Retrieval of Horizontal Visibility Using MODIS Data: A Deep Learning Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. MODIS AOD Product
2.2. European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts ERA-Interim Data
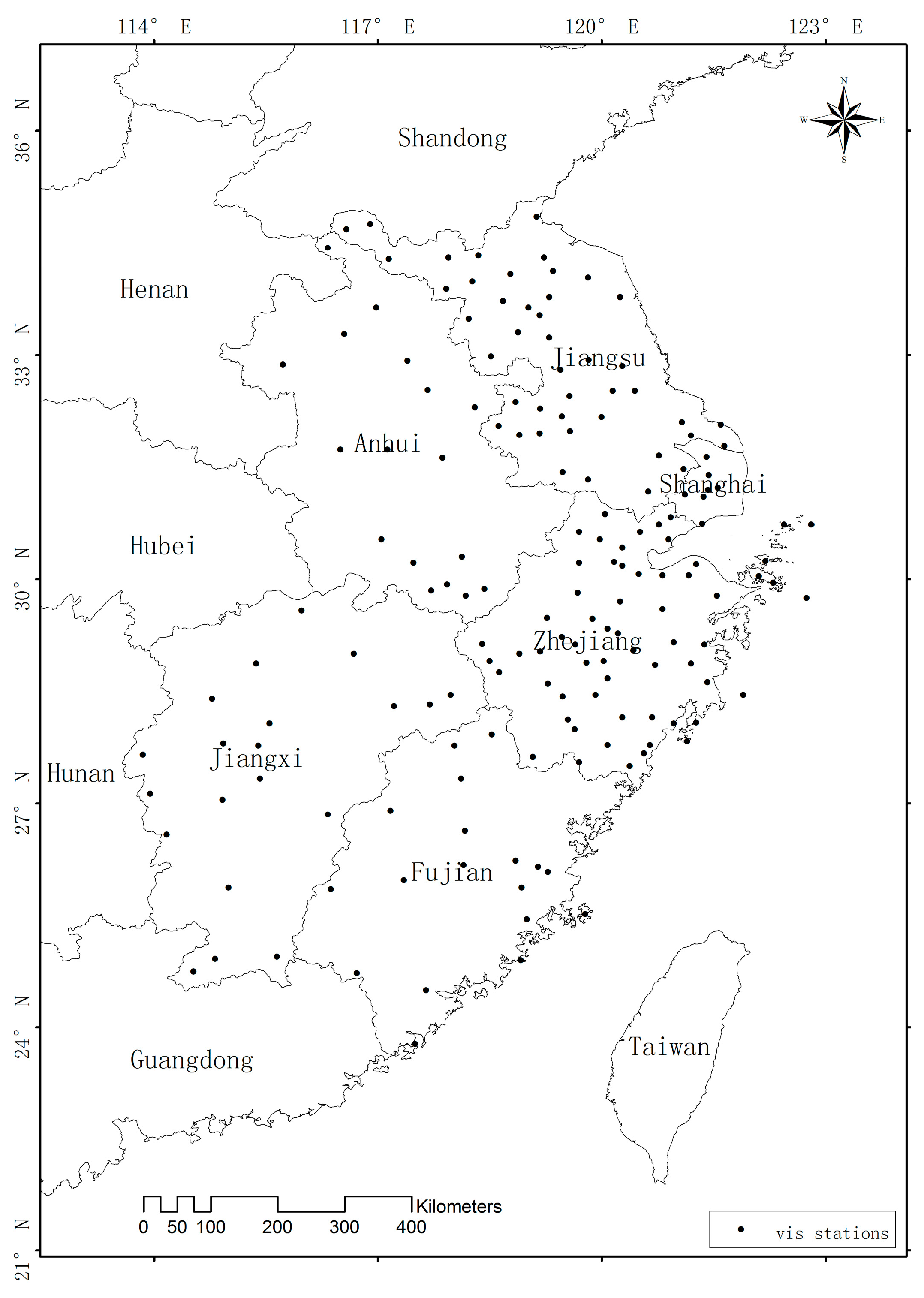
2.3. HVIS Data
2.4. Methodology
2.4.1. Pre-Processing
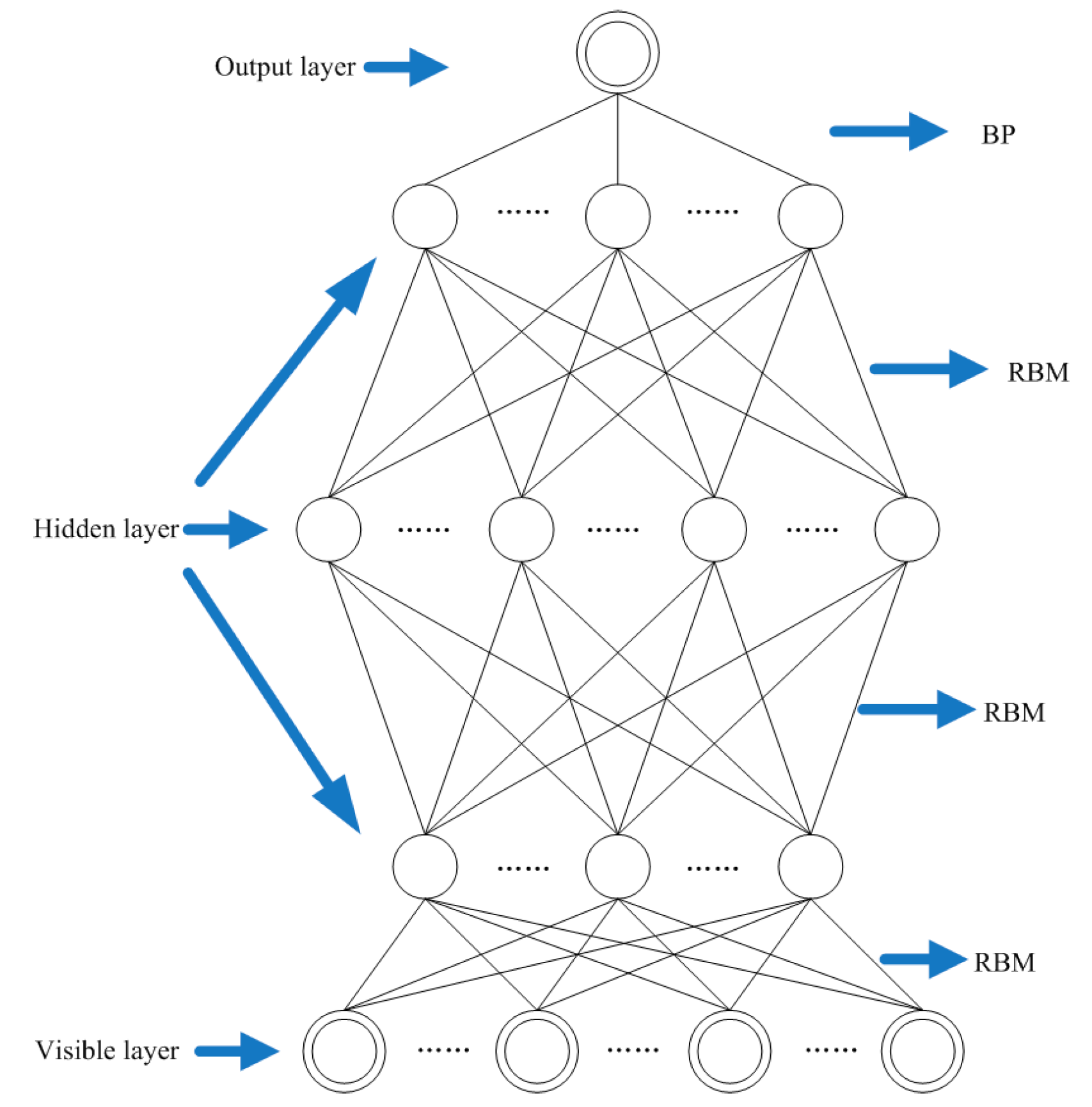
2.4.2. Pre-Training
2.4.3. Fine-Tuning
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Model Training and Pre-Validation
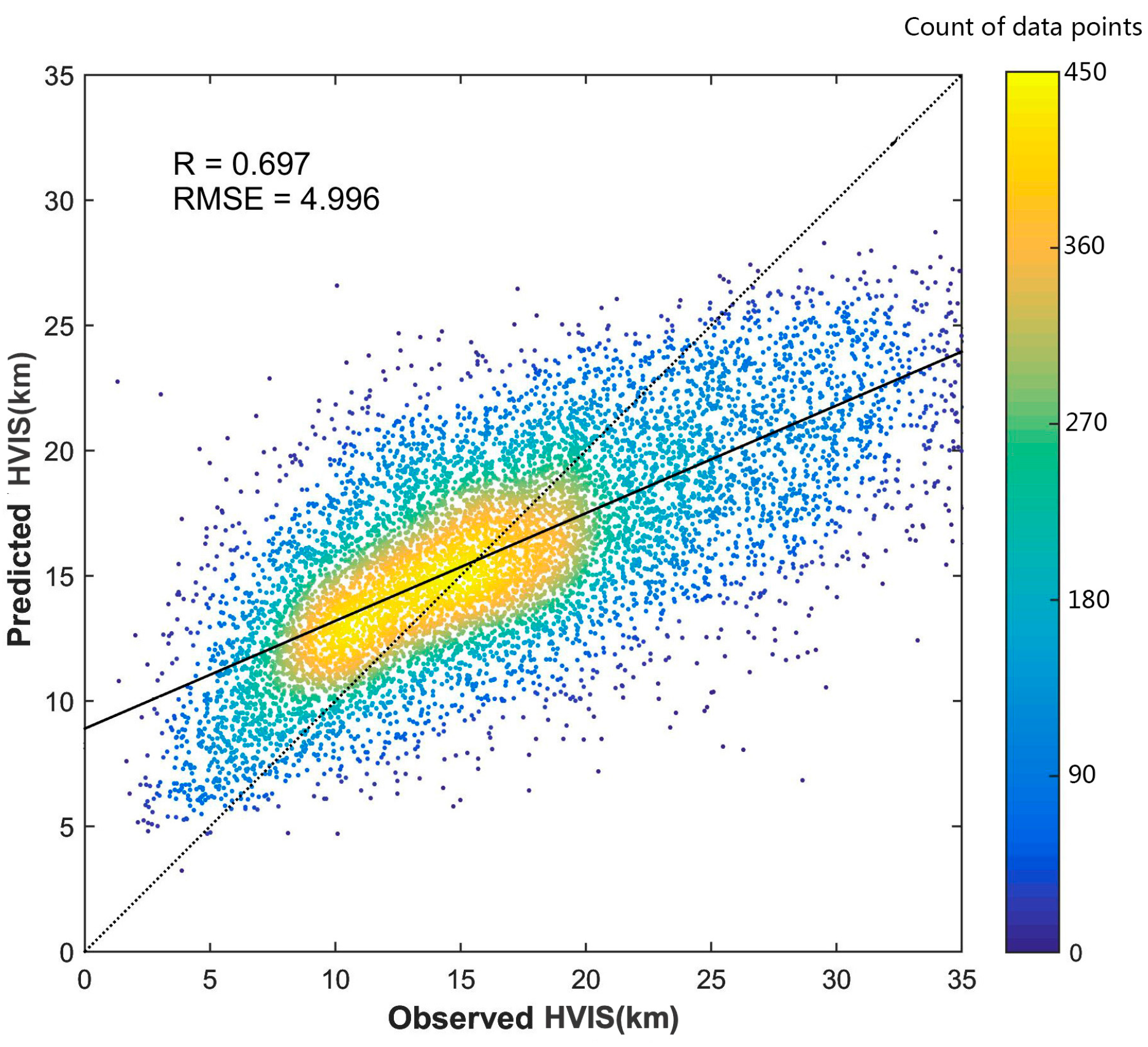
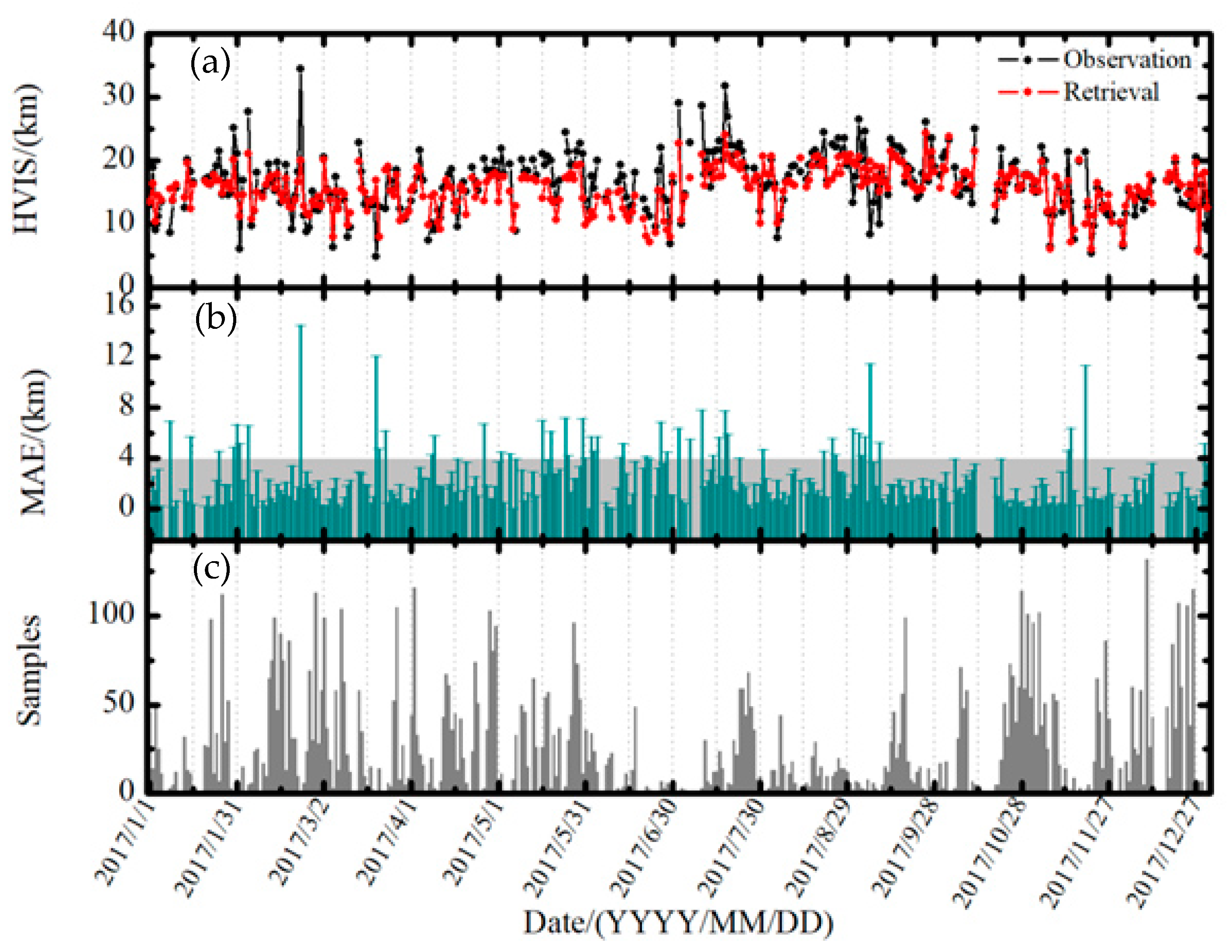
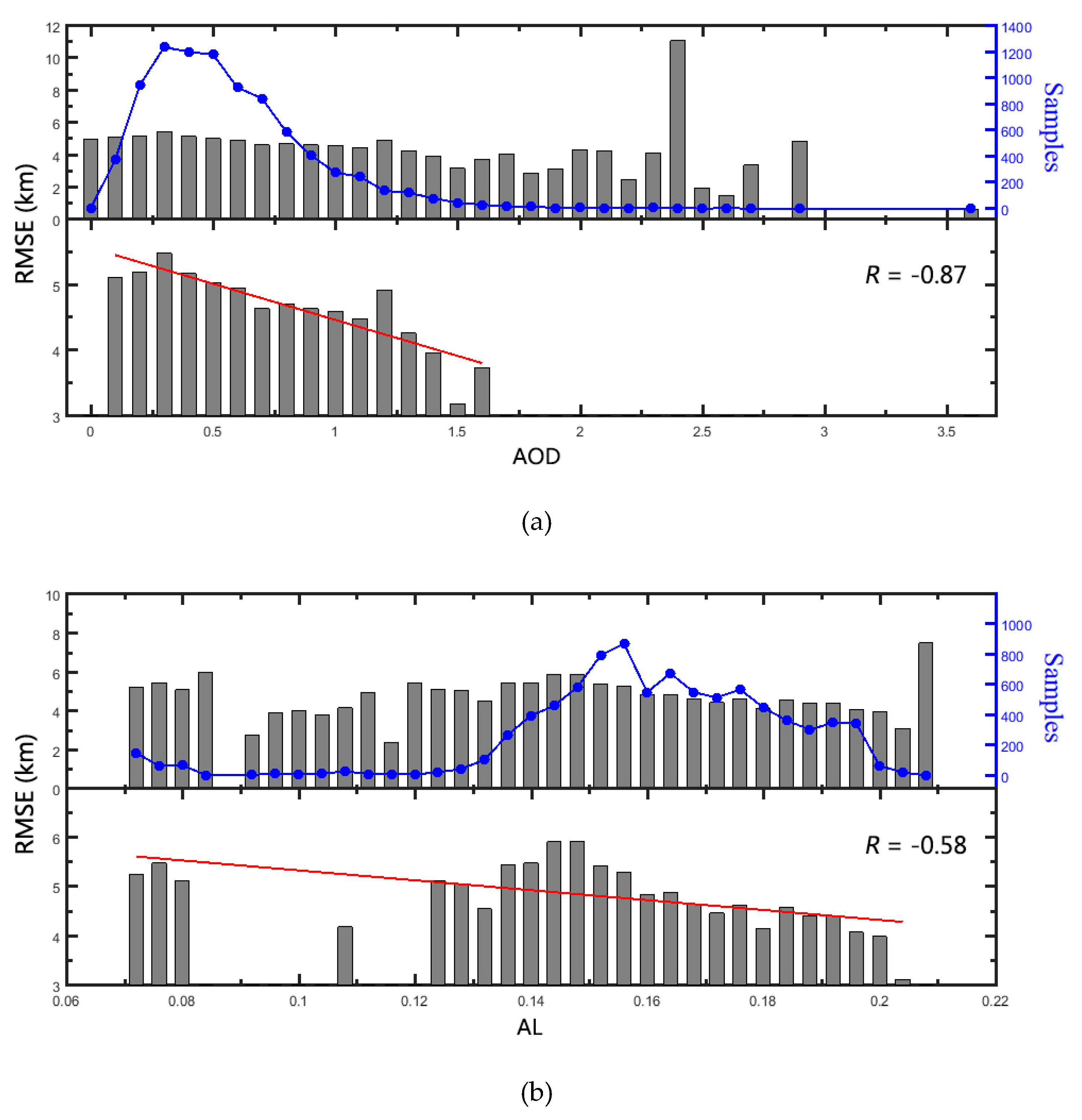
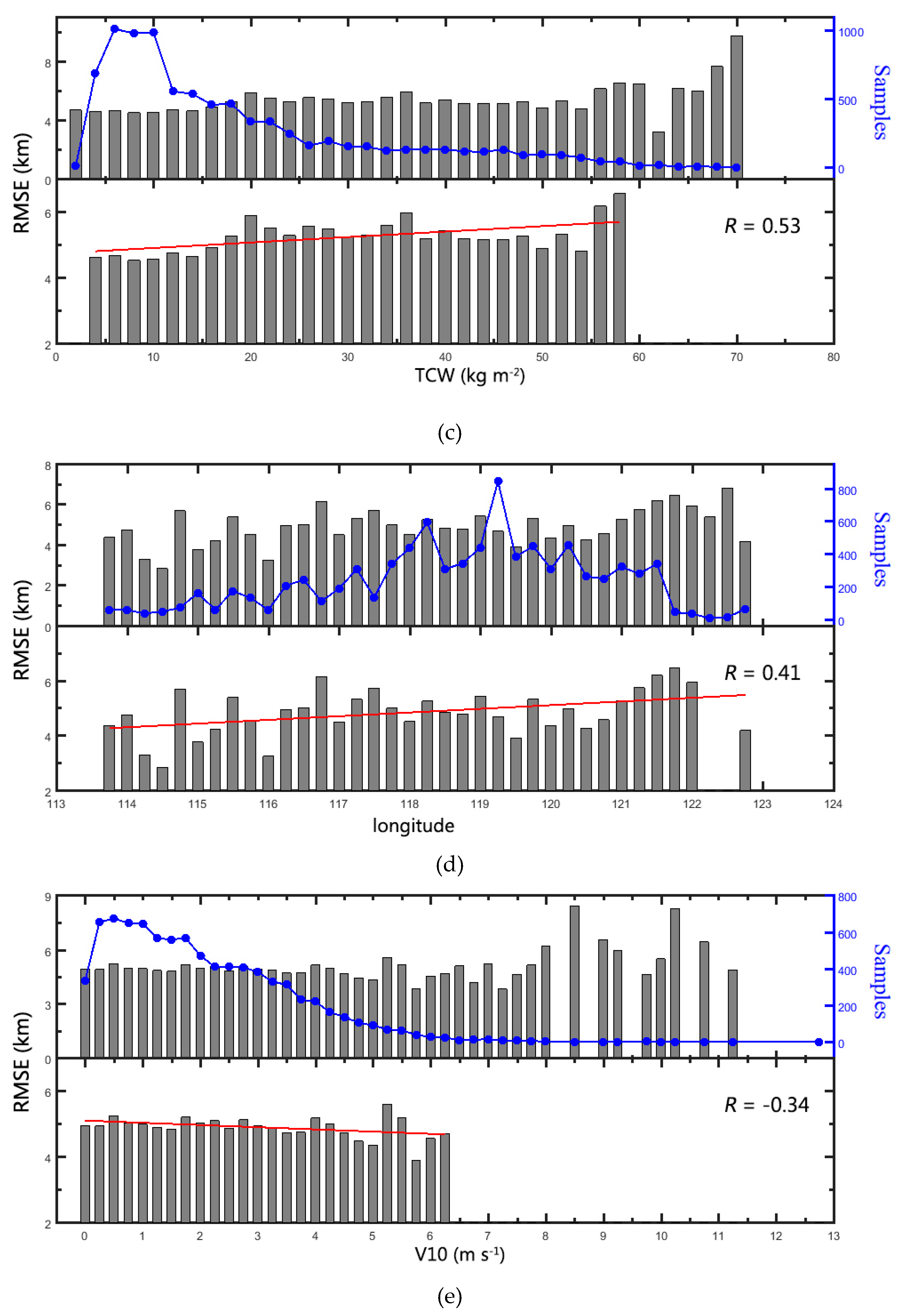
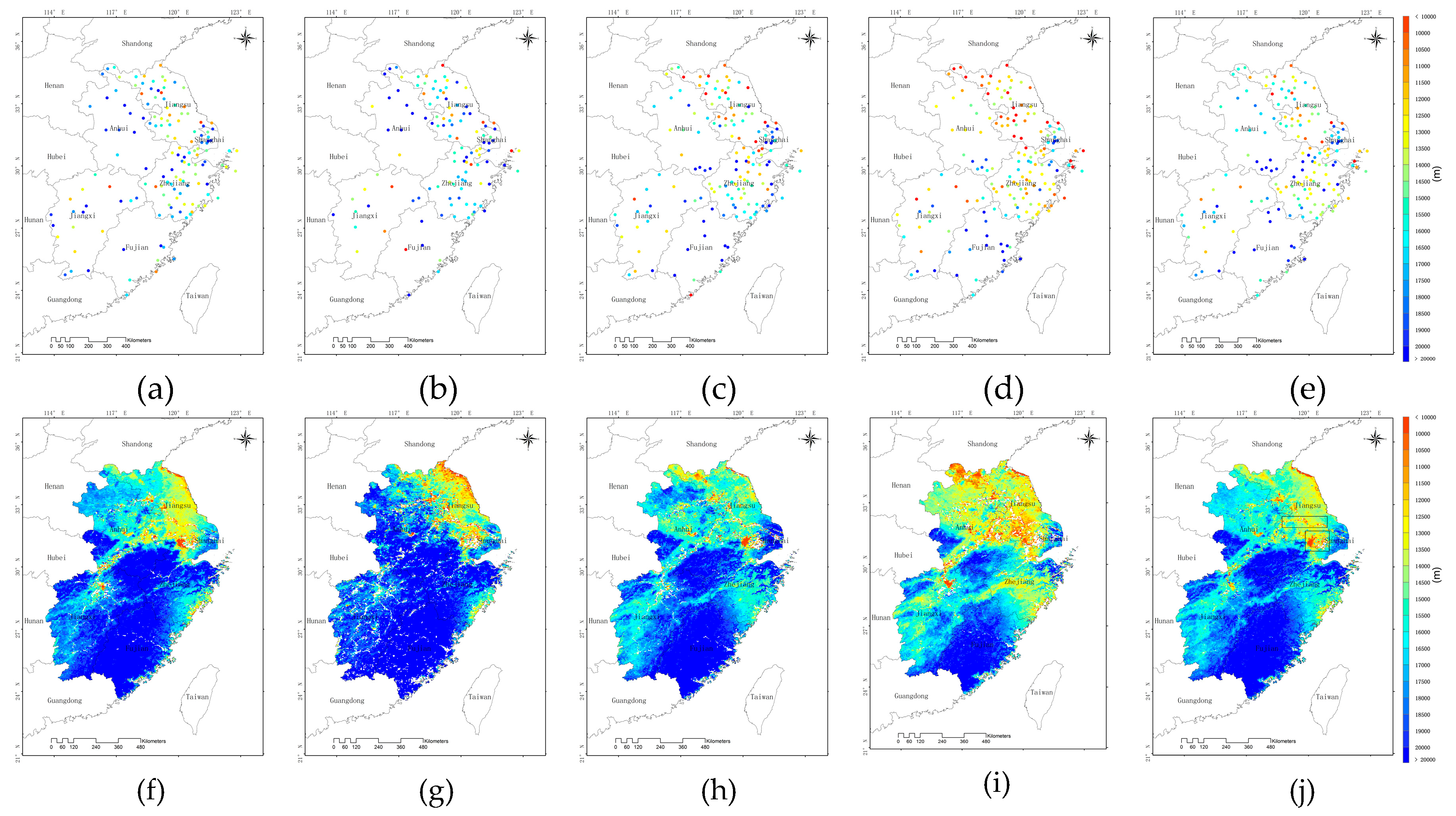
3.2. Model Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Watson, J.G. Visibility: Science and Regulation. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2002, 52, 628–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bäumer, D.; Vogel, B.; Versick, S.; Rinke, R.; Möhler, O.; Schnaiter, M. Relationship of visibility, aerosol optical thickness and aerosol size distribution in an ageing air mass over South-West Germany. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 989–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Tan, J.; Kan, H.; Zhao, N.; Song, W.; Song, G.; Chen, G.; Jiang, L.; Jiang, C.; Chen, R.; et al. Visibility, air quality and daily mortality in Shanghai, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 3295–3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, Q.; Mysliwiec, M.; Kleeman, M.J. Source apportionment of visibility impairment using a three-dimensional source-oriented air quality model. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 1089–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thach, T.Q.; Wong, C.M.; Chan, K.P.; Chau, Y.K.; Chung, Y.N.; Ou, C.Q.; Yang, L.; Hedley, A.J. Daily visibility and mortality: Assessment of health benefits from improved visibility in Hong Kong. Environ. Res. 2010, 110, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, J.G.; Chow, J.C. Clear sky visibility as a challenge for society. Annu. Rev. Energy Environ. 1994, 19, 241–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Dickinson, R.E.; Liang, S. Clear sky visibility has decrease over land globally from 1973 to 2007. Science 2009, 323, 1468–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, W.; Wang, J.; Gao, S.; Wu, T. Effect of the strengthened western Pacific subtropical high on summer visibility decrease over eastern China since 1973. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 7142–7156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Li, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Lau, A.K.; Li, C.; Fung, J.C. Using satellite remote sensing data to estimate the high-resolution distribution of ground-level PM2.5. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 156, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.C.; Mattoo, S.; Munchak, L.A.; Remer, L.A.; Sayer, A.M.; Patadia, F.; Hsu, N.C. The Collection 6 MODIS aerosol products over land and ocean. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 2989–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remer, L.A.; Mattoo, S.; Levy, R.C.; Munchak, L.A. MODIS 3km aerosol product: Algorithm and global perspective. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 1829–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Reid, J.S. A decadal regional and global trend analysis of the aerosol optical depth using a data-assimilation grade over-water MODIS and Level 2 MISR aerosol products. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 10949–10963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wong, M.; Nichol, J. Global trends of aerosol optical thickness using the ensemble empirical mode decomposition method. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 4358–4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloog, I.; Koutrakis, P.; Coull, B.A.; Lee, H.J.; Schwartz, J. Assessing temporally and spatially resolved PM2.5 exposures for epidemiological studies using satellite aerosol optical depth measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 6267–6275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Ferrare, R.A.; Newsom, R.K.; Welton, E.J. The effect ofaerosol vertical profiles on satellite-estimated surface particle sulfate concentrations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koschmieder, H. Theorie der Horizontalen Sichtweite: Kontrast und Sichtweite; Keim & Nemnich Press: Munich, Germany, 1925; pp. 25–33. [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Fraser, R.S. Light extinction by aerosols during summer air pollution. J. Clim. Appl. Meteorol. 