Black Carbon and Particulate Matter Concentrations in Eastern Mediterranean Urban Conditions: An Assessment Based on Integrated Stationary and Mobile Observations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Country and City Descriptions
2.2. Aerosol Measurements
2.2.1. Stationary Aerosol Measurement Campaigns
2.2.2. Mobile Aerosol Measurement Campaigns—Driving/Walking/Standing
2.2.3. Portable Aerosol Instruments
2.3. Data Handling and Harmony
3. Results
3.1. Average Concentrations at the Reference Sites—Urban Background
3.1.1. Submicron Aerosols
3.1.2. Super-Micron Aerosols
3.2. Remote Area (Beren) Outside Amman and Zarqa
3.2.1. Off-Road Conditions in a Remote Area
3.2.2. On-Road Conditions in a Remote Area
3.3. Exposure as an Urban Pedestrian
3.3.1. Educational Campus and Its Surroundings
3.3.2. Leisure Time—Amman and Zarqa City Centers
3.4. In-Vehicle Exposure—Driving on Main Roads
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fenger, J. Urban air quality. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 4877–4900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulmala, M. Build a global Earth observatory. Nature 2018, 553, 21–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klob, C.E.; Herndon, S.C.; McManus, J.B.; Shorter, J.H.; Zahniser, M.S.; Nelson, D.D.; Jayne, J.T.; Canagaratna, M.R.; Worsnop, D.R. Mobile laboratory with rapid response instruments for real-time measurements of urban and regional trace gas and particulate distributions and emission source characteristics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 5694–5703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, M.C.; Hudda, N.; Naumova, E.N.; Levy, J.I.; Brugge, D.; Durant, J.L. Comparisons of traffic-related ultrafine particle number concentrations measured in two urban areas by central, residential, and mobile monitoring. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 169, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.Y.; Lin, M.Y.; Chiang, H.C.; Chen, M.J.; Lin, T.Y.; Chen, Y.C. Using a mobile measurement to characterize number, surface area, and mass concentrations of ambient fine particles with spatial variability during and after a PM Event. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2016, 16, 1416–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Woo, D.; Lee, S.-B.; Bae, G.-N. On-road measurements of ultrafine particles and associated air pollutants in a densely populated area of Seoul, Korea. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2015, 15, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukowiecki, N.; Dommen, J.; Prévôt, A.S.H.; Richter, R.; Weingartner, E.; Baltensperger, U. A mobile pollutant measurement laboratory measuring gas phase and aerosol ambient concentrations with high spatial and temporal resolution. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 5569–5579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etyemezian, V.; Kuhns, H.; Nikolich, G. Precision and repeatability of the TRAKER vehicle-based paved road dust emission measurement. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 2953–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etyemezian, V.; Kuhns, H.; Gillies, J.; Chow, J.; Hendrickson, K.; McGown, M.; Pitchford, M. Vehicle-based road dust emissions measurement (Ш): Effect of speed, traffic volume, location, and season on PM10 road dust emissions in the Treasure Valley. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 4583–4593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etyemezian, V.; Kuhns, H.; Gillies, J.; Green, M.; Pitchford, M.; Watson, J. Vehicle-based road dust emissions measurements: I—Methods and calibration. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 4559–4571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhns, H.; Etyemezian, V.; Green, M.; Hendrickson, K.; McGrown, M.; Barton, K.; Pitchford, M. Vehicle based road dust emissions measurements—Part II: Effect of precipitation, wintertime road sanding, and street sweepers on inferred PM10 emission potentials from paved and unpaved roads. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 4573–4582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhns, H.; Etyemezian, V.; Landwehr, D.; MacDougall, C.; Pitchford, M.; Green, M. Testing re-entrained aerosol kinetic emissions from roads (TRAKER): A new approach to infer silt loading on roadways. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 2815–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirjola, L.; Parviainen, H.; Hussein, T.; Valli, A.; Hameri, K.; Aalto, P.; Virtanen, A.; Keskinen, J.; Pakkanen, T.; Makela, J.; et al. Sniffer—A novel tool for chasing vehicles and measuring traffic pollutants. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 3625–3635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirjola, I.; Paasonen, P.; Pfeiffer, D.; Hussein, T.; Hameri, K.; Koskentalo, T.; Virtanen, A.; Ronkko, T.; Keskinen, J.; Pakkanen, T.; et al. Dispersion of particles and trace gases nearby a city highway: Mobile laboratory measurements in Finland. