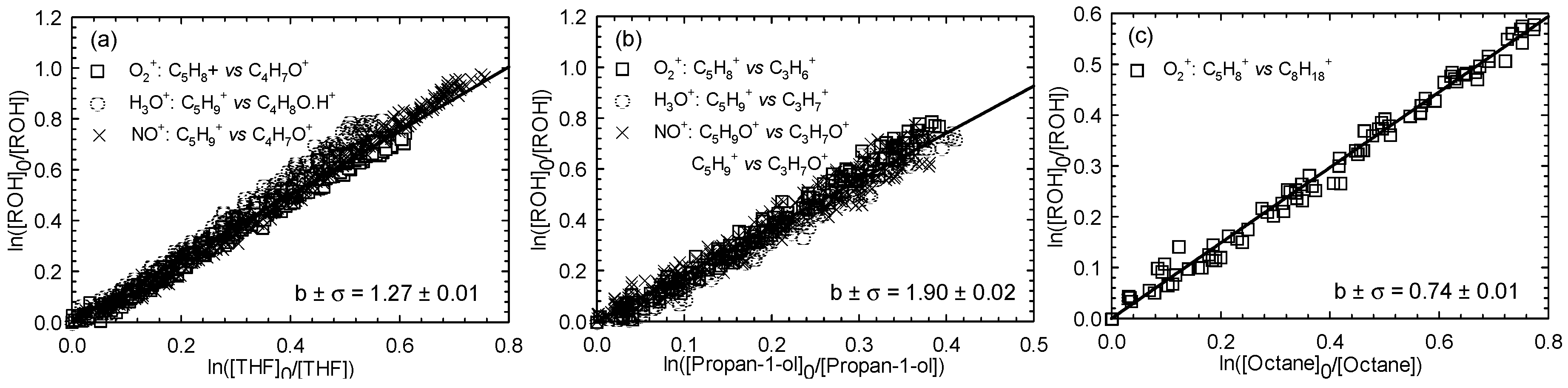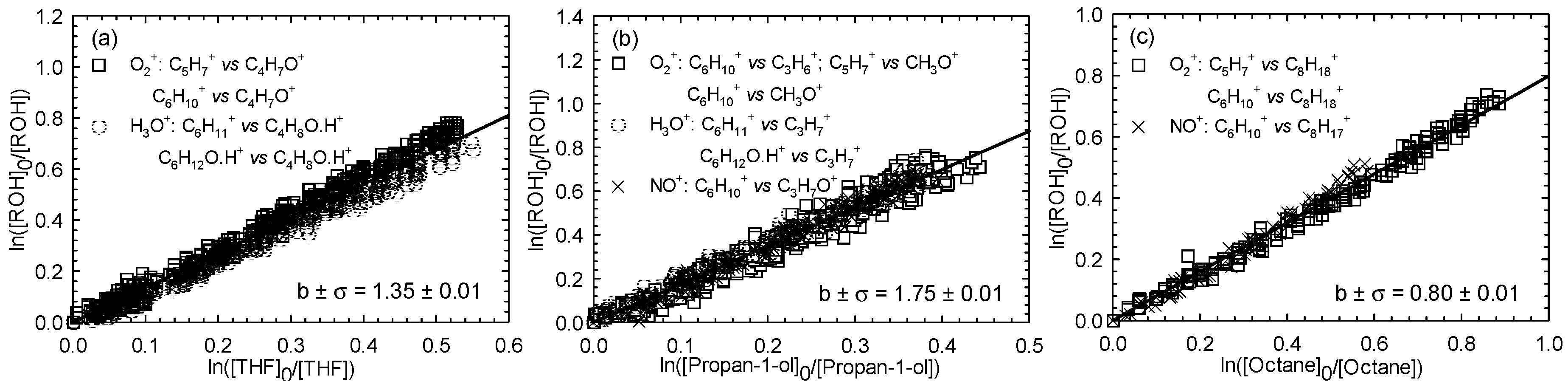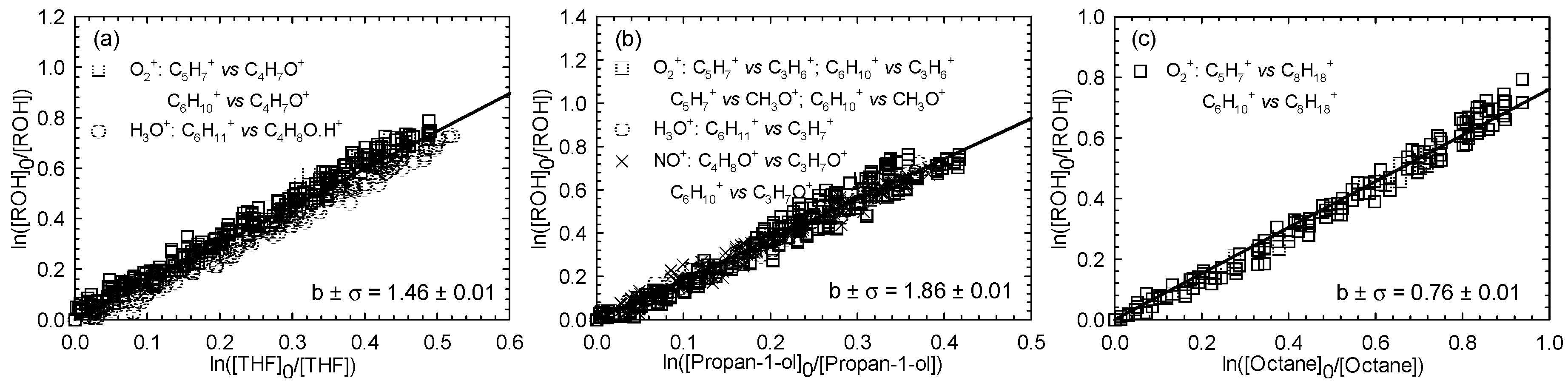Abstract
The reactions of five structurally similar unsaturated alcohols, i.e., (Z)-2-penten-1-ol, (E)-2-hexen-1-ol, (E)-3-hexen-1-ol, (Z)-3-hexen-1-ol, and 1-octen-3-ol, with Cl atoms in the gas phase, were investigated at 296 ± 2 K and 1 atm by the relative-rate kinetic technique using a 600-L Teflon reaction chamber. Selected ion flow tube mass spectrometry (SIFT-MS) was used simultaneously to monitor the decay of the alcohols of interest and selected reference compounds. Tetrahydrofuran (THF), propan-1-ol, and octane were used as reference compounds. Chlorine atoms were produced by the photolysis of molecular chlorine (Cl2) using broadband actinic lamps near 365 nm. The estimated rate constant values (in 10−10 cm3∙molecule−1∙s−1) followed the order 2.99 ± 0.53 ((Z)-2-penten-1-ol) < 3.05 ± 0.59 ((E)-3-hexen-1-ol) < 3.15 ± 0.58 ((Z)-3-hexen-1-ol) < 3.41 ± 0.65 ((E)-2-hexen-1-ol) < 4.03 ± 0.77 (1-octen-3-ol). The present work provides the first value of the rate constant for the reaction of 1-octen-3-ol with Cl atoms. The results are discussed and interpreted in relation to other studies where literature data are available. The structure–activity relationship and the atmospheric implications are discussed as well.
1. Introduction
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are trace gases generally present in the troposphere at sub-ppb concentrations. Yet, they play a major role in the chemistry of the troposphere through the formation of free radicals, ozone, and potentially secondary organic aerosols (SOA) [1,2]. It is recognized that the amount of VOCs emitted from biogenic sources (BVOC) largely exceeds that released from anthropogenic sources (AVOC) [3,4]. Green leaf volatiles (GLV), such as unsaturated alcohols [5], are BVOCs which are emitted from vegetation either spontaneously or under stress conditions [6]. Moreover, their emissions may increase due to climate change [7]. Despite this, the atmospheric reactivity of these compounds is less studied with respect to other BVOCs like monoterpenes.
Several biological materials like grasses, grains, fruits, dried fruits, vegetables, trees, and shrubs were shown to be a source of (Z)-3-hexen-1-ol and a series of (E)-3-alken-1-ols in the atmosphere [8,9,10]. Unsaturated alcohols with longer carbon chains such as 1-octen-3-ol were detected in grass emissions such as clover [11,12] and fungi [13]. Some unsaturated alcohols such as (Z)-3-hexen-1-ol and 1-octen-3-ol released by wheat, oat, and barley grains are thought to be insect attractors [14]. Biotic and abiotic stress factors lead to plant damage and stimulate emissions of higher concentrations of unsaturated alcohols in the troposphere [8,15,16]. In the Austrian Alps, (Z)-2-penten-1-ol was detected at a few-ppb level and its presence in such an area was attributed to the peroxidation of fatty acids occurring as a result of freeze damage on leaves [17].
