Determine the Land-Use Land-Cover Changes, Urban Expansion and Their Driving Factors for Sustainable Development in Gazipur Bangladesh
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- Quantify and assess the overall land-use/land-cover changes in the Gazipur district, a rapidly developing industrial hub area in Bangladesh, over the period from 1990 to 2020;
- (2)
- (Compute the changes in built-up areas in terms of both direction and distance during the time frame of 1990–2020;
- (3)
- Determine the major driving factors of land-use/land-cover changes, especially the reasons for the rapid progression of urbanization.
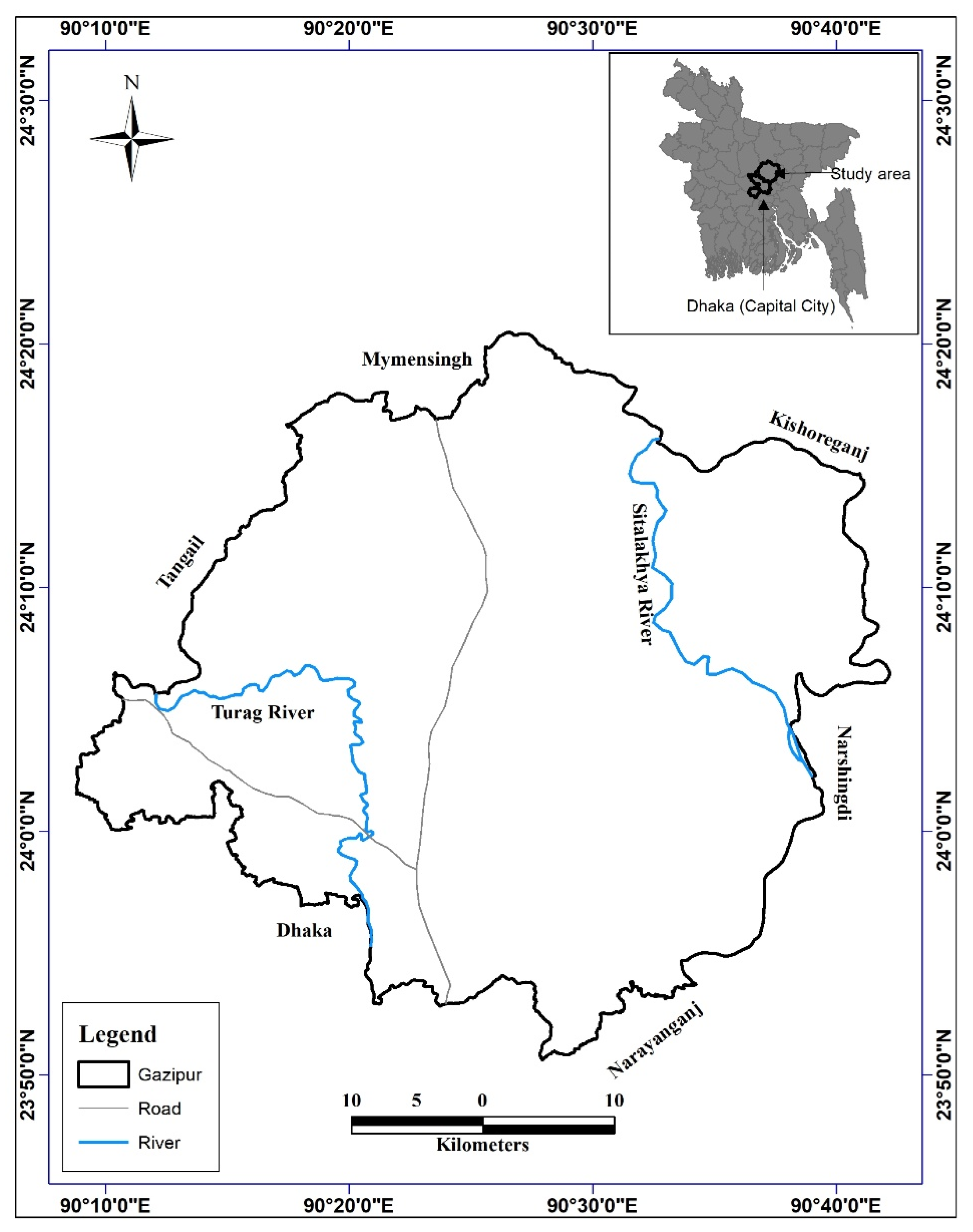
2. Study Area
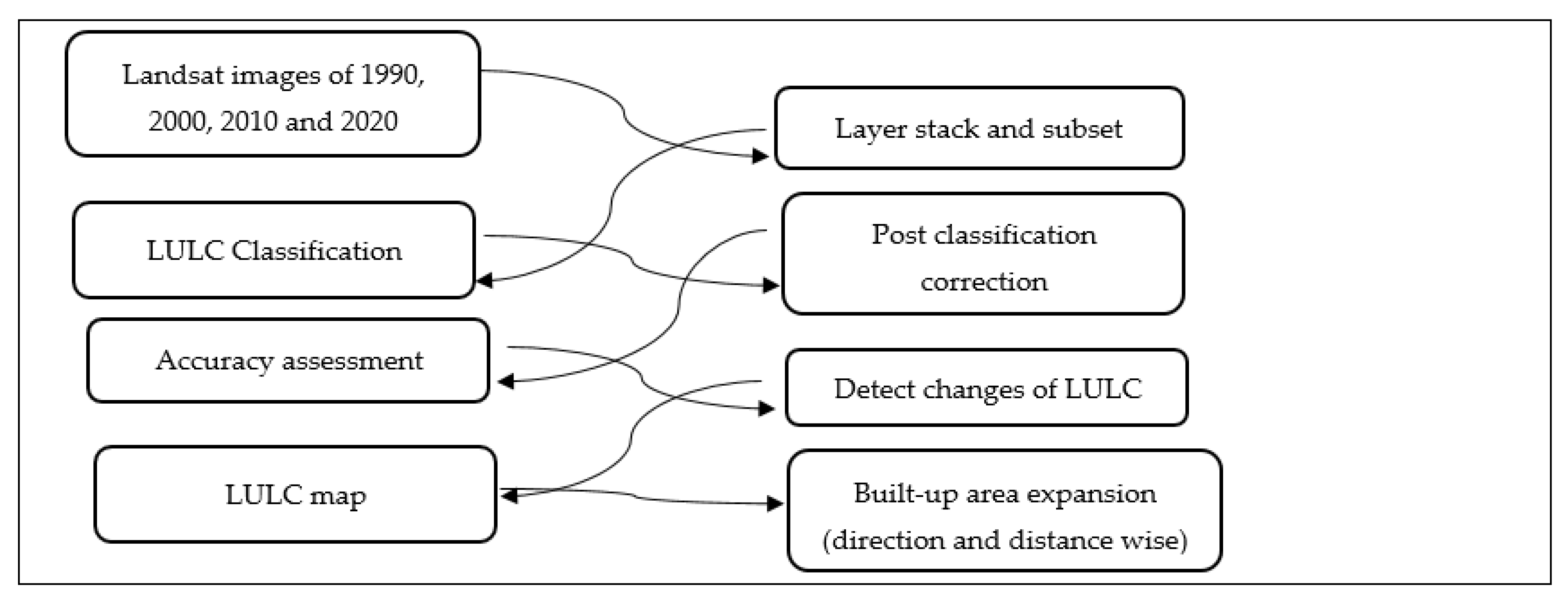
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Data
3.2. Image Preprocessing
3.3. Image Classification
3.4. Land-Use Land-Cover Classification Scheme
3.5. Accuracy Assessment
3.6. Change Detection
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Accuracy
