Comparison of the Causes of High-Frequency Heavy and Light Snowfall on Interannual Timescales over Northeast China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
- The station’s daily snowfall is ≥5 mm (>0 mm, but ≤2.5 mm);
- The station’s daily surface air temperature is <0 °C;
- The station’s ground temperature is also <0 °C.
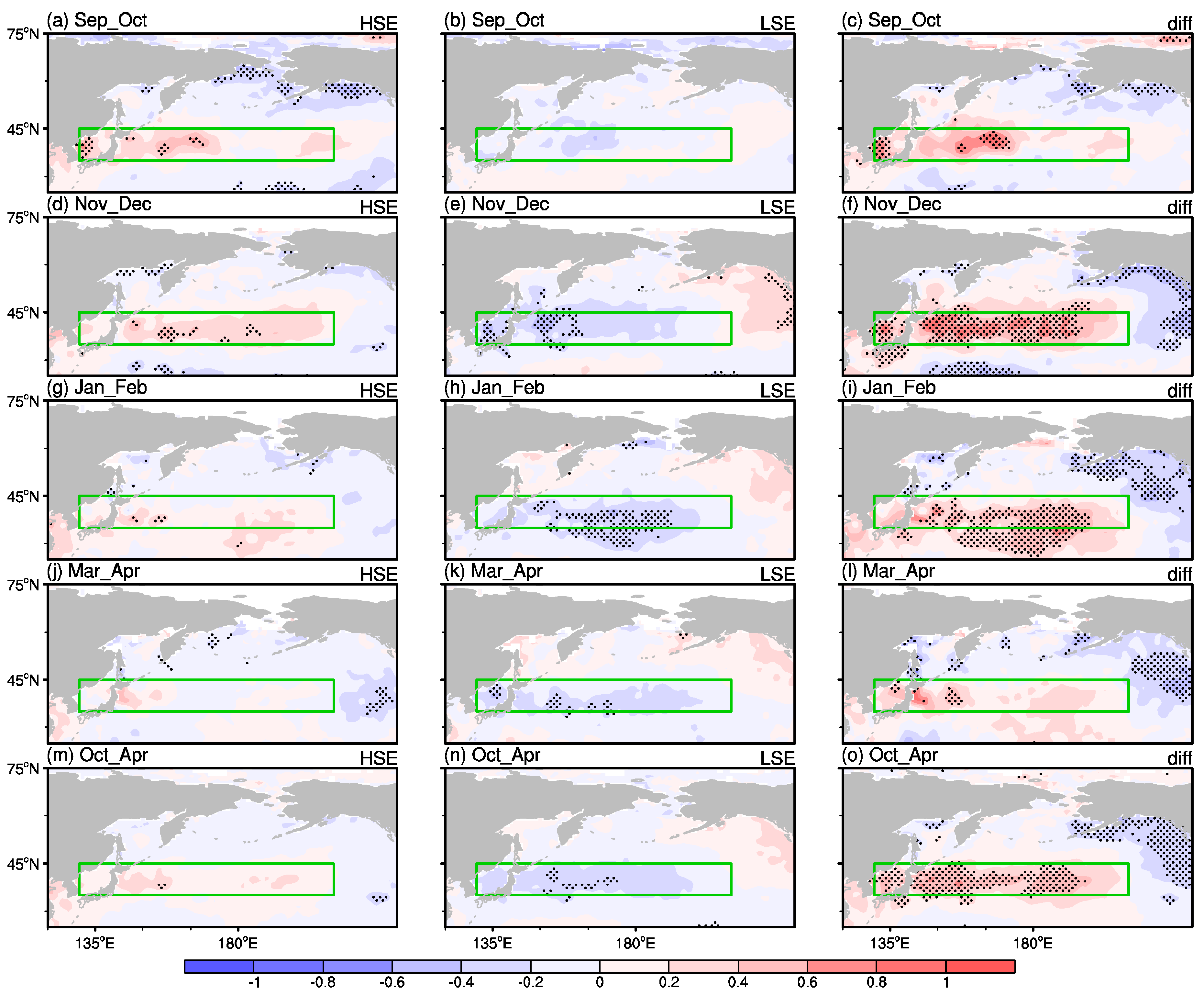
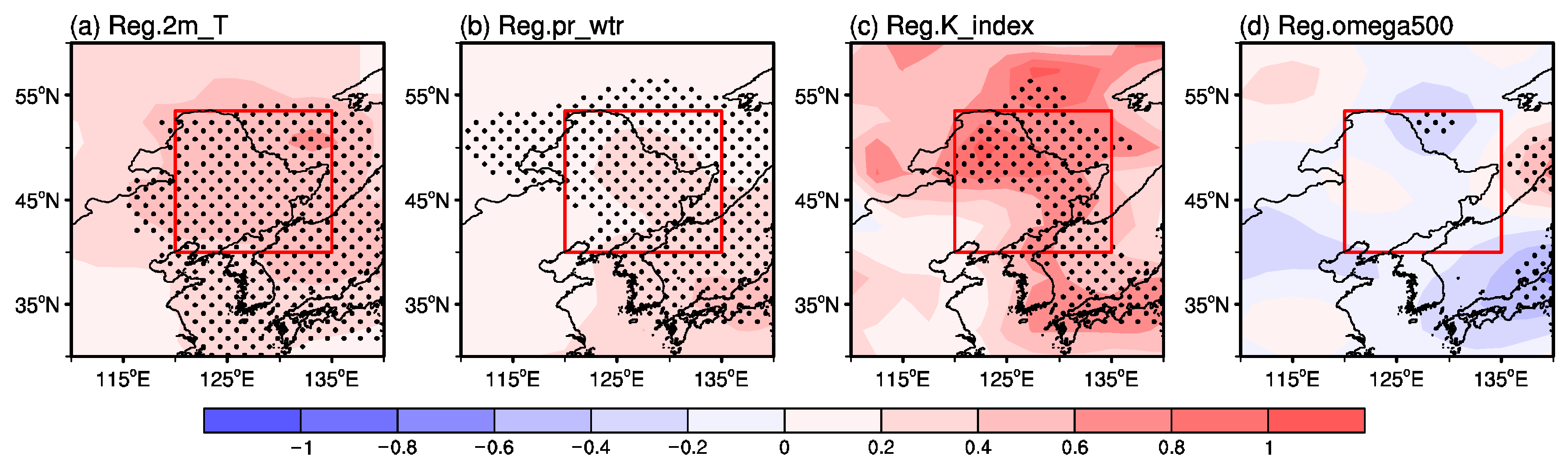
3. Results
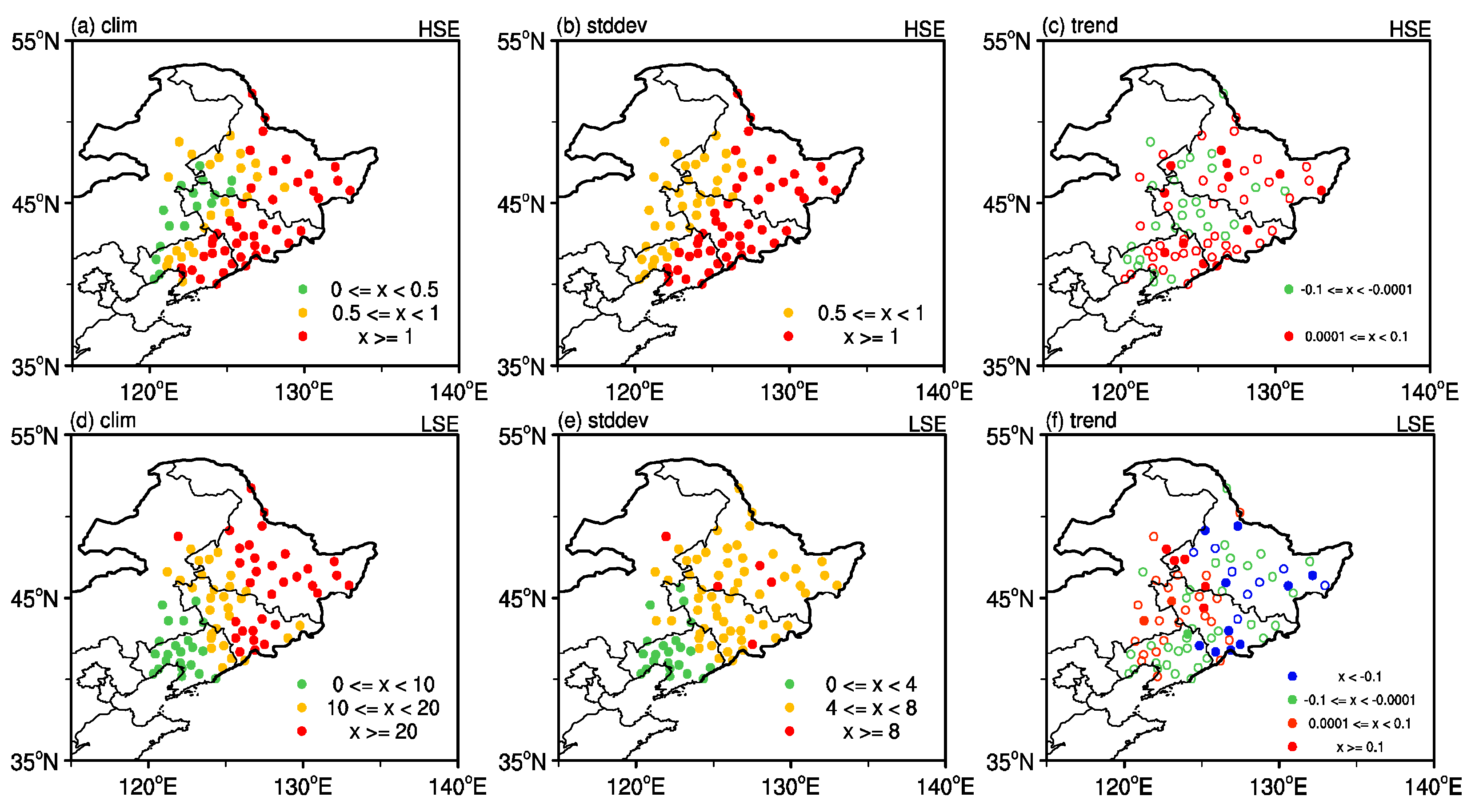
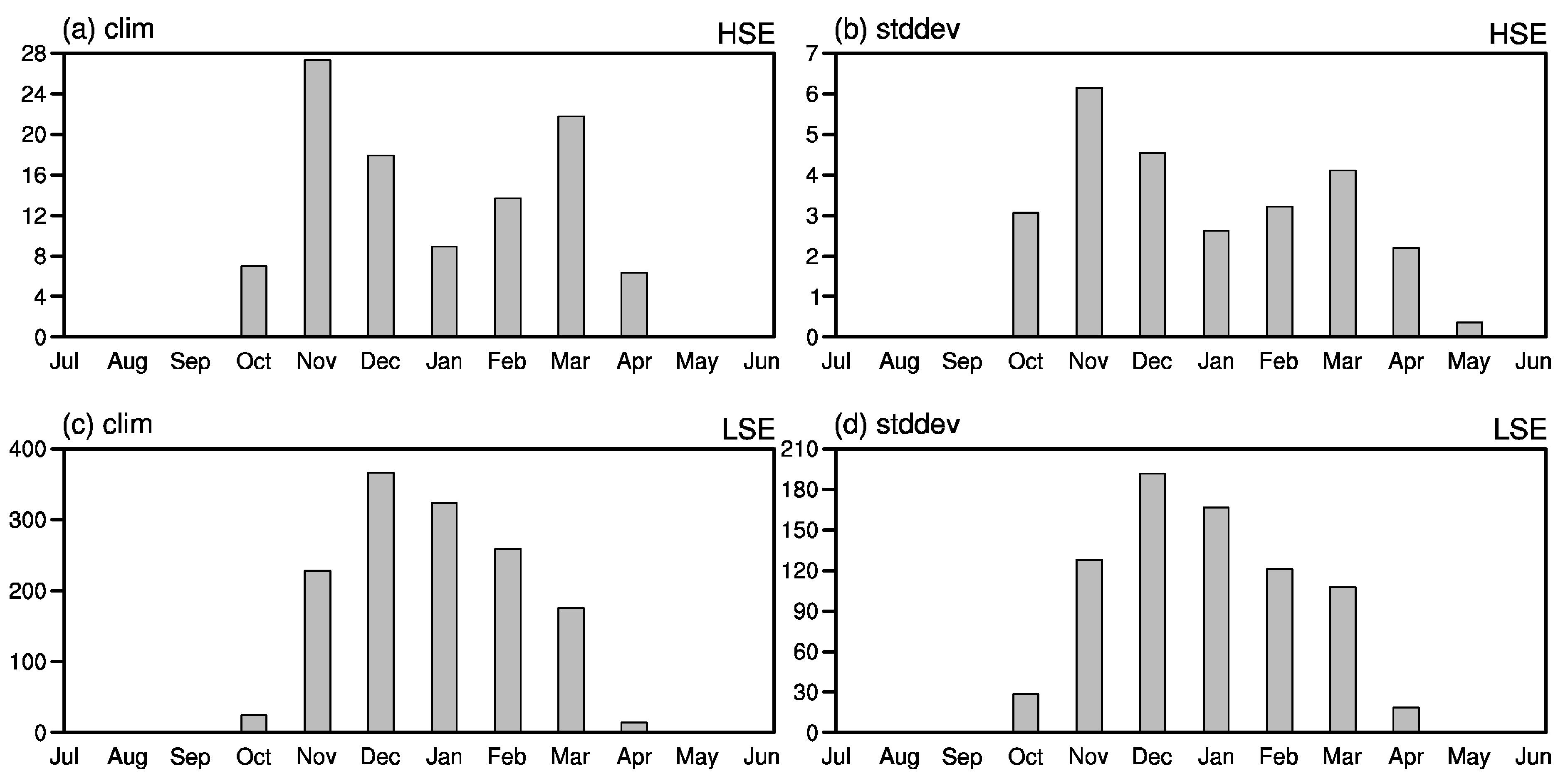
3.1. Climatic Features
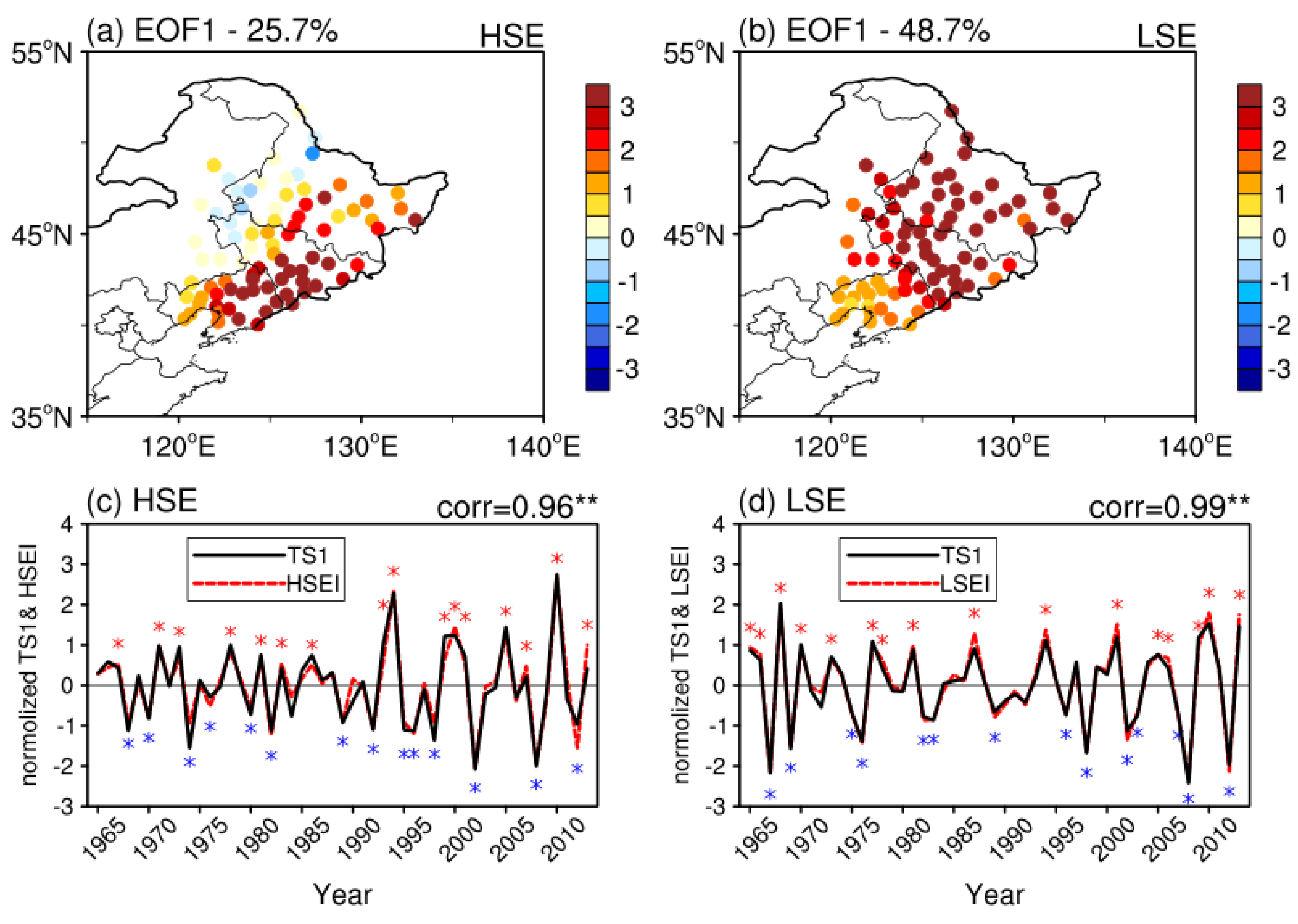
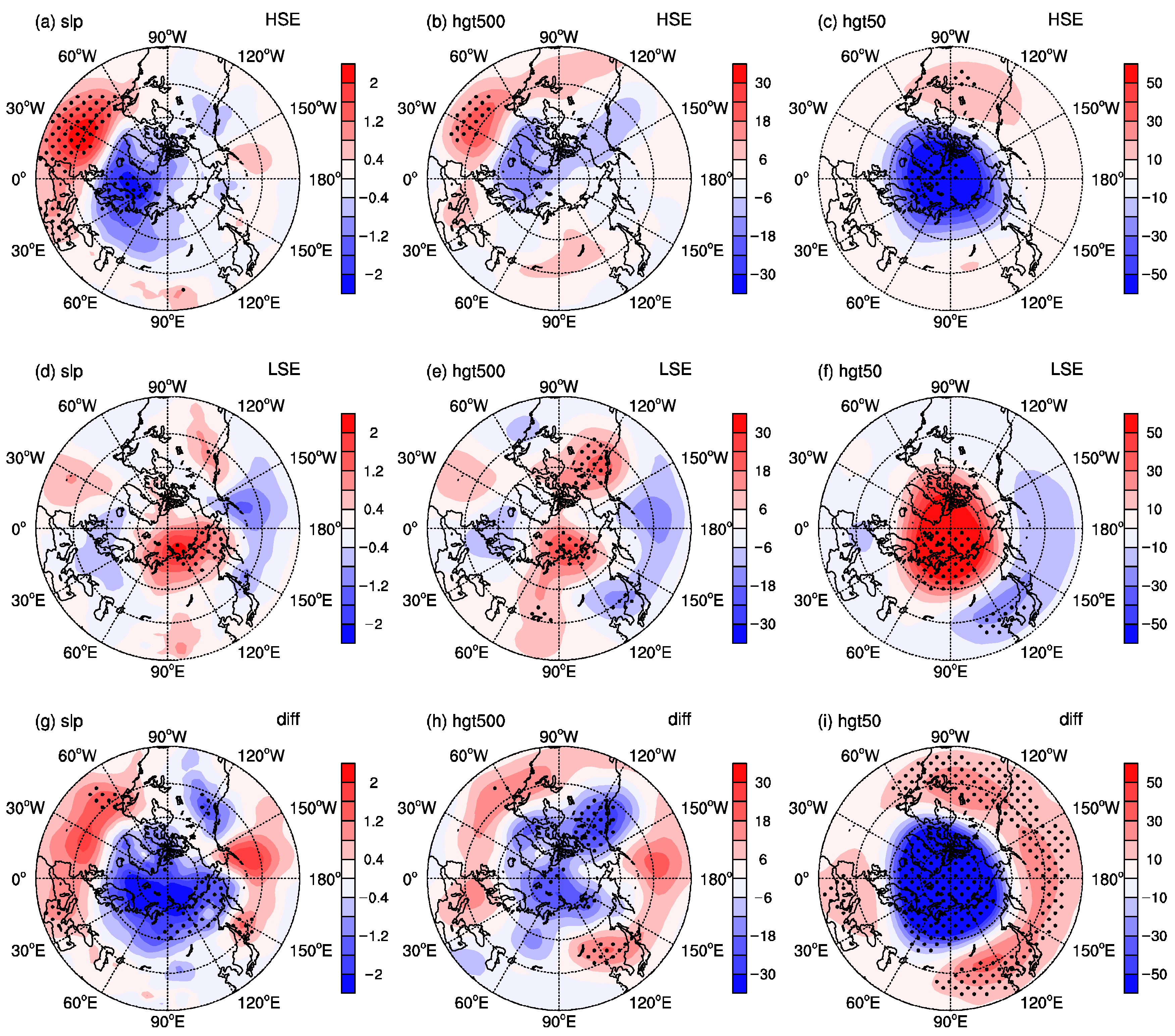
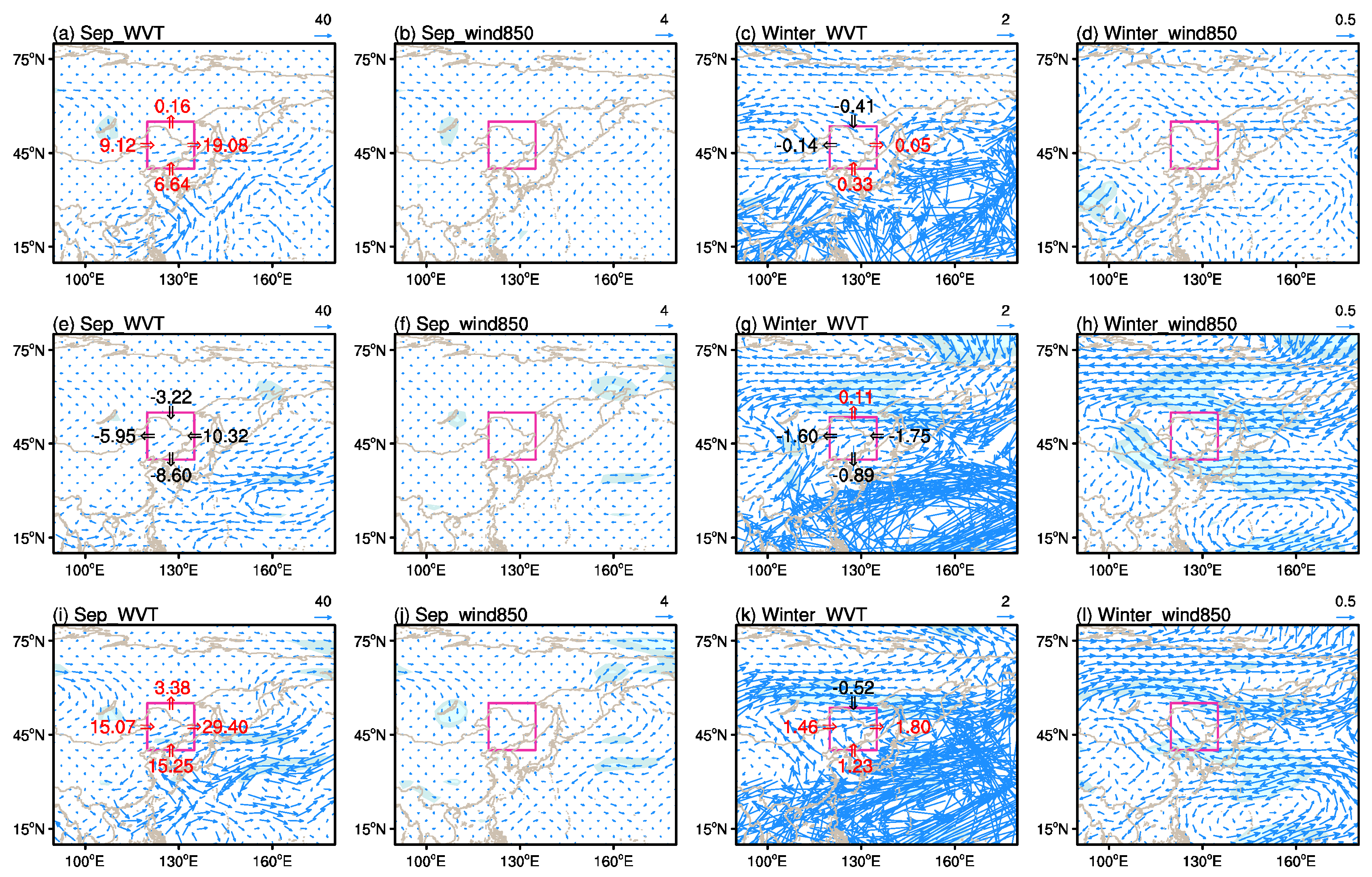
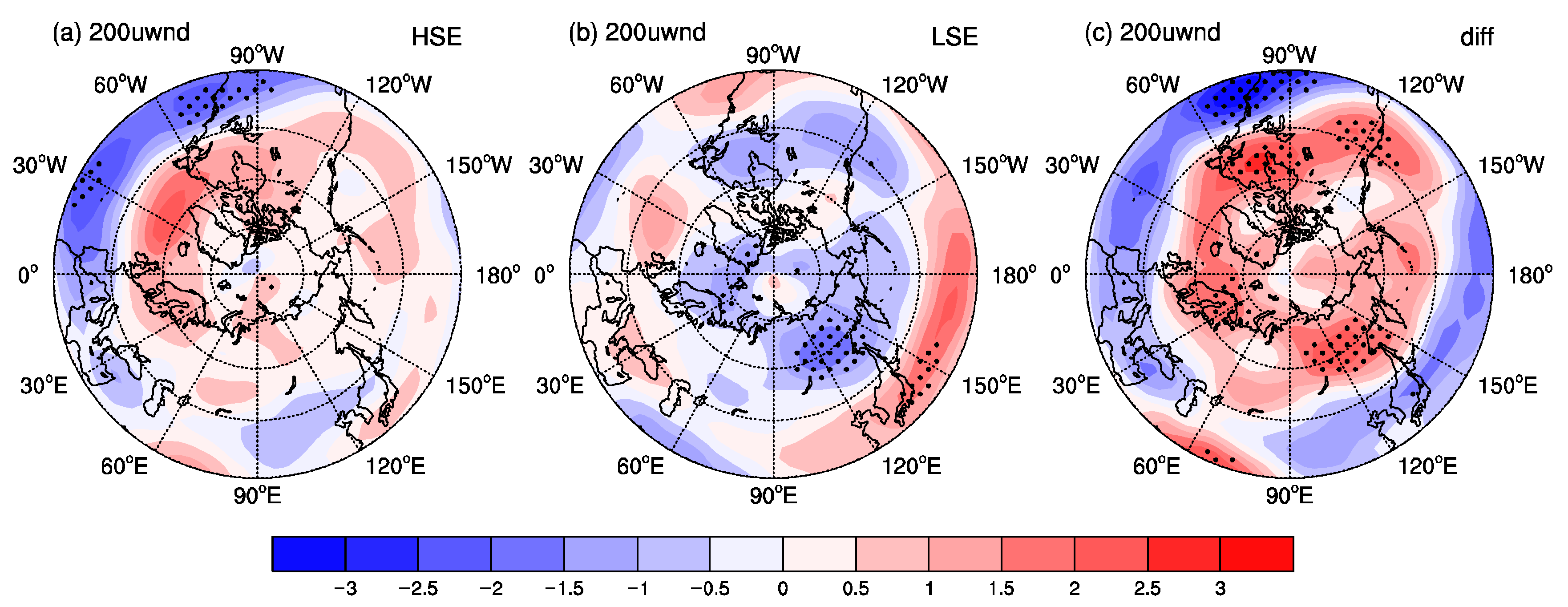
3.2. Large-Scale Atmospheric Circulation Patterns and WVT
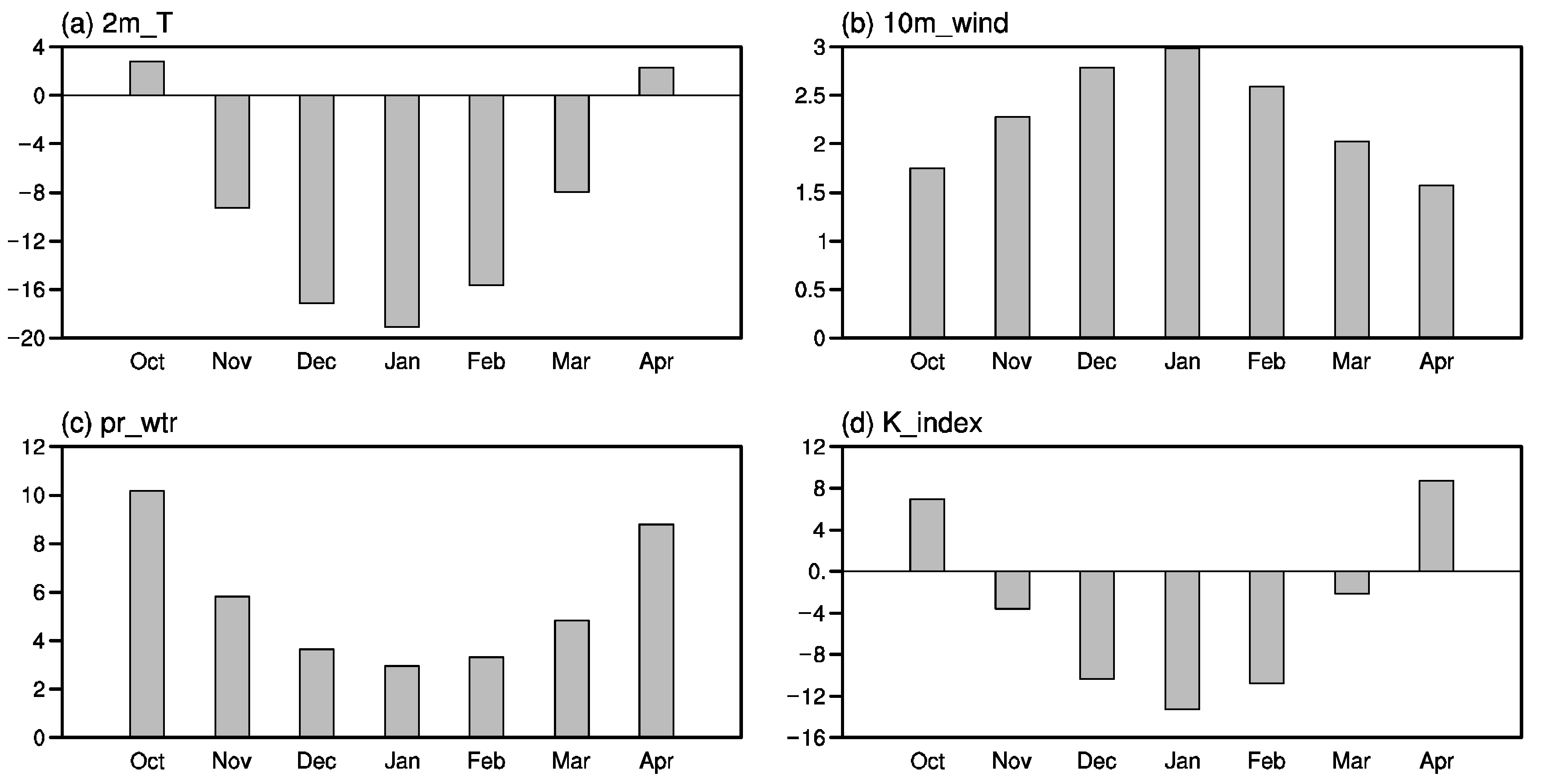
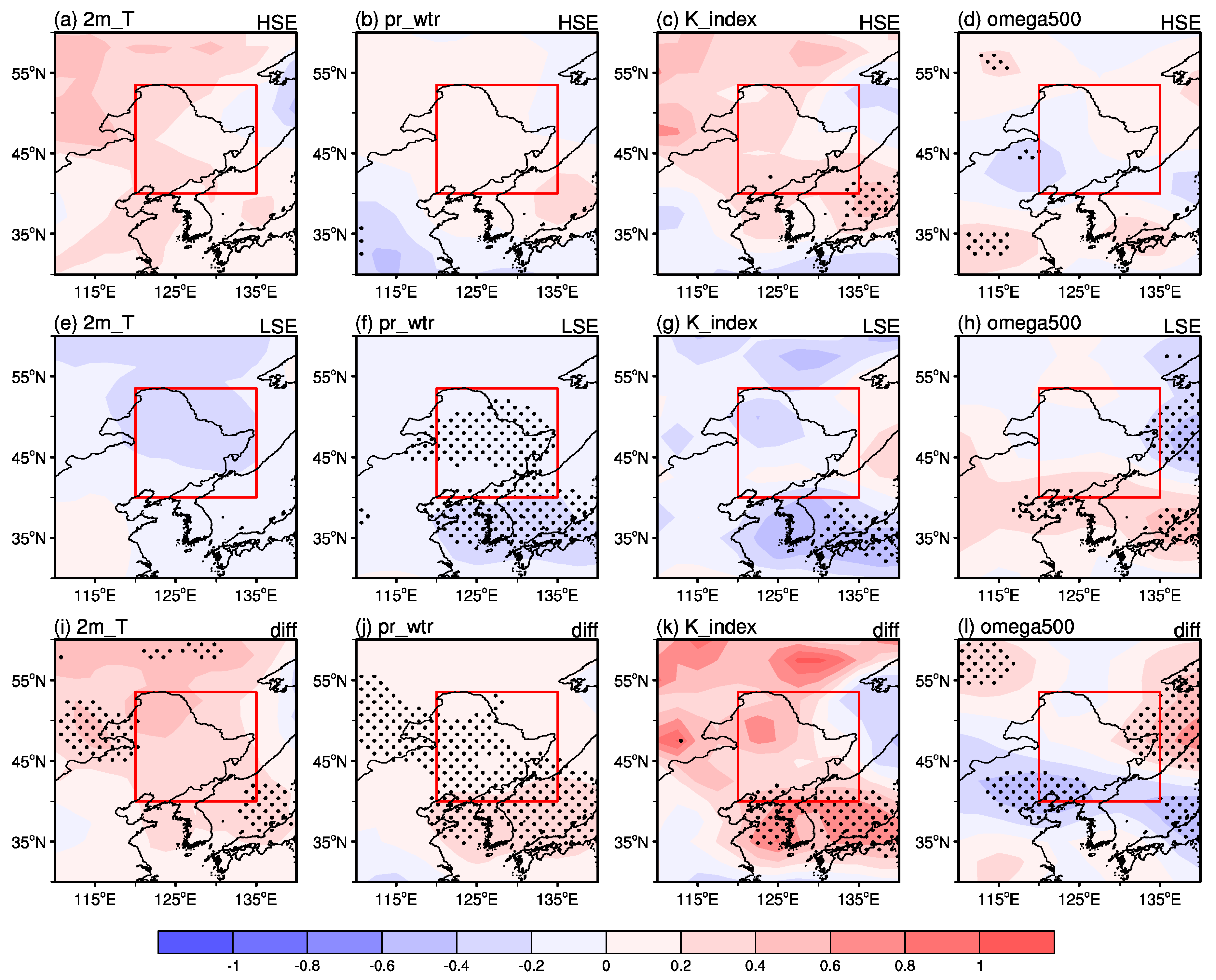
3.3. Physical Mechanisms
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Snow Disaster and Low Temperature Damage Occurred in Parts of Northeast China. Available online: http://www.ndrcc.org.cn/zxzq/22790.jhtml (accessed on 29 July 2020).
- Wang, J.; Ding, Y. Research on Moist Symmetric Instability in a Strong Snowfall in North China. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 1995, 9, 456–467. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Zhao, S. A Numerical Simulation of Snowfall in North China on 7 December 2001. Clim. Environ. Res. 2003, 387–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Meng, J.; Sui, C.