1983, 22, 1694–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjimitsis, D.G.; Clayton, C.; Toulios, L. Retrieving visibility values using satellite remote sensing data. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2010, 35, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Donkelaar, A.; Martin, R.V.; Park, R.J. Estimating ground-level PM2.5 using aerosol optical depth determined from satellite remote sensing. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111, D21201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Li, C.; Lau, A.K.; Li, Y. Long-term measurement of daytime atmospheric mixing layer height over Hong Kong. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 2422–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessner, A.L.; Wang, J.; Levy, R.C.; Colarco, P.R. Remote sensing of surface visibility from space: A look at the United States East Coast. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 81, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Li, C.; Geng, F.; Zhou, G.; Gao, W.; Yu, W.; Li, Z.; Du, M. A parameterization scheme of aerosol vertical distribution for surface-level visibility retrieval from satellite remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 181, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malm, W.C.; Day, D.E. Estimates of aerosol species scattering characteristics as a function of relative humidity. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 2845–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.I.; Cheng, M.T. Effects of sulfate and humidity on visibility in the Taichung harbor are (Taiwan). J. Aerosol. Sci. 1998, 29, S1213–S1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.I.; Cheng, M.T. Visibility and aerosol chemical compositions near the coastal area in central Taiwan. Sci. Total Environ. 1999, 231, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, M.C.; Flocchini, R.G.; Myrup, L.O. The relationship of the extinction coefficient distribution to wind field patterns in southern California. Atmos. Environ. Part A Gen. Top. 1992, 26, 827–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G.E. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengio, Y. Learning Deep Architectures for AI. Found. Trends Mach. Learn. 2009, 2, 1–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinton, G.E.; Osindero, S.; Teh, Y.W. A fast learning algorithm for deep belief nets. Neural Comput. 2006, 18, 1527–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, H.; Lee, S. Multi-channel electromyography pattern classification using deep belief networks for enhanced user experience. J. Cent. South Univ. 2015, 22, 1801–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.; Jia, K.; Gao, S.; Lu, J.; Zeng, Z.; Ma, Y. PCANet: A simple deep learning baseline for image classification? IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2015, 24, 5017–5032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinton, G.E.; Deng, L.; Yu, D.; Dahl, G.; Mohsmed, A.; Jaitly, N.; Senior, A.; Vanhoucke, V.; Nguyen, P.; Sainath, T.; et al. Deep neural networks for acoustic modeling in speech recognition: The shared views of four research groups. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2012, 29, 82–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronao, C.A.; Cho, S.B. Human activity recognition with smartphone sensors using deep learning neural networks. Expert Syst. Appl. 2016, 59, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Cai, Q.; Yang, Y.; Dong, N.; Zhang, S. Visibility graph from adaptive optimal kernel time-frequency representation for classification of epileptiform EEG. Int. J. Neural Syst. 2017, 27, 1750005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silver, D.; Huang, A.; Maddison, C.J.; Guez, A.; Sifre, L.; Van Den Driessche, G.; Schrittwieser, J.; Antonoglou, I.; Panneershelvam, V.; Lanctot, M.; et al. Mastering the game of Go with deep neural networks and tree search. Nature 2016, 529, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.; Sainath, T.N.; Dahl, G.; Ramabhadran, B.; Hinton, G.E.; Picheny, M.A. Deep belief networks using discriminative features for phone recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Prague, Czech Republic, 22–27 May 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengio, Y.; Courville, A.; Vincent, P. Representation learning: A review and new perspectives. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2013, 35, 1798–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Zhang, L.; Ren, Y.; Suganthan, P.N.; Amaratunga, G. Ensemble deep learning for regression and time series forecasting. In Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Computational Intelligence in Ensemble Learning, Orlando, FL, USA, 9–12 December 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, X.; Jia, X. Spectral-Spatial Classification of Hyperspectral Data Based on Deep Belief Network. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 2381–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Xiang, L. Method for Meteorological Early Warning of Precipitation-Induced Landslides Based on Deep Neural Network. Neural Process. Lett. 2018, 48, 1243–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Peng, L.; Hu, Y.; Shao, J.; Chi, T. Deep learning architecture for air quality predictions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 22408–22417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Peng, L.; Yao, X.; Cui, S.; Hu, Y.; You, C.; Chi, T. Long short-term memory neural network for air pollutant concentration predictions: Method development and evaluation. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 997–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Z. Remote sensing of atmospheric fine particulate matter (PM2.5) mass concentration near the ground from satellite observation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 160, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Dong, W.; Lv, B.; Bai, Y. Daily Estimation of Ground-Level PM2.5 Concentrations over Beijing Using 3 km Resolution MODIS AOD. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 12280–12288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dee, D.P.; Uppala, S.M.; Simmons, A.J.; Berrisford, P.; Poli, P.; Kobayashi, S.; Andrae, U.; Balmaseda, M.A.; Balsamo, G.; Bauer, P. The ERA-Interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 553–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, P.; Mao, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, A.; Sang, J.; Pan, N. Atmospheric Physics; Peking University Press: Beijing, China, 2005; pp. 20–21. [Google Scholar]
- Hilborn, E.D.; Catanzaro, D.G.; Jackson, L.E. Repeated holdout cross-validation of model to estimate risk of Lyme disease by landscape characteristics. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2011, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, B.; Zhang, X.; Sun, R.; Zhu, X. Retrieval of Horizontal Visibility Using MODIS Data: A Deep Learning Approach. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 740. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10120740
Hu B, Zhang X, Sun R, Zhu X. Retrieval of Horizontal Visibility Using MODIS Data: A Deep Learning Approach. Atmosphere. 2019; 10(12):740. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10120740
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Bo, Xingying Zhang, Rui Sun, and Xianchun Zhu. 2019. "Retrieval of Horizontal Visibility Using MODIS Data: A Deep Learning Approach" Atmosphere 10, no. 12: 740. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10120740
APA StyleHu, B., Zhang, X., Sun, R., & Zhu, X. (2019). Retrieval of Horizontal Visibility Using MODIS Data: A Deep Learning Approach. Atmosphere, 10(12), 740. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10120740






