Does the IOD Independently Influence Seasonal Monsoon Patterns in Northern Ethiopia?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Rainfall Data
2.2. Large–Scale Circulation Indices
2.3. Identification of Rainfall Predictors
3. Results and Discussions
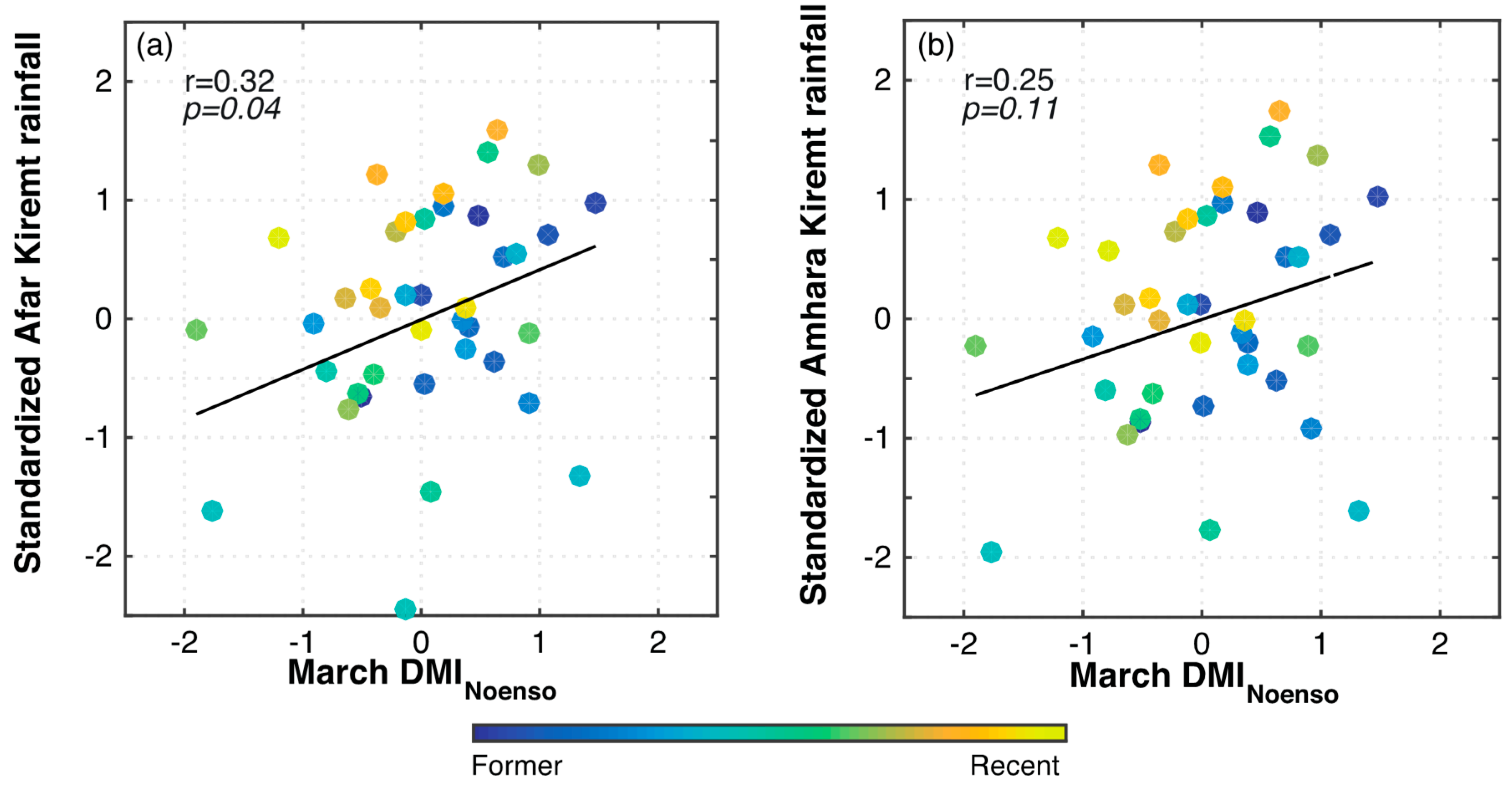
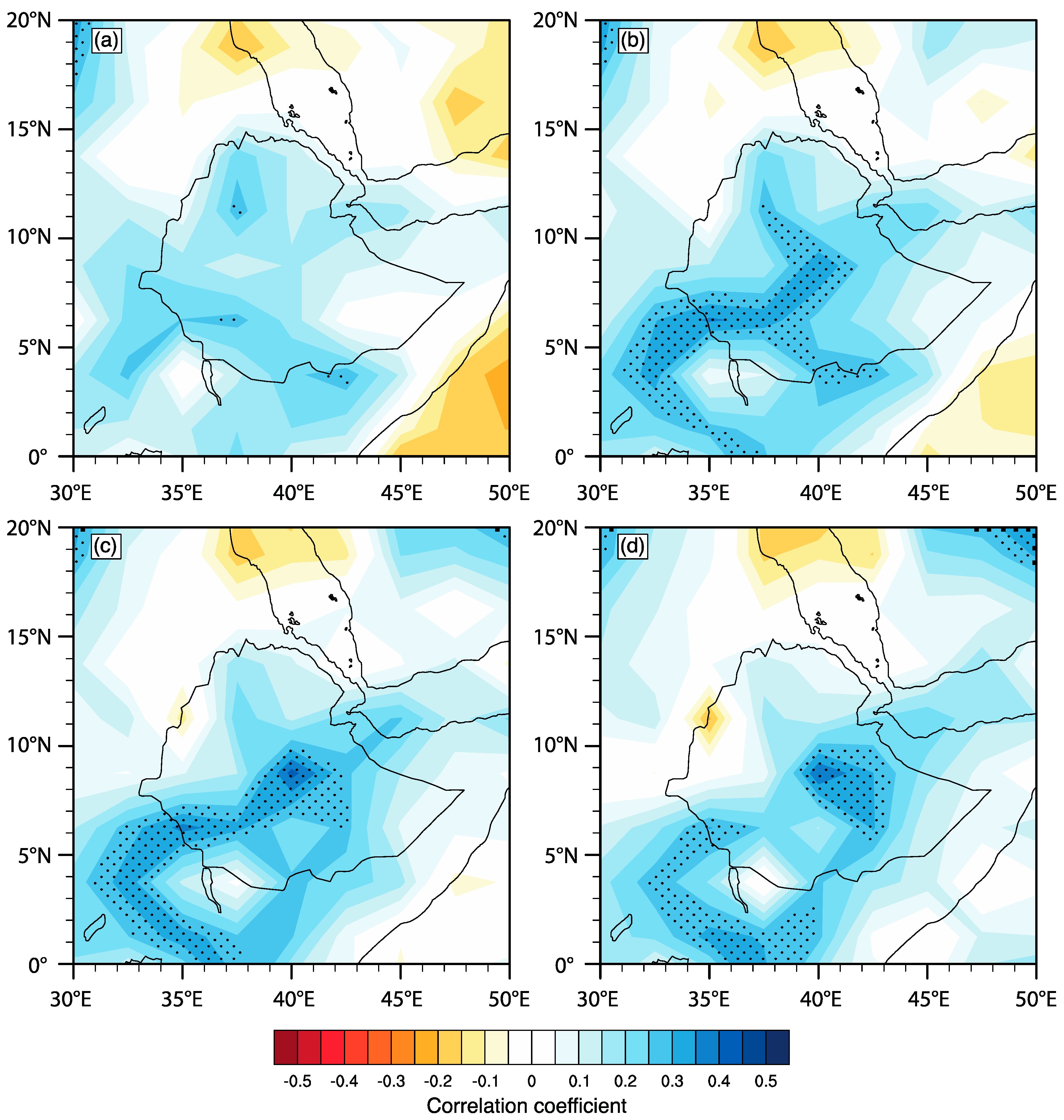
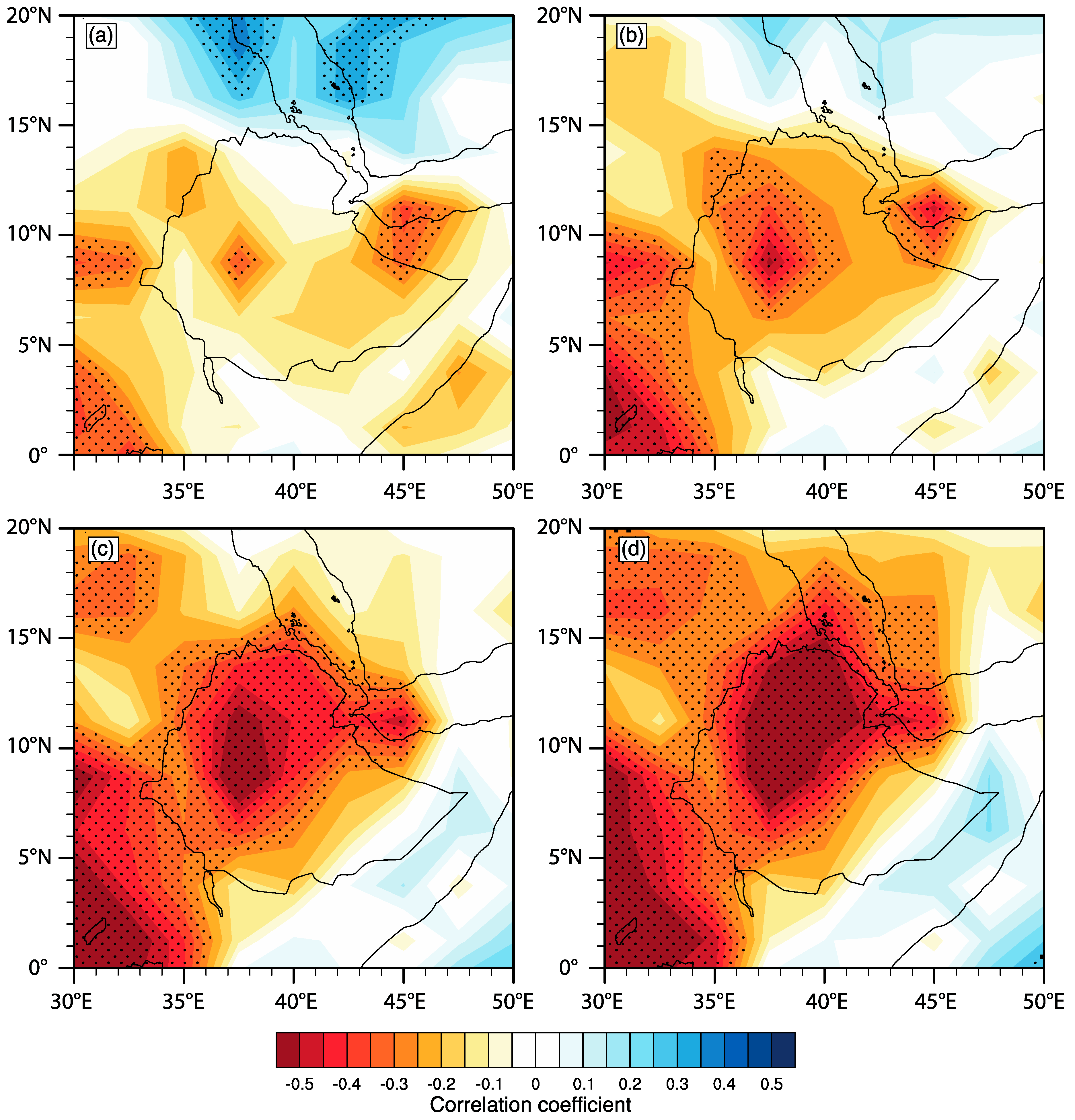
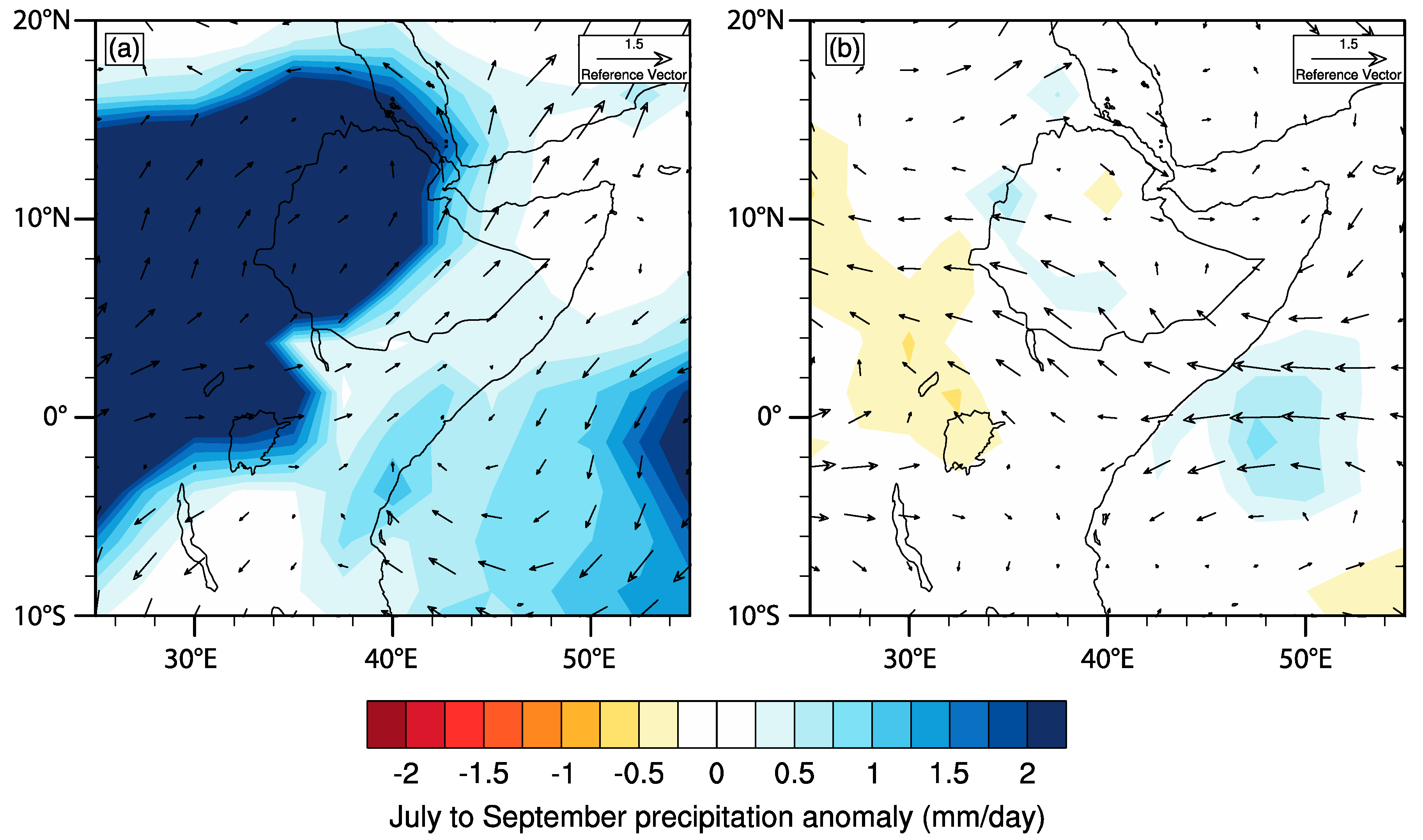
3.1. Trends in Regional Rainfall and Correlations with Large-Scale Circulation Indices
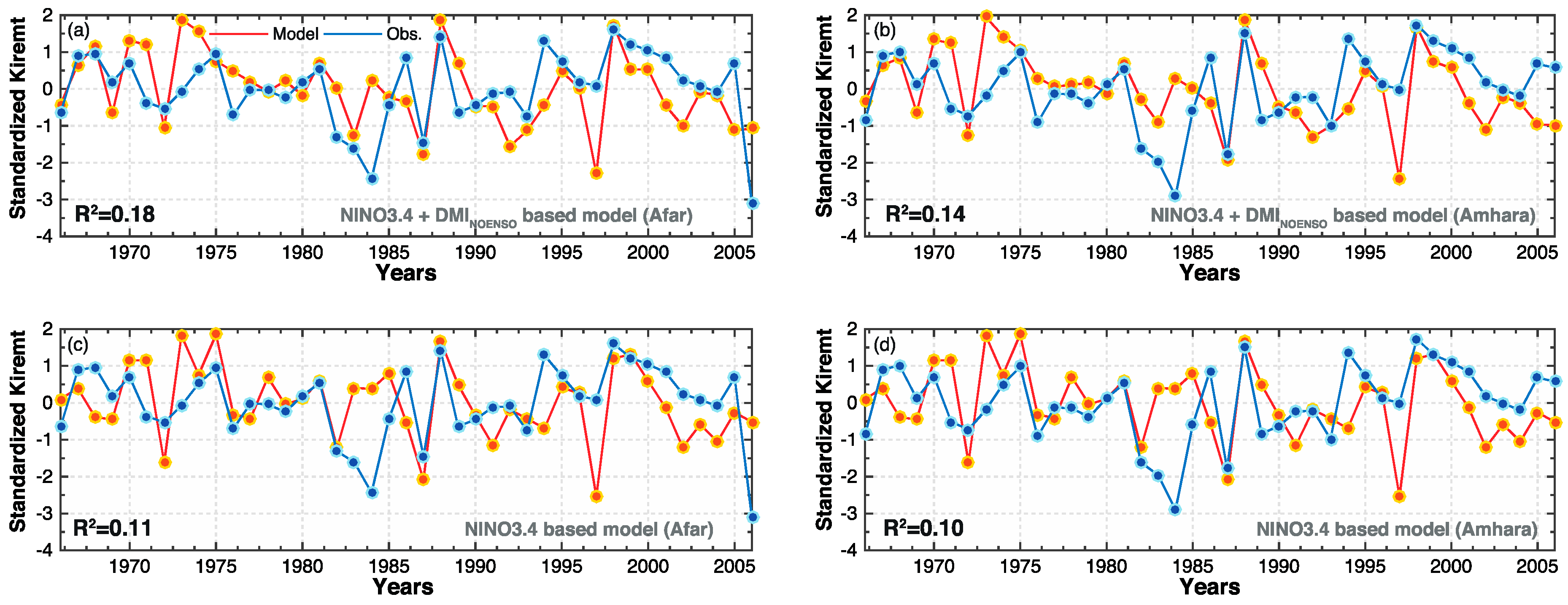
3.2. New Statistical Models for Regional Kiremt Rainfall
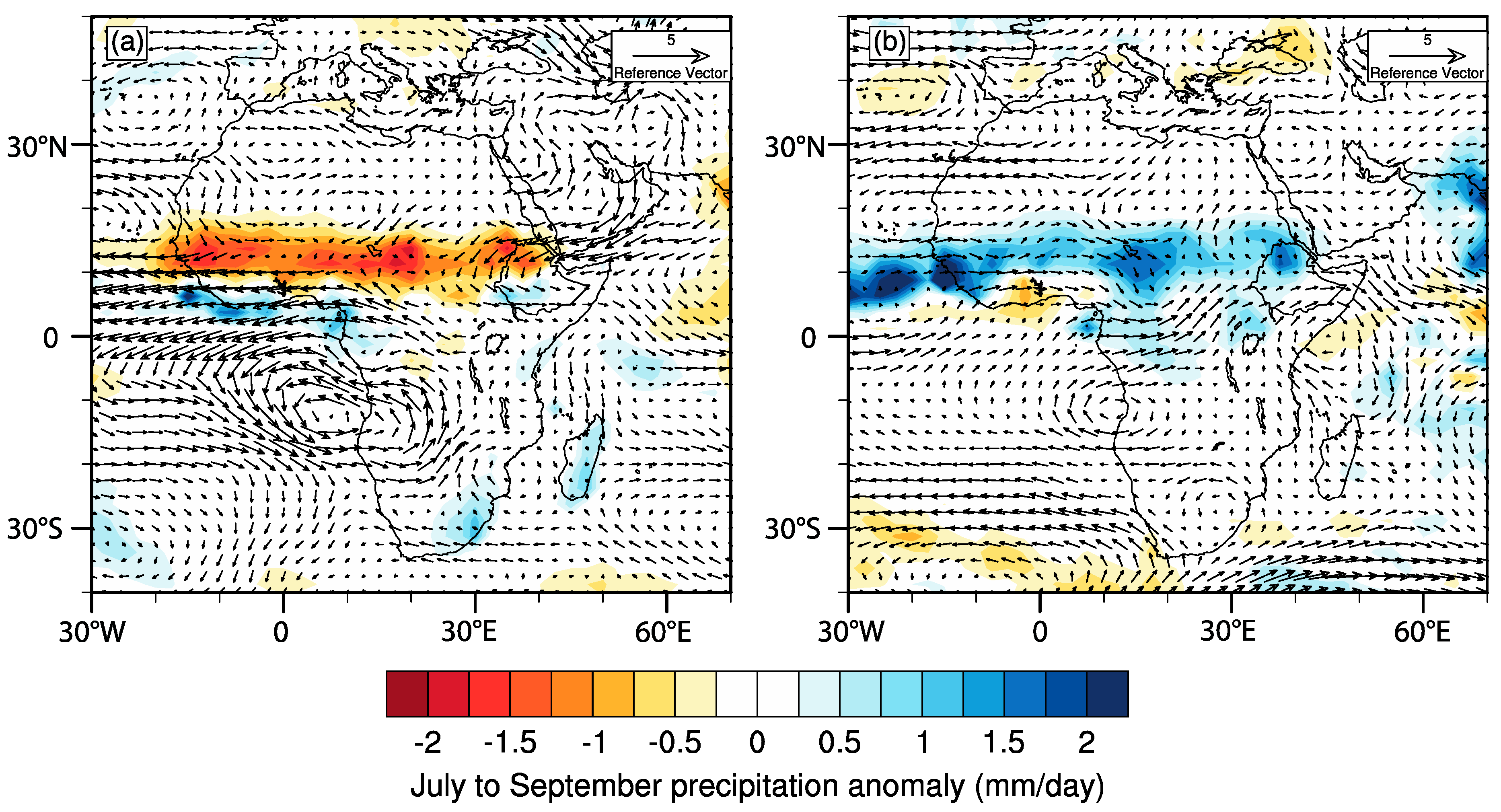
3.3. The Role of the IOD in Eastern African Rainfall
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gissila, T.; Black, E.; Grimes, D.I.F.; Slingo, J.M. Seasonal forecasting of the Ethiopian summer rains. Int. J. Climatol. 2004, 24, 1345–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indeje, M.; Semazzi, F.H.; Ogallo, L.J. ENSO signals in East African rainfall seasons. Int. J. Climatol. 2000, 20, 19–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korecha, D.; Barnston, A.G. Predictability of June–September Rainfall in Ethiopia. Mon. Weather Rev. 2007, 135, 