Abstract
The evolution of intrinsic barriers to gene flow is a crucial step in the process of speciation. Chromosomal changes caused by fusion and fission events are one such barrier and are common in several groups of Lepidoptera. However, it remains unclear if and how chromosomal changes have contributed to speciation in this group. I tested for a phylogenetic signal of varying chromosome numbers in Erebia butterflies by combining existing sequence data with karyological information. I also compared different models of trait evolution in order to infer the underlying evolutionary mechanisms. Overall, I found significant phylogenetic signals that are consistent with non-neutral trait evolution only when parts of the mitochondrial genome were included, suggesting cytonuclear discordances. The adaptive evolutionary model tested in this study consistently outperformed the neutral model of trait evolution. Taken together, these results suggest that, unlike other Lepidoptera groups, changes in chromosome numbers may have played a role in the diversification of Erebia butterflies.
1. Introduction
The process of speciation can be seen as a continuum, ranging from initially undifferentiated populations to ultimately genetically distinct and reproductively isolated species [1,2,3]. Early stages along this continuum are often ephemeral, as potential maladaptive gene flow is mainly prevented by extrinsic factors, and interspecific gene flow, e.g., upon secondary contact, is still possible [2,3,4]. The evolution of intrinsic barriers that shield part of the genome from recombination and prevent the breakup of co-adapted genomic regions is thus vital for the progression of speciation [5,6]. Intrinsic barriers may not only stabilize initial differentiation [3,7,8], but also promote the subsequent coexistence of closely related species [9,10]. Theory supports the idea that chromosomal rearrangements, such as translocations, inversions and the change in chromosome numbers through fusion and fission of existing chromosomes, can act as intrinsic barriers [11,12,13]. Changes in chromosome numbers through fusion and fission may, in particular, result in reproductive isolation, and thus promote speciation. This is because complex and unstable meiotic chains can form in hybrids between species with different chromosome numbers, leading to meiotic nondisjunction and sterility [14]. Hybrid sterility may, however, take a long time to establish. This is indicated by often widespread hybridization between closely related species or chromosomal races in the wild [15,16], especially in butterflies [17]. Recent genomic data further suggests that chromosomal barriers may be more porous than formerly thought [18]. Differences in chromosome numbers nevertheless often reduce gene flow and thus provide some initial degree of isolation [19]. The extent to which such differences contribute to speciation remains yet unknown [12,13,20,21].
Speciation through fusion and fission of chromosomes has, for example, been suggested to drive diversification in some groups of mammals [13,20] or Lepidoptera [21,22,23]. Chromosome numbers are often highly conserved among many Lepidoptera genera and families with a haploid chromosome number (n) of ~31 [22]. However, several groups of butterflies, such as Agrodiaetus [21] or Lysandra [24], exhibit high karyotypic diversity [22]. The Agrodiaetus group (n range: 10–134) has become a model system for studying the evolutionary interplay between chromosome numbers, speciation and the coexistence of species [21,23]. In contrast, the evolutionary mechanisms remain unclear for most other Lepidopteran groups, including Erebia. Erebia is a genus of Palearctic butterflies consisting of more than one hundred described species that differ phenotypically, ecologically and karyotypically from each other [22,25,26]. Phylogenetic inferences suggest that the radiation of European Erebia emerged over the last ~15 million years [26]. However, among European Erebia, the E. tyndarus group is much younger (0.15–1 million years; [26,27,28]). The process of speciation is not complete in the E. tyndarus group, as interspecific gene flow is still possible [17,26,28]. Similar to Agrodiaetus, speciation in Erebia is suggested to be driven by changes in chromosome numbers (n range: 7–51), associated with allopatric phases followed by secondary contact [26,29]. The high karyotypic diversity in E. tyndarus (n range: 8–51; Figure 1) suggests that chromosomal fusion and fission processes, in combination with ecological adaptation, could have promoted the rapid diversification in this group [17,22,25,30,31].

Figure 1.
Dot plot summarizing the variation in haploid chromosome numbers among the five European Erebia groups according to [26]. Data is from [22]. Erebia medusa group (orange), E. ephiron group (green), E. pronoe group (blue), E. ligea group (pink), E. tyndarus group (red).