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 867–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirjola, L.; Kupiainen, K.J.; Perhoniemi, P.; Tervahattu, H.; Vesala, H. Nonexhaust emission measurement system of the mobile laboratory SNIFFER. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 4703–4713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirjola, L.; Lähde, T.; Niemi, J.; Kousa, A.; Rönkkö, T.; Karjalainen, P.; Keskinen, J.; Frey, A.; Hillamo, R. Spatial and temporal characterization of traffic emissions in urban microenvironments with a mobile laboratory. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 63, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupiainen, K.; Pirjola, L. Vehicle non-exhaust emissions from the tyre-road interface e effect of stud properties and traction sanding. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 4141–4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lähde, T.; Niemi, J.V.; Kousa, A.; Rönkkö, T.; Karjalainen, P.; Keskinen, J.; Frey, A.; Hillamo, R.; Pirjola, L. Mobile particle and NOx emission characterization at helsinki downtown: Comparison of different traffic flow areas. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2014, 14, 1372–1382. [Google Scholar]
- Hussein, T.; Johansson, C.; Karlsson, H.; Hansson, H.C. Factors affecting nontailpipe aerosol particle missions from paved roads: On-road measurements in Stockholm, Sweden. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 688–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirjola, L.; Johansson, C.; Kupiainen, K.; Stojiljkovic, A.; Karlsson, H.; Hussein, T. Road dust emissions from paved roads measured using different mobile systems. J. Air Waste Manag. 2010, 60, 1422–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagemann, R.; Corsmeier, U.; Kottmeier, C.; Rinke, R.; Wieser, A.; Vogel, B. Spatial variability of particle number concentrations and NOx in the Karlsruhe (Germany) area obtained with the mobile laboratory ‘AERO-TRAM’. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 94, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellini, S.; Moroni, B.; Cappelletti, D. PMetro: Measurement of urban aerosols on a mobile platform. Measurement 2014, 49, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, T.; Boor, B.E.; Dos Santos, V.N.; Kangasluoma, J.; Petäjä, T.; Lihavainen, H. Mobile aerosol measurement in the eastern Mediterranean—A utilization of portable instruments. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2017, 17, 1775–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.Y.; Jiang, H.; Zhao, H.R.; Stephens, B. Mobile monitoring of personal NOx exposures during scripted daily activities in Chicago, IL. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2017, 17, 1999–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Targino, A.C.; Gibson, M.D.; Krecl, P.; Rodrigues, M.V.C.; dos Santos, M.M.; de Paula Correa, M. Hotspots of black carbon and PM2.5 in an urban area and relationships to traffic characteristics. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossche, V.J.; Peter, J.; Verwaeren, J.; Botteldooren, D.; Theunis, J.; De Baets, B. Mobile monitoring for mapping spatial variation in urban air quality: Development and validation of a methodology based on an extensive dataset. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 105, 148–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Kaul, D.; Wong, K.; Westerdahl, D.; Sun, L.; Ho, K.; Tian, L.; Brimblecombe, P.; Ning, Z. Heterogeneity of passenger exposure to air pollutants in public transport microenvironments. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 109, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruths, M.; von Bismarck-Osten, C.; Weber, C. Measuring and modelling the local-scale spatio-temporal variation of urban particle number size distributions and black carbon. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 96, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xing, Z.; Zhao, S.; Zheng, M.; Mu, C.; Du, K. Are emissions of black carbon from gasoline vehicles overestimated? Real-time, in situ measurement of black carbon emission factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 547, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, J.; Theunis, J.; Van Poppel, M.; Berghmans, P. Monitoring PM10 and ultrafine particles in urban environments using mobile measurements. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2013, 13, 509–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, N.; Lukac, M.; Ahmed, T.; Kar, A.; Siva, P.; Honles, T.; Leong, I.; Rehman, I.H.; Schauer, J.; Ramanathan, V. A cellphone based system for global monitoring of black carbon. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 4481–4487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MegaSense. Available online: https://www.helsinki.fi/en/researchgroups/sensing-and-analytics-of-air-quality (accessed on 7 June 2019).
