Analysis of Pollution Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Main Pollutants in the Atmosphere of Shenyang City
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiments
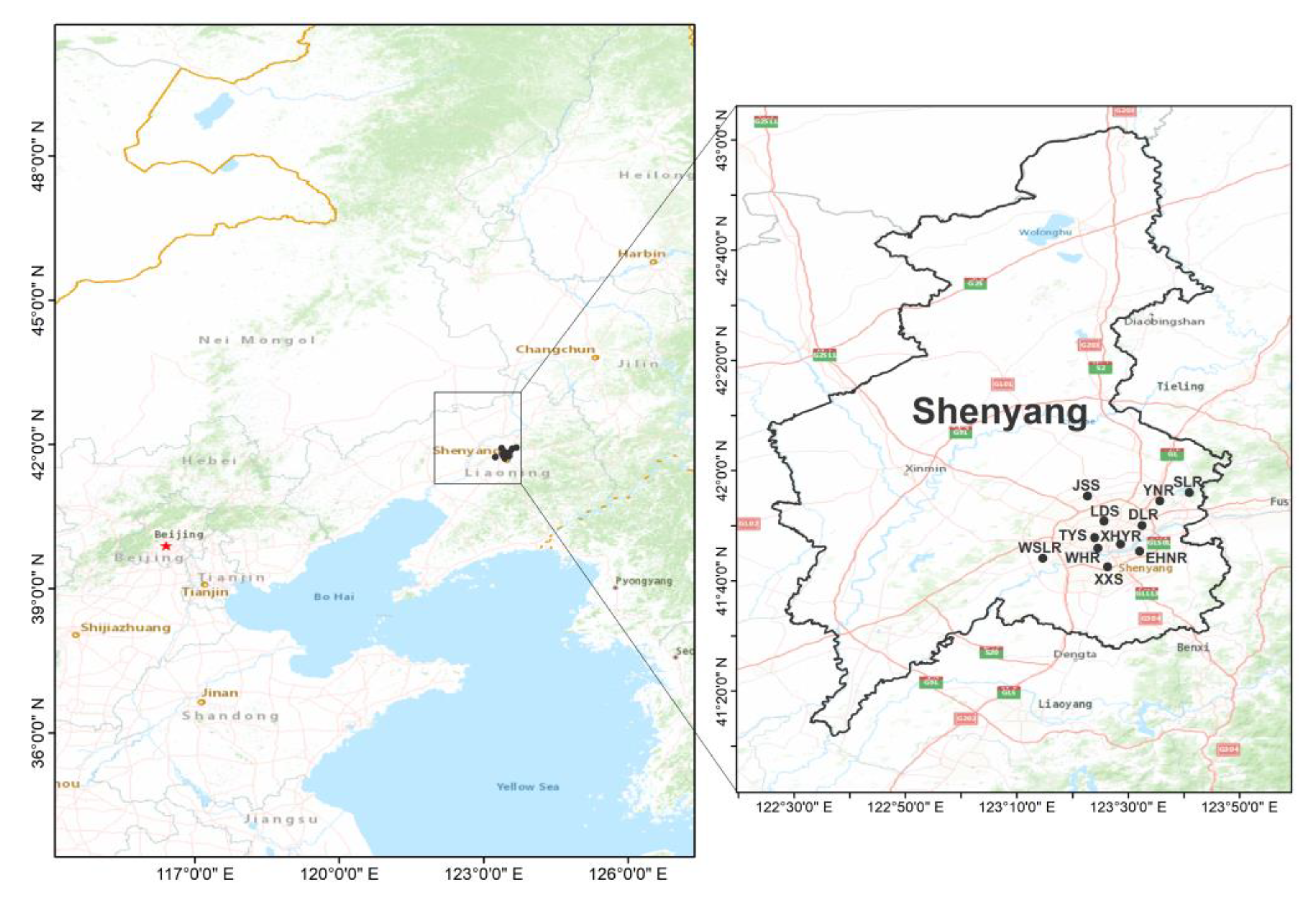
2.1. Research Area and Data Source
2.2. Analysis of Spatio-Temporal Distribution Characteristics
2.3. Meteorological Element Analysis and Backward Trajectory Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of Spatio-Temporal Distribution Characteristics of Six Air Pollutants
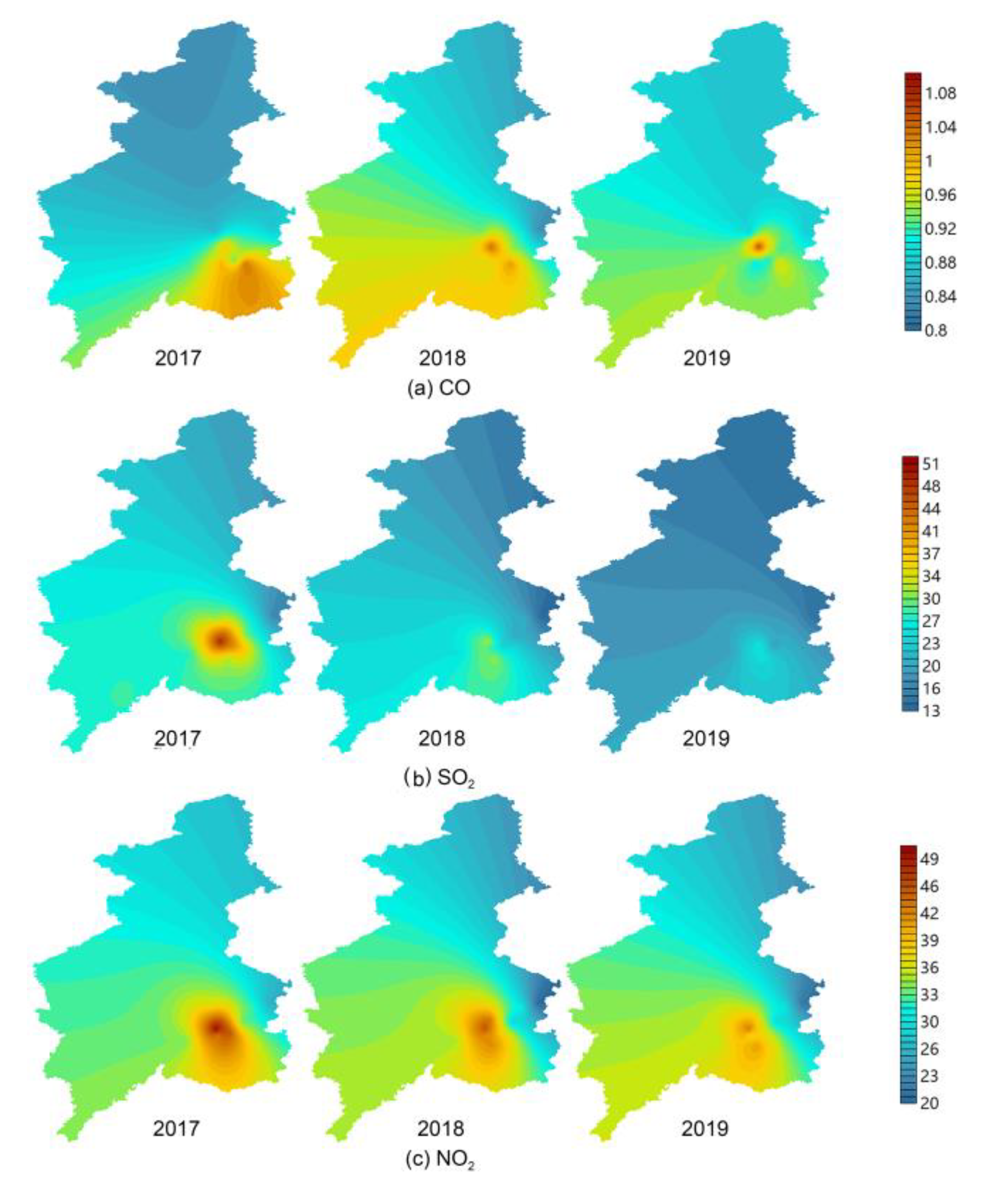
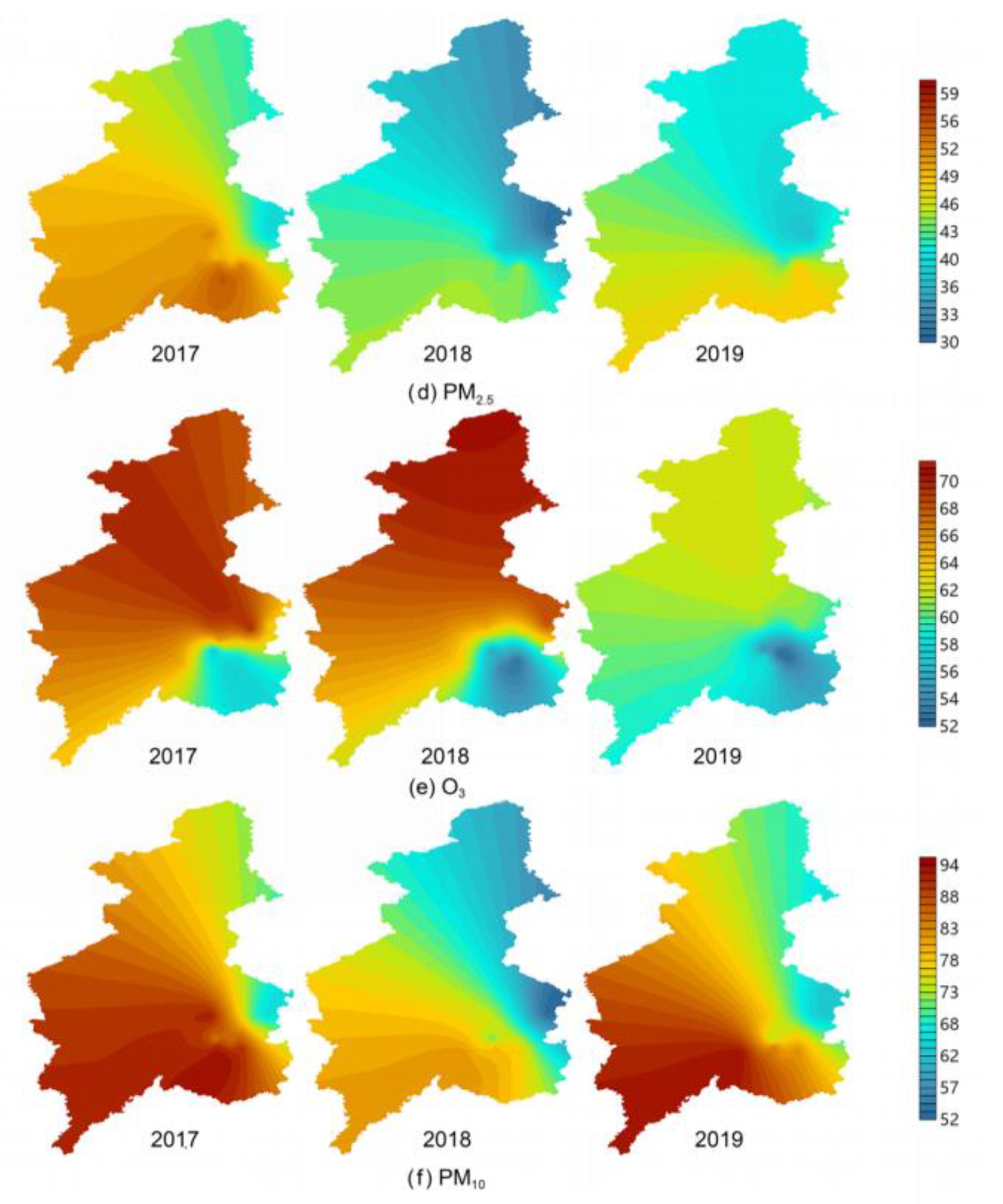
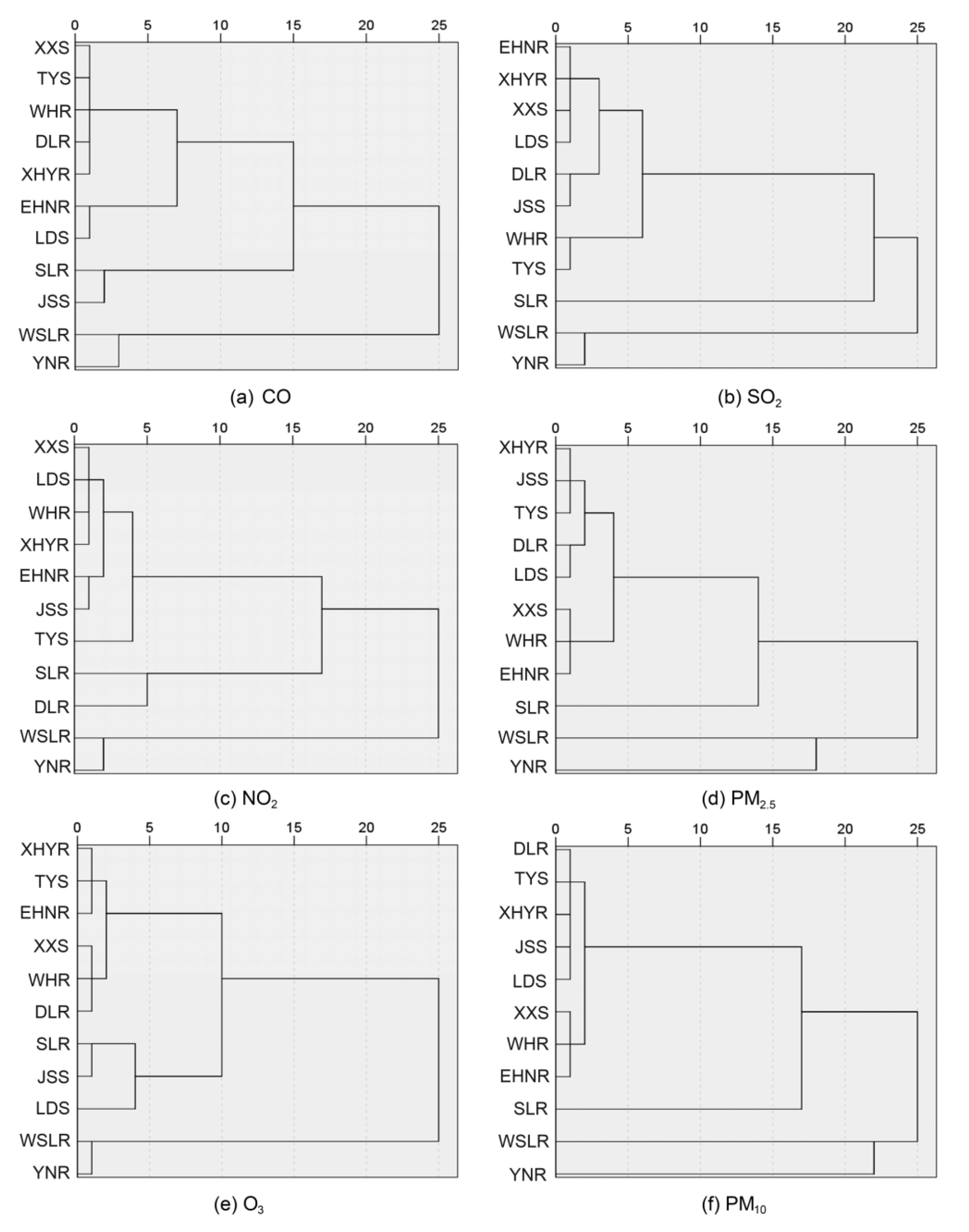
3.1.1. Difference in Spatial Distributions of Pollutant Concentrations
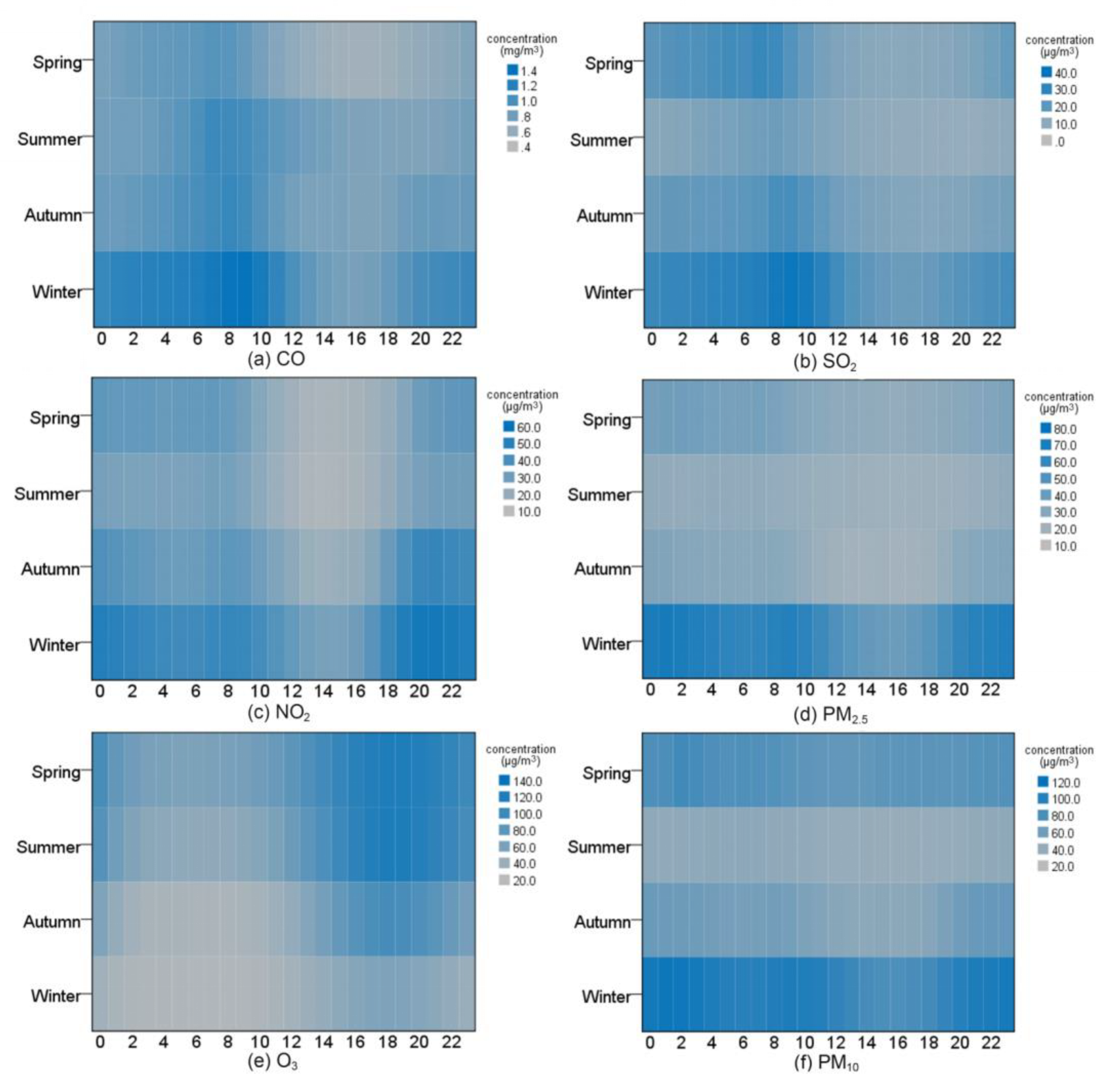
3.1.2. Seasonal Variation of Pollutant Concentrations
3.1.3. Monthly Variation of Pollutant Concentrations
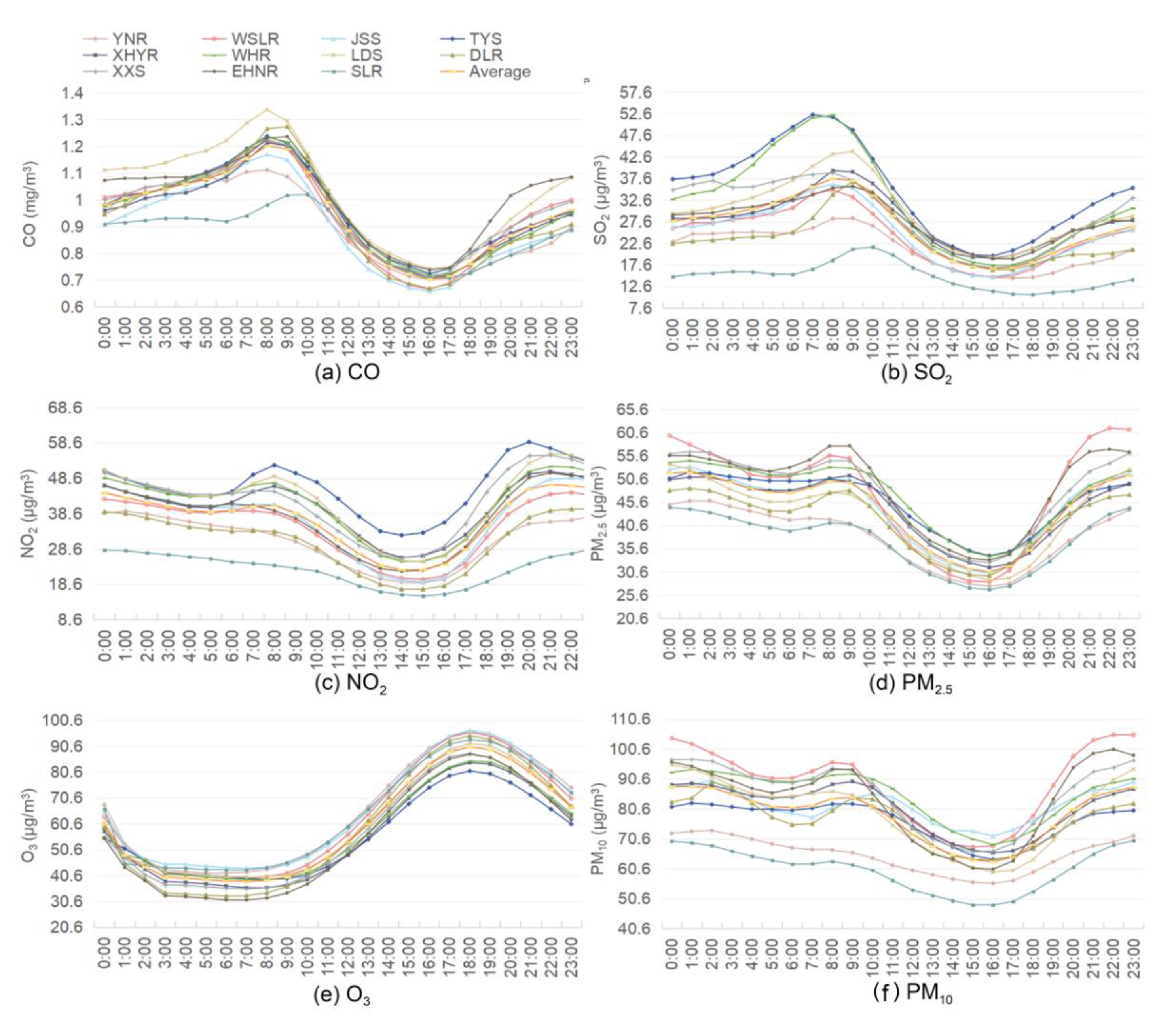
3.1.4. Diurnal Variation of Pollutant Concentrations
3.2. Influence of Meteorological Factors on Pollutant Concentrations
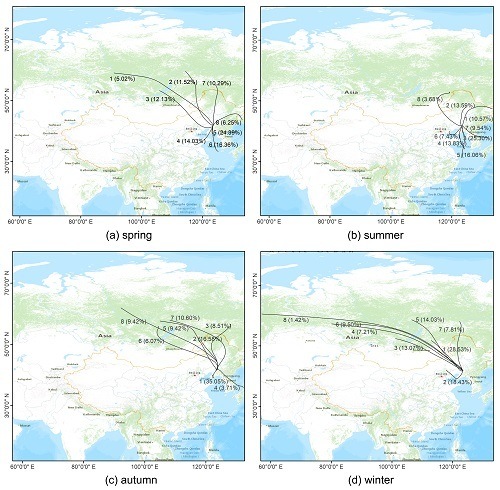
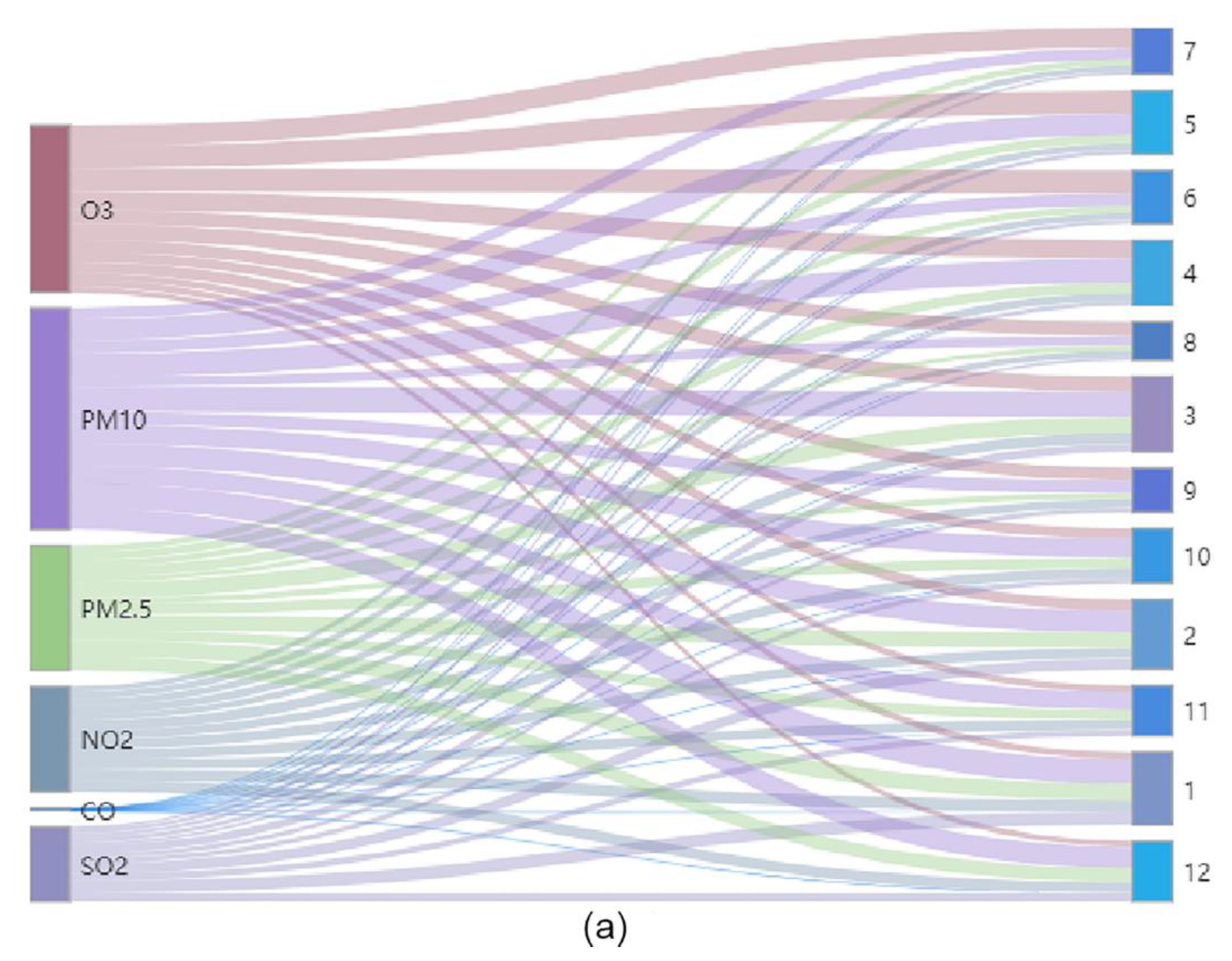
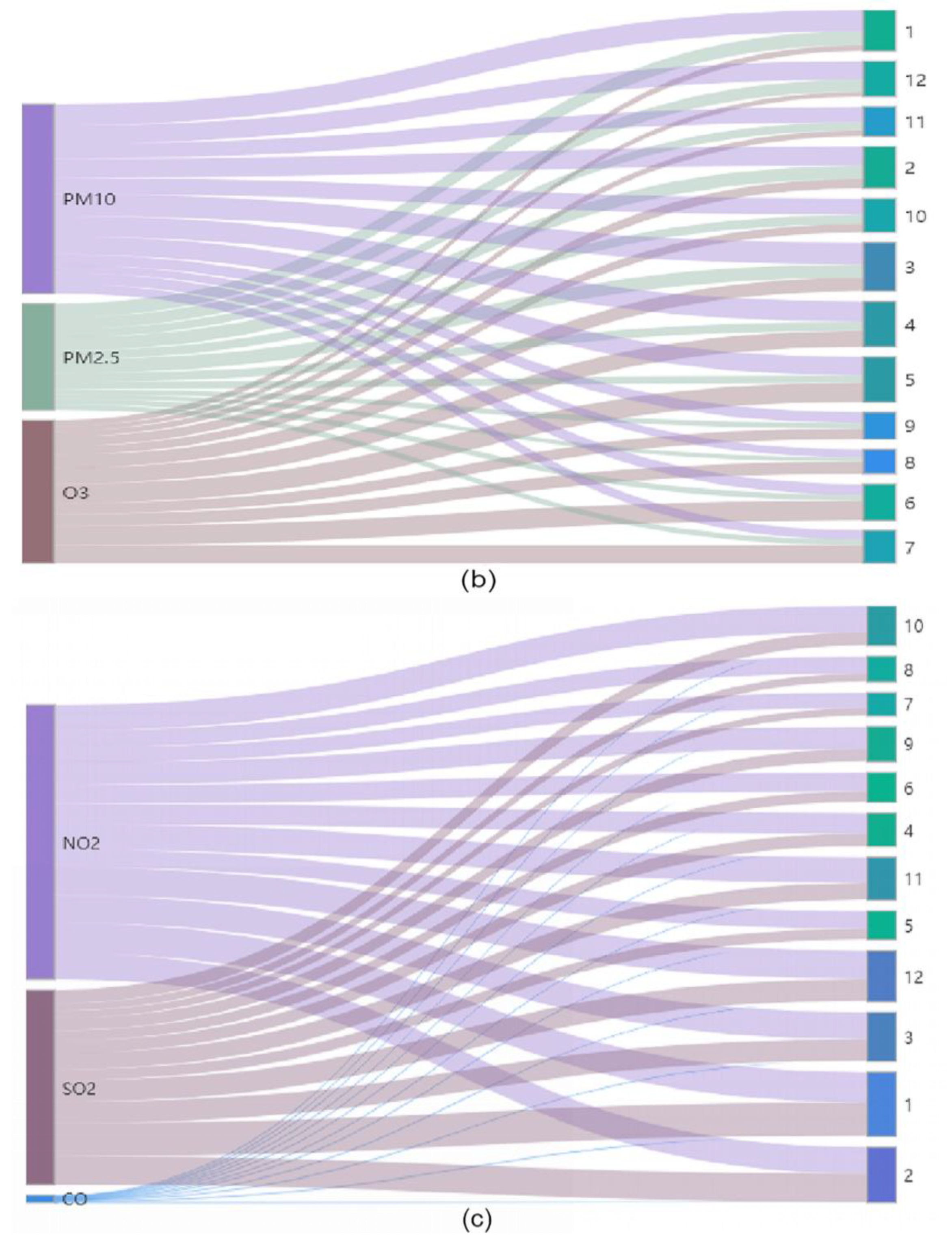
3.3. Backward Trajectory Clustering Analysis
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Affected by vegetation coverage, the concentrations of CO, SO2, NO2, PM10, and PM2.5 in the northern part of Shenyang were relatively low, while the trend of O3 concentration was the inverse. The high concentrations of CO, SO2, and NO2 were located in the central urban area. Because Tiexi (northeast old industrial base) was located in the southwest, the high concentrations area of PM10 and PM2.5 were located in the southwest.