628–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segele, Z.T.; Lamb, P.J.; Leslie, L.M. Large-scale atmospheric circulation and global sea surface temperature associations with Horn of Africa June–September rainfall. Int. J. Climatol. 2009, 29, 1075–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diro, G.T.; Black, E.; Grimes, D.I.F. Seasonal forecasting of Ethiopian spring rains. Meteorol. Appl. 2008, 1, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diro, G.T.; Grimes, D.I.F.; Black, E. Teleconnections between Ethiopian summer rainfall and sea surface temperature: Part II. Seasonal forecasting. Clim. Dyn. 2011, 37, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endris, H.S.; Lennard, C.; Hewitson, B.; Dosio, A.; Nikulin, G.; Panitz, H.J. Teleconnection responses in multi-GCM driven CORDEX RCMs over Eastern Africa. Clim. Dyn. 2016, 46, 2821–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, S.E. The spatial coherence of African rainfall anomalies: Interhemispheric teleconnections. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 1986, 25, 1365–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchant, R.; Mumbi, C.; Behera, S.; Yamagata, T. The Indian Ocean dipole–the unsung driver of climatic variability in East Africa. Afr. J. Ecol. 2007, 45, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, E. The relationship between Indian Ocean sea–surface temperature and East African rainfall. Philos. Trans. A. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2005, 363, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degefu, M.A.; Rowell, D.P.; Bewket, W. Teleconnections between Ethiopian rainfall variability and global SSTs: Observations and methods for model evaluation. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2017, 129, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashok, K.; Guan, Z.; Yamagata, T. A look at the relationship between the ENSO and the Indian Ocean dipole. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2003, 81, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuecker, M.F.; Timmermann, A.; Jin, F.F.; Chikamoto, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wittenberg, A.T.; Widiasih, E.; Zhao, S. Revisiting ENSO/Indian Ocean dipole phase relationships. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 2481–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, R.; Chambers, D.; Drosdowsky, W.; Hendon, H.; Latif, M.; Nicholls, N.; Smith, I.; Stone, R.; Tourre, Y. Is there an Indian Ocean dipole and is it independent of the El Niño-Southern Oscillation. CLIVAR Exch. 2001, 21, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Saji, N.; Goswami, B.N.; Vinayachandran, P.; Yamagata, T. A dipole mode in the tropical Indian Ocean. Nature 1999, 401, 360–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, P.J.; Moore, A.M.; Loschnigg, J.P.; Leben, R.R. Coupled ocean–atmosphere dynamics in the Indian Ocean during 1997–98. Nature 1999, 401, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanko, D.; Camberlin, P. The effects of the Southwest Indian Ocean tropical cyclones on Ethiopian drought. Int. J. Climatol. 1998, 18, 1373–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degefu, W. Some Aspects of Meteorological Drought in Ethiopia; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Diro, G.T.; Tompkins, A.M.; Bi, X. Dynamical downscaling of ECMWF Ensemble seasonal forecasts over East Africa with RegCM3. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, D16103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleixner, S.; Keenlyside, N.S.; Demissie, T.D.; Counillon, F.; Wang, Y.; Viste, E. Seasonal predictability of Kiremt rainfall in coupled general circulation models. Environ. Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 114016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, A.; Maharaj, A.M.; Holbrook, N.J. A new method for extracting the ENSO-independent Indian Ocean Dipole: Application to Australian region tropical cyclone counts. Clim. Dyn. 2012, 38, 2503–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandersson, H. A homogeneity test applied to precipitation data. Int. J. Climatol. 1986, 6, 661–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helsel, D.R.; Hirsch, R.M. Statistical Methods in Water Resources; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Sen, P.K. Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall’s tau. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niño 3.4 Index. Available online: http://www.cpc.ncep.noaa.gov/data/indices/ (accessed on 4 January 2013).
- Yamagata, T.; Behera, S.K.; Rao, S.A.; Guan, Z.; Ashok, K.; Saji, H.N. Comments on “Dipoles, Temperature Gradients, and Tropical Climate Anomalies”. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2003, 84, 1418–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DMI Index. Available online: http://www.jamstec.go.jp/frcgc/research/d1/iod/ (accessed on 4 January 2013).
- NOAA PSD Vector Wind and Precipitation Data. Available online: https://www.esrl.noaa.gov/psd/ (accessed on 13 June 2018).
