Generative Adversarial Networks Capabilities for Super-Resolution Reconstruction of Weather Radar Echo Images
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Radar Echo Super-Resolution Reconstruction
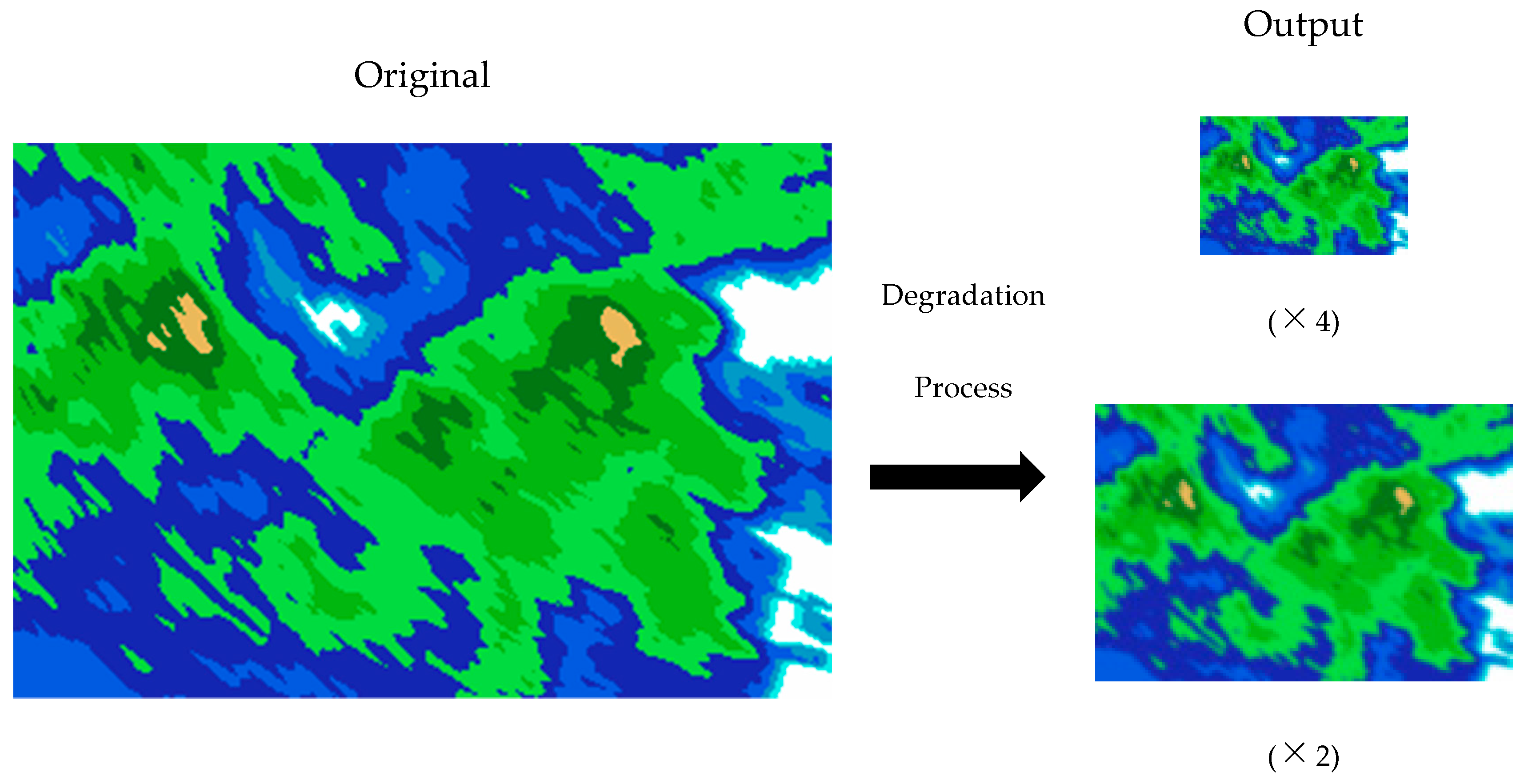
2.1. Problem Definitions
2.2. GAN for Radar Echo Super-Resoultion Reconstruction
2.3. Radar Echo Image Quality Assessment
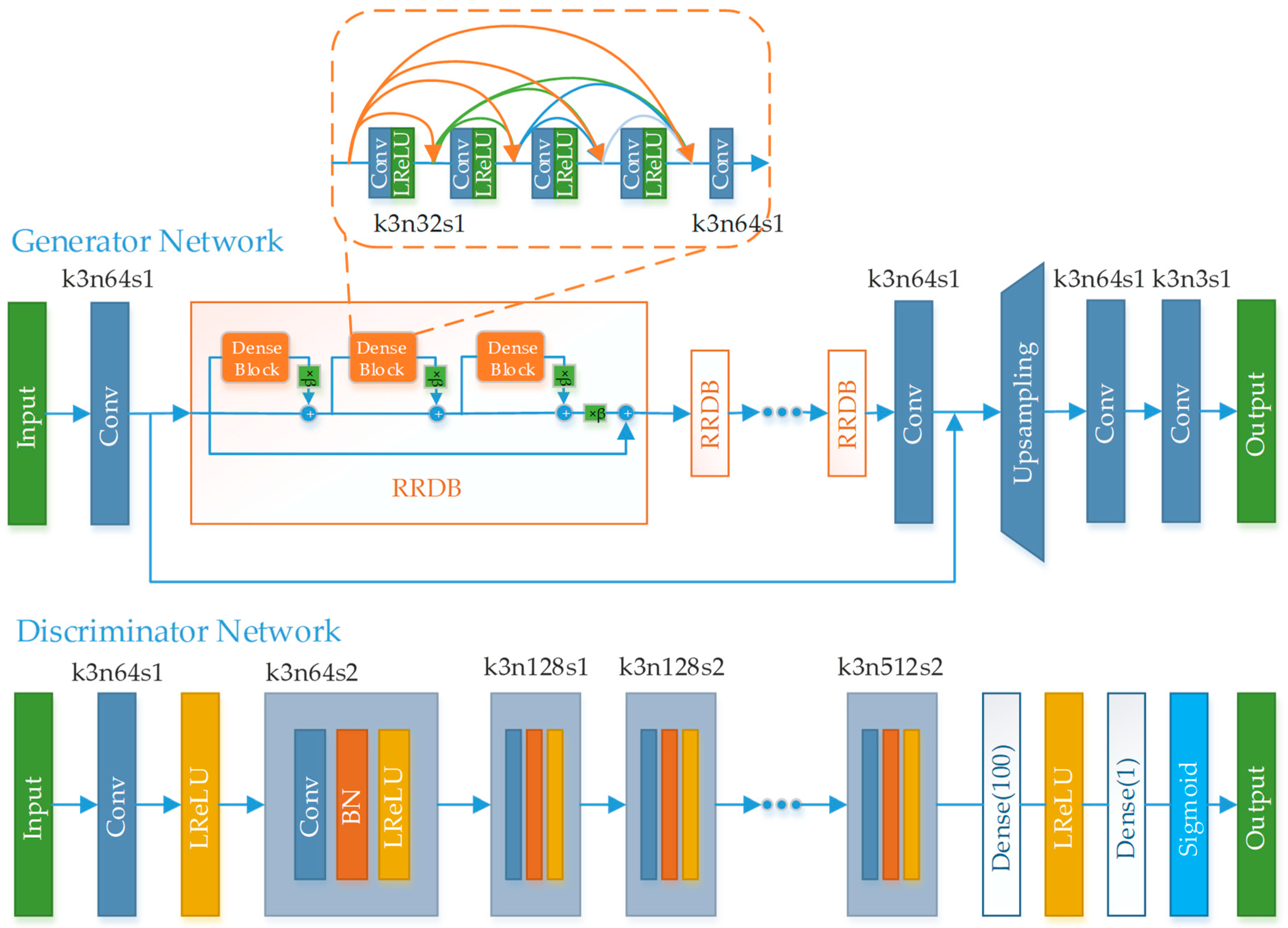
3. Generative Adversarial Network of the Proposed Method
4. Experiments
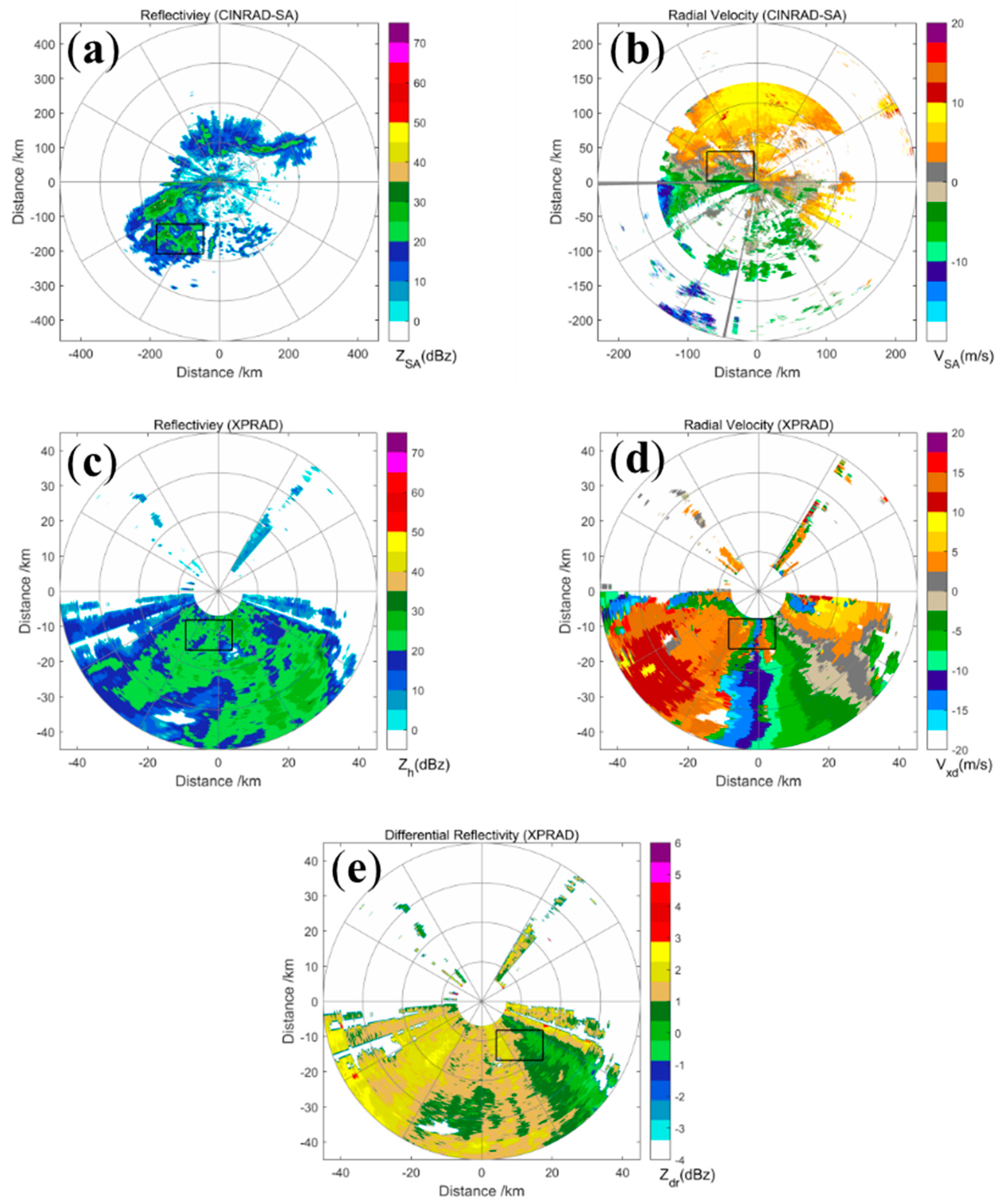
4.1. Data
4.2. Methods and Training Details
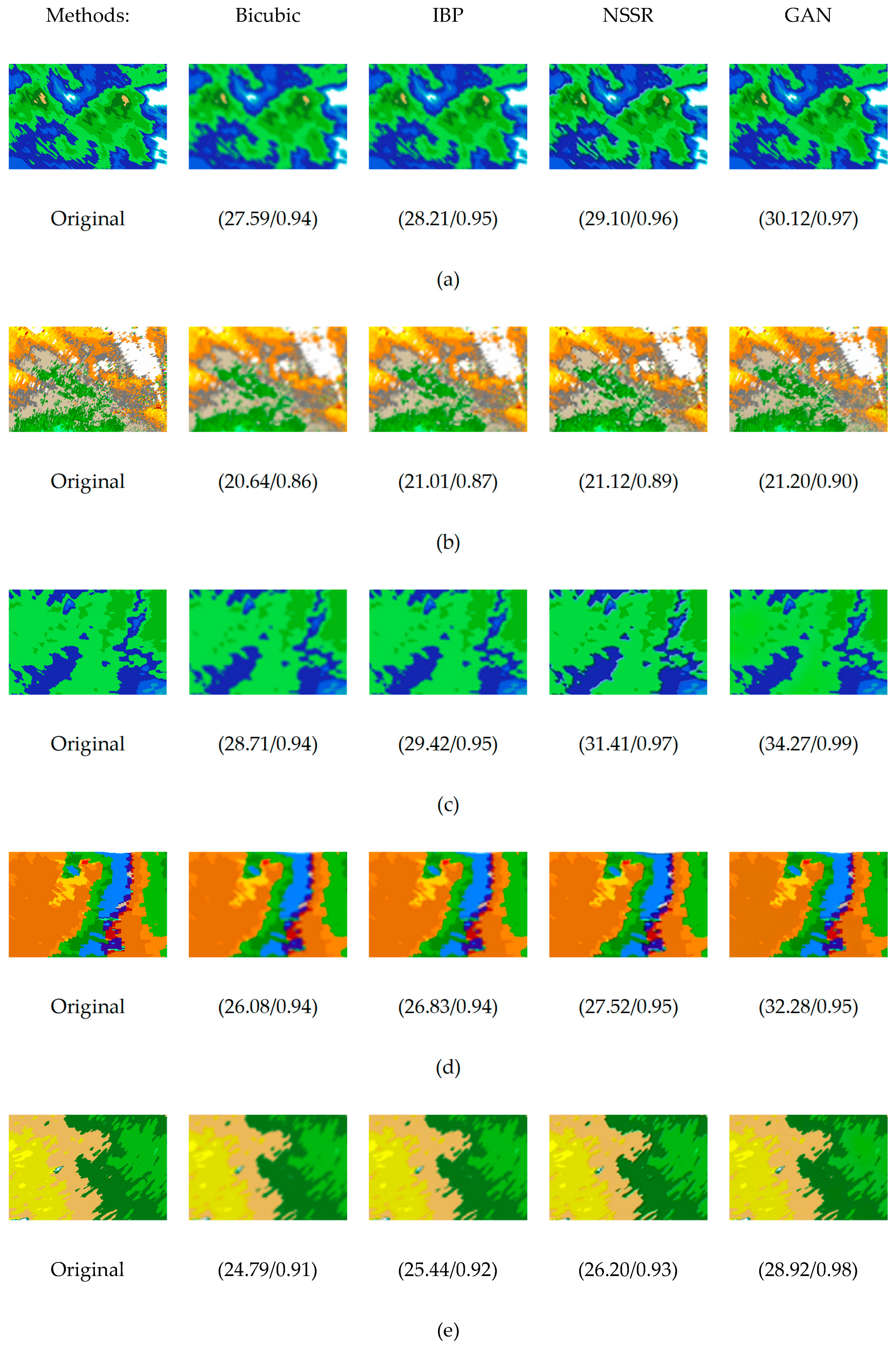
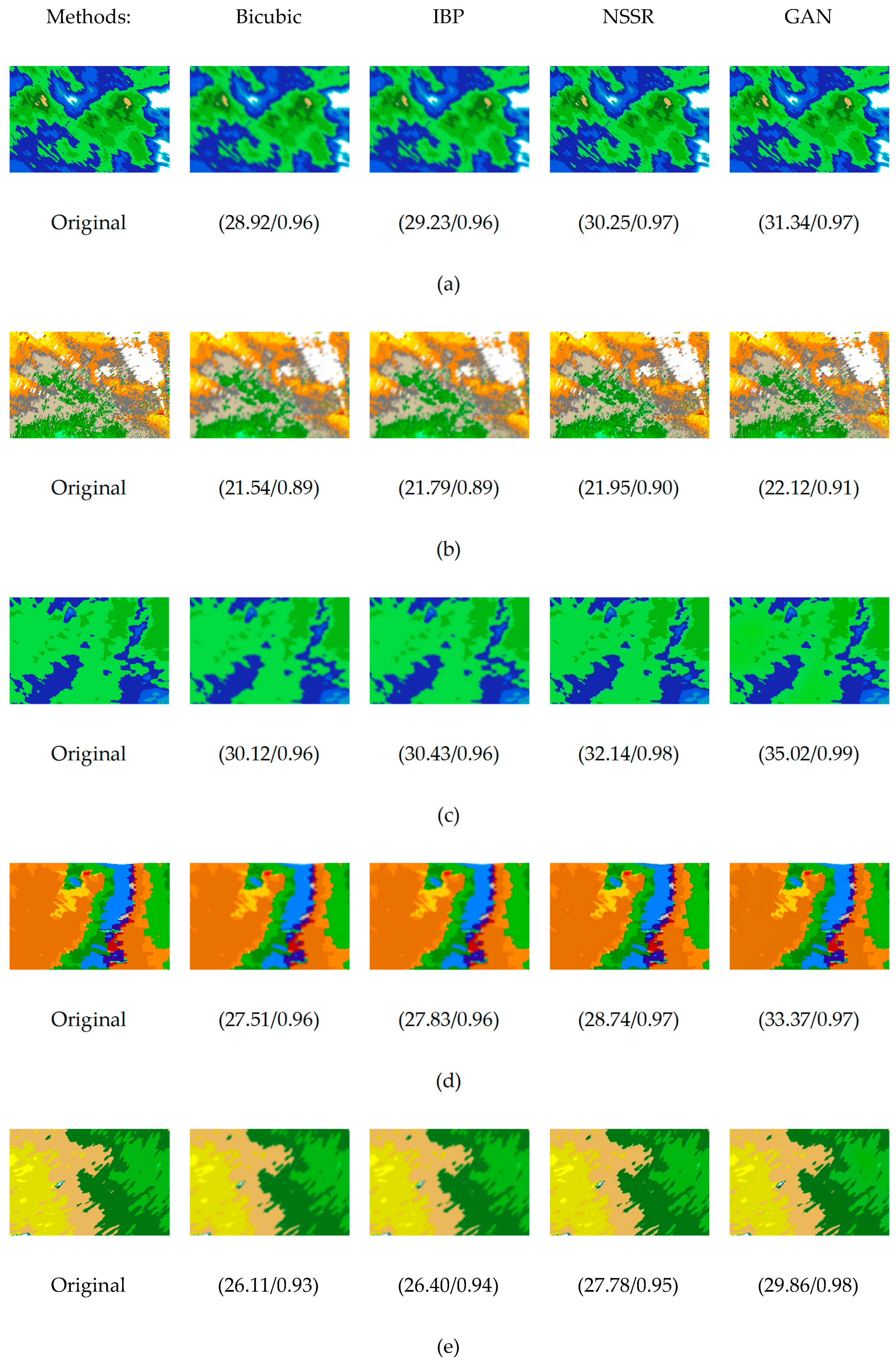
4.3. Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- China: National Climate Change Adaptation Strategy. Available online: http://preventionweb.net/go/35854 (accessed on 30 July 2019).
- Peleg, N.; Marra, F.; Fatichi, S.; Molnar, P.; Morin, E.; Sharma, A.; Burlando, P. Intensification of Convective Rain Cells at Warmer Temperatures Observed from High-Resolution Weather Radar Data. J. Hydrometeorol. 2018, 19, 715–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.A.; Baeck, M.L.; Villarini, G.; Welty, C.; Miller, A.J.; Krajewski, W.F. Analyses of a long-term, high-resolution radar rainfall data set for the Baltimore metropolitan region. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fries, A.; Rollenbeck, R.; Bayer, F.; Gonzalez, V.; Oñate-Valivieso, F.; Peters, T.; Bendix, J. Catchment precipitation processes in the San Francisco valley in southern Ecuador: Combined approach using high-resolution radar images and in situ observations. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2014, 126, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, S.M.; Curtis, C.D. Initial Implementation of Super-Resolution Data on The Nexrad Network. In Proceedings of the AMS Annual Meeting: 23rd Conference on IIPS, San Antonio, TX, USA, 15–18 January 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, X. A Minimum Entropy Spectrum Extrapolation Technique and Its Application to Radar Super-Resolution. Mod. Radar 2005, 27, 18–19. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, J.E.; Thorndahl, S.; Rasmussen, M.R. A numerical method to generate high temporal resolution precipitation time series by combining weather radar measurements with a nowcast model. Atmos. Res. 2014, 138, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo-Hernando, B.; Muñoz-Ferreras, J.M.; Pérez-Martínez, F. Super-resolution techniques for wind turbine clutter spectrum enhancement in meteorological radars. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2011, 5, 924–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; He, J.; He, Z.; Zeng, Q. Weather radar range and angular super-resolution reconstruction technique on oversampled reflectivity data. J. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2011, 8, 2553–2562. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; He, J.; He, Z. Weather radar angular resolution improvement of reflectivity data. Comput. Eng. Appl. 2011, 47, 18–20. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, K.; Li, W.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, Y.; Wu, J.; Yang, J.M. Penalized Maximum Likelihood Angular Super-Resolution Method for Scanning Radar Forward-Looking Imaging. Sensors 2018, 18, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; He, J.; He, Z.; Zeng, Q. Geostationary weather radar super-resolution modelling and reconstruction process. Int. J. Simul. Process Model. 2012, 7, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, Y.; Liu, L.; Yang, J.; Huang, Y. An alternating direction method for angular super-resolution in scanning radar. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Fort Worth, TX, USA, 23–28 July 2017; pp. 1626–1629. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Yang, J. TSVD with least squares optimization for scanning radar angular super-resolution. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf), Seattle, WA, USA, 8–12 May 2017; pp. 1450–1454. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Ren, H.; Zeng, Q.; Li, X. Super-Resolution reconstruction algorithm of weather radar based on IBP. J. Sichuan Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2014, 51, 947–952. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Q.; He, J.; Shi, Z.; Li, X. Weather Radar Data Compression Based on Spatial and Temporal Prediction. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; He, J.; Zeng, Q.; Shi, Z. Weather Radar Echo Super-Resolution Reconstruction Based on Nonlocal Self-Similarity Sparse Representation. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandapaka, P.V.; Germann, U.; Panziera, L.; Hering, A. Can Lagrangian Extrapolation of Radar Fields Be Used for Precipitation Nowcasting over Complex Alpine Orography? Weather Forecast. 2011, 27, 28–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop, L.; Sokol, Z.; Minářová, J. Nowcasting of the probability of accumulated precipitation based on the radar echo extrapolation. Atmos. Res. 2019, 216, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Wu, S.; Shan, J.; Yi, X. A Method of Radar Echo Extrapolation Based on TREC and Barnes Filter. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2019, 36, 1713–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Chen, Z.; Wang, H.; Yeung, D.-Y.; Wong, W.; Woo, W. Convolutional LSTM Network: A machine learning approach for precipitation nowcasting. In Proceedings of the Neural Information Processing Systems 28: Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems 2015, Montreal, QC, Canada, 7–12 December 2015; pp. 802–810. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, E.; Li, Q.; Gu, D.; Zhao, Z. Convolutional Neural Networks Applied on Weather Radar Echo Extrapolation. DEStech Trans. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krinitskiy, M.; Verezemskaya, P.; Grashchenkov, K.; Tilinina, N.; Gulev, S.; Lazzara, M. Deep Convolutional Neural Networks Capabilities for Binary Classification of Polar Mesocyclones in Satellite Mosaics. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booz, J.; Yu, W.; Xu, G.; Griffith, D.; Golmie, N. A Deep Learning-Based Weather Forecast System for Data Volume and Recency Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Computing, Networking and Communications (ICNC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 18–21 February 2019; pp. 697–701. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; Hoi, S.C.H. Deep Learning for Image Super-resolution: A Survey. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1902.06068. Available online: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1902.06068.pdf (accessed on 12 September 2019).
- Dong, C.; Loy, C.C.; He, K.; Tang, X. Learning a Deep Convolutional Network for Image Super-Resolution. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2014, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; Fleet, D., Pajdla, T., Schiele, B., Tuytelaars, T., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 184–199. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, C.; Loy, C.C.; He, K.; Tang, X. Image Super-Resolution Using Deep Convolutional Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 38, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative Adversarial Nets. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 27; Ghahramani, Z., Welling, M., Cortes, C., Lawrence, N.D., Weinberger, K.Q., Eds.; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 2672–2680. [Google Scholar]
- Ledig, C.; Theis, L.; Huszar, F.; Caballero, J.; Cunningham, A.; Acosta, A.; Aitken, A.; Tejani, A.; Totz, J.; Wang, Z.; et al. Photo-Realistic Single Image Super-Resolution Using a Generative Adversarial Network. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 105–114. [Google Scholar]
- Nasrollahi, K.; Moeslund, T.B. Super-resolution: A comprehensive survey. Mach. Vis. Appl. 2014, 25, 1423–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.; Alahi, A.; Fei-Fei, L. Perceptual Losses for Real-Time Style Transfer and Super-Resolution. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1603.08155. Available online: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1603.08155.pdf (accessed on 12 September 2019).
- Bruna, J.; Sprechmann, P.; LeCun, Y. Super-Resolution with Deep Convolutional Sufficient Statistics. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1511.05666. Available online: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1511.05666.pdf (accessed on 12 September 2019).