- (2)
- Affected by coal combustion for heating purposes and rainfall, the accumulated concentrations of the six pollutants were higher from January to March and lower from July to September and November. In terms of the daily variation characteristics, the concentrations of CO, SO2, and O3 were of the “single peak” type, while NO2, PM10, and PM2.5 were of the “double peak and double valley” type. The study area belongs to the northeast old industrial base, with many industrial point sources. There was a significant positive correlation between CO, NO2, SO2, PM2.5, and PM10. Because the precursors were consumed and produced by photochemical reactions, the concentrations of NO2 and O3 showed a significant negative correlation. Low temperature increases the activity of emission sources; thus, the temperature was negatively correlated with the concentration of most pollutants.
- (3)
- The airflow transport distance was longer in winter due to the influence of the winter monsoon. The pollution in the main urban area in spring and summer was mainly affected by the ocean current from the Yellow Sea. In summer, the airflow pollution of SO2 and PM2.5 mainly originated in Shandong Province. Affected by the semi-permanent cold high in Mongolia–Siberia, the regional transport of pollutants in autumn and winter was mainly affected by the northwest airflow. Because the northwest airflow path area was close to the desert and the low temperature in winter leads to more anthropogenic emissions, the concentration of pollutants was highest in winter.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brauer, M.; Freedman, G.; Frostad, J.; van Donkelaar, A.; Martin, R.V.; Dentener, F.; Dingenen, R.; Estep, K.; Amini, H.; Apte, J.S.; et al. Ambient Air Pollution Exposure Estimation for the Global Burden of Disease 2013. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, A.J.; Brauer, M.; Burnett, R.; Anderson, H.R.; Frostad, J.; Estep, K.; Balakrishnan, K.; Brunekreef, B.; Dandona, L.; Dandona, R.; et al. Estimates and 25-year trends of the global burden of disease attributable to ambient air pollution: An analysis of data from the Global Burden of Diseases Study 2015. Lancet 2017, 389, 1907–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zanobetti, A.; Wang, Y.; Koutrakis, P.; Choirat, C.; Dominici, F.; Schwartz, J.D. Air Pollution and Mortality in the Medicare Population. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 2513–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kan, H.; Chen, R.; Tong, S. Ambient air pollution, climate change, and population health in China. Environ. Int. 2012, 42, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.H.; Jahan, S.A.; Kabir, E. A review on human health perspective of air pollution with respect to allergies and asthma. Environ. Int. 2013, 59, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoek, G.; Krishnan, R.M.; Beelen, R.; Peters, A.; Ostro, B.; Brunekreef, B.; Kaufman, J.D. Long-term