Arable Weed Patterns According to Temperature and Latitude Gradient in Central and Southern Spain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
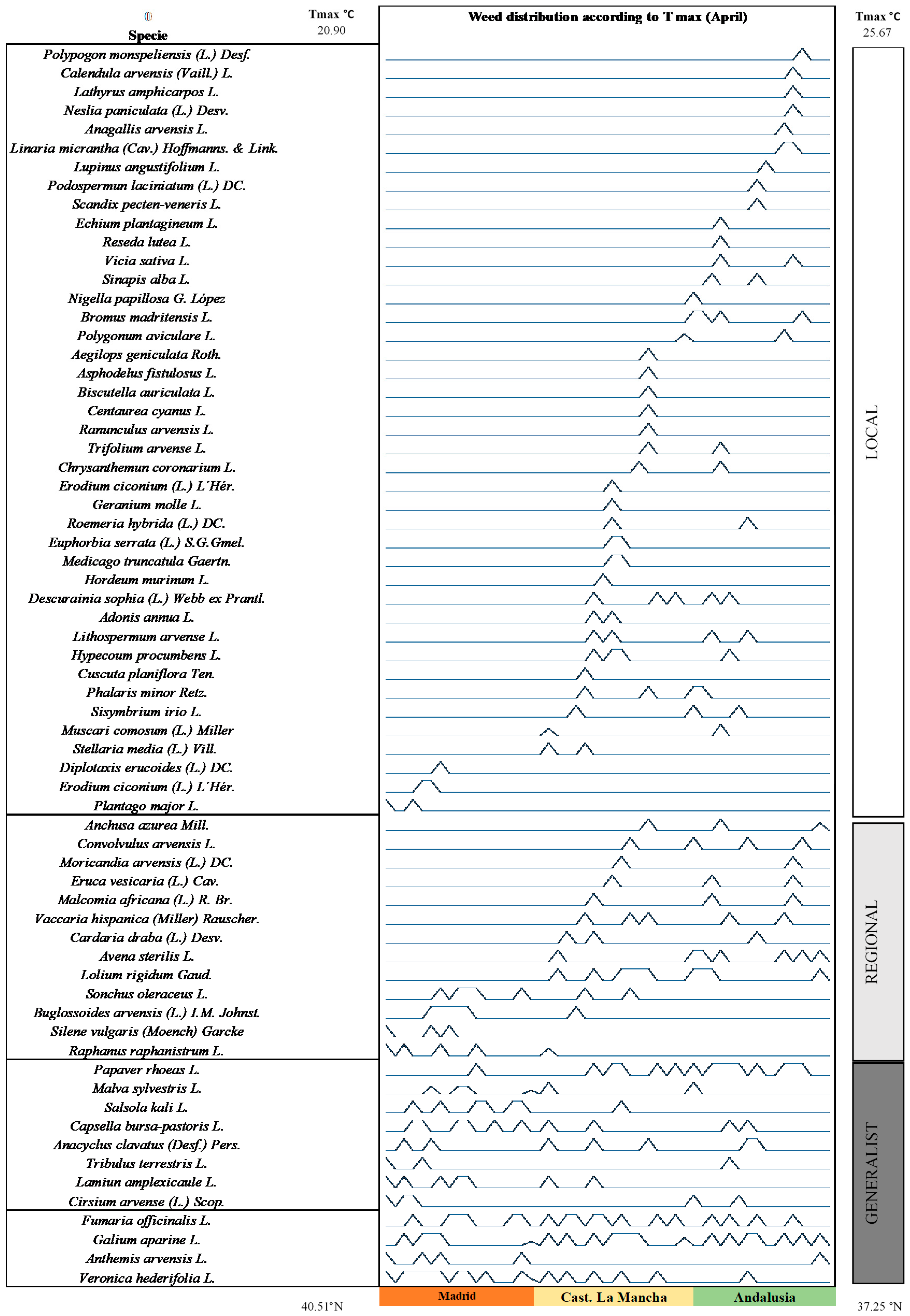
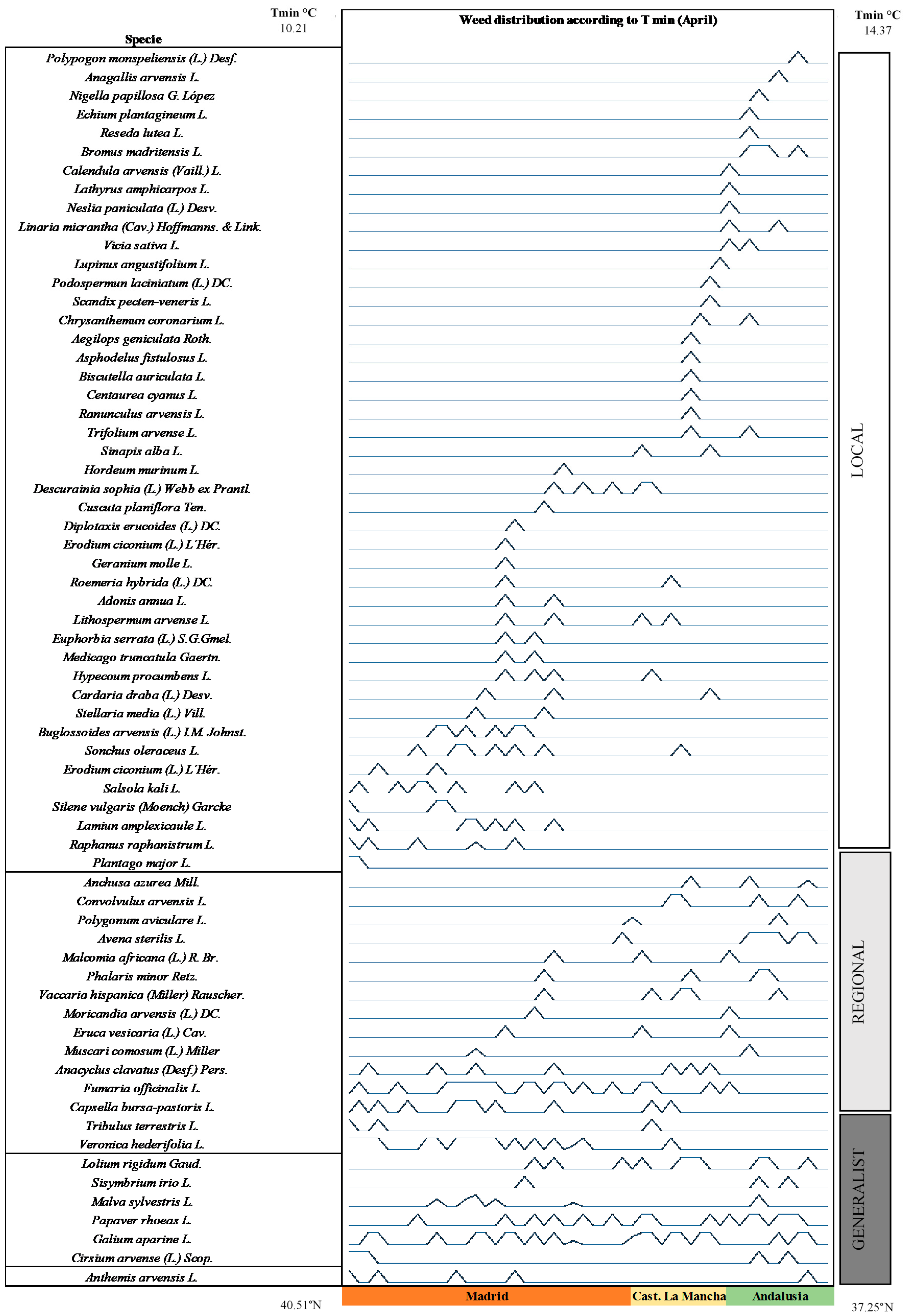
3. Results
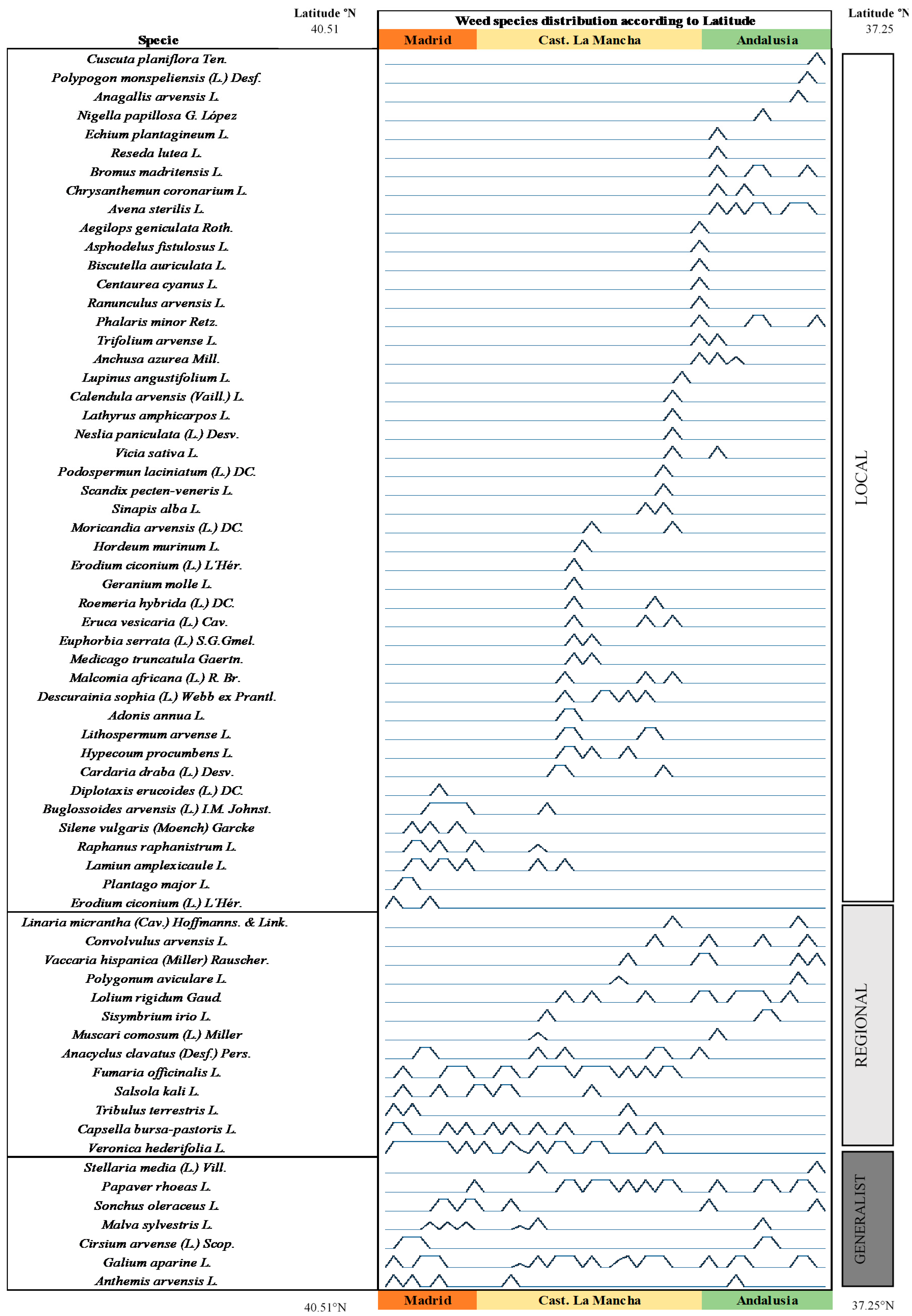
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reidsma, P.; Tekelenbur, T.; van den Berg, M.; Alkemade, R. Impacts of land-use change on biodiversity: An assessment of agricultural biodiversity in the European Union. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2006, 114, 86–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, O.E.; Chapin, F.S.; Armesto, J.J.; Berlow, E.; Bloomfield, J.; Dirzo, R.; Huber-Sanwald, E.; Huenneke, L.F.; Jackson, R.B.; Kinzig, A.; et al. Biodiversity—Global biodiversity scenarios for the year 2100. Science 2000, 287, 1770–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brock, W.A.; Carpenter, S.R.; Scheffer, M. Regime Shifts, Environmental Signals, Uncertainty, and Policy Choice. In Complexity Theory for a Sustainable Future; Norberg, J., Cumming, G.S., Eds.; Columbia University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 180–206. [Google Scholar]
- Samhouri, J.F.; Levin, P.S.; Ainsworth, C.H. Identifying thresholds for ecosystem-based management. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pautasso, M.; Dehnen-Schmutz, K.; Holdenrieder, O.; Pietravalle, S.; Salama, N.; Jeger, M.J.; Lange, E.; Hehl-Lange, S. Plant health and global change—Some implications for landscape management. Biol. Rev. 2010, 85, 729–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, A.; Havlík, P.; Schmid, E.; Valin, H.; Mosnier, A.; Obersteiner, M.; Böttcher, H.; Skalsky´, R.; Balkovič, J.; Sauer, T.; et al. Impacts of population growth, economic development, and technical change on global food production and consumption. Agric. Syst. 2011, 104, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, D.K.; Mueller, N.D.; West, P.C.; Foley, J.A. Yield trends are insufficient to double global crop production by 2050. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, J.R.; Jouzel, J.; Raynaud, D.; Barkov, N.I.; Barnola, J.M.; Basile, I.; Bender, M.; Chappellaz, J.; Davis, M.; Delaygue, G.; et al. Climate and atmospheric history of the past 420,000 years from the Vostok ice core, Antarctica. Nature 1999, 399, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loss, S.R.; Terwilliger, L.A.; Peterson, A.C. Assisted colonization: Integrating conservation strategies in the face of climate change. Biol. Conserv. 