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. Available online: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1409.1556.pdf (accessed on 12 September 2019).
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Lu, L. Why is image quality assessment so difficult? In Proceedings of the 2002 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Orlando, FL, USA, 13–7 May 2002; Volume 4, pp. IV-3313–IV-3316. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, W.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C. Mean squared error: Love it or leave it? A new look at Signal Fidelity Measures. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2009, 26, 98–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weather Radar. Wikipedia. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Weather_radar (accessed on 12 September 2019).
- Ioffe, S.; Szegedy, C. Batch Normalization: Accelerating Deep Network Training by Reducing Internal Covariate Shift. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1502.03167. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Yu, K.; Wu, S.; Gu, J.; Liu, Y.; Dong, C.; Loy, C.C.; Qiao, Y.; Tang, X. ESRGAN: Enhanced Super-Resolution Generative Adversarial Networks. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1809.00219. Available online: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1809.00219.pdf (accessed on 12 September 2019).
- Lim, B.; Son, S.; Kim, H.; Nah, S.; Lee, K.M. Enhanced Deep Residual Networks for Single Image Super-Resolution. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1707.02921. Available online: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1707.02921.pdf (accessed on 12 September 2019).
- Zhang, Y.; Li, K.; Li, K.; Wang, L.; Zhong, B.; Fu, Y. Image Super-Resolution Using Very Deep Residual Channel Attention Networks. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.02758. Available online: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1807.02758.pdf (accessed on 12 September 2019).
- Xu, B.; Wang, N.; Chen, T.; Li, M. Empirical Evaluation of Rectified Activations in Convolutional Network. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1505.00853. Available online: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1505.00853.pdf (accessed on 12 September 2019).
- Radford, A.; Metz, L.; Chintala, S. Unsupervised Representation Learning with Deep Convolutional Generative Adversarial Networks. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1511.06434. Available online: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1511.06434.pdf (accessed on 12 September 2019).
- Jolicoeur-Martineau, A. The relativistic discriminator: A key element missing from standard GAN. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.00734. Available online: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1807.00734.pdf (accessed on 12 September 2019).
- Mikołajczyk, A.; Grochowski, M. Data augmentation for improving deep learning in image classification problem. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Interdisciplinary PhD Workshop (IIPhDW), Swinoujście, Poland, 9–12 May 2018; pp. 117–122. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, W.; Zhang, L.; Shi, G.; Li, X. Nonlocally Centralized Sparse Representation for Image Restoration. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2013, 22, 1620–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glasner, D.; Bagon, S.; Irani, M. Super-resolution from a single image. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision, Kyoto, Japan, 29 September–2 October 2009; pp. 349–356. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. Available online: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1412.6980.pdf (accessed on 12 September 2019).


| Methods | Severe Weather | Rainfall | Cloudless | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reflectivity | Velocity | Reflectivity | Velocity | Reflectivity | Velocity | |
| Bicubic | 26.5709 | 21.4417 | 27.5785 | 20.6383 | 29.0000 | 24.0140 |