I tested for a phylogenetic signal of chromosomal changes in Erebia by combining data from a recent phylogenetic study [26] with classic karyological information on this genus (reviewed in [22]). I further aimed to identify the evolutionary mechanism that best fits the chromosomal changes. This involved testing if chromosomal changes evolved in a more neutral fashion [32], as in Agrodiaetus [21] or through adaptive evolution [33,34]. Given the recent radiation and the variation in chromosome numbers, particularly within in the E. tyndarus species complex (Figure 1), I expected that changes in chromosome numbers would be correlated with the phylogeny and hence the diversification of Erebia. If chromosomal changes have indeed promoted the diversification of Erebia, then an adaptive evolutionary model of trait evolution will likely best explain variation in chromosome numbers.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
Chromosome numbers for 31 Erebia species sequenced by Peña et al. [26] were available from Robinson [22]. The chromosome number for E. graucasica was further taken from Albre et al. [35]. In addition, I included three species for which I found chromosome numbers, and which had previously been used as outgroups (Maniola jurtina, Oeneis jutta, Pyronia cecilia; [26]). For each species, I selected the individuals with the most complete sequences from GenBank (Table S1). The final alignment comprised sequence data for four genes: 620 bp of the mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase subunit I (COI), 598 bp of the nuclear glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH), 565 bp of the nuclear ribosomal protein S5 (RpS5) and 343 bp of the nuclear wingless gene (WG).
To increase the taxonomic scope, I searched for additional Erebia species whose sequences were not included in Peña et al. [26] and for which the number of chromosomes was also available [22]. Sequences of the mitochondrial COI gene could be retrieved for another seven species. In two cases, the available sequences were identical between two species—all of which were from the recently diversified E. tyndarus group, i.e., between E. nivalis (n = 11) and E. cassioides (n = 10), as well as between E. rondoui (n = 24) and E. hispanica (n = 25). For these, I retained the species with the more complete sequence data in the analysis, i.e., E. cassioides and E. hispanica (Table S1). This resulted in a dataset comprising 40 taxa, including three outgroups, sequenced for 620 bp.
2.2. Phylogenetic Analyses
I used PartitionFinder 2 [36] to infer the best partition scheme and associated substitution model for each codon position and gene. The resulting best partitioning scheme for the Bayesian inference is given in Table S2. For the maximum likelihood (ML)-based phylogeny, I used the GTR model with invariant sites and gamma correction (GTR+I+G) in RAxML 8.2.8. [37] with the corresponding partition scheme from PartitionFinder. I employed 1000 bootstrap replicates to assess significance. I ran RAxML for the dataset comprising either all four genes, the mitochondrial COI gene only or the three nuclear genes. In the latter case, data was only available for 35 taxa (Table S1). I conducted the Bayesian analysis in MrBayes 3.2.2. [38] for either dataset using, in each case, 5,000,000 generations with four chains—three heated and one cold. Trees were sampled every 1000 generations and I examined convergence and mixing based on effective sample sizes (ESS) in Tracer 1.6.0. [39]. Finally, I removed 80% of the MrBayes trees as burn-in and constructed a majority rule consensus tree.
To test for a phylogenetic signal of chromosome number onto the Bayesian phylogenies, I calculated three different indices for each dataset–Moran’s I, Blomberg’s κ and Pagel’s λ–using the package phylosignal [40] in R 3.3.1. [41]. Moran's I is a statistical measure for the autocorrelation of trait values on a phylogeny based on phylogenetic distances. A significant Moran’s I indicates that closely related species are more similar than expected by chance [42]. I calculated Moran’s I both across the entire phylogeny as well as locally between tips. While Moran’s I makes no assumptions about the underlying evolutionary model, both κ and λ assume a Brownian Motion (BM) model of neutral trait evolution ([43], see also below). Deviations from expectations under BM may thus also reflect that the underlying phylogeny could follow a different evolutionary mechanism as for example captured with the Ornstein-Uhlenbeck model ([42], see below). Blomberg’s κ measures the strength of a phylogenetic signal as the ratio of the mean squared error of the tip data in relation to the mean squared error of the phylogenetic (co)variance matrix. Under BM, κ is expected to be 1. κ > 1 suggests that close relatives on the tree are more similar than expected under BM, whereas κ < 1 indicates that closely related species resemble each other less than expected under BM [42,43]. Finally, Pagel’s λ is a phylogenetic scaling parameter and measures the phylogenetic dependence of a trait. λ ranges from 0—where the studied trait evolves independently of the phylogeny—to 1—where the studied trait evolves under BM [42]. I tested each index against the null hypothesis of absence of a phylogenetic signal in which case trait values would be randomly distributed along the phylogeny, using 1000 randomization steps with phylosignal. To also account for phylogenetic uncertainty, I calculated all indices for each of the 1000 post burn-in Bayesian phylograms using the package sensiPhy [44].