- Akaike, H. A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Trans. Automat. Control 1974, 19, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurvich, C.M.; Tsai, C.-L. Regression and time series model selection in small samples. Biometrika 1989, 76, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seleshi, Y.; Zanke, U. Recent changes in rainfall and rainy days in Ethiopia. Int. J. Climatol. 2004, 24, 973–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, D. The Climate and Hydrology of the Upper Blue Nile River. Geogr. J. 2000, 166, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, D.; Mould, C.; Bewket, W. Over one century of rainfall and temperature observations in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Int. J. Climatol. 2004, 24, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meze-Hausken, E. Contrasting climate variability and meteorological drought with perceived drought and climate change in northern Ethiopia. Clim. Res. 2004, 27, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, C.; Haug, G.H.; Timmermann, A.; Damsté, J.S.S.; Brauer, A.; Sigman, D.M.; Cane, M.A.; Verschuren, D. Reduced Interannual Rainfall Variability in East Africa During the Last Ice Age. Science 2011, 333, 743–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutai, C.C.; Ward, M.N. East African rainfall and the tropical circulation/convection on intraseasonal to interannual timescales. J. Clim. 2000, 13, 3915–3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashok, K.; Guan, Z.; Yamagata, T. Impact of the Indian Ocean dipole on the relationship between the Indian monsoon rainfall and ENSO. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2001, 28, 4499–4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Van Rensch, P.; Cowan, T.; Hendon, H.H. An asymmetry in the IOD and ENSO teleconnection pathway and its impact on Australian climate. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 6318–6329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- England, M.H.; Ummenhofer, C.C.; Santoso, A. Interannual rainfall extremes over southwest Western Australia linked to Indian Ocean climate variability. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 1948–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ummenhofer, C.C.; England, M.H.; McIntosh, P.C.; Meyers, G.A.; Pook, M.J.; Risbey, J.S.; Gupta, A.S.; Taschetto, A.S. What causes southeast Australia’s worst droughts? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, D.; Hanson, C.E.; Doherty, R.; Persechino, A. GCM simulations of the Indian Ocean dipole influence on East African rainfall: Present and future. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ummenhofer, C.C.; Sen Gupta, A.; England, M.H.; Reason, C.J. Contributions of Indian Ocean sea surface temperatures to enhanced East African rainfall. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 993–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsidu, G.M. High-resolution monthly rainfall database for Ethiopia: Homogenization, reconstruction, and gridding. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 8422–8443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
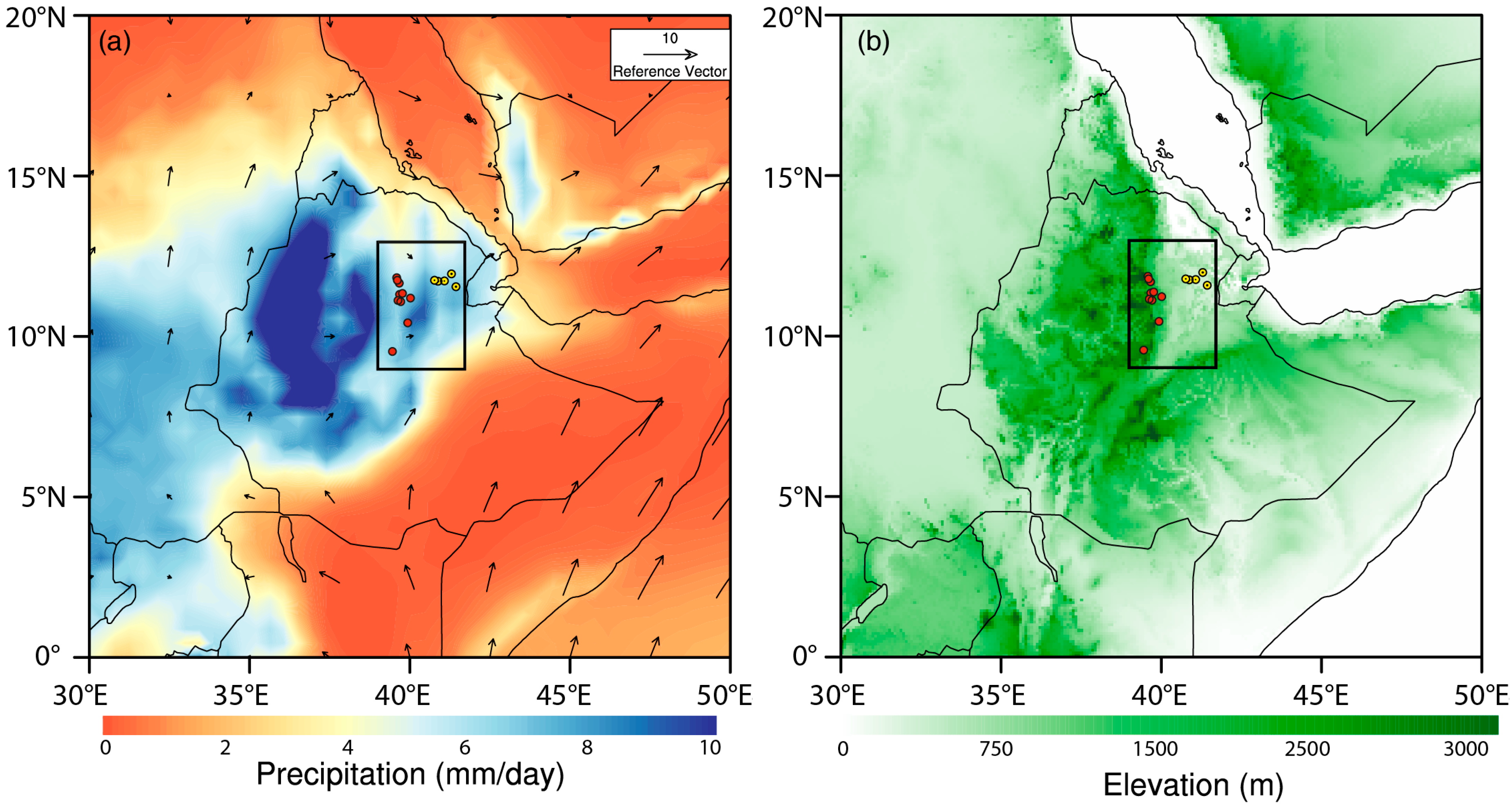
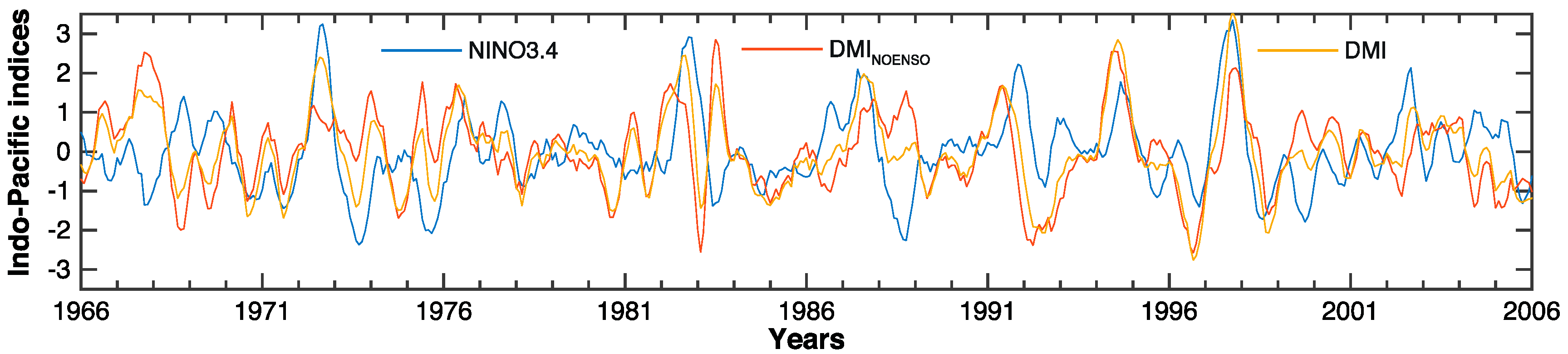
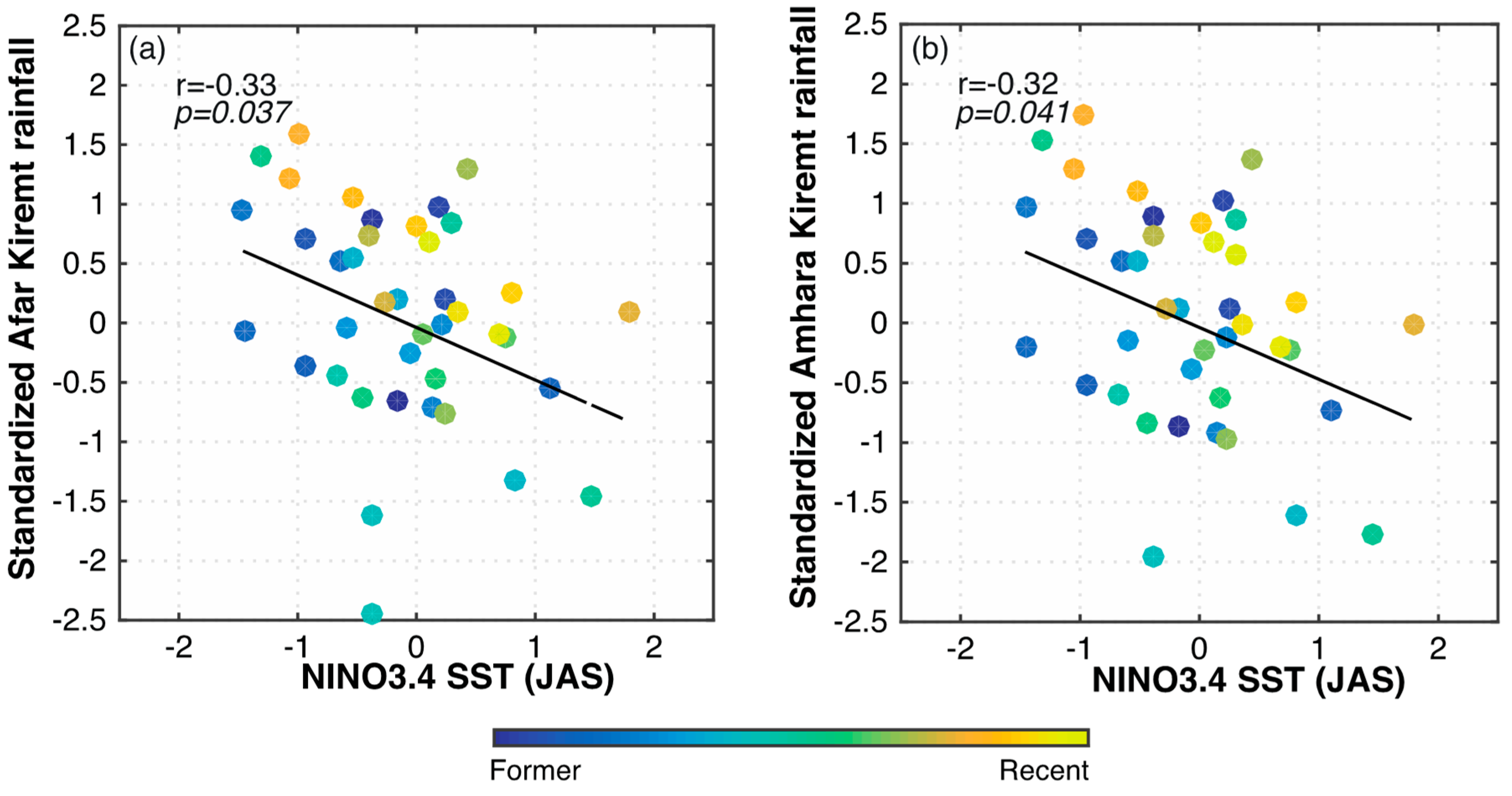
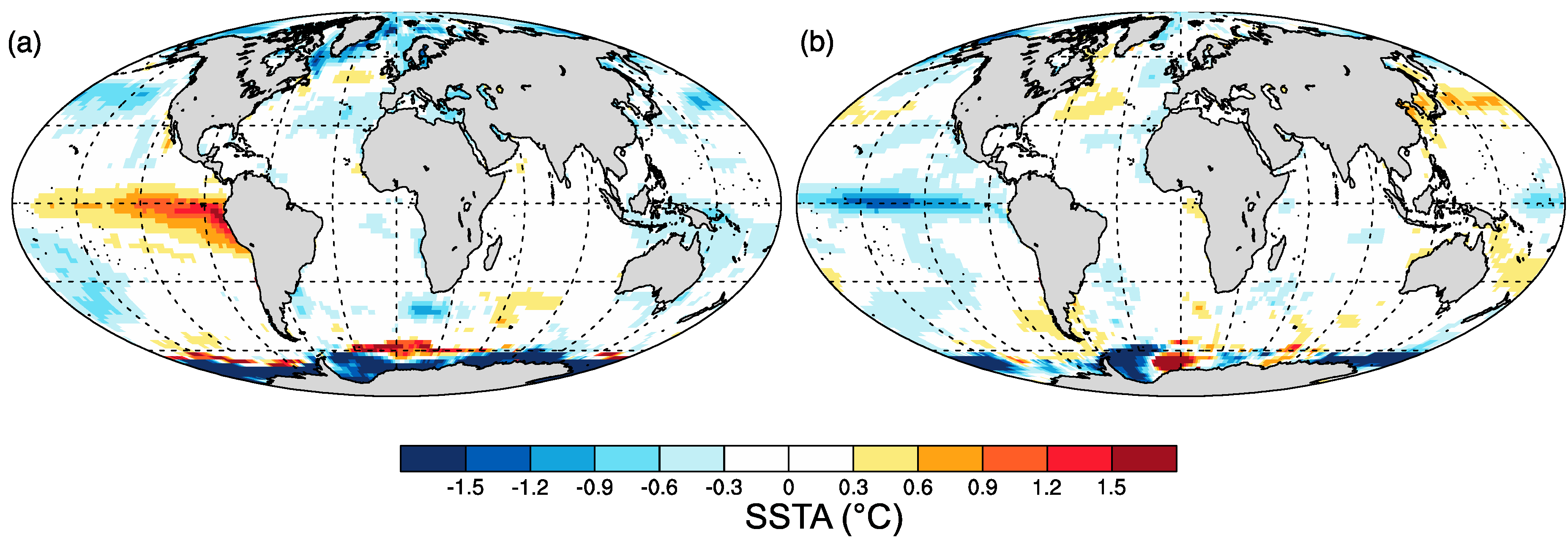
| Station Name | Altitude (m) | Observation | Missing (years) | Cluster |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Assayita | 430 | 1966–2006 | 7 | Afar |
| Bati | 1501 | 1987–2005 | 0 | Amhara |
| Bokokesa | 1673 | 1975–2005 | 9 | Amhara |
| Dessie | 2402 | 1971–2006 | 2 | Amhara |
| Dubti | 377 | 1981–2006 | 5 | Afar |
| Hayq | 2030 | 1966–2006 | 1 | Amhara |
| Karakore | 1696 | 1966–2003 | 1 | Amhara |
| Kombolcha | 1916 | 1966–2006 | 0 | Amhara |