Once in the atmosphere, unsaturated alcohols can be removed via reactions with atmospheric oxidants such as OH and NO3 radicals, O3, and Cl atoms [18]. The average concentration of Cl atoms in the troposphere is on the order of 103–104 atoms∙cm−3 but concentrations as high as 105 atoms∙cm−3 were observed at dawn in the marine boundary layer. At such concentrations, the Cl-driven chemistry might play an important role in VOC oxidation in the troposphere [19,20,21,22]. In fact, as the OH concentration is on the order of 106 radicals∙cm−3 [23], Cl could present a competitive oxidation process for various VOCs especially during morning hours, at the times of maximum rates of Cl-precursor photolysis [24,25]. Recent findings suggest that chlorine atom reactivity in the atmosphere could be important even far inward from the coasts [26,27], where ClNO2 pools are highly available as important Cl atom reservoirs [28,29]. Moreover, for some specific sites, like landfills, the impact of chlorine atoms on the atmospheric oxidation capacity might bring up to 10 times higher contributions to the local processes [25]. The formation of chlorine atoms in the atmosphere proceeds mainly through the oxidation of HCl by OH radicals and the photolysis of photolabile chlorine reservoir compounds (Cl2, ClNO2, and BrCl) [28,29,30]. Heterogeneous reactions involving sea salt and ozone are also a source of Cl atoms in the marine boundary layer [31,32]. Over the last two decades, although several experimental and theoretical works debated the potential impact of Cl oxidation with numerous VOCs in the tropospheric chemistry [33,34,35,36,37], the reactivity of some unsaturated alcohols is still not well established.
The aim of the present study was to determine the rate constants for the reactions of the following series of unsaturated alcohols with Cl atoms:
(Z)-2-penten-1-ol + Cl → Products,
(E)-2-hexen-1-ol + Cl → Products,
(E)-3-hexen-1-ol + Cl → Products,
(Z)-3-hexen-1-ol + Cl → Products,
1-octen-3-ol + Cl → Products.
The reactivity of these unsaturated alcohols with Cl atoms was scarcely investigated [18]. The kinetics of (Z)-2-penten-1-ol with Cl atoms was solely determined in 2010 in a 400-L Teflon bag, using off-line gas chromatography with a flame ionization detector (GC-FID) and following a relative-rate kinetic approach [38]. For unsaturated hexenols, the rate constants for (E)-2-hexen-1-ol, (E)-3-hexen-1-ol, and (Z)-3-hexen-1-ol were determined only once also using the relative-rate kinetic approach in a 1080-L quartz glass simulation chamber with in situ Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy [39]. No data are available regarding the rate constant of 1-octen-3-ol with chlorine atoms. The present work represents the first study on the relative-rate constant kinetic approach for the 1-octen-3-ol and Cl reaction and the second for (Z)-2-penten-1-ol and the series of hexenols cited above. Moreover, it has to be emphasized that, to our knowledge, the present kinetic measurements were performed for the first time using a selected ion flow tube mass spectrometer (SIFT-MS). The SIFT-MS instrument was used to measure the time decay of the above-listed compounds. A consistent determination of the reaction kinetics will help to better understand the atmospheric impacts of such compounds and develop structure–activity relationships for atmospheric chemistry models.
2. Experiments
Rate constants were measured at room temperature (296 ± 2 K) in zero air at atmospheric pressure (760 Torr) using the Thalamos simulation chamber which is a 600-L cubic Teflon photoreactor (Figure S1, Supplementary Materials). More details of the experimental set-up can be found elsewhere [40], and only a brief description is given hereafter. The Teflon bag of the chamber is fixed inside a temperature-controlled box which can be regulated between 231 and 453 K. The chamber is surrounded by a set of 20 ultraviolet (UV) lamps emitting around 365 nm (PL-L 24W/10/4P, Philips, The Netherlands). The lamps were used to produce Cl atoms through the photolysis of Cl2. The chamber is equipped with inlet and outlet ports used for reactant injection and reaction mixture sampling, respectively. Two fans are mounted inside the reactor in order to ensure the homogeneity of the gas mixture.
In the present work initial concentrations of reactants were from 0.7 to 1.5 ppm for both alcohols and reference compounds and around 1.7 ppm for molecular chlorine. Such high organic concentrations are not expected to induce secondary chemistry, since reactions of organic peroxy radicals generated as intermediates in atmospheric chemical mechanisms react very slowly with organic compounds [41]. The reaction mixture was continuously pumped through a sample loop using a dry Teflon diaphragm pump and reinjected into the reaction chamber with a flow rate of 4 L∙min−1.
A Voice200® SIFT-MS (Syft Technologies, New Zealand) instrument connected to the loop sampled the chamber at 10 mL∙min−1, allowing the decays of the reactants (alcohols and reference compounds) to be recorded. The SIFT-MS used in this study contains technical features similar to those from its first design [42] and all additional descriptions can be found in other recent papers [43,44,45,46]. Details on the SIFT-MS efficiency in measuring unsaturated alcohols (including those investigated in the present study) and about the ion reaction mechanisms were reported by Schoon et al. [47]. The detection limit of the commercially available SIFT-MS is at about pptv levels with a time resolution of 1 s.
The SIFT-MS measurement process is started by the production of reagent ions (R+: H3O+, NO+, and O2+) in a microwave discharge of a mixture of zero air and water vapor. The reagent ions are focused on a first quadrupole mass filter. Every few milliseconds, a single ionic species is selected based on its mass-to-charge ratio (m/z). Then, the selected ion passes to the flow tube reactor in a stream of carrier gas (He at 1 Torr). In addition, the Thalamos gas sample enters into this flow tube and undergoes a soft ionization reaction depending on the chemical properties of its components (A) (either alcohol or reference compound in this work) such as proton affinity and ionization energies. The reaction between the reagent ions (R+) and the components (A) generates ion products (P+) and neutral products (N). These processes involve (i) ionization by H3O+ occurring mainly via proton transfer and water elimination, (ii) NO+ reactions proceeding in different ways, such as charge transfer, hydride and/or hydroxide ion transfer, and/or three body association, and (iii) O2+ reactions generally occurring via charge transfer [43,47]. All these chemical species (R+, A, P+, and N) are injected into a second quadrupole mass filter in order to select ions based on their m/z. An electron multiplier detector placed at the exit of the second quadrupole is used to measure the count rates of the ions in the selected m/z range. In the present work, for SIFT-MS measurements, at least 10,000 counts were set as the limit before the instrument switched from one mass to another and the dwell time was on the order of one second. In addition, the mass spectrometer was internally calibrated on a daily basis with the help of a standard mixture of nine compounds provided by the supplier (Scotty, UN1956, Interscience, Belgium). The internal calibration procedure and the known reaction rate constants of the precursor ions with the analytes allow estimating the theoretical concentrations of any organic compound.
Table S1 (Supplementary Materials) summarizes all the product ions (P+) observed for alcohols and references. To determine the relative rate constants, pairs of representative product ions from the used alcohol and reference compounds were selected and used to plot the reactant decays according to the relative-rate kinetic approach. The ions that could be used for the kinetic analysis were selected based on the absence of any possible interference arising from other chemical processes happening simultaneously with the studied reaction. Therefore, a series of tests were carried out before any experiment, where only the compound of interest (either the alcohol or the reference) and Cl2 were present and mixed with purified air in the Thalamos chamber. Gas samples were analyzed by SIFT-MS, selecting all the product ions arising from alcohols and references. The alcohol and reference product ions displaying interferences with reaction products ions were excluded from the analysis.
Each experiment started by cleaning the reaction chamber at least for 2 h at 50 °C using a flow rate of about 20 L∙min−1 of zero air. Once the temperature of the reactor dropped to room temperature, the cleanliness of the reactor was evaluated by measuring the background levels of the selected ions for both alcohol and reference compound using the SIFT-MS system over 10 min. The background levels for all the selected ions never exceeded 5% of their initial experimental concentrations. Wall losses of the alcohols and the reference compounds in the dark were investigated in preliminary experiments, and negligible contributions were determined for these processes. The coefficient of variation (CV, expressed as the ratio of one standard deviation to the mean value of 40-min measurements) for the recorded signals showed <2.7% values. The reported values actually reflect small fluctuatios in the performances of the instrument such as small variations in the precursor ion concentrations, temperature of the instrument core, etc. The stability of the alcohols and reference compounds under UV-A irradiation was also tested, and all compounds were shown to be stable (CV < 2.8% over 30 min). The studied alcohol was injected in the chamber. The ion signal delivered by the SIFT-MS apparatus was recorded for 30 to 45 min until signal stabilization was achieved. The reference compound was then added to the reaction mixture and left to stabilize in the dark for 15 min. The precursor of chlorine atoms (Cl2) was finally introduced into the reactor, and the mixture was left again for 20 min in the dark. The UV lamps were turned on for 30 min in order to monitor the reaction initiated by Cl atoms.