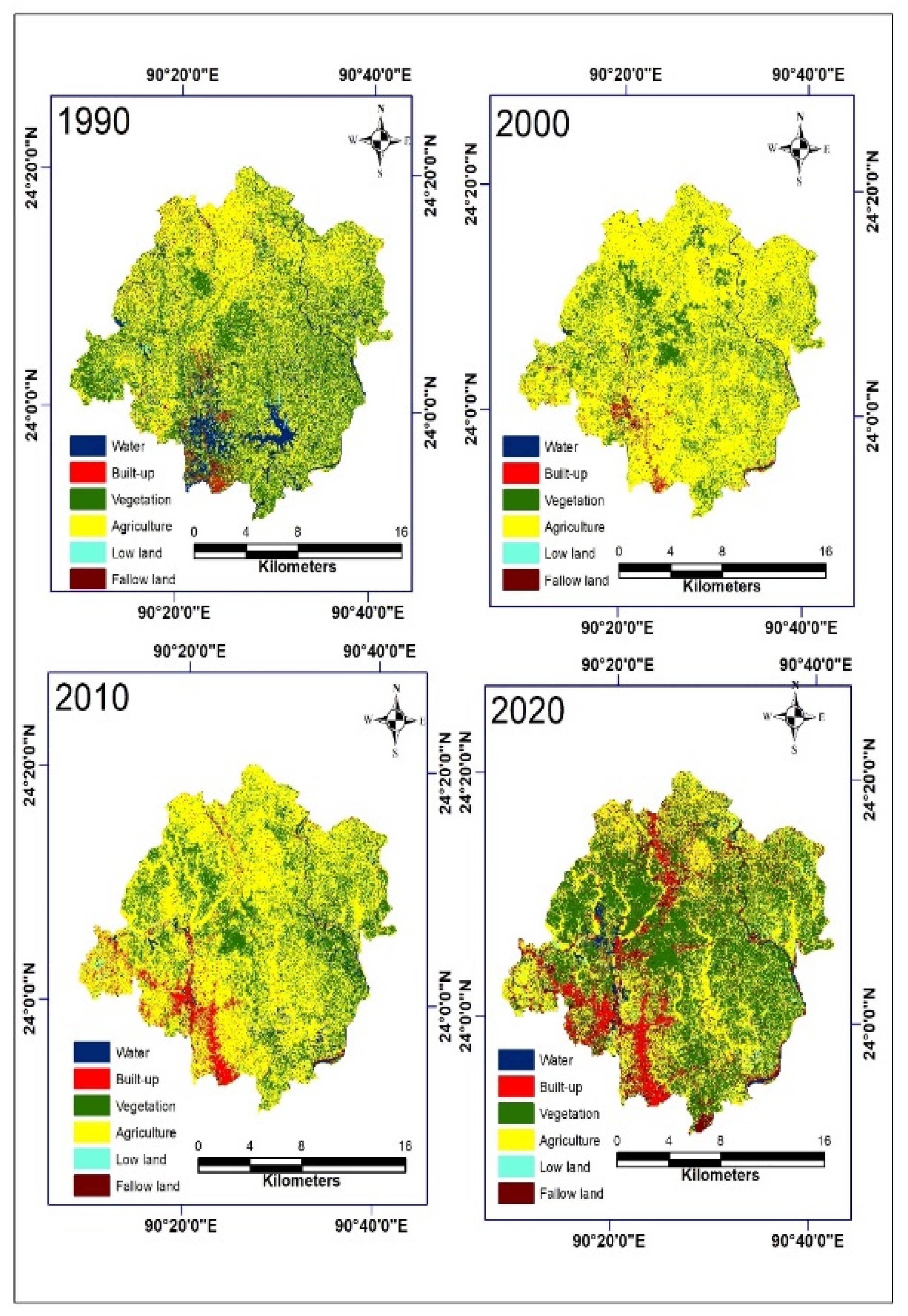
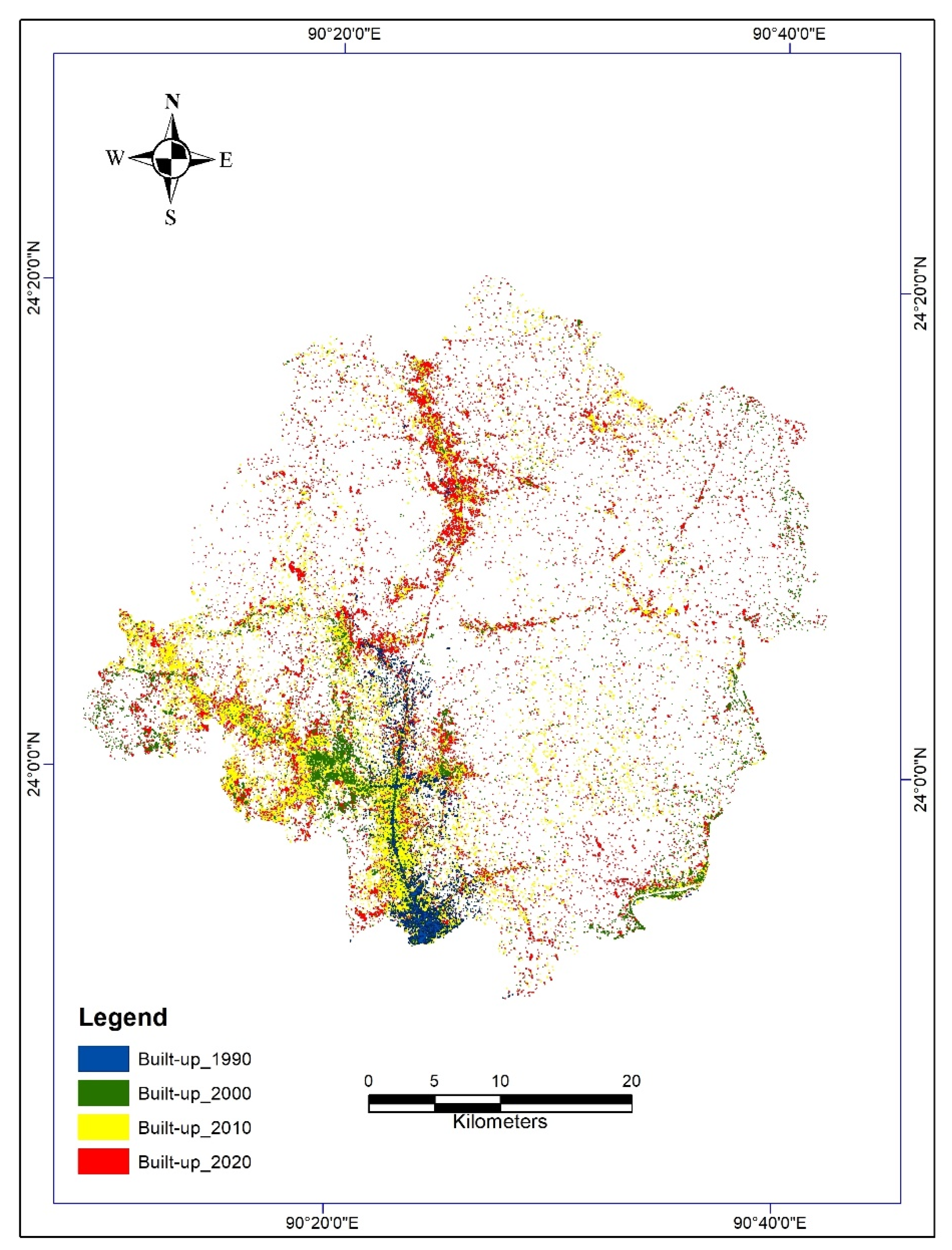
4.2. Land-Use/Land-Cover Change
4.3. Change Detection
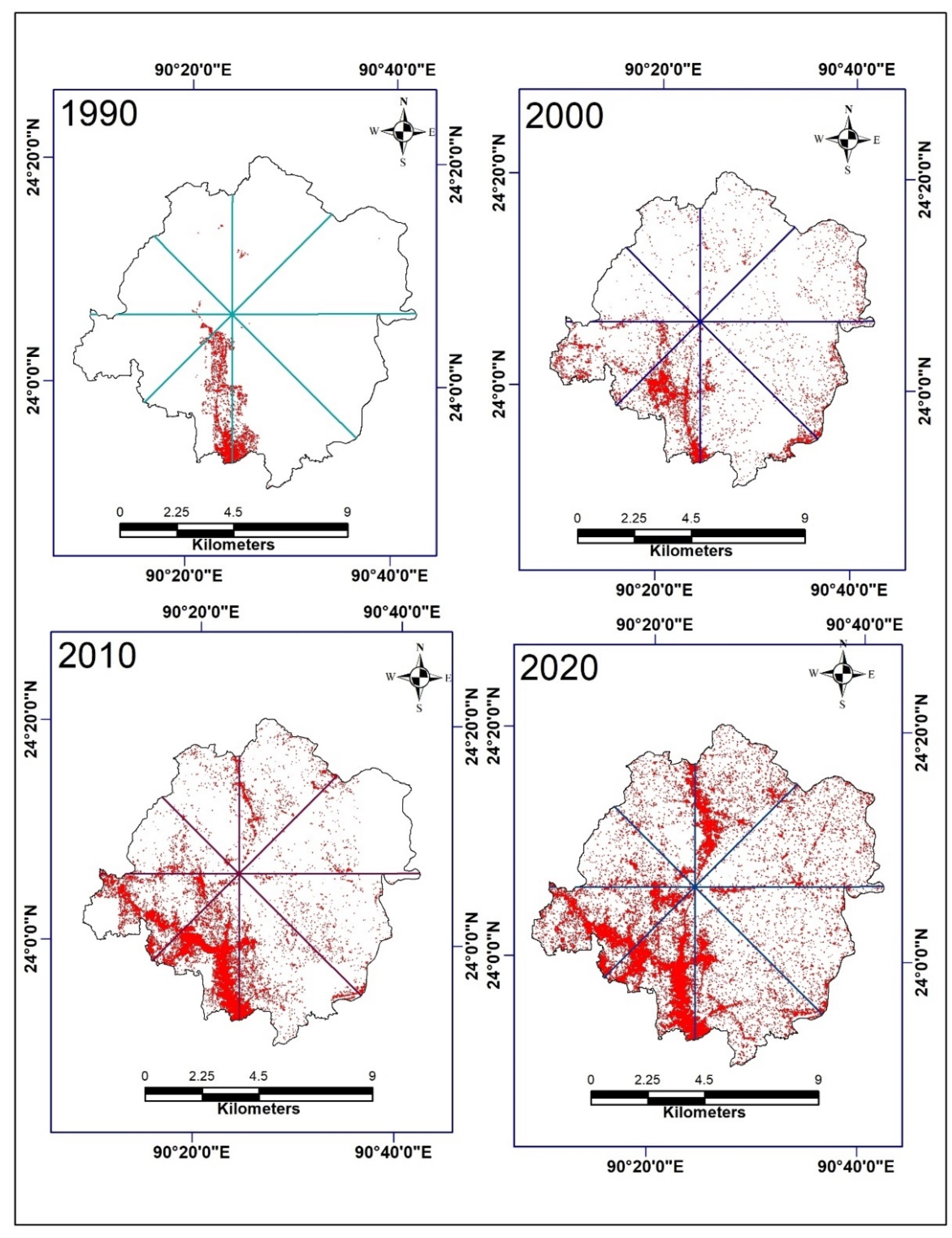
5. Urban Expansion
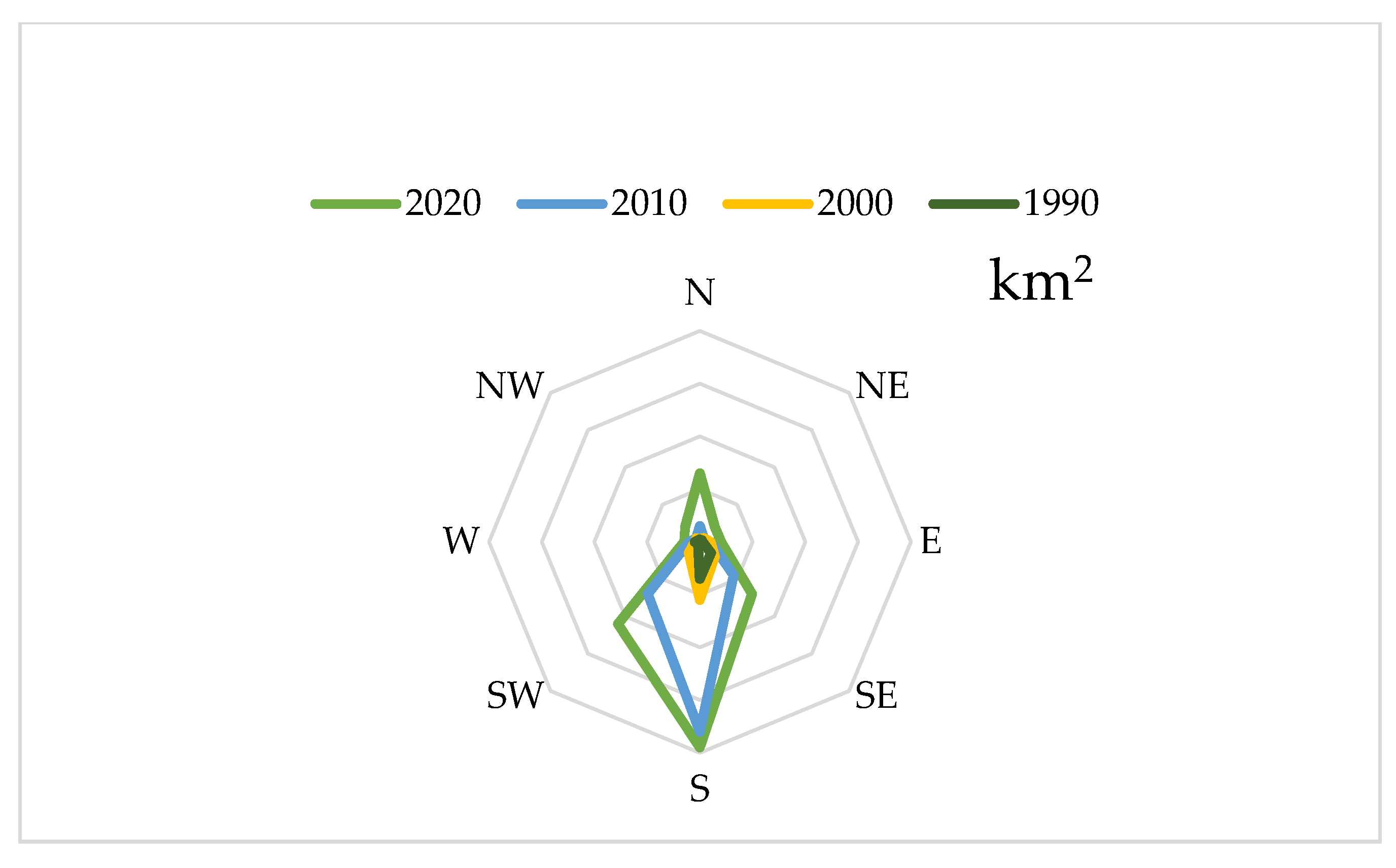
5.1. Direction of Urban Expansion
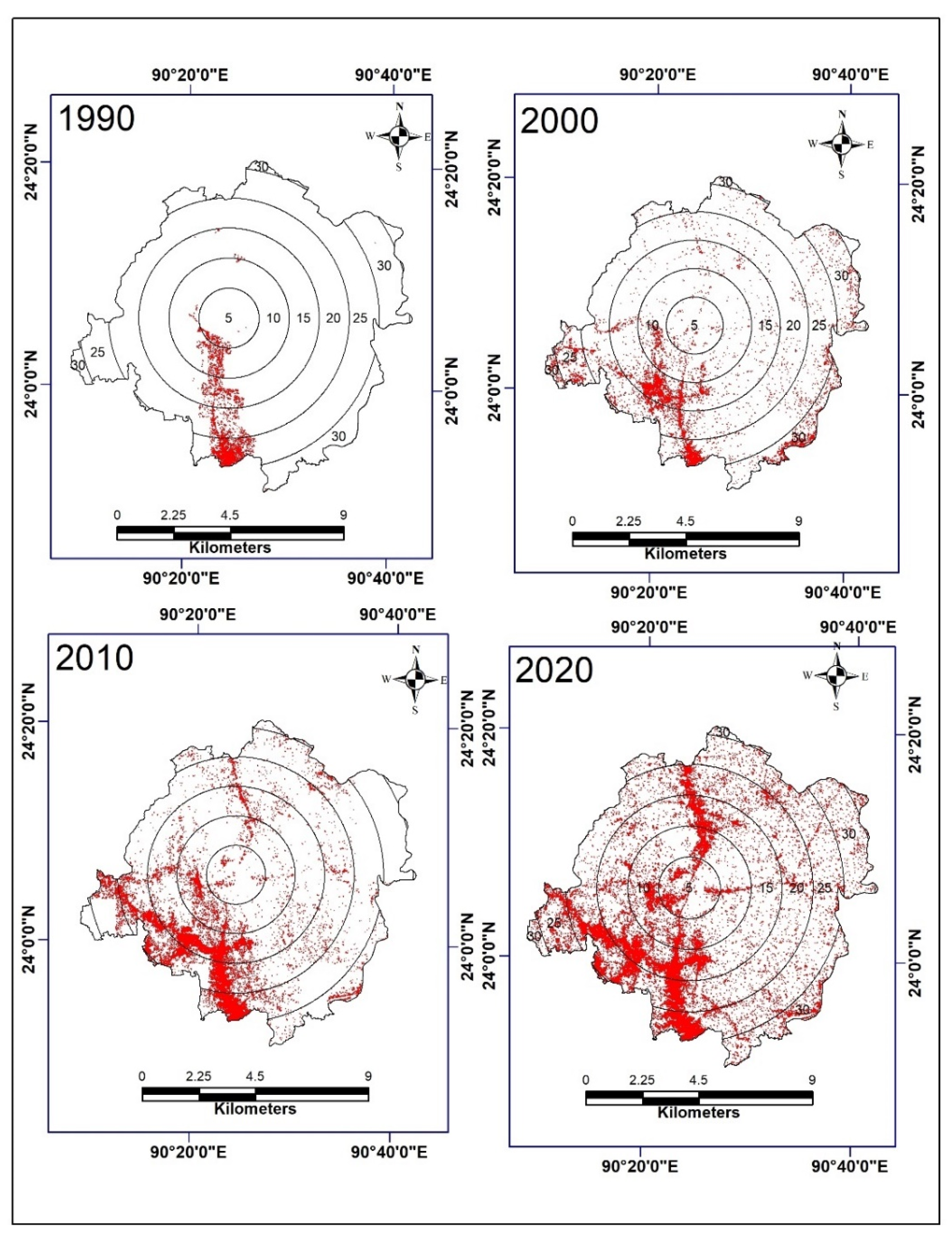
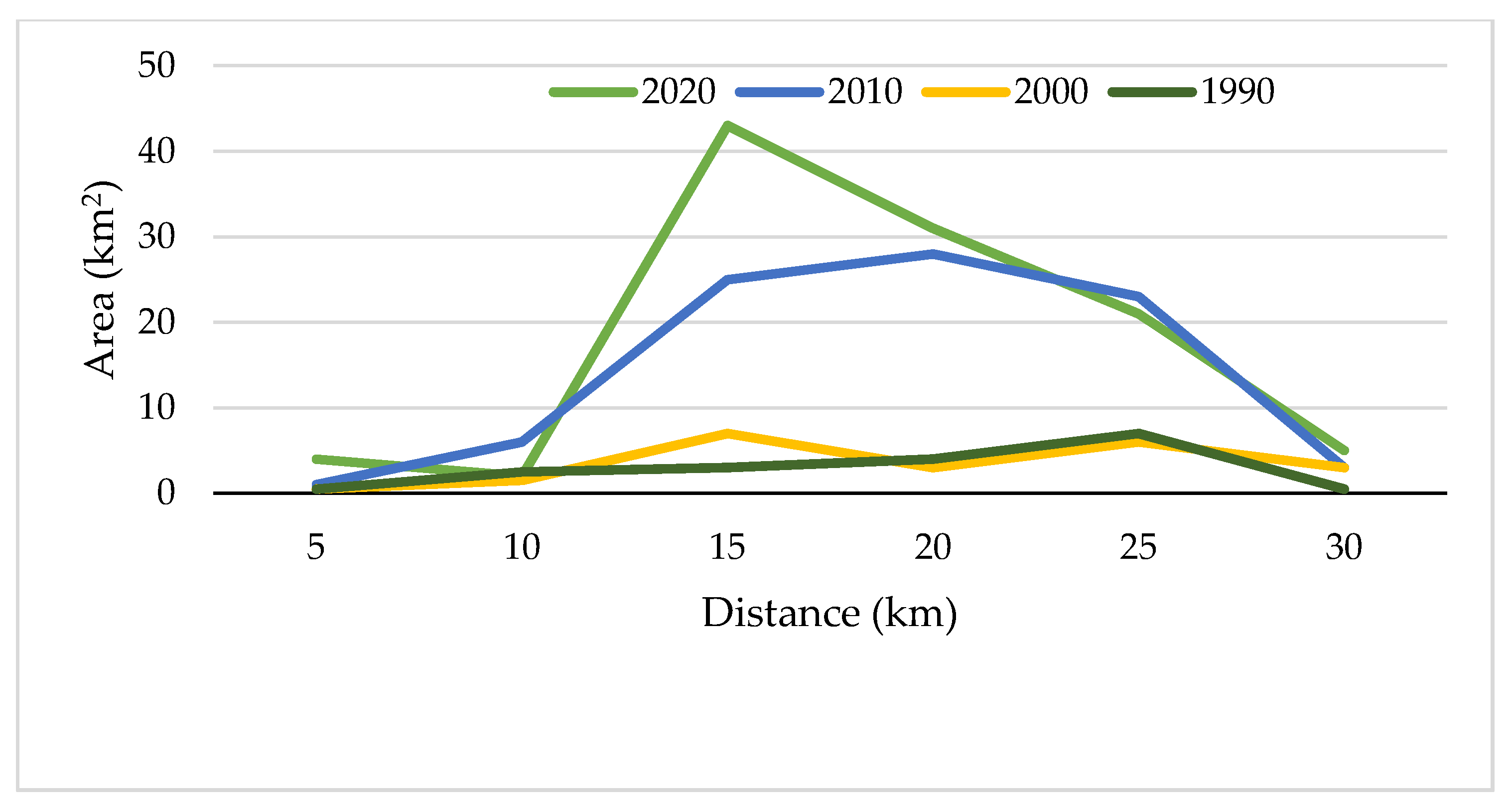
5.2. Distance Assessment of the Urban Expansion
6. Driving Factors
6.1. Population Growth
6.2. Economic Growth
6.3. Location and Accessibility
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- European Environmental Agency (EEA). Urban Sprawl in Europe Joint EEA-FOEN Report; European Environmental Agency—Swiss Federal Office for the Environment: Ittigen, Switzerland, 2016; Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/urban-sprawl-in-europe (accessed on 20 March 2021).
- Goswami, M. Conceptualizing Peri-Urban-Rural Landscape Change for Sustainable Management. Available online: http://www.isec.ac.in/WP%20425%20-%20Mrinalini%20Goswami%20-%20Final.pdf (accessed on 10 January 2020).
- Alipbeki, O.; Alipbekova, C.; Sterenharz, A.; Toleubekova, Z.; Aliyev, M.; Mineyev, N.; Amangaliyev, K. A Spatiotemporal Assessment of Land Use and Land Cover Changes in Peri-Urban Areas: A Case Study of Arshaly District, Kazakhstan. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- World Bank. Urban Population Growth. 2019. Available online: https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SP.URB.GROW (accessed on 10 October 2021).
