.; Rösel, A.; Itkin, P.; King, J.; Merkouriadi, I.; Haapala, J. A Distributed Snow-evolution Model for Sea-ice Applications (SnowModel). J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2018, 123, 3786–3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, D.A.; Koerner, R.M.; Paterson, W.; Dansgaard, W.; Gundestrup, N.; Reeh, N. Effect of Wind Scouring on Climatic Records from Ice-Core Oxygen-Isotope Profiles. Nature 1983, 301, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, S.; Sharp, R.P.; Gow, A.J. Six-year Record of Oxygen and Hydrogen Isotope Variations in South Pole Firn. J. Geophys. Res. 1965, 70, 1809–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.; Feng, X.; Renshaw, C.E.; Kirchner, J.W. Isotopic Evolution of Snowmelt 2. Verification and Parameterization of a One-dimensional Model using Laboratory Experiments. Water Resour. Res. 2002, 38, 36–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, E.; Martin, E.; Simon, V.; Gendre, C.; Coleou, C. An Energy and Mass Model of Snow Cover Suitable for Operational Avalanche Forecasting. J. Glaciol. 1989, 35, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartelt, P.; Lehning, M. A Physical SNOWPACK Model for the Swiss Avalanche Warning: Part I: Numerical Model. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2002, 35, 123–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akers, P.D.; Kopec, B.G.; Mattingly, K.S.; Klein, E.S.; Causey, D.; Welker, J.M. Baffin Bay Sea Ice Extent and Synoptic Moisture Transport Drive Water Vapor Isotope (δ18O, δD, D-Excess) Variability in Coastal Northwest Greenland. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2020. under review. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardakani, M.M.; Bailey, H.; Mustonen, K.R.; Marttila, H.; Klein, E.S.; Gribanov, K.; Bret-Harte, M.S.; Chupakov, A.V.; Divine, D.V.; Else, B.; et al. Hydroclimatic controls on the isotopic (δ18O, δ2H, d-excess) traits of pan-Arctic summer rainfall events. Front. Earth Sci. Geochem. 2021. under review. [Google Scholar]
- Mellat, M.; Mustonen, K.; Bailey, H.; Klein, E.; Marttila, H.; Welker, J.M. Pan-Arctic Summer Moisture Sources Revealed using an Event-Based Precipitation Isotope (δ18O, δ2H, D-Excess) Network (PAPIN). Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. Submitt. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).