Generation and Analysis of Gridded Visibility Data in the Arctic
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Introduction of the Technology and Method
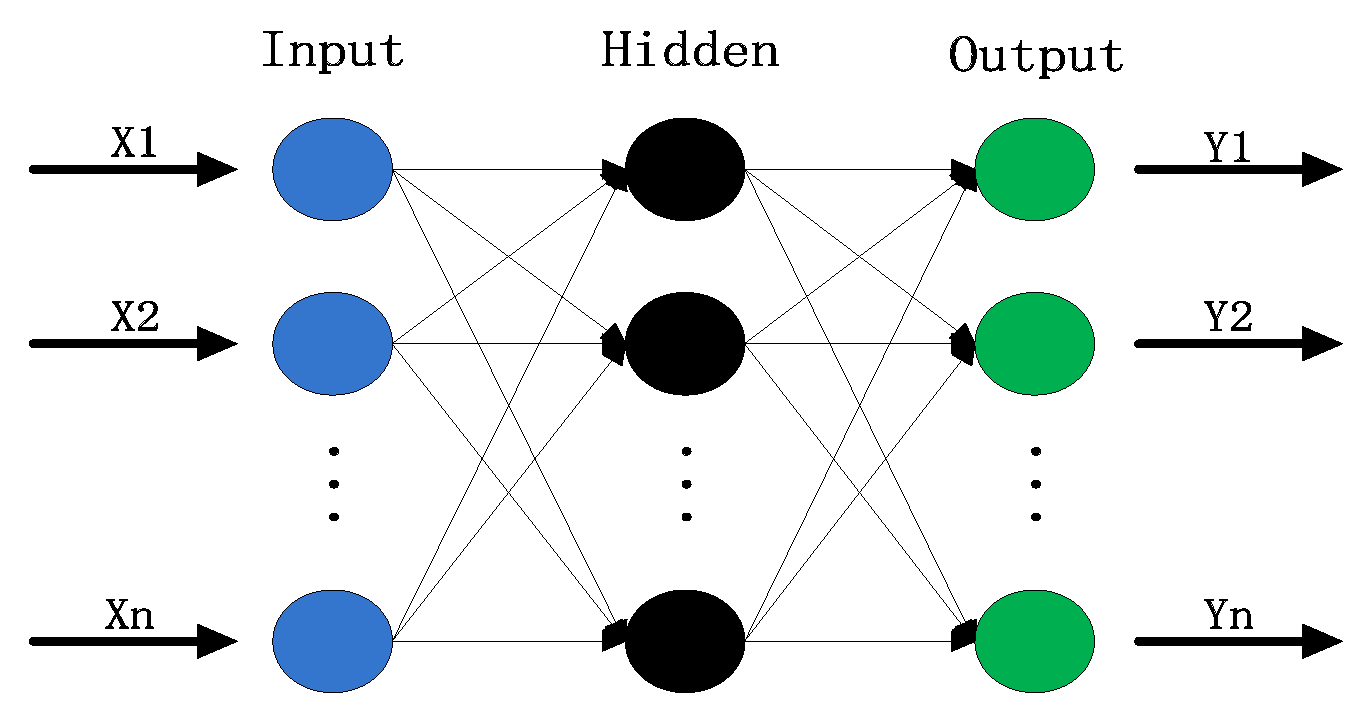
2.1. Artificial Neural Network Technology
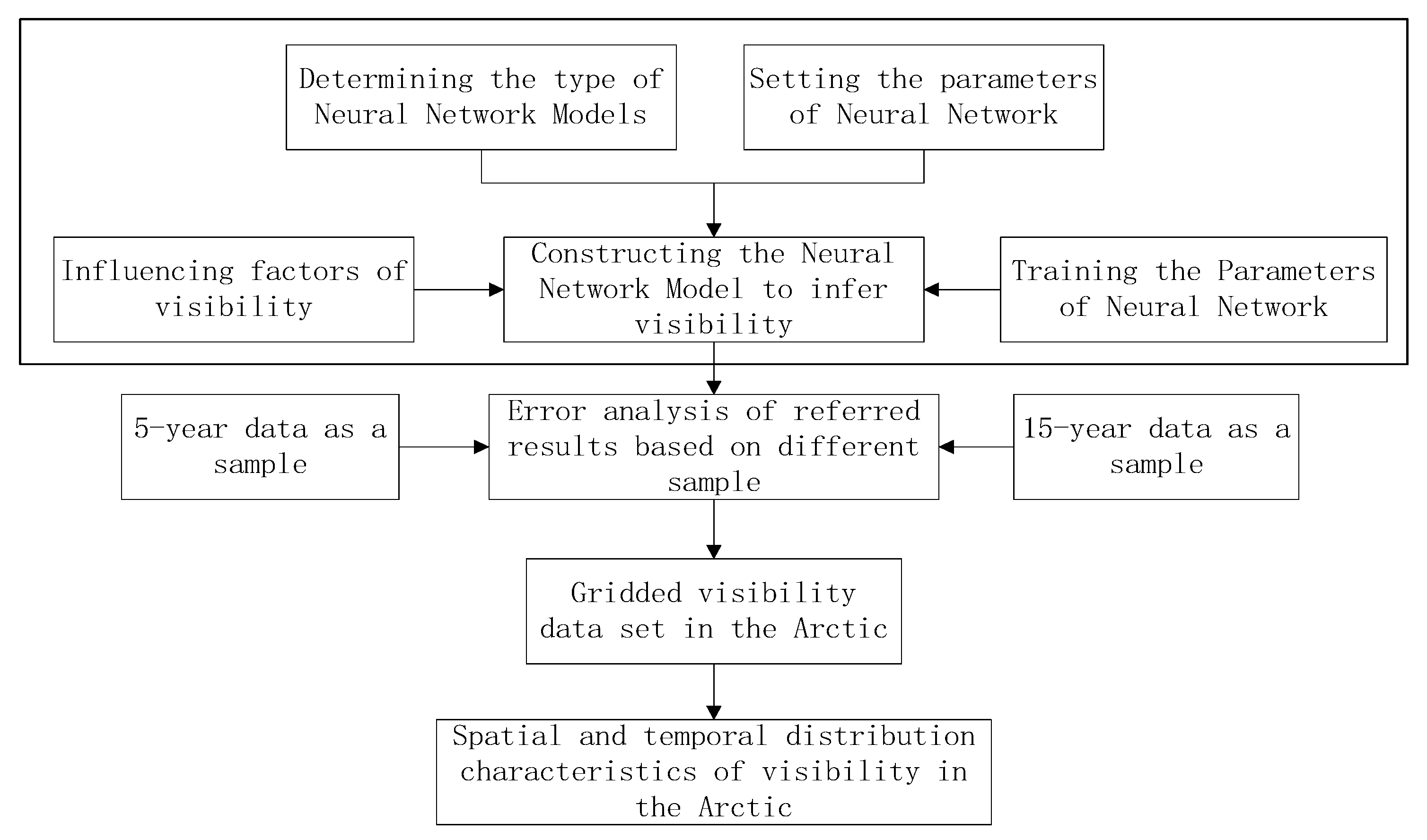
2.2. Technical Process of This Study
3. Data Preparation
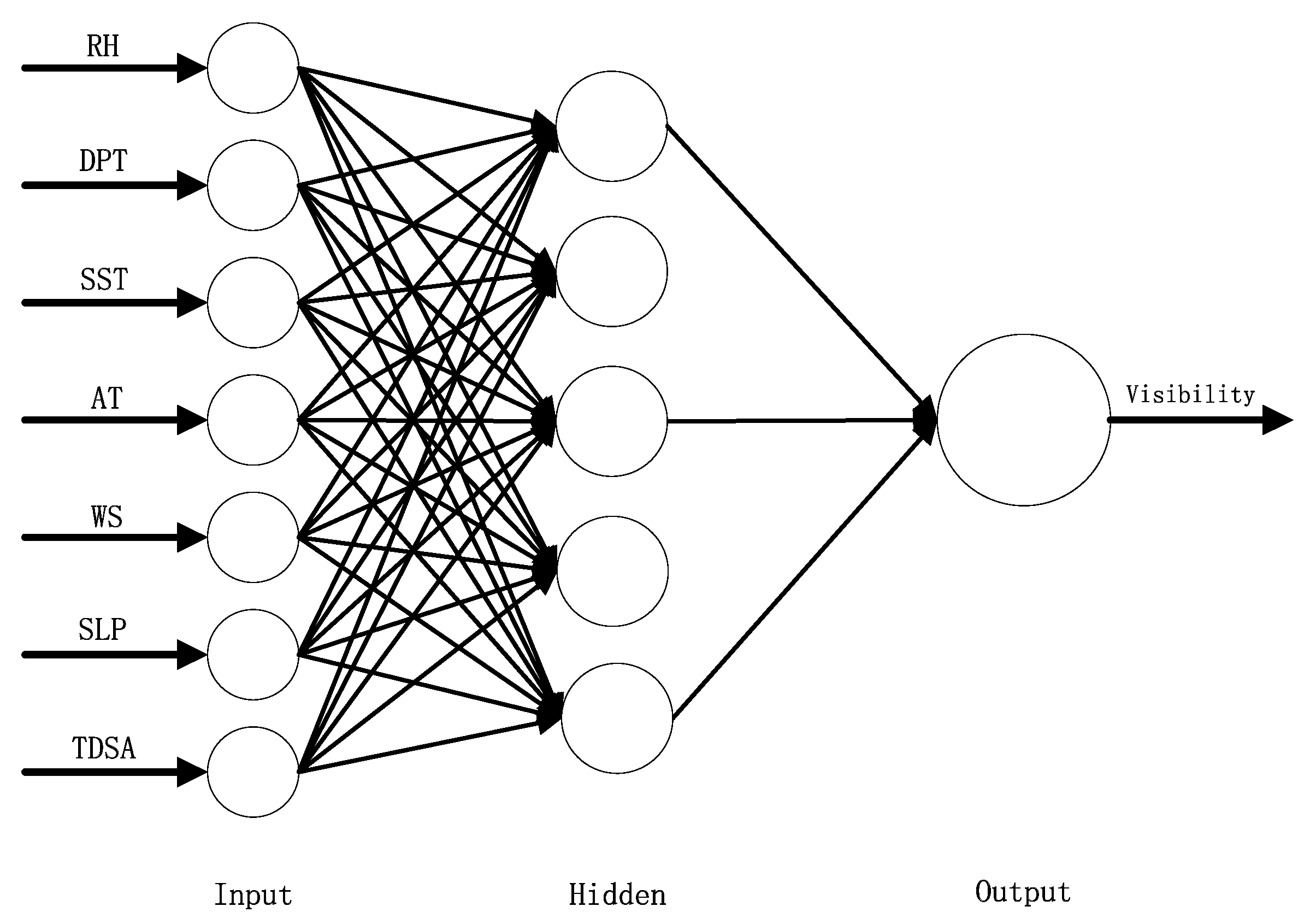
3.1. Influencing Factors on Visibility
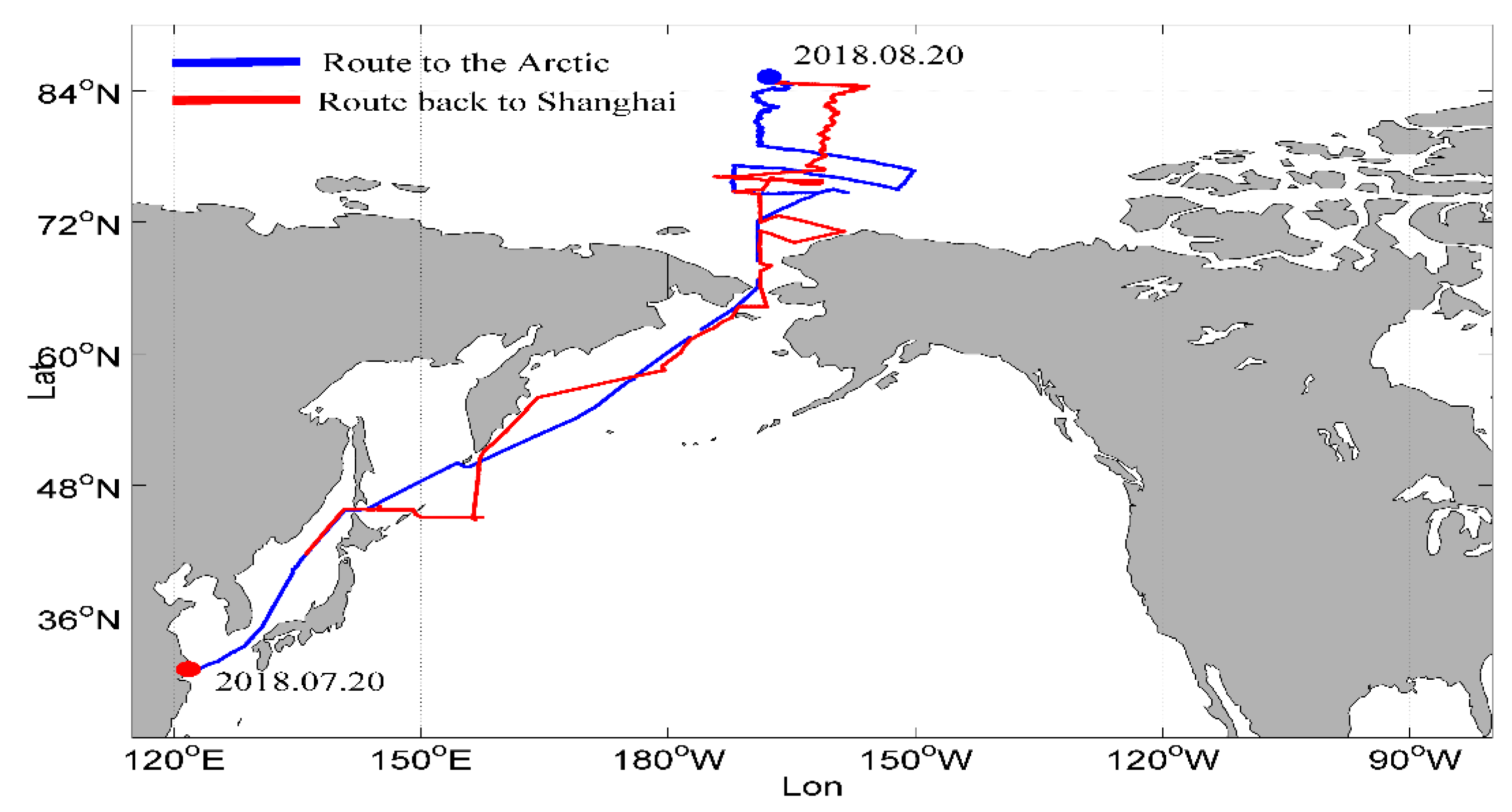
3.2. Introduction of the Data Used
4. Analyzing the Error of Referred Visibility
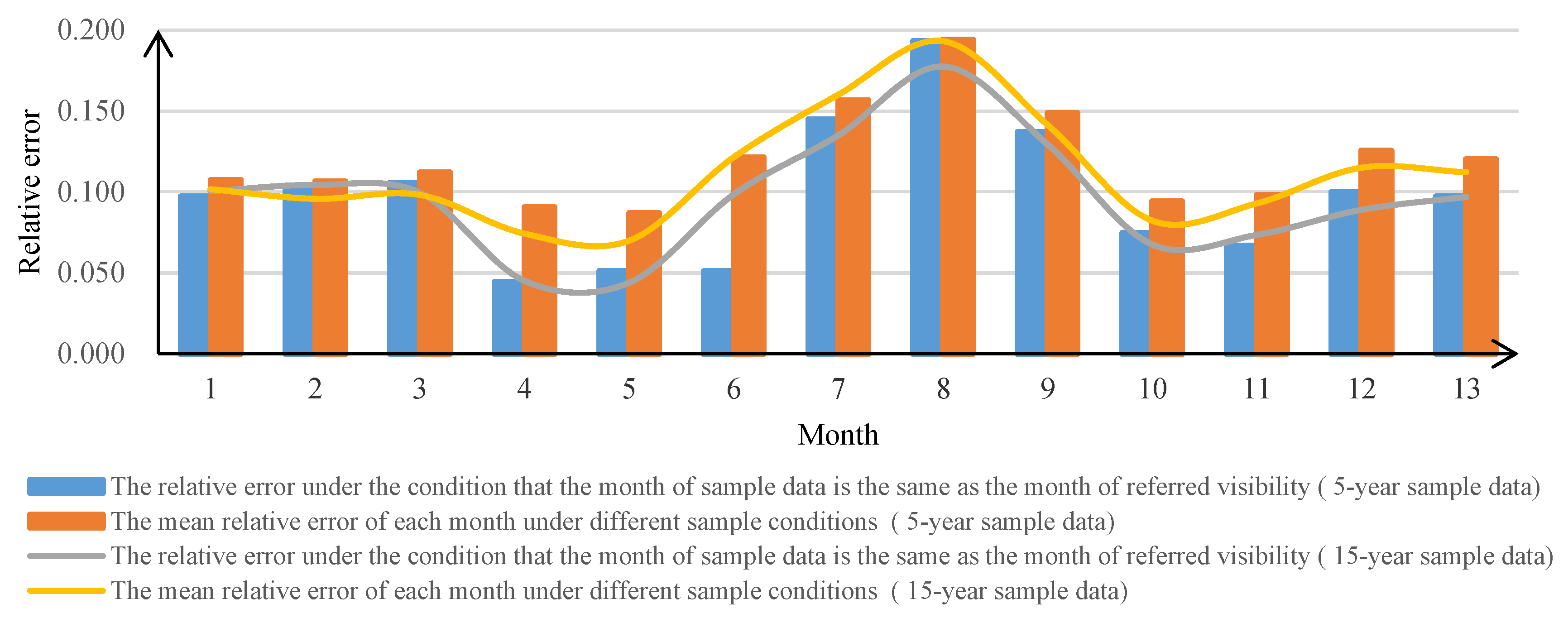
4.1. Reasoning Test and Error Analysis under Different Sample Conditions
4.2. Effect of Sample Data Quantity on the Accuracy of Referred Visibility
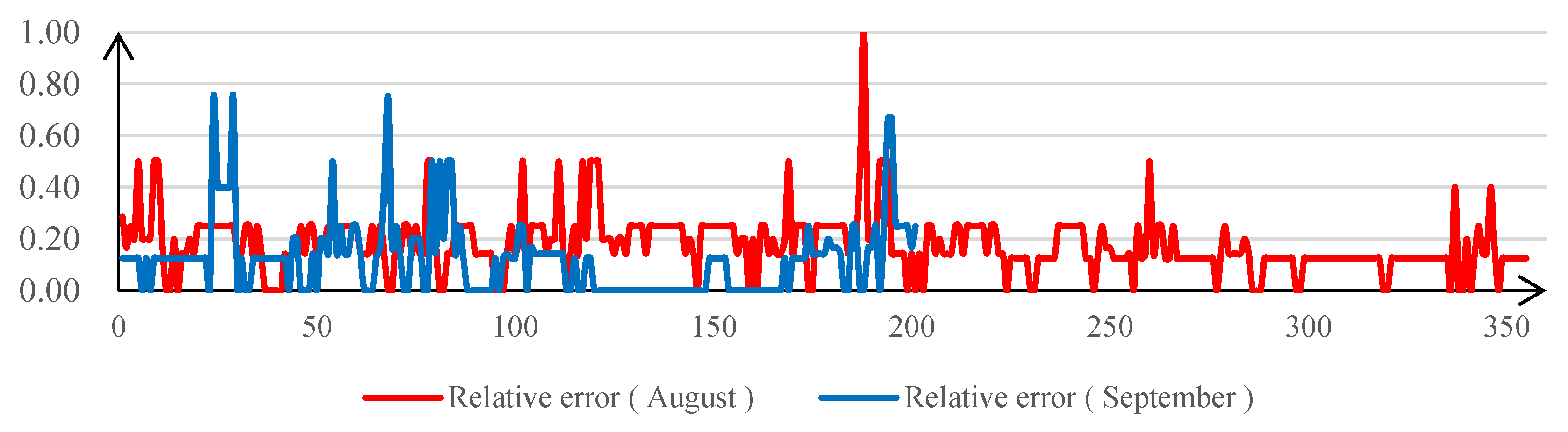
4.3. Test of the Model Using Data from CNASE
5. Analysis of the Visibility Characteristics in the Arctic
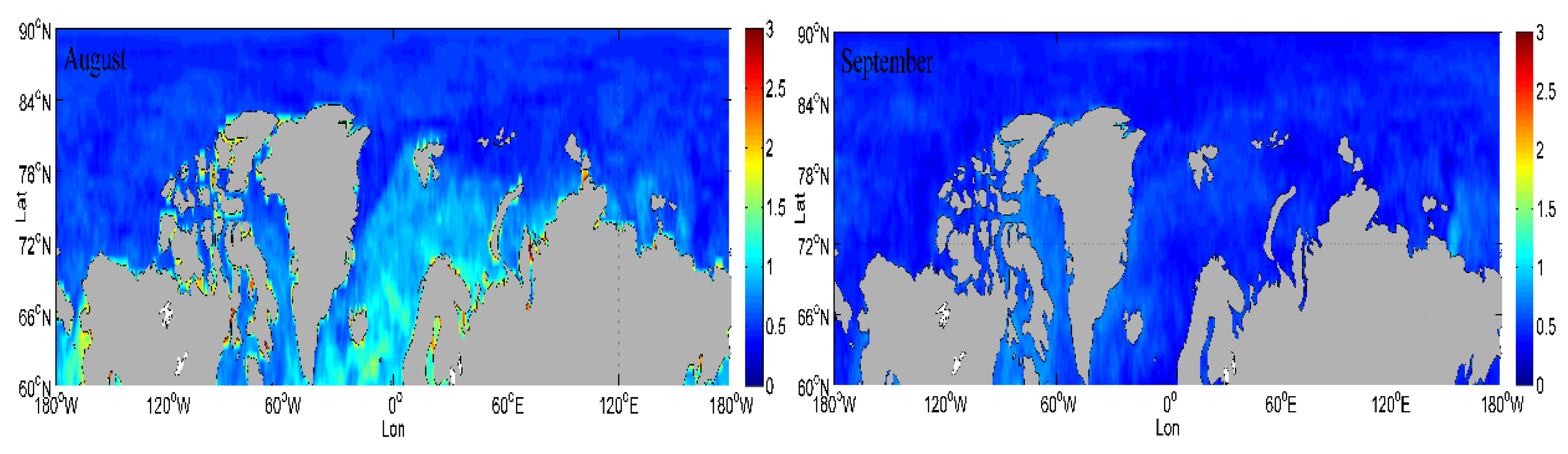
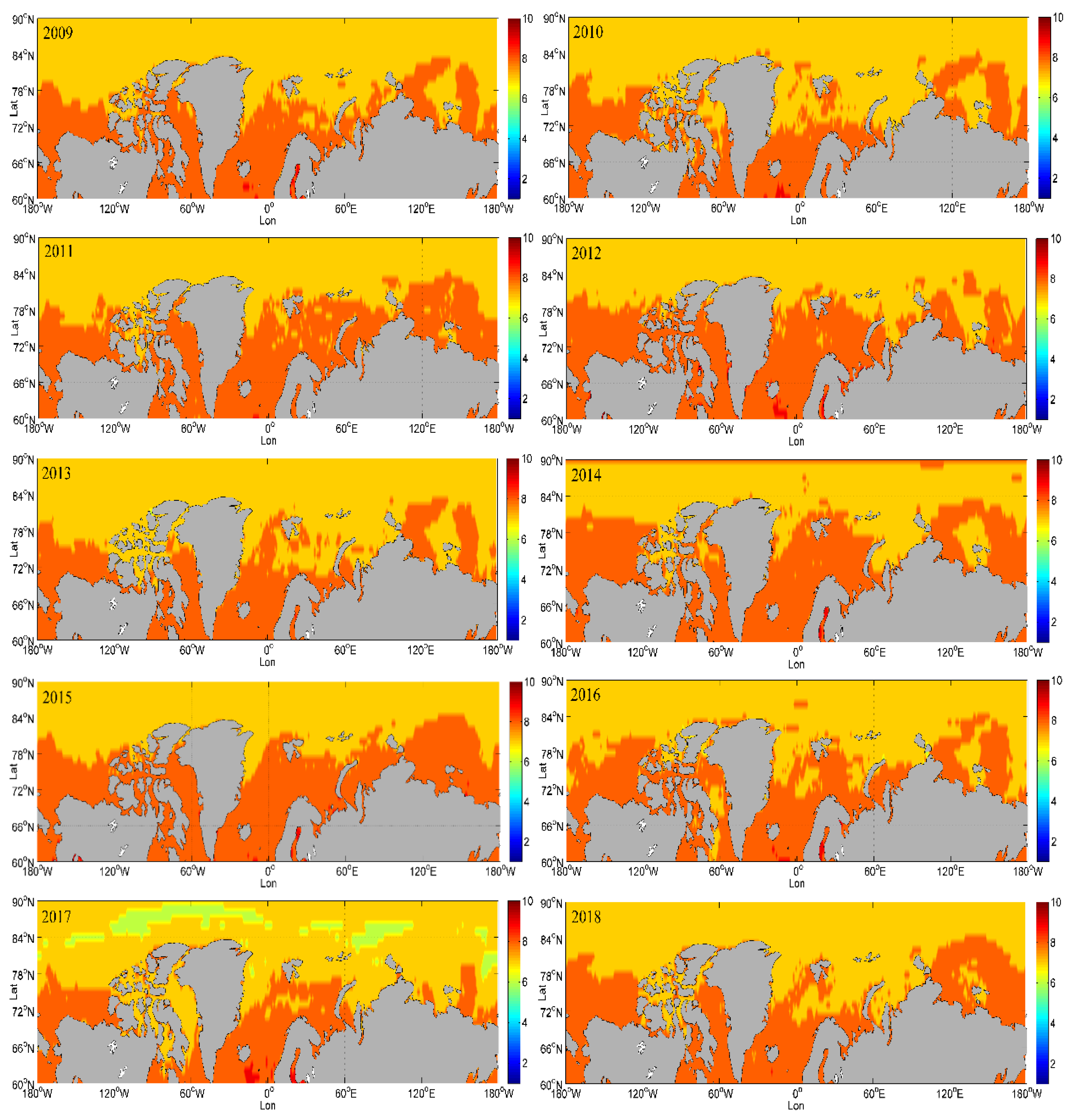
5.1. Temporal Changes of Visibility in the Arctic
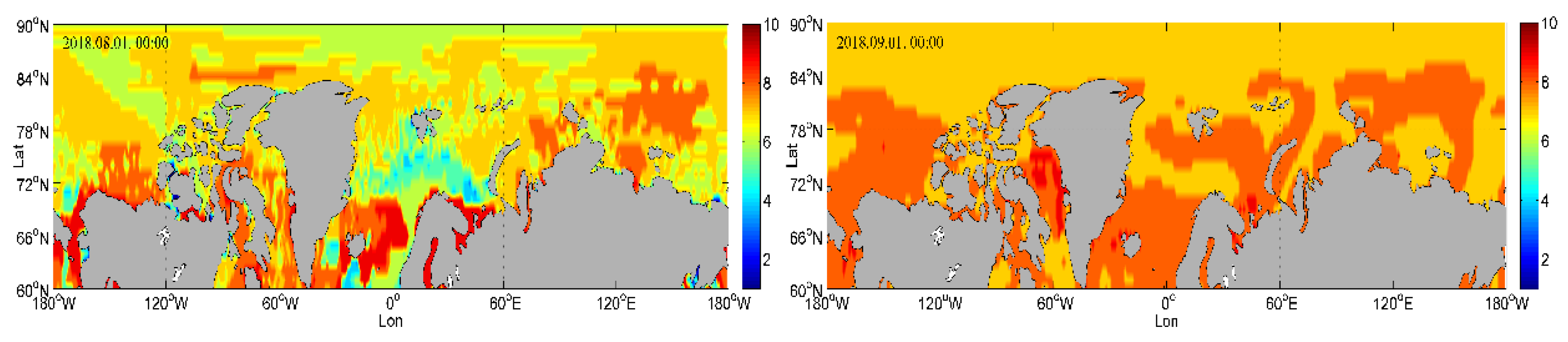
5.2. Spatial Changes of Visibility in the Arctic
6. Discussion and Conclusions
Reference
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gultepe, I.; Isaac, G.A.; Rasmussen, R.M.; Ungar, K. A Freezing Fog/Drizzle Event during the FRAM-S Project; SAE Technical Paper, No. 2011-38-0028; SAE International in United States: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Gultepe, I.; Sharman, R.; Williams, P.D.; Zhou, B.; Ellrod, G.; Minnis, P.; Trier, S.; Griffin, S.; Yum, S.S.; Gharabaghi, B.; et al. A review of high impact weather for aviation meteorology. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2019, 176, 1869–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gultepe, I.; Isaac, G.A.; Williams, A.; Marcotte, D.; Strawbridge, K.B. Turbulent heat fluxes over leads and polynyas, and their effects on Arctic clouds during FIRE. ACE: Aircraft observations for April 1998. Atmos. Ocean 2003, 41, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessner, A.L.; Wang, J.; Levy, R.C.; Colarco, P.R. Remote sensing of surface visibility from space: A look at the United States East Coast. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 81, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gultepe, I.; Müller, M.D.; Boybeyi, Z. A new visibility parameterization for warm-fog applications in numerical weather prediction models. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2006, 45, 1469–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gultepe, I.; Milbrandt, J.A.; Zhou, B. Marine Fog: A Review on Microphysics and Visibility Prediction, Marine Fog: Challenges and Advancements in Observations, Modeling Forecasting; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 345–394. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B.; Du, J.; Gultepe, I.; Dimego, G. Forecast of low visibility and fog from NCEP: Current status and efforts. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2012, 169, 895–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gultepe, I.; Pagowski, M.; Reid, J. A satellite-based fog detection scheme using screen air temperature. Weather Forecast 2007, 22, 444–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gultepe, I.; Pearson, G.; Milbrandt, J.A.; Hansen, B.; Platnick, S.; Taylor, P.; Cober, S.G. The fog remote sensing and modeling field project. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2009, 90, 341–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koschmieder, H. Therie der horizontalen sichtweite. Beitrage zur Physik der freien Atmosphare 1924, 12, 171–181. [Google Scholar]
- Gultepe, I.; Milbrand, J. Microphysical observations and mesoscale model simulation of a warm fog case during FRAM project. J. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2007, 164, 1161–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beheng, K.D. A parameterization of warm cloud microphysical conversion processes. Atmos. Res. 1994, 33, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claxton, B.M. Using a neural network to benchmark a diagnostic parameterization: The Met Office’s visibility scheme. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2008, 134, 1527–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gultepe, I.; Isaac, G.A. An analysis of cloud droplet number concentration for climate studies: Emphasis on constant Nd. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2004, 130, 2377–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, J.M.; Porson, A.N.F.; Bornemann, F.J.; Weeks, M.; Field, P.R.; Lock, A.P. Improved microphysical parameterization of drizzle and fog for operational forecasting using the Met Office Unified Model. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 139, 488–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gultepe, I.; Isaac, G.A. Scale effects on averaging of cloud droplet and aerosol number concentrations: Observations and models. J. Clim. 1999, 12, 1268–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, H.; Hong, W.; Junping, Q.; Guofu, W. Retrieval of atmospheric horizontal visibility by statistical regression from NOAA/AVHRR satellite data. J. Ocean Univ. China 2006, 5, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjimitsis, D.G.; Clayton, C.; Toulios, L. Retrieving visibility values using satellite remote sensing data. Phys. Chem. Earth 2010, 35, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Hanesiak, J.; Savelyev, S.; Papakyriakou, T.; Taylor, P.A. Visibility during blowing snow events over arctic sea ice. Weather Forecast 2008, 23, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldridge, R.G. The relationship between visibility and liquid water content in fog. J. Atmos. Sci. 1971, 28, 1183–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiwei, Z.; Suping, Z.; Xiaojing, W.; Yingchen, L.; Jingwu, L. The Research on Yellow Sea Sea Fog Based on MODIS Data: Sea Fog Properties Retrieval and Spatial-Tempo-ral Distribution. J. Ocean Univ. China 2009, 39, 311–318. [Google Scholar]
- Gultepe, I.; Zhou, B.; Milbrandt, J.; Bott, A.; Li, Y.; Heymsfield, A.J.; Ferrier, B.; Ware, R.; Pavolonis, M.; Kuhn, T. A review on ice fog measurements and modelling. Atmos. Res. 2014, 151, 2–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClelland, J.L.; Rumelhart, D.E. PDP Research Group. Parallel distributed processing. Psychol. Biol. Models 1986, 2, 216–271. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, D.; Li, C.; Liu, Q. Visibility characteristics and the impacts of air pollutants and meteorological conditions over Shanghai, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, H. The Trend of Visibility and Its Affecting Factors in Chongqing. J. Chongqing Univ. 2003, 5, 151–154. [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence, M.G. The relationship between relative humidity and the dewpoint temperature in moist air: A simple conversion and applications. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2005, 86, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Q. A summer weather index in the East Asian pressure field and associated atmospheric circulation and rainfall. Int. J. Climatol. 2012, 32, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutiel, H.; Hirsch-Eshkol, T.R.; Türkeş, M. Sea level pressure patterns associated with dry or wet monthly rainfall conditions in Turkey. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2001, 69, 39–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, Q.; Yiyang, X.; Lili, L.; Yi, L.; Naiguang, H. Character Analysis of Sea Fog in Bohai Bay from 1988 to 2010. Plat. Meteorol. 2014, 33, 285–293. [Google Scholar]
- Weibing, W. Navigation Experience of Northeast Arctic Channel. Mar. Technol. 2016, 4, 7–9. [Google Scholar]