I compared the fit between the number of chromosomes with the phylogeny using three different evolutionary models implemented in the package mvMORPH [45]: (i) BM, which is based on a random walk process [32]. (ii) Ornstein-Uhlenbeck (OU), which fits a random walk with a central tendency towards a particular range of phenotypes representing an adaptive optimum [34]. (iii) Early Burst (EB), which assumes initially rapid evolution that is followed by relative stasis [33]. While BM is a model of neutral evolution, both OU and EB assume adaptive evolutionary mechanisms. I fitted each model to all of the 1000 post burn-in Bayesian phylograms and compared them using Aikaike’s information criterion corrected for finite sample sizes (AICc). I performed all statistical analyses in R. The sequence alignments and estimated trees are available from the Zenodo repository (10.5281/zenodo.1183375).
3. Results
3.1. Phylogenetic Reconstruction
All ESS values for the 1000 post burn-in trees from the MrBayes analyses were >200, suggesting an adequate sampling of the posteriors. Branch support generally was generally in agreement between the Bayesian and ML inferences (Figure 2), where phylogenetic resolution was highest when all four genes were analyzed together (Figure 2a). This was further highlighted by the position of the outgroup species O. jutta, which occurred outside the Erebia clade with 100% support when using all four genes combined (Figure 2a) or the three nuclear genes (Figure 2c) but was nested among Erebia species when only the mitochondrial COI gene was used (Figure 2b), suggesting little differentiation at this marker. Independent of the analyzed dataset, species from the European E. ephiron, E. pronoe, and E. tyndarus groups form distinct clades, whereas the E. medusa and E. ligea groups are not clearly resolved (Figure 2).
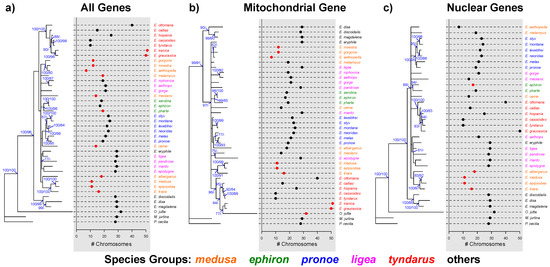
Figure 2.
Majority rule consensus phylograms, each based on 1000 post burn-in trees using either (a) all four genes combined (n = 40 taxa), (b) the mitochondrial COI gene (n = 40 taxa), and (c) sequences of three nuclear genes (glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH), ribosomal protein S5 (RpS5), wingless (WG)) combined (n = 35 taxa). Numbers at each node indicate the posterior Bayesian probabilities followed by the bootstrap support for maximum likelihood trees. Only support values ≥75% are indicated. The haploid chromosome number is indicated for each species. Red dots highlight cases with a significant local Moran’s I based on 1000 permutations. Species label colors designate different Erebia groups (see also Figure 1).
3.2. Phylogenetic Signals
Local estimates of Moran’s I across the majority rule consensus trees suggest a consistently significant correlation between chromosomal numbers and the respective phylogeny among all species of the E. medusa group when analyzing all genes combined (Figure 2a). Using only mitochondrial or nuclear genes, this was, however, only true for six and four species of the E. medusa group respectively (Figure 2b,c). Significant local Moran’s I further occurs in two species of the E. tyndarus group (E. iranica and E. graucasica) when analyzing all genes combined and the mitochondrial COI gene only (Figure 2a,b).