-H.; Meng, W.; Li, J. A study of the microphysical processes in a numerically simulated heavy snowfall event in North China: The sensitivity of different snow intercept parameters. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2009, 104, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Qi, L.; Han, J. The Analyses of an Unusual Snowstorm Caused by the Northbound Vortex over Liaoning Province in China. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2009, 33, 275–284. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Wang, H.; Yuan, W. A preliminary investigation on causes of the catastrophic snowstorm in March, 2007 in the northeastern parts of China. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2009, 67, 469–477. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Yu, E.; Yang, S. An exceptionally heavy snowfall in Northeast china: Large-scale circulation anomalies and hindcast of the NCAR WRF model. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2011, 113, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laternser, M.; Schneebeli, M. Long-term snow climate trends of the Swiss Alps (1931–99). Int. J. Climatol. 2003, 23, 733–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wang, H.; Yuan, W.; Chen, H. Spatial-temporal features of intense snowfall events in China and their possible change. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Xiao, Z.; Li, Z. The Spatial and Temporal Characteristics of Winter Snowfall in Northeast China and Its Relation with Global Sea Surface Temperature Anomaly. Meteorol. Mon. 2012, 38, 411–418. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Ren, G.; Yu, H.M. Climatology of Snowfall in China. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2012, 32, 1176–1185. [Google Scholar]