2011, 144, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fried, G.; Norton, L.R.; Reboud, X. Environmental and management factors determining weed species composition and diversity in France. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2008, 128, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potts, G.R.; Ewald, J.A.; Aebischer, N.J. Long-term changes in the flora of the cereal ecosystem on the Sussex Downs, England, focusing on the years 1968–2005. J. Appl. Ecol. 2010, 47, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreasen, C.; Streibig, J.C. Evaluation of changes in weed flora in arable fields of Nordic countries—Based on Danish long-term surveys. Weed Res. 2011, 51, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salonen, J.; Hyvönen, T.; Kaseva, J.; Jalli, H. Impact of changed cropping practices on weed occurrence in spring cereals in Finland—A comparison of surveys in 1997–1999 and 2007–2009. Weed Res. 2013, 53, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, E.; Forchhammer, M.C.; Stenseth, N.C.; Callaghan, T.V. The timing of life-history events in a changing climate. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B. 2001, 268, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogues-Bravo, D. Predicting the past distribution of species climatic niches. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2009, 18, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrella, N.; Sparks, T.H.; Menzel, A. Effects of temperature, phase type and timing, location, and human density on plant phenological responses in Europe. Clim. Res. 2009, 39, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaukoranta, T.; Hakala, K. Impact of spring warming on sowing times of cereal, potato and sugar beet in Finland. Agric. Food Sci. 2008, 17, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, A.; Vanclay, F. Farmer responses to climate change and sustainable agriculture. A review. Agron. Sustain. Develop. 2010, 30, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daccache, A.; Keay, C.A.; Jones, R.J.A.; Weatherhead, E.K.; Stalham, M.A.; Knox, J.W. Climate change and land suitability for potato production in England and Wales: Impacts and adaptation. J. Agric. Sci. 2012, 150, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerowitt, B.; Bertke, E.; Hespelt, S.