Using the majority rule consensus phylograms, I found a small but significant degree of overall autocorrelation (Moran’s I: 0.040, p = 0.003), where κ (κ: 0.336, p = 0.030) but not λ (λ: 0.245, p = 0.500) were significant for the dataset comprising all four genes. Phylogenetic signals were stronger for the mitochondrial (COI) dataset (Moran’s I: 0.074, p = 0.008; κ: 0.439, p = 0.006; λ: 0.601, p = 0.327), but absent when only nuclear genes were used (Moran’s I: 0.019, p = 0.224; κ: 0.238, p = 0.258; λ: 0.472, p = 0.261). When looking at the phylogenetic uncertainty across the 1000 post burn-in phylograms, I found a generally significant (i.e., p < 0.05) overall autocorrelation—reflected by Moran’s I—and κ, whereas λ varied for the two datasets that comprised the mitochondrial COI gene. The phylogenetic signals for I and κ were generally stronger when only COI was used. For the dataset comprising only nuclear genes, significant estimates were mostly absent across the 1000 post burn-in phylograms (Figure 3).
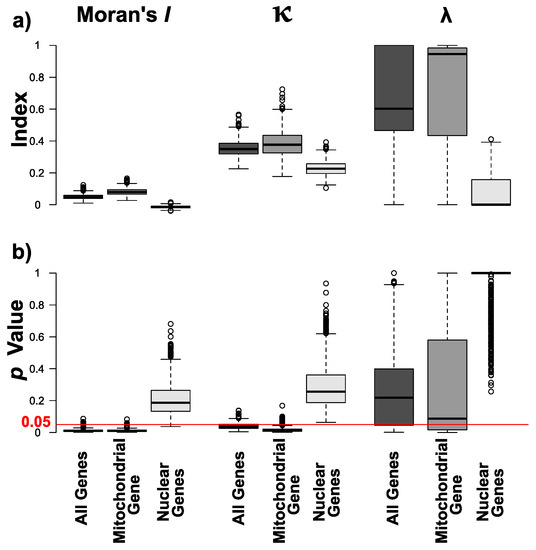
Figure 3.
Summary of phylogenetic estimates across 1000 post burn-in trees for each dataset. Boxplots depict (a) the observed estimates for Moran’s I, Blomberg’s κ and Pagel’s λ with their (b) associated p values. The red line highlights a p value cut-off of 0.05.
Independent of the analyzed dataset, the OU models significantly outperformed both the EB (all genes: ΔAICc = 5.82, t1,999 = 78.7, p < 0.001; mitochondrial gene: ΔAICc = 7.77, t1,999 = 73.6, p < 0.001; nuclear genes: ΔAICc =14.30, t1,999 = 87.6, p < 0.001) and BM (all genes: ΔAICc = 3.48, t1,999 = 47.1, p < 0.001; mitochondrial gene: ΔAICc = 5.44, t1,999 = 51.6, p < 0.001; nuclear genes: ΔAICc = 11.90, t1,999 = 72.9, p < 0.001) models based on paired t-tests between their respective AICc values (Figure 4).
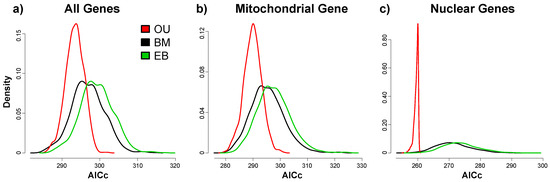
Figure 4.
Density distributions for Akaike’s information criterion, corrected for finite sample sizes (AICc) estimated for three different models across the 1000 post burn-in trees for each dataset: black —Brownian motion (BM), red—Ornstein-Uhlenbeck (OU), green—early burst (EB).
