Analyzing Atmospheric Circulation Patterns Using Mass Fluxes Calculated from Weather Balloon Measurements: North Atlantic Region as a Case Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
It is nearly 60 years since Tucker made the observation quoted above, yet it is still remarkably relevant. Terms such as “the general circulation of the atmosphere”, “atmospheric general circulation” or simply “atmospheric circulation” are clearly very important for describing both short-term weather patterns (e.g., meteorology) and longer-term climatic changes (e.g., climatology). However, as Tucker observed, the exact meanings of these terms are sufficiently loose that they can mean different things to different people at different times.“Of all the phrases in everyday use in meteorology the term ‘the general circulation of the atmosphere’ is high on the list for meaning ‘most things to most people’. This is not surprising for in the literature under the General Circulation heading we find everything from vague qualitative ideas and imaginative cellular circulations to intricate mathematical analyses, and from surface-bound observational studies to complex investigations of three-dimensional motion extending well above the tropopause.”—Dr. Gilbert B. Tucker, “The general circulation of the atmosphere” (1962) [1]
1.1. Historical Development of the Current “Three-Cell General Circulation Model”
- A “direct” Hadley cell from equator to about 30° latitude that is thermally driven by the heating from the large amount of incoming tropical sunlight.
- An “indirect” Ferrel cell between about 30° and 60° latitude that is driven by the circulations of the cells on either side of it.
- A “direct” Polar cell from about 60° latitude to the pole that is thermally driven by the cooling of the atmosphere at the poles.
1.2. Regional Atmospheric Circulation Patterns and the Relationships between Them
1.3. Proposed Links between Solar Activity and Atmospheric Circulations
1.4. Empirical, Semi-Empirical and Theoretical/Model-Based Approaches to Analyzing Atmospheric Circulations
1.5. Aims of This Case Study
2. Data and Methods
2.1. How to Calculate the Atmospheric Mass Fluxes from a Weather Balloon Sounding
2.2. Sampling of Five Stations Used for This Paper
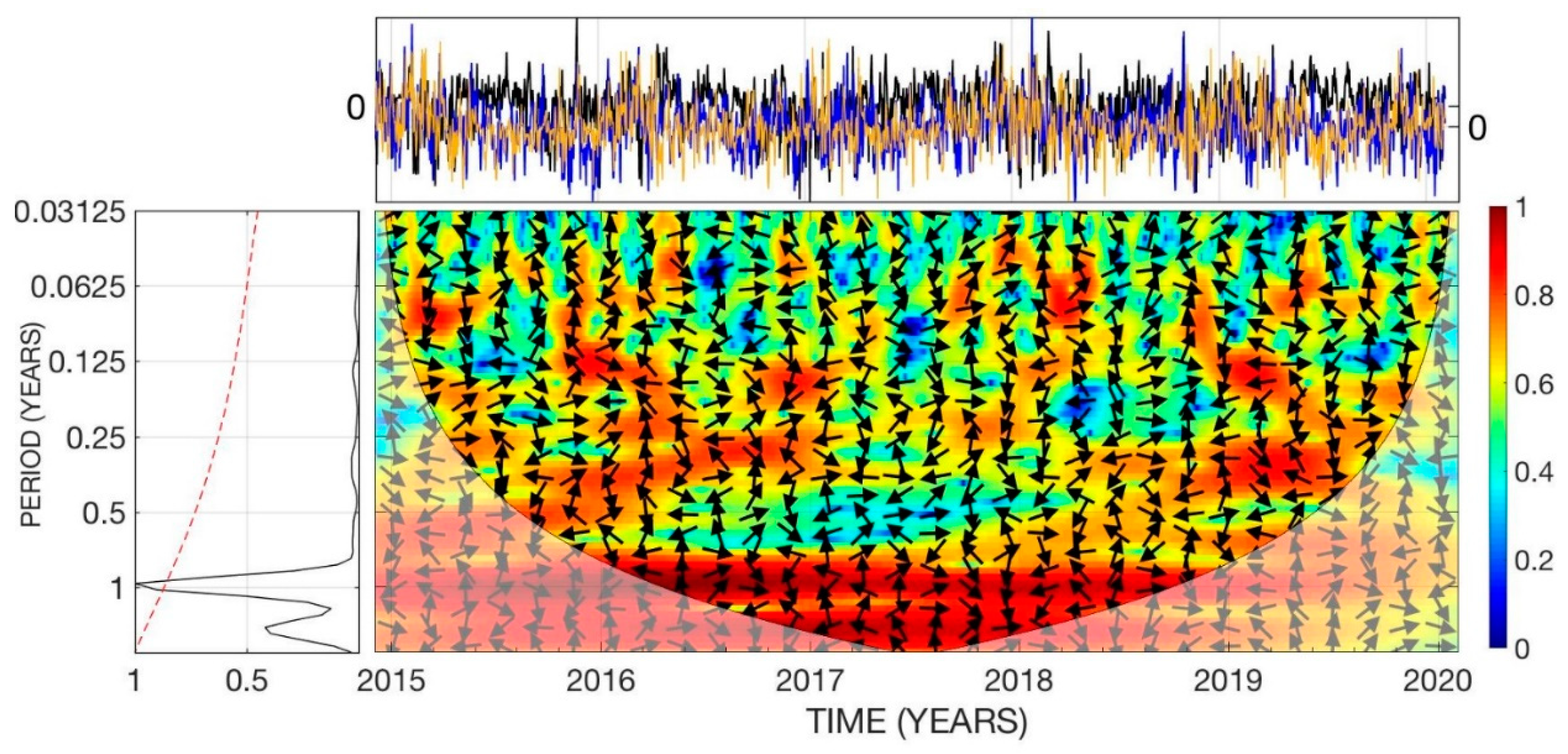
2.3. Wavelet Analysis of the Co-Variability of the Atmospheric Mass Flux Parameters
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Analysis of the 5-Year Time Series
3.2. Analysis of the 5-Year Average Statistics
3.3. Preliminary Frequency Analysis of the Time Series
3.4. Applicability of These Techniques to Investigating Links between Atmospheric Circulations and Solar Activity as Well as Other Climatic Drivers
4. Conclusions and Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tucker, G.B. The General Circulation of the Atmosphere. Weather 1962, 17, 320–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knox, J.A.; Knox, P.N. Atmospheric/General Circulation. In International Encyclopedia of Geography; American Cancer Society: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2017; pp. 1–8. ISBN 978-1-118-78635-2. [Google Scholar]
- Durre, I.; Vose, R.S.; Wuertz, D.B. Overview of the Integrated Global Radiosonde Archive. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durre, I.; Vose, R.S.; Wuertz, D.B. Robust Automated Quality Assurance of Radiosonde Temperatures. J. Appl. Meteor. Climatol. 2008, 47, 2081–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durre, I.; Yin, X.; Vose, R.S.; Applequist, S.; Arnfield, J. Enhancing the Data Coverage in the Integrated Global Radiosonde Archive. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2018, 35, 1753–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, E.N. The Nature and Theory of the General Circulation of the Atmosphere; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Webster, P.J. The Elementary Hadley Circulation. In The Hadley Circulation: Present, Past and Future; Diaz, H.F., Bradley, R.S., Eds.; Advances in Global Change Research; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2004; pp. 9–60. ISBN 978-1-4020-2944-8. [Google Scholar]
- Persson, A.O. Hadley’s Principle: Understanding and Misunderstanding the Trade Winds. Hist. Meteorol. 2006, 3, 26. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Vecchi, G.A. Tropical Meteorology & Climate|Hadley Circulation. In Encyclopedia of Atmospheric Sciences, 2nd ed.; North, G.R., Pyle, J., Zhang, F., Eds.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2015; pp. 113–120. ISBN 978-0-12-382225-3. [Google Scholar]
- University of Chicago (Department of Meteorology). On the General Circulation of the Atmosphere in Middle Latitudes: A Preliminary Summary Report on Certain Investigations Conducted at the University of Chicago during the Academic Year 1946–1947. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1947, 28, 255–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossby, C.G.; Willett, H.C. The Circulation of the Upper Troposphere and Lower Stratosphere. Science 1948, 108, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, J.M.; Fearon, M.G.; Klieforth, H.E. Herbert Riehl: Intrepid and Enigmatic Scholar. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2012, 93, 963–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, J.M. Clarifying the Dynamics of the General Circulation: Phillips’s 1956 Experiment. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 79, 39–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossby, C.-G.; Starr, V.P. Interpretations of the Angular-Momentum Principle as Applied to the General Circulation of the Atmosphere. J. Atmos. Sci. 1949, 6, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmen, E. Meridional Circulations and the Transfer of Angular Momentum in the Atmosphere. J. Atmos. Sci. 1949, 6, 429–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starr, V.P. Reply. J. Atmos. Sci. 1949, 6, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Starr, V.P. A Note on the Eddy Transport of Angular Momentum. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1951, 77, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starr, V.P.; White, R.M. A Hemispherical Study of the Atmospheric Angular-Momentum Balance. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1951, 77, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starr, V.P. Note Concerning the Nature of the Large-Scale Eddies in the Atmosphere. Tellus 1953, 5, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, H.-L. On the Production of Mean Zonal Currents in the Atmosphere by Large Disturbances. Tellus 1953, 5, 475–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starr, V.P. Commentaries Concerning Research on the General Circulation. Tellus 1954, 6, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starr, V.P. What Constitutes Our New Outlook Dot the General Circulation? J. Met. Soc. Japan 1958, 36, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Starr, V.P. Trends of Thought Concerning Meteorological Research. Geofis. Pura Appl. 1959, 43, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newell, R.E. The General Circulation of the Atmosphere and Its Effects on the Movement of Trace Substances. J. Geophys. Res. 1963, 68, 3949–3962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossby, C.-G. On the Distribution of Angular Velocity in Gaseous Envelopes Under the Influence of Large-Scale Horizontal Mixing Processes. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1947, 28, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priestley, C.H.B. Heat Transport and Zonal Stress between Latitudes. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1949, 75, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priestley, C.H.B. On the Dynamics of the General Atmospheric Circulation. Aust. J. Chem. 1950, 3, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riehl, H.; Yeh, T.C. The Intensity of the Net Meridional Circulation. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1950, 76, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riehl, H.; Yeh, T.C.; Seur, N.E.L. A Study of the Variations of the General Circulation. J. Atmos. Sci. 1950, 7, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, N.A. The General Circulation of the Atmosphere: A Numerical Experiment. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1956, 82, 123–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, G.B. Evidence of a Mean Meridional Circulation in the Atmosphere from Surface Wind Observations. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1957, 83, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmén, E.; Riehl, H.; Vuorela, L.A. On the Meridional Circulation and Release of Kinetic Energy in the Tropics. J. Atmos. Sci. 1958, 15, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tucker, G.B. Mean Meridional Circulations in the Atmosphere. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1959, 85, 209–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, G.B. The Atmospheric Budget of Angular Momentum. Tellus 1960, 12, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmén, E.; Vuorela, L.A. On the Mean Meridional Circulations in the Northern Hemisphere during the Winter Season. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1963, 89, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defant, F.; Boogaard, H.M.E.V.D. The Global Circulation Features of the Troposphere between the Equator and 40° N, Based on a Single Day’s Data. Tellus 1963, 15, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holopainen, E.O. On the Role of Mean Meridional Circulations in the Energy Balance of the Atmosphere. Tellus 1965, 17, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holopainen, E.O. On the Mean Meridional Circulation and the Flux of Angular Momentum over the Northern Hemisphere. Tellus 1967, 19, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Vuorela, L.A.; Tuominen, I. On the Mean Zonal and Meridional Circulations and the Flux of Moisture in the Northern Hemisphere during the Summer Season. Pure Appl. Geophys. 1964, 57, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastenrath, S.L. A Study of the Atmospheric Circulation between Equator and 60oN during the Winter and Summer Seasons. Pure Appl. Geophys. 1969, 77, 207–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, R.; Parker, A.E.; Collison, P. Some Computations of Meridional Flow, Angular Momentum and Energy in the Atmosphere Based on IGY Data for Latitude 30° N. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1969, 95, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidson, J.W.; Vincent, D.G.; Newell, R.E. Observational Studies of the General Circulation of the Tropics: Long Term Mean Values. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1969, 95, 258–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oort, A.H.; Rasmusson, E.M. On the Annual Variation of the Monthly Mean Meridional Circulation. Mon. Weather. Rev. 1970, 98, 423–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starr, V.P.; Peixoto, J.P.; Gaut, N.E. Momentum and Zonal Kinetic Energy Balance of the Atmosphere from Five Years of Hemispheric Data. Tellus 1970, 22, 251–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulman, L.L. On the Summer Hemisphere Hadley Cell. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1973, 99, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, E.K.; Lindzen, R.S. Axially Symmetric Steady-State Models of the Basic State for Instability and Climate Studies. Part, I. Linearized Calculations. J. Atmos. Sci. 1977, 34, 263–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Held, I.M.; Hou, A.Y. Nonlinear Axially Symmetric Circulations in a Nearly Inviscid Atmosphere. J. Atmos. Sci. 1980, 37, 515–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindzen, R.S.; Hou, A.V. Hadley Circulations for Zonally Averaged Heating Centered off the Equator. J. Atmos. Sci. 1988, 45, 2416–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutgens, F.K.; Tarbuck, E.J.; Tasa, D.G. The Atmosphere: An Introduction to Meteorology, 11th ed.; Pearson: New York, NY, USA, 2009; ISBN 978-0-321-58733-6. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, C.C.; Schneider, T. Eddy Influences on Hadley Circulations: Simulations with an Idealized GCM. J. Atmos. Sci. 2006, 63, 3333–3350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, N.A.; Birner, T. Eddy Influences on the Hadley Circulation. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2019, 11, 1563–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-L.; Wang, Y.; Wu, R.-S. A New View on the Ferrel Cell. Chin. J. Geophys. 2005, 48, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Wu, K.; Chen, D. The Arctic and Polar Cells Act on the Arctic Sea Ice Variation. Tellus A Dyn. Meteorol. Oceanogr. 2015, 67, 27692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Wu, K.; Liang, H. Arctic and Antarctic Cells in the Troposphere. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2016, 125, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Wu, K.; Leung, J.C.-H. Climatic Anomalous Patterns Associated with the Arctic and Polar Cell Strength Variations. Clim. Dyn. 2017, 48, 169–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oort, A.H.; Yienger, J.J. Observed Interannual Variability in the Hadley Circulation and Its Connection to ENSO. J. Clim. 1996, 9, 2751–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C. Atmospheric Circulation Cells Associated with the El Niño–Southern Oscillation. J. Clim. 2002, 15, 399–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C. Atlantic Climate Variability and Its Associated Atmospheric Circulation Cells. J. Clim. 2002, 15, 1516–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Wang, B. Circumglobal Teleconnection in the Northern Hemisphere Summer. J. Clim. 2005, 18, 3483–3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Ding, Q. Global Monsoon: Dominant Mode of Annual Variation in the Tropics. Dyn. Atmos. Ocean. 2008, 44, 165–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Liu, J.; Kim, H.-J.; Webster, P.J.; Yim, S.-Y.; Xiang, B. Northern Hemisphere Summer Monsoon Intensified by Mega-El Niño/Southern Oscillation and Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 5347–5352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, K.-S.; Timmermann, A.; Stuecker, M.F. Synchronized Spatial Shifts of Hadley and Walker Circulations. Earth Syst. Dyn. 2021, 12, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwendike, J.; Govekar, P.; Reeder, M.J.; Wardle, R.; Berry, G.J.; Jakob, C. Local Partitioning of the Overturning Circulation in the Tropics and the Connection to the Hadley and Walker Circulations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 1322–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwendike, J.; Berry, G.J.; Reeder, M.J.; Jakob, C.; Govekar, P.; Wardle, R. Trends in the Local Hadley and Local Walker Circulations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 7599–7618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwendike, J.; Berry, G.J.; Fodor, K.; Reeder, M.J. On the Relationship Between the Madden-Julian Oscillation and the Hadley and Walker Circulations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2021, 126, e2019JD032117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnauskas, K.B.; Ummenhofer, C.C. On the Dynamics of the Hadley Circulation and Subtropical Drying. Clim. Dyn. 2014, 42, 2259–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, D.W.J.; Wallace, J.M. Annular Modes in the Extratropical Circulation. Part I: Month-to-Month Variability. J. Clim. 2000, 13, 1000–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-F.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Sun, C. Role of Ferrel Cell in Daily Variability of Northern Hemisphere Annular Mode. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2014, 59, 3457–3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Guo, Y.-P.; Tan, Z.-M.; Guan, Z. Interannual Relationship between the Boreal Spring Arctic Oscillation and the Northern Hemisphere Hadley Circulation Extent. J. Clim. 2019, 32, 4395–4408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Curry, J.A.; Hu, Y. Recent Arctic Sea Ice Variability: Connections to the Arctic Oscillation and the ENSO. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kryzhov, V.N.; Gorelits, O.V. The Arctic Oscillation and Its Impact on Temperature and Precipitation in Northern Eurasia in the 20th Century. Russ. Meteorol. Hydrol. 2015, 40, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgieva, K.; Kirov, B.; Tonev, P.; Guineva, V.; Atanasov, D. Long-Term Variations in the Correlation between NAO and Solar Activity: The Importance of North–South Solar Activity Asymmetry for Atmospheric Circulation. Adv. Space Res. 2007, 40, 1152–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Soon, W.; Connolly, R.; Connolly, M. Re-Evaluating the Role of Solar Variability on Northern Hemisphere Temperature Trends since the 19th Century. Earth Sci. Rev. 2015, 150, 409–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cionco, R.G.; Valentini, J.E.; Quaranta, N.E.; Soon, W.W.-H. Lunar Fingerprints in the Modulated Incoming Solar Radiation: In Situ Insolation and Latitudinal Insolation Gradients as Two Important Interpretative Metrics for Paleoclimatic Data Records and Theoretical Climate Modeling. New Astron. 2018, 58, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cionco, R.G.; Soon, W.W.-H.; Quaranta, N.E. On the Calculation of Latitudinal Insolation Gradients throughout the Holocene. Adv. Space Res. 2020, 66, 720–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, R.; Soon, W.; Connolly, M.; Baliunas, S.; Berglund, J.; Butler, C.J.; Cionco, R.G.; Elias, A.G.; Fedorov, V.M.; Harde, H.; et al. How Much Has the Sun Influenced Northern Hemisphere Temperature Trends? An Ongoing Debate. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 2021, 21, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durre, I.; Yin, X. Enhanced Radiosonde Data for Studies of Vertical Structure. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2008, 89, 1257–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meehl, G.A.; Arblaster, J.M.; Matthes, K.; Sassi, F.; Loon, H. van Amplifying the Pacific Climate System Response to a Small 11-Year Solar Cycle Forcing. Science 2009, 325, 1114–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Loon, H.; Meehl, G.A. The Average Influence of Decadal Solar Forcing on the Atmosphere in the South Pacific Region. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Huo, W.; Xiao, Z. Modulations of Solar Activity on El Niño Modoki and Possible Mechanisms. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2017, 160, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukianova, R.; Alekseev, G. Long-Term Correlation Between the Nao and Solar Activity. Sol. Phys. 2004, 224, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boberg, F.; Lundstedt, H. Solar Wind Electric Field Modulation of the NAO: A Correlation Analysis in the Lower Atmosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Loon, H.; Brown, J.; Milliff, R.F. Trends in Sunspots and North Atlantic Sea Level Pressure. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Borie, M.A.; Thabet, A.A.; El-Mallah, E.S.; Abd El-Zaher, M.; Bishara, A.A. The Combined Influences for Solar-Geomagnetic Activities and the Atmospheric Circulation NAO on Global Surface Temperatures. Indian J. Phys. 2021, 95, 1041–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroda, Y.; Kodera, K.; Yoshida, K.; Yukimoto, S.; Gray, L.J. Influence of the Solar Cycle on the North Atlantic Oscillation. Available online: http://www.essoar.org/doi/10.1002/essoar.10507546.1 (accessed on 22 September 2021).
- Hernández, A.; Sánchez-López, G.; Pla-Rabes, S.; Comas-Bru, L.; Parnell, A.; Cahill, N.; Geyer, A.; Trigo, R.M.; Giralt, S. A 2,000-Year Bayesian NAO Reconstruction from the Iberian Peninsula. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ait Brahim, Y.; Wassenburg, J.A.; Cruz, F.W.; Sifeddine, A.; Scholz, D.; Bouchaou, L.; Dassié, E.P.; Jochum, K.P.; Edwards, R.L.; Cheng, H. Multi-Decadal to Centennial Hydro-Climate Variability and Linkage to Solar Forcing in the Western Mediterranean during the Last 1000 Years. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruzmaikin, A.; Feynman, J.; Jiang, X.; Noone, D.C.; Waple, A.M.; Yung, Y.L. The Pattern of Northern Hemisphere Surface Air Temperature during Prolonged Periods of Low Solar Output. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L12201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, C.G.; von Savigny, C. Indications for a Potential Synchronization between the Phase Evolution of the Madden–Julian Oscillation and the Solar 27-Day Cycle. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 4235–4256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Mouël, J.-L.; Lopes, F.; Courtillot, V. A Solar Signature in Many Climate Indices. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 2600–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, F. The Relation among the Solar Activity, the Total Ozone, QBO, NAO, and ENSO by Wavelet-Based Multifractal Analysis. J. Appl. Math. Phys. 2018, 6, 1301–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.R.; Tiwari, C.M.; Agrawal, S.L.; Pant, T.K. Periodicity Variation of Solar Activity and Cosmic Rays During Solar Cycles 22–24. Sol. Phys. 2019, 294, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, B. QBO-MJO Connection. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 2957–2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Caron, J.M.; Richter, J.H.; Simpson, I.R. The Lack of QBO-MJO Connection in CMIP6 Models. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL087295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christoforou, P.; Hameed, S. Solar Cycle and the Pacific ‘centers of Action’. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1997, 24, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfîcă, L.; Voiculescu, M. Possible Effects of Atmospheric Teleconnections and Solar Variability on Tropospheric and Stratospheric Temperatures in the Northern Hemisphere. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2014, 109, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfîcă, L.; Iordache, I.; Voiculescu, M. Solar Signal on Regional Scale: A Study of Possible Solar Impact upon Romania’s Climate. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2018, 177, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, I. The Role of the Sun in Atmosphere–Ocean Coupling. Int. J. Climatol. 2014, 34, 655–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, I. Climate Variability and Sunspot Activity: Analysis of the Solar Influence on Climate; Springer Atmospheric Sciences; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; ISBN 978-3-319-77106-9. [Google Scholar]
- Dobrica, V.; Pirloaga, R.; Stefan, C.; Demetrescu, C. Inferring Geoeffective Solar Variability Signature in Stratospheric and Tropospheric Northern Hemisphere Temperatures. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2018, 180, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Xu, H.; Lan, J.; Zhou, K.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, J.; An, Z.; Yeager, K.M. Solar Activity and the Westerlies Dominate Decadal Hydroclimatic Changes over Arid Central Asia. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2019, 173, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüdecke, H.-J.; Cina, R.; Dammschneider, H.-J.; Lüning, S. Decadal and Multidecadal Natural Variability in European Temperature. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2020, 205, 105294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veretenenko, S.; Ogurtsov, M. Regional and Temporal Variability of Solar Activity and Galactic Cosmic Ray Effects on the Lower Atmosphere Circulation. Adv. Space Res. 2012, 49, 770–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogurtsov, M.; Lindholm, M.; Jalkanen, R.; Veretenenko, S. Evidence for the Gleissberg Solar Cycle at the High-Latitudes of the Northern Hemisphere. Adv. Space Res. 2015, 55, 1285–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veretenenko, S.; Ogurtsov, M. Manifestation and Possible Reasons of ∼60-Year Oscillations in Solar-Atmospheric Links. Adv. Space Res. 2019, 64, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogurtsov, M. Decadal and Bi-Decadal Periodicities in Temperature of Southern Scandinavia: Manifestations of Natural Variability or Climatic Response to Solar Cycles? Atmosphere 2021, 12, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waliser, D.E.; Shi, Z.; Lanzante, J.R.; Oort, A.H. The Hadley Circulation: Assessing NCEP/NCAR Reanalysis and Sparse in-Situ Estimates. Clim. Dyn. 1999, 15, 719–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitas, C.M.; Clement, A. Has the Hadley Cell Been Strengthening in Recent Decades? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johanson, C.M.; Fu, Q. Hadley Cell Widening: Model Simulations versus Observations. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 2713–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachnik, J.P.; Schumacher, C. A Comparison of the Hadley Circulation in Modern Reanalyses. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Song, M.; Hu, Y.; Ren, X. Changes in the Strength and Width of the Hadley Circulation since 1871. Clim. Past 2012, 8, 1169–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.; Evans, A.; Lucas, C.; Smith, I.; Timbal, B. The Hadley Circulation in Reanalyses: Climatology, Variability, and Change. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 3357–3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 Global Reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Vecchi, G.A.; Reichler, T. Expansion of the Hadley Cell under Global Warming. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garfinkel, C.I.; Waugh, D.W.; Polvani, L.M. Recent Hadley Cell Expansion: The Role of Internal Atmospheric Variability in Reconciling Modeled and Observed Trends. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 10824–10831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.-P.; Li, J.-P.; Feng, J. Climatology and Interannual Variability of the Annual Mean Hadley Circulation in CMIP5 Models. Adv. Clim. Chang. Res. 2016, 7, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, N.; Birner, T. On the Discrepancies in Tropical Belt Expansion between Reanalyses and Climate Models and among Tropical Belt Width Metrics. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 1211–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grise, K.M.; Davis, S.M. Hadley Cell Expansion in CMIP6 Models. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 5249–5268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Hu, Y.; Liu, J. Comparison of Trends in the Hadley Circulation between CMIP6 and CMIP5. Sci. Bull. 2020, 65, 1667–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, C.; Timbal, B.; Nguyen, H. The Expanding Tropics: A Critical Assessment of the Observational and Modeling Studies. WIREs Clim. Chang. 2014, 5, 89–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.J.; Kovilakam, M. The Role of Natural Climate Variability in Recent Tropical Expansion. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 6329–6350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Huang, H.; Zhou, C. Widening and Weakening of the Hadley Circulation under Global Warming. Sci. Bull. 2018, 63, 640–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, N.A.; Davis, S.M. Reconciling Hadley Cell Expansion Trend Estimates in Reanalyses. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 11439–11446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemke, R.; Polvani, L.M. Opposite Tropical Circulation Trends in Climate Models and in Reanalyses. Nat. Geosci. 2019, 12, 528–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, C.; Nguyen, H.; Timbal, B. An Observational Analysis of Southern Hemisphere Tropical Expansion. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, D17112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, N.A.; Birner, T. Seasonal to Multidecadal Variability of the Width of the Tropical Belt. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 7773–7787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, A.; Polvani, L.M.; Waugh, D.W.; Davis, S.M. Contrasting Upper and Lower Atmospheric Metrics of Tropical Expansion in the Southern Hemisphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 10496–10503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hu, Y.; Zhou, C.; Liu, J. Observational Evidence for Poleward Expansion of the Hadley Circulation. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2011, 28, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, R.; Connolly, M.; Soon, W.; Legates, D.R.; Cionco, R.G.; Velasco Herrera, V.M. Northern Hemisphere Snow-Cover Trends (1967–2018): A Comparison between Climate Models and Observations. Geosciences 2019, 9, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKitrick, R.; Christy, J. Pervasive Warming Bias in CMIP6 Tropospheric Layers. Earth Space Sci. 2020, 7, e2020EA001281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stith, J.L.; Baumgardner, D.; Haggerty, J.; Hardesty, R.M.; Lee, W.-C.; Lenschow, D.; Pilewskie, P.; Smith, P.L.; Steiner, M.; Vömel, H. 100 Years of Progress in Atmospheric Observing Systems. Meteorol. Monogr. 2018, 59, 2.1–2.55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilczak, J.M.; Gossard, E.E.; Neff, W.D.; Eberhard, W.L. Ground-Based Remote Sensing of the Atmospheric Boundary Layer: 25 Years of Progress. In Boundary-Layer Meteorology 25th Anniversary Volume, 1970–1995: Invited Reviews and Selected Contributions to Recognise Ted Munn’s Contribution as Editor over the Past 25 Years; Garratt, J.R., Taylor, P.A., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1996; pp. 321–349. ISBN 978-94-017-0944-6. [Google Scholar]
- Bianco, L.; Friedrich, K.; Wilczak, J.M.; Hazen, D.; Wolfe, D.; Delgado, R.; Oncley, S.P.; Lundquist, J.K. Assessing the Accuracy of Microwave Radiometers and Radio Acoustic Sounding Systems for Wind Energy Applications. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 1707–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Kim, S.-W.; Park, M.-S.; Song, C.-K. Measurement of Planetary Boundary Layer Winds with Scanning Doppler Lidar. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, R.; Yang, Y.; Hu, X.-M.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, S. A Review of Techniques for Diagnosing the Atmospheric Boundary Layer Height (ABLH) Using Aerosol Lidar Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzi, L.; Wotawa, G.; Schoeppner, M.; Kalinowski, M.; Saey, P.R.J.; Steinmann, P.; Luan, L.; Staten, P.W. Radioisotopes Demonstrate Changes in Global Atmospheric Circulation Possibly Caused by Global Warming. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron, P.; Murtagh, D.; Eriksson, P.; Mendrok, J.; Ochiai, S.; Pérot, K.; Sagawa, H.; Suzuki, M. Simulation Study for the Stratospheric Inferred Winds (SIW) Sub-Millimeter Limb Sounder. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 4545–4566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duruisseau, F.; Huret, N.; Andral, A.; Camy-Peyret, C. Assessment of the ERA-Interim Winds Using High-Altitude Stratospheric Balloons. J. Atmos. Sci. 2017, 74, 2065–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Lin, Z.; Santanello, J.A., Jr.; Gao, Z., Jr. Development and Evaluation of a Long-Term Data Record of Planetary Boundary Layer Profiles from Aircraft Meteorological Reports. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 2008–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, M.; Connolly, R. The Physics of the Earth’s Atmosphere, I. Phase Change Associated with Tropopause. Open Peer Rev. J. 2014, 19. Available online: http://oprj.net/articles/atmospheric-science/19 (accessed on 25 October 2021).
- Connolly, M.; Connolly, R. The Physics of the Earth’s Atmosphere II. Multimerization of Atmospheric Gases above the Troposphere. Open Peer Rev. J. 2014, 22. Available online: http://oprj.net/articles/atmospheric-science/22 (accessed on 25 October 2021).
- Connolly, M.; Connolly, R. The Physics of the Earth’s Atmosphere III. Pervective Power. Open Peer Rev. J. 2014, 25. Available online: http://oprj.net/articles/atmospheric-science/25 (accessed on 25 October 2021).