At the moment of Cl2 injection in the dark, the alcohol concentration showed a very fast decay in its concentration in the first 2–3 min, which was immediately followed by stabilization. Alcohol decays were of the order of 5–10% for 1-octen-3-ol, 15–20% for (Z)-2-penten-1-ol, and about 30% for the C6 alcohols. In the experimental set-up, the inlet and outlet ports are relatively close to each other (20 cm) and, therefore, it is believed that Cl2 concentrations inside the injection port could be for a while up to 104 times higher than their final values in the chamber. These very high local concentrations of Cl2 may accelerate the reaction with the studied alcohol in the dark within the first few minutes after Cl2 injection. Details concerning such dark reactions were already reported in previous studies for similar structurally unsaturated compounds [38,39,48,49,50]. Nevertheless, these suspected side reactions are not expected to modify the kinetic measurements since (1) alcohol concentrations were stabilized a few minutes after the Cl2 injection, and (2) studied kinetics between unsaturated alcohols and Cl atoms are very fast compared to the kinetics of these side reactions.
The relative-rate kinetic method was used to determine the alcohol + Cl rate constants. The alcohols of interest and reference compounds simultaneously react with Cl atoms with rate constants kAlc+Cl and kRef+Cl, respectively.
Assuming that the alcohol and reference compounds only disappear through reaction with Cl atoms, their concentration changes between t = 0 and time t can be related through the following equation:
where [Alc]0, [Alc]t, [Ref]0, and [Ref]t are the alcohol and reference concentrations at time 0 and t, respectively. Thus, a plot of ln([Alc]0/[Alc]t) vs. ln([Ref]0/[Ref]t) should yield a straight line whose slope (b) is the rate constant ratio kAlc+Cl/kRef+Cl. The uncertainty of the slope (σ) corresponds to the uncertainty of the fitting.
For each reference, using the determined slope (b) and the known kRef+Cl, the kAlc+Cl values could be calculated. The uncertainty of the determined rate constant (ΔkAlc+Cl) was estimated with the following expression:
where σ and ΔkRef+Cl are the uncertainties of the slope (b) and kRef+Cl, respectively. The final rate constant kAverage and its uncertainty ΔkAverage (standard error of the mean) were calculated using Equations (10) and (11), respectively.
where ki and Δki represent kAlc+Cl and ΔkAlc+Cl for each reference i, respectively.
Rate constant values for the Cl atom-initiated oxidation of the reference compounds used in the present work (i.e., tetrahydrofuran (THF), propan-1-ol, and octane) are well known and are (in 10−10 cm3∙molecule−1∙s−1) 2.39 ± 0.57 for THF + Cl [51,52,53], 1.60 ± 0.07 for propan-1-ol + Cl [54], and 3.91 ± 0.63 for octane + Cl [55,56,57,58,59]. Reported uncertainties on the rate constants of THF + Cl and octane + Cl (kTHF+Cl and koctane+Cl) are 2σ, whereas no specification was mentioned for the uncertainty of kpropan-1-ol +Cl ([54]).
The following chemicals were used as received: (Z)-2-penten-1-ol (≥96%, Aldrich, Saint-Quentin Fallavier, France), (E)-2-hexen-1-ol (≥95%, Aldrich, Saint-Quentin Fallavier, France), (E)-3-hexen-1-ol (97%, Aldrich, Saint-Quentin Fallavier, France), (Z)-3-hexen-1-ol (>98%, Fluka, Seelze, Germany), 1-octen-3-ol (≥ 98%, Aldrich, Saint-Quentin Fallavier, France), tetrahydrofuran (99.9%, Acros, Noisy-le-Grand, France), propan-1-ol (98.9%, Aldrich, Saint-Quentin Fallavier, France), and octane (>99%, Aldrich, Saint-Quentin Fallavier, France). Molecular chlorine (Cl2) was from Air Products (10% ± 0.5% Cl2 in 90% ± 0.2% N2). Extra pure zero air was produced with a pure air generator (AZ-2020, Claind, Italy) with relative humidity (RH) <2 ppm, and CO and CO2 < 80 ppb. N2 was from Messer France (99.999%, RH < 3 ppm).
3. Results
3.1. Kinetic Measurements for (Z)-2-Penten-1-ol
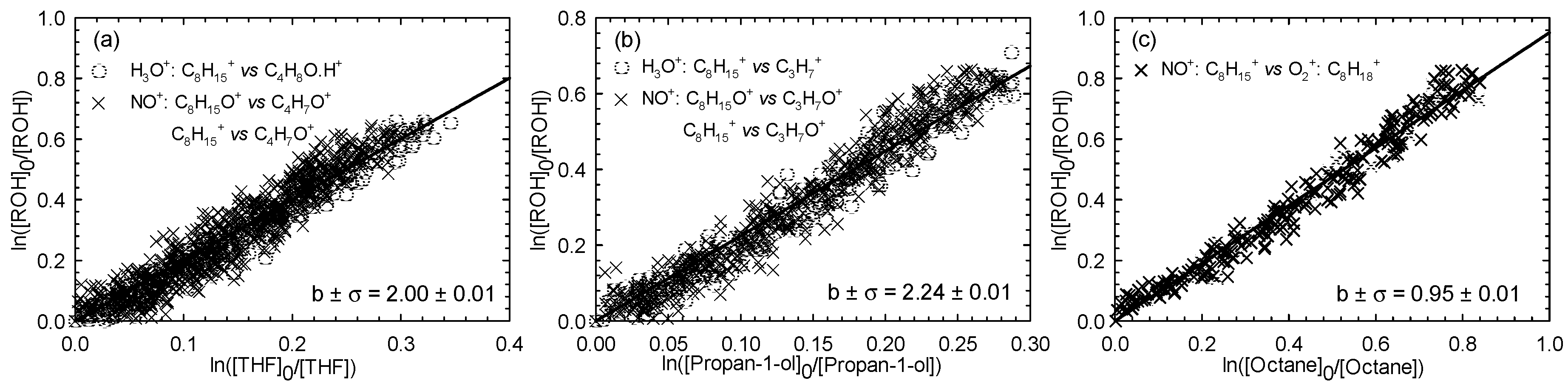
Three experiments were performed for the (Z)-2-penten-1-ol reaction with Cl atoms in zero air. Each experiment was done with one of the three reference compounds (THF, propan-1-ol, and octane), with this strategy leading finally to three distinct determinations. The kinetic plots for (Z)-2-penten-1-ol using THF, propan-1-ol, and octane as reference compounds are displayed in Figure 1a–c, respectively, for all the selected combinations of fragment ions.
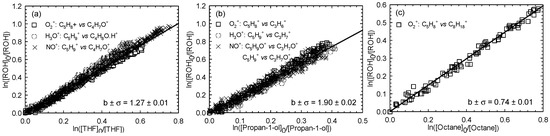
Figure 1.
Relative loss of (Z)-2-penten-1-ol vs. that of tetrahydrofuran (THF) (a), propan-1-ol (b), and octane (c) in the Cl atom-initiated reaction.
The relative rate plots show very good linearity with zero intercepts, indicating absence of secondary reactions. Use of the known reference rate constants kRef+Cl allows kAlc+Cl to be determined for each investigated situation. All the kAlc+Cl/kRef+Cl ratios and the corresponding rate constant values for (Z)-2-penten-1-ol reactions with Cl atoms are reported in Table 1. For the (Z)-2-penten-1-ol with Cl atom reaction, an average rate constant value of (2.99 ± 0.53) × 10−10 cm3∙molecule−1∙s−1 was determined.

Table 1.
Summary of all the rate constants for the reactions of alcohols with Cl atoms (all rate constants are expressed in 10−10 cm3∙molecule−1∙s−1).
3.2. Kinetic Measurements for (E)-2-Hexen-1-ol, (E)-3-Hexen-1-ol, and (Z)-3-Hexen-1-ol
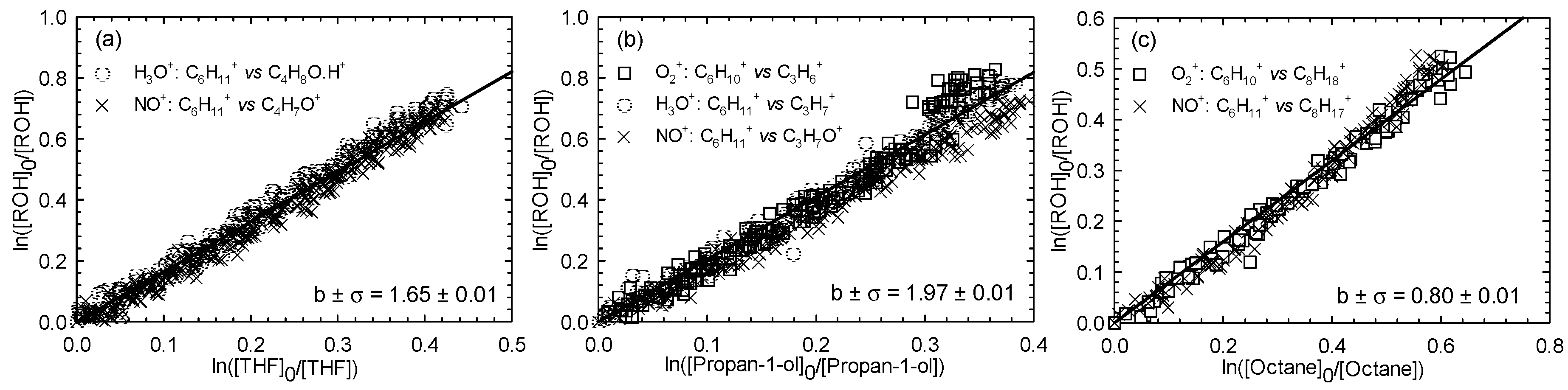
Kinetics of Cl atom with three hexenols, including (E)-2-hexen-1-ol, (E)-3-hexen-1-ol, and (Z)-3-hexen-1-ol, were investigated using the same reference compounds as in the case of (Z)-2-penten-1-ol. One experiment per reference was carried out. Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4 show the kinetic plots for the Cl reaction of (E)-2-hexen-1-ol (Figure 2), (E)-3-hexen-1-ol (Figure 3), and (Z)-3-hexen-1-ol (Figure 4), respectively.