4. Discussion
Several classic models of speciation predict that chromosomal changes, such as inversions or the fusion and fission of entire chromosomes, can advance the speciation process by acting as intrinsic barriers to gene flow [12,46]. This view has been challenged by theoretical and empirical advances, which suggest that gene flow can occur despite such genomic rearrangements [13,18]. The potential for chromosomal speciation by combining genetic and karyotypic data has, however, only been assessed for a restricted set of taxa [13,20,21,47]. Combining existing sequence data with karyotypic information, I tested for a phylogenetic signal underlying the varying chromosome numbers in Erebia butterflies (Figure 2 and Figure 3). I also inferred the underlying evolutionary mechanisms by comparing different models of trait evolution (Figure 4). I found a small yet significant level of overall correlation between chromosome numbers and the phylogenetic inference as measured by Moran’s I, when the mitochondrial COI gene was included. Closely related species were therefore more similar than expected by chance. This is likely driven by groups of Erebia, particularly E. medusa, that show consistently significant local correlations (I) among datasets (Figure 2), as well as conservatism in terms of their chromosome numbers (Figure 1). The absence of such a correlation when only nuclear genes were used may further implicate different evolutionary histories between the nuclear and the mitochondrial genome [26]. Mitochondrial and nuclear discordance is a widespread phenomenon in animals (reviewed in [48]). This is often a result of incomplete lineage sorting and/or introgression in the nuclear genome [48], the latter being common in tropical Heliconius butterflies [49]. The endosymbiotic bacterium Wolbachia can cause similar discordance in butterflies [50,51]. Introgression and hybridization also occurs in Erebia [17,29], yet broader taxonomic and genomic studies are needed to determine the extent and causes of cytonuclear discordance observed in this study.
For the datasets comprising the mitochondrial COI gene, Blomberg’s κ was significantly smaller than one (Figure 3). Under a Brownian motion model of trait evolution, this suggests that closely related species are less similar than expected [43], e.g., when chromosomal changes occur independently from each other during allopatric phases [21]. Alternatively, the observed reduction in κ could be caused by adaptive trait evolution. This is suggested by the better fit of the Ornstein-Uhlenbeck model of trait evolution compared to the neutral model [42]. However, the restricted taxonomic sampling and the limited amount of available genetic data combined with the inconclusive results when estimating Pagel’s λ (Figure 3), the placement of O. jutta within the Erebia clade (Figure 2b) and the abundance of polytomies highlight the limits of this study (Figure 2). Whereas Moran’s I has been shown to be a robust estimator of phylogenetic autocorrelation in the presence of polytomies [42], phylogenetic uncertainty can inflate Blomberg’s κ under a Brownian motion model [52]. That said, the fact that the phylogenies comprising COI are better resolved indicates that the relative difference in κ between datasets (Figure 3) is unlikely to have been caused by such an artifact.
The Ornstein-Uhlenbeck model of adaptive trait evolution significantly outperformed the neutral Brownian motion model for all three genetic datasets (Figure 4). Such differences can also emerge by chance, i.e., when differences in likelihood estimates between two models are small (i.e., ΔAICc < 2 [53]). This is, however, not the case for Erebia (Figure 4). The better fit of the Ornstein-Uhlenbeck model contrasts with a recent study on Agrodiaetus butterflies, where chromosomal changes were best explained by neutral Brownian motion [21]. Differences in the evolutionary history between the two butterfly groups may account for this inconsistency. Agrodiaetus butterflies are thought to have mainly diversified in allopatry, where they gradually accumulate karyotypic changes [23,47,54]. This often results in small chromosomal differences between closely related species [21]. Upon secondary contact between closely related species, Agrodiaetus butterflies evolve increased phenotypic differentiation through reinforcement, which subsequently promotes coexistence [23,47,54]. In contrast, patterns of chromosomal evolution differ among distinct Erebia groups. Both the E. medusa and E. ligea group show conservatism in terms of chromosome numbers compared to the E. tyndarus group (Figure 1). Erebia species from the same group do, moreover, coexist while often being phenotypically cryptic, but show ecological differentiation in their microhabitat use [31]. This can be further reinforced in contact zones of closely related species, as in the E. tyndarus group [25,30,31]. The signal of adaptive evolution (Figure 4) observed in Erebia could therefore have been driven by (i) stabilizing selection in E. medusa and E. ligea [55] and/or (ii) the rapid diversification of the E. tyndarus group. A resolved phylogeny with broader taxonomic sampling is required to distinguish between these scenarios. Whether the chromosomal changes initiated divergence in this group also cannot be determined with the current dataset.
