A Case Study of Stratus Cloud Properties Using In Situ Aircraft Observations over Huanghua, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
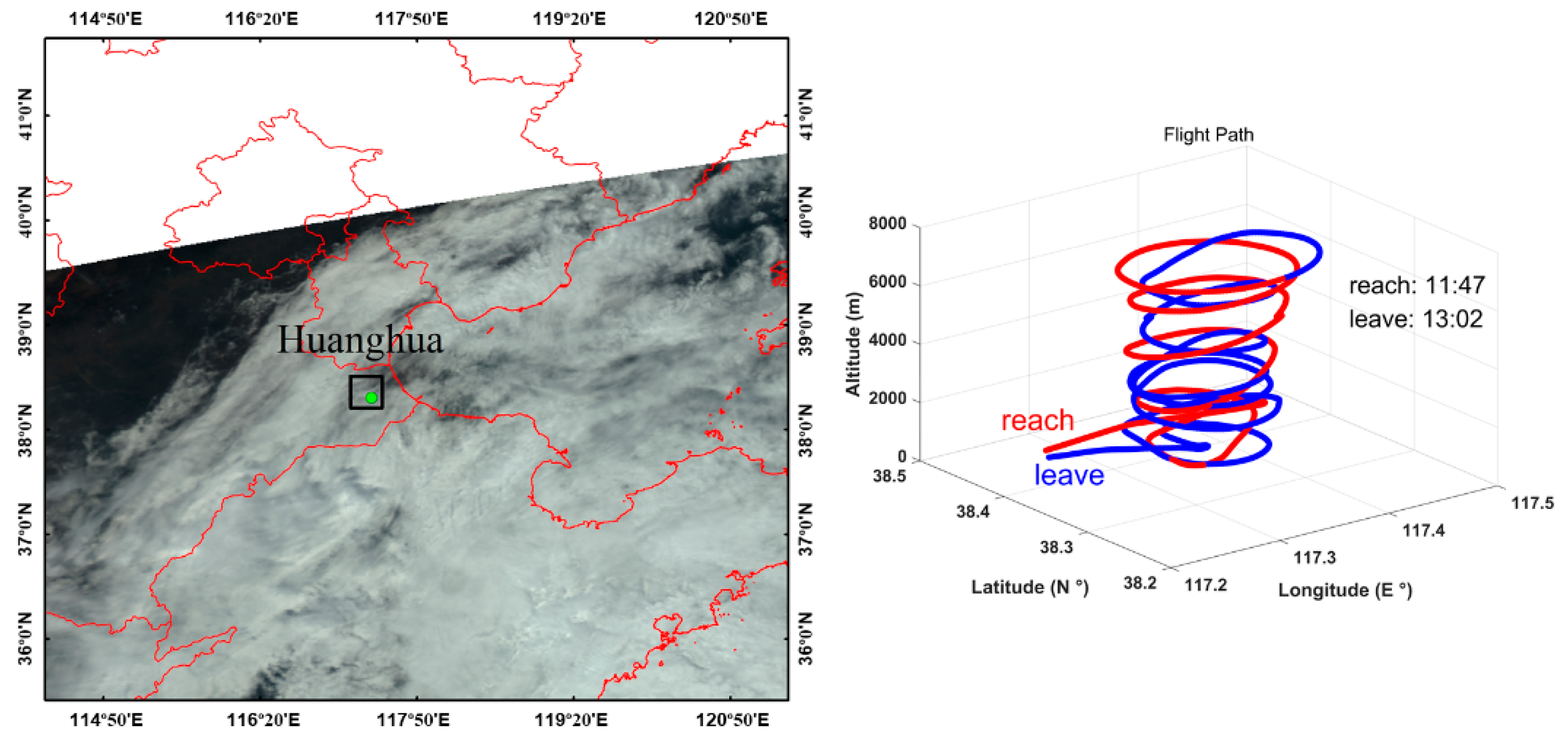
2. Instrument and Measurements
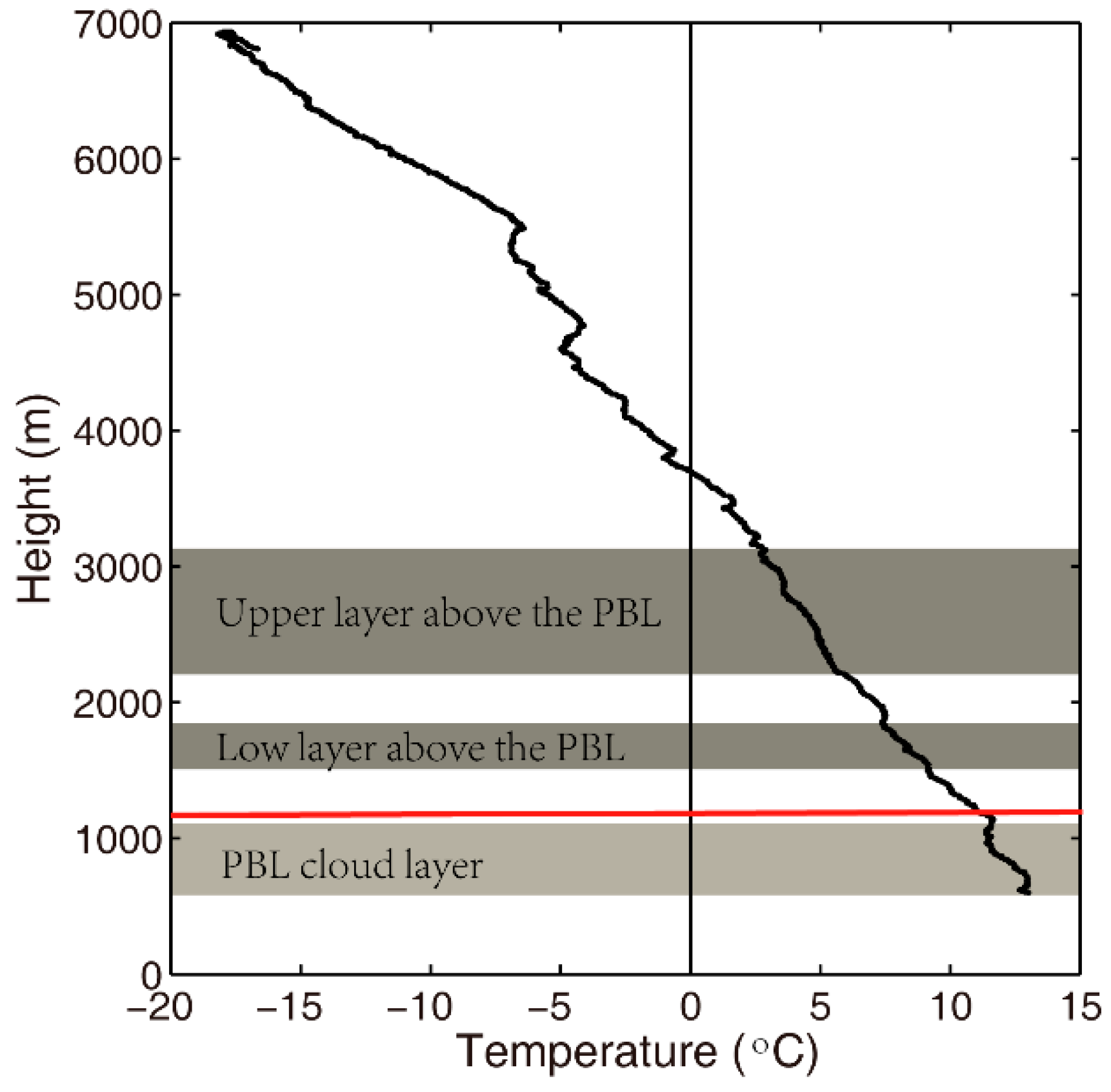
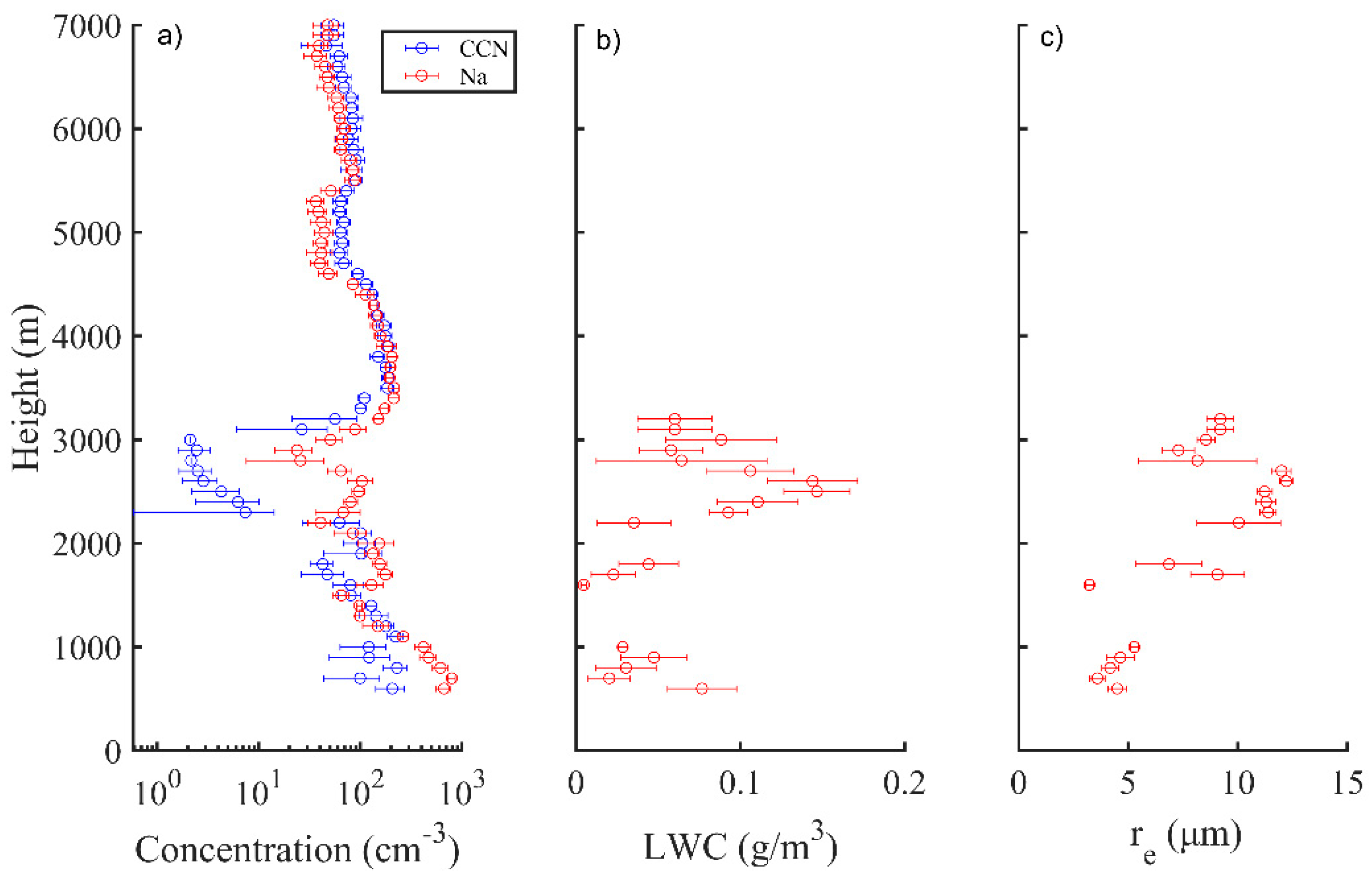
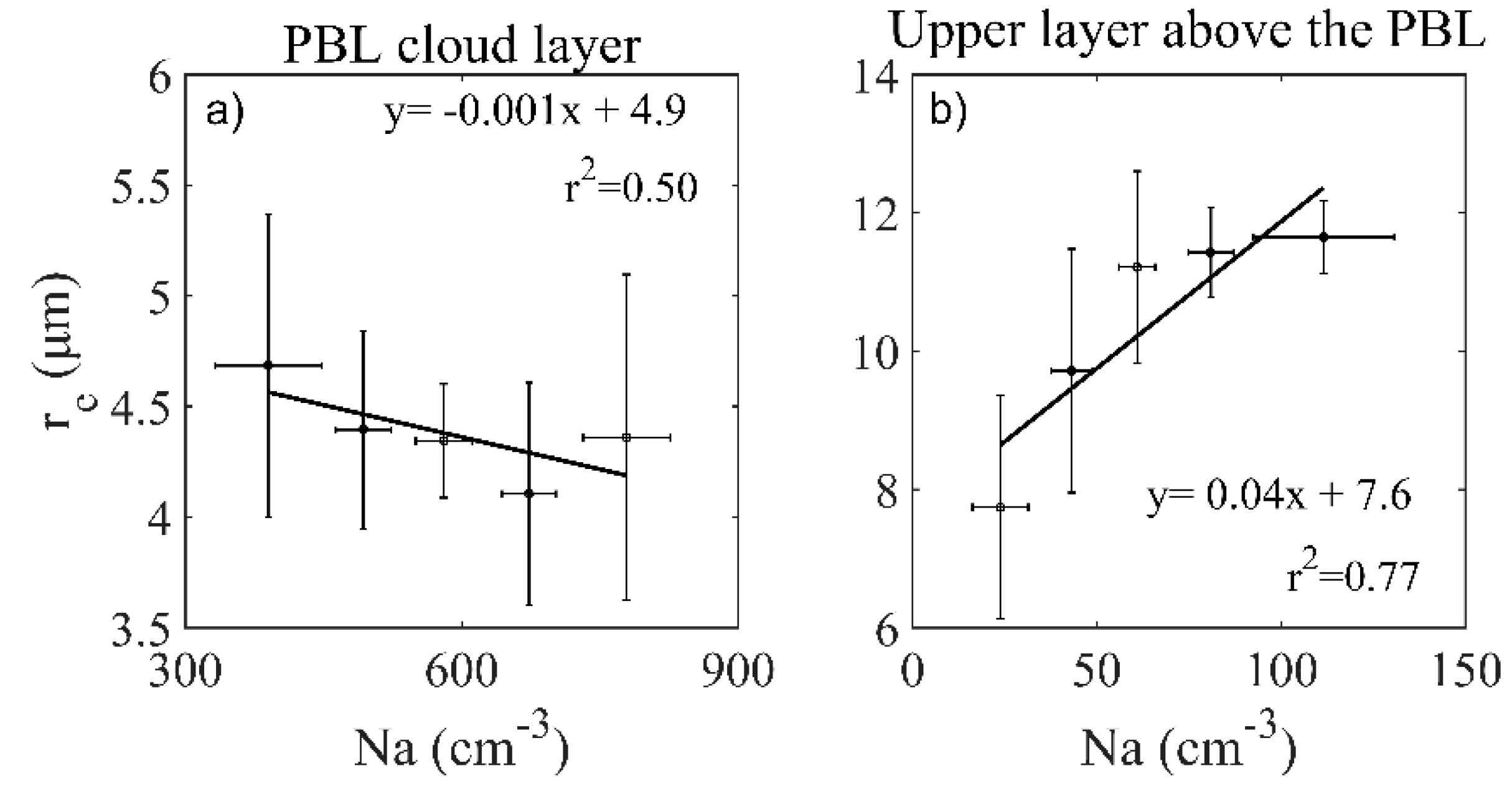
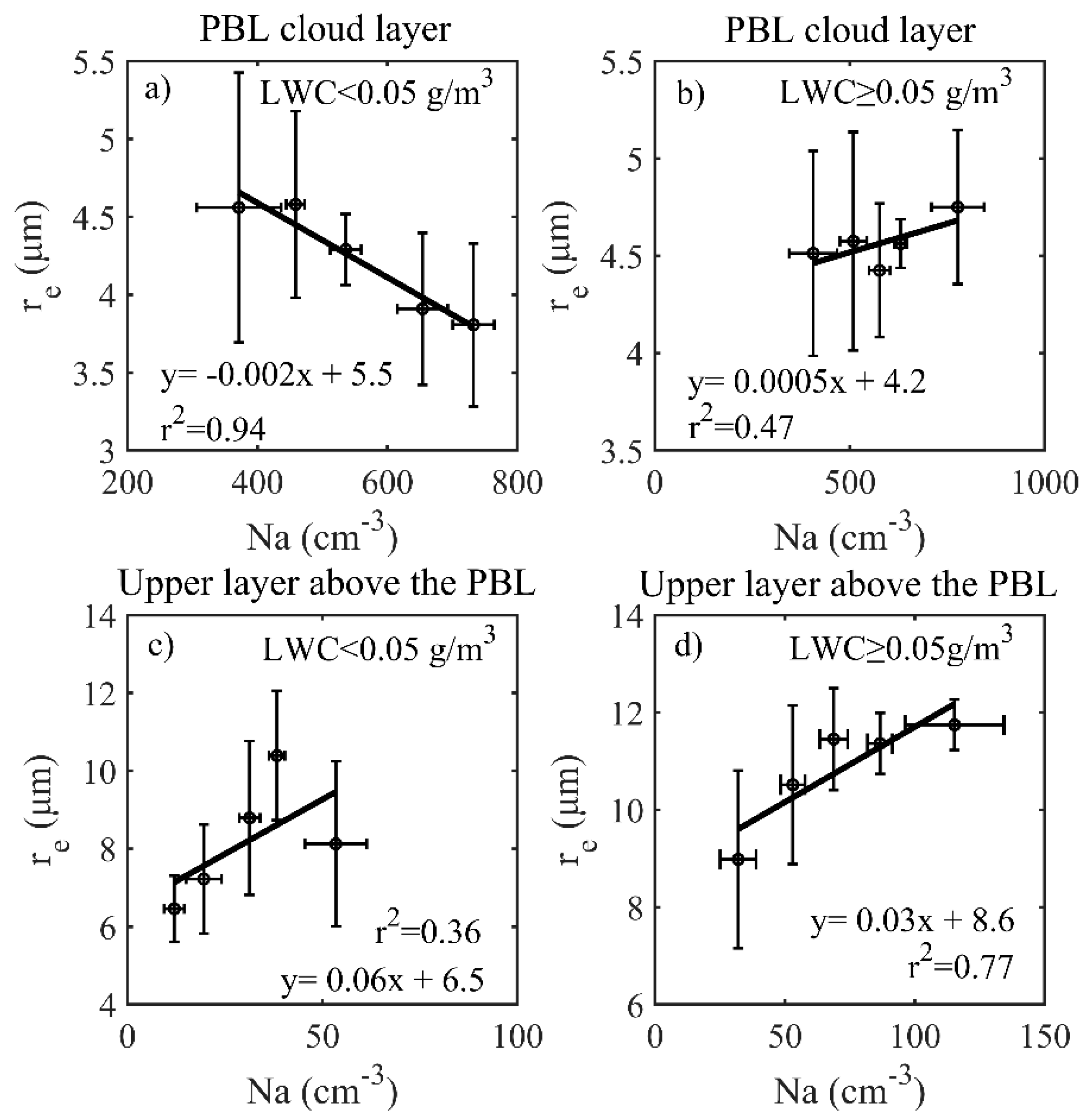
3. Analysis and Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Warren, S.G.; Hahn, C.J.; London, J.; Chervin, R.M.; Jenne, R.L. Global Distribution of Total Cloud Cover and Cloud Type Amounts over the Ocean; NCAR Tech. Notes TN-317+STR or DOE/ER-0406; NCAR: Boulder, CO, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Manabe, S.; Wetherald, R.T. Thermal equilibrium of the atmosphere with a given distribution of relative humidity. J. Atmos. Sci. 1967, 24, 241–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, S.H. Cloudiness as a global climatic feedback mechanism: The effects on the radiation balance and surface temperature of variations in cloudiness. J. Atmos. Sci. 1972, 29, 1413–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, V.; Cess, R.D.; Harrison, E.F.; Minnis, P.; Barkstrom, B.R. Cloud-radiative forcing and climate: Results from the Earth radiation budget experiment. Science 1989, 243, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, E.F.; Minnis, P.; Barkstrom, B.R.; Ramanathan, V.; Cess, R.D.; Gibson, G.G. Seasonal variation of cloud radiative forcing derived from the Earth radiation budget experiment. J. Geophys. Res. 1990, 95, 18687–18703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sporre, M.K.; Glantz, P.; Tunved, P.; Swietlicki, E.; Kulmala, M.; Lihavainen, H. A study of the indirect aerosol effect on subarctic marine liquid low-level clouds using MODIS cloud 30 data and ground-based aerosol