- Hussein, T.; Juwhari, H.; Al Kuisi, M.; Alkattan, H.; Lahlouh, B.; Al-Hunaiti, A. Accumulation and coarse mode aerosol concentrations and carbonaceous contents in the urban background atmosphere in Amman—Jordan. Arab. J. GeoSci. 2018, 11, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, T.; Halayka, M.; Abu Al-Ruz, R.; Abdullah, H.; Mølgaard, B.; Petäjä, T. Fine particle number concentrations in Amman and Zarqa during spring 2014. Jordan J. Phys. 2016, 9, 31–46. [Google Scholar]
- Hussein, T.; Rasha, A.; Tuukka, P.; Heikki, J.; Arafah, D.; Kaarle, H.; Markku, K. Local air pollution versus short–range transported dust episodes: A comparative study for submicron particle number concentration. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2011, 11, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, T.; Betar, A. Size-fractionated number and mass concentrations in the urban background atmosphere during spring 2014 in Amman—Jordan. Jordan J. Phys. 2017, 10, 51–60. [Google Scholar]
- Lihavainen, H.; Alghamdi, M.A.; Hyvärinen, A.; Hussein, T.; Neitola, K.; Khoder, M.; Abdelmaksoud, A.S.; Al-Jeelani, H.; Shabbaj, I.I.; Almehmadi, F.M. Aerosol optical properties at rural background area in Western Saudi Arabia. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 197, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafa, M.; Mohamed, A.; Ahmed, A.-R.; Nazmy, H. Mass size distributions of elemental aerosols in industrial area. J. Adv. Res. 2015, 6, 827–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munir, S.; Habeebullah, T.M.; Seroji, A.R.; Gabr, S.S.; Mohammed, A.M.F.; Abu Saud, W.; Abdou, A.E.A.; Awad, A.H.; Gabr, S.S.; Mohammed, A.M.F.; et al. Modelling particulate matter concentrations in Makkah, applying a statistical modelling approach. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2013, 13, 901–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, S.; Habeebullah, T.M.; Seroji, A.R.; Gabr, S.S.; Mohammed, A.M.F.; Morsy, E.A. Quantifying temporal trends of atmospheric pollutants in Makkah (1997–2012). Atmos. Environ. 2013, 77, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waked, A.; Seigneur, C.; Couvidat, F.; Kim, Y.; Sartelet, K.; Afif, C.; Borbon, A.; Formenti, P.; Sauvage, S. Modeling air pollution in Lebanon: Evaluation at a suburban site in Beirut during summer. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 5873–5886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadros, M.T.Y.; Madkour, M.; El-Metwally, M. Size distribution of aerosol particles: Comparison between agricultural and industrial areas in Egypt. Renew. Energy 1999, 17, 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifford, S.; Mazaheri, M.; Salimi, F.; Ezz, W.N.; Yeganeh, B.; Low-Choy, S.; Walker, K.; Mengersen, K.; Marks, G.B.; Morawska, L. Effects of exposure to ambient ultrafine particles on respiratory health and systemic inflammation in children. Environ. Int. 2018, 114, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobías, A.; Rivas, I.; Reche, C.; Alastuey, A.; Rodríguez, S.; Fernández-Camacho, R.; Sánchez de la Campa, A.M.; de la Rosa, J.; Sunyer, J.; Querol, X. Short-term effects of ultrafine particles on daily mortality by primary vehicle exhaust versus secondary origin in three Spanish cities. Environ. Int. 2018, 111, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Hu, B.; Liu, Y.; Xu, J.; Yang, G.; Xu, D.; Chen, C. Beyond PM2.5: The role of ultrafine particles on adverse health effects of air pollution. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Gen. Subj. 2016, 1860, 2844–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Chancellor, G.; Evenstad, J.; Farnsworth, J.; Hase, A.; Olson, G.; Sreenath, A.; Agarwal, J. A novel optical instrument for estimating size segregated aerosol mass concentration in real time. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 939–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maricq, M.M. Monitoring Motor Vehicle PM Emissions: An Evaluation of Three Portable Low-Cost Aerosol Instruments. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, A.; Chang, D.P.Y.; Kleeman, M.J.; Perry, K.; Cahill, T.A.; Dutcher, D.; McDougal, E.M.; Stroud, K. Comparison of real-time instruments used to monitor airborne particulate matter. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2001, 51, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyarku, M.; Mazaheri, M.; Jayaratne, R.; Dunbabin, M.; Rahman, M.M.; Uhde, E.; Morawska, L. Mobile phones as monitors of personal exposure to air pollution: Is this the future? PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.H.; Lin, M.H. Real-time performance of the micro-aeth AE51 and the effects of aerosol loading on its measurement results at a traffic site. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2013, 13, 1853–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Yan, B.; Ross, J.; Zhang, D.; Kinney, P.L.; Perzanowski, M.S.; Jung, K.; Miller, R.; Chillrud, S.N. Validation of MicroAeth® as a black carbon monitor for fixed-site measurement and optimization for personal exposure characterization. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2014, 14, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hämeri, K.; Koponen, I.K.; Aalto, P.P.; Kulmala, M. The particle detection efficiency of the TSI3007 condensation particle counter. Aerosol Sci. 2002, 33, 1463–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Mazaheri, M.; Clifford, S.; Morawska, L. Estimate of main local sources to ambient ultrafine particle number concentrations in an urban area. Atmos. Res. 2017, 194, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, A.; Kumar, P. A review of fundamental drivers governing the emissions, dispersion and exposure to vehicle-emitted nanoparticles at signalised traffic intersections. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 97, 316–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, T.; Mølgaard, B.; Hannuniemi, H.; Martikainen, J.; Järvi, L.; Wegner, T.; Ripamonti, G.; Weber, S.; Vesala, T.; Hämeri, K. Fingerprints of the urban particle number size distribution in Helsinki, Finland: Local versus regional characteristics. Boreal Environ. Res. 2014, 19, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Padro-Martinez, L.T.; Patton, A.P.; Trull, J.B.; Zamore, W.; Brugge, D.; Durant, J.L. Mobile monitoring of particle number concentration and other traffic-related air pollutants in a near-highway neighbourhood over the course of a year. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 61, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussein, T.; Puustinen, A.; Aalto, P.P.; Mäkelä, J.M.; Hämeri, K.; Kulmala, M. Urban aerosol number size distributions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2004, 4, 391–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krecl, P.; Johansson, C.; Créso Targino, A.; Ström, J.; Burman, L. Trends in black carbon and sizeresolved particle number concentrations and veihicle emission factors under realworld conditions. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 165, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, T.; Alghamdi, M.A.; Khoder, M.; AbdelMaksoud, A.S.; Al-Jeelani, H.; Goknil, M.K.; Shabbaj, I.I.; Almehmadi, F.M.; Hyvärinen, A.; Lihavainen, H.; et al. Particulate matter and number concentrations of particles larger than 0.25 µm in the urban atmosphere of Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2014, 14, 1383–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backman, J.; Rizzo, L.V.; Hakala, J.; Nieminen, T.; Manninen, H.E.; Morais, F.; Aalto, P.P.; Siivola, E.; Carbone, S.; Hillamo, R.; et al. On the diurnal cycle of urban aerosols, black carbon and the occurrence of new particle formation events in springtime São Paulo, Brazil. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 11733–11751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.C.; Chou, C.C.K.; Chan, C.C.; Lee, C.T. Temporal characteristics from continuous measurements of PM2.5 and speciation at the taipei aerosol supersite from 2002 to 2008. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 1088–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.Y. Characterization of ambient PM2.5 concentrations. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 2902–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Hu, M.; Lin, P.; Liu, S.; Wehner, B.; Wiedensohler, A. Particle number size distribution in the urban atmosphere of Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 7967–7980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares, G.; Johansson, C.; Strom, J.; Hasson, H.C. The role of ambient temperature for particle number concentrations in a street canyon. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 2145–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehner, B.; Wiedensohler, A. Long term measurements of submicrometer urban aerosols: Statistical analysis for correlations with meteorological conditions and trace gases. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2003, 3, 867–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehner, B.; Wiedensohler, A.; Tuch, T.M.; Wu, Z.J.; Hu, M.; Slanina, J.; Kiang, C.S. Variability of the aerosol number size distribution in Beijing, China: New particle formation, dust storms, and high continental background. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L22108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mølgaard, B.; Birmili, W.; Clifford, S.; Massling, A.; Eleftheriadis, K.; Norman, M.; Vratolis, S.; Wehner, B.; Corander, J.; Hämeri, K.; et al. Evaluation of a statistical forecast model for size-fractionated urban particle number concentrations using data from five European cities. J. Aerosol Sci. 2013, 66, 96–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragettli, M.S.; Corradi, E.; Braun-Fahrländer, C.; Schindler, C.; de Nazelle, A.; Jerrett, M.; Ducret-Stich, R.E.; Künzli, N.; Phuleria, H.C. Commuter exposure to ultrafine particles in different urban locations, transportation modes and routes. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 77, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco, E.; Tan, S.H. Particles exposure while sitting at bus stops of hot and humid Singapore. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 142, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.H.; Chang, H.P.; Hsieh, C.J. Short-term exposure to PM10, PM2.5, ultrafine particles and CO2 for passengers at an intercity bus terminal. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 2034–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, D.B.; Ray, P.D.; Stinson, A.E.; Park, J. Determinants of exposure to fine particulate matter (PM2.5) for waiting passengers at bus stops. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 5174–5182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdi, M.R.; Bdour, A.; Tarawneh, Z. Diesel quality in Jordan: Impacts of vehicular and industrial emissions on urban air quality. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2008, 25, 1333–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudda, N.; Fruin, S.A. Carbon dioxide accumulation inside vehicles: The effect of ventilation and driving conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610–611, 1448–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leavey, A.; Reed, N.; Patel, S.; Bradley, K.; Kulkarni, P.; Biswas, P. Comparing on-road Real-time Simultaneous in-cabin and Outdoor Particulate and Gaseous Concentrations for a Range of Ventilation Scenarios. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 166, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Lee, E.S.; Zhou, B.; Liu, J.; Zhu, Y. Effects of the window openings on the micro-environmental condition in a school bus. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 167, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alameddine, I.; Abi Esber, L.; Bou Zeid, E.; Hatzopoulou, M.; El-Fadel, M. Operational and environmental determinants of in-vehicle CO and PM2.5 exposure. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 551–552, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, H.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, H.; Feng, L. Analysis of PM2.5 distribution and transfer characteristics in a car cabin. Energy Build. 2016, 127, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.S.; Stenstrom, M.K.; Zhu, Y. Ultrafine particle infiltration into passenger vehicles. Part I: Experimental evidence. Transp. Res. D 2015, 38, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.S.; Stenstrom, M.K.; Zhu, Y. Ultrafine particle infiltration into passenger vehicles. II: Model analysis. Transp. Res. D 2015, 38, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, S.; Yu, N.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Y. Measuring and modeling air exchange rates inside taxi cabs in Los Angeles, California. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 122, 628–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abi-Esber, L.; El-Fadel, M. Indoor to outdoor air quality associations with self pollution implications inside passenger car cabins. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 81, 450–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigazzi, A.Y.; Figliozzi, M.A. Impacts of freeway traffic conditions on in-vehicle exposure to ultrafine particulate matter. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 60, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudda, N.; Eckel, S.P.; Knibbs, L.D.; Sioutas, C.; Delfino, R.J.; Fruin, S.A. Linking in-vehicle ultrafine particle exposures to on-road concentrations. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 59, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knibbs, L.D.; de Dear, R.J. Exposure to ultrafine particles and PM2.5 in four Sydney transport modes. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 3224–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattinson, W.; Longley, I.; Kingham, S. Using mobile monitoring to visualise diurnal variation of traffic pollutants across two near-highway neighbourhoods. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 94, 782–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Lei, X.N.; Xiu, G.L.; Gao, C.Y.; Gao, S.; Qian, N.S. Personal exposure to black carbon during commuting in peak and off-peak hours in Shanghai. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 524–525, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacNaughton, P.; Melly, S.; Vallarino, J.; Adamkiewicz, G.; Spengler, J.D. Impact of 731 bicycle route type on exposure to traffic-related air pollution. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 490, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Rivas, I.; Sachdeva, L. Exposure of in-pram babies to airborne particles during morning drop-in and afternoon pick-up of school children. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 224, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okokon, E.O.; Yli-Tuomi, T.; Turunen, A.W.; Taimisto, P.; Pennanen, A.; Vouitsis, I.; Samaras, Z.; Voogt, M.; Keuken, M.; Lanki, T. Particulates and noise exposure during bicycle, bus and car commuting: A study in three European cities. Environ. Res. 2017, 154, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazelle, A.; Fruin, S.; Westerdahl, D.; Mareinez, D.; Ripoll, A.; Kubesch, N.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M. A travel mode comparison of commuters’ exposures to air pollutants in Barcelona. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 59, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panis, I.L.; de Geus, B.; Vandenbulcke, G.; Willems, H.; Degraeuwe, B.; Bleux, N.; Mishra, V.; Thomas, I.; Meeusen, R. Exposure to particulate matter in traffic: A comparison of cyclists and car passengers. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 2263–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dons, E.; Int Panis, I.L.; Poppel, M.V.; Theunis, J.; Wets, G. Personal exposure to Black Carbon in transport microenvironments. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 55, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiros, D.C.; Lee, E.S.; Wang, R.; Zhu, Y. Ultrafine particle exposures while walking, cycling, and driving along an urban residential roadway. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 73, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ham, W.; Vijayan, A.; Schulte, N.; Herner, J.D. Commuter exposure to PM2.5, BC, and UFP in six common transport microenvironments in Sacramento, California. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 167, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boarnet, M.G.; Houston, D.; Edwards, R.; Princevac, M.; Ferguson, G.; Pan, H.; Bartolome, C. Fine particulate concentrations on sidewalks in five Southern California cities. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 4025–4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hankey, S.; Marshall, J.D. On-bicycle exposure to particulate air pollution: Particle number, black carbon, PM2.5, and particle size. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 122, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apte, J.S.; Kirchstetter, T.W.; Reich, A.H.; Deshpande, S.J.; Kaushik, G.; Chel, A.; Marshall, J.D.; Nazaroff, W.W. Concentrations of fine, ultrafine, and black carbon particles in auto-rickshaws in New Delhi, India. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 4470–4480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, R.; Gani, S.; Guttikunda, S.K.; Wilson, D.; Tiwari, G. On-road PM2.5 pollution exposure in multiple transport microenvironments in Delhi. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 123, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Xu, X.; Song, J.; Luo, Y.; Zhao, R.; Zhou, B.X.W.; Li, X.; Hao, Y. Pedestrian exposure to traffic PM on different types of urban roads: A case study of Xi’an, China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2017, 32, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Song, J.; Xu, X.; Luo, Y.; Zhao, R.; Zhou, W.; Xiang, B.; Hao, Y. Commuter exposure to particulate matter for different transportation modes in Xi’an, China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2017, 8, 940–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Deng, F.; Wu, S.; Guo, X. Comparisons of personal exposure to PM2.5 and CO by different commuting modes in Beijing, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 425, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betancourt, R.M.; Galvis, B.; Balachandran, S.; Ramos-Bonilla, J.P.; Sarmiento, O.L.; Gallo-Murcia, S.M.; Contreras, Y. Exposure to fine particulate, black carbon, and particle number concentration in transportation microenvironments. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 157, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odeh, I.; Hussein, T. Activity pattern of urban adult students in an Eastern Mediterranean Society. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, E960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussein, T.; Paasonen, P.; Kulmala, M. Activity pattern of a selected group of school occupants and their family members in Helsinki-Finland. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 425, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knibbs, L.D.; Cole-Hunter, T.; Morawska, L. A review of commuter exposure to ultrafine particles and its health effects. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 2611–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Dirks, K.N.; Salmond, J.A.; Xie, S. Determinants of spikes in ultrafine particle concentration whilst commuting by bus. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 112, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Both, A.F.; Westerdahl, D.; Fruin, S.; Haryanto, B.; Marshall, J.D. Exposure to carbon monoxide, fine particle mass, and ultrafine particle number in Jakarta, Indonesia: Effect of commute mode. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 443, 965–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Fischer, H.J.; Weiss, R.E.; Zhu, Y. Ultrafine particle concentrations in and around idling school buses. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 69, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.J.S.; Phuleria, H.C.; Webber, W.; Davey, M.; Lawson, D.R.; Ireson, R.G.; Zielinska, B.; Ondov, J.M.; Weaver, C.S.; Lapin, C.A.; et al. Quantification of self pollution from two diesel school buses using three independent methods. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 3422–3431. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhu, Y. Measurements of ultrafine particles and other vehicular pollutants inside school buses in South Texas. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knibbs, L.D.; de Dear, R.J.; Morawska, L. Effect of cabin ventilation rate on ultrafine particle exposure inside automobiles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 3546–3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costabile, F.; Alas, H.; Aufderheide, M.; Avino, P.; Amato, F.; Argentini, S.; Barnaba, F.; Berico, M.; Bernardoni, V.; Biondi, R.; et al. First results of the “Carbonaceous aerosol in Rome and Environs (CARE)” experiment: Beyond current standards for PM10. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alas, H.D.; Weinhold, K.; Costabile, F.; Di Ianni, A.; Müller, T.; Pfeifer, S.; Di Liberto, L.; Turner, J.R.; Wiedensohler, A. Methodology for high quality mobile measurement with focus on black carbon and particle mass concentrations. Atmos. Meas. Tech. Disc. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messier, K.P.; Chambliss, S.E.; Gani, S.; Alvarez, R.; Brauer, M.; Choi, J.J.; Hamburg, S.P.; Kerckhoffs, J.; La Franchi, B.; Lunden, M.M.; et al. Mapping air pollution with google street view cars: Efficient Approaches with mobile monitoring and land use regression. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 12563–12572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hankey, S.; Sforza, P.; Pierson, M. Using mobile monitoring to develop hourly empirical models of particulate air pollution in a rural Appalachian community. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 4305–4315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

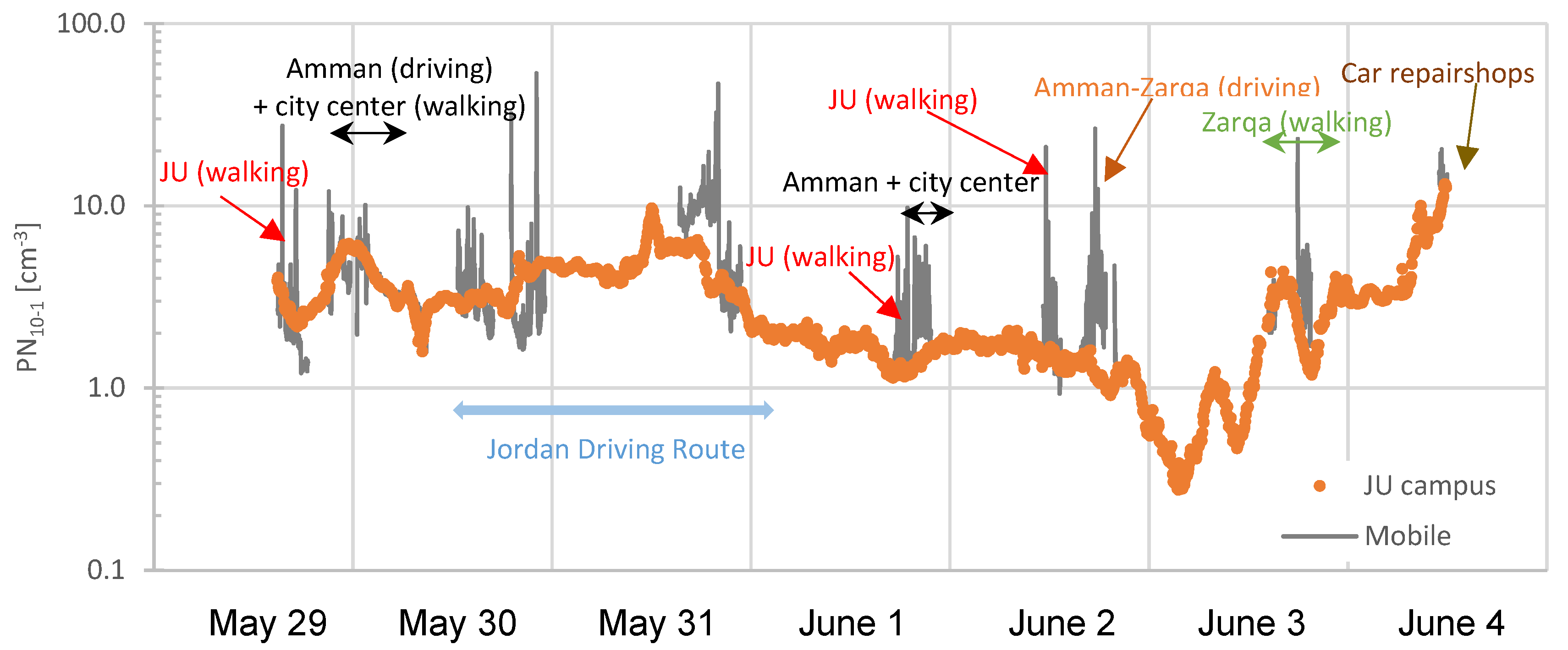
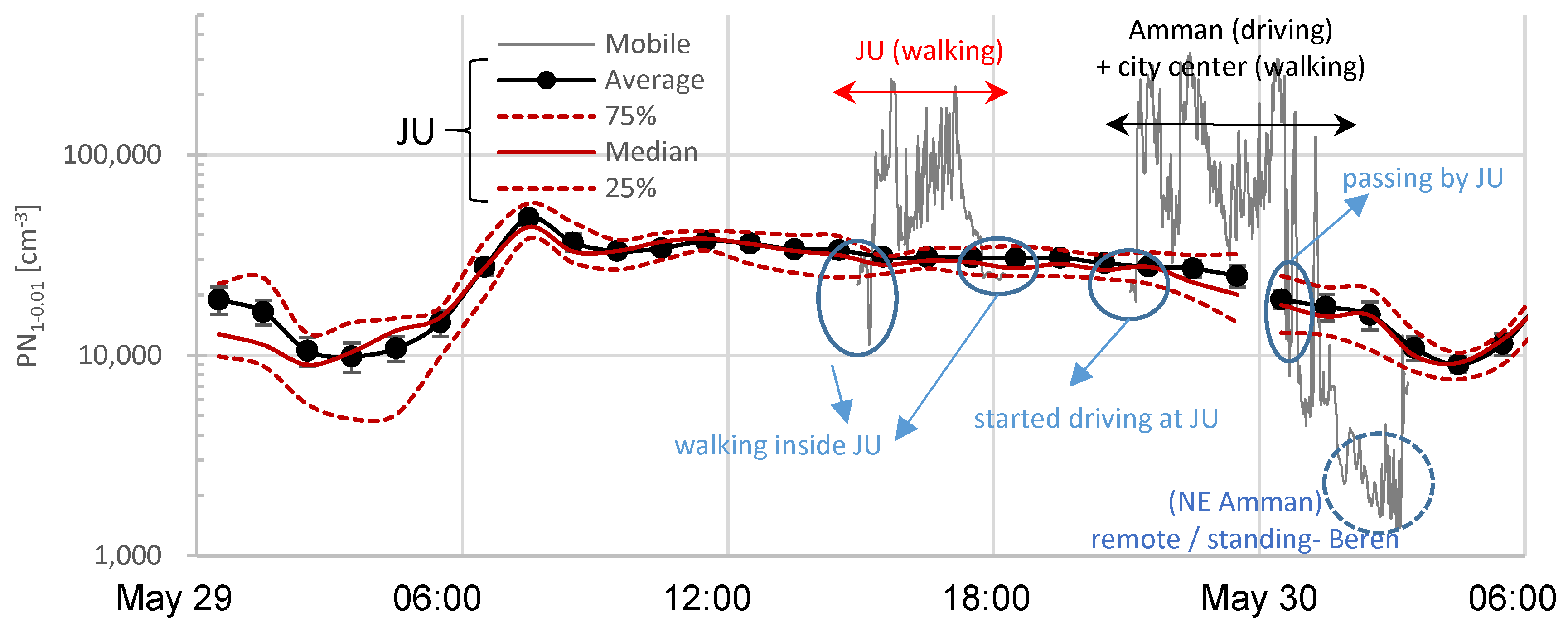
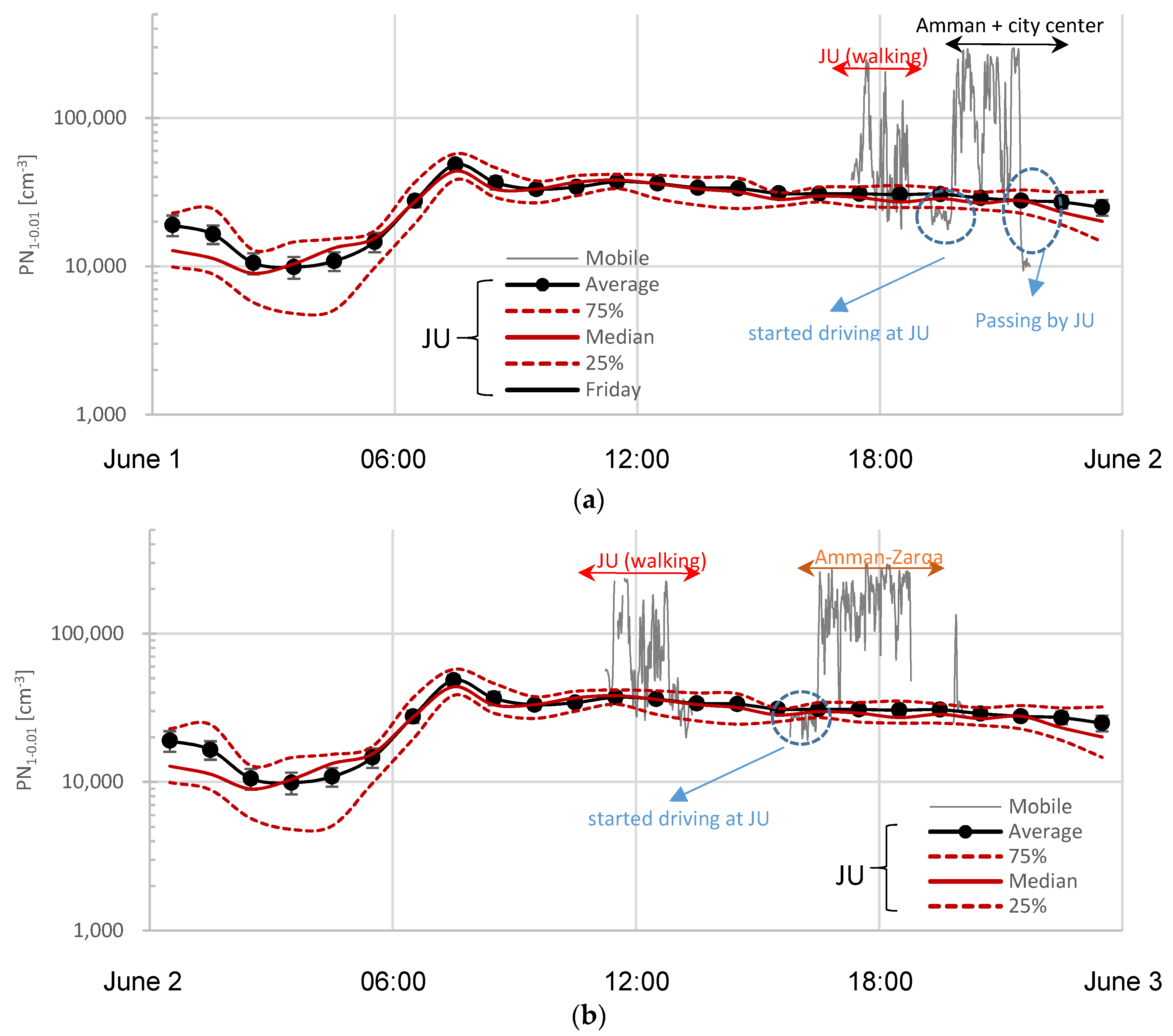
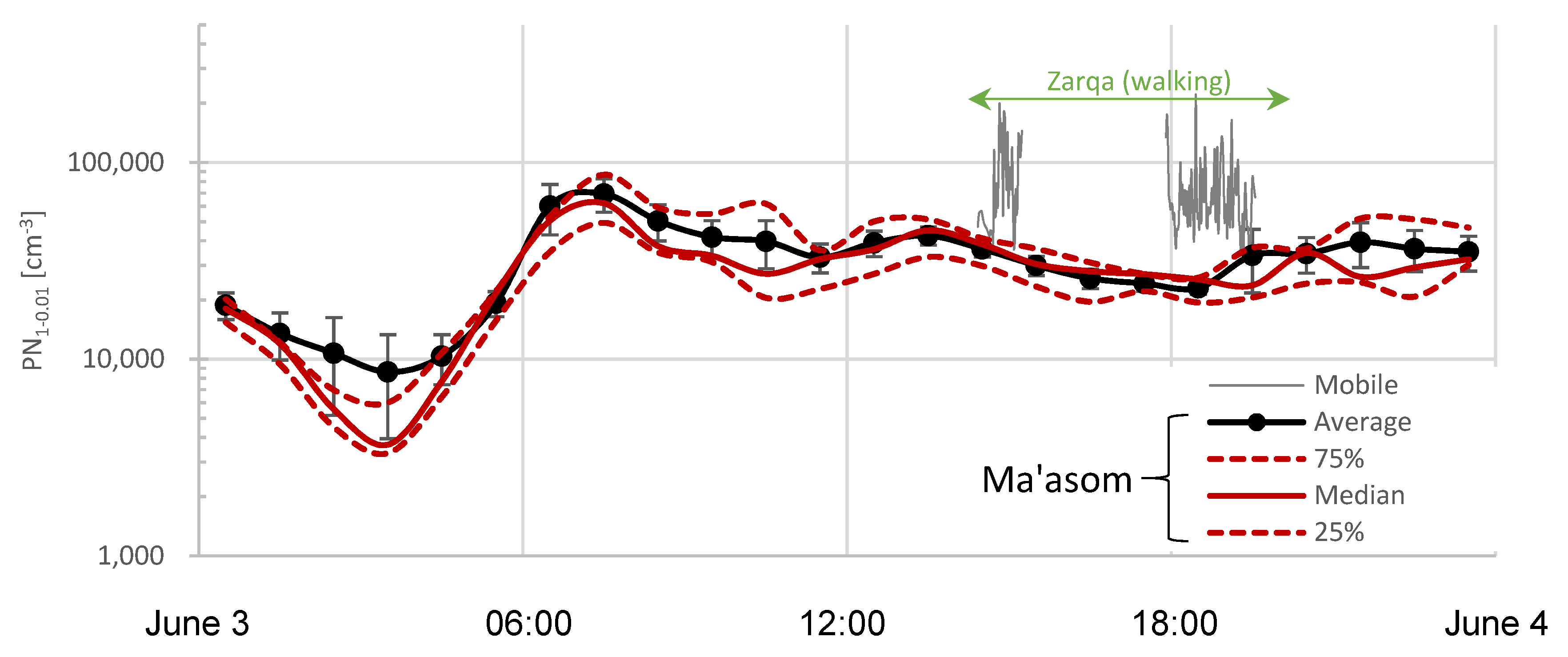
| Type | Campaign | Date | Time Period | Distance | Location | City | Classification 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stationary | Pre-campaign Ia | March 6–18 | continuous | - | JU campus 2 | Amman | UB |
| Pre-campaign Ib | April 14–30 | continuous | - | JU campus 2 | Amman | UB | |
| Pre-campaign II | May 12–18 | continuous | - | Ma’asom | Zarqa | UB | |
| Parallel-campaign | May 29–June 4 | continuous | - | JU campus | Amman | UB | |
| Mobile | Walking Ia | May 29 | 15:00–17:39 | ~7 km | JU campus | Amman | UB 3 + T 4 |
| Walking Ib | June 1 | 17:29–18:45 | ~7 km | JU campus | Amman | UB 3 + T 4 | |
| Walking Ic | June 1 | 11:21–13:03 | ~7 km | JU campus | Amman | UB 3 + T 4 | |
| Walking II | May 29 | 21:45–00:18 | ~4 km | City center | Amman | U + T | |
| Walking III | June 3 | 17:55–19:28 | ~5 km | City center | Zarqa | U + T | |
| Driving Ia | May 29 | 21:11–21:44 | ~17 km | Main roads | Amman | U/SU + T | |
| Driving Ib | May 30 | 00:19–00:36 | ~15 km | Main roads | Amman | U/SU + T | |
| Driving IIa | June 1 | 19:45–20:21 | ~18 km | Main roads | Amman | U/SU + T | |
| Driving IIb | June 1 | 21:21–21:14 | ~4 km | City center | Amman | U+T | |
| Driving IIc | June 1 | 21:14–21:27 | ~11 km | Main roads | Amman | U/SU + T | |
| Driving III | June 2 | 16:51–20:00 | ~67 km | Main roads | Amman/Zarqa | U/SU/R + T | |
| Driving IV | June 4 | 11:01–11:52 | ~2.3 km | Repair shop | Amman | U + T | |
| Remote Ia | May 30 | 00:36–00:51 | ~9 km | Beren | Amman/Zarqa | R | |
| Remote Ia | May 30 | 01:14–01:24 | ~9 km | Beren | Amman/Zarqa | R | |
| Standing | Remote Ib | May 30 | 00:52–01:13 | - | Beren | Amman + Zarqa | R |
| Country | City | Mobile Setup | BC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nazelle et al. [90] | Spain | Barcelona | Walking, biking, car/bus | 6–17 |