Taken together, the adaptive phylogenetic responses observed here (Figure 4), together with the recent radiation of the E. tyndarus group, demonstrate the utility of the Erebia genus to study the role of chromosomal fusion and fission during speciation. Further studies using genome-wide data are now needed to overcome potential issues associated with the observed phylogenetic uncertainties caused by polytomies [56] and to assess the role of interspecific gene flow in relation to incomplete lineage sorting. Genome-wide data would also allow the inclusion of even more recently diverged species, which were excluded from this study because they had identical COI sequences. Particularly E. nivalis, which has a different chromosome number (n = 11) than its two close relatives E. cassioides and E. tyndarus (both n = 10) may provide a great system to study the role of recent chromosomal changes during speciation as species ranges overlap and interspecific gene flow is still possible [17,29]. Lastly, because similar variation in chromosome numbers occurs in several other Lepidoptera groups [22,57], the study of Erebia may help to shed light on how and why chromosome numbers vary within this highly diverse order.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at http://www.mdpi.com/2073-4425/9/3/166/s1. Table S1: Accession numbers for each gene and individual included in this study, Table S2: Codon partitioning scheme for each gene used for the Bayesian analysis.
Acknowledgments
I thank Nora Hohmann (University of Basel, Basel, Switzerland), Mélissa Lemoine (Lausanne University Hospital, Lausanne, Switzerland), and Timothy J. Alexander (University of Bern, Bern, Switzerland) for their valuable help with the analysis and comments on the manuscript. I am further indebted to the three anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments on an earlier version of this manuscript. I was partially supported by the University of Basel and a SNSF grant 31003A_166322 to Yvonne Willi (University of Basel, Basel, Switzerland).
Conflict of interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Hendry, A.P. Ecological speciation! Or the lack thereof? Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2009, 66, 1383–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosil, P. Ecological Speciation; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Seehausen, O.; Butlin, R.K.; Keller, I.; Wagner, C.E.; Boughman, J.W.; Hohenlohe, P.A.; Peichel, C.L.; Saetre, G.-P.; Bank, C.; Brännström, Å.; et al. Genomics and the origin of species. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014, 15, 176–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nosil, P.; Harmon, L.J.; Seehausen, O. Ecological explanations for (incomplete) speciation. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2009, 24, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butlin, R.K. Recombination and speciation. Mol. Ecol. 2005, 14, 2621–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkpatrick, M.; Barton, N.J. Chromosome inversions, local adaptation and speciation. Genetics 2006, 173, 419–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Via, S. Natural selection in action during speciation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106 (Suppl. 1), 9939–9946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulmuni, J.; Westram, A.M. Intrinsic incompatibilities evolving as a by-product of divergent ecological selection: Considering them in empirical studies on divergence with gene flow. Mol. Ecol. 2017, 26, 3093–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, P.A.; Zurano, J.P.; Amado, T.F.; Penone, C.; Betancur-R, R.; Bidau, C.J.; Jacobina, U.P. Chromosomal diversity in tropical reef fishes is related to body size and depth range. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2015, 93, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooper, D.M.; Price, T.D. Chromosomal inversion differences correlate with range overlap in passerine birds. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 1, 1526–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, M.J.D. Modes of Speciation; W.H. Freeman: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- King, M. Species Evolution; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Faria, R.; Navarro, A. Chromosomal speciation revisited: Rearranging theory with pieces of evidence. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2010, 25, 660–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dion-Côté, A.-M.; Barbash, D.A. Beyond speciation genes: An overview of genome stability in evolution and speciation. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2017, 47, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohuet, A.; Dia, I.; Simard, F.; Raymond, M.; Rousset, F.; Antonio-Nkondjio, C.; Awono-Ambene, P.H.; Wondji, C.S.; Fontenille, D. Gene flow between chromosomal forms of the malaria vector Anopheles funestus in Cameroon, Central Africa, and its relevance in malaria fighting. Genetics 2005, 169, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polyakov, A.V.; White, T.A.; Jones, R.M.; Borodin, P.M.; Searle, J.B. Natural hybridization between extremely divergent chromosomal races of the common shrew (Sorex araneus, Soricidae, Soricomorpha): Hybrid zone in European Russia. J. Evol. Biol. 2011, 24, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Descimon, H.; Mallet, J. Bad Species. In Ecology of Butterflies in Europe; Settle, R., Shreeve, T., Konvicka, M., van Dyck, H., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Mallet, J.; Besansky, N.; Hahn, M.W. How reticulated are species? Bioessays 2016, 38, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charron, G.; Leducq, J.-B.; Landry, C.R. Chromosomal variation segregates within incipient species and correlates with reproductive isolation. Mol. Ecol. 2014, 23, 4362–4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potter, S.; Bragg, J.G.; Blom, M.P.K.; Deakin, J.E.; Kirkpatrick, M.; Eldridge, M.D.B.; Moritz, C. Chromosomal speciation in the genomics era: Disentangling phylogenetic evolution of rock-wallabies. Front. Genet. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vershinina, A.O.; Lukhtanov, V.A. Evolutionary mechanisms of runaway chromosome number change in Agrodiaetus butterflies. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, R. Lepidoptera Genetics; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Lukhtanov, V.A.; Kandul, N.P.; Plotkin, J.B.; Dantchenko, A.V.; Haig, D.; Pierce, N.E. Reinforcement of pre-zygotic isolation and karyotype evolution in Agrodiaetus butterflies. Nature 2005, 436, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talavera, G.; Lukhtanov, V.A.; Rieppel, L.; Pierce, N.E.; Vila, R. In the shadow of phylogenetic uncertainty: The recent diversification of Lysandra butterflies through chromosomal change. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2013, 69, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorkovic, Z. Some peculiarities of spatially and sexually restricted gene exchange in the Erebia tyndarus group. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 1958, 23, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peña, C.; Witthauer, H.; Kleckova, I.; Fric, Z. Adaptive radiations in butterflies: Evolutionary history of the genus Erebia (Nymphalidae: Satyrinae). Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2015, 116, 449–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.F.; Gilles, A.; Lortscher, M.; Descimon, H. Phylogenetics and differentiation among the western taxa of the Erebia tyndarus group (Lepidoptera: Nymphalidae). Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2002, 75, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albre, J.; Gers, C.; Legal, L. Molecular phylogeny of the Erebia tyndarus (Lepidoptera, Rhopalocera, Nymphalidae, Satyrinae) species group combining CoxII and ND5 mitochondrial genes: A case study of a recent radiation. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2008, 47, 196–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gratton, P.; Trucchi, E.; Trasatti, A.; Riccarducci, G.; Marta, S.; Allegrucci, G.; Cesaroni, D.; Sbordoni, V. Testing classical species properties with contemporary data: How “Bad Species” in the brassy ringlets (Erebia tyndarus complex, Lepidoptera) turned good. Syst. Biol. 2016, 65, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorkovic, Z. Die Speziationsstufen in der Erebia tyndarus Gruppe. Biol. Glas. 1957, 10, 61–110. [Google Scholar]
- Kleckova, I.; Konvicka, M.; Klecka, J. Thermoregulation and microhabitat use in mountain butterflies of the genus Erebia: Importance of fine-scale habitat heterogeneity. J. Therm. Biol. 2014, 41, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felsenstein, J. Maximum-likelihood estimation of evolutionary trees from continuous characters. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1973, 25, 471–492. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Harmon, L.J.; Losos, J.B.; Jonathan Davies, T.; Gillespie, R.G.; Gittleman, J.L.; Bryan Jennings, W.; Kozak, K.H.; McPeek, M.A.; Moreno-Roark, F.; Near, T.J.; et al. Early bursts of body size and shape evolution are rare in comparative data. Evolution 2010, 64, 2385–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cressler, C.E.; Butler, M.A.; King, A.A. Detecting adaptive evolution in phylogenetic comparative analysis using the Ornstein-Uhlenbeck model. Syst. Biol. 2015, 64, 953–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albre, J.; Gers, C.; Legal, L. Taxonomic notes on the species of the Erebia tyndarus group (Lepidoptera, Nymphalidae, Satyrinae). Lépidoptères 2008, 17, 12–28. [Google Scholar]
- Lanfear, R.; Frandsen, P.B.; Wright, A.M.; Senfeld, T.; Calcott, B. PartitionFinder 2: New methods for selecting partitioned models of evolution for molecular and morphological phylogenetic analyses. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 772–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; van der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rambaut, A.; Suchard, M.A.; Xie, D.; Drummond, A.J. Tracer v1.6. Available online: http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/tracer (accessed on 26 October 2017).