| 0.9145 | 0.8801 | 0.9412 | 0.8597 | 0.9652 | 0.9353 | |
| IBP | 27.1974 | 21.8557 | 28.1976 | 21.0084 | 29.6042 | 24.3899 |
| 0.9236 | 0.8887 | 0.9474 | 0.8692 | 0.9689 | 0.9395 | |
| NSSR | 28.1819 | 22.0604 | 29.3312 | 21.0326 | 30.8083 | 24.3498 |
| 0.9380 | 0.9041 | 0.9509 | 0.8708 | 0.9718 | 0.9437 | |
| GAN | 29.8260 | 22.0710 | 30.0911 | 21.1637 | 31.3048 | 24.3735 |
| 0.9621 | 0.9097 | 0.9697 | 0.8973 | 0.9826 | 0.9519 | |
| Methods | Severe Weather | Rainfall | Cloudless | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reflectivity | Velocity | Reflectivity | Velocity | Reflectivity | Velocity | |
| Bicubic | 27.8990 | 22.3740 | 28.9032 | 21.5330 | 30.3516 | 24.8831 |
| 0.9370 | 0.9044 | 0.9563 | 0.8866 | 0.9744 | 0.9476 | |
| IBP | 28.2045 | 22.6047 | 29.2123 | 21.7666 | 30.6683 | 25.1020 |
| 0.9415 | 0.9098 | 0.9594 | 0.8929 | 0.9763 | 0.9504 | |
| NSSR | 29.5480 | 22.4849 | 30.0018 | 21.5484 | 31.5229 | 24.7074 |
| 0.9482 | 0.9226 | 0.9610 | 0.8748 | 0.9773 | 0.9536 | |
| GAN | 30.5941 | 22.7071 | 30.4960 | 22.1960 | 32.0998 | 25.5752 |
| 0.9805 | 0.9235 | 0.9783 | 0.9102 | 0.9889 | 0.9612 | |
| Methods | Severe Weather | Rainfall | Cloudless | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zh | Vxd | Zdr | Zh | Vxd | Zdr | Zh | Vxd | Zdr | |
| Bicubic | 28.8036 | 26.0172 | 24.3761 | 31.9382 | 28.5004 | 27.1535 | 36.9246 | 33.9114 | 31.1582 |
| 0.9427 | 0.9428 | 0.9048 | 0.9747 | 0.9720 | 0.9553 | 0.9924 | 0.9916 | 0.9848 | |
| IBP | 29.5159 | 26.7602 | 25.0281 | 32.6644 | 29.2243 | 27.7933 | 37.6453 | 34.6458 | 31.7911 |
| 0.9491 | 0.9463 | 0.9151 | 0.9776 | 0.9736 | 0.9601 | 0.9933 | 0.9921 | 0.9865 | |
| NSSR | 31.4081 | 28.8602 | 27.1537 | 36.7442 | 33.4992 | 29.4041 | 40.3813 | 38.3754 | 32.5530 |
| 0.9627 | 0.9487 | 0.9596 | 0.9824 | 0.9771 | 0.9743 | 0.9946 | 0.9941 | 0.9939 | |
| GAN | 34.5679 | 32.3670 | 28.5642 | 38.6138 | 35.4582 | 30.9614 | 43.7936 | 42.4108 | 34.5021 |
| 0.9858 | 0.9496 | 0.9686 | 0.9935 | 0.9850 | 0.9851 | 0.9981 | 0.9973 | 0.9947 | |
| Methods | Severe Weather | Rainfall | Cloudless | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zh | Vxd | Zdr | Zh | Vxd | Zdr | Zh | Vxd | Zdr | |
| Bicubic | 30.2139 | 27.4481 | 25.6973 | 33.3688 | 29.9164 | 28.4615 | 38.3733 | 35.3564 | 32.4229 |
| 0.9597 | 0.9597 | 0.9310 | 0.9822 | 0.9802 | 0.9674 | 0.9947 | 0.9941 | 0.9888 | |
| IBP | 30.5227 | 27.7617 | 25.9918 | 33.6826 | 30.2276 | 28.7546 | 38.6933 | 35.6711 | 32.7062 |
| 0.9627 | 0.9625 | 0.9359 | 0.9835 | 0.9816 | 0.9697 | 0.9951 | 0.9945 | 0.9896 | |
| NSSR | 32.2404 | 28.1724 | 27.9154 | 37.9592 | 34.5194 | 30.1147 | 41.6135 | 39.4510 | 33.5485 |
| 0.9757 | 0.9554 | 0.9645 | 0.9870 | 0.9818 | 0.9807 | 0.9976 | 0.9954 | 0.9966 | |
| GAN | 35.6035 | 33.0355 | 29.0030 | 39.2935 | 35.8812 | 31.5394 | 44.6363 | 43.4145 | 34.9678 |
| 0.9974 | 0.9613 | 0.9865 | 0.9959 | 0.9959 | 0.9923 | 0.9985 | 0.9991 | 0.9968 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, H.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, Q. Generative Adversarial Networks Capabilities for Super-Resolution Reconstruction of Weather Radar Echo Images. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 555. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10090555
Chen H, Zhang X, Liu Y, Zeng Q. Generative Adversarial Networks Capabilities for Super-Resolution Reconstruction of Weather Radar Echo Images. Atmosphere. 2019; 10(9):555. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10090555
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Hongguang, Xing Zhang, Yintian Liu, and Qiangyu Zeng. 2019. "Generative Adversarial Networks Capabilities for Super-Resolution Reconstruction of Weather Radar Echo Images" Atmosphere 10, no. 9: 555. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10090555
APA StyleChen, H., Zhang, X., Liu, Y., & Zeng, Q. (2019). Generative Adversarial Networks Capabilities for Super-Resolution Reconstruction of Weather Radar Echo Images. Atmosphere, 10(9), 555. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10090555