- Guoqiang, X. Research on the Navigation Environment and Safety Navigation of the Arctic Northeast Route. Master’s Thesis, Dalian Maritime University, Dalian, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y. The Research on the Navigation Environment of Arctic Passage. Master’s Thesis, Dalian Maritime University, Dalian, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]


| Visibility Level | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Visibility Value (km) | <=0.05 | 0.05~0.2 | 0.2~0.5 | 0.5~1 | 1~2 | 2~4 | 4~10 | 10~20 | 20~50 | >=50 |
| Month | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amount (1981–2015) | 14457 | 14476 | 17947 | 19602 | 21390 | 26887 | 34676 | 32826 | 30249 | 22352 | 17585 | 15920 |
| Amount (2016) | 935 | 961 | 974 | 916 | 1117 | 1248 | 1329 | 1513 | 1395 | 1179 | 1057 | 1092 |
| Data | Test | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | ||
| Training Sample | 1 | 0.097 | 0.108 | 0.127 | 0.137 | 0.143 | 0.182 | 0.206 | 0.218 | 0.167 | 0.094 | 0.086 | 0.095 |
| 2 | 0.093 | 0.101 | 0.116 | 0.111 | 0.095 | 0.125 | 0.157 | 0.195 | 0.154 | 0.086 | 0.083 | 0.092 | |
| 3 | 0.128 | 0.120 | 0.106 | 0.075 | 0.096 | 0.151 | 0.193 | 0.217 | 0.176 | 0.097 | 0.103 | 0.118 | |
| 4 | 0.078 | 0.070 | 0.075 | 0.044 | 0.065 | 0.127 | 0.174 | 0.210 | 0.160 | 0.082 | 0.072 | 0.099 | |
| 5 | 0.086 | 0.078 | 0.086 | 0.060 | 0.051 | 0.099 | 0.142 | 0.183 | 0.134 | 0.068 | 0.075 | 0.097 | |
| 6 | 0.131 | 0.128 | 0.144 | 0.054 | 0.045 | 0.093 | 0.124 | 0.164 | 0.138 | 0.144 | 0.161 | 0.219 | |
| 7 | 0.163 | 0.157 | 0.144 | 0.106 | 0.088 | 0.111 | 0.145 | 0.190 | 0.155 | 0.153 | 0.167 | 0.202 | |