- Keck, F.; Rimet, F.; Bouchez, A.; Franc, A. Phylosignal: An R package to measure, test, and explore the phylogenetic signal. Ecol. Evol. 2016, 6, 2774–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R Foundation for Statistical Computing; R 3.3.1; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Münkemüller, T.; Lavergne, S.; Bzeznik, B.; Dray, S.; Jombart, T.; Schiffers, K.; Thuiller, W. How to measure and test phylogenetic signal. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2012, 3, 743–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz-Filho, J.A.F.; Santos, T.; Rangel, T.F.; Bini, L.M. A comparison of metrics for estimating phylogenetic signal under alternative evolutionary models. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2012, 35, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustavo, P.; Werner, G.; Caterina, P. SensiPhy: Sensitivity Analysis for Comparative Methods. Available online: https://github.com/paternogbc/sensiPhy (accessed on 6 December 2017).
- Clavel, J.; Escarguel, G.; Merceron, G. mv morph: An R package for fitting multivariate evolutionary models to morphometric data. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2015, 6, 1311–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sites, J.W., Jr.; Moritz, C. Chromosomal evolution and speciation revisited. Syst. Biol. 1987, 36, 153–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandul, N.P.; Lukhtanov, V.A.; Pierce, N.E. Karyotypic diversity and speciation in Agrodiaetus butterflies. Evolution 2007, 61, 546–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toews, D.P.L.; Brelsford, A. The biogeography of mitochondrial and nuclear discordance in animals. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 3907–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardo-Diaz, C.; Salazar, C.; Baxter, S.W.; Merot, C.; Figueiredo-Ready, W.; Joron, M.; Mcmillan, W.O.; Jiggins, C.D. Adaptive introgression across species boundaries in Heliconius butterflies. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narita, S.; Nomura, M.; Kato, Y.; Fukatsu, T. Genetic structure of sibling butterfly species affected by Wolbachia infection sweep: Evolutionary and biogeographical implications. Mol. Ecol. 2006, 15, 1095–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gompert, Z.; Forister, M.L.; Fordyce, J.A.; Nice, C.C. Widespread mito-nuclear discordance with evidence for introgressive hybridization and selective sweeps in Lycaeides. Mol. Ecol. 2008, 17, 5231–5244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, T.J.; Kraft, N.J.B.; Salamin, N.; Wolkovich, E.M. Incompletely resolved phylogenetic trees inflate estimates of phylogenetic conservatism. Ecology 2012, 93, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, N.; Thomas, G.H.; Venditti, C.; Meade, A.; Freckleton, R.P. A cautionary note on the use of Ornstein Uhlenbeck models in macroevolutionary studies. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2016, 118, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandul, N.P.; Lukhtanov, V.A.; Dantchenko, A.V.; Coleman, J.W.S.; Sekercioglu, C.H.; Haig, D.; Pierce, N.E. Phylogeny of Agrodiaetus Hübner 1822 (Lepidoptera: Lycaenidae) inferred from mtDNA sequences of COI and COII and nuclear sequences of EF1α: Karyotype diversification and species radiation. Syst. Biol. 2004, 53, 278–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, M.A.; King, A.A. Phylogenetic comparative analysis: A modeling approach for adaptive evolution. Am. Nat. 2004, 164, 683–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Venegas, R.; Rodríguez, M.Á. Revisiting phylogenetic signal; strong or negligible impacts of polytomies and branch length information? BMC Evol. Biol. 2017, 17, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saura, A.; Von Schoultz, B.; Saura, A.O.; Brown, K.S.J. Chromosome evolution in neotropical butterflies. Hereditas 2013, 150, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).