-K.; Tute, C. Towards multifunctional agriculture—Weeds as ecological goods? Weed Res. 2003, 43, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grime, J.P. Evidence for the existence of three primary strategies in plants and its relevance to ecological and evolutionary theory. Am. Nat. 1977, 111, 1169–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrer, J. Agroecosystem responses to combinations of elevated CO2, ozone, and global climate change. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2003, 97, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, E.J.P.; Brown, V.K.; Boatman, N.D.; Lutman, P.J.W.; Squire, G.R.; Ward, L.K. The role of weeds in supporting biological diversity within crop fields. Weed Res. 2003, 43, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, S.; Boursault, A.; Le Guilloux, M.; Munier-Jolain, N.; Reboud, X. Weeds in agricultural landscapes. A review. Agron. Sustain. Develop. 2011, 31, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, D.R.; Weise, S.F.; Swanton, C.J. Integrated weed management and weed species diversity. Phytoprotection 1994, 75, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fried, G.; Petit, S.; Reboud, X. A specialist-generalist classification of the arable flora and its response to changes in agricultural practices. BMC Ecol. 2010, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapin, F.S., III; Zavaleta, E.S.; Eviner, V.T.; Naylor, R.L.; Vitousek P., M.; Reynolds, H.L.; Hooper, D.U.; Lavorel, S.; Sala, O.E.; Hobbie, S.E.; et al. Consequences of changing biodiversity. Nature 2000, 405, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, B.D.; Swanton, C.J. Assembly theory applied to weed communities. Weed Sci. 2002, 50, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, O. Species pools in cultural landscapes—Niche construction, ecological opportunity and niche shifts. Ecography 2013, 36, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawes, C.; Haughton, A.J.; Bohan, D.A.; Squire, G.R. Functional approaches for assessing plant and invertebrate abundance patterns in arable systems. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2009, 10, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urruty, N.; Deveaud, T.; Guyomard, H.; Boiffin, J. Impacts of agricultural land use changes on pesticide use in French agriculture. Eur. J. Agron. 