| Okokon et al. [89] | Greece | Thessaloniki | In-car 1 | 11 |
| Okokon et al. [89] | Finland | Helsinki | Bike, bus, and car | 3–8 |
| Dons et al. [92] | Belgium | Flanders | In train | 2.4 |
| Biking/walking | 3.6 | |||
| car/bus/metro | 6–7 | |||
| Targino et al. [25] | Brazil | Mid-sized city | On-bike 2 | ~8 |
| On-bike 3 | 6 | |||
| Ham et al. [94] | USA | Sacramento, California | Car | 0.5 |
| Bus | 0.95 | |||
| Light-rail | 0.25 | |||
| Train | 2.54 | |||
| Bike | 0.71 | |||
| Hankey and Marshall [96] | USA | Minneapolis, Minnesota | On-bike 4 | ~2.5 (0.7) |
| MacNaughton et al. [87] | USA | Boston | Bike lanes 5 | 2.4 |
| Bike paths 6 | 1.7 | |||
| Background | 0.6 | |||
| Apte et al. [97] | India | New Delhi | Auto-rickshaw 7 | 42 |
| Auto-rickshaw 8 | 85 | |||
| Li et al. [86] | China | Xuhui, Shanghai | Taxi | 8.6 |
| Bus | 7.3 | |||
| Subway | 9.4 | |||
| Cycling | 6.6 | |||
| Walking | 5.6 |
| Country | City | Mobile Setup | UFP | Fine | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nazelle et al. [90] | Spain | Barcelona | Walking, biking, car/bus | 51–120 | - |
| Okokon et al. [89] | Greece | Thessaloniki | On-bus | - | 50 |
| In-car 1 | - | - | |||
| In-car 2 | - | 80 | |||
| Okokon et al. [89] | Finland | Helsinki | Bike, bus, and car | - | 10–40 |
| Kumar et al. [88] | UK | Surrey | Babies prams | - | up to 10 |
| Ragettli et al. [68] | Switzerland | Basel | In-car | 32 | - |
| On-bike | 23 | - | |||
| Walking | 19 | - | |||
| Public transportation | 14–19 | - | |||
| Panis et al. [91] | Belgium | Brussels 3 | On-bike/in-car | - | ~30 |
| Wallonia 4 | On-bike/in-car | - | ~12 | ||
| Flanders 5 | On-bike/in-car | - | 10 | ||
| Pattinson et al. [85] | N. Zealand | S. Auckland | On-bike | 5–40 | - |
| Quiros et al. [93] | USA | S. Monica, California | Walking 6 | 12–28 | - |
| Ham et al. [94] | USA | Sacramento, California | Car | 7.9 | - |
| Bus | 13 | - | |||
| Light-rail | 5.5 | - | |||
| Train | 42 | - | |||
| Bike | 22 | - | |||
| Hankey and Marshall [96] | USA | Minneapolis Minnesota | On-bike 7 | - | ~3.3 (~1.7) |
| Apte et al. [97] | India | New Delhi | Auto-rickshaw 8 | 280 | - |
| Auto-rickshaw 9 | 650 | - |
| Country | City | Mobile Setup | PM10 | PM2.5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abi-Esber and El-Fadel [81] | Lebanon | Beirut | In-car 1 | - | 38–93 |
| Nazelle et al. [90] | Spain | Barcelona | Walking, biking, car/bus | - | 21–35 |
| Okokon et al. [89] | Greece | Thessaloniki | On-bus | 131 | 85 |
| Okokon et al. [89] | Finland | Helsinki | Bike, bus, and car | 40 | 30 |
| Kumar et al. [88] | UK | Surrey | Babies prams | ~40 | ~18 |
| Panis et al. [91] | Belgium | Brussels 4 | On-bike/in-car | 62/35 | - |
| Wallonia 5 | On-bike/in-car | 48/32 | - | ||
| Flanders 6 | On-bike/in-car | 72/75 | - | ||
| Pattinson et al. [85] | N. Zealand | Auckland | On-bike | 10–30 | - |
| On-bike 9 | - | ~8.5 | |||
| Quiros et al. [91] | USA | S. Monica, California | Walking 10 | - | 6–11 |
| Ham et al. [94] | USA | Sacramento, California | Car | - | 7.1 |
| Bus | - | 7.5 | |||
| Light-rail | - | 5.7 | |||
| Train | - | 32.5 | |||
| Bike | - | 9.6 | |||
| Boarnet et al. [95] | USA | Los Angeles | Commuters 11 | - | 20–70 |
| Hankey and Marshall [96] | USA | Minneapolis, Minnesota | On-bike 12 | - | ~8.7 (8.3) |
| Apte et al. [97] | India | New Delhi | Auto-rickshaw 15 | - | 190 |
| Auto-rickshaw 16 | - | 300 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hussein, T.; Saleh, S.S.A.; dos Santos, V.N.; Abdullah, H.; Boor, B.E. Black Carbon and Particulate Matter Concentrations in Eastern Mediterranean Urban Conditions: An Assessment Based on Integrated Stationary and Mobile Observations. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 323. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10060323
Hussein T, Saleh SSA, dos Santos VN, Abdullah H, Boor BE. Black Carbon and Particulate Matter Concentrations in Eastern Mediterranean Urban Conditions: An Assessment Based on Integrated Stationary and Mobile Observations. Atmosphere. 2019; 10(6):323. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10060323
Chicago/Turabian StyleHussein, Tareq, Shatha Suleiman Ali Saleh, Vanessa N. dos Santos, Huthaifah Abdullah, and Brandon E. Boor. 2019. "Black Carbon and Particulate Matter Concentrations in Eastern Mediterranean Urban Conditions: An Assessment Based on Integrated Stationary and Mobile Observations" Atmosphere 10, no. 6: 323. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10060323
APA StyleHussein, T., Saleh, S. S. A., dos Santos, V. N., Abdullah, H., & Boor, B. E. (2019). Black Carbon and Particulate Matter Concentrations in Eastern Mediterranean Urban Conditions: An Assessment Based on Integrated Stationary and Mobile Observations. Atmosphere, 10(6), 323. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10060323