air pollution exposure and cardio- respiratory mortality: A review. Environ. Health 2013, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Huang, L.; Chen, M.; Liao, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Ying, Q. Premature Mortality Attributable to Particulate Matter in China: Source Contributions and Responses to Reductions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 9950–9959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Han, Y.; Tang, X.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, T. Estimating adult mortality attributable to PM2.5 exposure in China with assimilated PM2.5 concentrations based on a ground monitoring network. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 568, 1253–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, N.; Hannigan, M.P.; Miller, S.L.; Peel, J.L.; Milford, J.B. Comparisons of urban and rural PM10−2.5 and PM2.5 mass concentrations and semi-volatile fractions in northeastern Colorado. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 7469–7484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Donkelaar, A.; Martin, R.V.; Brauer, M.; Hsu, N.C.; Kahn, R.A.; Levy, R.C.; Lyapustin, A.; Sayer, A.M.; Winker, D.M. Global Estimates of Fine Particulate Matter using a Combined Geophysical-Statistical Method with Information from Satellites, Models, and Monitors. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 3762–3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Zhou, W.; Li, W.; Li, L. Impact of urbanization level on urban air quality: A case of fine particles (PM(2.5)) in Chinese cities. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 194, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Gong, S.; Yu, Y.; Yu, L.; Wu, L.; Mao, H.; Song, C.; Zhao, S.; Liu, H.; Li, X.; et al. Air pollution characteristics and their relation to meteorological conditions during 2014-2015 in major Chinese cities. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 484–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B. The Spatial and Temporal Variation of Air Pollution Characteristics in China Adopting Air Pollution Index (API) Analysis. Master’s Thesis, Ocean University of China, Qingdao, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Song, C.; Wu, L.; Xie, Y.; He, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, T.; Lin, Y.; Jin, T.; Wang, A.; Liu, Y.; et al. Air pollution in China: Status and spatiotemporal variations. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 227, 334–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Chen, S.; Lü, H.; Liu, Y.; Wu, J. Spatiotemporal patterns of remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration in China from 1999 to 2011. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 174, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO Air Quality Guidelines for Particulate Matter, Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide and Sulfur Dioxide (Global Update 2005): Summary of Risk Assessment; WHO Press: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005; pp. 9–11.