2016, 80, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyvönen, T.; Huusela-Veistola, E. Arable weeds as indicators of agricultural intensity—A case study from Finland. Biol. Conserv. 2008, 141, 2857–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dukes, J.S.; Pontius, J.; Orwig, D.; Garnas, J.R.; Rodgers, V.L.; Brazee, N.; Cooke, B.; Theoharides, K.A.; Stange, E.E.; Harrington, R.; et al. Responses of insect pests, pathogens, and invasive plant species to climate change in the forests of northeastern North America: What can we predict? Can. J. For. Res. 2009, 39, 231–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, A.; Travism, J.M.J.; Johst, K. Interspecific interactions affect species and community responses to climate shifts. Oikos 2013, 122, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malavasi, M.; Santoro, R.; Cutini, M.; Acosta, A.T.R.; Carranza, M.L. The impact of human pressure on landscape patterns and plant species richness in Mediterranean coastal dunes. Plant Biosyst. 2016, 150, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloomfield, J.P.; Williams, R.J.; Gooddy, D.C.; Cape, J.N.; Guha, P. Impacts of climate change on the fate and behaviour of pesticides in surface and groundwater—A UK perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 369, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walck, J.L.; Hidayati, S.N.; Dixon, K.W.; Thompson, K.; Poschlod, P. Climate change and plant regeneration from seed. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2011, 17, 2145–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanzlik, K.; Gerowitt, B. Occurrence and distribution of important weed species in German winter oilseed rape fields. J. Plant. Dis. Prot. 2012, 119, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimdahl, R.L. Weed-Crop Competition: A Review, 2nd ed.; Blackwell: Ames, IA, USA, 2004; p. 220. [Google Scholar]