- Mansour, S.; Al-Belushi, M.; Al-Awadhi, T. Monitoring land use and land cover changes in the mountainous cities of Oman using GIS and CA-Markov modelling techniques. Land Use Policy 2020, 91, 104414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acheampong, M.; Yu, Q.; Enomah, L.D.; Anchang, J.; Eduful, M. Land use/cover change in Ghana’s oil city: Assessing the impact of neoliberal economic policies and implications for sustainable development goal number one—A remote sensing and GIS approach. Land Use Policy 2018, 73, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matlhodi, B.; Kenabatho, P.K.; Parida, B.P.; Maphanyane, J.G. Evaluating Land Use and Land Cover Change in the Gaborone Dam Catchment, Botswana, from 1984–2015 Using GIS and Remote Sensing. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yekeen, S.T.; Balogun, A.-L. Advances in Remote Sensing Technology, Machine Learning and Deep Learning for Marine Oil Spill Detection, Prediction and Vulnerability Assessment. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrin, S.; Gupta, A.; Farjad, B.; Ahmed, M.R.; Achari, G.; Hassan, Q.K. Development of Land-Use/Land-Cover Maps Using Landsat-8 and MODIS Data, and Their Integration for Hydro-Ecological Applications. Sensors 2019, 19, 4891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phiri, D.; Morgenroth, J. Developments in Landsat Land Cover Classification Methods: A Review. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khatancharoen, C.; Tsuyuki, S.; Bryanin, S.; Sugiura, K.; Seino, T.; Lisovsky, V.; Borisova, I.; Wada, N. Long-Time Interval Satellite Image Analysis on Forest-Cover Changes and Disturbances around Protected Area, Zeya State Nature Reserve, in the Russian Far East. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Angadi, D.P. Land use land cover change detection and monitoring of urban growth using remote sensing and GIS techniques: A micro-level study. Geo J. 2021, 2021, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sefrin, O.; Riese, F.; Keller, S. Deep Learning for Land Cover Change Detection. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinayak, B.; Lee, H.; Gedem, S. Prediction of Land Use and Land Cover Changes in Mumbai City, India, Using Remote Sensing Data and a Multilayer Perceptron Neural Network-Based Markov Chain Model. Sustainability 2021, 13, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, J.; Kumar, M. Monitoring land use/cover change using remote sensing and GIS techniques: A case study of Hawalbagh block, district Almora, Uttarakhand, India. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2015, 18, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hathout, S. The use of GIS for monitoring and predicting urban growth in east and west St Paul, Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada. J. Environ. Manag. 2002, 66, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herold, M.; Goldstein, N.C.; Clarke, K. The spatiotemporal form of urban growth: Measurement, analysis and modeling. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 86, 286–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, E.F.; Geist, H.J.; Lepers, E. Dynamics of land-use and land-cover change in tropical regions. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2003, 28, 205–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, G.; Jiang, N.; Yao, L. Land Use and Cover Change during the Rapid Economic Growth Period from 1990 to 2010: A Case Study of Shanghai. Sustainability 2018, 10, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fonji, S.F.; Taff, G.N. Using satellite data to monitor land-use land-cover change in North-eastern Latvia. SpringerPlus 2014, 3, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tran, H.; Tran, T.; Kervyn, M. Dynamics of land cover/land use changes in the Mekong Delta, 1973–2011: A remote sensing analysis of the Tran Van Thoi District, Ca Mau Province, Vietnam. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 2899–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akinyemi, F.O. Land change in the central Albertine rift: Insights from analysis and mapping of land use-land cover change in north-western Rwanda. Appl. Geogr. 2017, 87, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, M.P.; Chavan, M.; Pardeshi, S.; Joshi, C.; Verma, P.A.; Roy, P.S.; Srivastav, S.K.; Jha, A.K.; Chaudhari, S.; Giri, Y.; et al. Land-use and land-cover change in Western Ghats of India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arowolo, A.O.; Deng, X. Land use/land cover change and statistical modelling of cultivated land change drivers in Nigeria. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2018, 18, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Mubeen, M.; Akram, W.; Ahmad, A.; Habib-Ur-Rahman, M.; Ghaffar, A.; Amin, A.; Awais, M.; Farid, H.U.; Farooq, A.; et al. Study of land cover/land use changes using RS and GIS: A case study of Multan district, Pakistan. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 192, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alijani, Z.; Hosseinali, F.; Biswas, A. Spatio-temporal evolution of agricultural land use change drivers: A case study from Chalous region, Iran. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 262, 110326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewan, A.; Yamaguchi, Y. Land use and land cover change in Greater Dhaka, Bangladesh: Using remote sensing to promote sustainable urbanization. Appl. Geogr. 2009, 29, 390–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jat, M.K.; Garg, P.K.; Khare, D. Monitoring and modelling of urban sprawl using remote sensing and GIS techniques. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2008, 10, 26–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundia, C.N.; Aniya, M. Dynamics of landuse/cover changes and degradation of Nairobi City, Kenya. Land Degrad. Dev. 2006, 17, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lathrop, R., Jr. Urban change detection based on an artificial neural network. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 2513–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habitat, U. The State of the World’s Cities 2001; United Nations for Human Settlements: Nairobi, Kenya, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Ishtiaque, A.; Shrestha, M.; Chhetri, N. Rapid Urban Growth in the Kathmandu Valley, Nepal: Monitoring Land Use Land Cover Dynamics of a Himalayan City with Landsat Imageries. Environments 2017, 4, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldblatt, R.; Stuhlmacher, M.F.; Tellman, B.; Clinton, N.; Hanson, G.; Georgescu, M.; Wang, C.; Serrano-Candela, F.; Khandelwal, A.K.; Cheng, W.-H.; et al. Using Landsat and nighttime lights for supervised pixel-based image classification of urban land cover. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 205, 253–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, R.B.; Murayama, Y. Examining Spatiotemporal Urbanization Patterns in Kathmandu Valley, Nepal: Remote Sensing and Spatial Metrics Approaches. Remote Sens. 2009, 1, 534–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, F.; Goparaju, L.; Qayum, A. LULC analysis of urban spaces using Markov chain predictive model at Ranchi in India. Spat. Inf. Res. 2017, 25, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewan, A.M.; Yamaguchi, Y. Using remote sensing and GIS to detect and monitor land use and land cover change in Dhaka Metropolitan of Bangladesh during 1960–2005. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 150, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.I.; Basak, R. (Eds.) Land Cover Change Detection Using GIS and Remote Sensing Techniques: A Spatio-Temporal Study on Tanguar Haor, Sunamganj, Bangladesh. 2016 International Conference on Innovations in Science, Engineering and Technology (ICISET); IEEE: Piscataway Township, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, M.; Hasan, M.E.; Al Mamun, M.M.A. Land use/land cover change assessment of Halda watershed using remote sensing and GIS. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2020, 23, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank. 2020. Available online: Data.worldbank.org/indicator/NY.GDP.MKTP.KD.ZG?locations=BD (accessed on 16 November 2020).