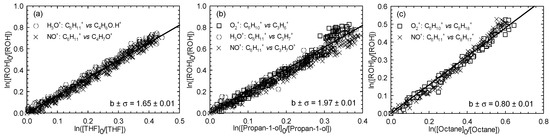
Figure 2.
Relative loss of (E)-2-hexen-1-ol vs. that of THF (a), propan-1-ol (b), and octane (c) in the Cl atom-initiated reaction.
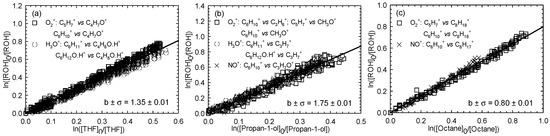
Figure 3.
Relative loss of (E)-3-hexen-1-ol vs. that of THF (a), propan-1-ol (b), and octane (c) in the Cl atom-initiated reaction.
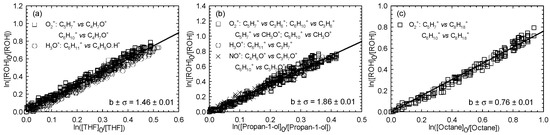
Figure 4.
Relative loss of (Z)-3-hexen-1-ol vs. that of THF (a), propan-1-ol (b), and octane (c) in the Cl atom-initiated reaction.
A summary of the average rate constants determined for the reactions between Cl atoms and the three investigated unsaturated hexenols is given in Table 1. For the investigated alcohols reaction with Cl atoms, determined average rate constant values were 3.41 ± 0.65, 3.05 ± 0.59, and 3.15 ± 0.58 (× 10−10 cm3∙molecule−1∙s−1) for (E)-2-hexen-1-ol, (E)-3-hexen-1-ol, and (Z)-3-hexen-1-ol, respectively.
3.3. Kinetic Measurements for 1-Octen-3-ol
Six experiments were carried out for 1-octen-3-ol (two experiments for each reference compound used in the present study). Figure 5 displays the kinetic plots corresponding to the performed experiments.
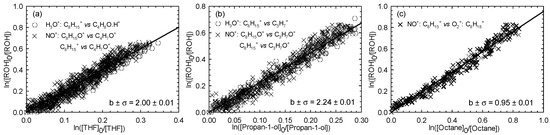
Figure 5.
Relative loss of 1-octen-3-ol vs. that of THF (a), propan-1-ol (b), and octane (c) in the Cl atom-initiated reaction.
All the kAlc+Cl/kRef+Cl ratios and the corresponding rate constants for each reference compound are reported in Table 1. The average rate constant for the Cl atom reaction with 1-octen-3-ol at 296 K was (4.03 ± 0.77) × 10−10 cm3∙molecule−1∙s−1.
4. Discussion
4.1. Summary of All the Determined Rate Constants and Comparison with Literature Data
The obtained rate constants (in 10−10 cm3∙molecule−1∙s−1) are summarized in Table 1 and compared with the available literature data. All the details for the calculations were explained above in the experimental description.
For the (Z)-2-penten-1-ol and Cl atom reaction, Rodríguez et al. [38] reported a rate constant value determined by the relative-rate kinetic method with CCl3COCl as the Cl atom precursor. In this study octane, propene, and cyclohexane were used as reference compounds. The average value between the three determinations of Rodríguez et al. [38] was 3.00 × 10−10 cm3∙molecule−1∙s−1. This value is in excellent agreement with the value determined in the present study (2.99 × 10−10 cm3∙molecule−1∙s−1).
A series of reactions between Cl atoms and several unsaturated alcohols was investigated by Gibilisco et al. [39] using Cl2 as a source of Cl atoms. Three hexenols among this series were also studied in the present work. The obtained rate constants are in good agreement with Gibilisco et al. [39], with the relative differences between our determinations and Gibilisco et al.’s determinations [39] being of the order of 10% or less for all hexenols. For 1-octen-3-ol, no other measurements are available in the literature.
Although, for 1-octen-3-ol, the rate constant values determined with THF as reference compound appear to be higher than those determined using propan-1-ol and octane, the values are reported as obtained since (i) these systematic higher values were not observed for C5 alkenols, and (ii) if necessary, the rate coefficient values for the alkenol reaction with Cl atom can be easily calculated by averaging the values obtained with the other two reference compounds. Moreover, one should also note that similar differences were observed for the hexenols. This may indicate a systematic error on k(THF + Cl) and, therefore, further studies on k(THF + Cl) are needed.
4.2. Structure–Activity Relationships
The reactions between unsaturated VOCs and Cl atoms proceed mainly via the addition to the double bond to produce a chlorine-containing alkyl radical. Addition occurs preferably on the least substituted carbon, thus forming the most stable radical [60]. This chlorinated alkyl radical adds O2 to form a chlorinated peroxy radical whose further reactions lead to oxygenated chlorine-containing compounds [48]. A second minor pathway is the abstraction of the allylic hydrogen from the C–H bond. For example, a very recent work showed that the reaction of (Z)-3-hexene proceeds via both Cl atom addition and hydrogen abstraction with branching ratios of around 70% and 30%, respectively [61].
4.2.1. Effect of the Chain Length
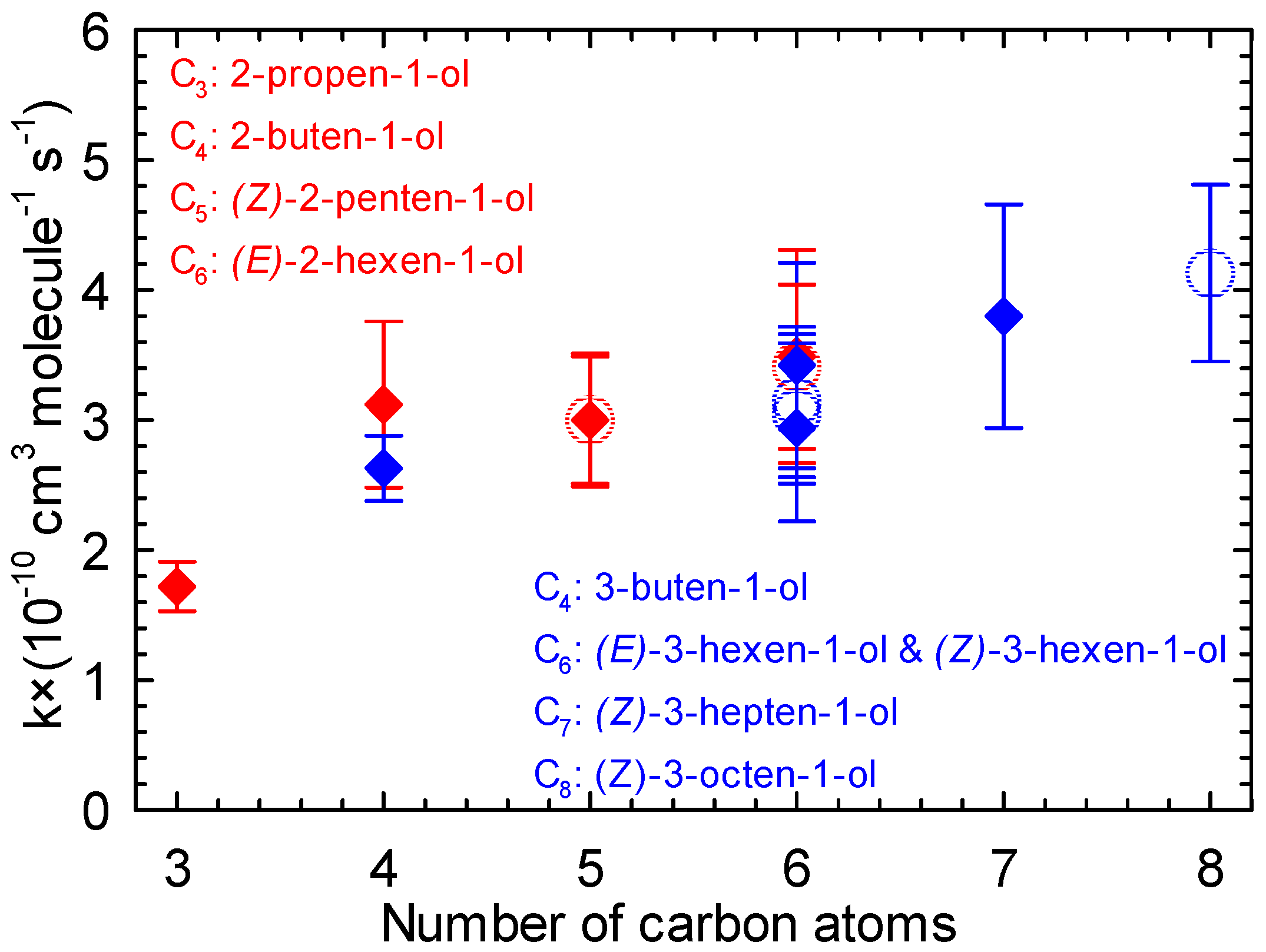
Table S2 (Supplementary Materials) presents a synthesis of all the known rate constants of unsaturated alcohol + Cl from C3 to C8. The comparison of these data could help to better understand the relationships between molecular structure and rate constants. For a group of alcohols with the alcohol function located on the first carbon atom (alken-1-ol) and a C=C bond placed the second or third carbon atom, data are presented in Figure 6 for comparison purposes.