- Jump, A.S.; Peñuelas, J. Running and stand still: Adaptation and the response of plants to rapid climate change. Ecol. Lett. 2005, 8, 1010–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimalova, S.; Lososova, Z. Arable weed vegetation of the northeastern part of the Czech Republic: Effects of environmental factors on species composition. Plant Ecol. 2009, 203, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silc, U.; Vrbnicanin, S.; Bozi, C.D.; Carni, A.; Stevanovic, Z.D. Weed vegetation in the northwestern Balkans: Diversity and species composition. Weed Res. 2009, 49, 602–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulme, P.E.; Barrett, S.C.H. Integrating trait- and niche-based approaches to assess contemporary evolution in alien plant species. J. Ecol. 2013, 101, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lososova, Z.; Chytry, M.; Kühn, I.; Hájeka, O.; Horáková, V.; Pysek, P.; Tichy, L. Patterns of plant traits in annual vegetation of man-made habitats in Central Europe. Perspect. Plant. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2006, 8, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyvönen, T.; Luoto, M.; Uotila, P. Assessment of weed establishment risk in a changing European climate. Agric. Food Sci. 2012, 21, 348–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, K.; Breitsameter, L.; Gerowitt, B. Impact of climate change on weeds in agriculture: A review. Agron. Sustain. Develop. 2014, 34, 707–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gandía, M.L.; Casanova, C.; Sánchez, F.J.; Tenorio, J.L.; Santín-Montanyá, M.I. Arable Weed Patterns According to Temperature and Latitude Gradient in Central and Southern Spain. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 853. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11080853
Gandía ML, Casanova C, Sánchez FJ, Tenorio JL, Santín-Montanyá MI. Arable Weed Patterns According to Temperature and Latitude Gradient in Central and Southern Spain. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(8):853. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11080853
Chicago/Turabian StyleGandía, María Luisa, Carlos Casanova, Francisco Javier Sánchez, José Luís Tenorio, and María Inés Santín-Montanyá. 2020. "Arable Weed Patterns According to Temperature and Latitude Gradient in Central and Southern Spain" Atmosphere 11, no. 8: 853. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11080853
APA StyleGandía, M. L., Casanova, C., Sánchez, F. J., Tenorio, J. L., & Santín-Montanyá, M. I. (2020). Arable Weed Patterns According to Temperature and Latitude Gradient in Central and Southern Spain. Atmosphere, 11(8), 853. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11080853