measurements. Atmos. Res. 2012, 116, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, D.L.; Ockert-Bell, M.E.; Michelsen, M.L. The effects of cloud type on the Earth’s energy balance: Global analysis. J. Clim. 1992, 5, 1281–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Xie, S.; Stephen, A.K.; Protat, A.; Shupe, M.D.; McFarlane, S.A.; Comstock, J.M.; Delanoë, J.; Deng, M.; Dunn, M.; et al. Toward understanding of differences in current cloud retrievals of ARM ground-based measurements. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, D10206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Xie, S.; Chen, X.; Jensen, M.P.; Dunn, M. Quantifying uncertainties of cloud microphysical property retrievals with a perturbation method. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 5375–5385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, N.L.; Verlinde, J.; Clothiaux, E.E. Cloud droplet size distributions in low-level stratiform clouds. J. Atmos. Sci. 2000, 57, 295–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, R.P.; Baker, B.A.; Schmitt, C.G. An overview of microphysical properties of Arctic clouds observed in May and July 1998 during FIRE ACE. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 14989–15014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Minnis, P.; Xi, B. A climatology of midlatitude continental clouds from the ARM SGP central facility: Part I: Low-level cloud macrophysical, microphysical, and radiative properties. J. Clim. 2005, 18, 1391–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.L.; Conant, W.C.; Jonsson, H.H.; Varutbangkul, V.; Flagan, R.C.; Seinfeld, J.H. The Marine Stratus/Stratocumulus Experiment (MASE): Aerosol-cloud relationships in marine stratocumulus. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, D10209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Xi, B.; Crosby, K.; Long, C.N.; Stone, R. A 10 year climatology of Arctic cloud fraction and radiative forcing at Barrow, Alaska. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, D12124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrett, T.J.; Zhao, C. Ground-based remote sensing of thin clouds in the Arctic. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 1227–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrett, T.J.; Zhao, C.; Dong, X.; Mace, G.G.; Hobbs, P.V. Effects of Long-Range Pollution Transport on North American Arctic Stratus. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L17105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twomey, S. The influence of pollution on the shortwave albedo of clouds. J. Atmos. Sci. 1977, 34, 1149–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassen, K.; Mace, G.G.; Wang, Z. Continetal stratus clouds: A case study using coordinated remote sensing and aircraft measurements. J. Atmos. Sci. 1999, 56, 2345–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.F.; Lei, H.C.; Wu, Y.X.; Xiao, W.A.; Zhang, X.Q. Size distributions of the water drops in the warm layer of stratiform clouds in Yanan. J. Nanjing Inst. Meteorol. 2005, 28, 787–793. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.L.; Mao, J.T.; Wei, Q.; Ying, Y.J.; Wang, L.; Han, Z.G.; Li, C.C. A study of vertical structure of spring stratiform clouds in Northwest China. Meteorol. Mon. 2010, 36, 71–77. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Li, C.C.; Yao, Z.G.; Zhao, Z.L.; Han, Z.G.; Wei, Q. Application of aircraft observations over Beijing in cloud microphysical property retrievals from CloudSat. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2014, 31, 926–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Qiu, Y.; Dong, X.; Wang, Z.; Peng, Y.; Li, B.