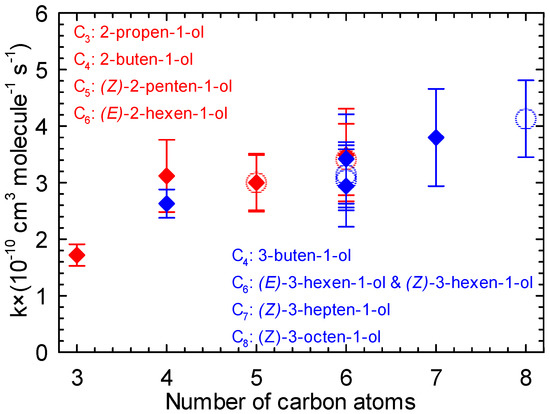
Figure 6.
Rate constants of the reaction of Cl atoms with 2-alken-1-ols (red) and 3-alken-1-ols (blue) vs. number of carbon atoms (the open circles represent the values of the current study).
Considering the series of 2-alken-1-ols (red) with 2-propen-1-ol [49], 2-buten-1-ol [50], (Z)-2-penten-1-ol ([38] and this work), and (E)-2-hexen-1-ol ([39] and this work), the increase in chain length seems to lead to higher rate constants. A similar trend is also observable for the reaction of Cl atoms with the series of 3-alken-1-ols (blue) with 3-buten-1-ol [62], (E)-3-hexen-1-ol, (Z)-3-hexen-1-ol ([39] and this work), (Z)-3-hepten-1-ol, and (Z)-3-octen-1-ol [39]. The activation effect of the chain length on the rate constants was also observed in previous works for the reaction of Cl atoms with linear alcohols [63] and alkenes [22,64,65,66].
4.2.2. Effect of the OH Group
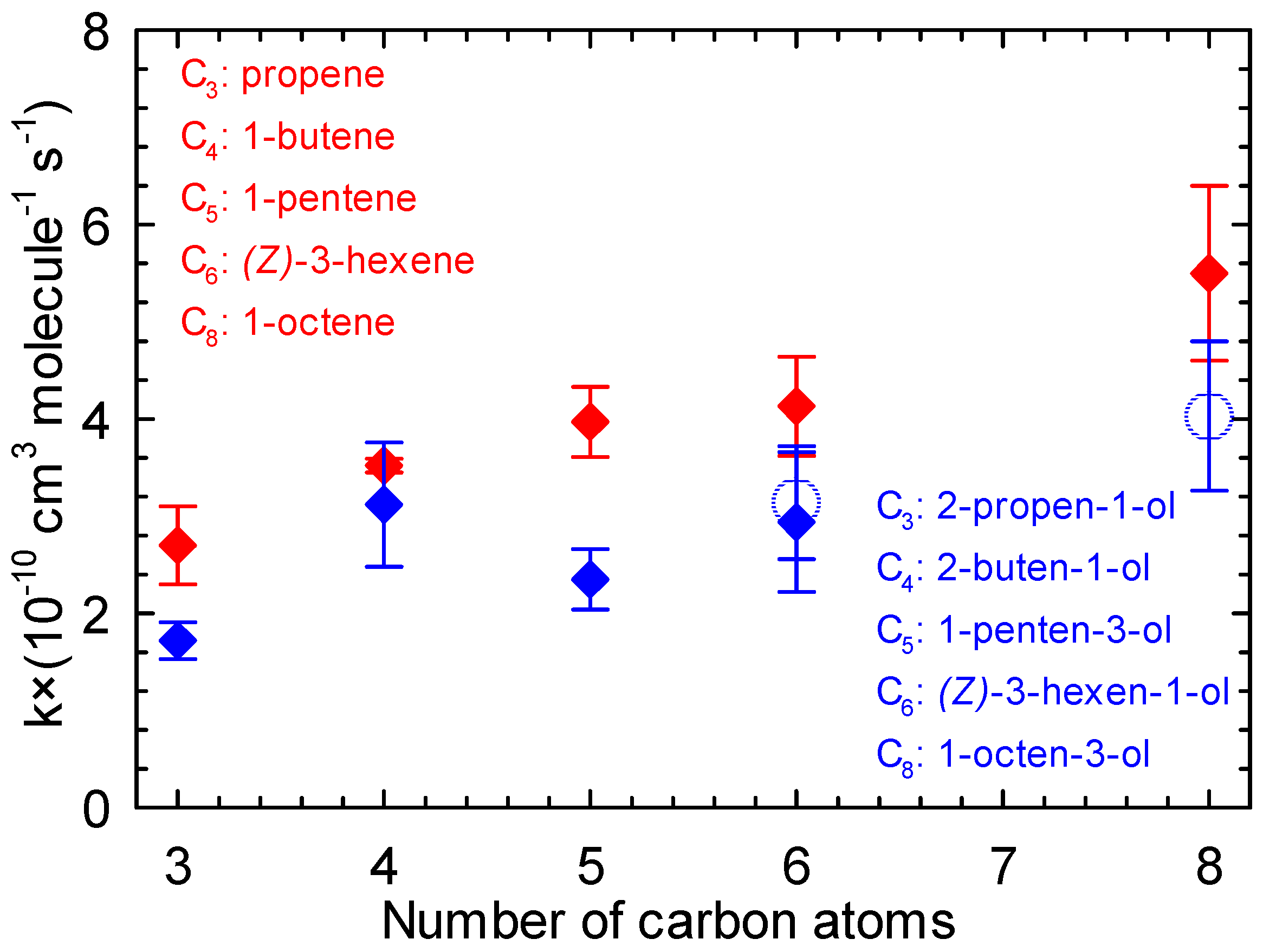
In order to better understand the role of the OH group in the unsaturated alcohol chains, the rate constants for the reaction of five unsaturated alcohols with Cl atoms were compared to the rate constants of their corresponding alkenes reaction with Cl atoms (Figure 7).
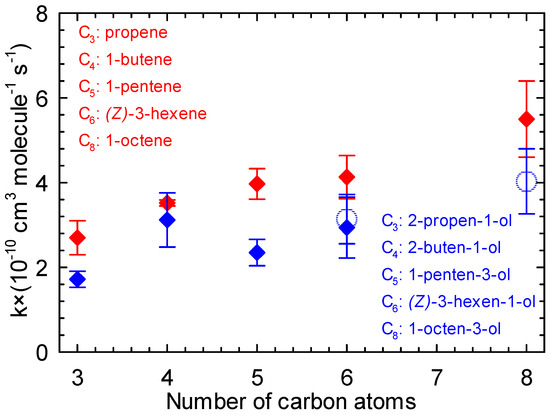
Figure 7.
Rate constant of the reaction of Cl atoms with a series of alkenes (red) and alken-1-ols (blue) vs. number of carbon atoms (the open circles represent the values of the current study).
Table S3 (Supplementary Materials) lists the rate constants for the reactions of Cl atoms with a series of alkenes, i.e., propene, 1-butene, 1-pentene, cis-3-hexene, and 1-octene. Comparing the data presented in Tables S2 and S3 (Supplementary Materials) clearly shows that the rate constants for the reactions of Cl atoms with propene [67], 1-butene [65], 1-pentene [22], and 1-octene [66] are higher than the rate constants for the reactions of Cl atoms with 2-propen-1-ol [49], 3-buten-1-ol [62], 1-penten-3-ol [38], and 1-octen-3-ol (this work), respectively. A similar trend is observed when comparing (Z)-3-hexene + Cl [61] and (Z)-3-hexen-1-ol + Cl ([39] and this work). However, the data from the present work prove also that the presence of the hydroxyl group in the molecular structure clearly has a deactivating effect on the kinetics of unsaturated alcohols with Cl atoms through a negative inductive influence.
Moreover, Gibilisco et al. [39] suggested a stronger deactivating effect of the OH group for α-alkenols compared to β-alkenols based on literature data. Yet, the present results do not confirm this assumption, probably because the measured rate constants are close to the collision rate. Finally, it can be underlined that an activating effect of the OH group was observed for OH radical addition to alkenols [68], suggesting different reaction mechanisms.