- Murphy, D.M.; Koop, T. Review of the Vapour Pressures of Ice and Supercooled Water for Atmospheric Applications. Quarterly J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2005, 131, 1539–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrence, C.; Compo, G.P. A Practical Guide to Wavelet Analysis. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 79, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soon, W.; Velasco Herrera, V.M.; Cionco, R.G.; Qiu, S.; Baliunas, S.; Egeland, R.; Henry, G.W.; Charvátová, I. Covariations of Chromospheric and Photometric Variability of the Young Sun Analogue HD 30495: Evidence for and Interpretation of Mid-Term Periodicities. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 483, 2748–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco Herrera, V.M.; Soon, W.; Velasco Herrera, G.; Traversi, R.; Horiuchi, K. Generalization of the Cross-Wavelet Function. New Astron. 2017, 56, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soon, W.; Velasco Herrera, V.M.; Selvaraj, K.; Traversi, R.; Usoskin, I.; Chen, C.-T.A.; Lou, J.-Y.; Kao, S.-J.; Carter, R.M.; Pipin, V.; et al. A Review of Holocene Solar-Linked Climatic Variation on Centennial to Millennial Timescales: Physical Processes, Interpretative Frameworks and a New Multiple Cross-Wavelet Transform Algorithm. Earth Sci. Rev. 2014, 134, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoinka, K.P. The Tropopause: Discovery, Definition and Demarcation. Meteorologische Zeitschrift 1997, 281–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristoufek, L. Has Global Warming Modified the Relationship between Sunspot Numbers and Global Temperatures? Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2017, 468, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallegati, M. A Systematic Wavelet-Based Exploratory Analysis of Climatic Variables. Clim. Chang. 2018, 148, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cionco, R.G.; Kudryavtsev, S.M.; Soon, W.W.-H. Possible Origin of Some Periodicities Detected in Solar-Terrestrial Studies: Earth’s Orbital Movements. Earth Space Sci. 2021, 8, e2021EA001805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmermans, M.-L.; Marshall, J. Understanding Arctic Ocean Circulation: A Review of Ocean Dynamics in a Changing Climate. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2020, 125, e2018JC014378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Winton, M.; Vecchi, G.; Jia, L.; Rugenstein, M. Transient Climate Sensitivity Depends on Base Climate Ocean Circulation. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 1493–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, J. Relationship between Sea Surface Salinity and Ocean Circulation and Climate Change. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2019, 62, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
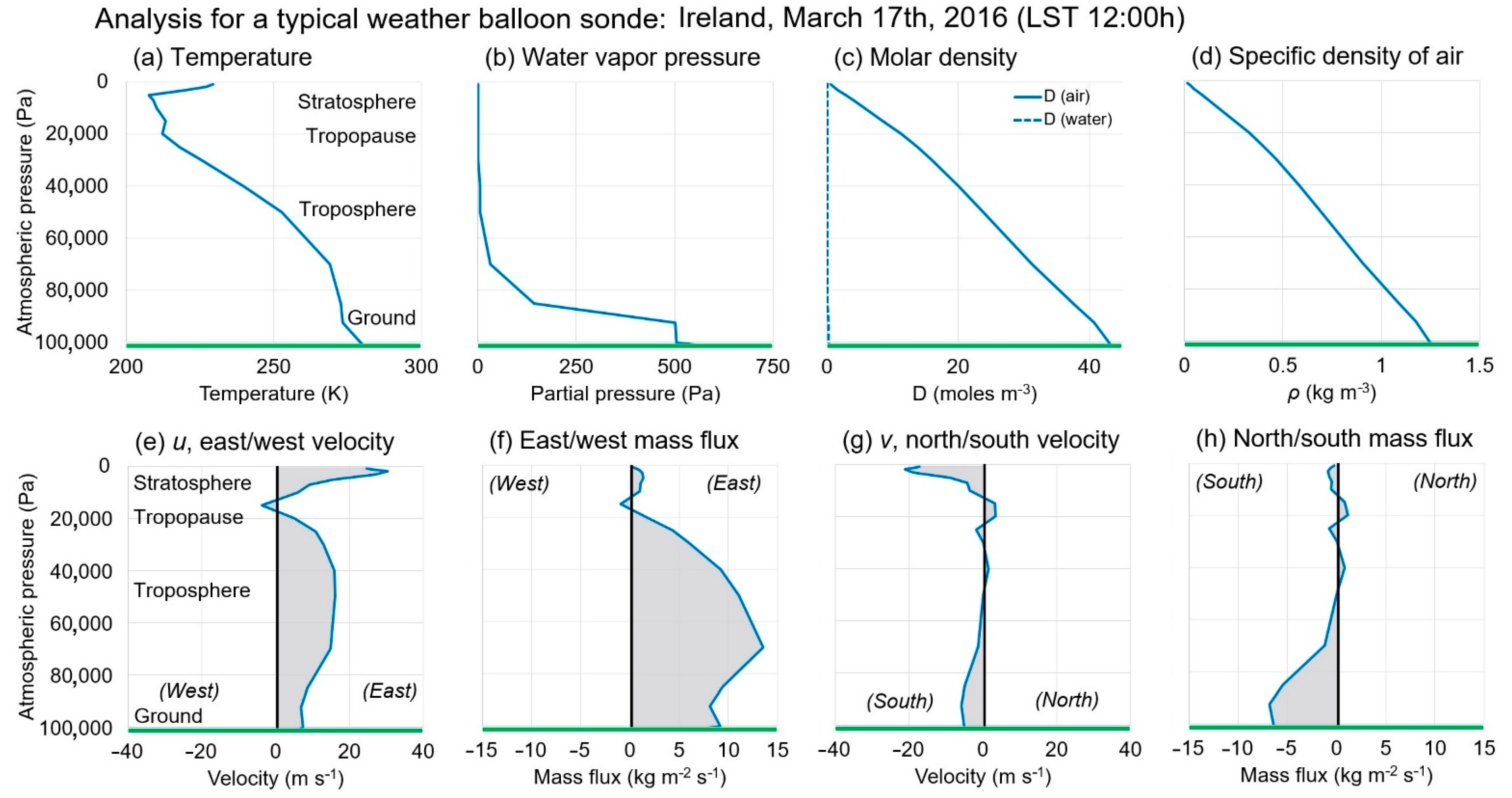
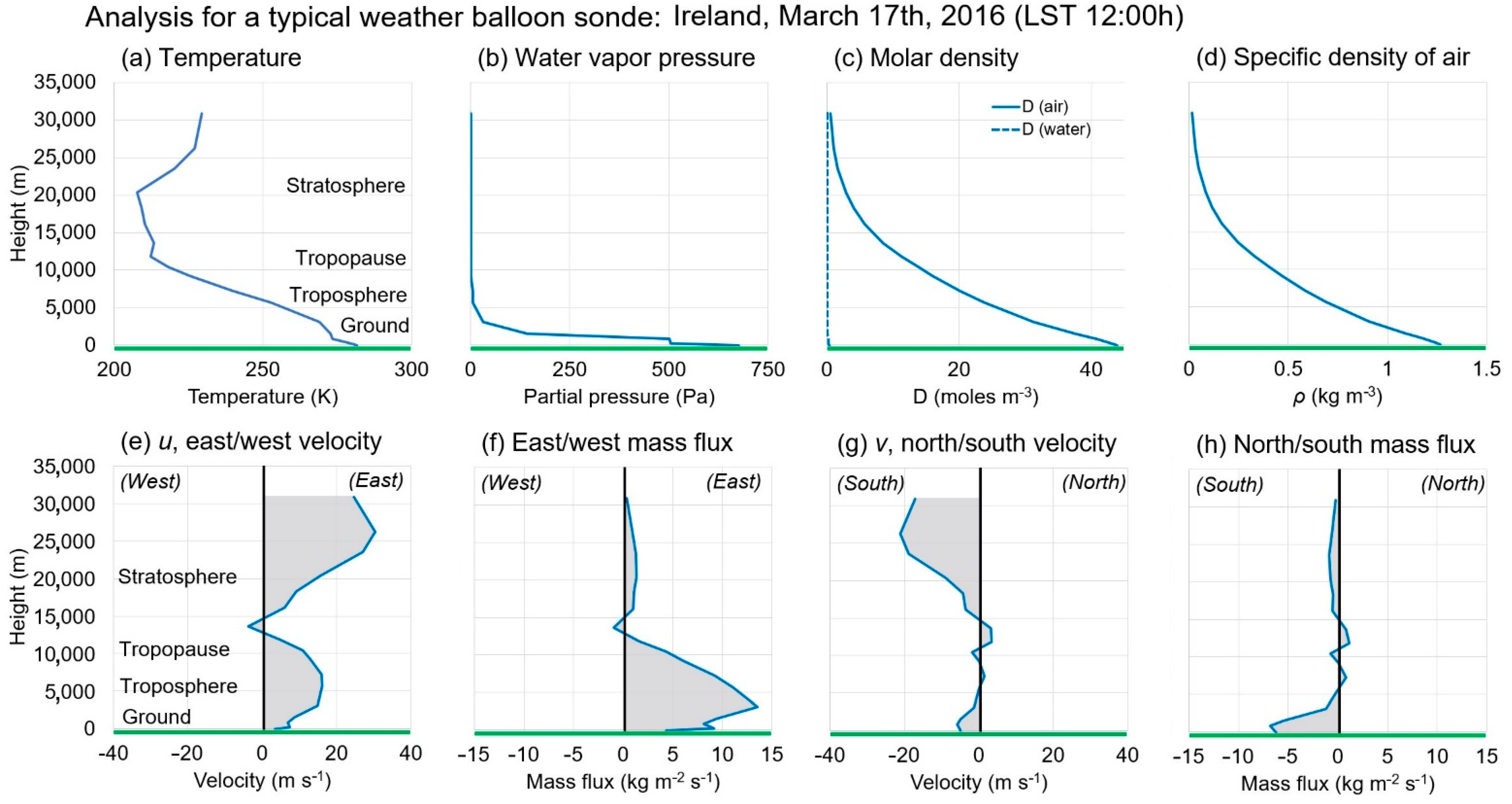
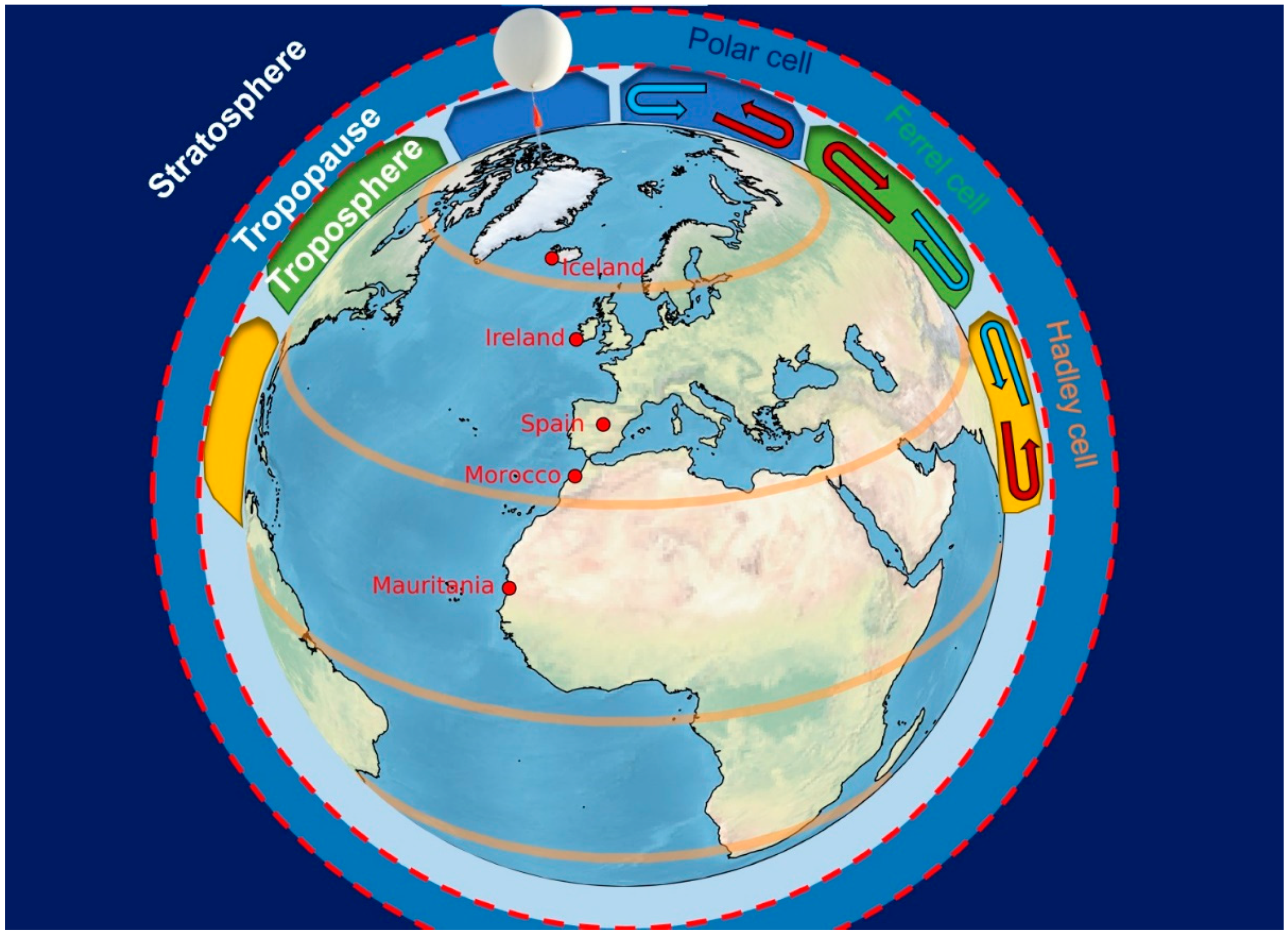
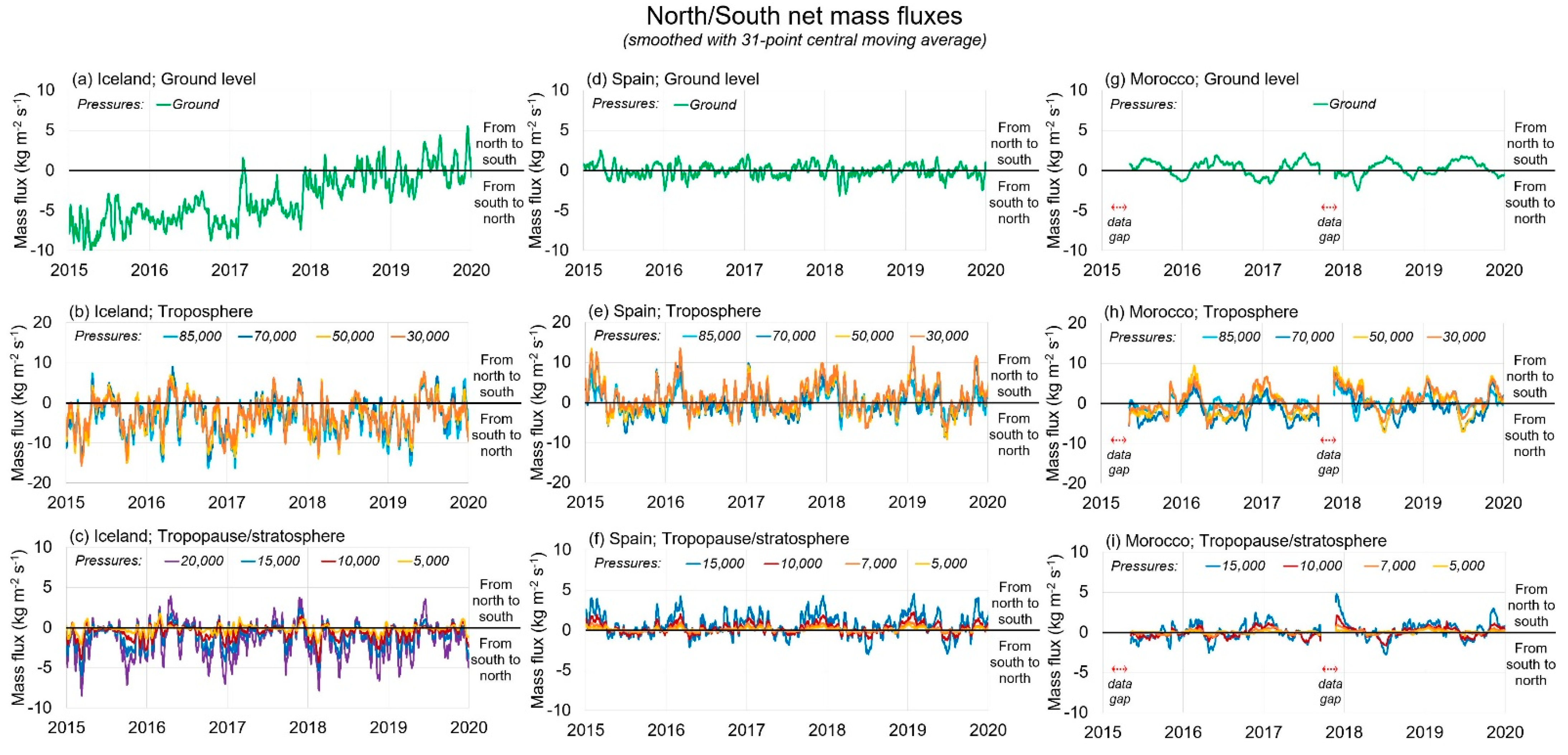
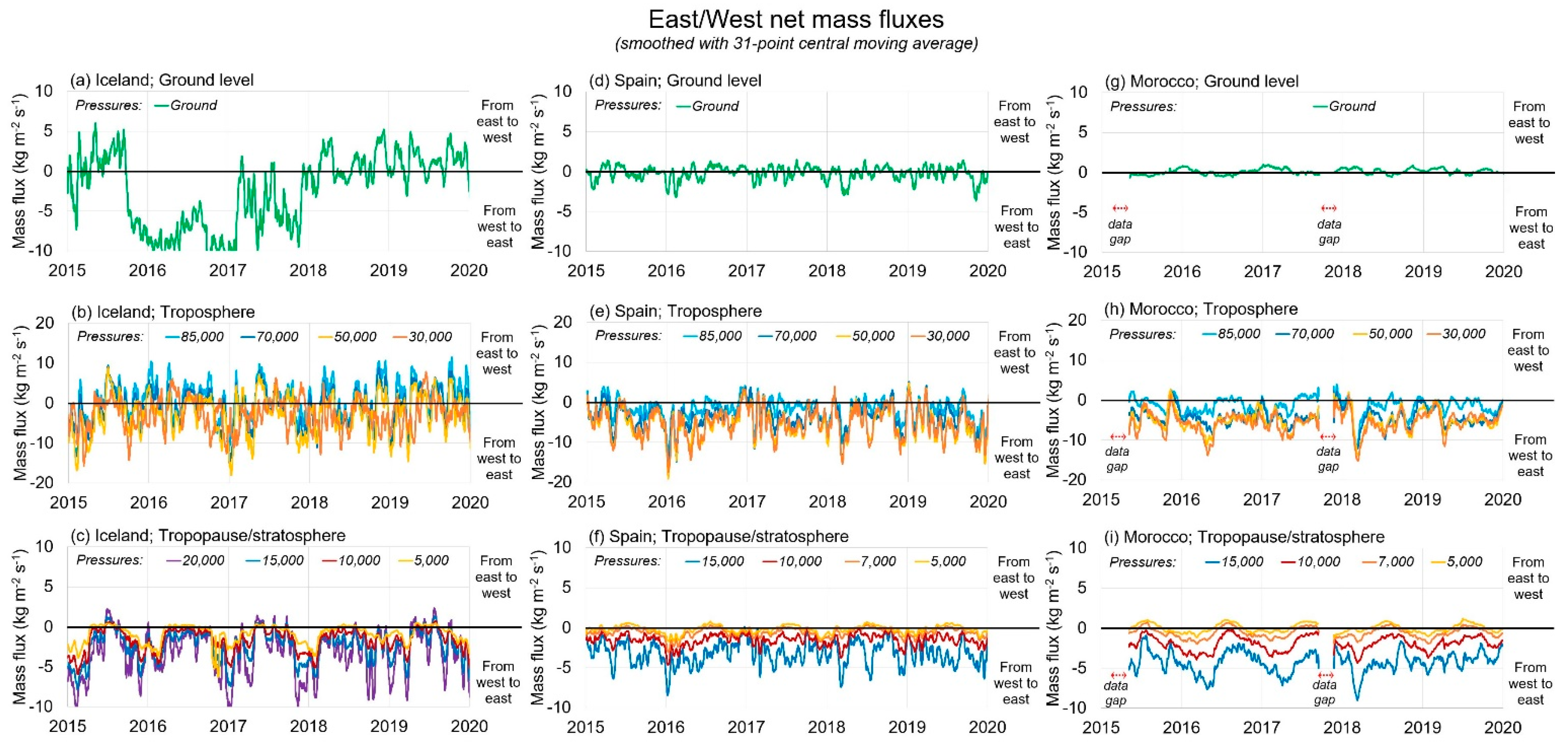
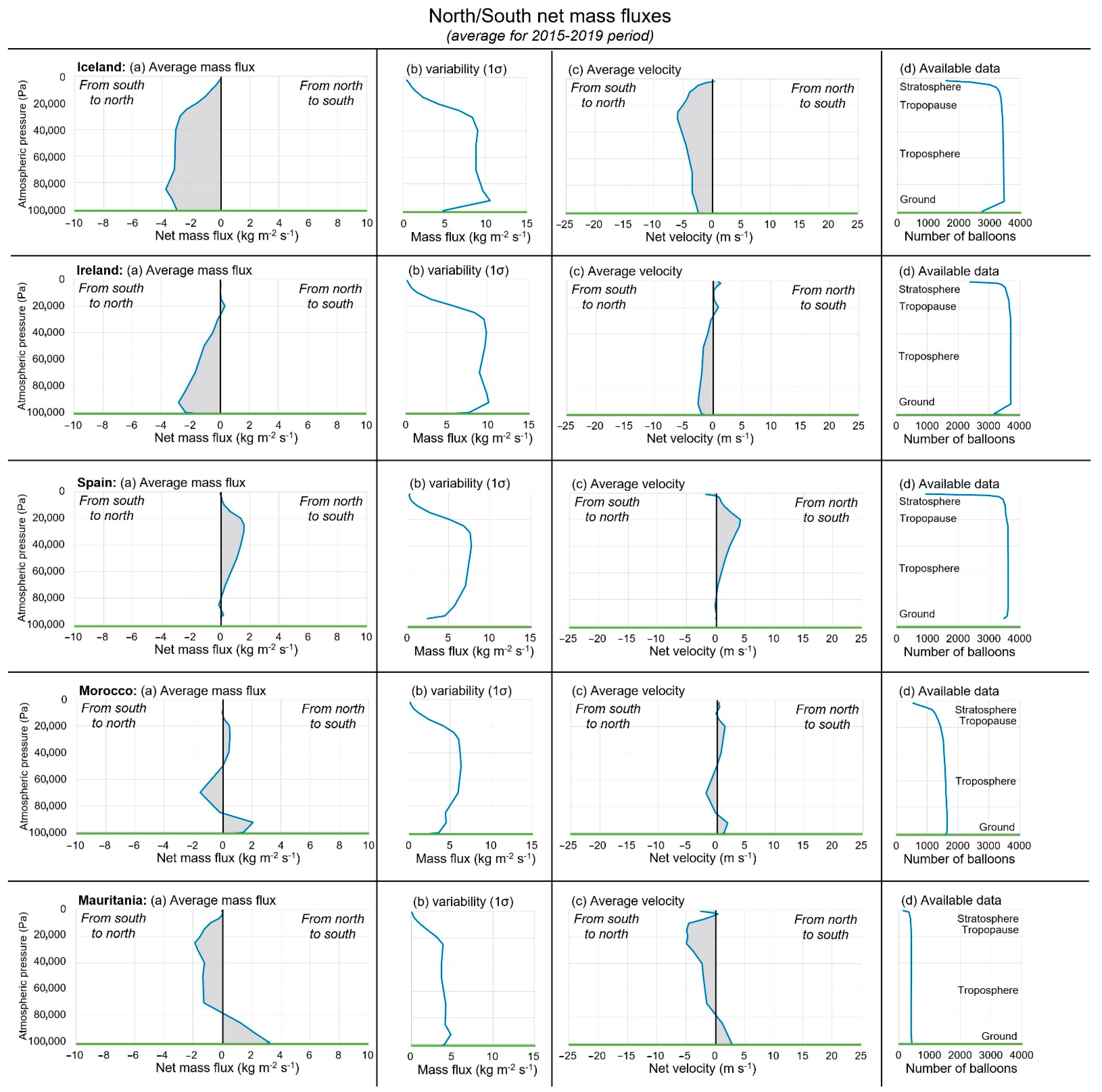
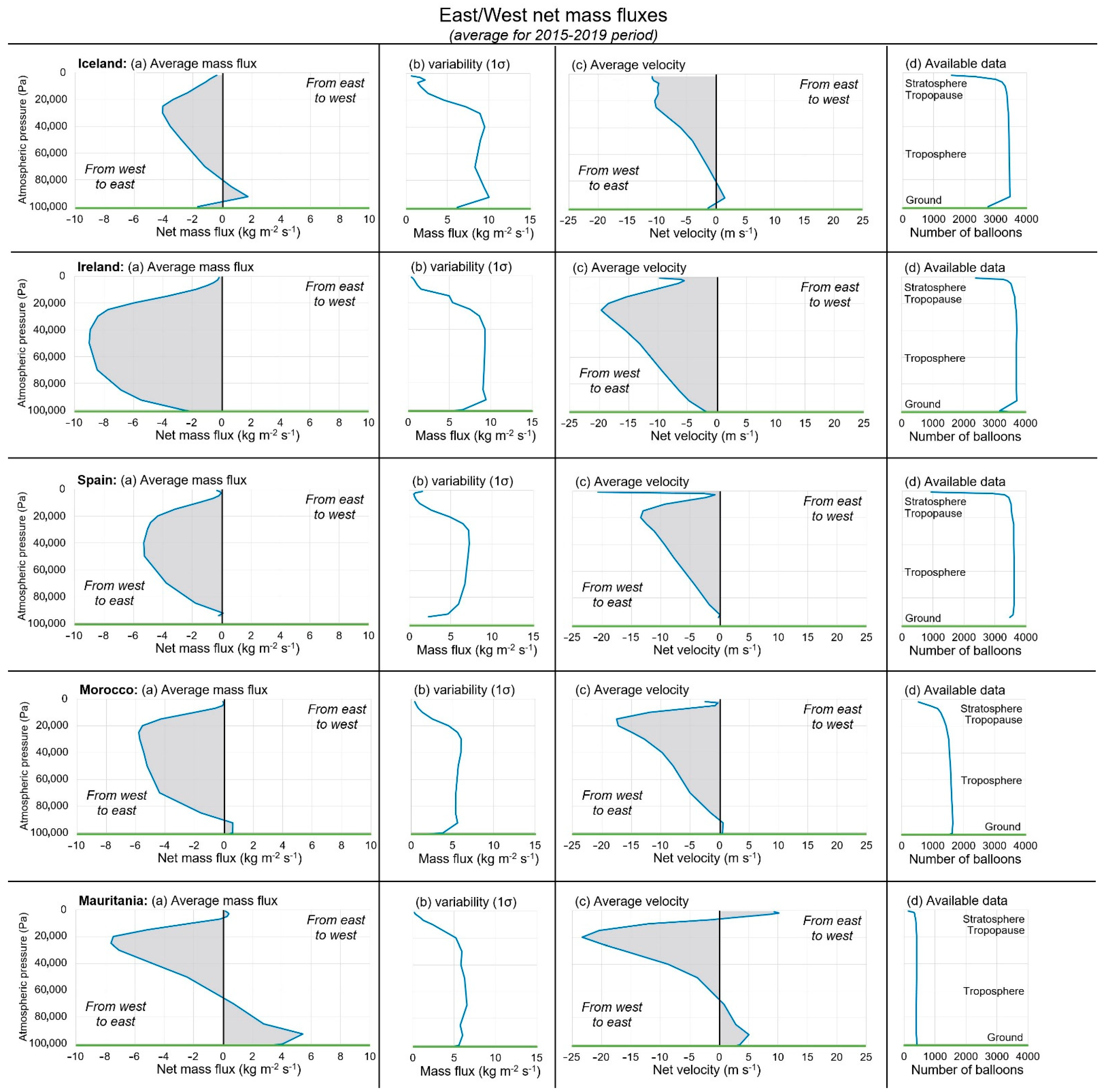
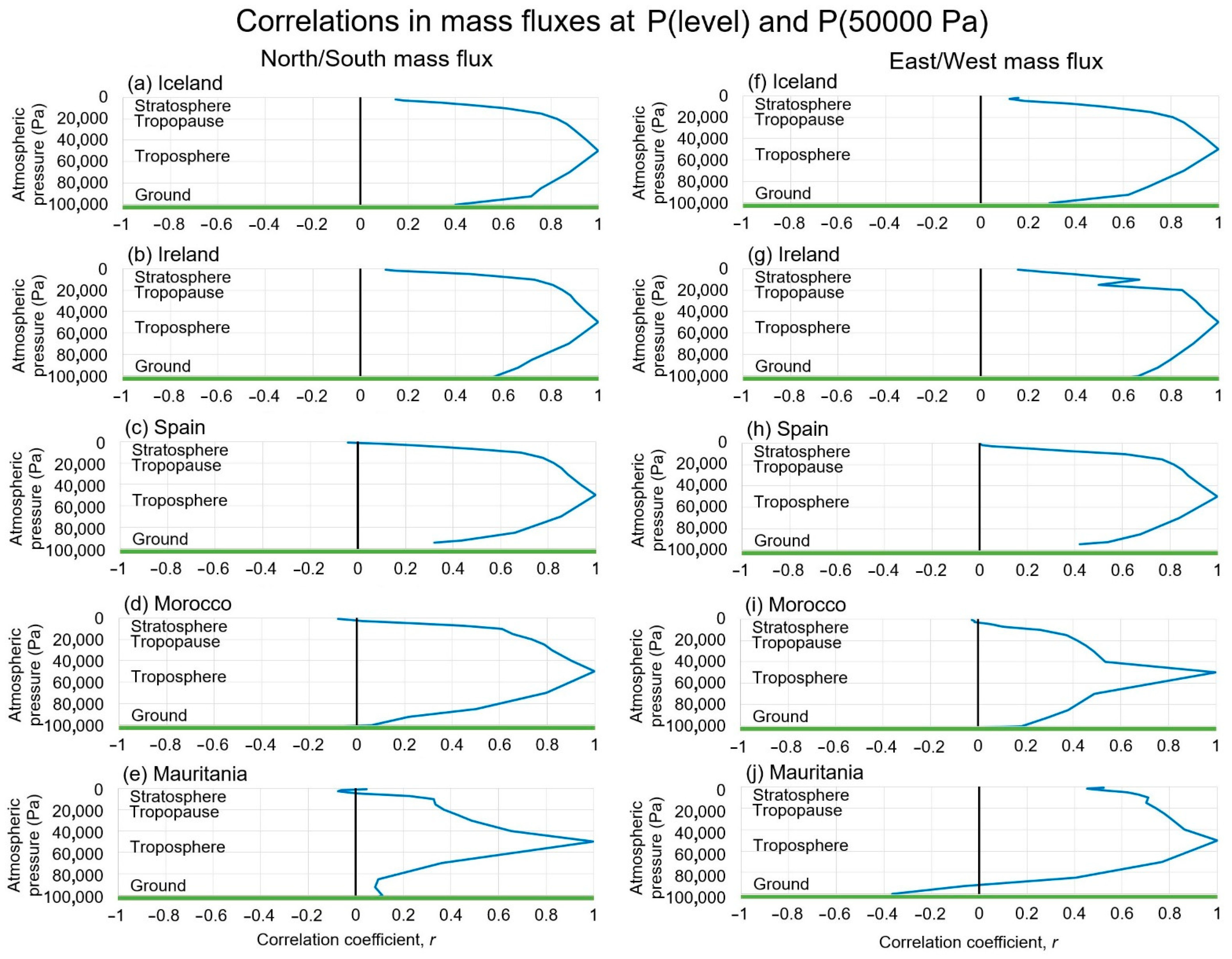

| Country | Location | Station ID | Latitude | Longitude | Elevation | Years Covered | Balloons Available |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Iceland | Keflavíkurflugvöllur | ICM00004018 | 63.9806° N | 22.5950° E | 52.0 m | 1946–2021 | 67,193 |
| Ireland | Valentia Observatory | EIM00003953 | 51.9381° N | 10.2433° E | 23.9 m | 1949–2021 | 68,495 |
| Spain | Madrid–Barajas | SPM00008221 | 40.4653° N | 3.5797° E | 631.0 m | 1950–2021 | 43,864 |
| Morocco | Casablanca | MOM00060155 | 33.5667° N | 7.6667° E | 56.0 m | 1949–2021 | 26,290 |
| Mauritania | Nouakchott | MRM00061442 | 18.10° N | 15.95° E | 2.0 m | 1941–2021 | 31,687 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Connolly, M.; Connolly, R.; Soon, W.; Velasco Herrera, V.M.; Cionco, R.G.; Quaranta, N.E. Analyzing Atmospheric Circulation Patterns Using Mass Fluxes Calculated from Weather Balloon Measurements: North Atlantic Region as a Case Study. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1439. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12111439
Connolly M, Connolly R, Soon W, Velasco Herrera VM, Cionco RG, Quaranta NE. Analyzing Atmospheric Circulation Patterns Using Mass Fluxes Calculated from Weather Balloon Measurements: North Atlantic Region as a Case Study. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(11):1439. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12111439
Chicago/Turabian StyleConnolly, Michael, Ronan Connolly, Willie Soon, Víctor M. Velasco Herrera, Rodolfo Gustavo Cionco, and Nancy E. Quaranta. 2021. "Analyzing Atmospheric Circulation Patterns Using Mass Fluxes Calculated from Weather Balloon Measurements: North Atlantic Region as a Case Study" Atmosphere 12, no. 11: 1439. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12111439
APA StyleConnolly, M., Connolly, R., Soon, W., Velasco Herrera, V. M., Cionco, R. G., & Quaranta, N. E. (2021). Analyzing Atmospheric Circulation Patterns Using Mass Fluxes Calculated from Weather Balloon Measurements: North Atlantic Region as a Case Study. Atmosphere, 12(11), 1439. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12111439