- District Statistics 2011, Gazipur; Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2011.
- Paul, S.S. Analysis of Land Use and Land Cover Change in Kiskatinaw River Watershed: A Remote Sensing, Gis & Modeling Approach. Masters’ Thesis, University of Northern British Columbia, Prince George, BC, Canada, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Paiboonvorachat, C. Using Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques to Assess Land Use/Land Cover Changes in the Nan Watershed, Thailand. Masters’ Thesis, Southern Illinois University at Carbondale, Carbondale, IL, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, B.J. Introduction to Remote Sensing, 3rd ed.; Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Stow, D. The effect of training strategies on supervised classification at different spatial resolutions. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2002, 68, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, J.R. Introductory Digital Image Processing: A Remote Sensing Perspective; Prentice-Hall Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Congalton, R.G. A review of assessing the accuracy of classifications of remotely sensed data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1991, 37, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, P.M.; Ventura, S.J. The integration of geographic data with remotely sensed imagery to improve classification in an urban area. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1995, 61, 993–998. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, M.M.; Nazem, M.N.I. Examination of land use/land cover changes, urban growth dynamics, and environmental sus-tainability in Chittagong city, Bangladesh. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2016, 18, 697–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.M. Monitoring land use/land cover change, urban growth dynamics and landscape pattern analysis in five fastest urbanized cities in Bangladesh. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2017, 7, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Sawaya, K.E.; Loeffelholz, B.C.; Bauer, M.E. Land cover classification and change analysis of the Twin Cities (Minnesota) Metropolitan Area by multitemporal Landsat remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 98, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutherford, G.N.; Bebi, P.; Edwards, P.J.; Zimmermann, N. Assessing land-use statistics to model land cover change in a mountainous landscape in the European Alps. Ecol. Model. 2008, 212, 460–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q. Remote sensing of impervious surfaces in the urban areas: Requirements, methods, and trends. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 34–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deilmai, B.R.; Bin Ahmad, B.; Zabihi, H. Comparison of two Classification methods (MLC and SVM) to extract land use and land cover in Johor Malaysia. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2014, 20, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.; Min, X. Quantifying spatiotemporal patterns of urban expansion in China using remote sensing data. Cities 2013, 35, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Zhou, W.; Yan, J.; Li, W.; Han, L.; Kerle, N.; Gerke, M.; Lefevre, S. Comparing machine learning classifiers for object-based land cover classification using very high resolution imagery. GEOBIA 2016 Solut. Synerg. 2016, 7, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.M.; Southworth, J. Analyzing land cover change and urban growth trajectories of the mega-urban region of Dhaka using remotely sensed data and an ensemble classifier. Sustainability 2018, 10, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, Z.; Hailin, L.; Zhen, C. Analysis of Land Use Dynamic Change and Its Impact on the Water Environment in Yunnan Plateau Lake Area –– A Case Study of the Dianchi Lake Drainage Area. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2011, 10, 2709–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Senseman, G.M.; Bagley, C.F.; Tweddale, S.A. Accuracy Assessment of the Discrete Classification of Remotely-Sensed Digital Data for Landcover Mapping; Construction Engineering Research Lab (Army) Champaign IL: Springfield, VA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, P.K.; Rai, A.; Rai, S.C. Land use and land cover change detection using geospatial techniques in the Sikkim Himalaya, India. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2020, 23, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawe, C.K.; Saikia, A. Unplanned urban growth: Land use/land cover change in the Guwahati Metropolitan Area, India. Geogr. Tidsskr. J. Geogr. 2018, 118, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Wu, Z.; Lv, Z.; Yao, N.; Wei, J. Quantifying different types of urban growth and the change dynamic in Guangzhou using multi-temporal remote sensing data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2013, 21, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, B.; Seto, K.C. Urbanization and agricultural land loss in India: Comparing satellite estimates with census data. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 148, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegazy, I.R.; Kaloop, M.R. Monitoring urban growth and land use change detection with GIS and remote sensing techniques in Daqahlia governorate Egypt. Int. J. Sustain. Built Environ. 2015, 4, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Population.de C. Gazipur Population. Available online: https//citypopulation.de/en/bangladesh/dhaka/3330__gazipur_sadar/ (accessed on 12 November 2020).
- Xu, X.; Jain, A.K.; Calvin, K.V. Quantifying the biophysical and socioeconomic drivers of changes in forest and agricultural land in South and Southeast Asia. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2019, 25, 2137–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukhbor, S.A. Daily Prothom Alo (National Bangla Newspaper of Bangladesh). Good News in Crisis Time, 6 November.