4.3. Atmospheric Implications
Atmospheric lifetimes τX of the studied alkenols were calculated using the expression τX = 1/kX[X], with kX being the rate constant for alkenol reaction with the oxidant X (Cl, OH, NO3, or O3) with an average concentration [X]. For the unsaturated alcohols investigated in the present work, the atmospheric lifetime with respect to Cl atom-induced reactions was estimated considering rate constant values expressed as averages of those determined in this work and in previous works. The following typical oxidant atmospheric concentrations were considered: (i) for Cl atoms, [Cl] = 1 × 104 molecule∙cm−3 [69] as representative of continental background atmosphere, and [Cl] = 1 × 105 molecule∙cm−3 as representative of the marine boundary layer and coastal areas [20,22,70], (ii) for O3, [O3] = 7 × 1011 molecule∙cm−3 [71], (iii) for NO3, a 12-h nighttime average NO3 concentration of 5 × 108 molecule−cm−3 [72], and (iv) for OH, a 12-h daylight average OH concentration of 2 × 106 molecule∙cm−3 [73]. Estimated atmospheric lifetimes are displayed in Table 2.

Table 2.
Calculated atmospheric lifetimes for the reactions of the studied unsaturated alcohols with Cl, O3, NO3, and OH. Cl-low and Cl-high refer to [Cl] of 1 × 104 and 1 × 105 atoms∙cm−3, respectively.
The estimated atmospheric lifetimes of the studied alcohols for their reactions with the atmospheric oxidants range from 1.24 to 4.7 h, except for the reactions with Cl atoms for which much higher lifetimes were found in a continental background atmosphere. Thus, C5–C8 unsaturated alcohols are rapidly removed in the gas phase by O3, NO3, or OH and disappear closely to their emission sources. Yet, it is worth stressing that, in the marine boundary layer and in coastal areas, the Cl-initiated oxidation of alkenols can become competitive compared to other oxidants with lifetimes on the order of a few hours. In addition to the marine boundary layer and coastal areas, specific continental areas were recently shown to display even higher Cl atom concentrations [27,81,82]. The present results will help in better understanding the atmospheric chemistry in these regions.
5. Conclusions
In the present work, five structurally similar unsaturated alcohols including (Z)-2-penten-1-ol, (E)-2-hexen-1-ol, (E)-3-hexen-1-ol, (Z)-3-hexen-1-ol, and 1-octen-3-ol were investigated with regard to their reactivity toward Cl atoms. Investigations were performed in a 600-L Teflon reaction chamber at 296 ± 2 K and 1 atm zero air. The relative-rate kinetic approach was used to determine rate constant values of the target unsaturated alcohols reaction with Cl atoms produced by the photolysis of molecular chlorine. Tetrahydrofuran, propan-1-ol, and octane were used as reference compounds. For the first time, the decays of alkenols and reference compounds were monitored using selected ion flow tube mass spectrometry (SIFT-MS).
The rate constant values (in 10−10 cm3∙molecule−1∙s−1) determined in the present work, 2.99 ± 0.53 for (Z)-2-penten-1-ol, 3.05 ± 0.59 for (E)-3-hexen-1-ol, 3.15 ± 0.58 for (Z)-3-hexen-1-ol, 3.41 ± 0.65 for (E)-2-hexen-1-ol, and 4.03 ± 0.77 for 1-octen-3-ol, within the experimental error limits, are in very good agreement with literature data. The present work reports, for the first time, the rate constant value for the reaction between 1-octen-3-ol and Cl atoms. Data obtained in the present work proves the activation effect of the chain length on the rate constants values specific for the kinetics between alkenols and Cl atoms. Moreover, evidence was obtained of the effect of the hydroxyl group presence in the molecular structure, with a deactivating effect on the kinetics of unsaturated alcohols with Cl atoms through negative inductive influence. The atmospheric lifetimes estimated in the present work with regard to atmospheric oxidant abundances suggest that alkenol reactivity toward Cl atoms becomes an important competitive process in alkenol sinks, especially in marine boundary layer and coastal areas.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4433/11/3/256/s1. Figure S1: General description of Thalamos facility, Table S1: Product ion distributions of the H3O+, NO+, and O2+ reactions with the studied unsaturated alcohols and reference compounds (BR—branching ratios of product ions; data come from the SIFT-MS library; BR could vary depending on the experimental conditions and working status of the instrument), Table S2: Rate constants for the reactions of Cl atoms with unsaturated alcohols at 298 K and atmospheric pressure (all rate constants are expressed in 10−10 cm3∙molecule−1∙s−1), Table S3: Rate constants for the reactions of Cl atoms with alkenes at 298 K and atmospheric pressure (all rate constants are expressed in 10−10 cm3∙molecule−1∙s−1).
Author Contributions
Data curation, A.G., C.A. (Cornelia Amarandei) and M.N.R.; Formal analysis, A.G., M.N.R., C.A. (Cecilia Arsene), I.G.B., R.I.O. and A.T.; Funding acquisition, C.A. (Cornelia Amarandei), R.I.O. and A.T.; Investigation, A.G. and C.A. (Cornelia Amarandei); Methodology, A.G., M.N.R., R.I.O. and A.T.; Project administration, G.E.D., A.C., R.I.O., P.C. and A.T.; Resources, R.I.O. and A.T.; Supervision, G.E.D., A.C., C.A. (Cecilia Arsene), I.G.B., R.I.O. and A.T.; Validation, M.N.R., C.A. (Cecilia Arsene), I.G.B., R.I.O. and A.T.; Visualization, A.G., C.A. (Cornelia Amarandei), M.N.R., C.A. (Cecilia Arsene), I.G.B., R.I.O. and A.T.; Writing—original draft, A.G., C.A. (Cecilia Arsene) and R.I.O.; Writing—review & editing, M.N.R., G.E.D., A.C., C.A. (Cecilia Arsene), R.I.O., P.C. and A.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
SAGE laboratory acknowledges funding by the French ANR agency under contract No. ANR-11-LabX-0005-01 CaPPA (Chemical and Physical Properties of the Atmosphere), the Région Hauts-de-France, the Ministère de l’Enseignement Supérieur et de la Recherche (CPER Climibio), and the European Fund for Regional Economic Development. A.G. is grateful for a PhD grant from Brittany Region and IMT Lille Douai. Authors from French laboratories are grateful to the INSU-LEFE-CHAT program for funding this research. All the authors are thankful to the PHC Brancusi program for funding the OzOA project (38385UD). C.A., I.G.B., R.I.O., and A.T. acknowledge the financial support from European Union’s Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation Framework Program, through the EUROCHAMP-2020 Infrastructure Activity Grant (grant agreement No 730997).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Atkinson, R.; Arey, J. Gas-phase tropospheric chemistry of biogenic volatile organic compounds: A review. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 197–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallquist, M.; Wenger, J.C.; Baltensperger, U.; Rudich, Y.; Simpson, D.; Claeys, M.; Dommen, J.; Donahue, N.M.; George, C.; Goldstein, A.H.; et al. The formation, properties and impact of secondary organic aerosol: Current and emerging issues. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 5155–5236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenther, A.; Hewitt, C.N.; Erickson, D.; Fall, R.; Geron, C.; Graedel, T.; Harley, P.; Klinger, L.; Lerdau, M.; McKay, W.A.; et al. A global model of natural volatile organic compound emissions. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1995, 100, 8873–8892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peñuelas, J.; Staudt, M. BVOCs and global change. Trends Plant Sci. 2010, 15, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- König, G.; Brunda, M.; Puxbaum, H.; Hewitt, C.N.; Duckham, S.C.; Rudolph, J. Relative contribution of oxygenated hydrocarbons to the total biogenic VOC emissions of selected mid-European agricultural and natural plant species. Atmos. Environ. 1995, 29, 861–874. [Google Scholar]
- Loreto, F.; Schnitzler, J.P. Abiotic stresses and induced BVOCs. Trends Plant Sci. 2010, 15, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleist, E.; Mentel, T.F.; Andres, S.; Bohne, A.; Folkers, A.; Kindler-Scharr, A.; Rudich, Y.; Springer, M.; Tillmann, R.; Wildt, J. Irreversible impacts of heat on the emissions of monoterpenes, sesquiterpenes, phenolic BVOC and green leaf volatiles from several tree species. Biogeosciences 2012, 9, 5111–5123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arey, J.; Winer, A.M.; Atkinson, R.; Aschmann, S.M.; Long, W.D.; Morrison, C.L. The emission of (Z)-3-hexen-1-ol, (Z)-3-hexenylacetate and other oxygenated hydrocarbons from agricultural plant species. Atmos. Environ. Part A Gen. Top. 1991, 25, 1063–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, E. The chemistry of fresh tomato flavor. Turk. J. Agric. For. 2001, 25, 149–155. [Google Scholar]