- Sui, Y.; Jiang, D.; Tian, Z. Latest update of the climatology and changes in the seasonal distribution of precipitation over China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2013, 113, 599–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Ma, L.; Ma, M.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, W. Spatial–Temporal Variability of Snow Cover and Depth in the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 1521–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.T.; Wang, Z.Y.; Shi, Y.; Xu, Y.; Han, Z.Y. Historical and Future Changes of Snowfall Events in China under a Warming Background. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 5873–5889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Li, Q.; Liu, W.; Liu, X.; Li, L.; De Maeyer, P. Spatiotemporal variability of snowfall and its concentration in northern Xinjiang, Northwest China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2020, 139, 1247–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Luo, J.; Han, F. Interdecadal variation of heavy snowfall in northern China and its linkages with atmospheric circulation and Arctic sea ice. Trans. Atmos. Sci. 2019, 42, 68–77. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, J.; Xiaoyu, Y.A.N.; Ying, W.; Yong, L.U.O. Climatic characteristics and regionalization of winter snowfall in Northeast China. J. Nat. Disasters 2009, 18, 29–35. [Google Scholar]
- Enzi, S.; Bertolin, C.; Diodato, N. Snowfall time-series reconstruction in Italy over the last 300 years. Holocene 2014, 24, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diodato, N.; Büntgen, U.; Bellocchi, G. Mediterranean winter snowfall variability over the past millennium. Int. J. Climatol. 2019, 39, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Ibarra, E.; Serrano-Montes, J.L.; Arias-García, J. Reconstruction and analysis of 1900–2017 snowfall events on the southeast coast of Spain. Clim. Res. 2019, 78, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Yu, Y.; Ge, Q.; Zheng, J. Reconstruction of high-resolution climate data over China from rainfall and snowfall records in the Qing Dynasty. WIREs Clim. Chang. 2018, 9, e517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Wang, H. Water Vapor Transport Paths and Accumulation during Widespread Snowfall Events in Northeastern China. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Sun, B. The impacts of different land surface parameterization schemes on Northeast China snowfall simulation. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2018, 130, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Curry, J.A.; Wang, H.; Song, M.; Horton, R.M. Impact of declining Arctic sea ice on winter snowfall. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 4074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Chen, H. Warming over the North Pacific can intensify snow events in Northeast China. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. Lett. 2016, 9, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; He, S. The increase of snowfall in Northeast China after the mid-1980s. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Wang, Z.; Shi, Y. Possible Role of Hadley Circulation Strengthening in Interdecadal Intensification of Snowfalls Over Northeastern China Under Climate Change. J. Geophys. Res. 2017, 122, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; He, S.P.; Xin, H.; Huijun, W. Recent interdecadal shift in the relationship between Northeast China’s winter precipitation and the North Atlantic and Indian Oceans. Clim. Dyn. 2018, 50, 1413–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalnay, E.; Kanamitsu, M.; Kistler, R.; Collins, W.; Deaven, D.; Gandin, L.; Iredell, M.; Saha, S.; White, G.; Woollen, J.; et al. The NCEP/NCAR 40-Year Reanalysis Project. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1996, 77, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayner, N.A. Global analyses of sea surface temperature, sea ice, and night marine air temperature since the late nineteenth century. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, H. The recent interdecadal and interannual variation of water vapor transport over eastern China. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2011, 28, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaya, K.; Nakamura, H. A Formulation of a Phase-Independent Wave-Activity Flux for Stationary and Migratory Quasigeostrophic Eddies on a Zonally Varying Basic Flow. J. Atmos. Sci. 2001, 58, 608–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Jiao, M.; Li, Y. Techniques and Methods of Contemporary Weather Forecast; China Meteorological Press: Beijing, China, 2007; p. 117. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, L.; Shi, C.; Shi, Q.; Li, L.; Wu, J.; Yang, Y.; Sun, S.; Zhang, F.; Meng, J. Change in the spatiotemporal pattern of snowfall during the cold season under climate change in a snow-dominated region of China. Int. J. Climatol. 2019, 39, 5702–5719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, J. Weather Forecasting for Aeronautics; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1960; Volume 87, p. 120. [Google Scholar]
- North, G.R.; Bell, T.L.; Cahalan, R.F.; Moeng, F.J. Sampling Errors in the Estimation of Empirical Orthogonal Functions. Mon. Weather. Rev. 1982, 110, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, D.-Y.; Wang, S.-W.; Zhu, J.-H. East Asian Winter Monsoon and Arctic Oscillation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2001, 28, 2073–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M. Asian Jet Waveguide and a Downstream Extension of the North Atlantic Oscillation. J. Clim. 2004, 17, 4674–4691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Wang, L.; Chen, Q.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z. Definition of Early and Late Winter and Associated Interannual Variations of Surface Air Temperature in China. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2020, 44, 122–137. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, J.; Li, W.; Sun, C.; Xu, L.; Ren, H.-L. Impact of the North Atlantic sea surface temperature tripole on the East Asian summer monsoon. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2013, 30, 1173–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wei, K. Anomalous Propagation of the Quasi-stationary Planetary Waves in the Atmosphere and Its Roles in the Impact of the Stratosphere on the East Asian winter Climate. Adv. Earth Sci. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushnir, Y.; Robinson, W.A.; Bladé, I.; Hall, N.M.J.; Peng, S.; Sutton, R. Atmospheric GCM Response to Extratropical SST Anomalies: Synthesis and Evaluation. J. Clim. 2002, 15, 2233–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Robinson, W.A.; Hoerling, M.P. The Modeled Atmospheric Response to Midlatitude SST Anomalies and Its Dependence on Background Circulation States. J. Clim. 1997, 10, 971–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardeshmukh, P.D.; Hoskins, B.J. The Generation of Global Rotational Flow by Steady Idealized Tropical Divergence. J. Atmos. Sci. 1988, 45, 1228–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Summary for Policymakers. In IPCC Special Report on the Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate; Pörtner, H.-O., Roberts, D., Masson-Delmotte, V., Zhai, P., Tignor, M., Poloczanska, E., Mintenbeck, K., Alegría, A., Nicolai, M., Okem, A., et al., Eds.; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J.; Barlow, M.; Kushner, P.J.; Saito, K. Stratosphere–Troposphere Coupling and Links with Eurasian Land Surface Variability. J. Clim. 2007, 20, 5335–5343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strong, C.; Magnusdottir, G.; Stern, H. Observed Feedback between Winter Sea Ice and the North Atlantic Oscillation. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 6021–6032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Fan, K.; Xu, Z. Comparison of the Causes of High-Frequency Heavy and Light Snowfall on Interannual Timescales over Northeast China. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 936. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11090936
Wang L, Fan K, Xu Z. Comparison of the Causes of High-Frequency Heavy and Light Snowfall on Interannual Timescales over Northeast China. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(9):936. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11090936
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Lushan, Ke Fan, and Zhiqing Xu. 2020. "Comparison of the Causes of High-Frequency Heavy and Light Snowfall on Interannual Timescales over Northeast China" Atmosphere 11, no. 9: 936. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11090936
APA StyleWang, L., Fan, K., & Xu, Z. (2020). Comparison of the Causes of High-Frequency Heavy and Light Snowfall on Interannual Timescales over Northeast China. Atmosphere, 11(9), 936. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11090936