- Rahman, S.; Mohiuddin, H.; Al Kafy, A.; Sheel, P.K.; Di, L. Classification of cities in Bangladesh based on remote sensing derived spatial characteristics. J. Urban Manag. 2019, 8, 206–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wu, C.; Shen, H. A GIS based model of urban land use growth in Beijing. Acta Geogr. Sin.-Chin. Ed. 2000, 55, 416–426. [Google Scholar]
- Sorensen, A. Land readjustment and metropolitan growth: An examination of suburban land development and urban sprawl in the Tokyo metropolitan area. Prog. Plan. 2000, 53, 217–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Satellite Imagery | Acquisition Date | MS Bands | Description | Spatial Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Landsat 5 TM | 29 April 1990 | Band 1–5, 7 | Coastal and aerosol, vegetation and deciduous, peak vegetation, discriminates vegetation slopes, biomass content and shorelines, moisture content of soil and vegetation; penetrates thin clouds | 30 m |
| Landsat 7 ETM+ | 2 February 2000 | Band 1–5, 7 | Coastal and aerosol, vegetation and deciduous, peak vegetation, discriminates vegetation slopes, biomass content and shorelines, moisture content of soil and vegetation; penetrates thin clouds | 30 m |
| Landsat 5 TM | 30 January 2010 | Band 1–5, 7 | Coastal and aerosol, vegetation and deciduous, peak vegetation, discriminates vegetation slopes, biomass content and shorelines, moisture content of soil and vegetation; penetrates thin clouds | 30 m |
| Landsat8 OLI/TIRS | 11 February 2020 | Band 1–7 | Coastal and aerosol, vegetation and deciduous, peak vegetation, discriminates vegetation slopes, biomass content and shorelines, moisture content of soil and vegetation; thermal mapping and estimated soil moisture; penetrates thin clouds | 30 m |
| LULC Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Agriculture | Paddies, crops, vegetables, etc. |
| Vegetation | Natural vegetation, homesteads with trees (hfs), plantations, etc. |
| Built-up | Houses, shops, industries, paved surfaces, roads, etc. |
| Fallow land | Barren land, playgrounds, open fields, uncultivated land, sand-filling sites, brick fields, grazing fields, yard, waste-dumping sites, etc. |
| Low land | Marshy lands, seasonal channels, wetland, etc. |
| Water | Rivers, canals, ponds, etc. |
| Year | Overall Accuracy | Kappa Coefficient |
|---|---|---|
| 1990 | 86 % | 0.75 |
| 2000 | 93% | 0.80 |
| 2010 | 94% | 0.88 |
| 2020 | 93% | 0.90 |
| LULC | Area 1990 | Area 2000 | Area 2010 | Area 2020 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| km2 | % | km2 | % | km2 | % | km2 | % | |
| Water | 171.67 | 9.43 | 42.66 | 2.34 | 64.77 | 3.56 | 51.13 | 2.81 |
| Built-up | 17.81 | 0.98 | 22.53 | 1.24 | 89.39 | 4.91 | 104.44 | 5.74 |
| Vegetation | 591.29 | 32.48 | 353.84 | 19.44 | 429.94 | 23.60 | 696.04 | 38.23 |
| Agriculture | 980.52 | 53.86 | 1382 | 75.92 | 1211.41 | 66.51 | 716.85 | 39.37 |
| Low land | 21.1 | 1.16 | 4.32 | 0.24 | 8.97 | 0.49 | 27.79 | 1.53 |
| Fallow land | 38.23 | 2.10 | 15.01 | 0.82 | 16.99 | 0.93 | 224.45 | 12.33 |
| 1990 to 2000 | 2000 to 2010 | 2010 to 2020 | 1990 to 2020 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (km2) | (%) | Annual (km2) | (km2) | (%) | Annual (km2) | (km2) | (%) | Annual (km2) | (km2) | (%) | Annual (km2) | |
| Water | −129.01 | −75.15 | −12.90 | 22.11 | 51.83 | 2.21 | −13.64 | −21.06 | −1.36 | −120.54 | −70.22 | −4.02 |
| Built-up | 4.72 | 26.50 | 0.47 | 66.86 | 296.76 | 6.69 | 15.05 | 16.84 | 1.51 | 86.63 | 486.41 | 2.89 |
| Vegetation | −237.45 | −40.16 | −23.75 | 76.10 | 21.51 | 7.61 | 266.10 | 61.89 | 26.61 | 104.75 | 17.72 | 3.49 |
| Agriculture | 401.48 | 40.95 | 40.15 | −170.59 | −12.34 | −17.06 | −494.56 | −40.83 | −49.46 | −263.67 | −26.89 | −8.79 |
| Low land | −16.78 | −79.53 | −1.68 | 4.65 | 107.64 | 0.47 | 18.82 | 209.81 | 1.88 | 6.69 | 31.71 | 0.22 |
| Fallow land | −23.22 | −60.74 | −2.32 | 1.98 | 13.19 | 0.20 | 207.46 | 1221.07 | 20.75 | 186.22 | 487.10 | 6.21 |
| Change Detection Matrix from 1990 to 2020 (km2) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1990–2020 | Water | Built-Up | Vegetation | Agriculture | Low Land | Fallow Land |
| Water | 21.69 | 0.21 | 12.03 | 15.98 | 0.97 | 0.25 |
| Built-up | 12.55 | 6.52 | 28.28 | 52.98 | 1.73 | 2.38 |
| Vegetation | 26.69 | 2.62 | 253.04 | 398.87 | 3.20 | 11.61 |
| Agriculture | 85.00 | 4.72 | 229.55 | 368.85 | 12.01 | 16.11 |
| Low land | 6.48 | 0.12 | 10.09 | 10.38 | 0.55 | 0.17 |
| Fallow land | 19.03 | 3.62 | 58.27 | 132.90 | 2.59 | 7.67 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arifeen, H.M.; Phoungthong, K.; Mostafaeipour, A.; Yuangyai, N.; Yuangyai, C.; Techato, K.; Jutidamrongphan, W. Determine the Land-Use Land-Cover Changes, Urban Expansion and Their Driving Factors for Sustainable Development in Gazipur Bangladesh. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1353. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12101353
Arifeen HM, Phoungthong K, Mostafaeipour A, Yuangyai N, Yuangyai C, Techato K, Jutidamrongphan W. Determine the Land-Use Land-Cover Changes, Urban Expansion and Their Driving Factors for Sustainable Development in Gazipur Bangladesh. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(10):1353. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12101353
Chicago/Turabian StyleArifeen, Hossain Mohammad, Khamphe Phoungthong, Ali Mostafaeipour, Nuttaya Yuangyai, Chumpol Yuangyai, Kuaanan Techato, and Warangkana Jutidamrongphan. 2021. "Determine the Land-Use Land-Cover Changes, Urban Expansion and Their Driving Factors for Sustainable Development in Gazipur Bangladesh" Atmosphere 12, no. 10: 1353. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12101353
APA StyleArifeen, H. M., Phoungthong, K., Mostafaeipour, A., Yuangyai, N., Yuangyai, C., Techato, K., & Jutidamrongphan, W. (2021). Determine the Land-Use Land-Cover Changes, Urban Expansion and Their Driving Factors for Sustainable Development in Gazipur Bangladesh. Atmosphere, 12(10), 1353. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12101353