- Lorber, K.; Buettner, A. Structure–odor relationships of (E)-3-alkenoic acids, (E)-3-alken-1-ols, and (E)-3-alkenals. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 6681–6688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buttery, R.G.; Kamm, J.A. Volatile components of alfalfa: Possible insect host plant attractants. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1980, 28, 978–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kline, D.L.; Allan, S.A.; Bernier, U.R.; Welch, C.H. Evaluation of the enantiomers of 1-octen-3-ol and 1-octyn-3-ol as attractants for mosquitoes associated with a freshwater swamp in Florida, USA. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2007, 21, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaminski, E.; Stawicki, S.; Wasowicz, E. Volatile flavor compounds produced by molds of Aspergillus, Penicillium, and Fungi imperfecti. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1974, 27, 1001–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buttery, R.G.; Ling, L.C.; Wellso, S.G. Oat leaf volatiles: Possible insect attractants. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1982, 30, 791–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croft, K.P.; Juttner, F.; Slusarenko, A.J. Volatile products of the lipoxygenase pathway evolved from Phaseolus vulgaris (L.) leaves inoculated with Pseudomonas syringae pv phaseolicola. Plant Physiol. 1993, 101, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heiden, A.C.; Kobel, K.; Langebartels, C.; Schuh-Thomas, G.; Wildt, J. Emissions of oxygenated volatile organic compounds from plants Part I: Emissions from lipoxygenase activity. J. Atmos. Chem. 2003, 45, 143–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karl, T.; Fall, R.; Crutzen, P.J.; Jordan, A.; Lindinger, W. High concentrations of reactive biogenic VOCs at a high altitude site in late autumn. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2001, 28, 507–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvert, J.; Mellouki, A.; Orlando, J. Mechanisms of Atmospheric Oxidation of the Oxygenates; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Pszenny, A.A.P.; Keene, W.C.; Jacob, D.J.; Fan, S.; Maben, J.R.; Zetwo, M.P.; Springer-Young, M.; Galloway, J.N. Evidence of inorganic chlorine gases other than hydrogen chloride in marine surface air. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1993, 20, 699–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spicer, C.W.; Chapman, E.G.; Finlayson-Pitts, B.J.; Plastridge, R.A.; Hubbe, J.M.; Fast, J.D.; Berkowitz, C.M. Unexpectedly high concentrations of molecular chlorine in coastal air. Nature 1998, 394, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tackett, P.J.; Cavender, A.E.; Keil, A.D.; Shepson, P.B.; Bottenheim, J.W.; Morin, S.; Deary, J.; Steffen, A.; Doerge, C. A study of the vertical scale of halogen chemistry in the Arctic troposphere during Polar Sunrise at Barrow, Alaska. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezell, M.J.; Wang, W.; Ezell, A.A.; Soskin, G.; Finlayson-Pitts, B.J. Kinetics of reactions of chlorine atoms with a series of alkenes at 1 atm and 298 K: Structure and reactivity. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2002, 4, 5813–5820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, M.G.; Jöckel, P.; Kuhlmann, R.V. What does the global mean OH concentration tell us? Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2001, 1, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, P.L.; Riemer, D.D.; Chang, S.; Yarwood, G.; McDonald-Butler, E.C.; Apel, E.C.; Orlando, J.J.; Silva, P.J.; Jimenez, J.L.; Canagaratna, M.R.; et al. Direct evidence for chlorine-enhanced urban ozone formation in Houston, Texas. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 1393–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannan, T.J.; Anwar, M.; Khan, H.; Le Breton, M.; Priestley, M.; Worrall, S.D.; Bacak, A.; Marsden, N.A.; Lowe, D.; Pitt, J.; et al. A large source of atomic chlorine from ClNO2 photolysis at a U.K. landfill site. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 8508–8516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, C.J.; Washenfelder, R.A.; Edwards, P.M.; Parrish, D.D.; Gilman, J.B.; Kuster, W.C.; Mielke, L.H.; Osthoff, H.D.; Tsai, C.; Pikelnaya, O.; et al. Chlorine as a primary radical: Evaluation of methods to understand its role in initiation of oxidative cycles. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 3427–3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.H.; Lopez-Hilfiker, F.D.; Schroder, J.C.; Campuzano-Jost, P.; Jimenez, J.L.; McDuffie, E.E.; Fibiger, D.L.; Veres, P.R.; Brown, S.S.; Campos, T.L.; et al. Airborne observations of reactive inorganic chlorine and bromine species in the exhaust of coal-fired power plants. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 11–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osthoff, H.D.; Roberts, J.M.; Ravishankara, A.R.; Williams, E.J.; Lerner, B.M.; Sommariva, R.; Bates, T.S.; Coffman, D.; Quinn, P.K.; Dibb, J.E.; et al. High levels of nitryl chloride in the polluted subtropical marine boundary layer. Nat. Geosci. 2008, 1, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, J.A.; Kercher, J.P.; Riedel, T.P.; Wagner, N.L.; Cozic, J.; Holloway, J.S.; Dubé, W.P.; Wolfe, G.M.; Quinn, P.K.; Middlebrook, A.M.; et al. A large atomic chlorine source inferred from mid-continental reactive nitrogen chemistry. Nature 2010, 464, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisp, T.A.; Lerner, B.M.; Williams, E.J.; Quinn, P.K.; Bates, T.S.; Bertram, T.H. Observations of gas phase hydrochloric acid in the polluted marine boundary layer. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 6897–6915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oum, K.W.; Lakin, M.J.; DeHaan, D.O.; Brauers, T.; Finlayson-Pitts, B.J. Formation of molecular chlorine from the photolysis of ozone and aqueous sea-salt particles. Science 1998, 279, 74–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, R.; Crutzen, P.J.; Sander, R. A mechanism for halogen release from sea-salt aerosol in the remote marine boundary layer. Nature 1996, 383, 327–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knipping, E.M.; Dabdub, D. Impact of chlorine emissions from sea-salt aerosol on coastal urban ozone. Environ. Technol. 2003, 37, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahu, L.K. Reactive halogens and their measurements in the troposphere. Indian J. Geo Mar. Sci. 2014, 43, 1615–1622. [Google Scholar]
- Barrera, J.A.; Garavagno, M.D.L.A.; Dalmasso, P.R.; Taccone, R.A. Atmospheric chemistry of 3-methoxy-1-propanol and 3-methoxy-1-butanol: Kinetics with OH radicals and Cl atoms, identification of the end-products in the presence of NO, mechanisms and atmospheric implications. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 202, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajuelo, M.; Bravo, I.; Rodríguez, A.; Aranda, A.; Díaz-de-Mera, Y.; Rodríguez, D. Atmospheric sink of styrene, α-methylstyrene, trans-β-methylstyrene and indene: Rate constants and mechanisms of Cl atom-initiated degradation. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 200, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhulipala, S.V.; Bhandari, S.; Ruiz, L.H. Formation of oxidized organic compounds from Cl-initiated oxidation of toluene. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 199, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, A.; Rodríguez, D.; Garzón, A.; Soto, A.; Aranda, A.; Notario, A. Kinetics and mechanism of the atmospheric reactions of atomic chlorine with 1-penten-3-ol and (Z)-2-penten-1-ol: An experimental and theoretical study. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 12245–12258. [Google Scholar]
- Gibilisco, R.G.; Bejan, I.; Barnes, I.; Wiesen, P.; Teruel, M.A. Rate coefficients at 298 K and 1 atm for the tropospheric degradation of a series of C6, C7 and C8 biogenic unsaturated alcohols initiated by Cl atoms. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 94, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osseiran, N.; Romanias, M.N.; Gaudion, V.; Angelaki, M.; Papadimitriou, V.C.; Tomas, A.; Coddeville, P.; Thevenet, F. Development and validation of a THermALly regulated AtMOSpheric simulation chamber (THALAMOS). A versatile tool to simulate atmospheric processes. J. Environ. Sci. 2020. (accepted). [Google Scholar]
- Selby, K.; Waddington, D.J. Reactions of oxygenated radicals in the gas phase. Part 5. Reactions of methylperoxyl radicals and alkenes. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. II 1980, 65–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, N.G.; Smith, D. The selected ion flow tube (SIFT); a technique for studying ion-neutral reactions. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. Ion. Phys. 1976, 21, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Španěl, P.; Smith, D. Selected ion flow tube studies of the reactions of H3O+, NO+, and O2+ with several aromatic and aliphatic hydrocarbons. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 1998, 181, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diskin, A.M.; Wang, T.; Smith, D.; Španěl, P. A selected ion flow tube (SIFT), study of the reactions of H3O+, NO+ and O2+ ions with a series of alkenes; in support of SIFT-MS. Int. J. Mass. Spectrom. 2002, 218, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Španěl, P.; Smith, D. Selected ion flow tube, SIFT, studies of the reactions of H3O+, NO+ and O2+ with eleven C10H16 monoterpenes. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2003, 228, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.; Španěl, P.; Dryahina, K. H3O+, NO+ and O2+ reactions with saturated and unsaturated monoketones and diones; focus on hydration of product ions. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2019, 435, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoon, N.; Amelynck, C.; Debie, E.; Bultinck, P.; Arijs, E. A selected ion flow tube study of the reactions of H3O+, NO+ and O2+ with a series of C5, C6 and C8 unsaturated biogenic alcohols. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2007, 263, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlayson-Pitts, B.J.; Pitts, J.N., Jr. Chemistry of the Upper and Lower Atmosphere: Theory, Experiments, and Applications, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez, A.; Rodríguez, D.; Soto, A.; Notario, A.; Aranda, A.; Díaz-de-Mera, Y.; Bravo, I. Relative rate measurements of reactions of unsaturated alcohols with atomic chlorine as a function of temperature. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 4693–4702. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez, D.; Rodriguez, A.; Soto, A.; Aranda, A.; Diaz-de-Mera, Y.; Notario, A. Kinetics of the reactions of Cl atoms with 2-buten-1-ol, 2-methyl-2-propen-1-ol, and 3-methyl-2-buten-1-ol as a function of temperature. J. Atmos. Chem. 2008, 59, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, B.R.; Roscoe, J.M. Kinetics of the reactions of Cl atoms with several ethers. J. Phys. Chem. A 2014, 114, 8369–8375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwe, H.D.; Walawalkar, M.; Sharma, A.; Pushpa, K.K.; Dhanya, S.; Naik, P.D. Rate Coefficients for the Gas-Phase Reactions of Chlorine Atoms with Cyclic Ethers at 298 K. Int. J. Chem. Kinet. 2013, 45, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, C.; Nielsen, O.J.; Østerstrøm, F.F.; Ausmeel, S.; Nilsson, E.J.; Sulbaek Andersen, M.P. Atmospheric Chemistry of Tetrahydrofuran, 2-Methyltetrahydrofuran, and 2, 5-Dimethyltetrahydrofuran: Kinetics of Reactions with Chlorine Atoms, OD Radicals, and Ozone. J. Phys. Chem. A 2016, 120, 7320–7326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, R.; Baulch, D.L.; Cox, R.A.; Crowley, J.N.; Hampson, R.F.; Hynes, R.G.; Jenkin, M.E.; Rossi, M.J.; Troe, J. IUPAC Subcommittee, Evaluated kinetic and photochemical data for atmospheric chemistry: Volume II – gas phase reactions of organic species. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 3625–4055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschmann, S.M.; Atkinson, R. Rate constants for the gas-phase reactions of alkanes with Cl atoms at 296±2 K. Int. J. Chem. Kinet. 1995, 27, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooshiyar, P.A.; Niki, H. Rate constants for the gas-phase reactions of Cl-atoms with C2 - C8 alkanes at T= 296±2 K. Int. J. Chem. Kinet. 1995, 27, 1197–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannone, R.; Anderson, R.S.; Vogel, A.; Eby, P.S.; Whiticar, M.J.; Rudolph, J. The hydrogen kinetic isotope effects of the reactions of n-alkanes with chlorine atoms in the gas phase. J. Atmos. Chem. 2005, 50, 121–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Pirasteh, A. Kinetic study of the reactions of atomic chlorine with several volatile organic compounds at 240–340 K. Int. J. Chem. Kinet. 2006, 38, 386–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.S.; Huang, L.; Iannone, R.; Rudolph, J. Measurements of the 12C/13C kinetic isotope effects in the gas-phase reactions of light alkanes with chlorine atoms. J. Phys. Chem. A 2007, 111, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wayne, R.P.; Barnes, I.; Biggs, P.; Burrows, J.P.; Canosa-Mas, C.E.; Hjorth, J.; Le Bras, G.; Moortgat, G.K.; Perner, D.; Poulet, G.; et al. The nitrate radical: Physics, chemistry, and the atmosphere. Atmos. Environ. Part A Gen. Top. 1991, 25, 1–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, T.S.; Barrera, J.A.; Toro, R.J.; Bauerfeldt, G.F.; Arbilla, G.; Lane, S.I. Rate Coefficient for the Reaction of Cl Atoms with cis-3-Hexene at 296±2 K. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2017, 28, 2267–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Mu, Y.J.; Daële, V.; Mellouki, A. Kinetic studies of Cl reactions with 3-buten-1-ol and 2-buten-1-ol over the temperature range 298–363 K. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2011, 502, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, L.; Rattigan, O.; Neavyn, R.; Sidebottom, H.; Treacy, J.; Nielsen, O.J. Absolute and relative rate constants for the reactions of hydroxyl radicals and chlorine atoms with a series of aliphatic alcohols and ethers at 298 K. Int. J. Chem. Kinet. 1990, 22, 1111–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, R.; Aschmann, S.M. Kinetics of the gas phase reaction of Cl atoms with a series of organics at 296±2 K and atmospheric pressure. Int. J. Chem. Kinet. 1985, 17, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coquet, S.; Ariya, P.A. Kinetics of the gas-phase reactions of Cl atom with selected C2–C5 unsaturated hydrocarbons at 283 < T < 323 K. Int. J. Chem. Kinet. 2000, 32, 478–484. [Google Scholar]
- Walavalkar, M.; Sharma, A.; Alwe, H.D.; Pushpa, K.K.; Dhanya, S.; Naik, P.D.; Bajaj, P.N. Cl atom initiated oxidation of 1-alkenes under atmospheric conditions. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 67, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, E.W.; Wallington, T.J. Pressure dependence of the reaction Cl + C3H6. J. Phys. Chem. 1996, 100, 9788–9793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papagni, C.; Arey, J.; Atkinson, R. Rate constants for the gas-phase reactions of OH radicals with a series of unsaturated alcohols. Int. J. Chem. Kinet. 2001, 33, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wingenter, O.W.; Kubo, M.K.; Blake, N.J.; Smith, T., Jr.; Blake, D.R.; Rowland, F.S. Hydrocarbon and halocarbon measurements as photochemical and dynamical indicators of atmospheric hydroxyl, atomic chlorine, and vertical mixing obtained during Lagrangian flights. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1996, 101, 4331–4340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedel, T.P.; Wagner, N.L.; Dubé, W.P.; Middlebrook, A.M.; Young, C.J.; Öztürk, F.; Bahreini, R.; VandenBoer, T.C.; Wolfe, D.E.; Williams, E.J.; et al. Chlorine activation within urban or power plant plumes: Vertically resolved ClNO2 and Cl2 measurements from a tall tower in a polluted continental setting. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 8702–8715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, J.A. Tropospheric ozone: Seasonal behavior, trends, and anthropogenic influence. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1985, 90, 10463–10482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.; Atkinson, R. Atmospheric lifetimes and fates of a series of sesquiterpenes. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1995, 100, 7275–7281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hein, R.; Crutzen, P.J.; Heimann, M. An inverse modeling approach to investigate the global atmospheric methane cycle. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 1997, 11, 43–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfrang, C.; Martin, R.S.; Canosa-Mas, C.E.; Wayne, R.P. Gas-phase reactions of NO3 and N2O5 with (Z)-hex-4-en-1-ol, (Z)-hex-3-en-1-ol (‘leaf alcohol’), (E)-hex-3-en-1-ol, (Z)-hex-2-en-1-ol and (E)-hex-2-en-1-ol. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2006, 8, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibilisco, R.G.; Santiago, A.N.; Teruel, M.A. OH-initiated degradation of a series of hexenols in the troposphere. Rate coefficients at 298 K and 1 atm. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 77, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibilisco, R.G.; Blanco, M.B.; Bejan, I.; Barnes, I.; Wiesen, P.; Teruel, M.A. Atmospheric sink of (E)-3-hexen-1-ol, (Z)-3-hepten-1-ol, and (Z)-3-octen-1-ol: Rate coefficients and mechanisms of the OH-radical initiated degradation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 7717–7725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peirone, S.A.; Barrera, J.A.; Taccone, R.A.; Cometto, P.M.; Lane, S.I. Relative rate coefficient measurements of OH radical reactions with (Z)-2-hexen-1-ol and (E)-3-hexen-1-ol under simulated atmospheric conditions. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 85, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, R.; Arey, J.; Aschmann, S.M.; Corchnoy, S.B.; Shu, Y. Rate constants for the gas-phase reactions of cis-3-hexen-1-ol, cis-3-hexenylacetate, trans-2-hexenal, and linalool with OH and NO3 radicals and O3 at 296±2 K, and OH radical formation yields from the O3 reactions. Int. J. Chem. Kinet. 1995, 27, 941–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, E.; Lanza, B.; Antinolo, M.; Albaladejo, J. Photooxidation of leaf-wound oxygenated compounds, 1-penten-3-ol,(Z)-3-hexen-1-ol, and 1-penten-3-one, initiated by OH radicals and sunlight. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 1831–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, M.E.; Burkholder, J.B. Rate coefficients for the gas-phase reaction of OH with (Z)-3-hexen-1-ol, 1-penten-3-ol, (E)-2-penten-1-ol, and (E)-2-hexen-1-ol between 243 and 404 K. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 3347. [Google Scholar]
- Faxon, C.B.; Allen, D.T. Chlorine chemistry in urban atmospheres: A review. Environ. Chem. 2013, 10, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breton, M.L.; Hallquist, Å.M.; Pathak, R.K.; Simpson, D.; Wang, Y.; Johansson, J.; Zheng, J.; Yang, Y.; Shang, D.; Wang, H.; et al. Chlorine oxidation of VOCs at a semi-rural site in Beijing: Significant chlorine liberation from ClNO2 and subsequent gas-and particle-phase Cl–VOC production. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 13013–13030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).