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Y. Negative Aerosol-Cloud re Relationship from Aircraft Observations over Hebei, China. Earth Space Sci. 2018, 5, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnet, F.; Brenguier, J.-L. Validation of droplet spectra and liquid water content measurements. Phys. Chem. 1999, 24, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgardner, D. An analysis and comparison of five water droplet measuring instruments. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1983, 22, 891–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgardner, D.; Strapp, W.; Dye, J.E. Evaluation of the forward scattering spectrometer probe. Part II: Corrections for coincidence and dead-time losses. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1985, 2, 626–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgardner, D.; Spowart, M. Evaluation of the forward scattering spectrometer probe. Part III: Time response and laser inhomogeneity limitations. J. Atmos. Oceanic. Technol. 1990, 7, 666–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinman, L.I.; Daum, P.H.; Lee, Y.-N.; Lewis, E.R.; Sedlacek, A.J., III; Senum, G.I.; Springston, S.R.; Wang, J.; Hubbe, J.; Jayne, J.; et al. Aerosol concentration and size distribution measured below, in, and above cloud from the DOE G-1 during VOCALS-Rex. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 207–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhao, C.; Dong, X.; Fan, G.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Lv, F.; Yan, F. Toward understanding the process-level impacts of aerosols on microphysical properties of shallow cumulus cloud using aircraft observations. Atmos. Res. 2018. in review. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Quan, J.; Tie, X.; Huang, M.; Ma, X. Impact of aerosol particles on cloud formation: aircraft measurements in China. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 665–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Z.J. Chemical compositions of precipitation and scavenging of particles in Beijing. Sci. China Ser. B Chem. 2005, 48, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Yin, Y.; Tong, Y.Q.; Wang, W.W.; Wei, Y.X. Characteristics of size distributions of atmospheric fine particles in the north suburban area of Nanjing. China Environ. Sci. 2008, 28, 18–22. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Zhu, B.; Shen, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Y. Size Distributions of Aerosol During the Spring Festival in Nanjing. Environ. Sci. 2014, 2, 442–450. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Li, Z.; Li, R.J.; Sun, L.; Zhao, C.; Wang, P.C.; Sun, Y.L.; Li, Y.N.; Liu, X.G.; Li, J.X.; et al. Aerosol hygroscopicity and CCN activity obtained from a combination analysis based on size-resolved CCN and aerosol chemical composition observations during the AC3Exp13 campaign. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 14889–14931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, Q.; Deng, Z.; Huang, M.; Ma, X.; Tie, X. Aircraft study of aerosol vertical distributions over Beijing and their optical properties. Tellus B 2009, 61, 756–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, J.G.; Frisbie, P.R. Cloud condensation nuclei near marine stratus. J. Geophys. Res. 1991, 96, 20795–20808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, J.G. Cloud condensation nuclei near marine cumulus. J. Geophys. Res. 1993, 98, 2693–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, R.J.; Clarke, A.D.; Litchy, M.; Li, J.; Kok, G.; Schillawski, R.D.; McMurry, P.H. Spurious aerosol measurements when sampling from aircraft in the vicinity of clouds. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 103, 28337–28346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, L.; Schanot, A.; Moharreri, A.; Roger, D.C.; Dhaniyala, S. Design and sampling characteristics of a new airborne aerosol inlet for aerosol measurements in clouds. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2013, 30, 1123–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, G.M.; Johnson, D.W.; Spice, A. The measurement and parameterization of effective radius of droplets in warm stratocumulus clouds. J. Atmos. Sci. 1994, 51, 1823–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, R. Parameterization of the effect of drizzle upon the droplets effective radius in stratocumulus clouds. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2000, 126, 3309–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verlinde, J.; Harrington, J.Y.; Yannuzzi, V.T.; Avramov, A.; Greenberg, S.; Richardson, S.J.; Bahrmann, C.P.; McFarquhar, G.M.; Zhang, G.; Johnson, N.; et al. The Mixed-Phase Arctic Cloud Experiment. Bull. Am. Meteor. Soc. 2007, 88, 205–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFarquhar, G.M.; Heymsfield, A.J. Microphysical characteristics of three anvils sampled during the Central Equatorial Pacific Experiment (CEPEX). J. Atmos. Sci. 1996, 53, 2401–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Minnis, P.; Mace, G.G.; Smith Jr, W.L.; Poellt, M.; Marchand, R.; Rapp, A.D. Comparison of stratus cloud properties deduced from surface, GOES, and aircraft data during the March 2000 ARM Cloud IOP. J. Atmos. Sci. 2002, 59, 3265–3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heymsfield, A.J.; Schmitt, C.G.; Bansemer, A.; Baumgardner, D.; Weinstock, E.M.; Smith, J.T.; Sayres, D. Effective ice particle densities for cold anvil cirrus. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L02101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFarquhar, G.M.; Zhang, G.; Poellot, M.R.; Kok, G.L.; McCoy, R.; Tooman, T.; Fridlind, A.; Heymsfield, A.J. Ice properties of single-layer stratocumulus during the Mixed-Phase Arctic Cloud Experiment: 1. Observations. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, D24201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yost, C.R.; Minnis, P.; Ayers, J.K.; Palikonda, R.; Spangenberg, D.; Change, F.L.; Sun-Mack, S.; Heck, P.W.; Lawson, R.P. Evaluation of In-Situ and Satellite-Derived Cirrus Microphysical Properties During SPARTICUS. Available online: https://asr.science.energy.gov/meetings/stm/posters/poster_pdf/2011/P000458.pdf (accessed on 25 November 2018).
- Lu, C.; Liu, Y.; Niu, S.; Krueger, S.; Wagner, T. Exploring parameterization for turbulent entrainment-mixing processes in clouds. J. Geophys. Res. 2013, 118, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennartz, R. Global assessment of marine boundary layer cloud droplet number concentration from satellite. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, D02201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Mielonen, T.; Grosvenor, D.; Portin, H.; Arola, A.; Mikkonen, S.; Kühn, T.; Leskinen, A.; Juotsensaari, J.; Komppula, M.; et al. Long-term measurements of cloud droplet concentrations and aerosol-cloud interactions in continental boundary layer clouds. Tellus B 2013, 65, 20138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, B.A. Aerosols, Cloud Microphysics, and Fractional Cloudiness. Science 1989, 245, 1227–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feingold, G.; Eberhard, W.L.; Veron, D.E.; Previdi, M. First measurements of the Twomey indirect effect using ground-based remote sensors. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrett, T.J.; Zhao, C. Increased Arctic cloud longwave emissivity associated with pollution from mid-latitudes. Nature 2006, 440, 787–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Zhao, C.; Guo, J.; Li, J. 8-Year ground-based observational analysis about the seasonal variation of the aerosol-cloud droplet effective radius relationship at SGP site. Atmos. Environm. 2017, 164, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | PBL Cloud Layer | Low Layer Above the PBL | Upper Layer Above the PBL | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Standard Deviation | Mean | Standard Deviation | Mean | Standard Deviation | |
| Na | 583.13 | 142.26 | 167.47 | 35.55 | 64.35 | 32.2 |
| CCN | 191.16 | 71.74 | 50.45 | 18.46 | 14.18 | 25.49 |
| Nc | 320.25 | 138.41 | 116.06 | 68.56 | 52.34 | 14.48 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, C.; Zhao, L.; Dong, X. A Case Study of Stratus Cloud Properties Using In Situ Aircraft Observations over Huanghua, China. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10010019
Zhao C, Zhao L, Dong X. A Case Study of Stratus Cloud Properties Using In Situ Aircraft Observations over Huanghua, China. Atmosphere. 2019; 10(1):19. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10010019
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Chuanfeng, Lijun Zhao, and Xiaobo Dong. 2019. "A Case Study of Stratus Cloud Properties Using In Situ Aircraft Observations over Huanghua, China" Atmosphere 10, no. 1: 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10010019
APA StyleZhao, C., Zhao, L., & Dong, X. (2019). A Case Study of Stratus Cloud Properties Using In Situ Aircraft Observations over Huanghua, China. Atmosphere, 10(1), 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10010019