| 8 | 0.114 | 0.106 | 0.104 | 0.077 | 0.069 | 0.116 | 0.143 | 0.193 | 0.144 | 0.094 | 0.111 | 0.133 | |
| 9 | 0.082 | 0.078 | 0.088 | 0.083 | 0.086 | 0.126 | 0.148 | 0.182 | 0.137 | 0.070 | 0.077 | 0.096 | |
| 10 | 0.126 | 0.128 | 0.124 | 0.127 | 0.110 | 0.115 | 0.138 | 0.180 | 0.133 | 0.075 | 0.102 | 0.158 | |
| 11 | 0.101 | 0.103 | 0.109 | 0.103 | 0.101 | 0.124 | 0.159 | 0.200 | 0.141 | 0.078 | 0.067 | 0.099 | |
| 12 | 0.089 | 0.100 | 0.122 | 0.108 | 0.095 | 0.128 | 0.152 | 0.197 | 0.146 | 0.088 | 0.074 | 0.100 | |
| Average | 0.107 | 0.106 | 0.112 | 0.090 | 0.087 | 0.125 | 0.157 | 0.194 | 0.149 | 0.094 | 0.098 | 0.126 | |
| Data | Test | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | ||
| Training Sample | 1 | 0.101 | 0.099 | 0.113 | 0.106 | 0.089 | 0.127 | 0.158 | 0.191 | 0.138 | 0.081 | 0.088 | 0.088 |
| 2 | 0.111 | 0.104 | 0.108 | 0.111 | 0.149 | 0.235 | 0.298 | 0.289 | 0.194 | 0.094 | 0.090 | 0.094 | |
| 3 | 0.120 | 0.110 | 0.100 | 0.075 | 0.085 | 0.156 | 0.204 | 0.219 | 0.154 | 0.092 | 0.111 | 0.117 | |
| 4 | 0.079 | 0.072 | 0.072 | 0.045 | 0.051 | 0.103 | 0.146 | 0.184 | 0.130 | 0.069 | 0.070 | 0.099 | |
| 5 | 0.086 | 0.078 | 0.078 | 0.050 | 0.044 | 0.097 | 0.134 | 0.169 | 0.131 | 0.063 | 0.071 | 0.108 | |
| 6 | 0.123 | 0.116 | 0.117 | 0.061 | 0.043 | 0.099 | 0.140 | 0.180 | 0.139 | 0.101 | 0.125 | 0.142 | |
| 7 | 0.136 | 0.130 | 0.119 | 0.079 | 0.055 | 0.097 | 0.135 | 0.185 | 0.151 | 0.118 | 0.142 | 0.181 | |
| 8 | 0.096 | 0.093 | 0.085 | 0.067 | 0.055 | 0.098 | 0.134 | 0.178 | 0.135 | 0.078 | 0.100 | 0.148 | |