- Ma, Z.; Hu, X.; Sayer, A.M.; Levy, R.; Zhang, Q.; Xue, Y.; Tong, S.; Bi, J.; Huang, L.; Liu, Y. Satellite-Based Spatiotemporal Trends in PM2.5 Concentrations: China, 2004–2013. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Wei, P.; Cheng, S.; Wang, W.; Xie, P.; Chen, Z.; Su, F.; ERen, Z. Air pollution characteristic and variation trend of Central Triangle urban agglomeration from 2005 to 2014. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2017, 11, 2977–2984. [Google Scholar]
- Nishanth, T.; Satheesh Kumar, M.K.; Valsaraj, K.T. Variations in surface ozone and NOx at Kannur: A tropical, coastal site in India. J. Atmos. Chem. 2012, 69, 101–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, L.; Jin, L.; Li, J.; Fu, P.; Yang, W.; Liu, D.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Z.; Li, X. PM2.5 in the Yangtze River Delta, China: Chemical compositions, seasonal variations, and regional pollution events. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Yang, L.; Yuan, Q.; Yan, C.; Dong, C.; Meng, C.; Sui, X.; Yang, F.; Lu, Y.; Wang, W. Sources apportionment of PM2.5 in a background site in the North China Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 590–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, X.; Du, W.; Xue, Y. Analysis of Air Pollution Index and Its Influence Factors in Beijing. Environ. Monit. China 2015, 31, 53–56. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Yu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Mao, H.; Wu, L.; Liu, N.; Zhao, S. Numerical Model-Based Artificial Neural Network Model and Its Application for Quantifying Impact Factors of Urban Air Quality. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhao, H.; Dong, Y.; Che, H.; Li, X.; Hong, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Comparison of Two Air Pollution Episodes over Northeast China in Winter 2016/17 Using Ground-Based Lidar. J. Meteorol. Res. 2018, 32, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Liu, Y.; Wu, X.; Bao, Q.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, S.; Xiu, A.; Chen, T. Spatial and Temporal Characteristics of Air Quality and Cause Analysis of Heavy Pollution in Northeast China. Environ. Sci. 2019, 40, 4810–4823. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Yuan, Z.; Wu, Y.; Ban, W.; Li, D.; Ji, C.; Gao, W. Analysis of Persistence and Intensification Mechanism of a Heavy Haze Event in Shenyang. Res. Environ. Sci. 2017, 30, 349–358. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, Y.; Li, C.L.; Li, X.L.; Ma, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.H.; Zhou, D.P.; Wang, Y.F.; Liu, N.W.; Chang, X.J. Analysis of Compositional Variation and Source Characteristics of Water-Soluble Ions in PM2.5 during Several Winter-Haze Pollution Episodes in Shenyang, China. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Peng, Q.; Zhou, J.; Song, G.; Gong, X. The unidirectional causality influence of factors on PM2.5 in Shenyang city of China. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.; Song, Y.; Liu, B. Visibility trends in six megacities in China 1973–2007. Atmos. Res. 2009, 94, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Xie, X.; Liu, R. Spatial, sources and risk assessment of heavy metal contamination of urban soils in typical regions of Shenyang, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 174, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China. HJ/T193-2005, Monitoring Regulation for Ambient Air Quality; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2005.
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China. HJ 663-2013, Technical Regulation for Ambient Air Quality Assessment (on Trial); China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2013.
- China Meteorological Administration. Division of Climate Season QX/T 152—2012; China Meteorological Administration, Meteorological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2012.
- Stein, A.F.; Draxler, R.R.; Rolph, G.D.; Stunder, B.J.B.; Cohen, M.D.; Ngan, F. NOAA’s hysplit atmospheric transport and dispersion modeling system. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, L. Analysis on dynamic evolution characteristics of vegetation in Liaoning Province from 2000 to 2014. Water Resour. Hydropower Eng. 2017, 48, 48–56. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, S.; Shen, Z.; Zhou, P.; Zou, X.; Che, S.; Wang, W. Quantifying air pollution attenuation within urban parks: An experimental approach in Shanghai, China. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 2155–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vingarzan, R. A review of surface ozone background levels and trends. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 3431–3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Keijzer, C.; Agis, D.; Ambros, A.; Arevalo, G.; Baldasano, J.M.; Bande, S.; Barrera-Gomez, J.; Benach, J.; Cirach, M.; Dadvand, P.; et al. The association of air pollution and greenness with mortality and life expectancy in Spain: A small-area study. Environ. Int. 2017, 99, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Xie, X.; Fang, C. Temporal and Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Atmospheric Particulate Matter (PM10 and PM2.5) in Changchun and Analysis of Its Influencing Factors. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arain, M.A.; Blair, R.; Finkelstein, N.; Brook, J.; Jerrett, M. Meteorological influences on the spatial and temporal variability of NO2 in Toronto and Hamilton. Can. Geogr. 2009, 53, 165–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dommen, J.; Prevot, A.S.H.; Baertsch-Ritter, N.; Maffeis, G.; Longoni, M.G.; Gruebler, F.C.; Thielmann, A. High-resolution emission inventory of the Lombardy region: Development and comparison with measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 4149–4161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassler, B.; McDonald, B.C.; Frost, G.J.; Borbon, A.; Carslaw, D.C.; Civerolo, K.; Granier, C.; Monks, P.S.; Monks, S.; Parrish, D.D.; et al. Analysis of long-term observations of NOx and CO in megacities and application to constraining emissions inventories. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 9920–9930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, S.F.; Ding, X.A.; Bai, Z.P.; Han, B.; Chen, L.; Shi, J.W.; Li, Z.Y. A seasonal study of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in PM2.5 and PM2.5-10 in five typical cities of Liaoning Province, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 183, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, H.; Fu, L.; Hao, J. Assessment of vehicle emission programs in China during 1998-2013: Achievement, challenges and implications. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 214, 556–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Yu, Z.; Gao, H.; Huang, T.; Ma, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y. Gridded emission inventories and spatial distribution characteristics of anthropogenic atmospheric pollutants in Lanzhou valley. Acta Sci. Circumst. 2017, 37, 1227–1242. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Feng, J.; Su, X.; Li, Y.; Sun, J. A seriously air pollution area affected by anthropogenic in the central China: Temporal-spatial distribution and potential sources. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wang, Y.; Ying, Q.; Zhang, H. Spatial and temporal variability of PM2.5 and PM 10 over the North China Plain and the Yangtze River Delta, China. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 95, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Q.; Zhao, H.; Wang, L.; Tao, R. Variations in PM10, PM2.5 and PM1.0 in an Urban Area of the Sichuan Basin and Their Relation to Meteorological Factors. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 150–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.; Basant, A.; Malik, A.; Singh, K.P. Iron-induced oxidative stress in a macrophyte: A chemometric approach. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2009, 72, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; McCormack, M.; Li, L.; Hall, Q.; Xiang, C.; Sheen, J. Glc-TOR signaling leads transcriptome reprogramming and meristem activation. Nature 2013, 496, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, F.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, L.; Tang, M.; Gai, X.; Chen, M.; Ge, X. Temporal variations of six ambient criteria air pollutants from 2015 to 2018, their spatial distributions, health risks and relationships with socioeconomic factors during 2018 in China. Environ. Int. 2020, 137, 105556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Fernández, M.I.; Gallego, M.C.; García, J.A.; Acero, F.J. A study of surface ozone variability over the Iberian Peninsula during the last fifty years. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 1946–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.; Wang, S.X.; Jang, C.; Zhu, Y.; Hao, J.M. Nonlinear response of ozone to precursor emission changes in China: A modeling study using response surface methodology. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 5027–5044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, R. Atmospheric chemistry of VOCs and NOx. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 2063–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, S.; Naja, M.; Subbaraya, B.H. Seasonal variations in surface ozone and its precursors over an urban site in India. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 2713–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boersma, K.F.; Jacob, D.J.; Trainic, M.; Rudich, Y.; DeSmedt, I.; Dirksen, R.; Eskes, H.J. Validation of urban NO2 concentrations and their diurnal and seasonal variations observed from the SCIAMACHY and OMI sensors using in situ surface measurements in Israeli cities. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 3867–3879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamsal, N.L.; Martin, R.V.; Donkelaar, A.; Celarier, E.A.; Bucsela, E.J.; Boersma, K.F.; Dirksen, R.; Luo, C.; Wang, Y. Indirect validation of tropospheric nitrogen dioxide retrieved from the OMI satellite instrument: Insight into the seasonal variation of nitrogen oxides at northern midlatitudes. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, Z.W.; Cheng, H.R.; Lv, X.P.; Gong, W.; Wang, X.M.; Zhang, G. Seasonal variations and chemical characteristics of PM(2.5) in Wuhan, central China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 518, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karar, K.; Gupta, A.K. Seasonal variations and chemical characterization of ambient PM 10 at residential and industrial sites of an urban region of Kolkata (Calcutta), India. Atmos. Res. 2005, 81, 36–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.B.; Yang, F.M.; Ma, Y.L.; Lv, X.P.; Gong, W.; Wang, X.M.; Zhang, G. The characteristics of PM2.5 in Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 4959–4970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, W.J.; Arimoto, R.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zhao, C.H.; Wang, Y.Q.; Sheng, L.F.; Fu, G. Spatial distribution and interannual variation of surface PM10 concentrations over eighty-six Chinese cities. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 5641–5662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.Y.; Wang, S.G. Influence of different weather events on concentrations of particulate matter with different sizes in Lanzhou, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 24, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Liu, Y.; Li, X. Spatiotemporal distribution of ground-level ozone in China at a city level. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Lv, J.; Tan, Y.; Guo, M.; Gu, Y.; Xu, S.; Zhou, Y. Temporospatial variations and Spearman correlation analysis of ozone concentrations to nitrogen dioxide, sulfur dioxide, particulate matters and carbon monoxide in ambient air, China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2019, 10, 1203–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, D.J.; Winner, D.A. Effect of climate change on air quality. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhao, Z.H. IOP, Comparative analysis of the variation characteristics of O3, NO2 and CO in the boundary layer in coastal cities and inland cities in the middle latitude regions in China. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Air Pollution and Environmental Engineering, Hong Kong, China, 26–28 October 2018; IOP Publishing Ltd.: Bristol, CT, USA, 2018; Volume 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, X.; Song, T.; Münkel, C.; Hu, B.; Schäfer, K.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; et al. Mixing layer height and its implications for air pollution over Beijing, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 2459–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Zhou, W.; Li, W.; Meshesha, D.T.; Li, L.; Zheng, M. Meteorological and urban landscape factors on severe air pollution in Beijing. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2015, 65, 782–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, R.; Yang, L.; Liu, M.; Li, C.; Yang, Y. Spatiotemporal Distribution of Air Pollution Characteristics in Jiangsu Province, China. Adv. Meteorol. 2019, 2019, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahato, S.; Pal, S.; Ghosh, K.G. Effect of lockdown amid COVID-19 pandemic on air quality of the megacity Delhi, India. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 730, 139086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, A.J.; Fu, C.B.; Yang, X.Q.; Sun, J.N.; Zheng, L.F.; Xie, Y.N.; Herrmann, E.; Nie, W.; Petäjä, T.; Kerminen, V.M.; et al. Ozone and fine particle in the western Yangtze River Delta: An overview of 1 yr data at the SORPES station. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 5813–5830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y. Assessment of ozone variations and meteorological effects in Beijing. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2009, 18, 944–951. [Google Scholar]
- He, H.D. Multifractal analysis of interactive patterns between meteorological factors and pollutants in urban and rural areas. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 149, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Wei, W.; Zhou, Y.; Cheng, S.; Wang, X. Cause and Effect Evaluation of PM2.5 during Three Red Alerts in Beijing from 2015 to 2016. Huan Jing Ke Xue 2019, 40, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ogawa, S. Effects of Meteorological Conditions on PM2.5 Concentrations in Nagasaki, Japan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 9089–9101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, J.I.; Park, R.J. Winter monsoon variability and its impact on aerosol concentrations in East Asia. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 221, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

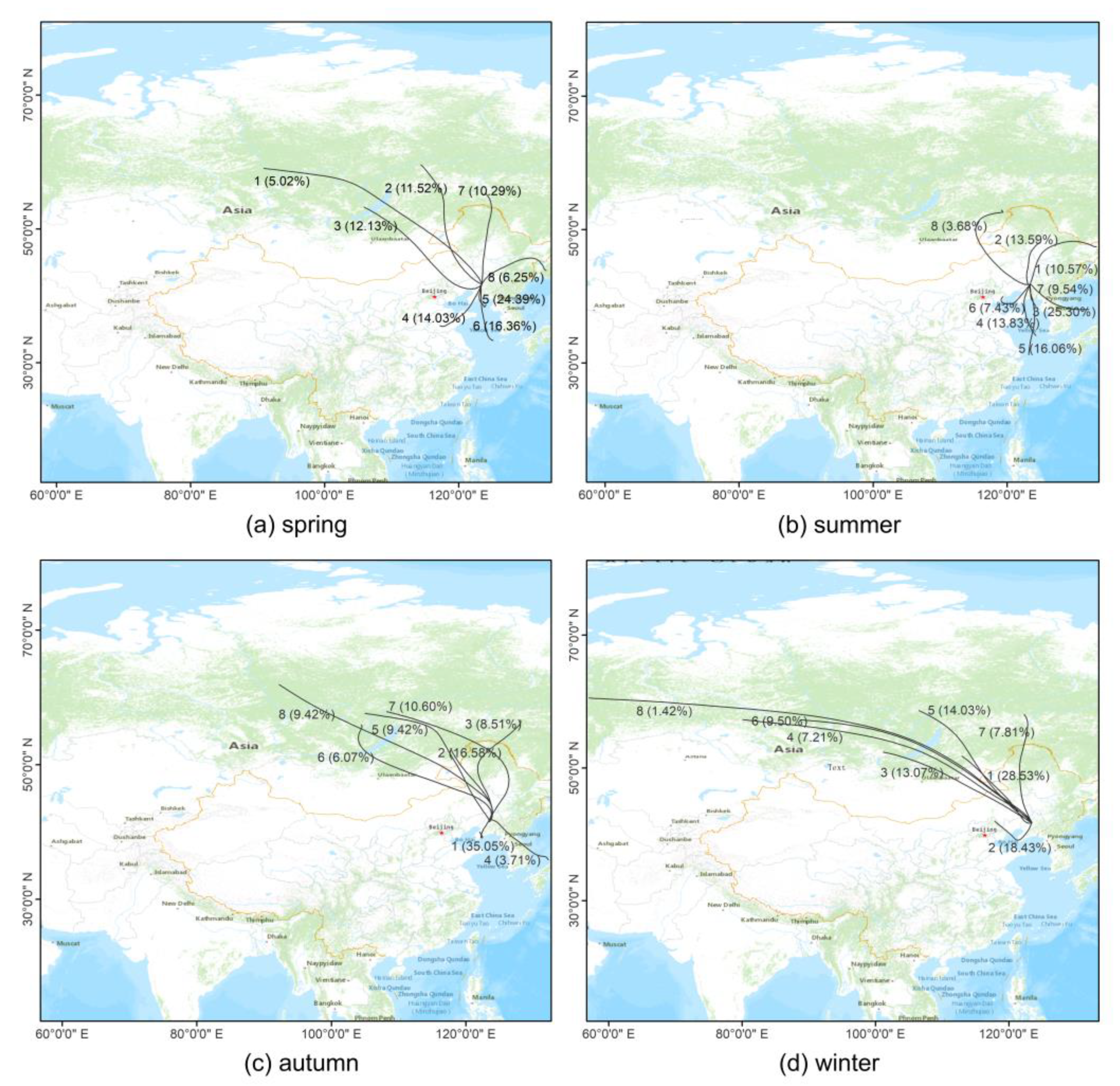
| Season | Cluster No. | Direction | Areas of Pathways | Percentage of Total Trajectory (%) | Trajectory Length (km) | SO2 (μg·m−3) | PM2.5 (μg·m−3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spring | 1 | Northwest | Russia, Mongolia, Inner Mongolia, Liaoning | 5.02 | 4938.45 | 4.74 | 19.28 |
| 2 | Northwest | Russia, Inner Mongolia, Mongolia, Liaoning | 11.52 | 3422.35 | 9.66 | 18.81 | |
| 3 | Northwest | Russia, Mongolia, Inner Mongolia, Liaoning | 12.13 | 2957.16 | 19.29 | 33.82 | |
| 4 | Southwest | Shandong, Yellow Sea, Liaoning | 14.03 | 1199.33 | 21.33 | 43.49 | |
| 5 | South by east | Yellow Sea, Liaoning | 24.39 | 573.56 | 16.41 | 33.25 | |
| 6 | South by east | Yellow Sea, Liaoning | 16.36 | 1231.93 | 13.10 | 28.34 | |
| 7 | North | Russia, Heilongjiang, Inner Mongolia, Jilin, Liaoning | 10.29 | 2322.18 | 12.06 | 27.75 | |
| 8 | Northeast | Russia, Heilongjiang, Jilin, Liaoning | 6.25 | 1456.86 | 9.83 | 16.99 | |
| Summer | 1 | Northeast | Heilongjiang, Russia, Jilin, Liaoning | 10.57 | 1788.60 | 8.61 | 9.28 |
| 2 | North by east | Heilongjiang, Jilin, Inner Mongolia, Liaoning | 13.59 | 1071.38 | 10.93 | 18.53 | |
| 3 | South | Yellow Sea, Liaoning | 25.30 | 487.35 | 8.43 | 23.10 | |
| 4 | South | Yellow Sea, Liaoning | 13.83 | 1133.66 | 9.55 | 28.90 | |
| 5 | South | Yellow Sea, Liaoning | 16.06 | 1474.54 | 6.88 | 23.81 | |
| 6 | Southwest | Hebei, Bohai, Liaoning | 7.43 | 831.56 | 10.63 | 27.39 | |
| 7 | Southeast | Yellow Sea, Korea, North Korea, Liaoning | 9.54 | 1178.89 | 6.39 | 15.00 | |
| 8 | Northwest | Russia, Mongolia, Inner Mongolia, Liaoning | 3.68 | 2478.67 | 7.84 | 13.07 | |
| Autumn | 1 | Southwest | Yellow Sea, Liaoning | 35.05 | 563.41 | 17.30 | 35.47 |
| 2 | Northwest | Russia, Inner Mongolia, Jilin, Liaoning | 16.58 | 1991.36 | 17.81 | 28.96 | |
| 3 | Northeast-northwest | Russia, Heilongjiang, Inner Mongolia, Jilin, Liaoning | 8.51 | 2805.97 | 9.87 | 13.76 | |
| 4 | Southeast | Yellow Sea, Korea, North Korea, Liaoning | 3.71 | 1337.83 | 8.37 | 12.66 | |
| 5 | Northwest | Russia, Inner Mongolia, Liaoning | 9.42 | 3715.28 | 15.79 | 18.54 | |
| 6 | Northwest | Russia, Mongolia, Inner Mongolia, Jilin, Liaoning | 6.70 | 3569.30 | 9.78 | 12.32 | |
| 7 | Northwest | Russia, Inner Mongolia, Heilongjiang, Jilin, Liaoning | 10.60 | 3888.95 | 13.01 | 15.79 | |
| 8 | Northwest | Russia, Mongolia, Inner Mongolia, Jilin, Liaoning | 9.42 | 5243.26 | 13.20 | 23.73 | |
| Winter | 1 | Northwest | Russia, Mongolia, Inner Mongolia, Liaoning | 28.53 | 2050.5 | 34.03 | 72.92 |
| 2 | West-southwest | Hebei, Inner Mongolia, Bohai, Liaoning | 18.43 | 1045.61 | 29.15 | 101.17 | |
| 3 | Northwest | Russia, Mongolia, Inner Mongolia, Liaoning | 13.07 | 3043.58 | 28.75 | 57.72 | |
| 4 | Northwest | Russia, Mongolia, Inner Mongolia, Liaoning | 7.21 | 5700.62 | 16.08 | 28.87 | |
| 5 | Northwest | Russia, Mongolia, Inner Mongolia, Liaoning | 14.03 | 3559.65 | 21.21 | 28.01 | |
| 6 | Northwest | Russia, Mongolia, Inner Mongolia, Liaoning | 9.50 | 4856.76 | 21.39 | 35.52 | |
| 7 | North | Russia, Heilongjiang, Inner Mongolia, Jilin, Liaoning | 7.81 | 2884.93 | 18.59 | 35.87 | |
| 8 | Northwest | Russia, Mongolia, Inner Mongolia, Liaoning | 1.42 | 8501.89 | 11.73 | 25.34 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, J.; Fang, C.; Qiu, J.; Wang, J. Analysis of Pollution Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Main Pollutants in the Atmosphere of Shenyang City. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 766. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11070766
Tian J, Fang C, Qiu J, Wang J. Analysis of Pollution Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Main Pollutants in the Atmosphere of Shenyang City. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(7):766. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11070766
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Jiaqi, Chunsheng Fang, Jiaxin Qiu, and Ju Wang. 2020. "Analysis of Pollution Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Main Pollutants in the Atmosphere of Shenyang City" Atmosphere 11, no. 7: 766. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11070766
APA StyleTian, J., Fang, C., Qiu, J., & Wang, J. (2020). Analysis of Pollution Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Main Pollutants in the Atmosphere of Shenyang City. Atmosphere, 11(7), 766. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11070766