| Logia | 400 | 1980–2006 | 3 | Afar |
| Mersa | 2300 | 1981–2006 | 3 | Amhara |
| Mille | 517 | 1966–2006 | 3 | Afar |
| Serdo | 445 | 1981–2005 | 7 | Afar |
| Srinka | 2080 | 1981–2006 | 4 | Amhara |
| Werebabo | 1650 | 1981–2006 | 2 | Amhara |
| Woldia | 2010 | 1966–2006 | 6 | Amhara |
| Indices | Regression Coefficients | Predictor Weights | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Afar | Amhara | Afar | Amhara | |
| NINO3.4 | 0.29 | 0.31 | 61% | 53% |
| DMINOENSO | 0.18 | 0.27 | 39% | 47% |
| Model | K | RSS | AIC | Δi (AICi − min AIC) | wi | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Afar | NINO3.4 + DMINOENSO | 4 | 29 | −4.45 | −4.45 + 4.45 = 0.00 | 0.60 |
| NINO3.4 | 3 | 32 | −3.02 | −3.05 + 4.45 = 1.30 | 0.40 | |
| Amhara | NINO3.4 + DMINOENSO | 4 | 30 | −2.97 | −2.97 + 2.97 = 0.00 | 0.51 |
| NINO3.4 | 3 | 32 | −2.82 | −2.82 + 2.97 = 0.15 | 0.49 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gebregiorgis, D.; Rayner, D.; Linderholm, H.W. Does the IOD Independently Influence Seasonal Monsoon Patterns in Northern Ethiopia? Atmosphere 2019, 10, 432. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10080432
Gebregiorgis D, Rayner D, Linderholm HW. Does the IOD Independently Influence Seasonal Monsoon Patterns in Northern Ethiopia? Atmosphere. 2019; 10(8):432. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10080432
Chicago/Turabian StyleGebregiorgis, Daniel, David Rayner, and Hans W. Linderholm. 2019. "Does the IOD Independently Influence Seasonal Monsoon Patterns in Northern Ethiopia?" Atmosphere 10, no. 8: 432. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10080432
APA StyleGebregiorgis, D., Rayner, D., & Linderholm, H. W. (2019). Does the IOD Independently Influence Seasonal Monsoon Patterns in Northern Ethiopia? Atmosphere, 10(8), 432. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10080432