| 9 | 0.091 | 0.085 | 0.090 | 0.071 | 0.059 | 0.105 | 0.136 | 0.173 | 0.129 | 0.068 | 0.087 | 0.109 | |
| 10 | 0.096 | 0.092 | 0.103 | 0.082 | 0.068 | 0.107 | 0.148 | 0.180 | 0.125 | 0.068 | 0.087 | 0.113 | |
| 11 | 0.092 | 0.084 | 0.096 | 0.074 | 0.073 | 0.117 | 0.146 | 0.187 | 0.135 | 0.078 | 0.074 | 0.093 | |
| 12 | 0.089 | 0.085 | 0.098 | 0.070 | 0.067 | 0.117 | 0.143 | 0.185 | 0.137 | 0.078 | 0.071 | 0.089 | |
| Average | 0.102 | 0.096 | 0.098 | 0.074 | 0.070 | 0.122 | 0.160 | 0.193 | 0.141 | 0.082 | 0.093 | 0.115 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shan, Y.; Zhang, R.; Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q.; Li, L. Generation and Analysis of Gridded Visibility Data in the Arctic. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 314. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10060314
Shan Y, Zhang R, Li M, Wang Y, Li Q, Li L. Generation and Analysis of Gridded Visibility Data in the Arctic. Atmosphere. 2019; 10(6):314. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10060314
Chicago/Turabian StyleShan, Yulong, Ren Zhang, Ming Li, Yangjun Wang, Qiuhan Li, and Lifeng Li. 2019. "Generation and Analysis of Gridded Visibility Data in the Arctic" Atmosphere 10, no. 6: 314. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10060314
APA StyleShan, Y., Zhang, R., Li, M., Wang, Y., Li, Q., & Li, L. (2019). Generation and Analysis of Gridded Visibility Data in the Arctic. Atmosphere, 10(6), 314. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10060314





